Stochastic Spatial Heterogeneity in Activities of H+-ATP-Ases in Electrically Connected Plant Cells Decreases Threshold for Cooling-Induced Electrical Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
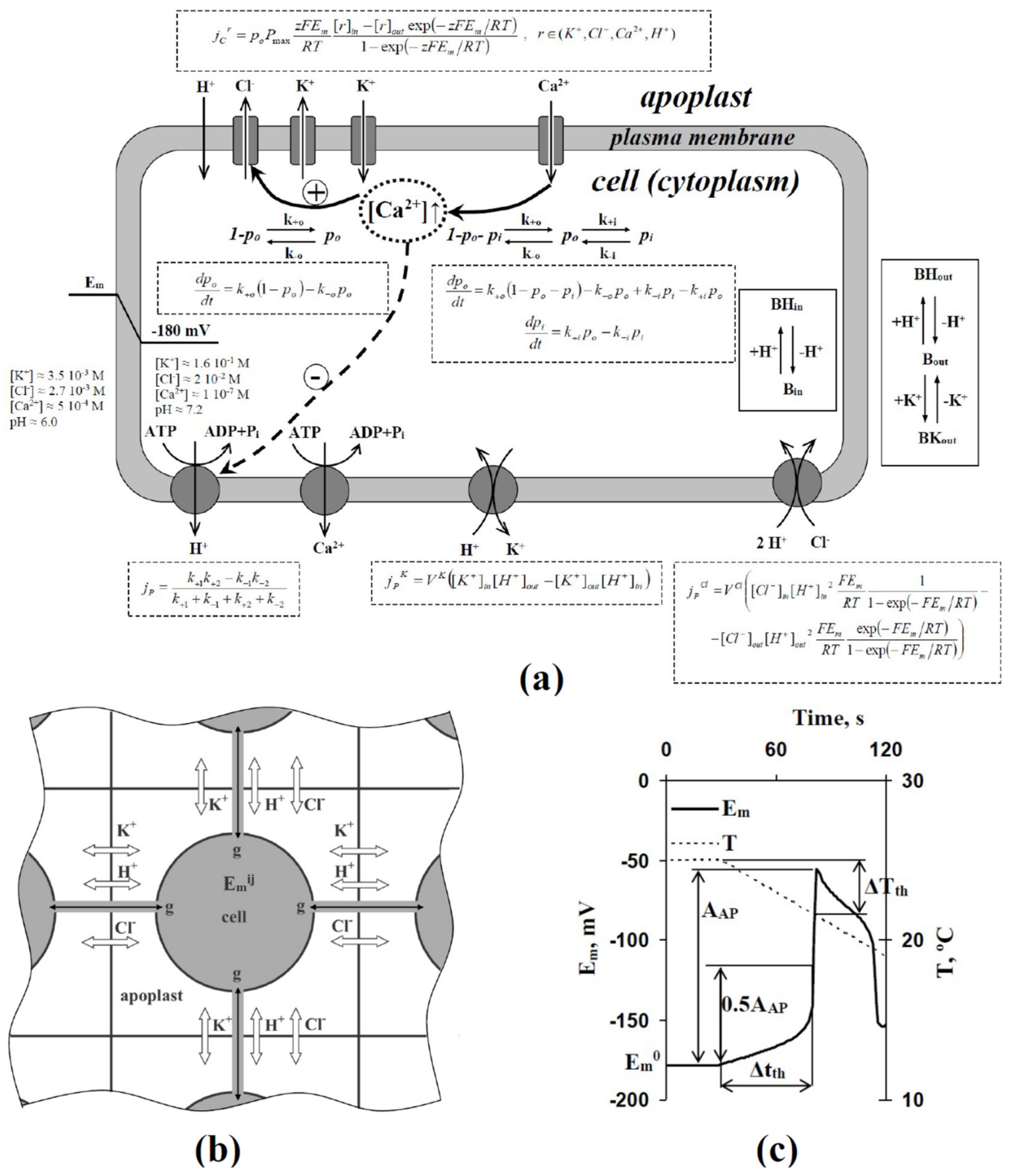
2. Description of Model of Cooling-Induced Electrical Response in Two-Dimensional System of Plant Excitable Cells with Heterogeneity in H+-ATP-Ase Activities
3. Results
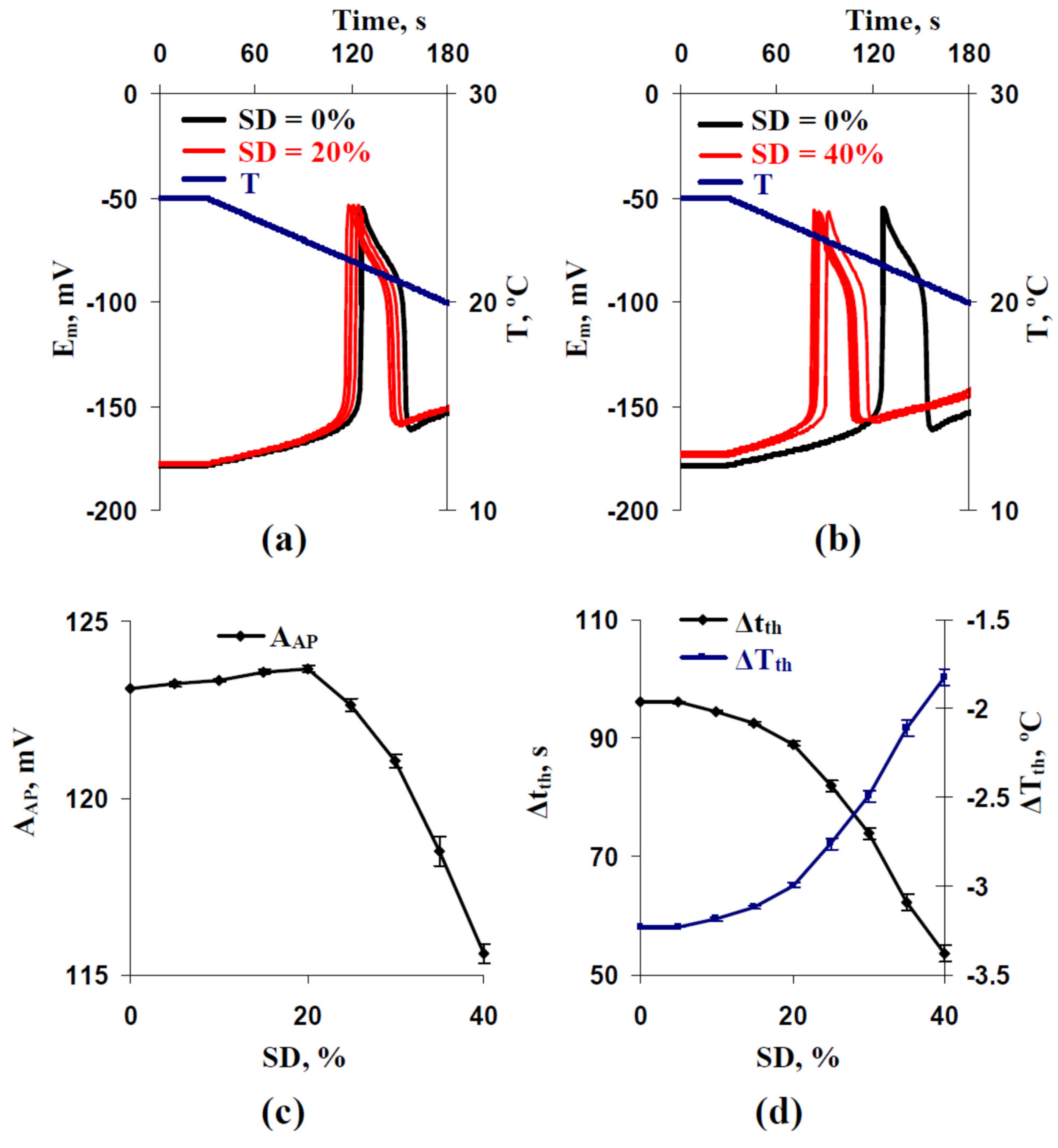
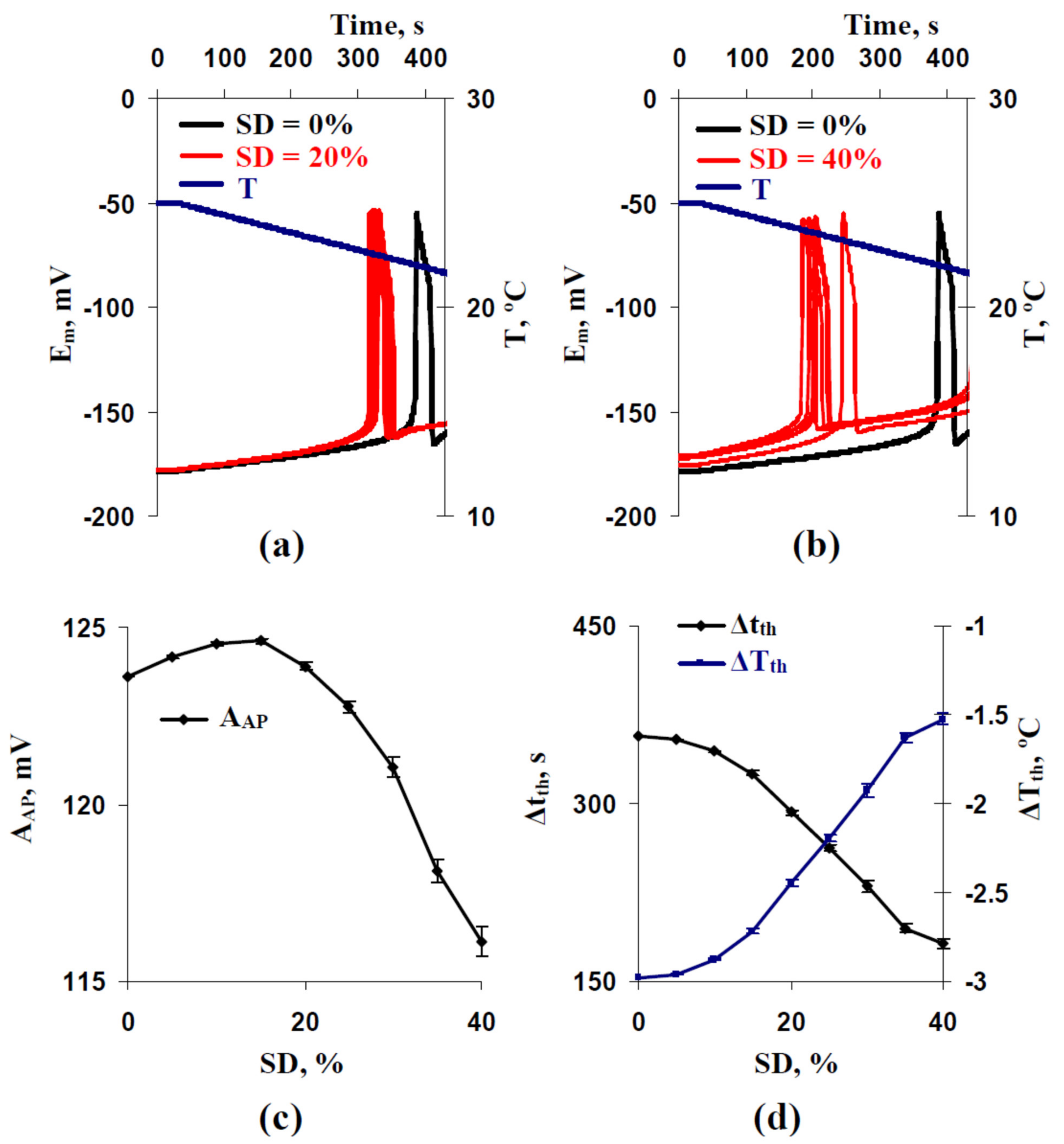
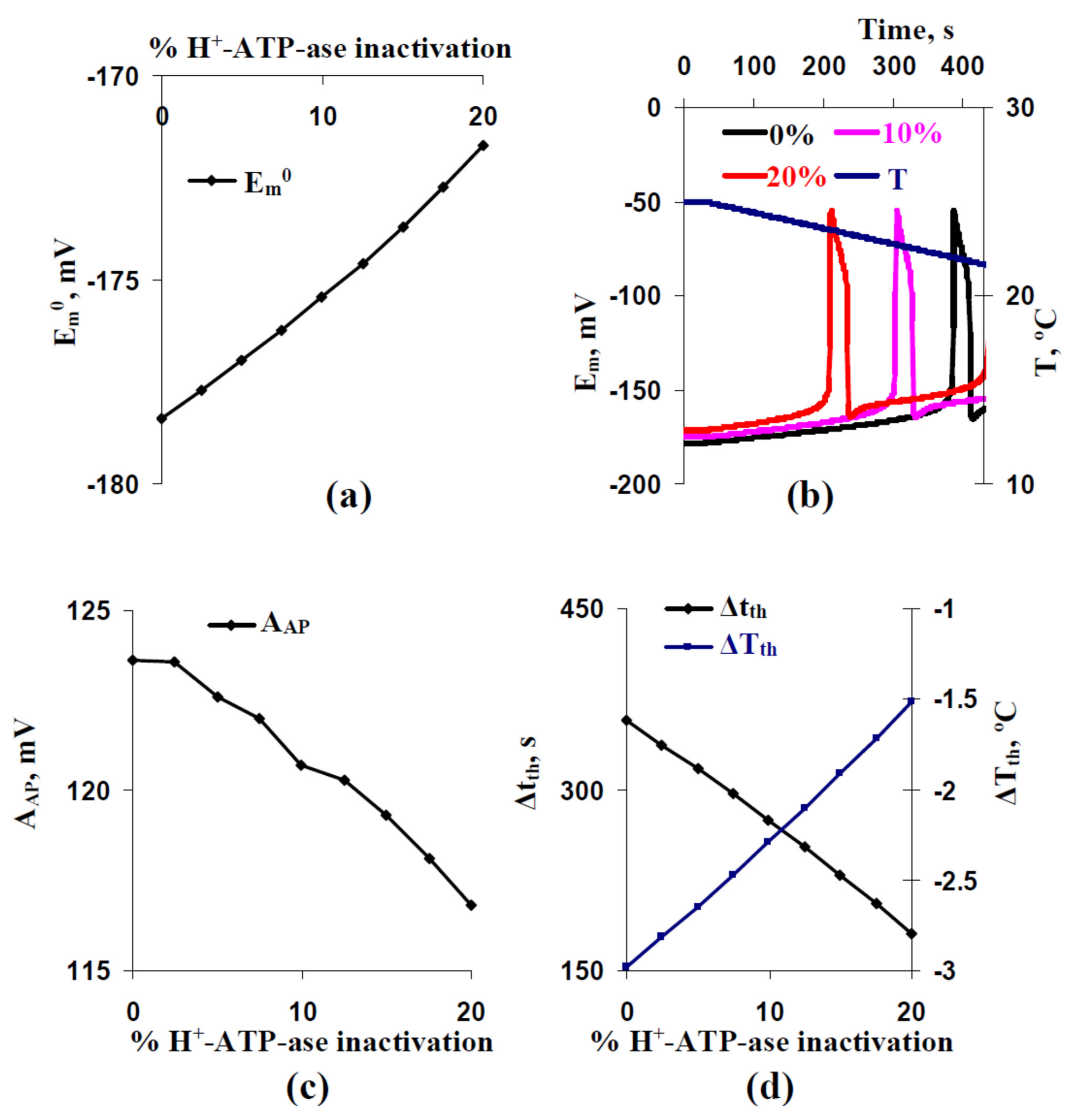
3.1. Analysis of Influence of Stochastic Spatial Heterogeneity in H+-ATP-Ase Activities on Parameters of Cooling-Induced Electrical Responses
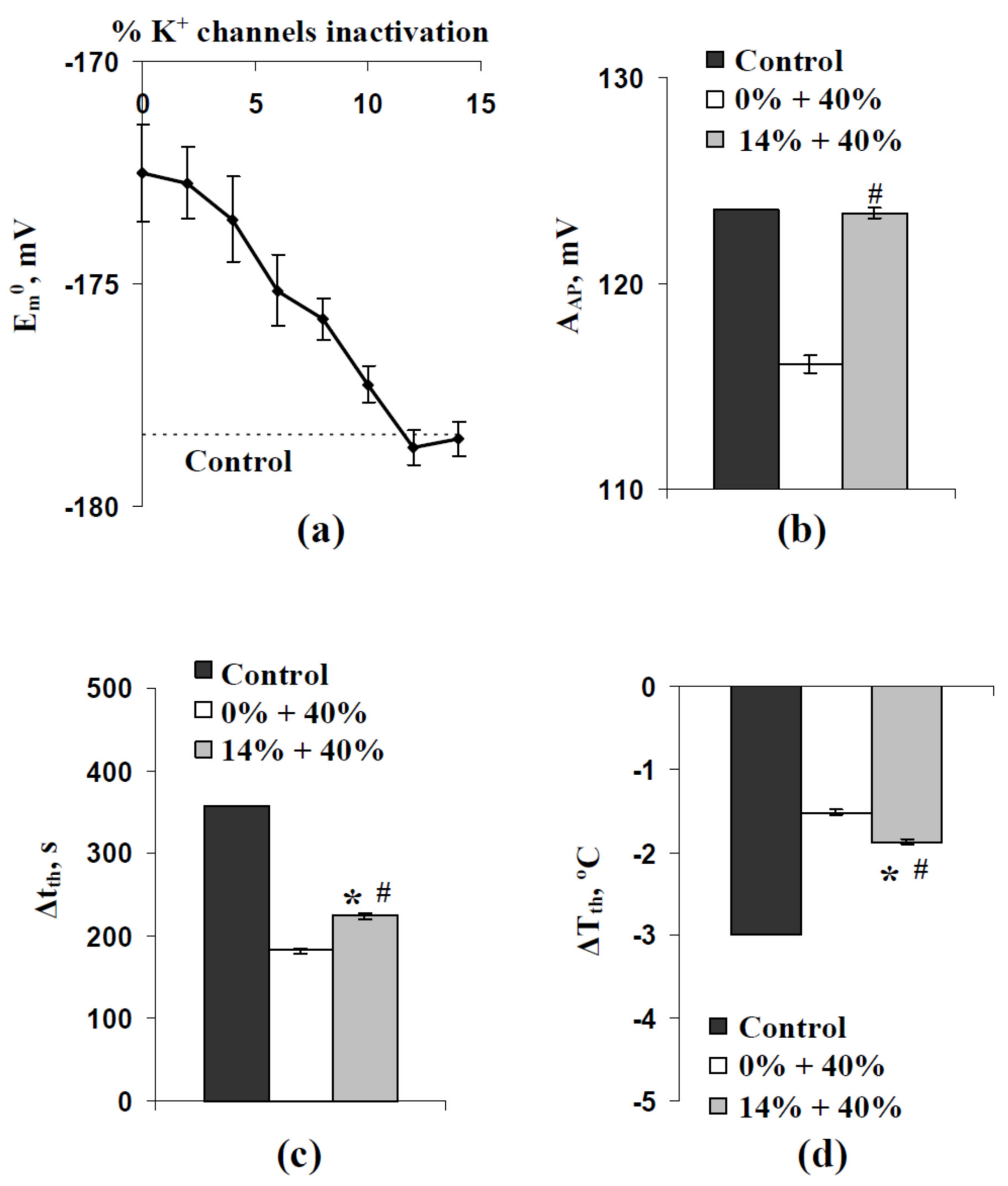
3.2. Two Potential Mechanisms of Influence of Stochastic Spatial Heterogeneity in H+-ATP-Ase Activities on Parameters of Cooling-Induced Electrical Responses
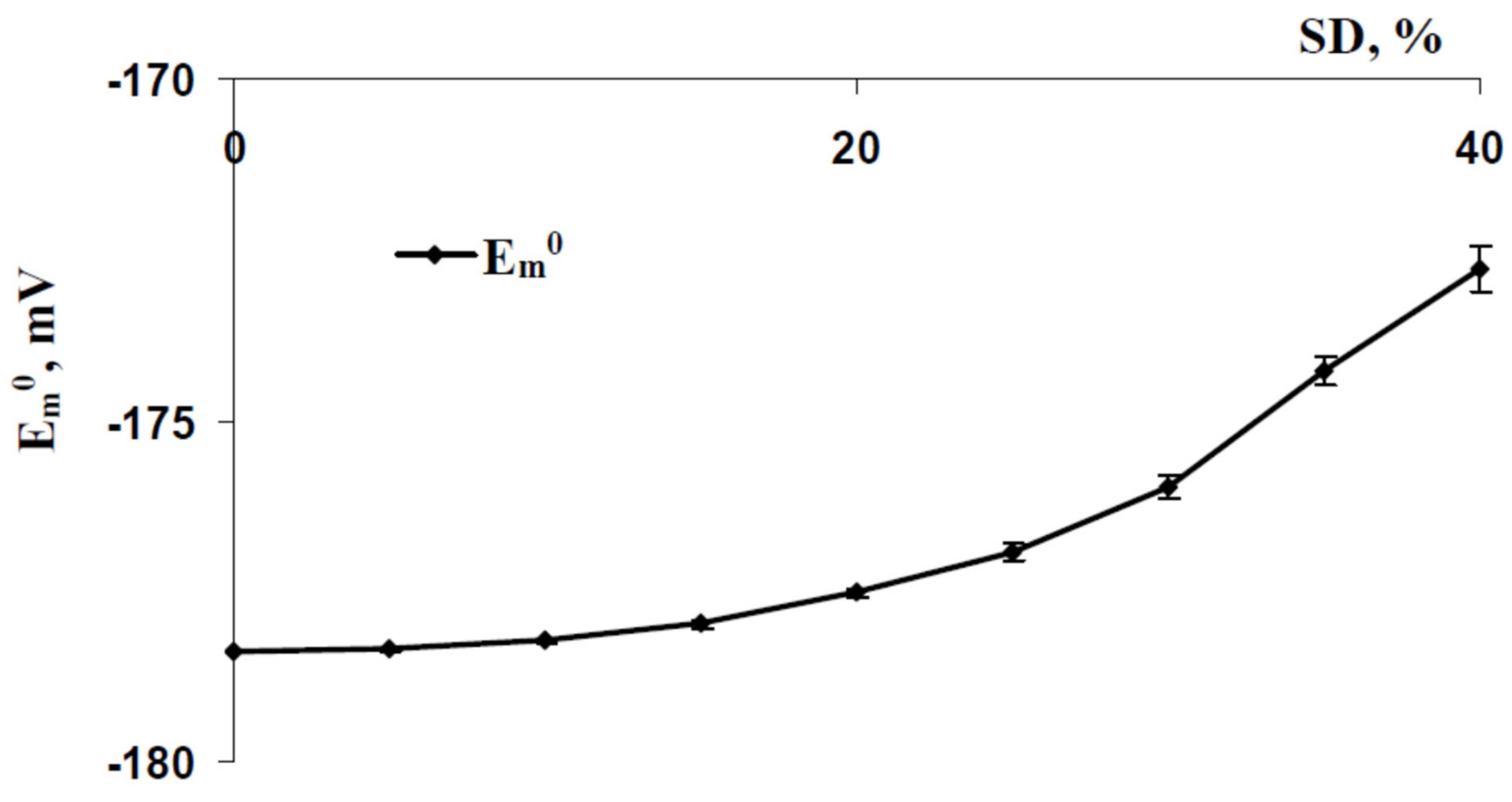
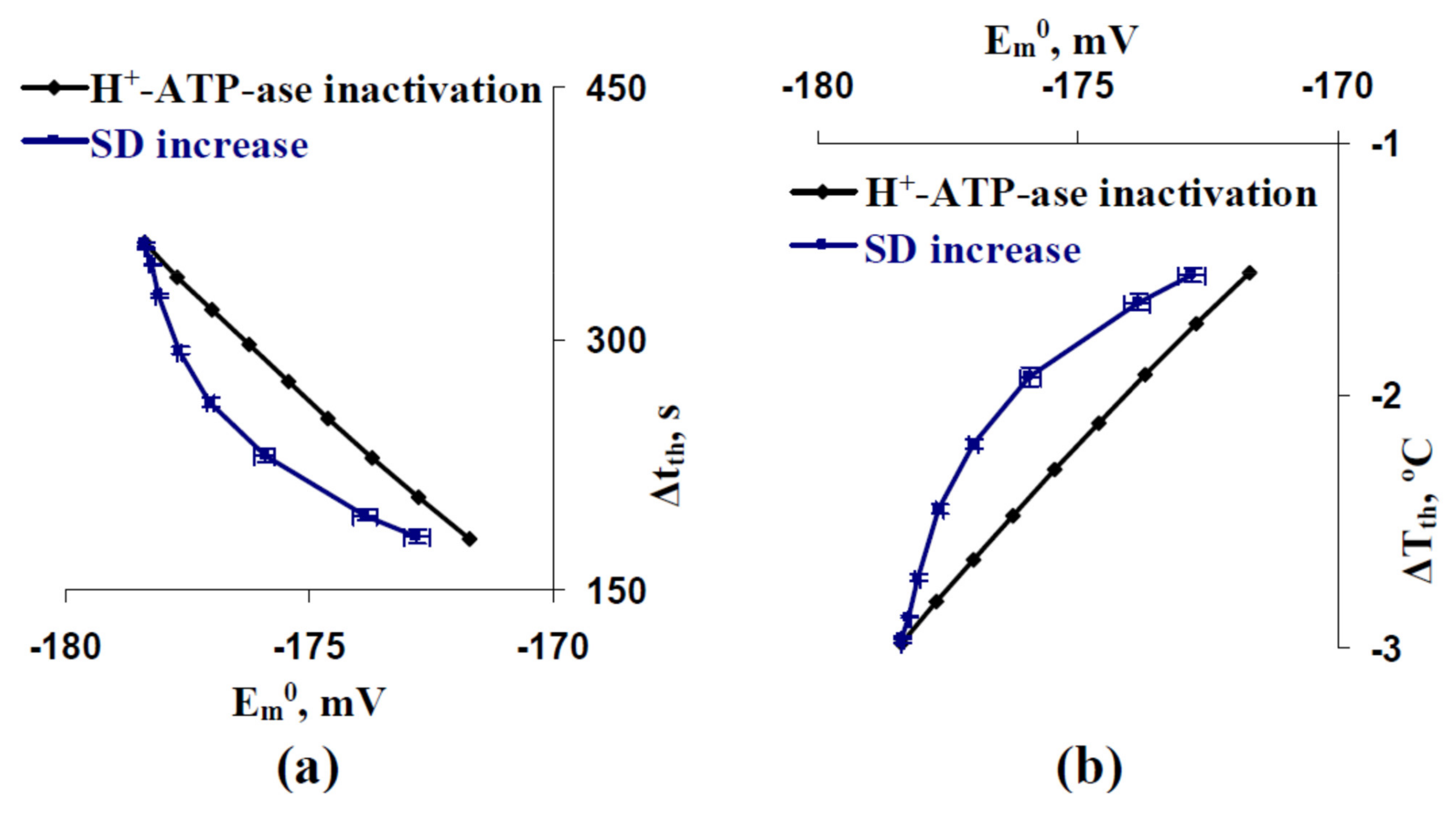
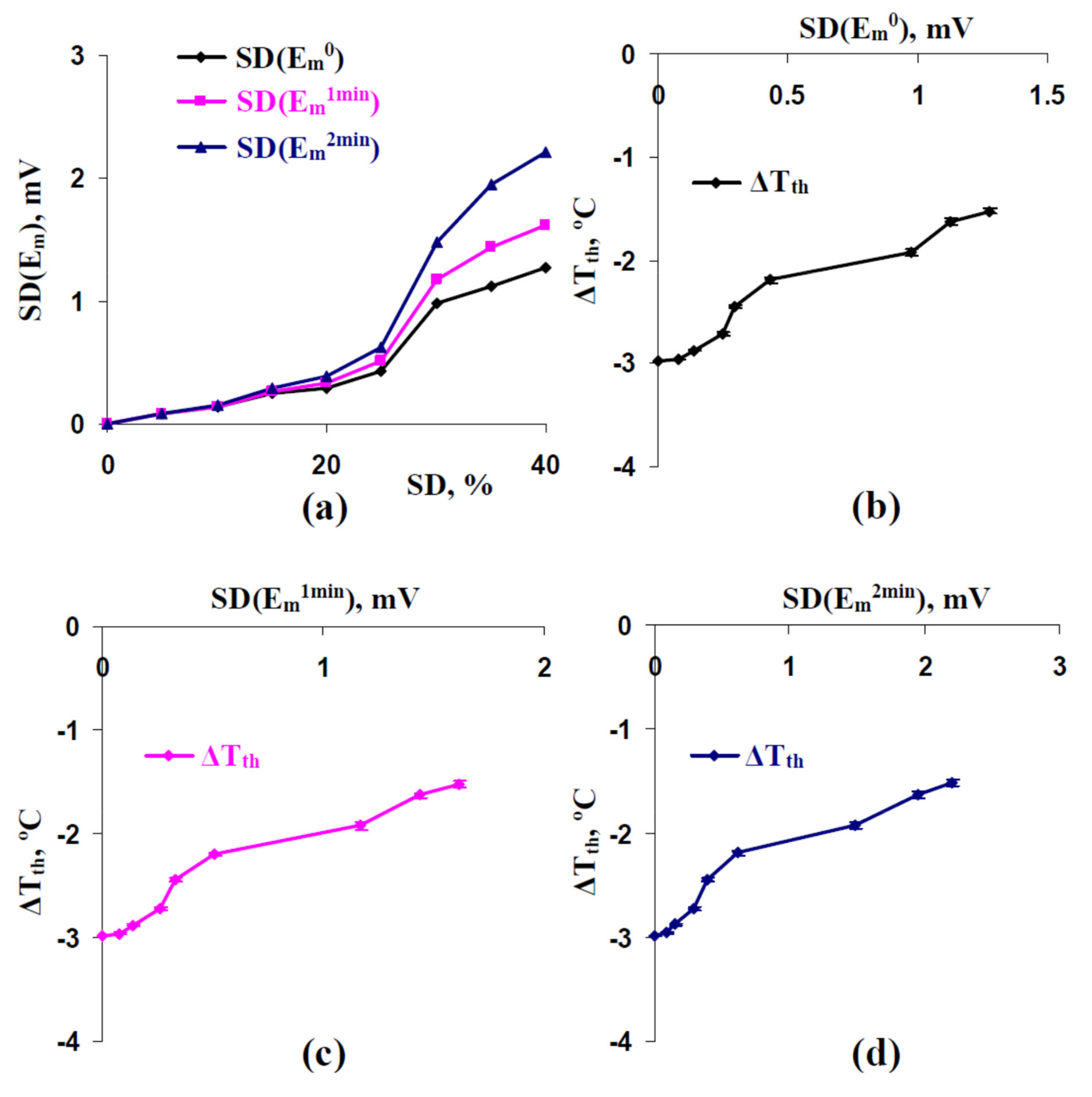
3.3. Relations between Standard Deviations of the Membrane Potentials before Cooling-Induced AP Generation and Temperature Threshold of This Generation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sze, H.; Li, X.; Palmgren, M.G. Energization of plant cell membranes by H+-pumping ATPases. Regulation and biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 677–690. [Google Scholar]
- Palmgren, M.G. Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPases: Powerhouses for nutrient uptake. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 52, 817–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmgren, M.; Morsomme, P. The plasma membrane H+-ATPase, a simple polypeptide with a long history. Yeast 2019, 36, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morsomme, P.; Boutry, M. The plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase: Structure, function and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1465, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felle, H.H. pH: Signal and messenger in plant cells. Plant Biol. 2001, 3, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebacz, K.; Dziubinska, H.; Krol, E. Electrical signals in long-distance communication in plants. In Communication in Plants. Neuronal Aspects of Plant Life; Baluška, F., Mancuso, S., Volkmann, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- Fromm, J.; Lautner, S. Electrical signals and their physiological significance in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallé, A.; Lautner, S.; Flexas, J.; Fromm, J. Environmental stimuli and physiological responses: The current view on electrical signaling. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 114, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodeneev, V.; Akinchits, E.; Sukhov, V. Variation potential in higher plants: Mechanisms of generation and propagation. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1057365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhov, V. Electrical signals as mechanism of photosynthesis regulation in plants. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 130, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhova, E.; Akinchits, E.; Sukhov, V. Mathematical models of electrical activity in plants. J. Membr. Biol. 2017, 250, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szechyńska-Hebda, M.; Lewandowska, M.; Karpiński, S. Electrical signaling, photosynthesis and systemic acquired acclimation. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhov, V.; Sukhova, E.; Vodeneev, V. Long-distance electrical signals as a link between the local action of stressors and the systemic physiological responses in higher plants. Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2019, 146, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, E.E.; Gao, Y.Q.; Lenzoni, G.; Wolfender, J.L.; Wu, Q. Wound- and mechanostimulated electrical signals control hormone responses. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, E.; Dziubińska, H.; Trebacz, K. Low-temperature-induced transmembrane potential changes in mesophyll cells of Arabidopsis thaliana, Helianthus annuus and Vicia faba. Physiol. Plant. 2004, 120, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyatygin, S.S. Role of plasma membrane in cold action perception in plant cells. Biol. Membr. Mosc. 2004, 21, 442–449. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhov, V.; Gaspirovich, V.; Mysyagin, S.; Vodeneev, V. High-temperature tolerance of photosynthesis can be linked to local electrical responses in leaves of pea. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, M. Wound-induced hydraulic signals and stimulus transmission in Mimosa pudica L. New Phytol. 1994, 128, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlberg, R.; Cosgrove, D.J. The propagation of slow wave potentials in pea epicotyls. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancuso, S. Hydraulic and electrical transmission of wound-induced signals in Vitis vinifera. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1999, 26, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, M.J.; Morris, R.J. Chemical agents transported by xylem mass flow propagate variation potentials. Plant J. 2017, 91, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toyota, M.; Spencer, D.; Sawai-Toyota, S.; Jiaqi, W.; Zhang, T.; Koo, A.J.; Howe, G.A.; Gilroy, S. Glutamate triggers long-distance, calcium-based plant defense signaling. Science 2018, 361, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyth, M.G.; Morris, R.J. Shear-enhanced dispersion of a wound substance as a candidate mechanism for variation potential transmission. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhova, E.; Akinchits, E.; Gudkov, S.V.; Pishchalnikov, R.Y.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. A Theoretical analysis of relations between pressure changes along xylem vessels and propagation of variation potential in higher plants. Plants 2021, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.R.; Maischak, H.; Mithöfer, A.; Boland, W.; Felle, H.H. System potentials, a novel electrical long-distance apoplastic signal in plants, induced by wounding. Plant. Physiol. 2009, 149, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M.R.; Mithöfer, A.; Will, T.; Felle, H.H.; Furch, A.C. Herbivore-triggered electrophysiological reactions: Candidates for systemic signals in higher plants and the challenge of their identification. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2407–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Bouche-Pillon, S.; Leloup, C.; Bonnemain, J.L. Distribution and activity of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase in Mimosa pudica L. in relation to ionic fluxes and leaf movements. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spanswick, R.M. Electrogenic Pumps. In Plant Electrophysiology. Theory and Methods; Volkov, A.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 221–246. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhov, V.; Nerush, V.; Orlova, L.; Vodeneev, V. Simulation of action potential propagation in plants. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 291, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodeneev, V.A.; Opritov, V.A.; Pyatygin, S.S. Reversible changes of extracellular pH during action potential generation in a higher plant Cucurbita pepo. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 53, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, J.L.; Frachisse, J.M. Involvement of the proton pump and proton conductance change in the wave of depolarization induced by wounding in Bidens pilosa. Can. J. Bot. Rev. 1992, 70, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, L.; Sherstneva, O.; Sukhova, E.; Grinberg, M.; Mysyagin, S.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Inactivation of H+-ATPase participates in the influence of variation potential on photosynthesis and respiration in peas. Plants 2020, 9, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupenina, N.A.; Bulychev, A.A. Action potential in a plant cell lowers the light requirement for non-photochemical energy-dependent quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1767, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlovič, A.; Slováková, L.; Pandolfi, C.; Mancuso, S. On the mechanism underlying photosynthetic limitation upon trigger hair irritation in the carnivorous plant Venus flytrap (Dionaea muscipula Ellis). J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallé, A.; Lautner, S.; Flexas, J.; Ribas-Carbo, M.; Hanson, D.; Roesgen, J.; Fromm, J. Photosynthetic responses of soybean (Glycine max L.) to heat-induced electrical signalling are predominantly governed by modifications of mesophyll conductance for CO2. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białasek, M.; Górecka, M.; Mittler, R.; Karpiński, S. Evidence for the Involvement of electrical, calcium and ROS signaling in the systemic regulation of non-photochemical quenching and photosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausko, M.; Perutka, Z.; Šebela, M.; Šamajová, O.; Šamaj, J.; Novák, O.; Pavlovič, A. The role of electrical and jasmonate signalling in the recognition of captured prey in the carnivorous sundew plant Drosera capensis. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1818–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sukhova, E.; Mudrilov, M.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Influence of the variation potential on photosynthetic flows of light energy and electrons in pea. Photosynth. Res. 2018, 136, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuralhan-Eckert, J.; Lautner, S.; Fromm, J. Effect of simultaneously induced environmental stimuli on electrical signalling and gas exchange in maize plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 223, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhov, V.; Sukhova, E.; Gromova, E.; Surova, L.; Nerush, V.; Vodeneev, V. The electrical signal-induced systemic photosynthetic response is accompanied by changes in the photochemical reflectance index in pea. Func. Plant Biol. 2019, 46, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhova, E.; Yudina, L.; Gromova, E.; Ryabkova, A.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Influence of local burning on difference reflectance indices based on 400-700 nm wavelengths in leaves of pea seedlings. Plants 2021, 10, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, T.E.; Lautner, S.; Felle, H.H.; Matyssek, R.; Fromm, J. Heat-induced electrical signals affect cytoplasmic and apoplastic pH as well as photosynthesis during propagation through the maize leaf. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhov, V.; Sherstneva, O.; Surova, L.; Katicheva, L.; Vodeneev, V. Proton cellular influx as a probable mechanism of variation potential influence on photosynthesis in pea. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 2532–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, L.; Sukhova, E.; Sherstneva, O.; Grinberg, M.; Ladeynova, M.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Exogenous abscisic acid can influence photosynthetic processes in peas through a decrease in activity of H+-ATPase in the plasma membrane. Biology 2020, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhov, V.; Surova, L.; Morozova, E.; Sherstneva, O.; Vodeneev, V. Changes in H+-ATP synthase activity, proton electrochemical gradient, and pH in pea chloroplast can be connected with variation potential. Front Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hodick, D.; Sievers, A. The action potential of Dionaea muscipula Ellis. Planta 1988, 174, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, J.L.; Desbiez, M.O.; Dejaegher, G.; Frachisse, J.M. Characteristics of the wave of depolarization induced by wounding in Bidens pilosa L. J. Exp. Bot. 1991, 42, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessone, C.J.; Mirasso, C.R.; Toral, R.; Gunton, J.D. Diversity-induced resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 194101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Diversity-induced resonance for optimally suprathreshold signals. Chaos 2020, 30, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, T.; Shimazaki, K.-i. Blue light activates the plasma membrane H+-ATPase by phosphorylation of the C-terminus in stomatal guard cells. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5548–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sukhov, V.S.; Gaspirovich, V.V.; Gromova, E.N.; Ladeynova, M.M.; Sinitsyna, Y.V.; Berezina, E.V.; Akinchits, E.K.; Vodeneev, V.A. Decrease of mesophyll conductance to CO2 is a possible mechanism of abscisic acid influence on photosynthesis in seedlings of pea and wheat. Biochem. Mosc. Suppl. Ser. A 2017, 11, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, M.A.; Gudkov, S.V.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Gromova, E.; Sinitsyna, Y.; Sukhov, V.; Vodeneev, V. Effect of chronic β-radiation on long-distance electrical signals in wheat and their role in adaptation to heat stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 184, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhov, V.S.; Sukhova, E.M.; Ratnitsyna, D.A.; Grinberga, M.A.; Yudina, L.M.; Vodeneev, V.A. Theoretical analysis of the influence of fluctuations in the activity of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase on low-temperature-induced electrical responses in a plant cell. Biochem. Mosc. Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2020, 14, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammaitoni, L.; Hanggi, P.; Jung, P.; Marchesoni, F. Stochastic resonance. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 223–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellens, T.; Shatokhin, V.; Buchleitner, A. Stochastic resonance. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2004, 67, 45–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, C. Fluctuations for good and bad: The role of noise in living systems. Phys. Life Rev. 2006, 3, 133–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhov, V.S.; Vodeneev, V.A. Mathematical model of action potential in higher plant. In Mathematics, Computing, Education; Riznichenko, G.Y., Ed.; Regular and Chaotic Dynamics: Moscow/Izhevsk, Russia, 2005; pp. 267–278. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sukhov, V.; Vodeneev, V. A mathematical model of action potential in cells of vascular plants. J. Membr. Biol. 2009, 232, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhov, V.; Akinchits, E.; Katicheva, L.; Vodeneev, V. Simulation of variation potential in higher plant cells. J. Membr. Biol. 2013, 246, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyerman, S.D.; Beilby, M.; Whittington, J.; Juswono, U.; Neyman, L.; Shabala, S. Oscillations in proton transport revealed from simultaneous measurements of net current and net proton fluxes from isolated root protopasts: MIFE meets patch-clamp. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 28, 591–604. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Das, S.; Manzella, V.; Vitaletti, A.; Masi, E.; Santopolo, L.; Mancuso, S.; Maharatna, K. Forward and inverse modelling approaches for prediction of light stimulus from electrophysiological response in plants. Measurement 2014, 53, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.K.; Das, S.; Maharatna, K.; Masi, E.; Santopolo, L.; Mancuso, S.; Vitaletti, A. Exploring strategies for classification of external stimuli using statistical features of the plant electrical response. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20141225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, D.-J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Tang, G.; Huang, L. Plant electrical signal classification based on waveform similarity. Algorithms 2016, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.M.; Ferreira, A.S.; Saraiva, G.F.; Toledo, G.R. Plant “electrome” can be pushed toward a self-organized critical state by external cues: Evidences from a study with soybean seedlings subject to different environmental conditions. Plant Signal Behav. 2017, 12, e1290040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saraiva, G.F.R.; Ferreira, A.S.; Souza, G.M. Osmotic stress decreases complexity underlying the electrophysiological dynamic in soybean. Plant Biol. 2017, 19, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.K.; Malik, O.; Gupta, S. Chemical sensing employing plant electrical signal response-classification of stimuli using curve fitting coefficients as features. Biosensors 2018, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debono, M.W.; Souza, G.M. Plants as electromic plastic interfaces: A mesological approach. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2019, 146, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-H.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Yao, J.-P.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, P.-F.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Huang, L. Using a one-dimensional convolutional neural network with a conditional generative adversarial network to classify plant electrical signals. Comp. Electron. Agr. 2020, 174, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmi, F.Z.; Dallagnol, L.J.; Ferreira, A.S.; Pereira, D.R.; Souza, G.M. Electrome alterations in a plant-pathogen system: Toward early diagnosis. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 133, 107493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, A.G.; Reissig, G.N.; Basso, L.F.; Senko, L.G.S.; Oliveira, T.F.C.; de Toledo, G.R.A.; Ferreira, A.S.; Souza, G.M. Detection of different hosts from a distance alters the behaviour and bioelectrical activity of Cuscuta racemosa. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 594195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhova, E.; Yudina, L.; Akinchits, E.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Influence of electrical signals on pea leaf reflectance in the 400-800-nm range. Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1610301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhova, E.; Yudina, L.; Gromova, E.; Nerush, V.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Burning-induced electrical signals influence broadband reflectance indices and water index in pea leaves. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1737786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildon, D.C.; Thain, J.F.; Minchin, P.E.H.; Gubb, I.R.; Reilly, A.J.; Skipper, Y.D.; Doherty, H.M.; O’Donnell, P.J.; Bowles, D. Electrical signalling and systemic proteinase inhibitor Induction in the wounded plant. Nature 1992, 360, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, B.; Davies, E. Both action potentials and variation potentials induce proteinase inhibitor gene expression in tomato. FEBS Lett. 1996, 390, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Chauvin, A.; Pascaud, F.; Kellenberger, S.; Farmer, E.E. GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR-LIKE genes mediate leaf-to-leaf wound signalling. Nature 2013, 500, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hlavácková, V.; Krchnák, P.; Naus, J.; Novák, O.; Spundová, M.; Strnad, M. Electrical and chemical signals involved in short-term systemic photosynthetic responses of tobacco plants to local burning. Planta 2006, 225, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavinka, J.; Nožková-Hlaváčková, V.; Floková, K.; Novák, O.; Nauš, J. Jasmonic acid accumulation and systemic photosynthetic and electrical changes in locally burned wild type tomato, ABA-deficient sitiens mutants and sitiens pre-treated by ABA. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 54, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furch, A.C.; van Bel, A.J.; Fricker, M.D.; Felle, H.H.; Fuchs, M.; Hafke, J.B. Regular and Chaotic Dynamics: Moskow-Izhevsk. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2118–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furch, A.C.; Zimmermann, M.R.; Will, T.; Hafke, J.B.; van Bel, A.J. Remote-controlled stop of phloem mass flow by biphasic occlusion in Cucurbita maxima. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filek, M.; Kościelniak, J. The effect of wounding the roots by high temperature on the respiration rate of the shoot and propagation of electric signal in horse bean seedlings (Vicia faba L. minor). Plant Sci. 1997, 123, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautner, S.; Stummer, M.; Matyssek, R.; Fromm, J.; Grams, T.E.E. Involvement of respiratory processes in the transient knockout of net CO2 uptake in Mimosa pudica upon heat stimulation. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surova, L.; Sherstneva, O.; Vodeneev, V.; Katicheva, L.; Semina, M.; Sukhov, V. Variation potential-induced photosynthetic and respiratory changes increase ATP content in pea leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 202, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retivin, V.G.; Opritov, V.A.; Fedulina, S.B. Generation of action potential induces preadaptation of Cucurbita pepo L. stem tissues to freezing injury. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 1997, 44, 432–442. [Google Scholar]
- Retivin, V.G.; Opritov, V.A.; Lobov, S.A.; Tarakanov, S.A.; Khudyakov, V.A. Changes in the resistance of photosynthesizing cotyledon cells of pumpkin seedlings to cooling and heating, as induced by the stimulation of the root system with KCl solution. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 1999, 46, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhov, V.; Surova, L.; Sherstneva, O.; Bushueva, A.; Vodeneev, V. Variation potential induces decreased PSI damage and increased PSII damage under high external temperatures in pea. Funct. Plant. Biol. 2015, 42, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surova, L.; Sherstneva, O.; Vodeneev, V.; Sukhov, V. Variation potential propagation decreases heat-related damage of pea photosystem I by 2 different pathways. Plant Sign. Behav. 2016, 11, e1145334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gassel, M.; Glatt, E.; Kaiser, F. Doubly diversity-induced resonance. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 016203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.B.; Yang, X.L.; Kurths, J. Diversity and time delays induce resonance in a modular neuronal network. Chaos 2014, 24, 043140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patriarca, M.; Postnova, S.; Braun, H.A.; Hernández-García, E.; Toral, R. Diversity and noise effects in a model of homeostatic regulation of the sleep-wake cycle. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steuer, R.; Zhou, C.; Kurths, J. Constructive effects of fluctuations in genetic and biochemical regulatory systems. Biosystems. 2003, 72, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Cortés, H.; Fisahn, J.; Willmitzer, L. Signals involved in wound-induced proteinase inhibitor II gene expression in tomato and potato plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4106–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Bel, A.J.; Knoblauch, M.; Furch, A.C.; Hafke, J.B. (Questions)(n) on phloem biology. 1. Electropotential waves, Ca2+ fluxes and cellular cascades along the propagation pathway. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 210-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species-dependent wound responses in animals and plants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.G.; Toyota, M.; Kim, S.H.; Hilleary, R.; Gilroy, S. Salt stress-induced Ca2+ waves are associated with rapid, long-distance root-to-shoot signaling in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6497–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Bel, A.J.; Furch, A.C.; Will, T.; Buxa, S.V.; Musetti, R.; Hafke, J.B. Spread the news: Systemic dissemination and local impact of Ca2⁺ signals along the phloem pathway. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1761–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilleary, R.; Gilroy, S. Systemic signaling in response to wounding and pathogens. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 43, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichman, Y.; Myers, R.J., Jr.; Grant, D.G.; Mittler, R. Plasmodesmata-localized proteins and ROS orchestrate light-induced rapid systemic signaling in Arabidopsis. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eabf0322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlenbock, P.; Szechynska-Hebda, M.; Plaszczyca, M.; Baudo, M.; Mateo, A.; Mullineaux, P.M.; Parker, J.E.; Karpinska, B.; Karpinski, S. Chloroplast signaling and LESION SIMULATING DISEASE1 regulate crosstalk between light acclimation and immunity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2339–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szechyńska-Hebda, M.; Kruk, J.; Górecka, M.; Karpińska, B.; Karpiński, S. Evidence for light wavelength-specific photoelectrophysiological signaling and memory of excess light episodes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2201–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukhova, E.; Ratnitsyna, D.; Sukhov, V. Stochastic Spatial Heterogeneity in Activities of H+-ATP-Ases in Electrically Connected Plant Cells Decreases Threshold for Cooling-Induced Electrical Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158254
Sukhova E, Ratnitsyna D, Sukhov V. Stochastic Spatial Heterogeneity in Activities of H+-ATP-Ases in Electrically Connected Plant Cells Decreases Threshold for Cooling-Induced Electrical Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):8254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158254
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukhova, Ekaterina, Daria Ratnitsyna, and Vladimir Sukhov. 2021. "Stochastic Spatial Heterogeneity in Activities of H+-ATP-Ases in Electrically Connected Plant Cells Decreases Threshold for Cooling-Induced Electrical Responses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 8254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158254
APA StyleSukhova, E., Ratnitsyna, D., & Sukhov, V. (2021). Stochastic Spatial Heterogeneity in Activities of H+-ATP-Ases in Electrically Connected Plant Cells Decreases Threshold for Cooling-Induced Electrical Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 8254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158254





