Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97: A Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer †
Abstract
1. Introduction
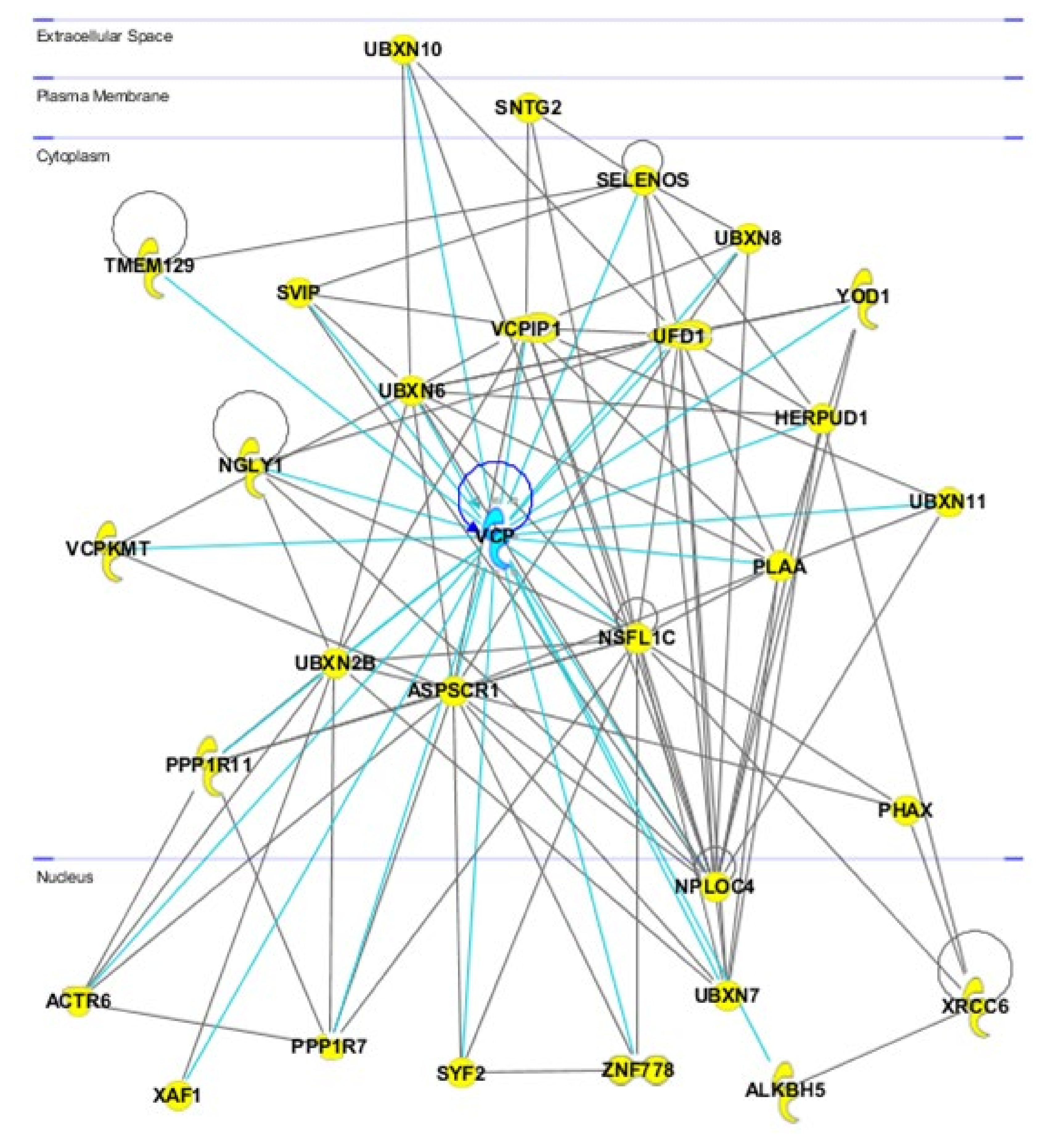
2. Cellular Functions of VCP/p97
2.1. Protein Quality Control
2.2. Cell Cycle
2.3. Cell Death: Apoptosis and Autophagy
2.4. Other Functions
3. VCP/p97 Expression and Function in Cancer
3.1. VCP/p97 in Gastrointestinal Cancers
3.1.1. Colorectal Cancer
3.1.2. Pancreatic Cancer
3.1.3. Liver Cancer
3.1.4. Gastric and Esophageal Cancer
3.2. VCP/p97 in Breast Cancer
3.3. VCP/p97 in Prostate Cancer
3.4. VCP/p97 in Lung Cancer
3.5. VCP/p97 in Bone Cancers
3.6. VCP/p97 in Head and Neck Cancers
3.7. VCP/p97 in Thyroid Cancer
3.8. VCP/p97 in Hematological Cancers
3.9. VCP/p97 in Other Cancers
4. Inhibitors of VCP
4.1. Quinazolines
4.2. CB-5083
4.3. Pyrimidines
4.4. Triazoles and Thiazoles
4.5. Indole Derivatives
4.6. Eeyarestatin I
4.7. Other Known Inhibitors
5. VCP/p97 Mutations and Their Involvement in the Mechanism of Inhibitor Resistance
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moir, D.; Stewart, S.E.; Osmond, B.C.; Botstein, D. Cold-sensitive cell-division-cycle mutants of yeast: Isolation, properties, and pseudoreversion studies. Genetics 1982, 100, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.; Weihl, C.C. The VCP/p97 system at a glance: Connecting cellular function to disease pathogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3877–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Tang, W.K.; Ye, Y. Structure and function of the AAA+ ATPase p97/Cdc48p. Gene 2016, 583, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Shen, Y.; Ballar, P.; Apostolou, A.; Agami, R.; Fang, S. AAA ATPase p97/valosin-containing protein interacts with gp78, a ubiquitin ligase for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45676–45684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.K.; Xia, D. Role of the D1-D2 Linker of Human VCP/p97 in the Asymmetry and ATPase Activity of the D1-domain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.K.; Xia, D. Mutations in the Human AAA(+) Chaperone p97 and Related Diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.T.; Hsueh, Y.P. VCP and ATL1 regulate endoplasmic reticulum and protein synthesis for dendritic spine formation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.; Bug, M.; Bremer, S. Emerging functions of the VCP/p97 AAA-ATPase in the ubiquitin system. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchberger, A.; Schindelin, H.; Hanzelmann, P. Control of p97 func-tion by cofactor binding. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2578–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Qiu, H. Valosin-Containing Protein, a Calcium-Associated ATPase Protein, in Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondrial Function and Its Implications for Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänzelmann, P.; Schindelin, H. The interplay of cofactor interactions and post-translational modifications in the regulation of the AAA+ ATPase p97. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumughan, A.; Roske, Y.; Barth, C.; Forero, L.L.; Bravo-Rodriguez, K.; Redel, A.; Kostova, S.; McShane, E.; Opitz, R.; Faelber, K.; et al. Quantitative interaction mapping reveals an extended UBX domain in ASPL that disrupts functional p97 hexamers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, K.J.; Jang, J.K.; Jeon, Y.H.; Ko, K.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, I.Y. Selenoprotein S-dependent Selenoprotein K Binding to p97(VCP) Protein Is Essential for Endoplasmic Reticulum-associated Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29941–29952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Mar, K.; Warren, G.; Wang, Y. Molecular mechanism of mitotic Golgi disassembly and reassembly revealed by a defined re-constitution assay. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6085–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wani, G.; Wani, A.A. UV-induced proteolysis of RNA polymerase II is mediated by VCP/p97 segregase and timely orchestration by Cockayne syndrome B protein. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11004–11019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, A.; Taranum, S.; Pietrocola, F.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Brahma, S.; Bartholomew, B.; Papamichos-Chronakis, M. INO80 Chromatin Remodeler Facilitates Release of RNA Polymerase II from Chromatin for Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteasomal Degradation. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Boom, J.; Wolf, M.; Weimann, L.; Schulze, N.; Li, F.; Kaschani, F.; Riemer, A.; Zierhut, C.; Kaiser, M.; Iliakis, G.; et al. VCP/p97 Extracts Sterically Trapped Ku70/80 Rings from DNA in Double-Strand Break Repair. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, W.S.; Chia, D.X.; Rao, F.; Nun, S.B.; Shochat, S.G. ATP binding to p97/VCP D1 domain regulates selective recruitment of adaptors to its proximal N-domain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballar, P.; Pabuccuoglu, A.; Kose, F.A. Different p97/VCP complexes function in retrotranslocation step of mammalian ER-associated degradation (ERAD). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubes, S.; Stemmann, O. The AAA-ATPase p97-Ufd1-Npl4 is re-quired for ERAD but not for spindle disassembly in Xenopus egg extracts. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nowis, D.; McConnell, E.; Wojcik, C. Destabilization of the VCP-Ufd1-Npl4 complex is associated with decreased levels of ERAD substrates. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 2921–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Boom, J.; Meyer, H. VCP/p97-Mediated Unfolding as a Principle in Protein Homeostasis and Signaling. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerang, M.; Ritz, D.; Paliwal, S.; Garajova, Z.; Bosshard, M.; Mailand, N.; Janscak, P.; Hübscher, U.; Meyer, H.; Ramadan, K. The ubiquitin-selective segregase VCP/p97 orchestrates the response to DNA double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, C.; Kirchner, P.; Bug, M.; Grum, D.; Koerver, L.; Schulze, N.; Poehler, R.; Dressler, A.; Fengler, S.; Arhzaouy, K.; et al. VCP/p97 cooperates with YOD1, UBXD1 and PLAA to drive clearance of ruptured lysosomes by autophagy. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielden, J.; Wiseman, K.; Torrecilla, I.; Li, S.; Hume, S.; Chiang, S.C.; Ruggiano, A.; Narayan Singh, A.; Freire, R.; Hassanieh, S.; et al. TEX264 coordinates p97- and SPRTN-mediated resolution of topoisomerase 1-DNA adducts. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Sasagawa, Y.; Ogura, T. Recent advances in p97/VCP/Cdc48 cellular functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012, 1823, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, B.K.; Yu, S.-W. Valosin-containing protein (VCP): Structure, functions, and implications in neurodegenerative diseases. Anim. Cells Syst. 2016, 20, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Tang, W.K.; Zhang, T.; Xia, D. A Mighty "Protein Extractor" of the Cell: Structure and Function of the p97/CDC48 ATPase. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, J.C.; Ye, Y. Cleaning up in the endoplasmic reticulum: Ubiquitin in charge. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldridge, R.D.; Rapoport, T.A. Autoubiquitination of the Hrd1 ligase triggers protein retrotranslocation in ERAD. Cell 2016, 166, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuber, O.; Jarosch, E.; Volkwein, C.; Walter, J.; Sommer, T. Ubx2 links the Cdc48 complex to ER-associated protein degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, R.M.; Sato, B.K.; Hampton, R.Y. In vitro analysis of Hrd1p-mediated retrotranslocation of its multispanning membrane substrate 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14710–14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ye, Y. The final moments of misfolded proteins en route to the proteasome. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemion, C.; Flammer, J.; Neutzner, A. Quality control of oxidatively damaged mitochondrial proteins is mediated by p97 and the proteasome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 75, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Fukushi, J.; Hori, S.; Matsuda, N.; Okatsu, K.; Kakiyama, Y.; Kawawaki, J.; Kakizuka, A.; Tanaka, K. Different dynamic movements of wild-type and pathogenic VCPs and their cofactors to damaged mitochondria in a Parkin-mediated mitochondrial quality control system. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.M.; Nielson, J.R.; Dephoure, N.; Gygi, S.P.; Rutter, J. Intramolecular interactions control Vms1 translocation to damaged mitochondria. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defenouillère, Q.; Yao, Y.; Mouaikel, J.; Namane, A.; Galopier, A.; Decourty, L.; Doyen, A.; Malabat, C.; Saveanu, C.; Jacquier, A.; et al. Cdc48-associated complex bound to 60S particles is required for the clearance of aberrant translation products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5046–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandman, O.; Stewart-Ornstein, J.; Wong, D.; Larson, A.; Williams, C.C.; Li, G.W.; Zhou, S.; King, D.; Shen, P.S.; Weibezahn, J.; et al. A ribosome-bound quality control complex triggers degradation of nascent peptides and signals translation stress. Cell 2012, 151, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouysset, J.; Deichsel, A.; Moser, S.; Hoege, C.; Hyman, A.A.; Gartner, A.; Hoppe, T. Cell cycle progression requires the CDC-48UFD-1/NPL-4 complex for efficient DNA replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12879–12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.M.; Li, C.C. Valosin-containing protein isamulti-ubiquitinchain-targeting factor required in ubiquitin-proteasome degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikai, N.; Yanagida, M. Cdc48 is required for the stability of Cut1/separase in mitotic anaphase. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 156, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, C.; Yano, M.; DeMartino, G.N. RNA interference of valosin-containing protein (VCP/p97) reveals multiple cellular roles linked to ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent proteolysis. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, K.; Bruderer, R.; Spiga, F.M.; Popp, O.; Baur, T.; Gotta, M.; Meyer, H.H. Cdc48/p97 promotes reformation of the nucleus by extracting the kinase Aurora B from chromatin. Nature 2007, 450, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasagawa, Y.; Higashitani, A.; Urano, T.; Ogura, T.; Yamanaka, K. CDC-48/p97 is required for proper meiotic chromosome segregation via controlling AIR-2/Aurora B kinase localization in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 179, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Schlauer, J.; Zischka, H.; Mecke, D.; Frohlich, K.U. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates cell cycle-dependent nuclear localization of Cdc48p. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Matuschewski, K.; Rape, M.; Thoms, S.; Jentsch, S. Role of the ubiquitin-selective CDC48(UFD1/NPL4)chaperone (segregase) in ERAD of OLE1 and other substrates. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirogane, T.; Fukada, T.; Muller, J.M.; Shima, D.T.; Hibi, M.; Hirano, T. Synergistic roles for Pim-1 and c-Myc in STAT3-mediated cell cycle progression and antiapoptosis. Immunity 1999, 11, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresse, E.; Salomons, F.A.; Vesa, J.; Bott, L.C.; Kimonis, V.; Yao, T.P.; Dantuma, N.P.; Taylor, J.P. VCP/p97 is essential for maturationof ubiquitin-containing autophagosomes and this function is impaired by mutations that cause IBMPFD. Autophagy 2010, 6, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.S.; Fuentealba, R.A.; Miller, S.E.; Jackson, E.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Baloh, R.H.; Weihl, C.C. Valosin-containing protein (VCP) is required for autophagy and is disrupted in VCP disease. J. Cell. Biol. 2009, 187, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.K.; Hong, C.J.; Chung, K.M.; Woo, H.; Kim, K.; Jung, S.; Kim, E.K.; Yu, S.W. Valosin-containing protein is a key mediator between autophagic cell death and apoptosis in adult hippocampal neural stem cells following insulin withdrawal. Mol. Brain 2016, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.M.; Park, H.; Jung, S.; Ha, S.; Yoo, S.J.; Woo, H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, E.K.; Moon, C.; et al. Calpain determines the propensity of adult Hippocampal neural stem cells to Autophagic cell death following insulin withdrawal. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 3052–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantuma, N.P.; Hoppe, T. Growing sphere of influence: Cdc48/p97 orchestrates ubiquitin-dependent extraction from chromatin. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, K.; Kondo, H. p97/p47-mediated biogenesis of Golgi and ER. J. Biochem. 2005, 137, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, K.; Totsukawa, G.; Puhka, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Jokitalo, E.; Dreveny, I.; Beuron, F.; Zhang, X.; Freemont, P.; Kondo, H. p37 is a p97 adaptor required for Golgi and ER biogenesis in interphase and at the end of mitosis. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.H.; Wang, Y.; Warren, G. Direct binding of ubiquitin conjugates by the mammalian p97 adaptor complexes, p47 and Ufd1-Npl4. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5645–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, K.; Jokitalo, E.; Kano, F.; Murata, M.; Zhang, X.; Canas, B.; Newman, R.; Rabouille, C.; Pappin, D.; Freemont, P.; et al. VCIP135, a novel essential factor for p97/p47-mediated membrane fusion, is required for Golgi and ER assembly in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, P.; Bug, M.; Meyer, H. Ubiquitination of the N-terminal region of caveolin-1 regulates endosomal sorting by theVCP/p97 AAA-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7363–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.; Drozdowska, A.; Dobrynin, G. A role for Cdc48/p97 and Aurora B in controlling chromatin condensation during exit from mitosis. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, D.; Vuk, M.; Kirchner, P.; Bug, M.; Schutz, S.; Hayer, A.; Bremer, S.; Lusk, C.; Baloh, R.H.; Lee, H.; et al. Endolysosomal sorting of ubiquitylated caveolin-1 is regulated by VCP and UBXD1 and impaired by VCP disease mutations. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olzmann, J.A.; Richter, C.M.; Kopito, R.R. Spatial regulation of UBXD8 and p97/VCP controls ATGL-mediated lipid droplet turnover. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Hoshida, Y.; Sakon, M.; Kameyama, M.; Imaoka, S.; Sekimoto, M.; Nakamori, S.; Monden, M.; Aozasa, K. Expression of valosin-containing protein in colorectal carcinomas as a predictor for disease recurrence and prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguë, M.N.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; Bonneil, É.; Boyer, A.; Pouletty, N.; Mes-Masson, A.M.; Thibault, P.; Nadeau, M.È.; Boerboom, D. Proteomic profiling of a mouse model for ovarian granulosa cell tumor identifies VCP as a highly sensitive serum tumor marker in several human cancers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Zhao, J. Valosin-containing protein (VCP) promotes the growth, invasion, and metastasis of colorectal cancer through activation of STAT3 signaling. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 418, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Mei, H.; Liu, X.; Peng, Z. USP11 induce resistance to 5-Fluorouracil in Colorectal Cancer through activating autophagy by stabilizing VCP. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Nakamori, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Iizuka, N.; Okami, J.; Nagano, H.; Dono, K.; Umeshita, K.; Sakon, M.; et al. Valosin-containing protein (p97) and Ki-67 expression is a useful marker in detecting malignant behavior of pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Oncology 2004, 66, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin-Muller, C.; Li, D.; Bharadwaj, U.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Hodges, S.E.; Fisher, W.E.; Mo, Q.; Hung, M.C.; Yao, Q. A tumorigenic factor interactome connected through tumor suppressor microRNA-198 in human pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5901–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Nakamori, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Nagano, H.; Dono, K.; Umeshita, K.; Sakon, M.; Monden, M.; Aozasa, K. Elevated expression of valosin-containing protein (p97) in hepatocellular carcinoma is correlated with increased incidence of tumor recurrence. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hei, Y.; Shu, Q.; Dong, J.; Gao, Y.; Fu, H.; Zheng, X.; Yang, G. VCP/p97, down-regulated by microRNA-129-5p.; could regulate the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Sun, J.; Pan, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Huang, P. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through the regulation of miR-129-5p-VCP-IkappaB. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 313, G150–G156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Higa, A.; Taouji, S.; Bexiga, M.G.; Marza, E.; Arma, D.; Castain, C.; Bail, B.L.; Simpson, J.C.; Rosenbaum, J.; et al. Sorafenib-mediated targeting of the AAA+ ATPase p97/VCP leads to disruption of the secretory pathway, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and hepatocellular cancer cell death. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.H.; Motiwala, T.; Roy, S.; Claus, R.; Mustafa, M.; Plass, C.; Freitas, M.A.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T. Methylation of the PTPRO gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma and identification of VCP as its substrate. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Hoshida, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Yano, M.; Nakamori, S.; Sakon, M.; Monden, M.; et al. Expression level of valosin-containing protein is strongly associated with progression and prognosis of gastric carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.H.; Ko, C.C.; Chang, J.G.; Chen, S.F.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T.; Chow, L.P. Subcellular and functional proteomic analysis of the cellular responses induced by Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2006, 5, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.C.; Yang, J.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Chuang, J.G.; Lin, C.W.; Wu, M.S.; Chow, L.P. VCP phosphorylation-dependent interaction partners prevent apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55724. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, M.A.; Taguchi, S.; Komatsuzaki, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Masuda, A.; Sampei, M.; Satoh, M.; Kado, S.; Ishibashi, M. Valosin-containing Protein is a Target of 5′-l Fuligocandin B and Enhances TRAIL Resistance in Cancer Cells. Chem. Open 2016, 5, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Hoshida, Y.; Iizuka, N.; Kidogami, S.; Miyata, H.; Takiguchi, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Yano, M. Expression level of valosin-containing protein (p97) is associated with prognosis of esophageal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5558–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Song, H.; Mao, R.; Gao, Q.; Feng, Z.; Wang, N.; Song, S.; Jiao, R.; Ni, P.; Ge, H. Targeting valosin-containing protein enhances the efficacy of radiation therapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3464–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Niu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, J.; Pang, D. High expression of valosin-containing protein predicts poor prognosis in patients with breast carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 9919–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Rogers, A.; Asleh, K.; Won, J.; Gao, D.; Leung, S.; Li, S.; Vij, K.R.; Zhu, J.; Held, J.M.; et al. Phospho-Ser(784)-VCP Is Required for DNA Damage Response and Is Associated with Poor Prognosis of Chemotherapy-Treated Breast Cancer. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J. Ser(784) phosphorylation: A clinically relevant enhancer of VCP function in the DNA damage response. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2020, 7, 1796179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhu, K.; Ye, Z.; Yue, J. VCP/p97 targets the nuclear export and degradation of p27(Kip1) during G1 to S phase transition. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 5193–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Quan, H.; Dong, Y.; Nie, M.; Wang, J.; Xie, F.; Ji, J.; Zhou, L.; et al. p97/VCP is highly expressed in the stem-like cells of breast cancer and controls cancer stemness partly through the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Tomita, Y.; Hoshida, Y.; Kono, T.; Oka, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Nonomura, N.; Okuyama, A.; Aozasa, K. Elevated expression of valosin-containing protein (p97) is associated with poor prognosis of prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3007–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duscharla, D.; Reddy, K.; Dasari, C.; Bhukya, S.; Ummanni, R. Interleukin-6 induced overexpression of valosin-containing protein (VCP)/p97 is associated with androgen-independent prostate cancer (AIPC) progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 7148–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogor, P.; Yoshida, T.; Koike, M.; Kakizuka, A. VCP relocalization limits mitochondrial activity, GSH depletion, and ferroptosis during starvation in PC3 prostate cancer cells. Genes Cells 2021, 6, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Hoshida, Y.; Iizuka, N.; Monden, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Iuchi, K.; Aozasa, K. Expression level of valosin-containing protein (p97) is correlated with progression and prognosis of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2004, 11, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, C.W.; Min, T.; Bodas, M.; Mazur, S.; Begum, S.; Tang, D.; Vij, N. Critical role of VCP/p97 in the pathogenesis and progression of non-small cell lung carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Wen, R.; He, J.; Tang, J. Epigenetic regulation of miR-129-2 and its effects on the proliferation and invasion in lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.P.; Beverly, L.J. Regulation of VCP/p97 demonstrates the critical balance between cell death and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) downstream of ER stress. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17725–17737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Tomita, Y.; Nakatsuka, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Myoui, A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Aozasa, K. VCP (p97) regulates NFkappaB signaling pathway, which is important for metastasis of osteosarcoma cell line. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2002, 93, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchini, C.; Rocchi, A.; Manara, M.C.; De Sanctis, P.; Capanni, C.; Bianchini, M.; Carinci, P.; Scotlandi, K.; Valvassori, L. Apoptotic genes as potential markers of metastatic phenotype in human osteosarcoma cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, J.Y.; Xi, W.H.; Zhu, L.B.; Long, X.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Luo, Q.F.; Zhu, X.P.; Liu, Z.L. Knockdown of Aurora-B alters osteosarcoma cell malignant phenotype via decreasing phosphorylation of VCP and NF-κB signaling. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 3895–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.H.; Zhou, Y.F.; Peng, A.F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Chen, W.Z.; Liu, J.M.; Huang, S.H.; Liu, Z.L. Demethylation-mediated miR-129-5p up-regulation inhibits malignant phenotype of osteogenic osteosarcoma by targeting Homo sapiens valosin-containing protein (VCP). Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 3799–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.H.; Zhou, Y.F.; Lan, M.; Huang, S.H.; Liu, Z.L.; Shu, Y. Valosin-containing protein promotes metastasis of osteosarcoma through autophagy induction and anoikis inhibition via the ERK/NF-κβ/beclin-1 signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagy, N.; Matskova, L.; Kis, L.L.; Hellman, U.; Klein, G.; Klein, E. The proapoptotic function of SAP provides a clue to the clinical picture of X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11966–11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaan, O.D.; Hendriks, W.; Uren, A.; Toretsky, J.A.; Erkizan, H.V. Valosin containing protein (VCP/p97) is a novel substrate for the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1. Exp. Cell. Res. 2013, 319, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Hoshida, Y.; Toyosawa, S.; Inohara, H.; Kishino, M.; Kogo, M.; Nakazawa, M.; Murakami, S.; Iizuka, N.; et al. Expression level of valosin-containing protein (VCP) as a prognostic marker for gingival squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towle, R.; Tsui, I.F.; Zhu, Y.; MacLellan, S.; Poh, C.F.; Garnis, C. Recurring DNA copy number gain at chromosome 9p13 plays a role in the activation of multiple candidate oncogenes in progressing oral premalignant lesions. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 1170–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.F.; Seuthe, I.M.; Drebber, U.; Siefer, O.; Kreppel, M.; Klein, M.O.; Mikolajczak, S.; Klussmann, J.P.; Preuss, S.F.; Huebbers, C.U. Valosin-containing protein (VCP/p97)-expression correlates with prognosis of HPV- negative oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.B.; Ma, W.L.; Liu, L.J.; Huang, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.H.; Peng, X.D.; Yin, J.Y.; Li, J.G.; Chen, S.J.; et al. Effects of gene polymorphisms in the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway on clinical outcomes of chemoradiotherapy in Chinese patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tomita, Y.; Uruno, T.; Hoshida, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Iizuka, N.; Nakamichi, I.; Miyauchi, A.; Aozasa, K. Increased expression of valosin-containing protein (p97) is correlated with disease recurrence in follicular thyroid cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 12, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kang, Y.; Tae, K.; Bae, G.U.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Yang, M. Proteomic Biomarkers for Bisphenol A-Early Exposure and Women’s Thyroid Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.; Read, M.L.; Thornton, C.E.M.; Larner, D.P.; Poole, V.L.; Brookes, K.; Nieto, H.R.; Alshahrani, M.; Thompson, R.J.; Lavery, G.G.; et al. Targeting Novel Sodium Iodide Symporter Interactors ADP-Ribosylation Factor 4 and Valosin-Containing Protein Enhances Radioiodine Uptake. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Li, D.; Xiao, L. Upregulation of valosin-containing protein (VCP) is associated with poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression of orbital B-cell lymphoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 12, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, N.; Radwan, M.O.; Amano, M.; Endo, S.; Fujii, E.; Hayashi, H.; Ueno, S.; Ueno, N.; Tatetsu, H.; Hata, H.; et al. Novel p97/VCP inhibitor induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in both bortezomib-sensitive and -resistant multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3275–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauten, M.; Schrauder, A.; Kardinal, C.; Harbott, J.; Welte, K.; Schlegelberger, B.; Schrappe, M.; von Neuhoff, N. Unsupervised proteome analysis of human leukaemia cells identifies the Valosin-containing protein as a putative marker for glucocorticoid resistance. Leukemia 2006, 20, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosque, A.; Dietz, L.; Gallego-Lleyda, A.; Sanclemente, M.; Iturralde, M.; Naval, J.; Alava, M.A.; Martínez-Lostao, L.; Thierse, H.J.; Anel, A. Comparative proteomics of exosomes secreted by tumoral Jurkat T cells and normal human T cell blasts unravels a potential tumorigenic role for valosin-containing protein. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29287–29305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedracka-Krok, S.; Jankowska, U.; Elas, M.; Sowa, U.; Swakon, J.; Cierniak, A.; Olko, P.; Romanowska-Dixon, B.; Urbanska, K. Proteomic analysis of proton beam irradiated human melanoma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ebstein, F.; Keller, M.; Paschen, A.; Walden, P.; Seeger, M.; Bürger, E.; Krüger, E.; Schadendorf, D.; Kloetzel, P.M.; Seifert, U. Exposure to Melan-A/MART-126-35 tumor epitope specific CD8(+)T cells reveals immune escape by affecting the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Shen, Y.; Fei, X.; Sheng, K.; Sun, P.; Qiu, Y.; Larner, J.; Cao, L.; Kong, X.; Mi, J. Valosin-containing protein regulates the proteasome-mediated degradation of DNA-PKcs in glioma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biau, J.; Chautard, E.; De Koning, L.; Court, F.; Pereira, B.; Verrelle, P.; Dutreix, M. Predictive biomarkers of resistance to hypofractionated radiotherapy in high grade glioma. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.D.; Li, Q.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, W.P. A novel HDAC6 inhibitor Tubastatin A: Controls HDAC6-p97/VCP-mediated ubiquitination-autophagy turnover and reverses Temozolomide-induced ER stress-tolerance in GBM cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Topouza, D.G.; Tarnouskaya, A.; Nesdoly, S.; Koti, M.; Duan, Q.L. Gene networks and expression quantitative trait loci associated with adjuvant chemotherapy response in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakkas, H.; Ocal, B.G.; Kipel, S.; Akcan, G.; Sahin, C.; Ardicoglu, A.; Cayli, S. Ubiquitin proteasome system and autophagy associated proteins in human testicular tumors. Tissue Cell 2021, 71, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgas, S.; Singh, A.N.; Paillas, S.; Then, C.K.; Torrecilla, I.; Nicholson, J.; Browning, L.; Vendrell, I.; Konietzny, R.; Kessler, B.M.; et al. p97/VCP inhibition causes excessive MRE11-dependent DNA end resection promoting cell killing after ionizing radiation. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, A.; Fernandes, K.; Chinner, N.; Ibrahim, A.F.M.; Garg, A.K.; Boag, G.; Hepburn, L.A.; Proby, C.M.; Leigh, I.M.; Saville, M.K. The Identification of Potential Therapeutic Targets for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Rebelo, A.; Kleeff, J.; Sunami, Y. Identification of prognostic lipid droplet-associated genes in pancreatic cancer patients via bioinformatics analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.M.; Zeng, H.D.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xu, J.W. Key genes associated with diabetes mellitus and hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Yang, L.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Gao, Z.Q.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.T.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, J.C.; Qian, J.; Chen, H.Y.; et al. VCP gene variation predicts outcome of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer platinum-based chemotherapy. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junk, S.; Cario, G.; Wittner, N.; Stanulla, M.; Scherer, R.; Schlegelberger, B.; Schrappe, M.; von Neuhoff, N.; Lauten, M. Bortezomib Treatment can Overcome Glucocorticoid Resistance in Childhood B-cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cell Lines. Klin. Padiatr. 2015, 227, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, P.; Neums, L.; Schoenen, F.J.; Chien, J. VCP inhibitors induce endoplasmic reticulum stress, cause cell cycle arrest, trigger caspase-mediated cell death and synergistically kill ovarian cancer cells in combination with Salubrinal. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1559–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, P.; Wang, F.; Schaich, M.A.; Gan, T.; Freudenthal, B.D.; Chou, T.F.; Chien, J. Specific mutations in the D1-D2 linker region of VCP/p97 enhance ATPase activity and confer resistance to VCP inhibitors. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.; Maksim, N.; de la Cruz, F.; La Clair, J.J. Inhibitors of the AAA+ chaperone p97. Molecules 2015, 20, 3027–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagarsamy, V.; Chitra, K.; Saravanan, G.; Solomon, V.R.; Sulthana, M.T.; Narendhar, B. An overview of quinazolines: Pharmacological significance and recent developments. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 628–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.F.; Deshaises, R.J. Development of p97 AAA ATPase inhibitors. Autophagy 2011, 7, 1091–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.F.; Brown, S.J.; Minond, D.; Nordin, B.E.; Li, K.; Jones, A.C.; Chase, P.; Porubsky, P.R.; Stoltz, B.M.; Schoenen, F.; et al. Reversible inhibitor of p97, DBeQ, impairs both ubiquitin-dependent and autophagic protein clearance pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4834–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auner, H.W.; Moody, A.M.; Ward, T.H.; Kraus, M.; Milan, E.; May, P.; Chaidos, A.; Driessen, C.; Cenci, S.; Dazzi, F.; et al. Combined inhibition of p97 and the proteasome causes lethal disruption of the secretory apparatus in multiple myeloma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Shi, Z.; Hao, Q.; Wang, W.; Song, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, S.; Zhou, Z. The Transitional Endoplasmic Reticulum ATPase p97 Regulates the Alternative Nuclear Factor NF-κB Signaling via Partial Degradation of the NF-κB Subunit p100. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 19558–19568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walworth, K.; Bodas, M.; Campbell, R.J.; Swanson, D.; Sharma, A.; Vij, N. Dendrimer-Based Selective Proteostasis-Inhibition Strategy to Control NSCLC Growth and Progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayli, S.; Sahin, C.; Sanci, T.O.; Nakkas, H. Inhibition of p97/VCP function leads to defective autophagosome maturation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in mouse Sertoli cells. Theriogenology 2020, 158, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desdicioglu, R.; Sahin, C.; Yavuz, F.; Cayli, S. Disruption of p97/VCP induces autophagosome accumulation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human choriocarcinoma cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.F.; Li, K.; Frankowski, K.J.; Schoenen, F.J.; Deshaies, R.J. Structure-activity relationship study reveals ML240 and ML241 as potent and selective inhibitors of p97 ATPase. Chem. Med. Chem. 2013, 8, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.J.; Gui, L.; Zhang, X.; Moen, D.R.; Li, K.; Frankowski, K.J.; Lin, H.J.; Schoenen, F.J.; Chou, T. Evaluating p97 inhibitor analogues for their domain selectivity and potency against the p97-p47 complex. Chem. Med. Chem. 2015, 10, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of 2-[3-(2-Aminoethyl)-1H-indol-1-yl]-N-benzylquinazolin-4-amine as a Novel p97/VCP Inhibitor Lead Capable of Inducing Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31784–31791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.J.; Wang, J.; Yao, B.; Wong, S.; Djakovic, S.; Kumar, B.; Rice, J.; Valle, E.; Soriano, F.; Menon, M.K.; et al. Discovery of a First-in-Class, Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of the p97 AAA ATPase (CB-5083). J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9480–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.J.; Moigne, R.L.; Djakovic, S.; Kumar, B.; Rice, J.; Wong, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, B.; Valle, E.; von Soly, S.K.; et al. Targeting the AAA ATPase p97 as an Approach to Treat Cancer through Disruption of Protein Homeostasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Moigne, R.; Aftab, B.T.; Djakovic, S.; Dhimolea, E.; Valle, E.; Murnane, M.; King, E.M.; Soriano, F.; Menon, M.K.; Wu, Z.Y.; et al. The p97 Inhibitor CB-5083 Is a Unique Disrupter of Protein Homeostasis in Models of Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugliotta, G.; Sudo, M.; Cao, Q.; Lin, D.; Sun, H.; Takao, S.; le Moigne, R.; Rolfe, M.; Gery, S.; Müschen, M.; et al. Valosin-Containing Protein/p97 as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekaria, P.H.; Kumar, A.; Subramaniam, D.; Dunavin, N.; Vallurupalli, A.; Schoenen, F.; Ganguly, S.; Anant, S.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jensen, R.A.; et al. Functional cooperativity of p97 and histone deacetylase 6 in mediating DNA repair in mantle cell lymphoma cells. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zou, C.; Huang, G.; Yin, J.; Xie, X.; Shen, J. CB-5083, an inhibitor of P97, suppresses osteosarcoma growth and stem cell properties by altering protein homeostasis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2956–2967. [Google Scholar]
- Her, N.G.; Kesari, S.; Nurmemmedov, E. Thrombospondin-1 counteracts the p97 inhibitor CB-5083 in colon carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1590–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Hao, Q.; Zeng, S.X.; Omari, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H. Valosin-containing protein stabilizes mutant p53 to promote pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4041–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, B.; Vaganay, C.; Vargas, J.D.; Alexe, G.; Benaksas, C.; Pardieu, B.; Fenouille, N.; Ellegast, J.M.; Malolepsza, E.; Ling, F.; et al. Targeting acute myeloid leukemia dependency on VCP-mediated DNA repair through a selective second-generation small-molecule inhibitor. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabg1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, H.; Cheng, C.; Pitkänen, M.; Sander, C.L.; Zhang, J.; Saeid, S.; Turunen, T.; Shmara, A.; Weiss, L.; Ta, L.; et al. A p97/valosin-containing protein inhibitor drug CB-5083 has a potent but reversible off-target effect on phosphodiesterase-6. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 378, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Narasimhan, B. Therapeutic potential of heterocyclic pyrimidine scaffolds. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarenezhad, E.; Farjam, M.; Iraji, A. Synthesis and biological activity of pyrimidines-containing hybrids: Focusing on pharmacological application. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1230, 129833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervi, G.; Magnaghi, P.; Asa, D.; Avanzi, N.; Badari, A.; Borghi, D.; Caruso, M.; Cirla, A.; Cozzi, L.; Felder, E.; et al. Discovery of 2-(cyclohexylmethylamino)pyrimidines as a new class of reversible valosine containing protein inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10443–10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, E.; Zhou, H.; Sha, S.; Miao, H.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Lei, M.; et al. Discovery of a new class of valosine containing protein (VCP/P97) inhibitors for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.C.; Bansal, K.K.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, D.; Deep, A. Thiazole-containing compounds as therapeutic targets for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 15, 188:112016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, T.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, Y. Discovery of novel pyrimidine molecules containing boronic acid as VCP/p97 Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 38, 116114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Jones, A.C.; Goldberg, A.F.G.; Lin, B.; Virgil, S.; Stoltz, B.M.; Deshaies, R.J.; Chou, T.F. A covalent p97/VCP ATPase inhibitor can overcome resistance to CB-5083 and NMS-873 in colorectal cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, J.K.; Ganguly, S.; Kaushik, A. Triazoles: A valuable insight into recent developments and biological activities. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.K. Thiazole Containing Heterocycles with Antimalarial Activity. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2018, 15, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabria, M.T.; Patel, S.; Modi, P.; Brahmkshatriya, P.S. Thiazole: A Review on Chemistry, Synthesis and Therapeutic Importance of its Derivatives. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 2841–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursavich, M.G.; Parker, D.P.; Willardsen, J.A.; Gao, Z.H.; Davis, T.; Ostanin, K.; Robinson, R.; Peterson, A.; Cimbora, D.M.; Zhu, J.F.; et al. 2-Anilino-4-aryl-1,3-thiazole inhibitors of valosin-containing protein (VCP or p97). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1677–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polucci, P.; Magnaghi, P.; Angiolini, M.; Asa, D.; Avanzi, N.; Badari, A.; Bertrand, J.; Casale, E.; Cauteruccio, S.; Cirla, A.; et al. Alkylsulfanyl-1,2,4-triazoles, a new class of allosteric valosine containing protein inhibitors. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnaghi, P.; D’Alessio, R.; Valsasina, B.; Avanzi, N.; Rizzi, S.; Asa, D.; Gasparri, F.; Cozzi, L.; Cucchi, U.; Orrenius, C.; et al. Covalent and allosteric inhibitors of the ATPase VCP/p97 induce cancer cell death. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, H.; Mathur, J.; Guleria, A. INDOLE DERIVATIVES AS POTENTIAL ANTICANCER AGENTS: A REVIEW. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2020, 65, 4900–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.A.; Jiang, W.G. Anti-Cancer agents in medicinal chemistry (Formerly current medicinal chemistry—Anti-cancer agents). Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alverez, C.; Bulfer, S.L.; Chakrasali, R.; Chimenti, M.S.; Deshaies, R.J.; Green, N.; Kelly, M.; LaPorte, M.G.; Lewis, T.S.; Liang, M.; et al. Allosteric Indole Amide Inhibitors of p97: Identification of a Novel Probe of the Ubiquitin Pathway. ACS Med Chem. Lett. 2015, 7, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alverez, C.; Arkin, M.R.; Bulfer, S.L.; Colombo, R.; Kovaliov, M.; LaPorte, M.G.; Lim, C.; Liang, M.; Moore, W.J.; Neitz, R.J.; et al. Structure-Activity Study of Bioisosteric Trifluoromethyl and Pentafluorosulfanyl Indole Inhibitors of the AAA ATPase p97. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPorte, M.G.; Burnett, J.C.; Colombo, R.; Green, N.; Moore, W.J.; Yue, Z.; Li, S.; Arkin, M.R.; Wipf, P.; Huryn, D.M.; et al. Optimization of Phenyl Indole Inhibitors of the AAA+ ATPase p97. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bartesaghi, A.; Merk, A.; Wipf, P.; Falconieri, V.; Deshaies, R.J.; Milne, J.L.S.; Huryn, D.; Arkin, M.; Subramaniam, S.; et al. 2.3 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of human p97 and mechanism of allosteric inhibition. Science 2016, 351, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieger, E.; Hirsch, C.; Vyas, J.M.; Gordon, E.; Ploegh, H.L.; Tortorella, D. Dissection of dislocation pathway for type I membrane proteins with a new small molecule inhibitor, eeyarstatin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Shinkre, B.A.; Lee, J.G.; Weniger, M.A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Wiestner, A.; Trenkle, W.C.; Ye, Y. The ERAD inhibitor Eeyarestatin I is a bifunctional compound with a membrane-binding domain and a p97/VCP inhibitory group. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Ye, Y. Inhibition of p97-dependent protein degradation by Eeyarestatin, I. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7445–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, B.C.; McKibbin, C.; Callan, A.C.; Roboti, P.; Piacenti, M.; Rabu, C.; Wilson, C.M.; Whitehead, R.; Flitsch, S.L.; Pool, M.R.; et al. Eeyarestatin I inhibits Sec61-mediated protein translocation at the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 4393–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamayun, I.; O’Keefe, S.; Pick, T.; Flitsch, S.L.; Whitehead, R.C.; Swanton, E.; Helms, V.; High, S.; Zimmermann, R.; Cavalié, A.; et al. Eeyarestatin Compounds Selectively Enhance Sec61-Mediated Ca2+ Leakage from the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 571–583.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Mora-Jensen, H.; Weniger, M.A.; Perez-Galan, P.; Wolford, C.; Hai, T.; Ron, D.; Chen, W.; Trenkle, W.; Wiestner, A.; et al. ERAD inhibitors integrate ER stress with an epigenetic mechanism to activate BH3-only protein NOXA in cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2200–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, G.J.; Myolans, I.; Bruning, A. Eeyarestatin causes cervical cancer cell sensitization to bortezomib treatment by augmenting ER stress and CHOP expression. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 128, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, K.; Lin, Y.; Xing, F.; Xiao, X.; Cai, J.; Zhu, W.; Liang, J.; Tan, Y.; Fu, L.; et al. Targeting VCP enhances anticancer activity of oncolytic virus M1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaam7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Sullivan, D.K.; Azizian, N.G.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Inhibition of ERAD synergizes with FTS to eradicate pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasazawa, Y.; Kanagaki, S.; Tashiro, E.; Nogawa, T.; Muroi, M.; Kondoh, Y.; Osada, H.; Imoto, M. Xanthohumol impairs autophagosome maturation through direct inhibition of valosin-containing protein. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikata, Y.; Yoshimaru, T.; Komatsu, M.; Kanagaki, S.; Okazaki, Y.; Toyokuni, S.; Tashiro, E.; Ishikawa, S.; Katagiri, T.; Imoto, M.; et al. Protein kinase A inhibition facilitates the antitumor activity of xanthohumol, a valosin-containing protein inhibitor. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figuerola-Conchas, A.; Saarbach, J.; Daguer, J.P.; Cieren, A.; Barluenga, S.; Winssinger, N.; Gotta, M. Small-Molecule Modulators of the ATPase VCP/p97 Affect Specific p97 Cellular Functions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-Cabrera, A.; Tripathi, R.; Zhang, X.; Gui, L.; Chou, T.F.; Komurov, K. A structure- and chemical genomics-based approach for repositioning of drugs against VCP/p97 ATPase. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellegaard, A.M.; Dehlendorff, C.; Vind, A.C.; Anand, A.; Cederkvist, L.; Petersen, N.; Nylandsted, J.; Stenvang, J.; Mellemgaard, A.; Østerlind, K.; et al. Repurposing Cationic Amphiphilic Antihistamines for Cancer Treatment. EBioMedicine 2016, 9, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, V.A.; Rivera, E.S. Histamine receptors and cancer pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, V.P.; Amin, S.G.; Pandey, M.K. Targeting ion channels for cancer therapy by repurposing the approved drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, K.; Honda, K.; Muroi, M.; Kondoh, Y.; Osada, H.; Watanabe, N. A small-molecule ligand of valosin-containing protein/p97 inhibits cancer cell-accelerated fibroblast migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2988–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.G.; Bamford, S.; Jubb, H.C.; Sondka, Z.; Beare, D.M.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Cole, C.G.; Creatore, C.; Dawson, E.; et al. COSMIC: The Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastola, P.; Bilkis, R.; De Souza, C.; Minn, K.; Chien, J. Heterozygous mutations in valosin-containing protein (VCP) and resistance to VCP inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Toth, J.I.; Blanco, G.A.; Bobkov, A.A.; Petroski, M.D. Adapted ATPase domain communication overcomes the cytotoxicity of p97 inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 20169–20180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Her, N.G.; Toth, J.I.; Ma, C.T.; Wei, Y.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Sergienko, E.; Petroski, M.D. p97 Composition Changes Caused by Allosteric Inhibition Are Suppressed by an On-Target Mechanism that Increases the Enzyme’s ATPase Activity. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, S.; Gan, T.; Stott, G.M.; Flint, A.; Chou, T.F. Allosteric p97 Inhibitors Can Overcome Resistance to ATP-Competitive p97 Inhibitors for Potential Anticancer Therapy. Chem. Med. Chem. 2020, 15, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cancer Type | Features with which Higher VCP/p97 Levels Correlated | References |
|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | greater invasion depth (T3–4), presence of venous invasion, higher tumor stage (III and IV), and higher recurrence rate | [61] |
| CEA diagnostic marker | [62] | |
| carcinogenesis and metastasis development in a xenograft model | [63] | |
| USP11 levels influence colon cancer drug resistance | [64] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | lymph node metastasis and disease-free and overall survival | [65] |
| low levels of miR-198 and poor patient outcomes | [66] | |
| high levels of Ki-67 and a malignant prognosis | [65] | |
| Liver cancer | shorter disease-free and overall survival | [67] |
| low levels of miR-129-5p and HCC development and progression | [68] | |
| high levels of Neat1 and HCC diagnosis and treatment | [69] | |
| sorafenib response in HCC cells | [70] | |
| PTPRO levels | [71] | |
| Gastric cancer | greater tumor size, presence of vascular and lymphatic invasion, lymph node metastasis, and shorter overall and disease free survival | [72] |
| cell survival, degradation of cellular regulators, and gastric carcinogenesis | [73,74] | |
| low levels of CHOP and DR5 | [75] | |
| Esophageal cancer | higher frequencies of lymph node metastasis, deeper invasion, metastasis, and shorter disease free and overall survival | [76] |
| shorter overall survival | [77] | |
| Breast cancer | shorter overall survival | [78] |
| poor outcomes of triple-negative patients receiving chemotherapy | [79,80] | |
| lower survival rates | [81] | |
| expression of the SOX2 protein | [82] | |
| Prostate cancer | poor prognosis and increased metastatic potential | [83] |
| high levels of IL-6 | [84] | |
| maintenance of mitochondrial activity | [85] | |
| Lung cancer | shorter disease-free and overall survival | [86] |
| NSCLC development, progression and metastasis | [87] | |
| low levels of miR-129 and NSCLC development and progression | [88] | |
| increased levels of ER stress and EMT markers, chemoresistance and shorter patient survival | [89] | |
| Bone cancer | higher metastatic potential (LM8) | [90,91] |
| expression of the Aurora B protein | [92] | |
| low levels of miR-129-5p and osteosarcoma development and progression | [93] | |
| autophagy, anoikis resistance and osteosarcoma metastasis | [94] | |
| apoptotic response modulated by SAP | [95] | |
| cellular transformation and tumorigenesis | [96] | |
| Head and neck cancer | tumor stages, lymph node metastasis and shorter overall survival | [97] |
| development of carcinoma in situ lesions and invasivity | [98] | |
| better 5-year disease-free survival rates for HPV-negative patients | [99] | |
| clinical outcomes of chemo-radiotherapy | [100] | |
| Thyroid cancer | disease recurrence in patients with follicular thyroid carcinoma | [101] |
| BPA exposure | [102] | |
| shorter disease-free survival and an increased risk of recurrence in patients with papillary thyroid cancer subjected to ablative radioiodine treatment | [103] | |
| Hematological cancer | tumor grade, stage, histological subtype, recurrence and shorter overall and disease-free survival of patients with B-cell lymphoma | [104] |
| multiple myeloma development and progression | [105] | |
| poor prednisone responders in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia | [106] | |
| exosome generation and secretion in Jurkat tumor cells | [107] | |
| Melanoma | advanced radiotherapy | [108] |
| immune escape | [109] | |
| Glioblastoma | radiosensitivity of glioblastoma cells, and survival time of xenografted mice with radiation treatment | [110,111] |
| HDAC6 levels and temozolomide resistance therapy | [112] | |
| Ovarian cancer | chemotherapy response in patients receiving the platinum-taxane combination | [113] |
| Testicular cancer | development of different types of human testicular tumors | [114] |
| Bladder cancer | shorter survival following bladder removal by cystectomy | [115] |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | development of squamous cell carcinoma | [116] |
| Number | Location | |
|---|---|---|
| Deletion-frameshift | 2 | both in the D2 domain |
| Deletion-in-frame | 1 | D1 domain |
| Insertion-frameshift | 2 | 1 in D2 and 1 in the C-terminal domain |
| Substitution-coding silent | 65 | 14 in the N-terminal domain, 1 in the N-D1 linker, 19 in D1, 4 in the D1-D2 linker, 24 in D2 and 3 in the C-terminal domain |
| Substitution-missense | 185 | 40 in the N-terminal domain, 7 in the N-D1 linker, 61 in D1, 3 in the D1-D2 linker and 74 in the D2 domain |
| Substitution-nonsense | 15 | 6 in the N-terminal domain, 3 in D1 and 6 in the D2 domain |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costantini, S.; Capone, F.; Polo, A.; Bagnara, P.; Budillon, A. Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97: A Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810177
Costantini S, Capone F, Polo A, Bagnara P, Budillon A. Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97: A Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):10177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810177
Chicago/Turabian StyleCostantini, Susan, Francesca Capone, Andrea Polo, Palmina Bagnara, and Alfredo Budillon. 2021. "Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97: A Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 10177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810177
APA StyleCostantini, S., Capone, F., Polo, A., Bagnara, P., & Budillon, A. (2021). Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97: A Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 10177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810177








