Treadmill Exercise Ameliorates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Possibly by Adjusting the APP Proteolytic Pathway in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
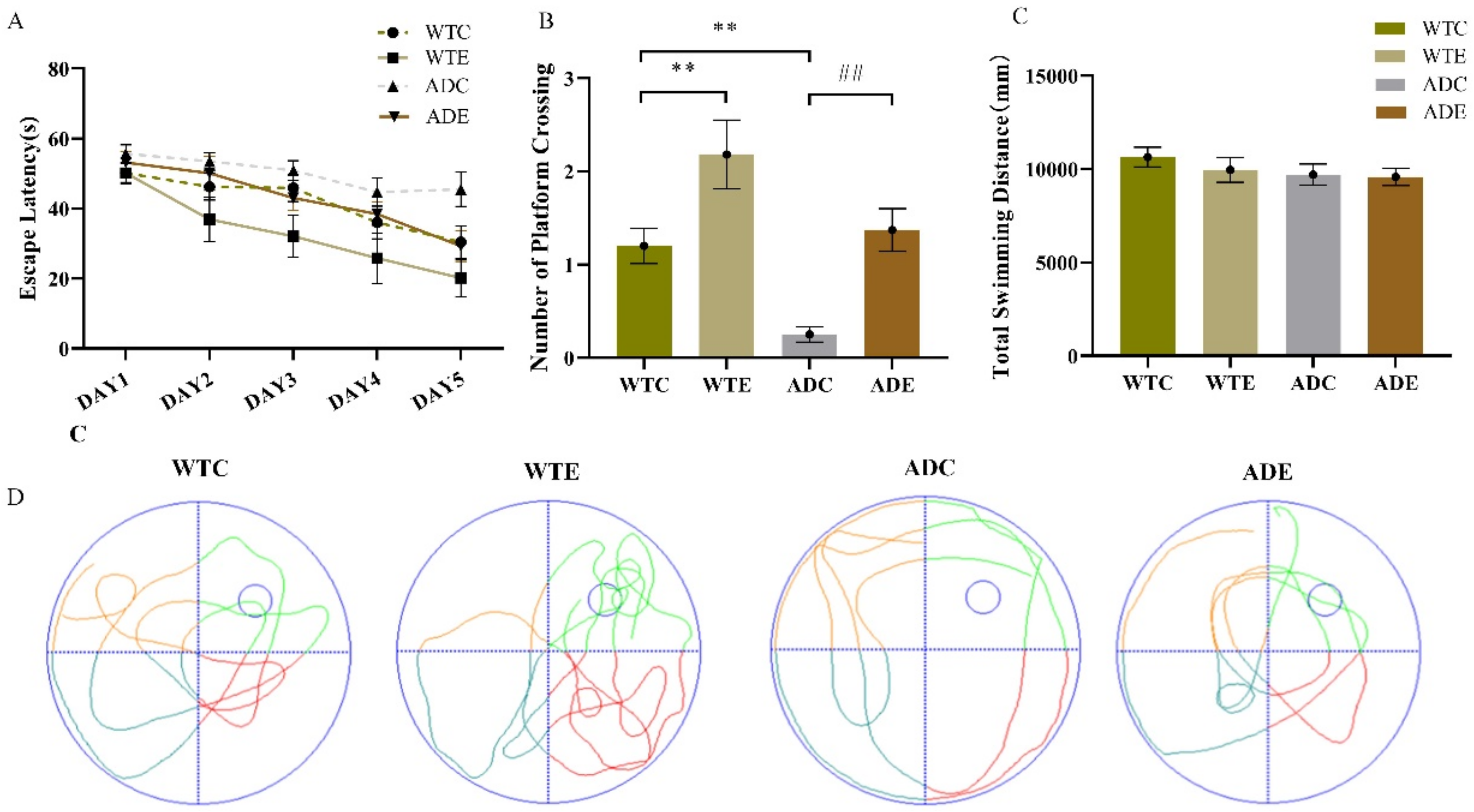
2.1. Treadmill Exercise Enhanced Learning and Memory Capacity in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
2.2. Treadmill Exercise Decreased Aβ Plaque Levels and Apoptosis in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
2.3. Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Hippocampal Neurogenesis
2.3.1. Treadmill Exercise Improved the Proliferation of NSCs
2.3.2. Treadmill Exercise Promoted Cell Survival
2.3.3. Treadmill Exercise Promoted Differentiation of Neurons and Suppressed Differentiation of Astrocytes
2.4. Effects of Treadmill Exercise on the APP Proteolytic Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2. Treadmill Exercise Protocols
4.3. 5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) Injections
4.4. Morris Water Maze Test
4.5. Tissue Preparation
4.6. Detection Methods
4.6.1. Detection of Aβ by Thioflavin-S Staining
4.6.2. Detection of Apoptosis by TUNEL Assay
4.6.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6.4. Western Blotting
4.6.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.7. Graph Acquisition and Cell Counting
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Kalra, J.; Khan, A. Reducing Aβ load and tau phosphorylation: Emerging perspective for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzi, R.E.; Bertram, L. Twenty Years of the Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Hypothesis: A Genetic Perspective. Cell 2005, 120, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Bylykbashi, E.; Chatila, Z.K.; Lee, S.W.; Pulli, B.; Clemenson, G.D.; Kim, E.; Rompala, A.; Oram, M.K.; Asselin, C.; et al. Combined adult neurogenesis and BDNF mimic exercise effects on cognition in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Science 2018, 361, eaan8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, L.; Qiao, S.; Lan, X.; Chi, L.; Luo, C.; Lien, L.; Yan Liu, Q.; Liu, R. Neurogenic responses to amyloid-beta plaques in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease-like transgenic (pPDGF-APPSw, Ind) mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 29, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.P.; Flor-García, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Rábano, A.; Cafini, F.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Ávila, J.; Llorens-Martín, M. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, P.S.; Lin, P.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Su, H.C.; Tsai, K.J. Neuroinflammation and Neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gage, F.H. Adult neurogenesis in mammals. Science 2019, 364, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Physical exercise induces hippocampal neurogenesis and prevents cognitive decline. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 317, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerberding, A.; Zampar, S.; Stazi, M.; Liebetanz, D.; Wirths, O. Physical Activity Ameliorates Impaired Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Tg4-42 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. ASN Neuro 2019, 11, 1759091419892692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Aimone, J.B.; Gage, F.H. New neurons and new memories: How does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.S.; Hong, N.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Wojtowicz, J.M. A role for adult neurogenesis in spatial long-term memory. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, D.; Neri, L.; Canalini, F.; Calevro, A.; Ottani, A.; Vandini, E.; Sena, P.; Zaffe, D.; Guarini, S. NDP-α-MSH induces intense neurogenesis and cognitive recovery in Alzheimer transgenic mice through activation of melanocortin MC4 receptors. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 67, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Qi, J.; Gao, R. Physical exercise reserved amyloid-beta induced brain dysfunctions by regulating hippocampal neurogenesis and inflammatory response via MAPK signaling. Brain Res. 2018, 1697, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivar, C.; Peterson, B.D.; van Praag, H. Running rewires the neuronal network of adult-born dentate granule cells. Neuroimage 2016, 131, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.Y.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Christie, B.R.; So, K.F. Physical exercise-induced adult neurogenesis: A good strategy to prevent cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases? BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 403120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, K.; Okamoto, M.; Shibato, J.; Lee, M.C.; Matsui, T.; Rakwal, R.; Soya, H. Long-Term Mild, rather than Intense, Exercise Enhances Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Greatly Changes the Transcriptomic Profile of the Hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coronel, R.; Palmer, C.; Bernabeu-Zornoza, A.; Monteagudo, M.; Rosca, A.; Zambrano, A.; Liste, I. Physiological effects of amyloid precursor protein and its derivatives on neural stem cell biology and signaling pathways involved. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haughey, N.J.; Nath, A.; Chan, S.L.; Borchard, A.C.; Rao, M.S.; Mattson, M.P. Disruption of neurogenesis by amyloid beta-peptide, and perturbed neural progenitor cell homeostasis, in models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirochnic, S.; Wolf, S.; Staufenbiel, M.; Kempermann, G. Age effects on the regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis by physical activity and environmental enrichment in the APP23 mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.F.; Ji, S.J.; Sun, R.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Tian, Y. Forced running exercise attenuates hippocampal neurogenesis impairment and the neurocognitive deficits induced by whole-brain irradiation via the BDNF-mediated pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxe, M.D.; Battaglia, F.; Wang, J.W.; Malleret, G.; David, D.J.; Monckton, J.E.; Garcia, A.D.; Sofroniew, M.V.; Kandel, E.R.; Santarelli, L.; et al. Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17501–17506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donovan, M.H.; Yazdani, U.; Norris, R.D.; Games, D.; German, D.C.; Eisch, A.J. Decreased adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 495, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetman, M.J.; Jankowsky, J.L. Wild-Type Neural Progenitors Divide and Differentiate Normally in an Amyloid-Rich Environment. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 17335–17341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shihabuddin, L.S.; Horner, P.J.; Ray, J.; Gage, F.H. Adult spinal cord stem cells generate neurons after transplantation in the adult dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8727–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riquelme, P.A.; Drapeau, E.; Doetsch, F. Brain micro-ecologies: Neural stem cell niches in the adult mammalian brain. Philos. Trans. Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alpár, A.; Naumann, N.; Ueberham, U.; Arendt, T.; Rtner, U.G. Deprivation-induced dendritic shrinkage might be oppositely affected by the expression of wild-type and mutated human amyloid precursor protein. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gakhar-Koppole, N.; Hundeshagen, P.; Mandl, C.; Weyer, S.W.; Allinquant, B.; Müller, U.; Ciccolini, F. Activity requires soluble amyloid precursor protein α to promote neurite outgrowth in neural stem cell-derived neurons via activation of the MAPK pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, N.; Alpár, A.; Ueberham, U.; Arendt, T.; Gärtner, U. Transgenic expression of human wild-type amyloid precursor protein decreases neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Hippocampus 2009, 20, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, A.L.; Calhoun, M.E.; Wolfer, D.P.; Lipp, H.P.; Zheng, H.; Jucker, M. No hippocampal neuron or synaptic bouton loss in learning-impaired aged β-Amyloid precursor protein-null mice. Neuroscience 1999, 90, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.M.; Schiapparelli, L.; Salazar-Colocho, P.; Cuadrado-Tejedor, M.; Escribano, L.; Lopez, D.M.R.; Del, R.J.; Perez-Mediavilla, A.; Frechilla, D. Overexpression of wild-type human APP in mice causes cognitive deficits and pathological features unrelated to Abeta levels. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, N.; Yan, Q.; Xia, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Yin, L.; Xu, B. Treadmill Exercise Attenuates Aβ-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Enhances Mitophagy Activity in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, F.; Ding, X.; Yan, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.; Huang, T.; Xu, B. Interval and continuous exercise overcome memory deficits related to β-Amyloid accumulation through modulating mitochondrial dynamics. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 376, 112171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Dede, A.J.; Hopkins, R.O.; Squire, L.R. Memory, scene construction, and the human hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4767–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.H.; Chen, A.G.; Hung, T.M.; Wang, C.C.; Chang, Y.K. Exercise and fitness modulate cognitive function in older adults. Psychol. Aging 2015, 30, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.C.; Inoue, K.; Okamoto, M.; Liu, Y.F.; Matsui, T.; Yook, J.S.; Soya, H. Voluntary resistance running induces increased hippocampal neurogenesis in rats comparable to load-free running. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 537, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms and Functional Implications of Adult Neurogenesis. Cell 2008, 132, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaynman, S.; Ying, Z.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Exercise induces BDNF and synapsin I to specific hippocampal subfields. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 76, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.M.; Xu, S.; Kritikou, J.S.; Marosi, K.; Brodin, L.; Mattson, M.P. Exercise and BDNF reduce Abeta production by enhancing alpha-secretase processing of APP. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirths, O. Altered neurogenesis in mouse models of Alzheimer disease. Neurogenesis 2017, 4, e1327002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Li, B.; Yin, L.; Zhao, N.; Yan, Q.; Xu, B. Treadmill exercise decreases beta-amyloid burden in APP/PS1 transgenic mice involving regulation of the unfolded protein response. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 703, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley-Brits, K.; Deng, Y.; Song, W. Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2011, e2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Zhang, C.; Xia, J.; Xu, B. Treadmill Exercise Ameliorates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Possibly by Adjusting the APP Proteolytic Pathway in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179570
Yu H, Zhang C, Xia J, Xu B. Treadmill Exercise Ameliorates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Possibly by Adjusting the APP Proteolytic Pathway in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179570
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Haizhen, Chenfei Zhang, Jie Xia, and Bo Xu. 2021. "Treadmill Exercise Ameliorates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Possibly by Adjusting the APP Proteolytic Pathway in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179570
APA StyleYu, H., Zhang, C., Xia, J., & Xu, B. (2021). Treadmill Exercise Ameliorates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Possibly by Adjusting the APP Proteolytic Pathway in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179570




