The Association between α-Synuclein and α-Tubulin in Brain Synapses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
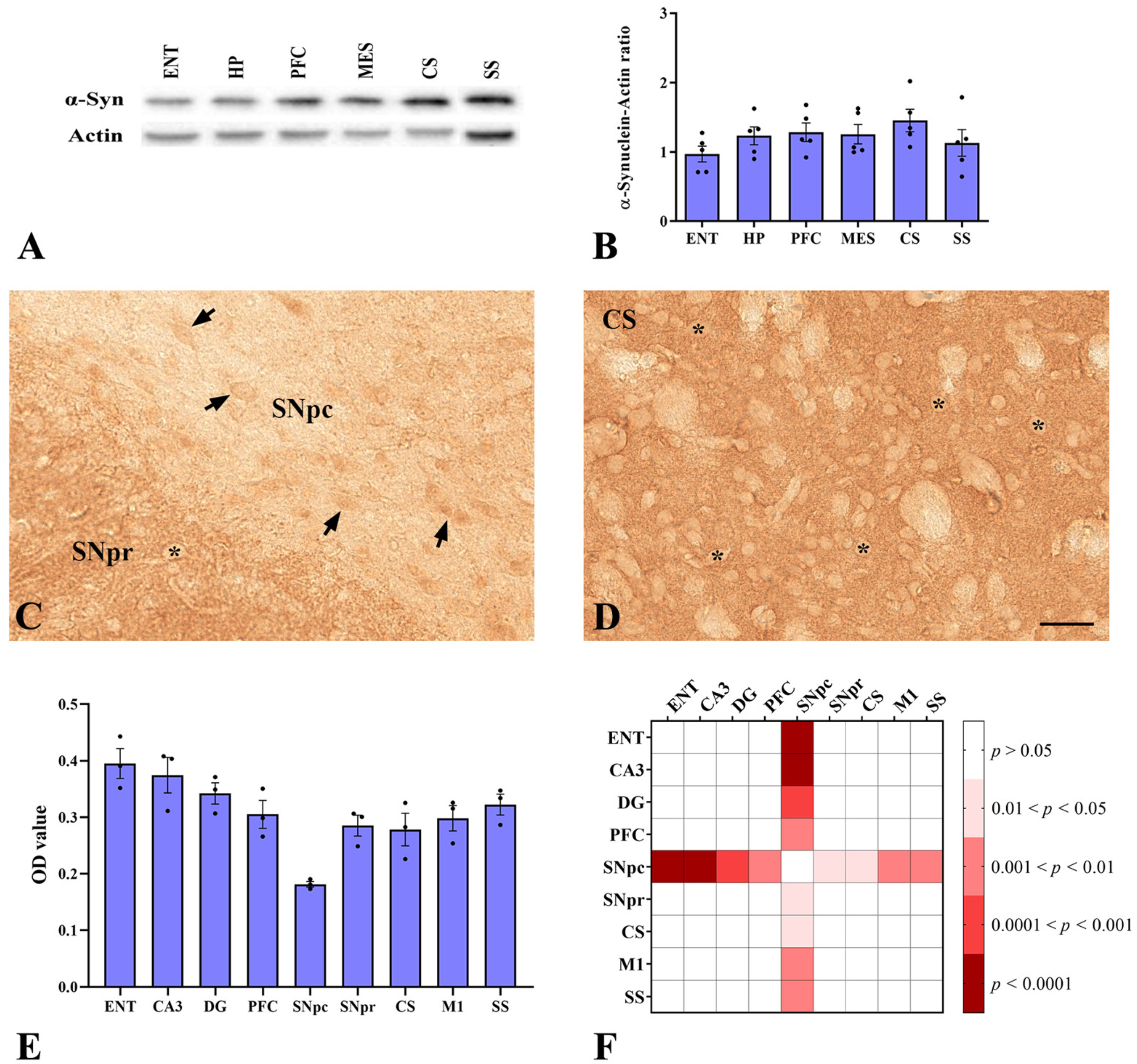
2.1. α-Synuclein Distribution Changes in Different Areas of Murine Brain
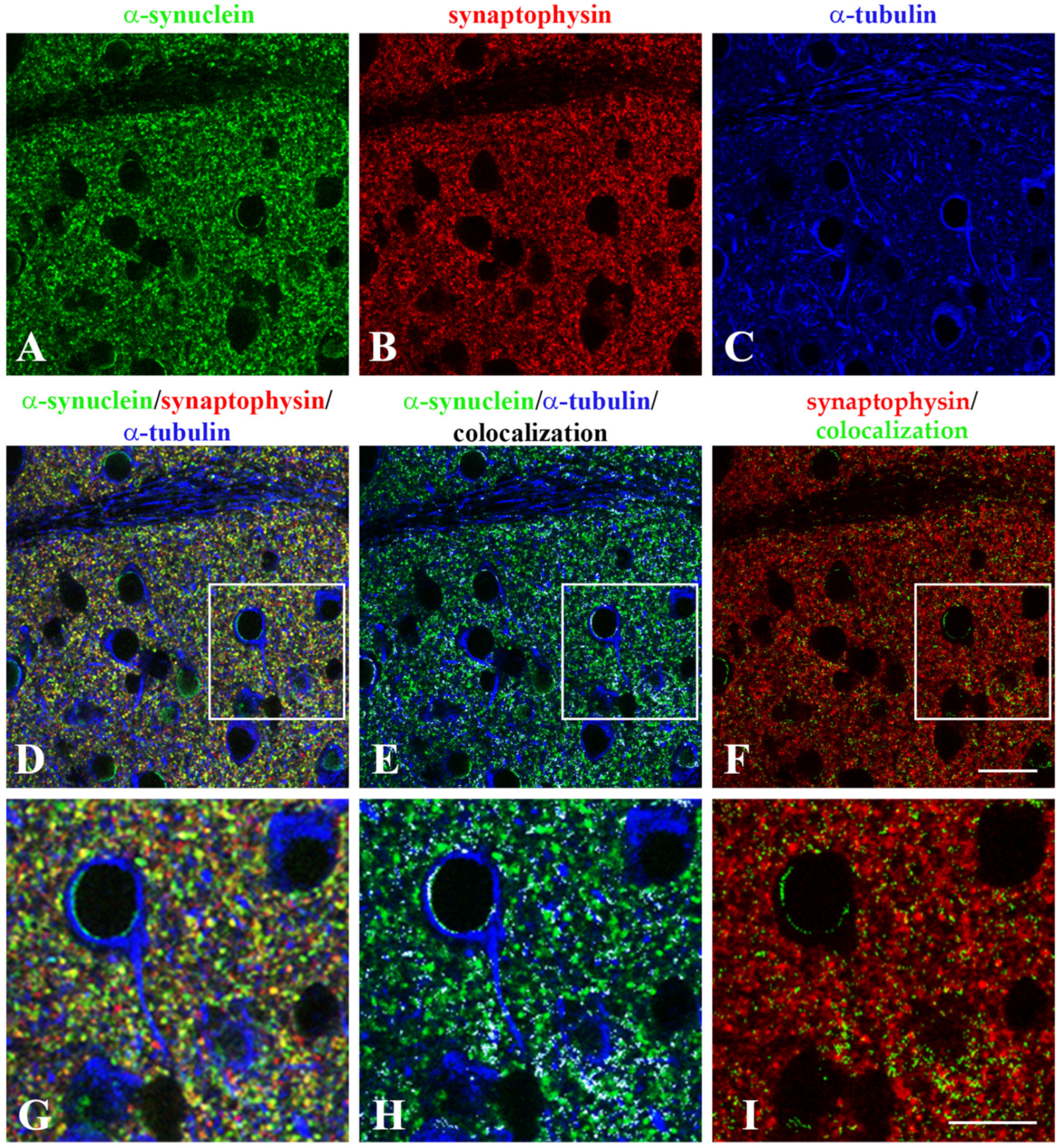
2.2. α-Synuclein and α-Tubulin Colocalize in the Brain at the Presynapse
2.3. α-Synuclein and α-Tubulin Interact in Mouse Corpus Striatum and in Human Brain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Samples
4.2. Primary Antibodies
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.4.1. Immunoperoxidase Procedure
4.4.2. Densitometric Immunoperoxidase Analysis
4.4.3. Immunofluorescence Procedure
4.5. Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
4.6. Colocalization Analysis
4.7. Electron Microscopy
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burré, J. The synaptic function of α-synuclein. J. Parkinsons. Dis. 2015, 5, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.; et al. Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andringa, G.; Du, F.; Chase, T.N.; Bennett, M.C. Mapping of rat brain using the Synuclein-1 monoclonal antibody reveals somatodendritic expression of α-synuclein in populations of neurons homologous to those vulnerable to Lewy body formation in human synucleopathies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Totterdell, S.; Hanger, D.; Meredith, G.E. The ultrastructural distribution of alpha-synuclein-like protein in normal mouse brain. Brain Res. 2004, 1004, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Chan, P.; Uéda, K.; Yu, S.; Yang, H. Semi-quantitative analysis of α-synuclein in subcellular pools of rat brain neurons: An immunogold electron microscopic study using a C-terminal specific monoclonal antibody. Brain Res. 2008, 1244, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivacqua, G.; Casini, A.; Vaccaro, R.; Fornai, F.; Yu, S.; D’Este, L. Different sub-cellular localization of alpha-synuclein in the C57BL\6J mouse’s central nervous system by two novel monoclonal antibodies. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tanaka, M. Brain region-dependent differential expression of alpha-synuclein. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1236–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tanaka, M. Expression of α-synuclein is regulated in a neuronal cell type-dependent manner. Anat. Sci. Int. 2019, 94, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erskine, D.; Patterson, L.; Alexandris, A.; Hanson, P.S.; McKeith, I.G.; Attems, J.; Morris, C.M. Regional levels of physiological α-synuclein are directly associated with Lewy body pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Han, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. Extensive nuclear localization of α-synuclein in normal rat brain neurons revealed by a novel monoclonal antibody. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Determining nuclear localization of alpha-synuclein in mouse brains. Neuroscience 2011, 199, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, M.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Presynaptic α-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with lewy bodies. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Reitböck, P.; Anichtchik, O.; Bellucci, A.; Iovino, M.; Ballini, C.; Fineberg, E.; Ghetti, B.; Della Corte, L.; Spano, P.; Tofaris, G.K.; et al. SNARE protein redistribution and synaptic failure in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2010, 133, 2032–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Nakayama, K.; Jin, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Yazawa, I. α-Synuclein accumulation reduces GABAergic inhibitory transmission in a model of multiple system atrophy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 428, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Taoufiq, Z.; Thorn-Seshold, O.; Trauner, D.; Hasegawa, M.; Takahashi, T. Wild-type monomeric α-synuclein can impair vesicle endocytosis and synaptic fidelity via tubulin polymerization at the calyx of held. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6043–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridi, J.C.; Hirth, F. Mechanisms of α-Synuclein induced synaptopathy in parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Südhof, T.C. Cell biology and pathophysiology of α-synuclein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a024091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.E.; Schmitz, Y.; Troyer, M.D.; Mosharov, E.; Dietrich, P.; Quazi, A.Z.; Savalle, M.; Nemani, V.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Edwards, R.H.; et al. α-Synuclein overexpression in PC12 and chromaffin cells impairs catecholamine release by interfering with a late step in exocytosis. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 11915–11922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. α-Synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diao, J.; Burré, J.; Vivona, S.; Cipriano, D.J.; Sharma, M.; Kyoung, M.; Südhof, T.C.; Brunger, A.T. Native α-synuclein induces clustering of synaptic-vesicle mimics via binding to phospholipids and synaptobrevin-2/VAMP2. Elife 2013, 2013, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Das, U.; Scott, D.A.; Tang, Y.; McLean, P.J.; Roy, S. α-Synuclein multimers cluster synaptic vesicles and attenuate recycling. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.; Kim, S.; Varkey, J.; Lou, X.; Song, J.K.; Diao, J.; Langen, R.; Shin, Y.K. Nonaggregated α-synuclein influences snare-dependent vesicle docking via membrane binding. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, B.; Saha, K.; Rana, T.; Becker, J.P.; Sambo, D.; Davari, P.; Goodwin, J.S.; Khoshbouei, H. Dopamine transporter activity is modulated by α-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29542–29554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.T.; Chen, A.Q.; Kong, Q.; Zhu, H.; Ma, C.M.; Qin, C. Inhibition of vesicular monoamine transporter-2 activity in α-synuclein stably transfected SH-SY5Y cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaltieri, M.; Grigoletto, J.; Longhena, F.; Navarria, L.; Favero, G.; Castrezzati, S.; Colivicchi, M.A.; Della Corte, L.; Rezzani, R.; Pizzi, M.; et al. α-synuclein and synapsin III cooperatively regulate synaptic function in dopamine neurons. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somayaji, M.; Cataldi, S.; Choi, S.J.; Edwards, R.H.; Mosharov, E.V.; Sulzer, D. A dual role for α-synuclein in facilitation and depression of dopamine release from substantia nigra neurons in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32701–32710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.L.; Bellani, S.; Giannandrea, M.; Yousuf, M.; Valtorta, F.; Meldolesi, J.; Chieregatti, E. α-Synuclein and its A30P mutant affect actin cytoskeletal structure and dynamics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 3725–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellani, S.; Sousa, V.L.; Ronzitti, G.; Valtorta, F.; Meldolesi, J.; Chieregatti, E. The regulation of synaptic function by α-synuclein. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2010, 3, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnwath, T.; Mohammed, R.; Tsiang, D. The direct and indirect effects of α-synuclein on microtubule stability in the pathogenesis of parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calogero, A.M.; Mazzetti, S.; Pezzoli, G.; Cappelletti, G. Neuronal microtubules and proteins linked to Parkinson’s disease: A relevant interaction? Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payton, J.E.; Perrin, R.J.; Clayton, D.F.; George, J.M. Protein-protein interactions of alpha-synuclein in brain homogenates and transfected cells. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 95, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Arima, K.; Takeda, K.; Izumiyama, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kaji, H.; Shinoda, T.; Hisanaga, S.; Uéda, K. Tubulin seeds α-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alim, M.A.; Ma, Q.L.; Takeda, K.; Aizawa, T.; Matsubara, M.; Nakamura, M.; Asada, A.; Saito, T.; Kaji, H.; Yoshii, M.; et al. Demonstration of a role for α-synuclein as a functional microtubule-associated protein. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2004, 6, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jin, J.; Davis, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lockhart, P.J.; Zhang, J. Oligomeric α-synuclein inhibits tubulin polymerization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 356, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.M.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; Chen, C.; Shi, Q.; Wang, G.R.; Tian, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Jing, Y.Y.; Gao, C.; et al. Molecular interaction of α-synuclein with tubulin influences on the polymerization of microtubule in vitro and structure of microtubule in cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, S.; Jin, M.; Yamada, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yasunaga, T.; Fukunaga, Y.; Miyazawa, A.; Fujita, S.; Itoh, K.; et al. Alpha-synuclein facilitates to form short unconventional microtubules that have a unique function in the axonal transport. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cartelli, D.; Aliverti, A.; Barbiroli, A.; Santambrogio, C.; Ragg, E.M.; Casagrande, F.V.M.; Cantele, F.; Beltramone, S.; Marangon, J.; De Gregorio, C.; et al. α-Synuclein is a Novel Microtubule Dynamase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, P.T.; Cotman, C.W. Synaptic Proteins. Characterization of Tubulin and Actin and Identification of a Distinct Postsynaptic Density Polypeptide The major proteins in isolated synaptic junctions (SJs) and postsynaptic densities (PSDs) have been compared to actin, tubulin. J. Cell Biol. 1978, 79, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zisapel, N.; Levi, M.; Gozes, I. Tubulin: An Integral Protein of Mammalian Synaptic Vesicle Membranes. J. Neurochem. 1980, 34, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-lozano, M.A.; Klemmer, P.; Gebuis, T.; Hassan, C.; Van Nierop, P. Dynamics of the mouse brain cortical synaptic proteome during postnatal brain development. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon-Weeks, P.R.; Burgoyne, R.D.; Gray, E.G. Presynaptic microtubules: Organisation and assembly/disassembly. Neuroscience 1982, 7, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrum, L.E.; Gray, E.G.; Burgoyne, R.D.; Barron, J. Synaptic development and microtubule organization. Cell Tissue Res. 1983, 231, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goellner, B.; Aberle, H. The synaptic cytoskeleton in development and disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodaleo, F.J.; Gonzalez-billault, C. The Presynaptic Microtubule Cytoskeleton in Physiological and Pathological Conditions: Lessons from Drosophila Fragile X Syndrome and Hereditary Spastic Paraplegias. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgen, M.A.; Giles, A.C.; Wang, D.; Grill, B. Synapse maintenance is impacted by ATAT-2 tubulin acetyltransferase activity and the RPM-1 signaling hub. Elife 2019, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Kumar, A.; Blockus, H.; Waites, C.; Bartolini, F. Activity-dependent nucleation of dynamic microtubules at presynaptic boutons is required for neurotransmission. bioRxiv 2019, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piriya, L.; Babu, A.; Wang, X.; Eguchi, X.; Guillaud, X.; Takahashi, X. Microtubule and Actin Differentially Regulate Synaptic Vesicle Cycling to Maintain High-Frequency Neurotransmission. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waites, C.; Qu, X.; Bartolini, F. The synaptic life of microtubules. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2021, 69, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Rüb, U.; Bratzke, H.; Del Tredici, K. Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, V.; De Iure, A.; Loffredo, V.; Vaikath, N.; De Risi, M.; Paciotti, S.; Quiroga-Varela, A.; Chiasserini, D.; Mellone, M.; Mazzocchetti, P.; et al. Alpha-synuclein targets GluN2A NMDA receptor subunit causing striatal synaptic dysfunction and visuospatial memory alteration. Brain 2019, 142, 1365–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klaus, A.; Da Silva, J.A.; Costa, R.M. What, If, and When to Move: Basal Ganglia Circuits and Self-Paced Action Initiation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 459–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Specht, C.G.; Schoepfer, R. Deletion of the alpha-synuclein locus in a subpopulation of C57BL/6J inbred mice. BMC Neurosci. 2001, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G. The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years on. J. Park. Dis. 2017, 7, S53–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartelli, D.; Cappelletti, G. Microtubule Destabilization Paves the Way to Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, L.; Wetzel, A.; Grannó, S.; Heaton, G.; Harvey, K. Back to the tubule: Microtubule dynamics in Parkinson’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dent, E.W. Dynamic microtubules at the synapse. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 63, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes-Dias, P.; Nirschl, J.J.; Abreu, N.; Tokito, M.K.; Janke, C.; Magiera, M.M.; Holzbaur, E.L.F. Kinesin-3 Responds to Local Microtubule Dynamics to Target Synaptic Cargo Delivery to the Presynapse. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 268–282.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hattori, T.; Takada, M.; Moriizumi, T.; Van Der Kooy, D. Single dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons form two chemically distinct synaptic types: Possible transmitter segregation within neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 309, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesack, S.R.; Hawrylak, V.A.; Matus, C.; Guido, M.A.; Levey, A.I. Dopamine axon varicosities in the prelimbic division of the rat prefrontal cortex exhibit sparse immunoreactivity for the dopamine transporter. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnay, Y. Brain serotonergic circuitries. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 12, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Burke, M.W.; Calakos, N.; Beaulieu, J.M.; Vaucher, E. Confocal analysis of cholinergic and dopaminergic inputs onto pyramidal cells in the prefrontal cortex of rodents. Front. Neuroanat. 2010, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tatebe, H.; Miyata, S.; Tokuda, T.; Mizuno, T.; Tanaka, M. Differential expression of alpha-synuclein in hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longhena, F.; Faustini, G.; Spillantini, M.G.; Bellucci, A. Living in promiscuity: The multiple partners of alpha-synuclein at the synapse in physiology and pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-G.; Zhu, X.; Takeda, A.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A. Emerging evidence for the neuroprotective role of α-synuclein. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 200, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outeiro, T.F.; McLean, P.J.; Hyman, B.T. Protein aggregation disorders. In Neurobiology of Disease; Gilman, S., Ed.; Elsevier-Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Morato Torres, C.A.; Wassouf, Z.; Zafar, F.; Sastre, D.; Outeiro, T.F.; Schüle, B. The role of alpha-synuclein and other parkinson’s genes in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, G.; Cartelli, D. Acetylation of tubulin: A feasible protective target from neurodevelopment to neurodegeneration. In Neuroprotection Autism, Schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s Disease; Gozes, I., Levine, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzetti, S.; Basellini, M.J.; Ferri, V.; Cassani, E.; Cereda, E.; Paolini, M.; Calogero, A.M.; Bolliri, C.; De Leonardis, M.; Sacilotto, G.; et al. α-Synuclein oligomers in skin biopsy of idiopathic and monozygotic twin patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2020, 143, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amadeo, A.; Coatti, A.; Aracri, P.; Ascagni, M.; Iannantuoni, D.; Modena, D.; Carraresi, L.; Brusco, S.; Meneghini, S.; Arcangeli, A.; et al. Postnatal Changes in K+ /Cl− Cotransporter-2 Expression in the Forebrain of Mice Bearing a Mutant Nicotinic Subunit Linked to Sleep-Related Epilepsy. Neuroscience 2018, 386, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Compact; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 978-0-12-374244-5. [Google Scholar]
- Longhena, F.; Faustini, G.; Missale, C.; Pizzi, M.; Bellucci, A. Dopamine transporter/α-synuclein complexes are altered in the post mortem caudate putamen of Parkinson’s disease: An in situ proximity ligation assay study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Söderberg, O.; Gullberg, M.; Jarvius, M.; Ridderstråle, K.; Leuchowius, K.-J.; Jarvius, J.; Wester, K.; Hydbring, P.; Bahram, F.; Larsson, L.-G.; et al. Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aracri, P.; Meneghini, S.; Coatti, A.; Amadeo, A.; Becchetti, A. α4β2∗ nicotinic receptors stimulate GABA release onto fast-spiking cells in layer V of mouse prefrontal (Fr2) cortex. Neuroscience 2017, 340, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelières, F.P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiardi, C.; Pasini, M.E.; Amadeo, A.; Gioria, M.; Berruti, G. The ESCRT-deubiquitinating enzyme USP8 in the cervical spinal cord of wild-type and Vps54-recessive (wobbler) mutant mice. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 141, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primary Antibody | Epitope | Host Species | Application | Dilution | Source | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actin | C-term fragment | Rabbit | WB | 1:2000 | Sigma- Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA | A2066 |
| α-synuclein | C-term human α-syn (aa 111–132) | Rabbit | WB | 1:2000 | Sigma- Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA | S3062 |
| IF/EM | 1:500 | |||||
| IHC | 1:1500 | |||||
| PLA | 1:100 | |||||
| α-synuclein (clone Syn211) | C-term human α-syn (aa 121–125) | Mouse | IF | 1:1500 | Sigma- Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA | S5566 |
| PLA | 1:100 | |||||
| α-tubulin (clone B-5-1-2) | C-term | Mouse | IF/EM | 1:500 | Sigma- Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA | T6074 |
| PLA | 1:50 | |||||
| α-tubulin | N-term (aa 1–100) | Rabbit | PLA | 1:50 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK | ab4074 |
| βIII-tubulin | C-term | Mouse | PLA | 1:300 | Sigma- Aldrich St. Louis, MO, USA | T8660 |
| βIII-tubulin (clone EP1331Y) | C-term (within aa400) | Rabbit | PLA | 1:250 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK | ab52901 |
| Synaptophysin1 | Human synaptophysin1 (aa 301–313) | Guinea pig | IF | 1:400 | Synaptic Systems, Goettingen, Germany | 101 004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amadeo, A.; Pizzi, S.; Comincini, A.; Modena, D.; Calogero, A.M.; Madaschi, L.; Faustini, G.; Rolando, C.; Bellucci, A.; Pezzoli, G.; et al. The Association between α-Synuclein and α-Tubulin in Brain Synapses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179153
Amadeo A, Pizzi S, Comincini A, Modena D, Calogero AM, Madaschi L, Faustini G, Rolando C, Bellucci A, Pezzoli G, et al. The Association between α-Synuclein and α-Tubulin in Brain Synapses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179153
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmadeo, Alida, Sara Pizzi, Alessandro Comincini, Debora Modena, Alessandra Maria Calogero, Laura Madaschi, Gaia Faustini, Chiara Rolando, Arianna Bellucci, Gianni Pezzoli, and et al. 2021. "The Association between α-Synuclein and α-Tubulin in Brain Synapses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179153
APA StyleAmadeo, A., Pizzi, S., Comincini, A., Modena, D., Calogero, A. M., Madaschi, L., Faustini, G., Rolando, C., Bellucci, A., Pezzoli, G., Mazzetti, S., & Cappelletti, G. (2021). The Association between α-Synuclein and α-Tubulin in Brain Synapses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179153







