Target Affinity and Structural Analysis for a Selection of Norovirus Aptamers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Aptamer Affinity to Norovirus VLPs
2.2. Structure Analysis of Biotinylated and Non-Biotinylated Oligonucleotides Using Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
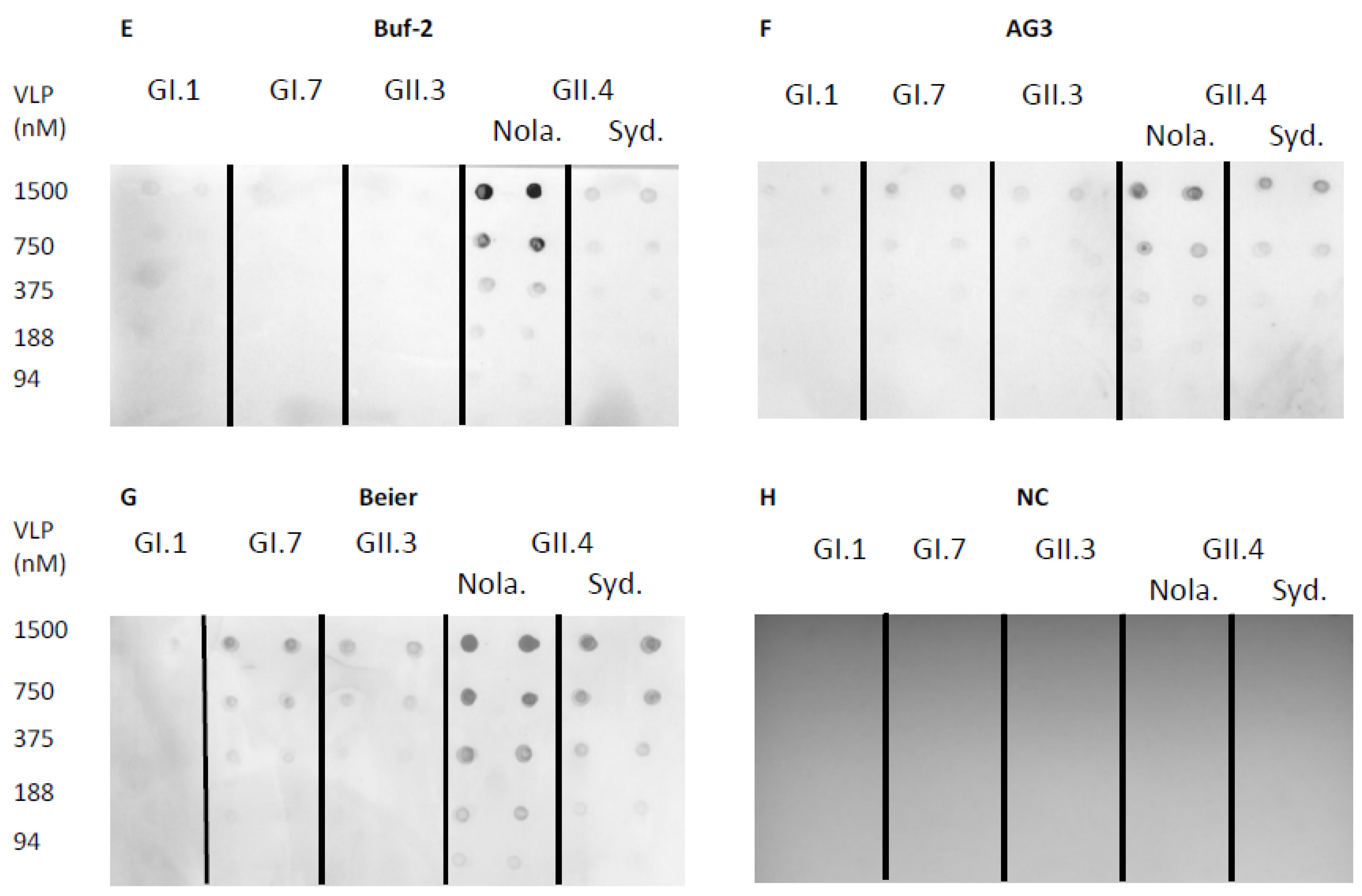
2.3. Aptamer-Mediated Dot-Blot for the Detection of Norovirus VLPs
2.4. Aptamer-Mediated Pull-down for the Extraction of Norovirus from Purified Stool Solution
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Oligonucleotides (Aptamers)
4.2. Norovirus VLPs
4.3. Filter Retention Assay to Investigate Target Binding of Selected Norovirus Aptamers
4.4. Analysis of Oligonucleotides Using Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
4.5. Aptamer-Mediated Dot-Blot Detecting Norovirus Virus like Particles
4.6. Aptamer-Mediated Pull-Down of Norovirus GII.4 from Purified Stool Solution
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koo, H.L.; Ajami, N.; Atmar, R.L.; DuPont, H.L. Noroviruses: The Principal Cause of Foodborne Disease Worldwide. Discov. Med. 2010, 10, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States—Major Pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.N.; Graham, D.Y.; Wang, K.N.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus genome cloning and characterization. Science 1990, 250, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K. Expression, self-assembly, and antigenicity of the Norwalk virus capsid protein. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6527–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Estes, M.K. Sequence and Genomic Organization of Norwalk Virus. Virology 1993, 195, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.V.V.; Hardy, M.E.; Dokland, T.; Bella, J.; Rossmann, M.G.; Estes, M.K. X-ray Crystallographic Structure of the Norwalk Virus Capsid. Science 1999, 286, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, P.; De Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.-W.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneman, A.; Vega, E.; Vennema, H.; Vinje, J.; White, P.; Hansman, G.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Katayama, K.; Koopmans, M. Proposal for a unified norovirus nomenclature and genotyping. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolin, R.; Blacklow, N.R.; DuPont, H.; Buscho, R.F.; Wyatt, R.G.; Kasel, J.A.; Hornick, R.; Chanock, R.M. Biological Properties of Norwalk Agent of Acute Infectious Nonbacterial Gastroenteritis. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1972, 140, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, S.R.; Leon, J.S.; Schwab, K.J.; Lyon, G.M.; Dowd, M.; McDaniels, M.; Abdulhafid, G.; Fernandez, M.L.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Baric, R.S.; et al. Norovirus Infectivity in Humans and Persistence in Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6884–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G.P.; Watson, M.A.; Meade, G.K.; Hovan, G.L.; Kingsley, D.H. Resilience of Norovirus GII.4 to Freezing and Thawing: Implications for Virus Infectivity. Food Environ. Virol. 2012, 4, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.W.; Barclay, L.; Macinga, D.; Charbonneau, D.; Pettigrew, C.A.; Vinje, J. Comparative Efficacy of Seven Hand Sanitizers against Murine Norovirus, Feline Calicivirus, and GII.4 Norovirus†. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 2232–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunis, P.F.; Moe, C.L.; Liu, P.; Miller, S.E.; Lindesmith, L.; Baric, R.S.; Le Pendu, J.; Calderon, R.L. Norwalk virus: How infectious is it? J. Med Virol. 2008, 80, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guyader, F.S.; Mittelholzer, C.; Haugarreau, L.; Hedlund, K.-O.; Alsterlund, R.; Pommepuy, M.; Svensson, L. Detection of noroviruses in raspberries associated with a gastroenteritis outbreak. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 97, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäde, D.; Trübner, K.; Neubert, E.; Höhne, M.; Johne, R. Detection and Typing of Norovirus from Frozen Strawberries Involved in a Large-Scale Gastroenteritis Outbreak in Germany. Food Environ. Virol. 2013, 5, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Rasmussen, L.D.; Jensen, T.; Schultz, A.C.; Kjelsø, C.; Barnadas, C.; Sigsgaard, K.; Larsen, A.R.; Widstrup Jensen, C.; Jeppesen, S.; et al. Series of Norovirus Outbreaks Caused by Consumption of Green Coral Lettuce, Denmark, April 2016. PLoS Curr. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guyader, F.S.; Bon, F.; DeMedici, D.; Parnaudeau, S.; Bertone, A.; Crudeli, S.; Doyle, A.; Zidane, M.; Suffredini, E.; Kohli, E.; et al. Detection of Multiple Noroviruses Associated with an International Gastroenteritis Outbreak Linked to Oyster Consumption. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.W.; Calci, K.R.; Marchant-Tambone, J.G.; Burkhardt, W. Detection and molecular characterization of norovirus from oysters implicated in outbreaks in the US. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutjes, S.A.; Lodder-Verschoor, F.; Van Der Poel, W.H.M.; Van Duijnhoven, Y.T.H.P.; Husman, A.M.D.R. Detection of Noroviruses in Foods: A Study on Virus Extraction Procedures in Foods Implicated in Outbreaks of Human Gastroenteritis. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vinjé, J. Advances in Laboratory Methods for Detection and Typing of Norovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Aptamer-Based Technology for Food Analysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-González, S.; De-Los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Aptamer-Based Analysis: A Promising Alternative for Food Safety Control. Sensors 2013, 13, 16292–16311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombelli, S.; Minunni, M.; Mascini, M. Aptamers-based assays for diagnostics, environmental and food analysis. Biomol. Eng. 2007, 24, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero-Abarca, B.I.; Suh, S.H.; Moore, M.; Dwivedi, H.P.; Jaykus, L.-A. Selection, Characterization and Application of Nucleic Acid Aptamers for the Capture and Detection of Human Norovirus Strains. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, R.; Pahlke, C.; Quenzel, P.; Henseleit, A.; Boschke, E.; Cuniberti, G.; LaBudde, D. Selection of a DNA aptamer against norovirus capsid protein VP1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 351, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.D.; Escudero-Abarca, B.I.; Suh, S.H.; Jaykus, L.-A. Generation and characterization of nucleic acid aptamers targeting the capsid P domain of a human norovirus GII.4 strain. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 209, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamberardino, A.; Labib, M.; Hassan, E.M.; Tetro, J.A.; Springthorpe, S.; Sattar, S.A.; Berezovski, M.V.; DeRosa, M.C. Ultrasensitive Norovirus Detection Using DNA Aptasensor Technology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.B.; DeGrasse, J.; Woods, J.W. The influence of food matrices on aptamer selection by SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) targeting the norovirus P-Domain. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Jia, F.; Wu, Q.; Tian, P.; Wang, D. Development and evaluation of a novel in situ target-capture approach for aptamer selection of human noroviruses. Talanta 2019, 193, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Moore, M.D. A Survey of Analytical Techniques for Noroviruses. Foods 2020, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeague, M.; De Girolamo, A.; Valenzano, S.; Pascale, M.; Ruscito, A.; Velu, R.; Frost, N.R.; Hill, K.; Smith, M.; McConnell, E.M.; et al. Comprehensive Analytical Comparison of Strategies Used for Small Molecule Aptamer Evaluation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8608–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Bowser, M.T. Methods for measuring aptamer-protein equilibria: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 686, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarkatti, R.; Bist, V.; Sun, S.; De Araújo, F.F.; Nakhasi, H.L.; Debrabant, A. Development of an Aptamer-Based Concentration Method for the Detection of Trypanosoma cruzi in Blood. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilgu, M.; Nilsen-Hamilton, M. Aptamers in analytics. Analyst 2016, 141, 1551–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckman, J.; Green, L.S.; Beeson, J.; Waugh, S.; Gillette, W.L.; Henninger, D.D.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Janjić, N. 2′-Fluoropyrimidine RNA-based Aptamers to the 165-Amino Acid Form of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF165): Inhibition of Receptor Binding and VEGF-Induced Vascular Permeability through Interactions Requiring the Exon 7-Encoded Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, L.C.; Griffin, L.C.; Latham, J.A.; Vermaas, E.H.; Toole, J.J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 1992, 355, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizenga, D.E.; Szostak, J.W. A DNA Aptamer That Binds Adenosine and ATP. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T.D. A Guide to Simple and Informative Binding Assays. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, T.; Okame, M.; Takanashi, S.; Khamrin, P.; Takagi, M.; Satou, K.; Masuoka, Y.; Yagyu, F.; Shimizu, Y.; Kohno, H.; et al. Characterization of a Broadly Reactive Monoclonal Antibody against Norovirus Genogroups I and II: Recognition of a Novel Conformational Epitope. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12298–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Ferris, M.T.; Mullan, C.; Ferreira, J.; Debbink, K.; Swanstrom, J.; Richardson, C.; Goodwin, R.R.; Baehner, F.; Mendelman, P.M.; et al. Broad Blockade Antibody Responses in Human Volunteers after Immunization with a Multivalent Norovirus VLP Candidate Vaccine: Immunological Analyses from a Phase I Clinical Trial. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Terano, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Sakon, N.; Kuzuguchi, T.; Oda, H.; Tsukamoto, T. Precise Characterization of Norovirus (Norwalk-Like Virus)-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies with Broad Reactivity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2367–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, A.K.; Kavanagh, O.V.; Estes, M.K.; Elimelech, M. Adsorption and Aggregation Properties of Norovirus GI and GII Virus-like Particles Demonstrate Differing Responses to Solution Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodridge, L.; Goodridge, C.; Wu, J.; Griffiths, M.; Pawliszyn, J. Isoelectric Point Determination of Norovirus Virus-like Particles by Capillary Isoelectric Focusing with Whole Column Imaging Detection. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hianik, T.; Ostatna, V.; Sonlajtnerova, M.; Grman, I. Influence of ionic strength, pH and aptamer configuration for binding affinity to thrombin. Bioelectrochemistry 2007, 70, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Pardo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Bashammakh, A.S.O.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Quantification of Nucleic Acid Concentration in the Nanoparticle or Polymer Conjugates Using Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kypr, J.; Kejnovská, I.; Renčiuk, D.; Vorlickova, M. Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-T.; DeStefano, J.J. DNA Aptamers to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Reverse Transcriptase Selected by a Primer-Free SELEX Method: Characterization and Comparison with Other Aptamers. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012, 22, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrus, A.; Chen, D.; Dai, J.; Bialis, T.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D. Human telomeric sequence forms a hybrid-type intramolecular G-quadruplex structure with mixed parallel/antiparallel strands in potassium solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, T.; Hu, J.; Wang, E. A novel dot-blot DNAzyme-linked aptamer assay for protein detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2923–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, G.; Ahmed, M.-S.L.; Dolf, A.; Endl, E.; Knolle, P.A.; Famulok, M. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting for aptamer SELEX with cell mixtures. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.B.; Kranz, J.K. Nitrocellulose filter binding for determination of dissociation constants. In RNA-Protein Interaction Protocols; Haynes, S.R., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Papoulas, O. Rapid separation of protein-bound DNA from Free DNA using nitrocellulose filters. In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- DePaola, A.; Jones, J.L.; Woods, J.; Burkhardt, W.; Calci, K.R.; Krantz, J.A.; Bowers, J.; Kasturi, K.; Byars, R.H.; Jacobs, E.; et al. Bacterial and Viral Pathogens in Live Oysters: 2007 United States Market Survey. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2754–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, K.; Parmar, S.; Mururi, D.; Wreghitt, T.; Jalal, H.; Zhang, H.; Curran, M. An internally controlled, one-step, real-time RT-PCR assay for norovirus detection and genogrouping. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 39, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, T.; Kojima, S.; Shinohara, M.; Uchida, K.; Fukushi, S.; Hoshino, F.B.; Takeda, N.; Katayama, K. Broadly Reactive and Highly Sensitive Assay for Norwalk-Like Viruses Based on Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhy, P.; Bremont, S.; Zinini, F.; Giry, C.; Picardeau, M. Comparison of Real-Time PCR Assays for Detection of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. in Blood and Identification of Variations in Target Sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Candidate | Sequence 5′-3′ | Target Protein | Kd |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 [27] | TGTTTATGGGGATAAACGTATCTAATTCGTGTACTAATCA | GII.4 P-domain with GST fusion protein | n.d. * |
| M6-2 [27] | TGGGAAGAGGTCCGGTAAATGCAGGGTCAGCCCGGAGAG | n.d. * | |
| SMV19 [25] | CACCAGTGTGTTGAGGTTTGAGCACACTGATAGAGTGTCA | Whole virus GII.2 | 191 nM ** |
| SMV21 [25] | CCATGTTTTGTAGGTGTAATAGGTCATGTTAGGGTTTCTG | 101 Nm ** | |
| Buf-2 [29] | GAAATTGGGTTCGGGTTTGGGTTGGGATTACTTAGCGATG | GII.4 P-domain with His-Tag | 17 ± 7 nM |
| AG3 [28] | GCTAGCGAATTCCGTACGAAGGGCGAATTCCACATTGGGCTGCAGCCCGGGGGATCC | MNV | pM range *** |
| Beier [26] | GTCTGTAGTAGGGAGGATGGTCCGGGGCCCCGAGACGACGTTATCAGGC | GII.4 VP1 with His-Tag | n.d. * |
| Aptamers | Kd for GI.1 [nM] | Kd for GI.7 [nM] | Kd for GII.3 [nM] | Kd for GII.4 New Orleans [nM] | Kd for GII.4 Sydney [nM] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | - | - | - | 963 ± 348 | 388 ± 238 |
| M6-2 | - | - | - | 928 ± 425 | 1130 ± 7895 |
| SMV19 | - | - | - | 9342 ± 7491 | - |
| SMV21 | - | - | 464 ± 370 | 1777 ± 1021 | 1247 ± 372 |
| Buf-2 | - | - | 465 ± 370 | 351 ± 89 | 241 ± 50 |
| AG3 | - | - | - | 1033 ± 433 | 313 ± 81 |
| Beier | - | 63 ± 28 | 115 ± 34 | 105 ± 47 | 71 ± 38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schilling-Loeffler, K.; Rodriguez, R.; Williams-Woods, J. Target Affinity and Structural Analysis for a Selection of Norovirus Aptamers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168868
Schilling-Loeffler K, Rodriguez R, Williams-Woods J. Target Affinity and Structural Analysis for a Selection of Norovirus Aptamers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(16):8868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168868
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchilling-Loeffler, Katja, Rachel Rodriguez, and Jacquelina Williams-Woods. 2021. "Target Affinity and Structural Analysis for a Selection of Norovirus Aptamers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 16: 8868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168868
APA StyleSchilling-Loeffler, K., Rodriguez, R., & Williams-Woods, J. (2021). Target Affinity and Structural Analysis for a Selection of Norovirus Aptamers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168868






