Hippocampal and Reticulo-Thalamic Parvalbumin Interneurons and Synaptic Re-Organization during Sleep Disorders in the Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease Neuropathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
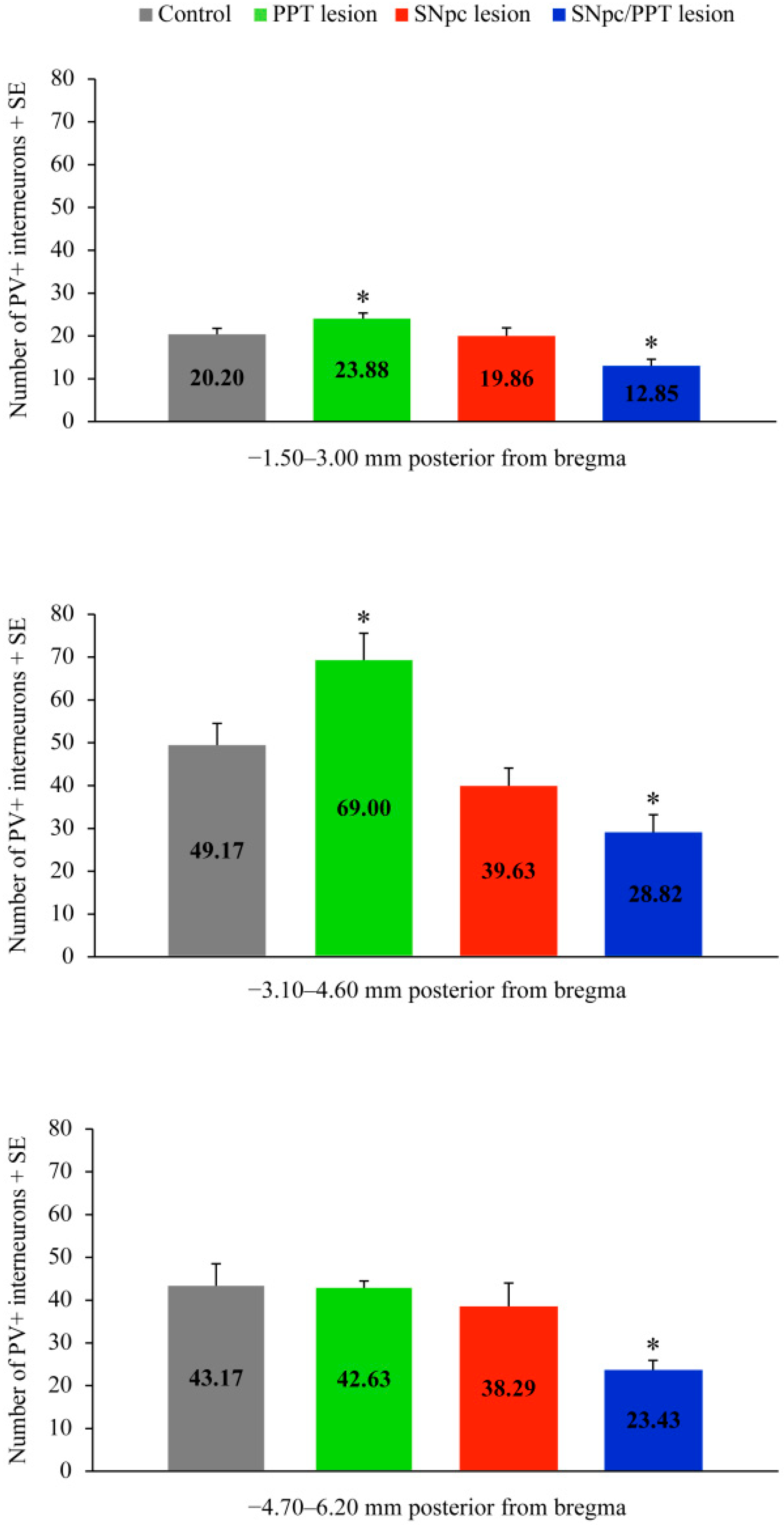
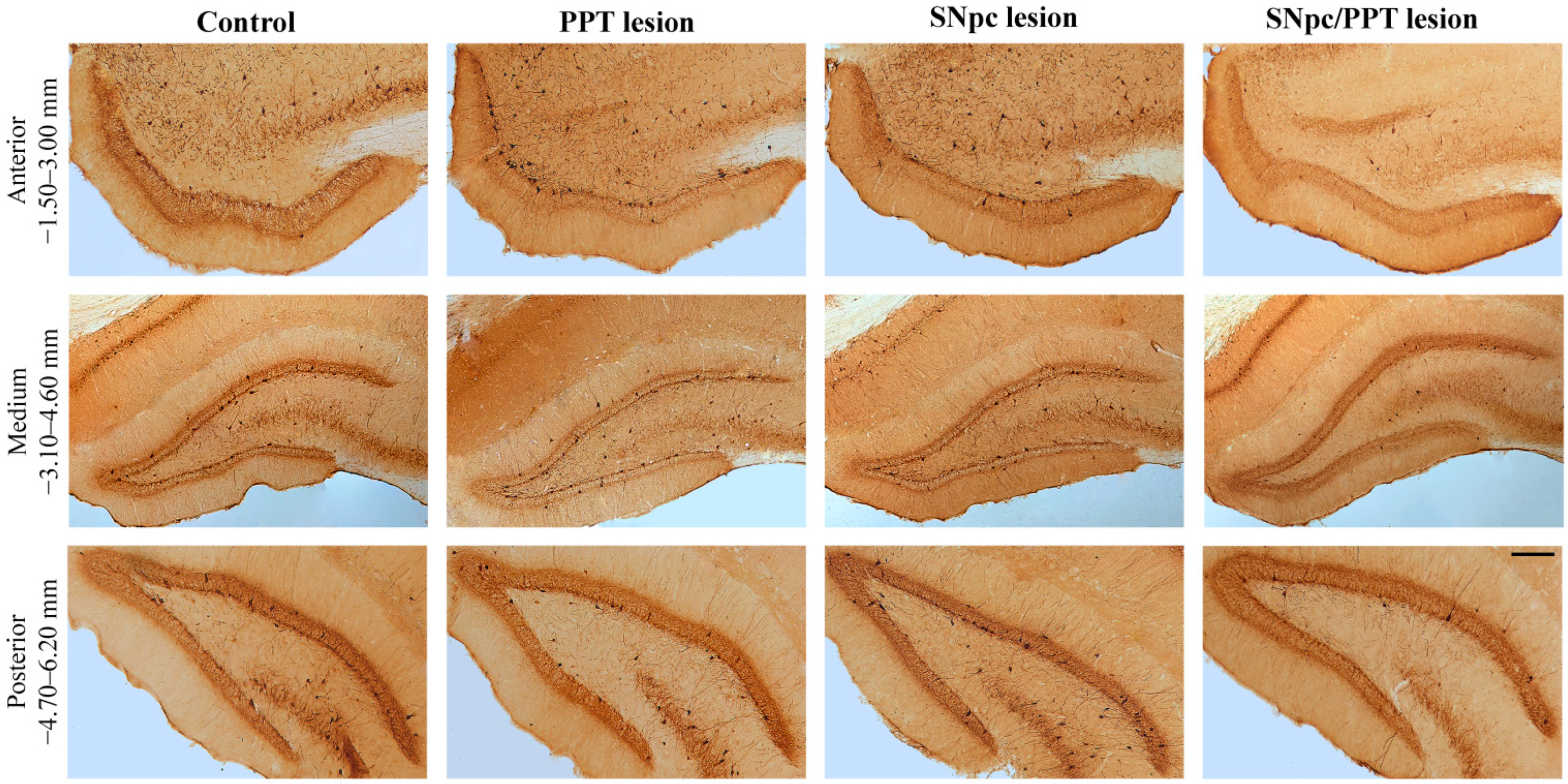
2.1. Alterations of the Hippocampal PV+ Interneurons in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
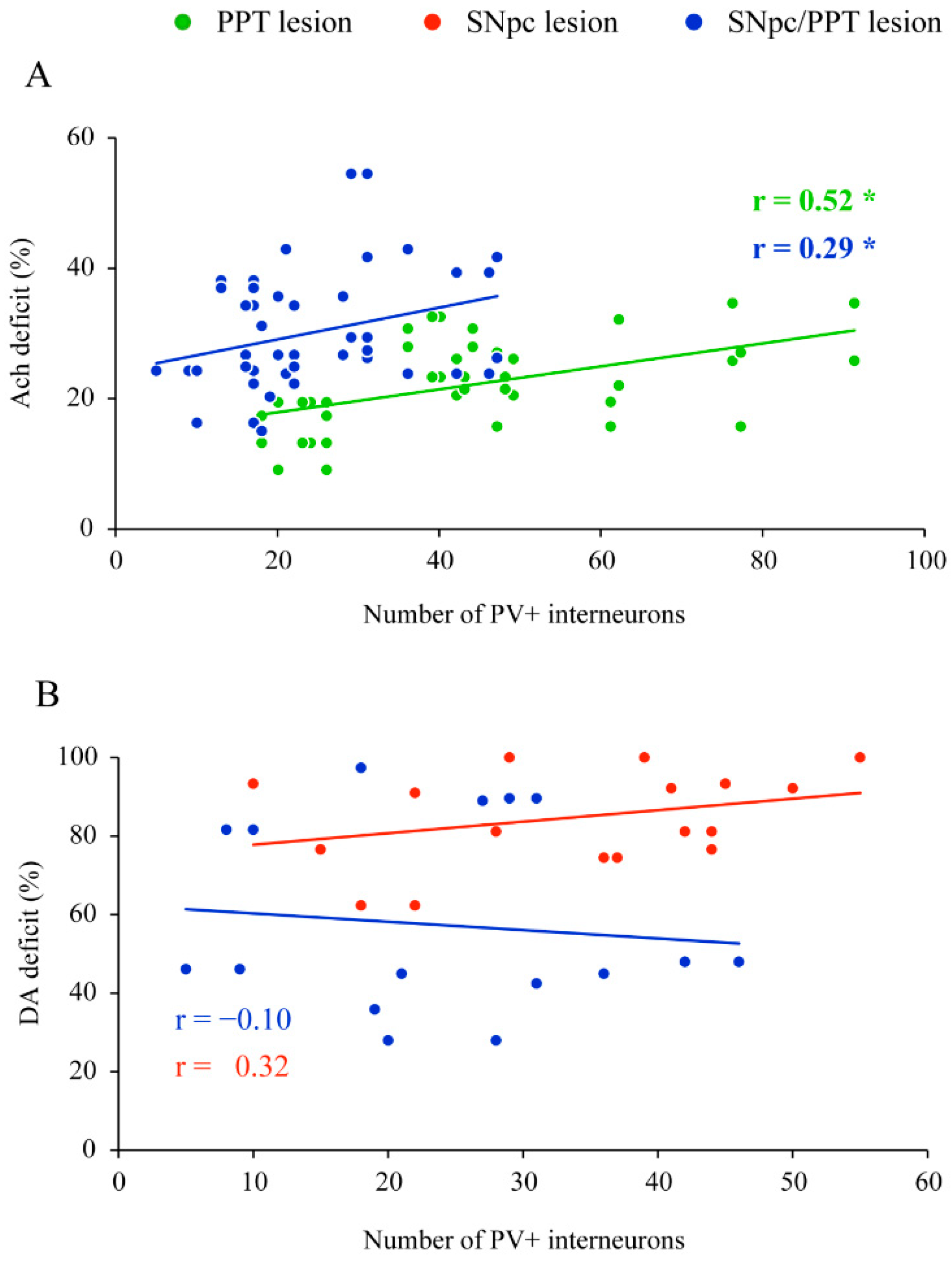
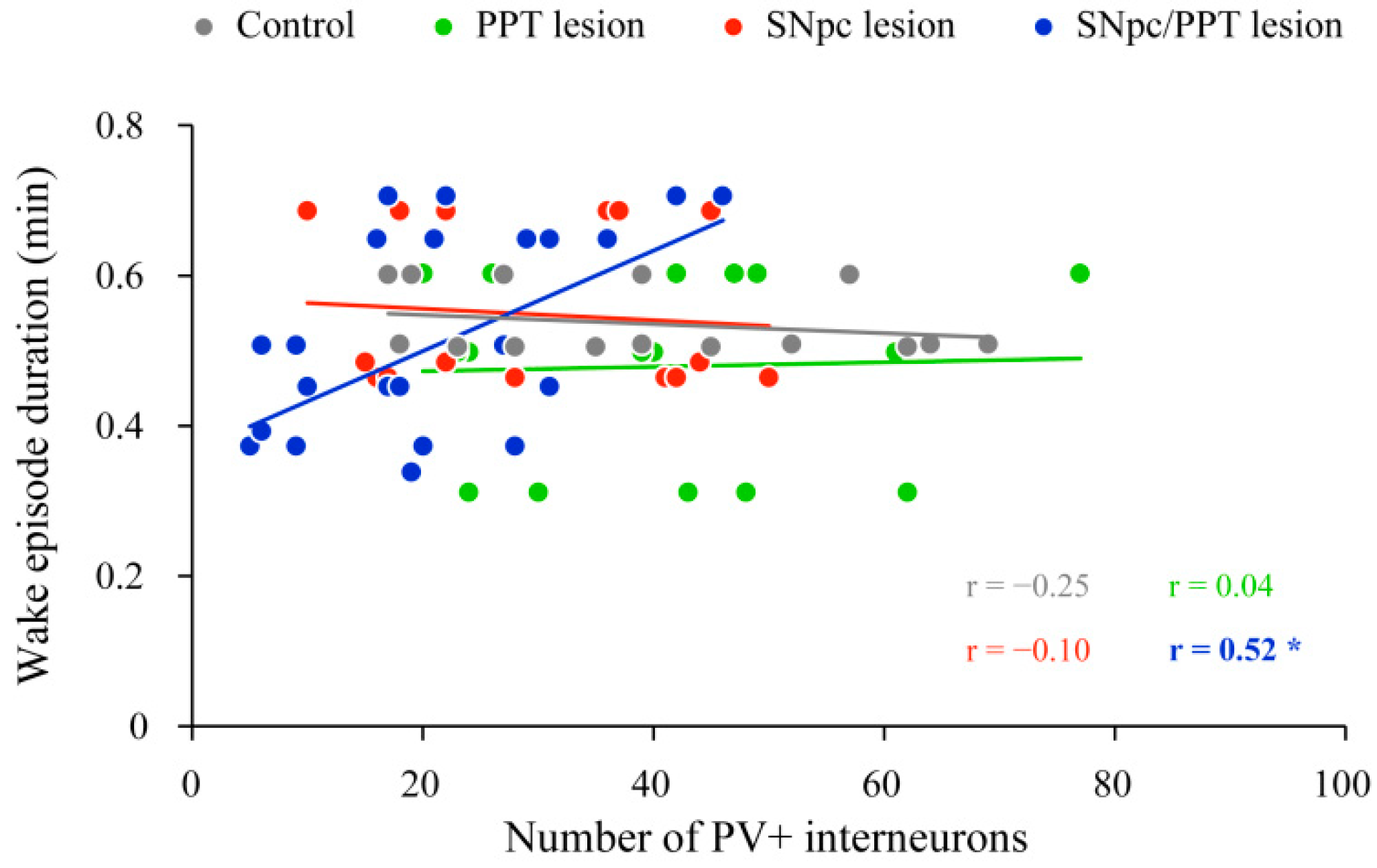
2.2. Impact of the Hippocampal PV+ Interneurons on Local Sleep Architecture and NREM/REM EEG Microstructure in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
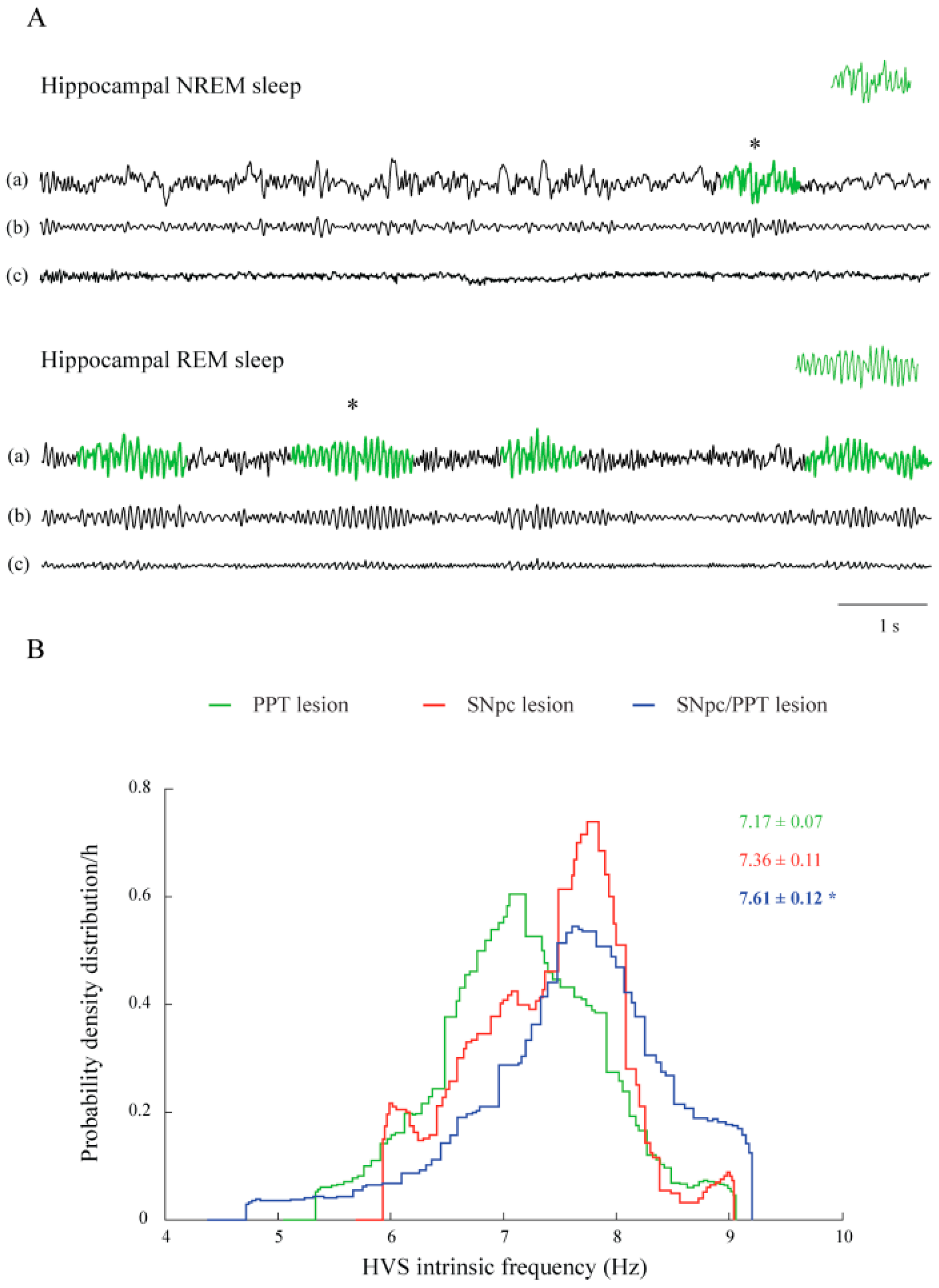
2.3. Sleep Spindle Dynamics in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
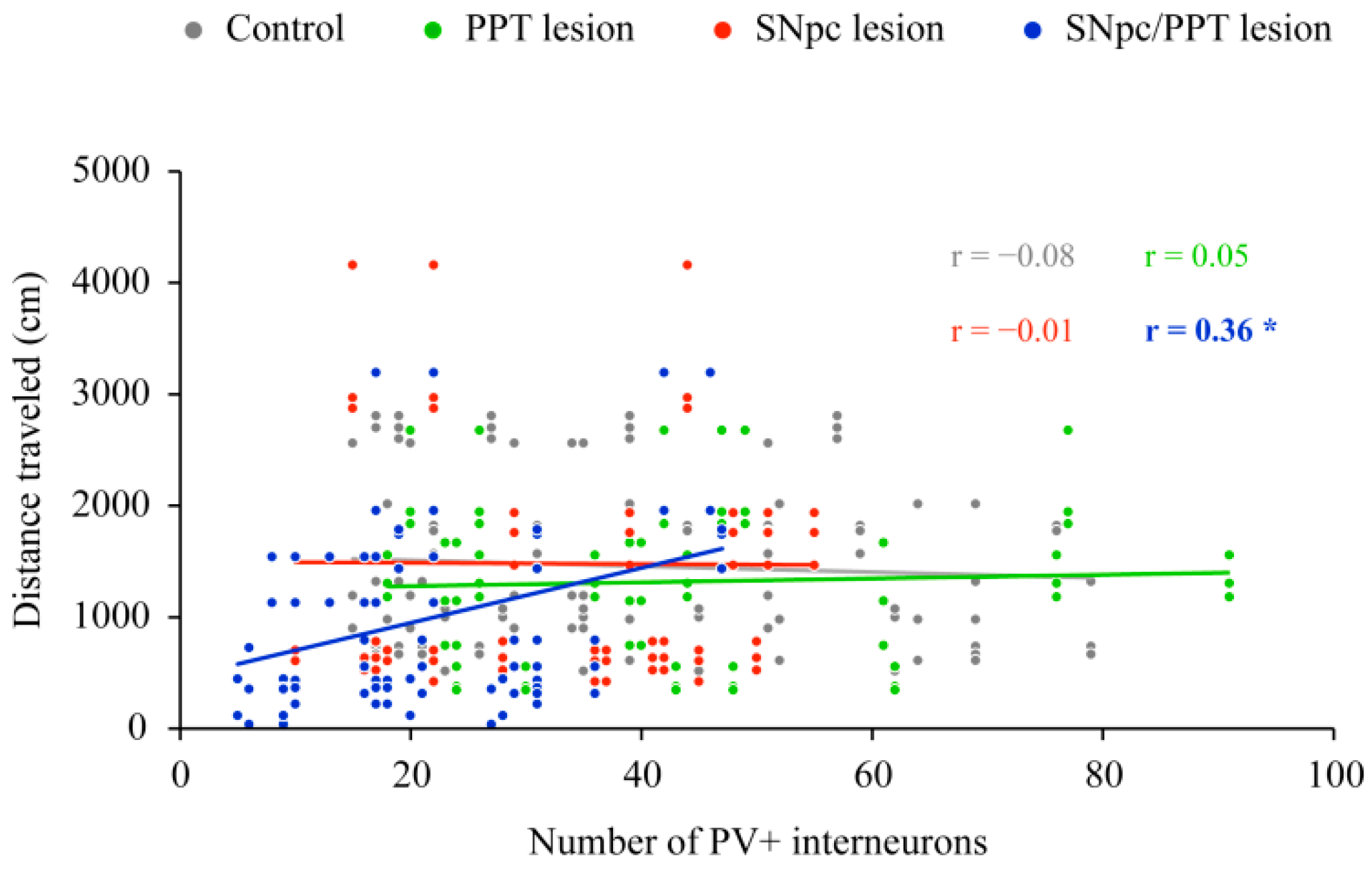
2.4. Impact of the Hippocampal PV+ Interneurons on the Spatial Memory Abilities (Habitual Response) in the Distinct Rat Models of PD
2.5. Hippocampal Synaptic Re-Organization and the PV+ Interneurons Alteration in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
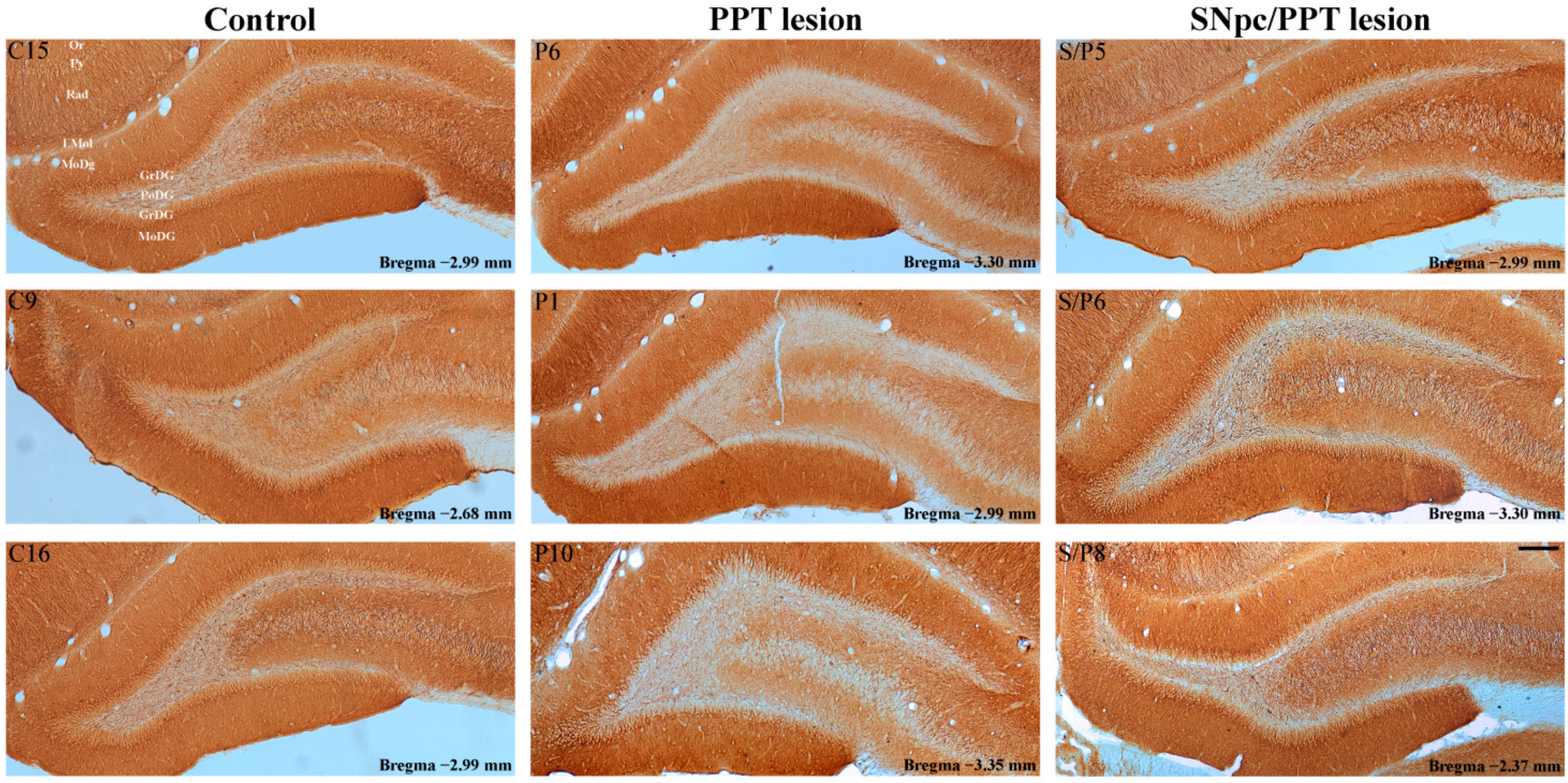
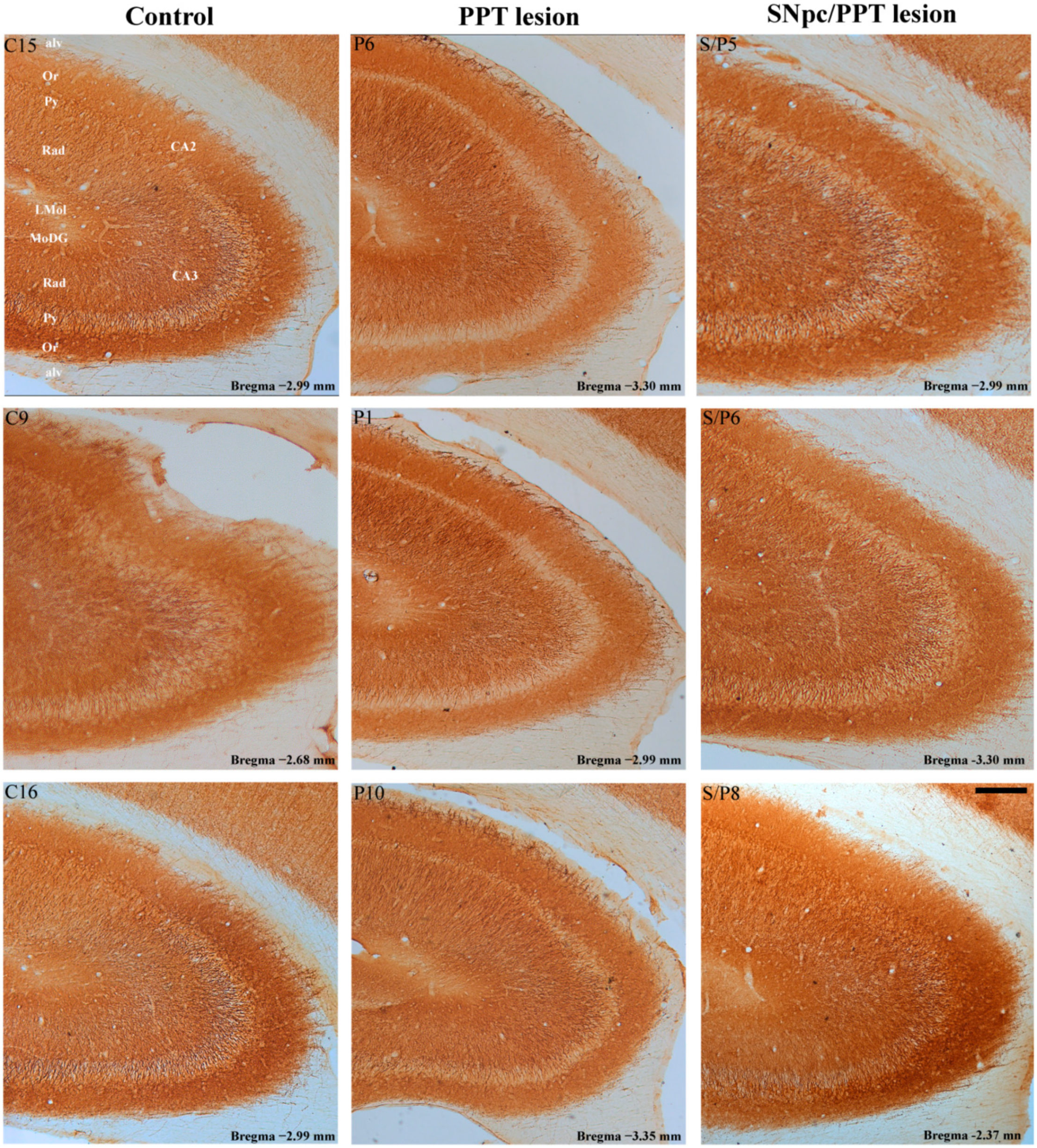
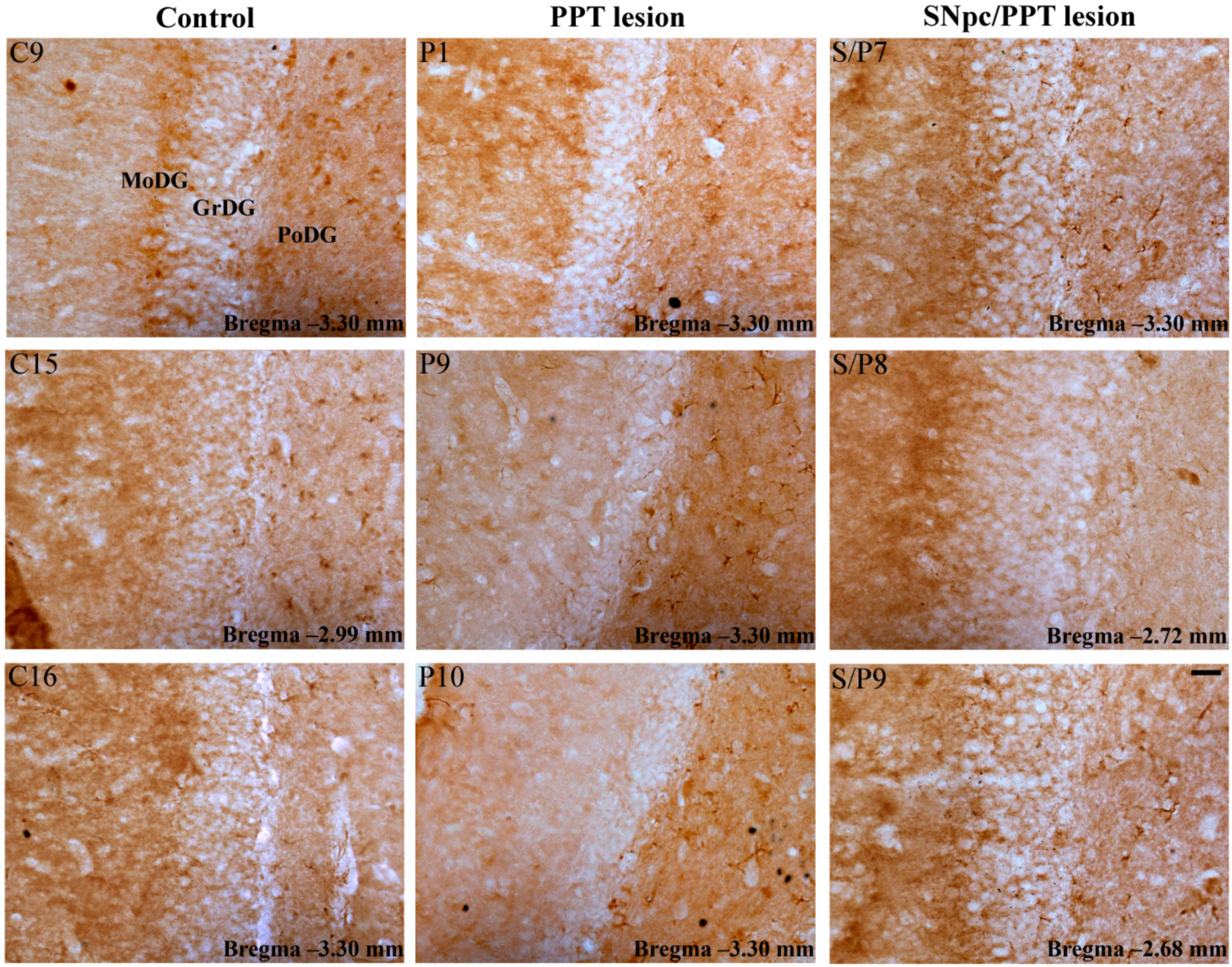
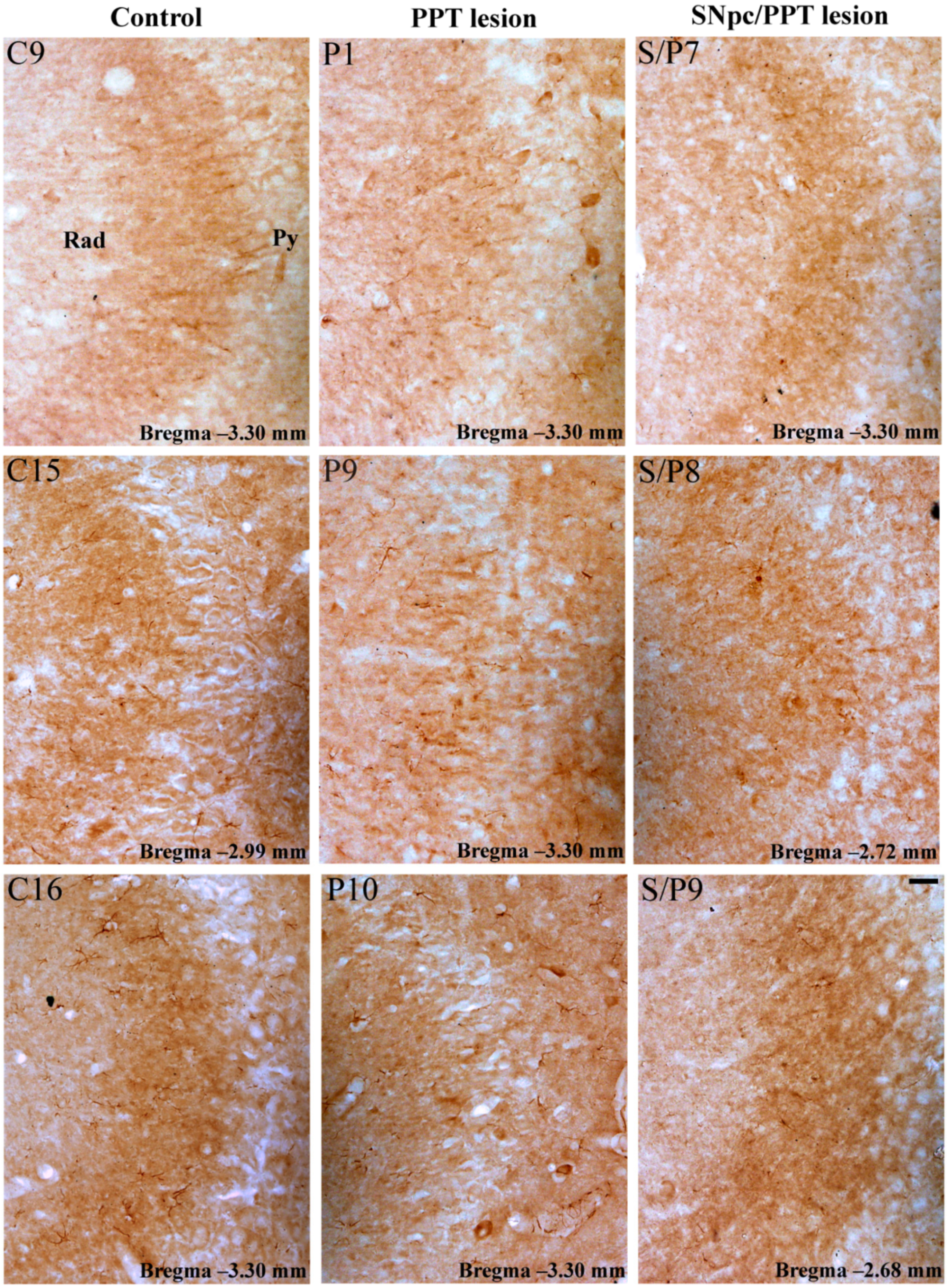
2.5.1. Hippocampal PV+ Interneurons Alteration and MAP2 Expression in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
2.5.2. Hippocampal PV+ Interneurons Alteration and PSD-95 Expression in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
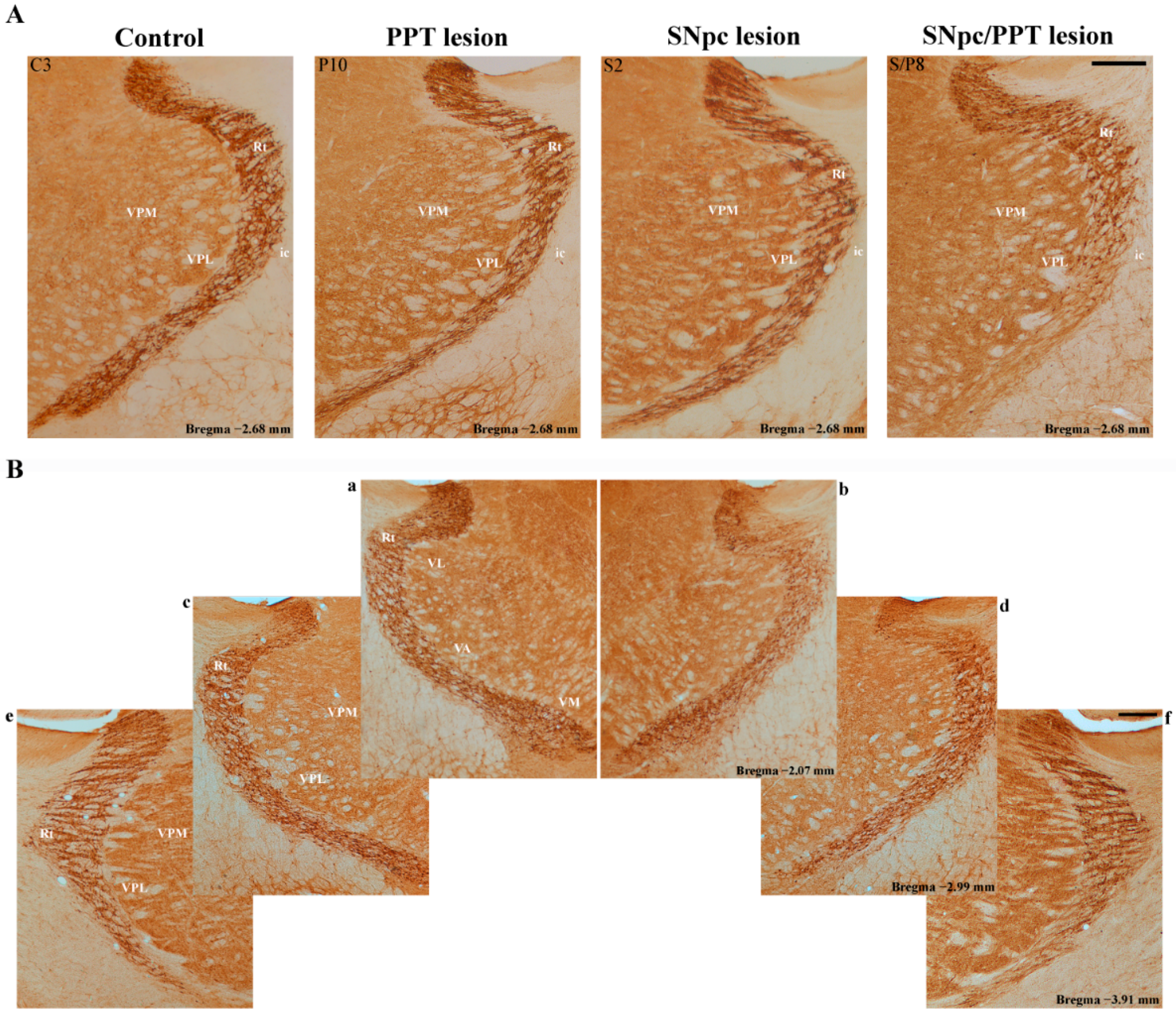
2.6. Alteration of the PV+ Interneurons in the Reticulo-Thalamic Nucleus (RT) in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
2.7. Synaptic Re-Organization of RT and the PV+ Interneurons Alteration in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
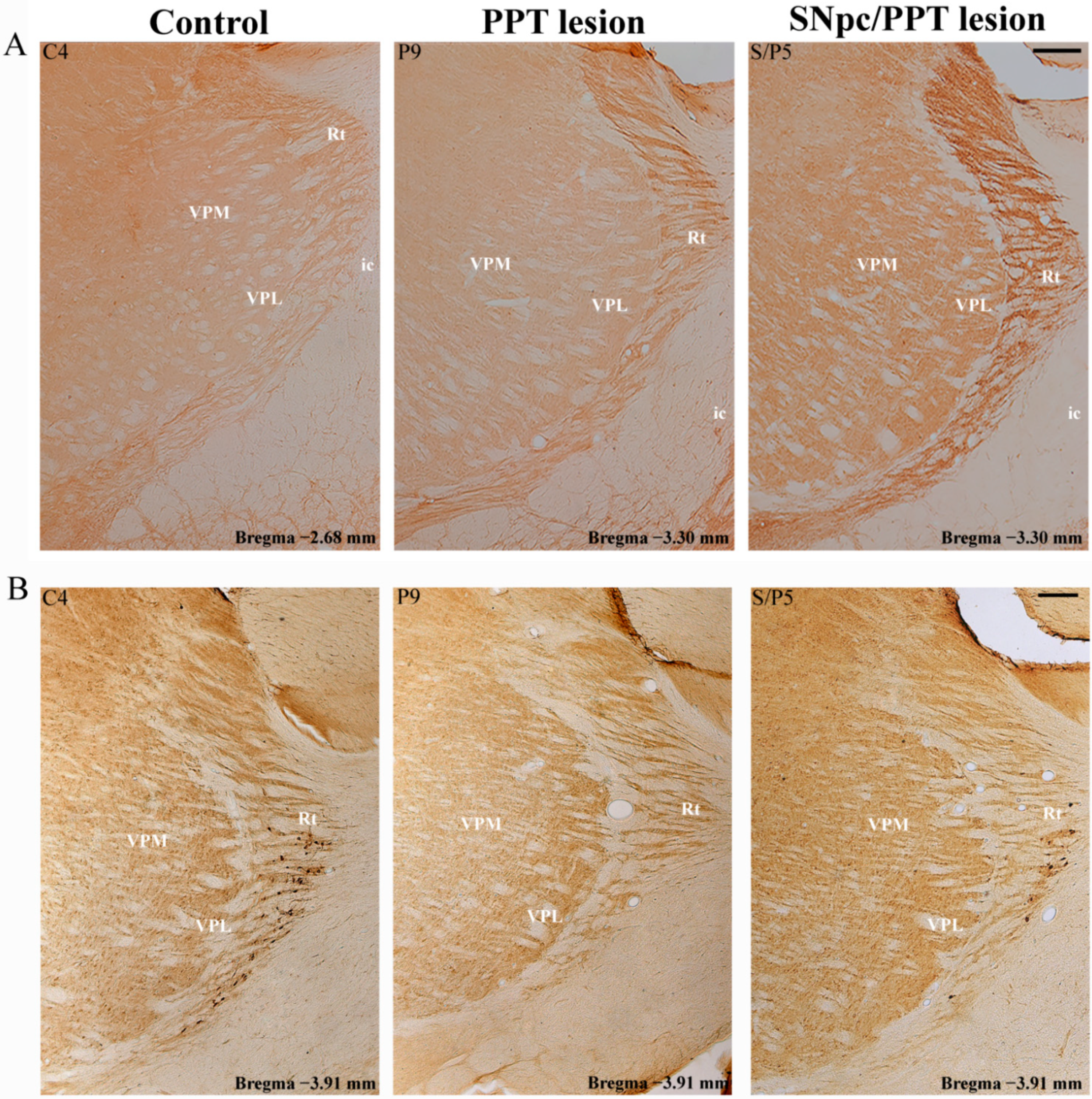
2.7.1. PV+ Interneurons Alteration of RT and MAP2 Expression in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
2.7.2. PV+ Interneurons Alteration of RT and PSD-95 Expression in the Distinct Rat Models of PD Neuropathology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Surgical Procedure
4.3. Recording Procedure
4.4. Behavioral Assessments
4.5. Tissue Processing for Histology
4.5.1. Lesion Identification and Quantification
4.5.2. Immunohistochemistry for PV, MAP2 and PSD-95
4.5.3. Quantification of PV Immunostaining
4.6. Sleep Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murueta-Goyena, A.; Andikoetxea, A.; Gomez-Esteban, J.C.; Gabilondo, I. Contribution of the GABAergic system to non-motor manifestations in premotor and early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczyk, J.W. Parkinson’s disease and neurodegeneration: GABA-collapse hypothesis. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.C.; Ulane, C.M.; Burke, R.E. Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D. Prodromal Parkinson’s disease: The decade past, the decade to come. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poewe, W. Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15 (Suppl. 1), 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, J.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: Animal models and dopaminergic cell vulnerability. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, D.d.C.; Lopes Aguiar, C.; Moraes, M.F.D.; Fisone, G. Sleep Disorders in Rodent Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.D.; Ross, G.W.; White, L.R.; Tanner, C.M.; Masaki, K.H.; Nelson, J.S.; Curb, J.D.; Petrovitch, H. Excessive daytime sleepiness and subsequent development of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2005, 65, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.C.; Li, Y.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Ascherio, A.; Gao, X. Restless legs syndrome: An early clinical feature of Parkinson disease in men. Sleep 2014, 37, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranzo, A.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Santamaria, J.; Serradell, M.; Marti, M.J.; Valldeoriola, F.; Tolosa, E. Rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder as an early marker for a neurodegenerative disorder: A descriptive study. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neikrug, A.B.; Maglione, J.E.; Liu, L.; Natarajan, L.; Avanzino, J.A.; Corey- Bloom, J.; Palmer, B.W.; Loredo, J.S.; Ancoli-Israel, S. Effects of sleep disorders on the non-motor symptoms of Parkinson disease. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, S.; Salvade, A.; Pace, M.; Sarasso, S.; Baracchi, F.; Bassetti, C.L.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Städler, C.; Stanzione, P.; Möller, J.C. Evidence of an association between sleep and levodopa-induced dyskinesia in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranzo, A.; Stefani, A.; Serradell, M.; Marti, M.J.; Lomena, F.; Mahlknecht, P.; Stockner, H.; Gaig, C.; Fernández-Arcos, A.; Poewe, W.; et al. SINBAR (Sleep Innsbruck Barcelona) group. Characterization of patients with longstanding idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder. Neurology 2017, 89, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjari Moghaddam, H.; Zare-Shahabadi, A.; Rahmani, F.; Rezaei, N. Neurotransmission systems in Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 28, 509–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Lloret, S.; Barrantes, F.J. Deficits in cholinergic neurotransmission and their clinical correlates in Parkinson’s disease. Npj Parkinson’s Dis. 2016, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesmann, C. GABA mechanism and sleep. Neuroscience 2002, 111, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B.; Fuller, P.M. Wake–sleep circuitry: An overview. Curr. Oppin. Neurobiol. 2017, 44, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eban-Rothschild, A.; Appelbaum, L.; de Lecea, L. Neuronal mechanisms for sleep/wake regulation and modulatory drive. Neuropharmacology 2018, 43, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman Tuura, R.L.; Baumann, C.R.; Baumann-Vogel, H. Beyond Dopamine: GABA, Glutamate, and the Axial Symptoms of Parkinson Disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, R.; Milet, A.; Toulorge, D.; Cholet, N.; Laffaire, J.; Foucquier, J.; Robelet, S.; Mitry, R.; Guedj, M.; Nabirotchkin, S.; et al. Combination of acamprosate and baclofen as a promising therapeutic approach for Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozovaya, N.; Eftekhari, S.; Cloarec, R.; Gouty-Colomer, L.A.; Dufour, A.; Riffault, B.; Billon-Grand, M.; Pons-Bennaceur, A.; Oumar, N.; Burnashev, N.; et al. GABAergic inhibition in dual-transmission cholinergic and GABAergic striatal interneurons is abolished in Parkinson disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, P.L.; Peever, J.H. Impaired GABA and glycine transmission triggers cardinal features of rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7111–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, J.; Ciric, J.; Lazic, K.; Kalauzi, A.; Saponjic, J. Lesion of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in rat augments cortical activation and disturbs sleep/wake state transitions structure. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 247, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, J.; Lazic, K.; Ciric, J.; Kalauzi, A.; Saponjic, J. Topography of the sleep/wake states related EEG microstructure and transitions structure differentiates the functionally distinct cholinergic innervation disorders in rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 256, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, J.; Lazic, K.; Kalauzi, A.; Saponjic, J. REM sleep diversity following the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesion in rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 271, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciric, J.; Lazic, K.; Petrovic, J.; Kalauzi, A.; Saponjic, J. Age-related disorders of sleep and motor control in the rat models of functionally distinct cholinergic neuropathology. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 301, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, J.; Lazic, K.; Petrovic, J.; Kalauzi, A.; Saponjic, J. Sleep spindles as an early biomarker of REM sleep disorder in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease cholinopathy. Transl. Brain Rhythm. 2017, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, J.; Lazic, K.; Kapor, S.; Perovic, M.; Petrovic, J.; Pesic, V.; Kanazir, S.; Saponjic, J. Sleep disorder and altered locomotor activity as biomarkers of the Parkinson’s disease cholinopathy in rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 339, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotagal, V.; Albin, R.L.; Muller, M.L.T.M.; Koeppe, R.A.; Chervin, R.D.; Frey, K.A.; Bohnen, N.I. Symptoms of rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder are associated with cholinergic denervation in Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, J.; Kapor, S.; Perovic, M.; Saponjic, J. Alteration of sleep and sleep oscillations in the hemiparkinsonian rat. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, J.; Radovanovic, L.; Saponjic, J. Prodromal local sleep disorders in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease cholinopathy, hemiparkinsonism and hemiparkinsonism with cholinopathy. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 397, 112957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, J.; Radovanovic, L.; Saponjic, J. Diversity of simultaneous sleep in the motor cortex and hippocampus in rats. J. Sleep Res. 2021, 30, e13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognjanovski, N.; Schaeffer, S.; Wu, J.; Mofakham, S.; Maruyama, D.; Zochowski, M.; Aton, S.J. Parvalbumin-expressing interneurons coordinate hippocampal network dynamics required for memory consolidation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, S.; Heistek, T.S.; Scheltens, P.; Neumann, U.; Shimshek, D.R.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Smit, A.B.; van Kesteren, R.E. Early restoration of parvalbumin interneuron activity prevents memory loss and network hyperexcitability in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 3380–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausberger, T.; Somogyi, P. Neuronal diversity and temporal dynamics: The unity of hippocampal circuit operations. Science 2008, 321, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausberger, T. GABAergic interneurons targeting dendrites of pyramidal cells in the CA1 area of the hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, J.M. The neurobiology of sleep. Semin. Neurol. 2009, 29, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeier, D.J.; Schumacker, P.T. Calcium, bioenergetics, and neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10736–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filice, F.; Vörckel, K.J.; Sungur, A.Ö.; Wöhr, M.; Schwaller, B. Reduction in parvalbumin expression not loss of the parvalbumin-expressing GABA interneuron subpopulation in genetic parvalbumin and shank mouse models of autism. Mol. Brain 2016, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipović, D.; Zlatković, J.; Gass, P.; Inta, D. The differential effects of acute vs. chronic stress and their combination on hippocampal parvalbumin and inducible heat shock protein 70 expression. Neuroscience 2013, 236, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landisman, C.E.; Long, M.A.; Beierlein, M.; Deans, M.R.; Paul, D.L.; Connors, B.W. Electrical Synapses in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, J.A.; Morris, B.J. The thalamic reticular nucleus: A functional hub for thalamocortical network dysfunction in schizophrenia and a target for drug discovery. J. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 29, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantomme, G.; Osorio-Forero, A.; Lüthi, A.; Fernandez, L.M.J. Regulation of local sleep by the thalamic reticular nucleus. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Koyanagi, I.; Carrier-Ruiz, A.; Vergara, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Sugaya, Y.; Kasuya, M.; Yu, T.S.; Vogt, K.E.; Muratani, M.; et al. Sparse activity of hippocampal adult-born neurons during REM sleep is necessary for memory consolidation. Neuron 2020, 107, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollnagel, J.O.; Elzoheiry, S.; Gorgas, K.; Kins, S.; Beretta, C.A.; Kirsch, J.; Kuhse, J.; Kann, O.; Kiss, E. Early alterations in hippocampal perisomatic GABAergic synapses and network oscillations in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease amyloidosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 5th ed.; Academic Pres: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; ISBN 9780080474120. [Google Scholar]
- Saponjic, J.; Petrovic, J.; Ciric, J.; Lazic, K. Disorders of sleep and motor control during the impaired cholinergic innervation in rat—relevance to Parkinson’s disease. In Challenges in Parkinson’s Disease; Dorszewska, J., Kozubski, W., Eds.; InTech Rijeka: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, N.; Ciric, J.; Milosevic, N.; Saponjic, J. Novel application of the gray-level.co-occurrence matrix analysis in the parvalbumin stained hippocampal gyrus dentatus in distinct rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 115, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C.; Carrive, P.; Kirkcaldie, M.; Ashwell, K.W.S. Chemoarchitectonic Atlas of the Rat Brain, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0123742377. [Google Scholar]
- Lazic, K.; Ciric, J.; Saponjic, J. Sleep spindle dynamics during NREM and REM sleep following distinct general anaesthesia in control rats and in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease cholinopathy. J. Sleep Res. 2019, 28, e12758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Genzel, L.; Dresler, M.; Steiger, A.; Friess, E. Automatic sleep spindle detection and genetic influence estimation using continuous wavelet transform. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control | ||||||||
| n | nSS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | SSdur/h (min) | SSdur (s) | SSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 5/8 (63%) | 29 | 0.34 ± 0.17 | 25.70 ± 4.28 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 1.34 ± 0.12 | 13.56± 0.21 |
| REM | 7/8 (88%) | 17 | 0.38 ± 0.11 | 7.00 ± 0.74 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 1.39 ± 0.18 | 13.65 ± 0.28 | |
| Hipp | NREM | 3/8 (38%) | 12 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| REM | 3/8 (38%) | 4 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | |
| PPT lesion | ||||||||
| n | nSS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | SSdur/h (min) | SSdur (s) | SSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 8/8 (100%) | 124 | 0.52 ± 0.10 | 31.02 ± 2.33 | 0.31 ± 0.05 | 1.18 ± 0.04 | 13.24 ± 0.09 |
| REM | 8/8 (100%) | 18 | 0.22 ± 0.07 * | 10.69 ± 1.40 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 1.52 ± 0.16 * | 12.69 ± 0.16 | |
| Hipp | NREM | 6/8 (75%) | 31 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 31.81 ± 2.91 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 1.21 ± 0.06 | 12.70 ± 0.10 |
| REM | 2/8 (25%) | 6 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | |
| SNpc lesion | ||||||||
| n | nSS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | SSdur/h (min) | SSdur (s) | SSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 5/7 (71%) | 132 | 0.91 ± 0.21 | 28.30 ± 4.10 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 1.23 ± 0.05 | 13.31 ± 0.08 |
| REM | 5/7 (71%) | 34 | 0.73 ± 0.21 | 9.00 ± 0.46 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 1.88 ± 0.14 * | 13.14 ± 0.11 | |
| Hipp | NREM | 5/7 (71%) | 36 | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 28.83 ± 3.73 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 1.19 ± 0.08 | 12.56 ± 0.11 |
| REM | 3/7 (43%) | 9 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | |
| SNpc/PPT lesion | ||||||||
| n | nSS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | SSdur/h (min) | SSdur (s) | SSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 8/8 (100%) | 166 | 0.81 ± 0.19 | 25.88 ± 3.05 | 0.44 ± 0.16 | 1.28 ± 0.04 | 13.27 ± 0.07 |
| REM | 5/8 (63%) | 21 | 0.52 ± 0.16 | 8.67 ± 1.30 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 1.47 ± 0.11 | 13.40 ± 0.22 | |
| Hipp | NREM | 3/8 (38%) | 19 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| REM | 5/8 (63%) | 12 | 0.33 ± 0.06 | 7.57 ± 1.20 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 1.51 ± 0.14 | 12.51 ± 0.38 | |
| Control | ||||||||
| n | nHVS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | HVSdur/h (min) | HVSdur (s) | HVSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 1/8 (13%) | 2 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| REM | 3/8 (38%) | 14 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | |
| Hipp | NREM | 1/8 (13%) | 3 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| REM | 2/8 (25%) | 25 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | |
| PPT lesion | ||||||||
| n | nHVS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | HVSdur/h (min) | HVSdur (s) | HVSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 7/8 (88%) | 33 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 31.17 ± 2.69 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 1.57 ± 0.08 | 7.67 ± 0.19 |
| REM | 8/8 (100%) | 79 | 1.15 ± 0.40 * | 10.69 ± 1.40 | 0.46 ± 0.09 | 2.79 ± 0.12 * | 7.53 ± 0.09 | |
| Hipp | NREM | 7/8 (88%) | 16 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 30.64 ± 2.66 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 1.74 ± 0.11 | 7.11 ± 0.17 |
| REM | 8/8 (100%) | 104 | 1.20 ± 0.26 * | 10.69 ± 1.40 | 0.56 ± 0.19 | 2.58 ± 0.09 * | 7.17 ± 0.07 | |
| SNpc lesion | ||||||||
| n | nHVS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | HVSdur/h (min) | HVSdur (s) | HVSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 3/7 (43%) | 9 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| REM | 5/7 (71%) | 69 | 1.56 ± 0.20 | 8.97 ± 0.47 | 0.61 ± 0.09 | 2.66 ± 0.14 | 7.68 ± 0.10 | |
| Hipp | NREM | 1/7 (14%) | 1 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| REM | 5/7 (71%) | 35 | 0.78 ± 0.13 | 8.97 ± 0.47 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 2.54 ± 0.18 | 7.36 ± 0.11 | |
| SNpc/PPT lesion | ||||||||
| n | nHVS | Density/h (1/min) | NREM/REM dur/h (min) | HVSdur/h (min) | HVSdur (s) | HVSf (Hz) | ||
| MCx | NREM | 7/8 (88%) | 87 | 0.47 ± 0.12 | 26.12 ± 3.51 | 0.33 ± 0.12 | 1.60 ± 0.01 | 7.61 ± 0.01 |
| REM | 8/8 (100%) | 52 | 0.94 ± 0.21 | 7.94 ± 1.18 | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 2.39 ± 0.11 * | 7.93 ± 0.09 * | |
| Hipp | NREM | 3/8 (38%) | 6 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| REM | 8/8 (100%) | 56 | 0.92 ± 0.26 | 7.94 ± 1.18 | 0.28 ± 0.09 | 2.36 ± 0.11 | 7.61 ± 0.12 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radovanovic, L.; Petrovic, J.; Saponjic, J. Hippocampal and Reticulo-Thalamic Parvalbumin Interneurons and Synaptic Re-Organization during Sleep Disorders in the Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease Neuropathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168922
Radovanovic L, Petrovic J, Saponjic J. Hippocampal and Reticulo-Thalamic Parvalbumin Interneurons and Synaptic Re-Organization during Sleep Disorders in the Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease Neuropathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(16):8922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168922
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadovanovic, Ljiljana, Jelena Petrovic, and Jasna Saponjic. 2021. "Hippocampal and Reticulo-Thalamic Parvalbumin Interneurons and Synaptic Re-Organization during Sleep Disorders in the Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease Neuropathology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 16: 8922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168922
APA StyleRadovanovic, L., Petrovic, J., & Saponjic, J. (2021). Hippocampal and Reticulo-Thalamic Parvalbumin Interneurons and Synaptic Re-Organization during Sleep Disorders in the Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease Neuropathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168922






