Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Migraine and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Gut–Brain Axis
3. Metabolism of l-Tryptophan
4. Migraine
5. Kynurenines in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Migraine
6. Kynurenines in Irritable Bowel Syndrome
7. Migraine and Functional GI Disorders
8. Concluding Remarks and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altamura, C.; Corbelli, I.; de Tommaso, M.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Di Renzo, A.; Filippi, M.; Jannini, T.B.; Messina, R.; Parisi, P.; et al. Pathophysiological Bases of Comorbidity in Migraine. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 640574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzani, M.; Jahromi, S.R.; Ghorbani, Z.; Vahabizad, F.; Martelletti, P.; Ghaemi, A.; Sacco, S.; Togha, M. Gut-brain Axis and migraine headache: A comprehensive review. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aurora, S.K.; Papapetropoulos, S.; Kori, S.H.; Kedar, A.; Abell, T.L. Gastric stasis in migraineurs: Etiology, characteristics, and clinical and therapeutic implications. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Holland, P.R.; Martins-Oliveira, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Schankin, C.; Akerman, S. Pathophysiology of Migraine: A Disorder of Sensory Processing. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 553–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurora, S.K.; Shrewsbury, S.B.; Ray, S.; Hindiyeh, N.; Nguyen, L. A link between gastrointestinal disorders and migraine: Insights into the gut-brain connection. Headache 2021, 61, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervenka, I.; Agudelo, L.Z.; Ruas, J.L. Kynurenines: Tryptophan’s metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science 2017, 357, eaaf9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Israelyan, N.; Del Colle, A.; Li, Z.; Park, Y.; Xing, A.; Jacobsen, J.P.R.; Luna, R.A.; Jensen, D.D.; Madra, M.; Saurman, V.; et al. Effects of Serotonin and Slow-Release 5-Hydroxytryptophan on Gastrointestinal Motility in a Mouse Model of Depression. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 507–521.e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelyan, N.; Margolis, K.G. Serotonin as a link between the gut-brain-microbiome axis in autism spectrum disorders. Pharm. Res. 2018, 132, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, C.; Popławski, T.; Gasiorowska, A.; Chojnacki, J.; Blasiak, J. Serotonin in the Pathogenesis of Lymphocytic Colitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, C.; Popławski, T.; Konrad, P.; Fila, M.; Chojnacki, J.; Błasiak, J. Serotonin Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth—A Pilot Study with Patients Diagnosed with Lactulose Hydrogen Breath Test and Treated with Rifaximin. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, S.; Ishimura, N.; Mikami, H.; Okimoto, E.; Uno, G.; Tamagawa, Y.; Aimi, M.; Oshima, N.; Sato, S.; Ishihara, S.; et al. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Refractory Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chojnacki, C.; Popławski, T.; Chojnacki, J.; Fila, M.; Konrad, P.; Blasiak, J. Tryptophan Intake and Metabolism in Older Adults with Mood Disorders. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Mu, C.L.; Farzi, A.; Zhu, W.Y. Tryptophan Metabolism: A Link Between the Gut Microbiota and Brain. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, P.D. Tryptophan depletion increases nausea, headache and photophobia in migraine sufferers. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosi, A.; Banfi, D.; Bistoletti, M.; Giaroni, C.; Baj, A. Tryptophan Metabolites Along the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: An Interkingdom Communication System Influencing the Gut in Health and Disease. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2020, 13, 1178646920928984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razeghi Jahromi, S.; Togha, M.; Ghorbani, Z.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Khorsha, F.; Rafiee, P.; Shirani, P.; Nourmohammadi, M.; Ansari, H. The association between dietary tryptophan intake and migraine. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducros, A.; de Gaalon, S.; Roos, C.; Donnet, A.; Giraud, P.; Guégan-Massardier, E.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Lucas, C.; Mawet, J.; Moisset, X.; et al. Revised guidelines of the French headache society for the diagnosis and management of migraine in adults. Part 2: Pharmacological treatment. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 734–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assas, B.M. Anti-migraine agents from an immunological point of view. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.P.; Al-Saoudi, A.; Ashina, M. Future prophylactic treatments in migraine: Beyond anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies and gepants. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Demartini, C.; Zanaboni, A.M.; Redavide, E.; Pampalone, S.; Toldi, J.; Fülöp, F.; Blandini, F.; Nappi, G.; Sandrini, G.; et al. Effects of kynurenic acid analogue 1 (KYNA-A1) in nitroglycerin-induced hyperalgesia: Targets and anti-migraine mechanisms. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1272–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamos, E.; Pardutz, A.; Klivenyi, P.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. The role of kynurenines in disorders of the central nervous system: Possibilities for neuroprotection. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 283, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteith, T.S.; Goadsby, P.J. Acute migraine therapy: New drugs and new approaches. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2011, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Vécsei, L. Are 5-HT(1) receptor agonists effective anti-migraine drugs? Expert Opin. Pharm. 2021, 22, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the Etiological Links behind Neurodegenerative Diseases: Inflammatory Cytokines and Bioactive Kynurenines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Tóth, F.; Polyák, H.; Szabó, Á.; Mándi, Y.; Vécsei, L. Immune Influencers in Action: Metabolites and Enzymes of the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, N.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Searching for Peripheral Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Diseases: The Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G. Integrating Pathophysiology in Migraine: Role of the Gut Microbiome and Melatonin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3550–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Monreal-Robles, R.; Marfil-Rivera, A. Gastrointestinal disorders associated with migraine: A comprehensive review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8149–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derakhshan, I. Association between Gastrointestinal Functional Disorders and Migraine Headache: A Therapeutic Link. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 10, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Ganz, J.; Bayrer, J.; Becker, L.; Bogunovic, M.; Rao, M. Advances in Enteric Neurobiology: The “Brain” in the Gut in Health and Disease. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 9346–9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, M.; Gershon, M.D. The bowel and beyond: The enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Browning, K.N.; Travagli, R.A. Central nervous system control of gastrointestinal motility and secretion and modulation of gastrointestinal functions. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 1339–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furness, J.B.; Callaghan, B.P.; Rivera, L.R.; Cho, H.J. The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: Integrated local and central control. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 39–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, M.G.; Chang, S.Y. Gut-Brain Connection: Microbiome, Gut Barrier, and Environmental Sensors. Immune Netw. 2021, 21, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve at the Interface of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suganya, K.; Koo, B.S. Gut-Brain Axis: Role of Gut Microbiota on Neurological Disorders and How Probiotics/Prebiotics Beneficially Modulate Microbial and Immune Pathways to Improve Brain Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, K.V.; Sherwin, E.; Schellekens, H.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Feeding the microbiota-gut-brain axis: Diet, microbiome, and neuropsychiatry. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2017, 179, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.T.; Davis, T.P. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharm. Rev. 2005, 57, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: Concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Tóth, F.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L. Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warwick, C.A.; Keyes, A.L.; Woodruff, T.M.; Usachev, Y.M. The complement cascade in the regulation of neuroinflammation, nociceptive sensitization, and pain. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dux, M.; Rosta, J.; Messlinger, K. TRP Channels in the Focus of Trigeminal Nociceptor Sensitization Contributing to Primary Headaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olesen, J.; Burstein, R.; Ashina, M.; Tfelt-Hansen, P. Origin of pain in migraine: Evidence for peripheral sensitisation. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, A.M.; Olesen, A.E.; Farmer, A.D.; Szigethy, E.; Rebours, V.; Olesen, S.S. Gastrointestinal pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinberg, K.; Sela, Y.; Nissanholtz-Gannot, R. New Insights about Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robblee, J.; Secora, K.A. Debunking Myths: Sinus Headache. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentella, M.C.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miggiano, G.A.D. Nutrition, IBD and Gut Microbiota: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walsh, J.; Griffin, B.T.; Clarke, G.; Hyland, N.P. Drug-gut microbiota interactions: Implications for neuropharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4415–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palego, L.; Betti, L.; Rossi, A.; Giannaccini, G. Tryptophan Biochemistry: Structural, Nutritional, Metabolic, and Medical Aspects in Humans. J. Amino Acids 2016, 2016, 8952520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujigaki, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Saito, K. L-Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway enzymes are therapeutic target for neuropsychiatric diseases: Focus on cell type differences. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuwatari, T. Possibility of Amino Acid Treatment to Prevent the Psychiatric Disorders via Modulation of the Production of Tryptophan Metabolite Kynurenic Acid. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modoux, M.; Rolhion, N.; Mani, S.; Sokol, H. Tryptophan Metabolism as a Pharmacological Target. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism: Regulatory and Functional Aspects. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2017, 10, 1178646917691938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Covarrubias, A.J.; Perrone, R.; Grozio, A.; Verdin, E. NAD(+) metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.P.; Guillemin, G.J.; Brew, B.J. The kynurenine pathway in stem cell biology. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2013, 6, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.M.; Shepherd, D.M. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by TCDD reduces inflammation associated with Crohn’s disease. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, F.A.; Bohár, Z.; Vécsei, L. Genetic alterations affecting the genes encoding the enzymes of the kynurenine pathway and their association with human diseases. Mutat. Res. 2018, 776, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galligan, J.J. Beneficial actions of microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
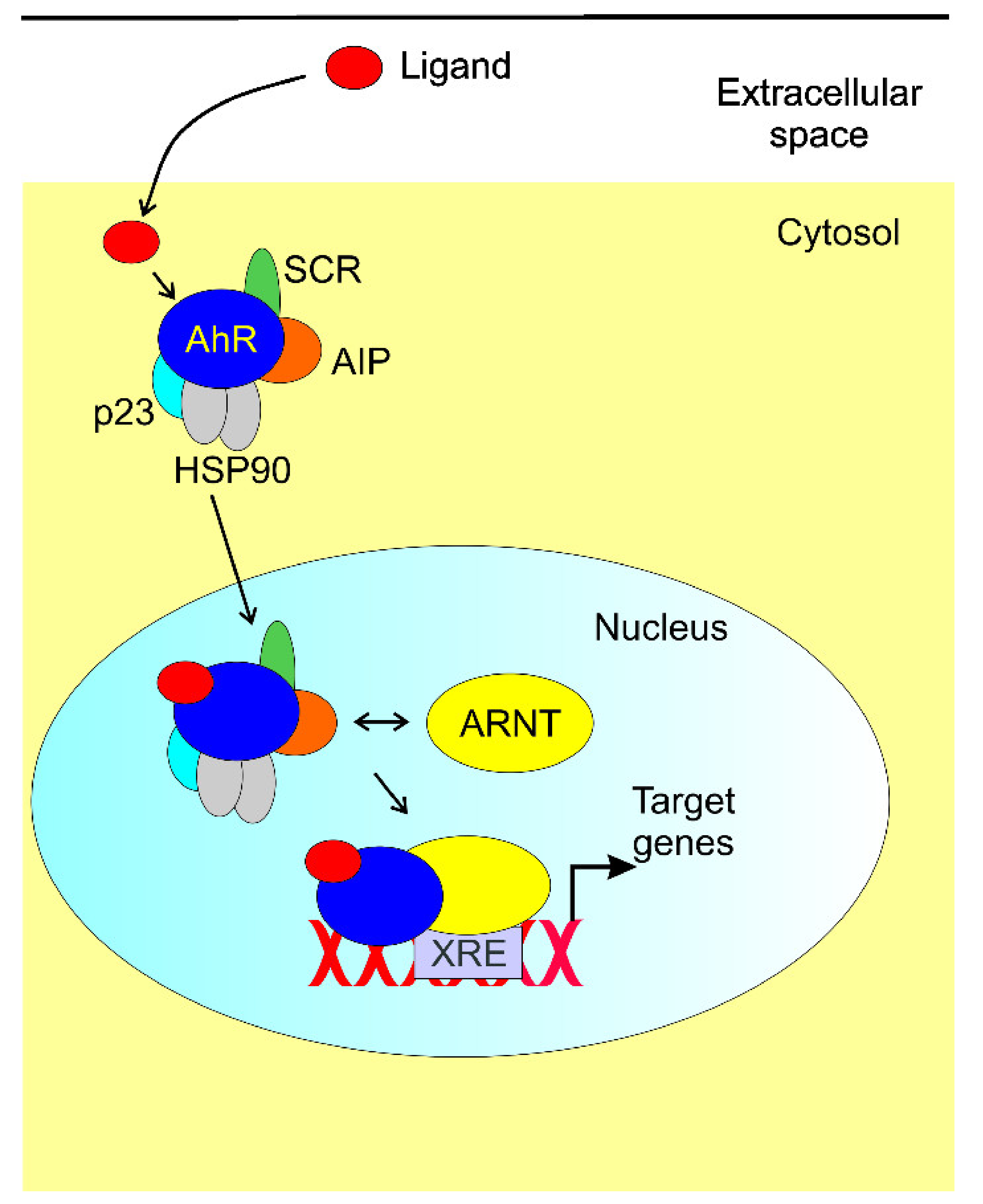
- Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Quintana, F.J. Regulation of the Immune Response by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Immunity 2018, 48, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konopelski, P.; Konop, M.; Gawrys-Kopczynska, M.; Podsadni, P.; Szczepanska, A.; Ufnal, M. Indole-3-Propionic Acid, a Tryptophan-Derived Bacterial Metabolite, Reduces Weight Gain in Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothhammer, V.; Quintana, F.J. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: An environmental sensor integrating immune responses in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtake, F.; Takeyama, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Kitagawa, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nohara, K.; Tohyama, C.; Krust, A.; Mimura, J.; Chambon, P.; et al. Modulation of oestrogen receptor signalling by association with the activated dioxin receptor. Nature 2003, 423, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Innocentin, S.; Withers, D.R.; Roberts, N.A.; Gallagher, A.R.; Grigorieva, E.F.; Wilhelm, C.; Veldhoen, M. Exogenous stimuli maintain intraepithelial lymphocytes via aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Cell 2011, 147, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Ren, L.; Chen, J.; Cao, R.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. MicroRNA-124 Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Targeting Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2016, 10, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Lan, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Gu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; et al. Critical role of all-trans retinoic acid in stabilizing human natural regulatory T cells under inflammatory conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3432–E3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintana, F.J.; Murugaiyan, G.; Farez, M.F.; Mitsdoerffer, M.; Tukpah, A.M.; Burns, E.J.; Weiner, H.L. An endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand acts on dendritic cells and T cells to suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20768–20773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mezrich, J.D.; Fechner, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, B.P.; Burlingham, W.J.; Bradfield, C.A. An interaction between kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3190–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Kimura, A.; Nakahama, T.; Chinen, I.; Masuda, K.; Nohara, K.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y.; Kishimoto, T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates dendritic cell immunogenicity via a kynurenine-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19961–19966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel, C.F.; Goth, S.R.; Dong, B.; Pessah, I.N.; Matsumura, F. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling mediates expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, U.H.; Lee, S.O.; Sridharan, G.; Lee, K.; Davidson, L.A.; Jayaraman, A.; Chapkin, R.S.; Alaniz, R.; Safe, S. Microbiome-derived tryptophan metabolites and their aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent agonist and antagonist activities. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 85, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilmas, C.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rassoulpour, A.; Schwarcz, R.; Albuquerque, E.X. The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits alpha7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-alpha7 nicotinic receptor expression: Physiopathological implications. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7463–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, M.; Terramani, T.; Lynch, G.; Baudry, M. A glycine site associated with N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptors: Characterization and identification of a new class of antagonists. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Simonavicius, N.; Wu, X.; Swaminath, G.; Reagan, J.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Kynurenic acid as a ligand for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR35. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22021–22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated neuronal cell death induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, 3-hydroxykynurenine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarcz, R.; Pellicciari, R. Manipulation of brain kynurenines: Glial targets, neuronal effects, and clinical opportunities. J. Pharm. Exp. 2002, 303, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reigstad, C.S.; Salmonson, C.E.; Rainey, J.F., 3rd; Szurszewski, J.H.; Linden, D.R.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Farrugia, G.; Kashyap, P.C. Gut microbes promote colonic serotonin production through an effect of short-chain fatty acids on enterochromaffin cells. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mawe, G.M.; Hoffman, J.M. Serotonin signalling in the gut--functions, dysfunctions and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Intestinal Immunity Mediated by Tryptophan Metabolism. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schanz, O.; Chijiiwa, R.; Cengiz, S.C.; Majlesain, Y.; Weighardt, H.; Takeyama, H.; Forster, I. Dietary AhR Ligands Regulate AhRR Expression in Intestinal Immune Cells and Intestinal Microbiota Composition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzella, C.R.; Ackerman, M.; Singhal, M.; Ticho, A.L.; Ceh, J.; Alrefai, W.A.; Saksena, S.; Dudeja, P.K.; Gill, R.K. Serotonin Modulates AhR Activation by Interfering with CYP1A1-Mediated Clearance of AhR Ligands. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 54, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosser, E.C.; Piper, C.J.M.; Matei, D.E.; Blair, P.A.; Rendeiro, A.F.; Orford, M.; Alber, D.G.; Krausgruber, T.; Catalan, D.; Klein, N.; et al. Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Suppress Arthritis by Amplifying Aryl-Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Regulatory B Cells. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 837–851.e810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissoon, N.R.; Cutrer, F.M. Aura and Other Neurologic Dysfunction in or with Migraine. Headache 2017, 57, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.J.; Stovner, L.J.; Birbeck, G.L. Migraine: The seventh disabler. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, M.B.; Hadjikhani, N. Migraine aura and related phenomena: Beyond scotomata and scintillations. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlović, J.M. Headache in Women. Continuum 2021, 27, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Asoom, L.I.A.; Sunni, A.A.; Rafique, N.; Latif, R.; Saif, S.A.; Almandil, N.B.; Almohazey, D.; AbdulAzeez, S.; Borgio, J.F. Genetics, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, management, and prevention of migraine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
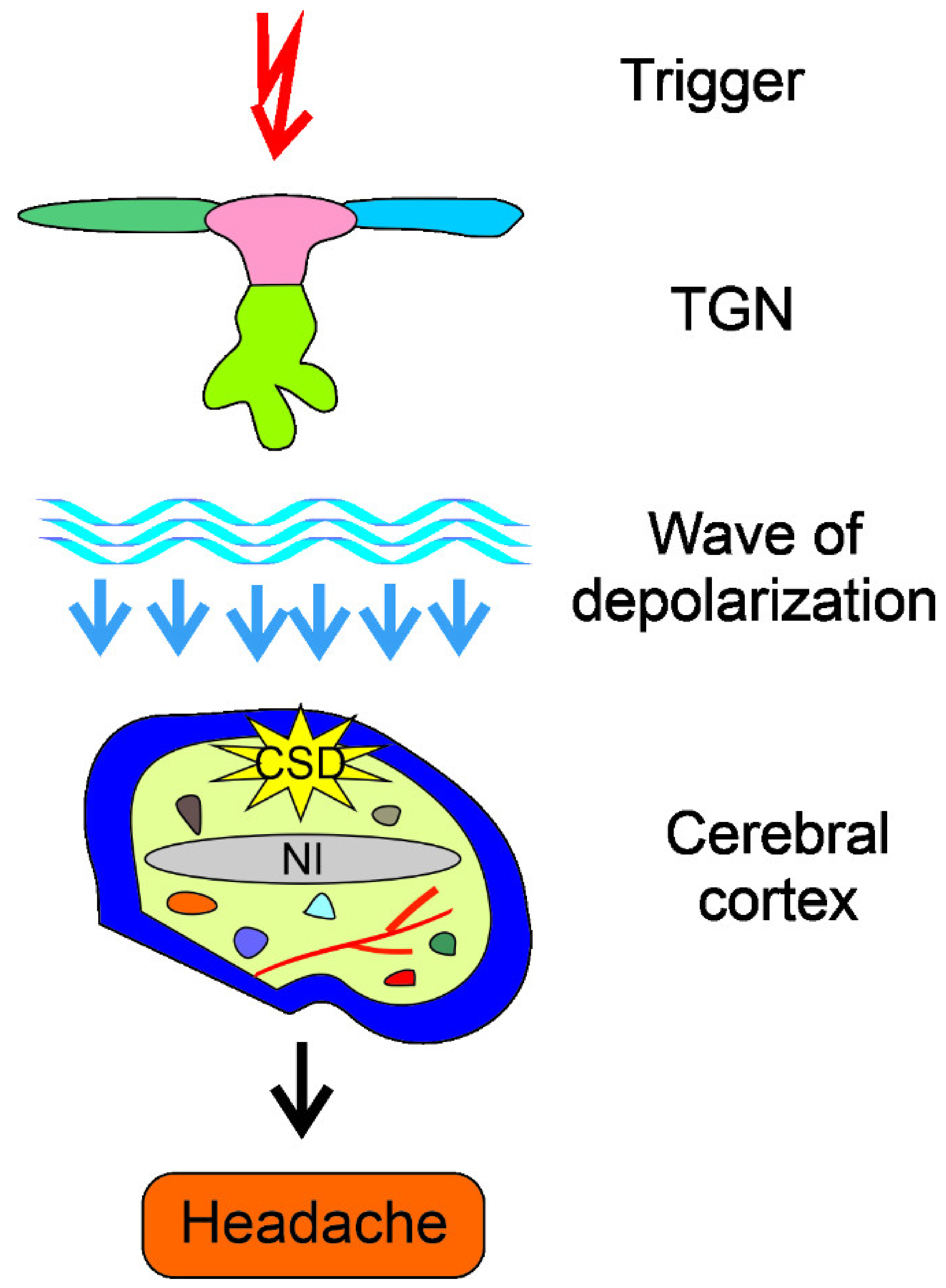
- Harriott, A.M.; Takizawa, T.; Chung, D.Y.; Chen, S.P. Spreading depression as a preclinical model of migraine. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolay, H.; Vuralli, D.; Goadsby, P.J. Aura and Head pain: Relationship and gaps in the translational models. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgdorff, P. Arguments against the role of cortical spreading depression in migraine. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mason, B.N.; Russo, A.F. Vascular Contributions to Migraine: Time to Revisit? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrer, F.M.; Charles, A. The neurogenic basis of migraine. Headache 2008, 48, 1411–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.; Dussor, G. Neurovascular contributions to migraine: Moving beyond vasodilation. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Coba, P.; Bruehl, S.; Del Paso, G.A.R. Slowly repeated evoked pain (SREP) as a central sensitization marker in episodic migraine patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshinsky, M.L.; Luo, J. Neurochemistry of trigeminal activation in an animal model of migraine. Headache 2006, 46 (Suppl. 1), S39–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R. Migraine and Tension-Type Headache: Diagnosis and Treatment. Med. Clin. 2019, 103, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, M.; Correnti, E.; Kamm, K.; Kelderman, T.; Papetti, L.; Rubio-Beltrán, E.; Vigneri, S.; Edvinsson, L.; Maassen Van Den Brink, A.; On behalf of the European Headache Federation School of Advanced Studies. Blocking CGRP in migraine patients—A review of pros and cons. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loder, E.W.; Burch, R.C. Who should try new antibody treatments for migraine? JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1039–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazerani, P. Migraine and Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fila, M.; Chojnacki, C.; Chojnacki, J.; Blasiak, J. Is an “Epigenetic Diet” for Migraines Justified? The Case of Folate and DNA Methylation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ailani, J.; Burch, R.C.; Robbins, M.S. The American Headache Society Consensus Statement: Update on integrating new migraine treatments into clinical practice. Headache 2021, 61, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Charles, A. Glutamate and Its Receptors as Therapeutic Targets for Migraine. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreou, A.P.; Holland, P.R.; Lasalandra, M.P.; Goadsby, P.J. Modulation of nociceptive dural input to the trigeminocervical complex through GluK1 kainate receptors. Pain 2015, 156, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waung, M.W.; Akerman, S.; Wakefield, M.; Keywood, C.; Goadsby, P.J. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5: A target for migraine therapy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, K.M.; Nagesh, V.; Aurora, S.K.; Gelman, N. Periaqueductal gray matter dysfunction in migraine: Cause or the burden of illness? Headache 2001, 41, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Levy, D.; Kainz, V.; Noseda, R.; Jakubowski, M.; Burstein, R. Activation of central trigeminovascular neurons by cortical spreading depression. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curto, M.; Lionetto, L.; Negro, A.; Capi, M.; Perugino, F.; Fazio, F.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Simmaco, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Martelletti, P. Altered serum levels of kynurenine metabolites in patients affected by cluster headache. J. Headache Pain 2015, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curto, M.; Lionetto, L.; Negro, A.; Capi, M.; Fazio, F.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Simmaco, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Martelletti, P. Altered kynurenine pathway metabolites in serum of chronic migraine patients. J. Headache Pain 2015, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oláh, G.; Herédi, J.; Menyhárt, A.; Czinege, Z.; Nagy, D.; Fuzik, J.; Kocsis, K.; Knapp, L.; Krucsó, E.; Gellért, L.; et al. Unexpected effects of peripherally administered kynurenic acid on cortical spreading depression and related blood-brain barrier permeability. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauvel, V.; Vamos, E.; Pardutz, A.; Vecsei, L.; Schoenen, J.; Multon, S. Effect of systemic kynurenine on cortical spreading depression and its modulation by sex hormones in rat. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 236, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuka, B.; Nyári, A.; Cseh, E.K.; Körtési, T.; Veréb, D.; Tömösi, F.; Kecskeméti, G.; Janáky, T.; Tajti, J.; Vécsei, L. Clinical relevance of depressed kynurenine pathway in episodic migraine patients: Potential prognostic markers in the peripheral plasma during the interictal period. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, W.; Zadeh, K.; Vekariya, R.; Ge, Y.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Tryptophan Metabolism and Gut-Brain Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berstad, A.; Raa, J.; Valeur, J. Tryptophan: ‘essential’ for the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, G.; McKernan, D.P.; Gaszner, G.; Quigley, E.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. A Distinct Profile of Tryptophan Metabolism along the Kynurenine Pathway Downstream of Toll-Like Receptor Activation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heitkemper, M.M.; Han, C.J.; Jarrett, M.E.; Gu, H.; Djukovic, D.; Shulman, R.J.; Raftery, D.; Henderson, W.A.; Cain, K.C. Serum Tryptophan Metabolite Levels During Sleep in Patients With and Without Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Biol. Res. Nurs. 2016, 18, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keszthelyi, D.; Troost, F.J.; Jonkers, D.M.; Kruimel, J.W.; Leue, C.; Masclee, A.A. Decreased levels of kynurenic acid in the intestinal mucosa of IBS patients: Relation to serotonin and psychological state. J. Psychosom. Res. 2013, 74, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J. Do Toll-like Receptors Play a New Role as a Biomarker of Irritable Bowel Syndrome? J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, R.; Wang, Z.; Saavedra, C.; DiNardo, A.; Corr, M.; Powell, S.B.; Yaksh, T.L. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in mast cell-mediated migraine pain pathway. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919867842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, A.; Abedini, M.; Hosseini, S.H.; Hosseini-Khah, Z.; Bazrafshan, B.; Tehrani, M. Toll like receptor-4 896A/G gene variation, a risk factor for migraine headaches. Iran. J. Immunol 2012, 9, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kursun, O.; Yemisci, M.; van den Maagdenberg, A.; Karatas, H. Migraine and neuroinflammation: The inflammasome perspective. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M. A role for the gut microbiota in IBS. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmas, D.M.; Badawy, A.A.; Hince, D.; Davies, S.J.; Probert, C.; Creed, T.; Smithson, J.; Afzal, M.; Nutt, D.J.; Potokar, J.P. Increased serum free tryptophan in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farup, P.G.; Ueland, T.; Rudi, K.; Lydersen, S.; Hestad, K. Functional Bowel Disorders Are Associated with a Central Immune Activation. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 1642912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, P.; Cassidy Eugene, M.; Clarke, G.; Scully, P.; Barry, S.; Quigley Eamonn, M.M.; Shanahan, F.; Cryan, J.; Dinan Timothy, G. Tryptophan catabolism in females with irritable bowel syndrome: Relationship to interferon-gamma, severity of symptoms and psychiatric co-morbidity. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Fitzgerald, P.; Cryan, J.F.; Cassidy, E.M.; Quigley, E.M.; Dinan, T.G. Tryptophan degradation in irritable bowel syndrome: Evidence of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in a male cohort. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovacic, K.; Li, B.U.K. Cyclic vomiting syndrome: A narrative review and guide to management. Headache 2021, 61, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.S.; Priyadharsini, S.S.Y.; Venkatesan, T. Migraine, Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome, and Other Gastrointestinal Disorders. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamodt, A.H.; Stovner, L.J.; Hagen, K.; Zwart, J.A. Comorbidity of headache and gastrointestinal complaints. The Head-HUNT Study. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katić, B.J.; Golden, W.; Cady, R.K.; Hu, X.H. GERD prevalence in migraine patients and the implication for acute migraine treatment. J. Headache Pain 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saberi-Firoozi, M.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.A.; Heidari, S.T.; Khademolhosseini, F.; Mehrabani, D. Correlation of gastroesophageal reflux disease with positive family history and headache in Shiraz city, southern Iran. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, M.; Pucci, E.; Miceli, E.; Pagani, E.; Brondino, N.; Nappi, G.; Corazza, G.R.; Di Sabatino, A. Prevalence and pathophysiology of post-prandial migraine in patients with functional dyspepsia. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankarani, K.B.; Akbari, M.; Tabrizi, R. Association of Gastrointestinal Functional Disorders and Migraine Headache: A Population Base Study. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 9, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Gal, J.; Michel, J.F.; Rinaldi, V.E.; Spiri, D.; Moretti, R.; Bettati, D.; Romanello, S.; Berlese, P.; Lualdi, R.; Boizeau, P.; et al. Association between functional gastrointestinal disorders and migraine in children and adolescents: A case-control study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaloo, S.; Dehghani, S.M.; Hashemi, S.M.; Heydari, M.; Heydari, S.T. Comorbidity of headache and functional constipation in children: A cross-sectional survey. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szperka, C. Headache in Children and Adolescents. Continuum 2021, 27, 703–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meucci, G.; Radaelli, F.; Prada, A.; Bortoli, A.; Crotta, S.; Cerrato, C.; Minoli, G. Increased prevalence of migraine in patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia referred for open-access upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Endoscopy 2005, 37, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, G.X. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and migraine: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14965–14972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Zarinfar, N.; Zanjani, A.T.; Morteza, A. The effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on migraine: A randomized, double blind, controlled trial. Pain Physician 2012, 15, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savi, L.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Fagoonee, S.; Pellicano, R. Is Helicobacter pylori the infectious trigger for headache?: A review. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 13, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, F.Y.; Lu, C.L. Irritable bowel syndrome and migraine: Bystanders or partners? J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, J.A.; Rothman, K.J.; Cabral, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Farraye, F.A. Migraine, fibromyalgia, and depression among people with IBS: A prevalence study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Hesketh, T. Irritable bowel syndrome and migraine: Evidence from Mendelian randomization analysis in the UK Biobank. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandvik, P.O.; Wilhelmsen, I.; Ihlebaek, C.; Farup, P.G. Comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome in general practice: A striking feature with clinical implications. Aliment. Pharm. 2004, 20, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongtrakul, W.; Charoenngam, N.; Ungprasert, P. Increased prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in migraine patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.I.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, W.H.; Wang, H.C.; Kao, C.H. Association between migraine and irritable bowel syndrome: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, H.; Shin, H.E.; Suh, G.I.; Choi, M.G. Concomitant functional gastrointestinal symptoms influence psychological status in Korean migraine patients. Gut Liver 2013, 7, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, W.C.; Sullivan, S.N.; Corke, M.; Rush, D. Globus and headache: Common symptoms of the irritable bowel syndrome. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1978, 118, 387–388. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yu, S.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, W.; Zhang, L. Clinical features and risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome in Migraine patients. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.F.; Yang, Y.W.; Chen, Y.Y. The effect of anxiety and depression on the risk of irritable bowel syndrome in migraine patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 44, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulberis, M.; Saleh, C.; Beyenburg, S. Is there an Association between Migraine and Gastrointestinal Disorders? J. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 13, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cady, R.K.; Farmer, K.; Dexter, J.K.; Hall, J. The bowel and migraine: Update on celiac disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2012, 16, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazerani, P. A Bidirectional View of Migraine and Diet Relationship. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, D.; Reisz, D.; Gurban, C.V.; Georgescu, L.A.; Ionita, I.; Ancusa, O.E.; Lighezan, D. Migraine in young females with irritable bowel syndrome: Still a challenge. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Georgescu, D.; Iurciuc, M.S.; Ionita, I.; Dragan, S.; Muntean, M.; Ancusa, O.E.; Reisz, D.; Ionita, M.; Lighezan, D. Migraine without Aura and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Young Females: Is Gut Microbiota to Blame? Medicina 2019, 55, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Hyde, E.; Sangwan, N.; Gilbert, J.A.; Viirre, E.; Knight, R. Migraines Are Correlated with Higher Levels of Nitrate-, Nitrite-, and Nitric Oxide-Reducing Oral Microbes in the American Gut Project Cohort. mSystems 2016, 1, e00105-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shu, H.; Yanagisawa, L.; Tao, F. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Enhances Migraine-Like Pain via TNFα Upregulation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, L.; Fioramonti, J. Visceral perception: Inflammatory and non-inflammatory mediators. Gut 2002, 51 (Suppl. 1), i19–i23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Chiu, I.M. Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, K.; Cui, M.; Ye, W.; Zhao, G.; Jin, L.; Chen, X. The progress of gut microbiome research related to brain disorders. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A.; Lin, Z. Structural and Functional Characterization of the Gut Microbiota in Elderly Women With Migraine. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Role of Kynurenine Pathway in Oxidative Stress during Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2021, 10, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Kaye, A.D.; Sun, Y.H. Potential Beneficial Effects of Probiotics on Human Migraine Headache: A Literature Review. Pain Physician 2017, 20, E251–E255. [Google Scholar]
- Parohan, M.; Djalali, M.; Sarraf, P.; Yaghoubi, S.; Seraj, A.; Foroushani, A.R.; Ranji-Burachaloo, S.; Javanbakht, M.H. Effect of probiotic supplementation on migraine prophylaxis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Monitoring the kynurenine system: Concentrations, ratios or what else? Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiboub, M.; Verburgt, C.M.; Sovran, B.; Benninga, M.A.; de Jonge, W.J.; Van Limbergen, J.E. Nutritional Therapy to Modulate Tryptophan Metabolism and Aryl Hydrocarbon-Receptor Signaling Activation in Human Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Snyder, M.; Kenison, J.E.; Yang, K.; Lara, B.; Lydell, E.; Bennani, K.; Novikov, O.; Federico, A.; Monti, S.; et al. How the AHR Became Important in Cancer: The Role of Chronically Active AHR in Cancer Aggression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Effect | Mechanism | Remarks | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ↑l-kyn a, ↓l-kyn/l-Trp, ↓KYNA, ↓KYNA/l-kyn | ↑IDO | Male IBS patients, small cohort | [127] |
| ↓melatonin/l-Trp | Unknown | d-IBS compared with c-IBS, lower sleep quality in d-IBS with diarrhea patients | [117] |
| ↓5-HT, ↓KYNA in duodenal mucosa ↑5-HT, ↑KYNA in plasma A positive correlation between mucosal but not plasma concentrations of KYNA and 5-HT and psychological state in IBS | ↑release of 5-HT and KYNA from the GI tract to the systemic compartment | Alterations in the psychological condition of IBS patients might be secondary to changes in GI functions | [118] |
| ↑l-kyn/l-Trp | Activation of the TLR family | TLR1/2,2,3,5,7,8 Association of TLR4 with migraine in an animal model | [120,127] |
| ↑l-Trp, ↓l-Trp oxidation | Alteration in l-Trp metabolism, ↓tryptophan dioxygenase | d-IBS patients, dairy-free diet did not change l-Trp or decrease IBS symptoms intensity | [124] |
| Positive correlation between IBS symptoms and l-Trp and l-kyn patient with depression or unexplained neurological symptoms | Unknown | Determined in cerebrospinal fluid | [125] |
| GI Disorder | Remarks | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CVS a | Many studies | [129] |
| GERD, diarrhea, constipation, and nausea | Large-cohort studies | [130,131,132] |
| Nausea, vomiting | Autonomic symptoms associated with pre- and post-dorsal phases of migraine attack | [155] |
| Epigastric pain syndrome, postprandial distress syndrome | Associations with postprandial hypersensitivity | [134] |
| GERD, IBS, dyspepsia | Population-based study | [135] |
| Positive correlation with functional dyspepsia, IBS and abdominal migraine, negative correlation with functional constipation | Children and adolescent diagnosed with migraine or tension-type headache | [136] |
| Negative correlation of headaches with functional constipation | Children and adolescent, significant only in nonmigraine subtypes | [138] |
| Functional dyspepsia | Patients aged 18–55 years, higher migraine prevalence in dysmotility-like dyspepsia as compared with controls, patients with ulcer-like dyspepsia and reflux-like dyspepsia | [139] |
| IBS | Many studies | [143] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fila, M.; Chojnacki, J.; Pawlowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Chojnacki, C.; Blasiak, J. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Migraine and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810134
Fila M, Chojnacki J, Pawlowska E, Szczepanska J, Chojnacki C, Blasiak J. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Migraine and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):10134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810134
Chicago/Turabian StyleFila, Michal, Jan Chojnacki, Elzbieta Pawlowska, Joanna Szczepanska, Cezary Chojnacki, and Janusz Blasiak. 2021. "Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Migraine and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 10134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810134
APA StyleFila, M., Chojnacki, J., Pawlowska, E., Szczepanska, J., Chojnacki, C., & Blasiak, J. (2021). Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Migraine and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 10134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810134








