Cell-Permeable Oct4 Gene Delivery Enhances Stem Cell-like Properties of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the Cell-Permeable Peptide, LMWP
2.2. Characterization of the Oct4-LMWP Complex
2.3. Assessing the Stability of the Oct4-LMWP Complex
2.4. Intracellular Uptake of the Oct4-LMWP Complex
2.5. Changes in MEF Cell Surface Markers by the Oct4-LMWP Complex Delivery
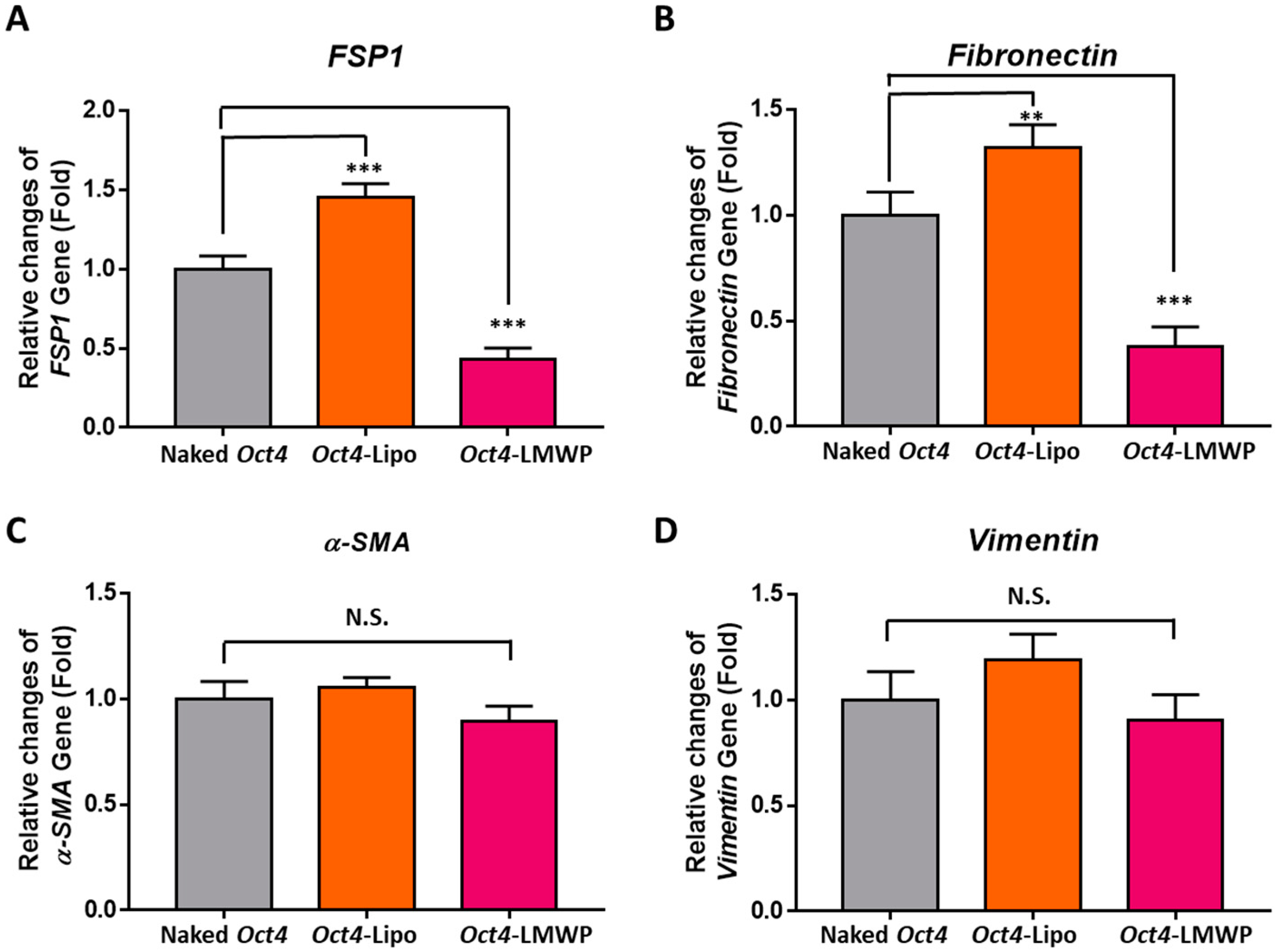
2.6. Fibroblast-Specific and Stemness Marker Gene Expression in Response to Oct4-LMWP Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Cell Permeable Peptides
4.2. Isolation and Culture of MEFs
4.3. Preparation of Oct4-LMWP Complexes
4.4. Measurement of Oct4-LMWP Complex Particle Size and Zeta Potential
4.5. DNase I and Serum Stability of the Oct4-LMWP Complex
4.6. Cellular Uptake Assay
4.7. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis
4.8. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mollinari, C.; Zhao, J.; Lupacchini, L.; Garaci, E.; Merlo, D.; Pei, G. Transdifferentiation: A new promise for neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.I.; Kim, T.K. Overcoming Current Dilemma in Cartilage Regeneration: Will Direct Conversion Provide a Breakthrough? Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 17, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierbuchen, T.; Wernig, M. Direct lineage conversions: Unnatural but useful? Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 892–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horisawa, K.; Suzuki, A. Direct cell-fate conversion of somatic cells: Toward regenerative medicine and industries. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2020, 96, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grath, A.; Dai, G. Direct cell reprogramming for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J. Biol. Eng. 2019, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-like properties in fibroblasts. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, G.; Bigliardi, P.L.; Bigliardi-Qi, M. Fibroblast heterogeneity and its implications for engineering organotypic skin models in vitro. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 94, 483–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, R.C.; Pastar, I.; Ojeh, N.; Chen, V.; Liu, S.; Garzon, K.I.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, E.; Rampalli, S.; Risueno, R.M.; Schnerch, A.; Mitchell, R.; Fiebig-Comyn, A.; Levadoux-Martin, M.; Bhatia, M. Direct conversion of human fibroblasts to multilineage blood progenitors. Nature 2010, 468, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kishida, T.; Nakai, K.; Sato, Y.; Kotani, S.I.; Nishizawa, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kanamura, N.; Mazda, O. Direct phenotypic conversion of human fibroblasts into functional osteoblasts triggered by a blockade of the transforming growth factor-beta signal. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.R.; Szabo, E.; Benoit, Y.D.; Case, D.T.; Mechael, R.; Alamilla, J.; Lee, J.H.; Fiebig-Comyn, A.; Gillespie, D.C.; Bhatia, M. Activation of neural cell fate programs toward direct conversion of adult human fibroblasts into tri-potent neural progenitors using OCT-4. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cha, H.H.; Park, H.H.; Park, J.H. Direct conversion of human fibroblasts into osteoblasts triggered by histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichim, T.E.; O’Heeron, P.; Kesari, S. Fibroblasts as a practical alternative to mesenchymal stem cells. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steens, J.; Unger, K.; Klar, L.; Neureiter, A.; Wieber, K.; Hess, J.; Jakob, H.G.; Klump, H.; Klein, D. Direct conversion of human fibroblasts into therapeutically active vascular wall-typical mesenchymal stem cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3401–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkasalias, T.; Moyano-Galceran, L.; Arsenian-Henriksson, M.; Lehti, K. Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment: Shield or Spear? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L. From fibroblast cells to cardiomyocytes: Direct lineage reprogramming. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2011, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.W.; Zhang, T.T.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Lin, X.L.; Jia, J.S.; Shen, H.F.; Wang, S.C.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.T. Direct conversion of pig fibroblasts to chondrocyte-like cells by c-Myc. Cell Death. Discov. 2019, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamori, D.; Akamine, H.; Takayama, K.; Sakurai, F.; Mizuguchi, H. Direct conversion of human fibroblasts into hepatocyte-like cells by ATF5, PROX1, FOXA2, FOXA3, and HNF4A transduction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulecio, J.; Alejo-Valle, O.; Capellera-Garcia, S.; Vitaloni, M.; Rio, P.; Mejia-Ramirez, E.; Caserta, I.; Bueren, J.A.; Flygare, J.; Raya, A. Direct Conversion of Fibroblasts to Megakaryocyte Progenitors. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zou, M.; Deng, Q.; Sun, D.; Bian, X.; Cai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S. Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into neural stem cells by single non-neural progenitor transcription factor Ptf1a. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Their, M.; Worsdorfer, P.; Lakes, Y.B.; Gorris, R.; Herms, S.; Opitz, T.; Seiferling, D.; Quandel, T.; Hoffmann, P.; Nothen, M.M. Direct conversion of fibroblasts into stably expandable neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Long, Q.; Xing, G.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Qi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, B.; Scholer, H.R. Heterochromatin loosening by the Oct4 linker region facilitates Klf4 binding and iPSC reprogramming. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e99165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Efficient production of cell-permeable oct4 protein using 30Kc19 protein originating from silkworm. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 24, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammam, S.; Malak, P.; Correa, D.; Rothfuss, O.; Azzazy, H.M.; Lamprecht, A.; Schulze-Osthoff, K. Nuclear delivery of recombinant OCT4 by chitosan nanoparticles for transgene-free generation of protein-induced pluripotent stem cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 37728–37739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Um, S.H. Delivering factors for reprogramming a somatic cell to pluripotency. Int. J. Stem Cells 2012, 5, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.K.; Menezes, M.E.; Bhatia, S.; Wang, X.Y.; Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Gene Therapies for Cancer: Strategies, Challenges and Successes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tipanee, J.; Chai, Y.C.; VandenDriessche, T.; Chuah, M.K. Preclinical and clinical advances in transposon-based gene therapy. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20160614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.J.; Liang, J.F.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, S.W.; Yang, V.C. Low molecular weight protamine as an efficient and nontoxic gene carrier: In vitro study. J. Gene Med. 2003, 5, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Ye, J.; Liu, E.; Liang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yang, V.C. Low molecular weight protamine (LMWP): A nontoxic protamine substitute and an effective cell-penetrating peptide. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Suh, J.S.; Kwon, Y.M.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, J.K.; Lee, D.S.; Yang, V.C.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. The systemic delivery of siRNAs by a cell penetrating peptide, low molecular weight protamine. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Nam, H.; Jo, B.S.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, C.P.; Lee, G.; Park, Y.J. Control of cancer stem cell like population by intracellular target identification followed by the treatment with peptide-siRNA complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 491, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; You, H.K.; Hong, S.D.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. Intracellular delivery of cell-penetrating peptide-transcriptional factor fusion protein and its role in selective osteogenesis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. Peptide-mediated intracellular delivery of miRNA-29b for osteogenic stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4347–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal, D.A.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.; Lim, K.M.; Jeon, T.I.; Seok, J.; Cho, A.S. Production of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Stem Cell Reprogramming. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Huerta, N.; Silva-Cazares, M.B.; Arriaga-Pizano, L.A.; Prieto-Chavez, J.L.; Lopez-Camarillo, C. LncRNAs and microRNAs as Essential Regulators of Stemness in Breast Cancer Stem Cells. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.F.; Grigsby, C.L.; Kulangara, K.; Wang, H.; Yasuda, R.; Leong, K.W. Nonviral direct conversion of primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts to neuronal cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantenbein, B.; Tang, S.; Guerrero, J.; Higuita-Castro, N.; Salazar-Puerta, A.I.; Croft, A.S.; Gazdhar, A.; Purmessur, D. Non-viral Gene Delivery Methods for Bone and Joints. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 598466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Suh, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Yang, V.C.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. Cell penetrating peptides for tumor targeting. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1166–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, J.; Hayashi, N.; Osada, N.; Sugitani, M.; Furukawa, Y. Conversion of human fibroblasts into multipotent cells by cell-penetrating peptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, J.; Jo, D. Partial somatic to stem cell transformations induced by cell-permeable reprogramming factors. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.K.; Vipparthi, K.; Thatikonda, V.; Arun, I.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Sharan, R.; Arun, P.; Singh, S. A subtype of cancer-associated fibroblasts with lower expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin suppresses stemness through BMP4 in oral carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S. Identification, Friend or Foe: Vimentin and alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4191–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thwaite, R.; Ji, J.; Torrealba, D.; Coll, J.; Sabes, M.; Villaverde, A.; Roher, N. Protein Nanoparticles Made of Recombinant Viral Antigens: A Promising Biomaterial for Oral Delivery of Fish Prophylactics. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Upadhyay, V.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Singh, S.M.; Panda, A.K. Protein recovery from inclusion bodies of Escherichia coli using mild solubilization process. Microb. Cell Factories 2015, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, F.; Boue, S.; Izpisua, J.C. Methods for making induced pluripotent stem cells: Reprogramming a la carte. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, D.H.; Lee, K.E.; Park, J.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, Y.S. Cell-Permeable Oct4 Gene Delivery Enhances Stem Cell-like Properties of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179357
Choi DH, Lee KE, Park J, Park YJ, Lee J-Y, Park YS. Cell-Permeable Oct4 Gene Delivery Enhances Stem Cell-like Properties of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179357
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Da Hyeon, Kyeong Eun Lee, Jiwon Park, Yoon Jeong Park, Jue-Yeon Lee, and Yoon Shin Park. 2021. "Cell-Permeable Oct4 Gene Delivery Enhances Stem Cell-like Properties of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179357
APA StyleChoi, D. H., Lee, K. E., Park, J., Park, Y. J., Lee, J.-Y., & Park, Y. S. (2021). Cell-Permeable Oct4 Gene Delivery Enhances Stem Cell-like Properties of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179357





