And Yet It Moves: Oxidation of the Nuclear Autoantigen La/SS-B Is the Driving Force for Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
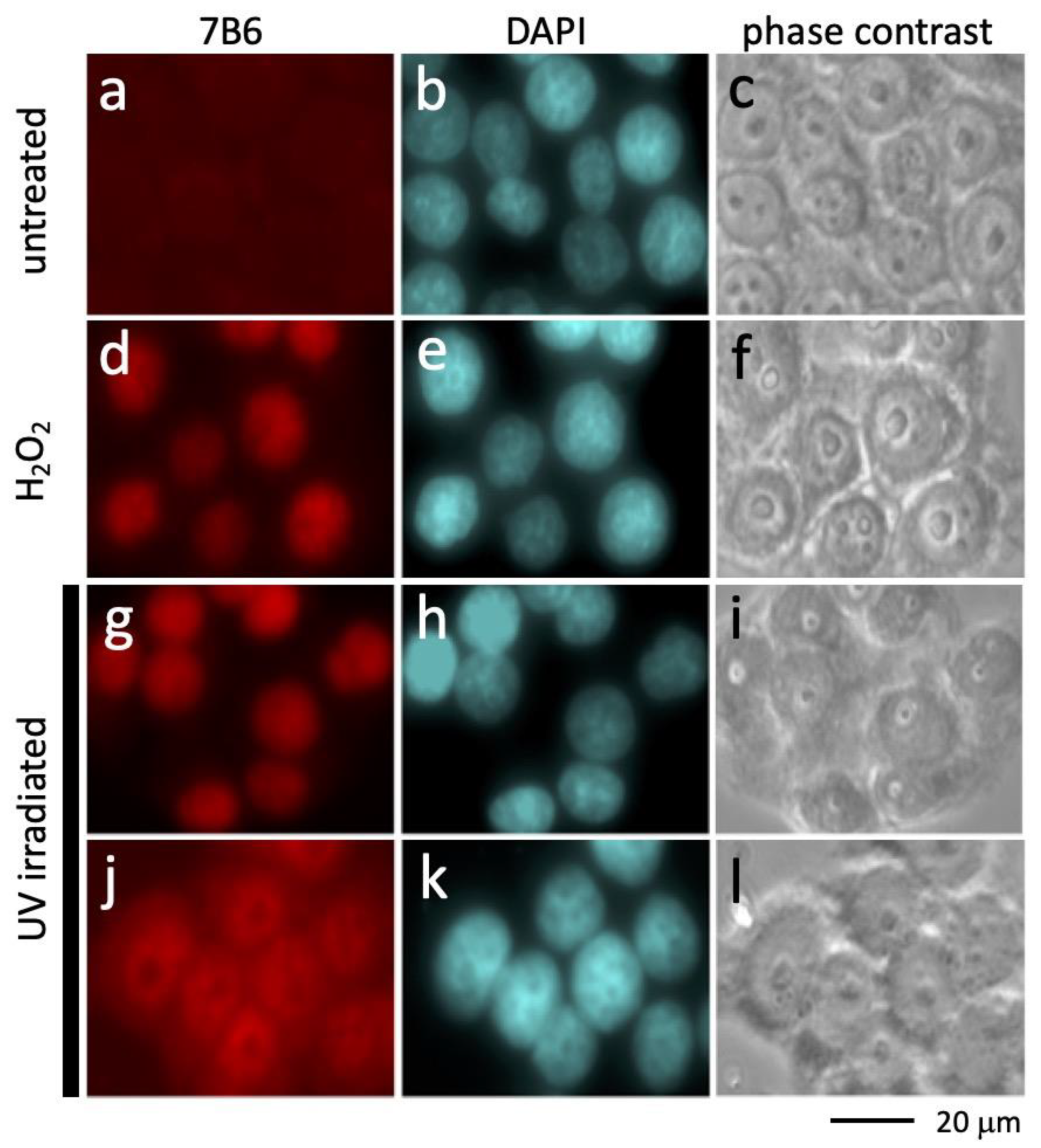
2.1. Accessibility of the Epitope Recognized by the Anti-La mAb 7B6 after UV Irradiation
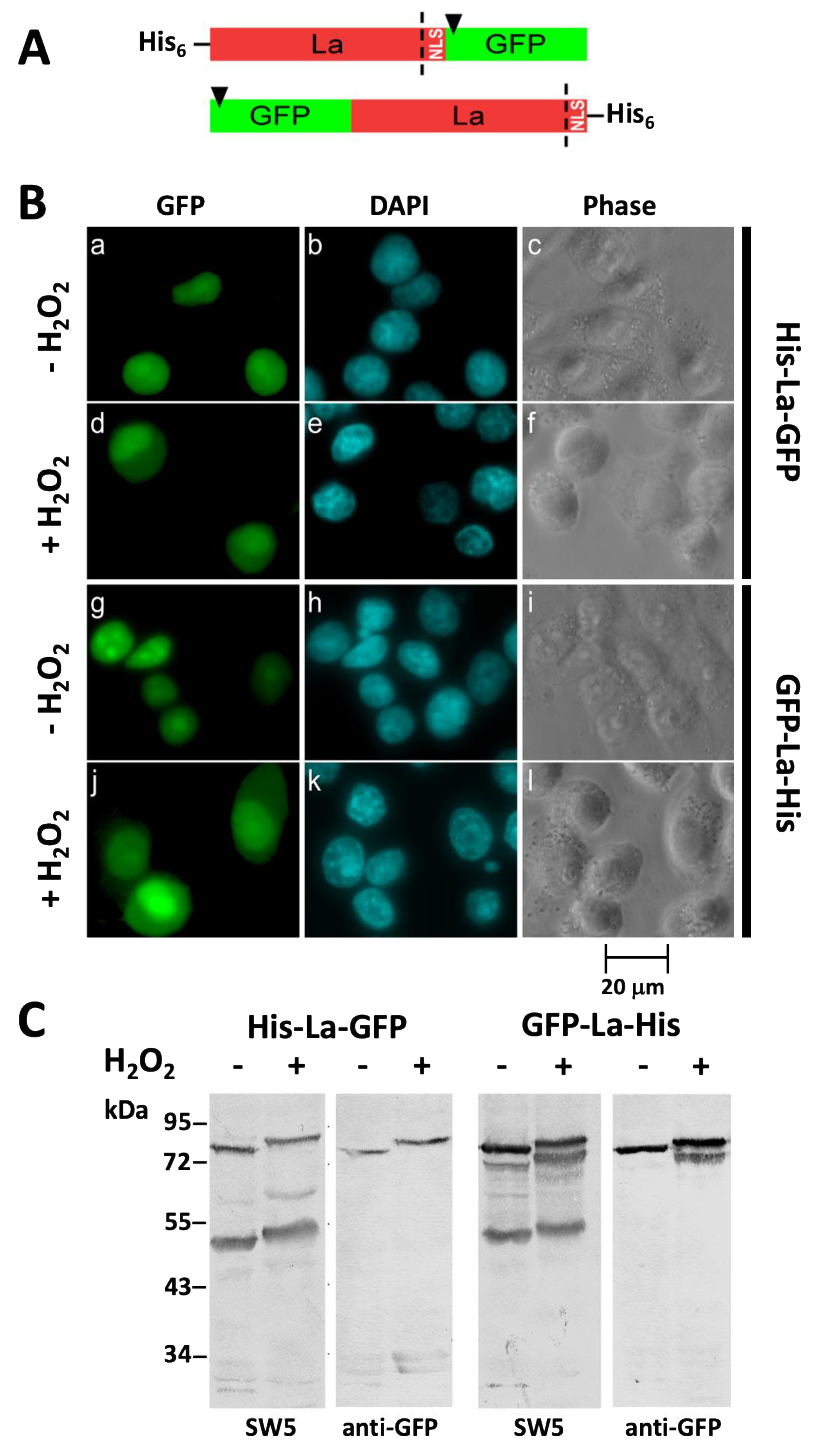
2.2. After Oxidation La Protein Remains Intact and Is Not Cleaved during Shuttling to the Cytoplasm
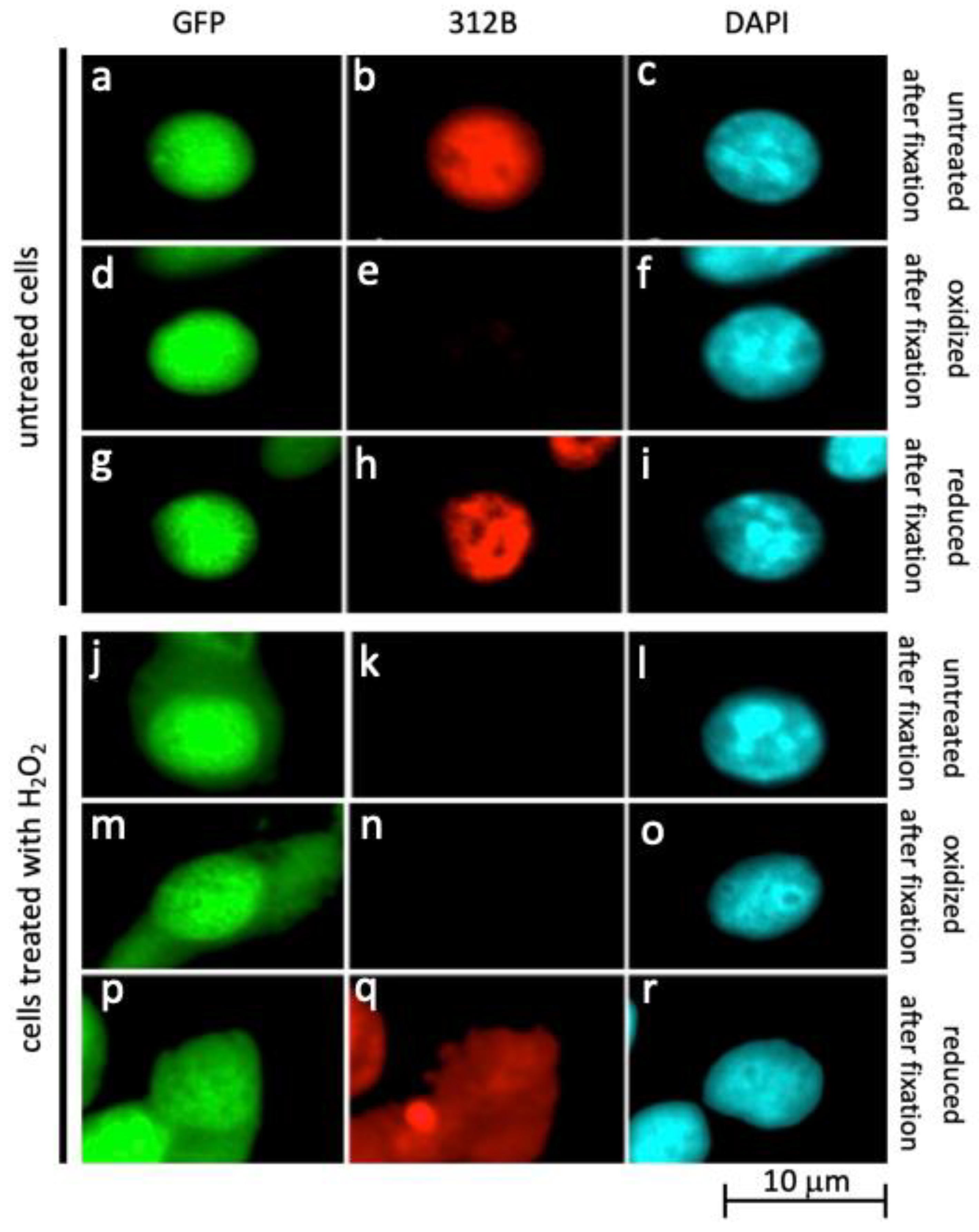
2.3. Oxidation of La Protein Is the Driving Force for Shuttling of La Protein
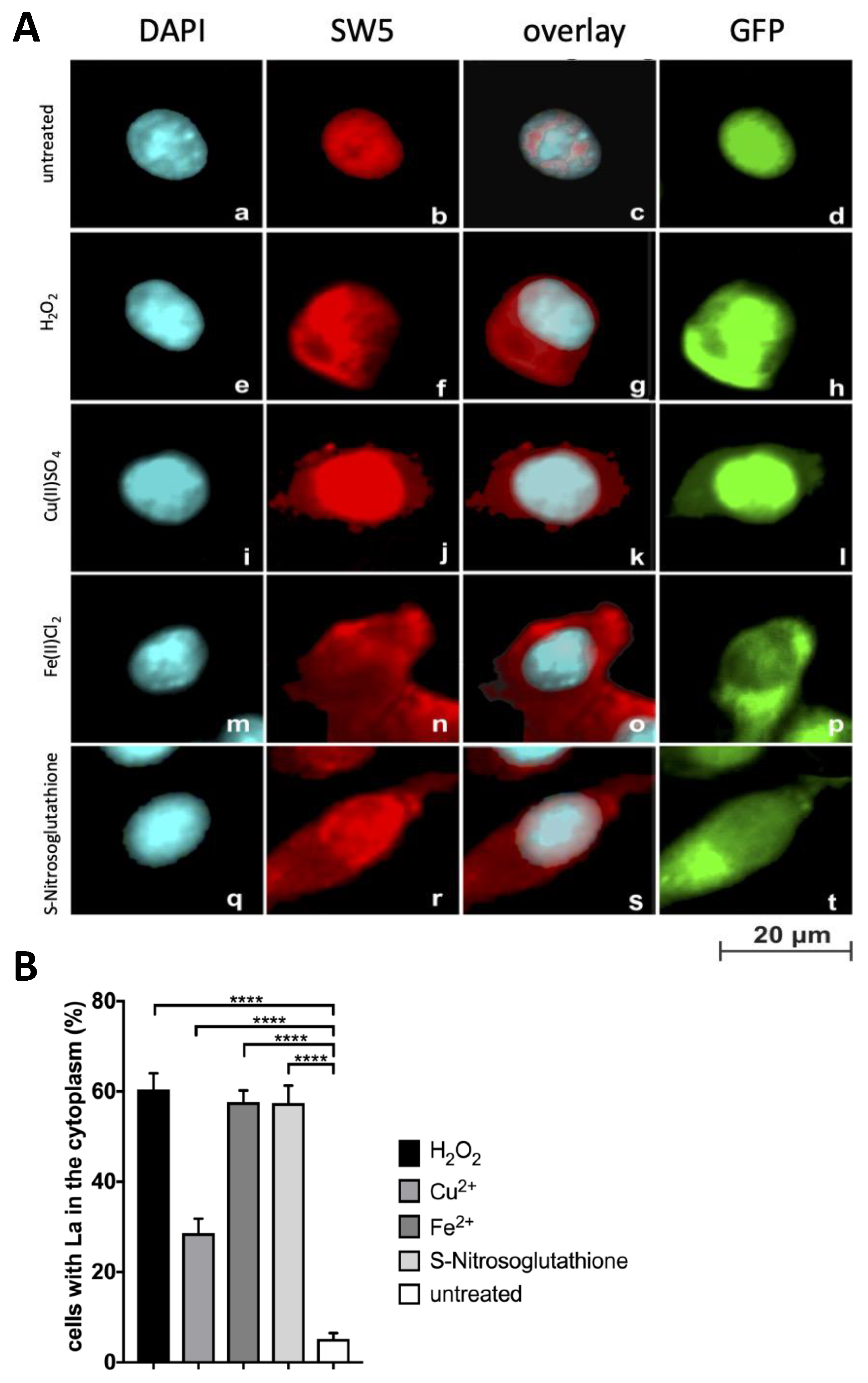
2.4. Further Evidence for Translocation of La Protein to the Cytplasm in Dependence on Oxidative Conditions
2.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Mediated Signalling Triggers Shuttling of La Protein
2.6. TLR Receptor Ligand Interactions Are Required for Shuttling of La Protein
2.7. The Level of Intracellular Reducing Equivalents Determines the Threshold for Shuttling of La Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.2. Induction of Shuttling
4.3. Fixation and Staining of Cells for Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.4. Anti-La mAbs
4.5. SDS-PAGE/Immunoblotting
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, B.R. Lacrimal and salivary precipitating antibodies in Sjogren’s syndrome. Lancet 1958, 11, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.R.; Gray, K.G.; Beck, J.S.; Kinnear, W.F. Precipitating autoantibodies in Sjogren’s syndrome. Lancet 1961, 2, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.R.; Gray, K.G.; Beck, J.S.; Buchanan, W.W.; McElhinney, A.J. Precipitating autoantibodies in the connective tissue diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1962, 21, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, G.; Reichlin, M.; Tomasi, T.B. Characterization of a soluble cytoplasmic antigen reactive with sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 1969, 102, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, M.; Reichlin, M. Heterogeneity of RNA protein antigens reactive with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Description of a cytoplasmic nonribosomal antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1974, 17, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alspaugh, M.A.; Tan, E.M. Antibodies to cellular antigens in Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 1975, 55, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alspaugh, M.; Maddison, P. Resolution of the identity of certain antigen-antibody systems in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome: An interlabora- tory collaboration. Arthritis Rheum. 1979, 22, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.M. Antinuclear antibodies: Diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv. Immunol. 1989, 44, 93–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, J.B.; Alexander, E.L.; Bias, W.B.; Fox, O.F.; Provost, T.T.; Reichlin, M.; Yamagata, H.; Arnett, F.C. Anti-Ro (SS-A) and Anti-La (SS-B) in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Garcia de la Torre, I.; Herold, M.; Klotz, W.; de Melo Cruvinel, W.; et al. Clinical relevance of HEp-2 indirect immunofluorescent patterns: The International Consensus on ANA patterns (ICAP) perspective. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stefano, J.E. Purified lupus antigen La recognizes an oligouridylate stretch common to the 3′ termini of RNA polymerase III transcripts. Cell 1984, 36, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Pfeifer, K.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E. Characterization of the autoantigen La as a nucleic acid-dependent ATPase/dATPase with melting properties. Cell 1990, 60, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hühn, P.; Pruijn, G.J.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Bachmann, M. Characterization of the autoantigen La (SS-B) as a dsRNA unwinding enzyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolin, S.L.; Cedervall, T. The La protein. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 375–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, G.; Sendlmeier, C.; Heise, T. Salt-Dependent Modulation of the RNA Chaperone Activity of RNA-Binding Protein La. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2106, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosio, C.; Boyl, P.P.; Loreni, F.; Pierandrei-Amaldi, P.; Amaldi, F. La protein has a positive effect on the translation of TOP mRNAs in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2927–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svitkin, Y.V.; Meerovitch, K.; Lee, H.S.; Dholakia, J.N.; Kenan, D.J.; Agol, V.I.; Sonenberg, N. Internal translation initiation on poliovirus RNA: Further characterization of La function in poliovirus translation in vitro. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, N.; Pruijn, G.J.; Kenan, D.J.; Keene, J.D.; Siddiqui, A. Human La antigen is required for the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27531–27540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, N.; Siddiqui, A. The La antigen binds 5′ noncoding region of the hepatitis C virus RNA in the context of the initiator AUG codon and stimulates internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holcik, M.; Korneluk, R.G. Functional characterization of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) internal ribosome entry site element: Role of La autoantigen in XIAP translation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petz, M.; Them, N.; Huber, H.; Beug, H.; Mikulits, W. La enhances IRES-mediated translation of laminin B1 during malignant epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, M.; Pfeifer, K.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E. The La antigen shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in CV-1 cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1989, 21, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Chang, S.; Slor, H.; Kukulies, J.; Müller, W.E. Shuttling of the autoantigen La between nucleus and cell surface after uv irradiation of human keratinocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 1990, 191, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Falke, D.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E. Intracellular distribution of the La antigen in CV-1 cells after herpes simplex virus type 1 infection compared with the localization of U small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J. Gen. Virol. 1989, 70, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Althoff, H.; Tröster, H.; Selenka, C.; Falke, D.; Müller, W.E. Translocation of the nuclear autoantigen La to the cell surface of herpes simplex virus type 1 infected cells. Autoimmunity 1992, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Schröder, H.C.; Falke, D.; Müller, W.E. Alteration of the intracellular localization of the La protein compared with the localization of U snRNPs. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 1988, 12, 765–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Chang, S.; Bernd, A.; Mayet, W.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.; Müller, W.E. Translocation of the nuclear autoantigen La to cell surface: Assembly and disassembly with the extracellular matrix. Autoimmunity 1991, 9, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koristka, S.; Cartellieri, M.; Arndt, C.; Bippes, C.C.; Feldmann, A.; Michalk, I.; Wiefel, K.; Stamova, S.; Schmitz, M.; Ehninger, G.; et al. Retargeting of regulatory T cells to surface-inducible autoantigen La/SS-B. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 42, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fok, V.; Friend, K.; Steitz, J.A. Epstein-Barr virus noncoding RNAs are confined to the nucleus, whereas their partner, the human La protein, undergoes nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, F.H.; Broers, F.J.; Van Venrooij, W.J.; Pruijn, G.J. Characterization of cis-acting signals for nuclear import and retention of the La (SS-B) autoantigen. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 224, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, J.S.; Pemberton, L.F.; Bonifaci, N.; Blobel, G. Nuclear Import and the Evolution of a multifunctional RNA-binding protein. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiroki, K.; Isoyama, T.; Kuge, S.; Ishii, T.; Ohmi, S.; Hata, S.; Suzuki, K.; Takasaki, Y.; Nomoto, A. Intracellular redistribution of truncated La protein produced by poliovirus 3Cpro-mediated cleavage. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berndt, N.; Bippes, C.C.; Michalk, I.; Bachmann, D.; Bachmann, J.; Puentes-Cala, E.; Bartsch, T.; Loureiro, L.R.; Kegler, A.; Bergmann, R.; et al. Two Be or Not Two Be: The Nuclear Autoantigen La/SS-B Is Able to Form Dimers and Oligomers in a Redox Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tröster, H.; Bartsch, H.; Klein, R.; Metzger, T.E.; Pollak, G.; Semsei, I.; Schwemmle, M.; Pruijn, G.J.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Bachmann, M. Activation of a murine autoreactive B cell by immunization with human recombinant autoantigen La/SS-B: Characterization of the autoepitope. J. Autoimmun. 1995, 8, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, M.P.; Bartsch, T.; Bippes, C.C.; Bachmann, D.; Puentes-Cala, E.; Bachmann, J. T cell mediated conversion of a non-anti-La reactive B cell to an autoreactive anti-La B cell by somatic hypermutation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraia, R.J.; Mattijssen, S.; Cruz-Gallardo, I.; Conte, M.R. The La and related RNA-binding proteins (LARPs): Structures, functions, and evolving perspectives. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alfano, C.; Sanfelice, D.; Babon, J.; Kelly, G.; Jacks, A.; Curry, S.; Conte, M.R. Structural analysis of cooperative RNA binding by the La motif and central RRM domain of human La protein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotik-Kogan, O.; Valentine, E.R.; Sanfelice, D.; Conte, M.R.; Curry, S. Structural analysis reveals conformational plasticity in the recognition of RNA 3′ ends by the human La protein. Structure 2008, 16, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanfelice, D.; Kelly, G.; Curry, S.; Conte, M.R. NMR assignment of the N-terminal region of human La free and in complex with RNA. Biomol. NMR Assign 2008, 2, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huth, J.R.; Mendoza, R.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Johnson, R.W.; Cothron, D.A.; Liu, Y.; Lerner, C.G.; Chen, J.; Hajduk, P.J. ALARM NMR: A rapid and robust experimental method to detect reactive false positives in biochemical screens. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huth, J.R.; Song, D.; Mendoza, R.R.; Black-Schaefer, C.L.; Mack, J.C.; Dorwin, S.A.; Ladror, U.S.; Severin, J.M.; Walter, K.A.; Bartley, D.M.; et al. Toxicological evaluation of thiol-reactive compounds identified using a la assay to detect reactive molecules by nuclear magnetic resonance. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, J.L.; Cuellar, M.; Singh, G.; Nelson, K.M.; Strasser, J.; Rappe, T.; Xia, Y.; Veglia, G.; Walters, M.A. ALARM NMR for HTS triage and chemical probe validation. Curr. Protoc. Chem. Biol. 2018, 10, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, F.; Döbel, T.; Schmitz, M.; Schäkel, K. Current Concepts on 6-sulfo LacNAc Expressing Monocytes (slanMo). Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänsel, A.; Günther, C.; Baran, W.; Bidier, M.; Lorenz, H.M.; Schmitz, M.; Bachmann, M.; Meurer, M.; Rieber, E.R.; Schäkel, K. Human slan (6-sulfo LacNAc) dendritic cells are inflammatory dermal dendritic cells in psoriasis and drive strong TH17/TH1 T-cell responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänsel, A.; Günther, C.; Baran, W.; Bidier, M.; Lorenz, H.M.; Schmitz, M.; Bachmann, M.; Döbel, T.; Enk, A.H.; Schäkel, K. Human 6-sulfo LacNAc (slan) dendritic cells have molecular and functional features of an important pro-inflammatory cell type in lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehner, R.; Bitterlich, A.; Meyer, N.; Kloß, A.; Schäkel, K.; Bachmann, M.; Schmitz, M. Impact of chemotherapeutic agents on the immunostimulatory properties of human 6-sulfo LacNAc+ (slan) dendritic cells. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bippes, C.C.; Feldmann, A.; Stamova, S.; Cartellieri, M.; Schwarzer, A.; Wehner, R.; Schmitz, M.; Rieber, E.P.; Zhao, S.; Schäkel, K.; et al. A novel modular antigen delivery system for immuno targeting of human 6-sulfo LacNAc-positive blood den-dritic cells (SlanDCs). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straube, C.; Wehner, R.; Wendisch, M.; Bornhäuser, M.; Bachmann, M.; Rieber, E.P.; Schmitz, M. Bortezomib significantly impairs the immunostimulatory capacity of human myeloid blood dendritic cells. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jähnisch, H.; Wehner, R.; Tunger, A.; Kunze, A.; Oehrl, S.; Schäkel, K.; Rohayem, J.; Bornhäuser, M.; Tonn, T.; Bachmann, M.; et al. TLR7/8 agonists trigger immunostimulatory properties of human 6-sulfo LacNAc dendritic cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehner, R.; Löbel, B.; Bornhäuser, M.; Schäkel, K.; Cartellieri, M.; Bachmann, M.; Rieber, E.P.; Schmitz, M. Reciprocal activating interaction between 6-sulfo LacNAc+ dendritic cells and NK cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehner, R.; Wehrum, D.; Bornhäuser, M.; Zhao, S.; Schäkel, K.; Bachmann, M.P.; Platzbecker, U.; Ehninger, G.; Rieber, E.P.; Schmitz, M. Mesenchymal stem cells efficiently inhibit the proinflammatory properties of 6-sulfo LacNAc dendritic cells. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celli, A.; Que, F.G.; Gores, G.J.; LaRusso, N.F. Glutathione depletion is associated with decreased Bcl-2 expression and increased apoptosis in cholangiocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G749–G757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odin, J.A.; Huebert, R.C.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; LaRusso, N.F.; Rosen, A. Bcl-2-dependent oxidation of pyruvate dehydrogenase-E2, a primary biliary cirrhosis autoantigen, during apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo-Fonseca, M.; Pfeifer, K.; Schröder, H.C.; Vaz, M.F.; Fonseca, J.E.; Müller, W.E.; Bachmann, M. Identification of La ribonucleoproteins as a component of interchromatin granules. Exp. Cell Res. 1989, 185, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.W.; Svitkin, Y.V.; Lee, H.S.; Belsham, G.J.; Sonenberg, N. The La autoantigen contains a dimerization domain that is essential for enhancing translation. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meerovitch, K.; Svitkin, Y.V.; Lee, H.S.; Lejbkowicz, F.; Kenan, D.J.; Chan, E.K.; Agol, V.I.; Keene, J.D.; Sonenberg, N. La autoantigen enhances and corrects aberrant translation of poliovirus RNA in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1993, 67, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa-Mattioli, M.; Svitkin, Y.; Sonenberg, N. La autoantigen is necessary for optimal function of the poliovirus and hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 6861–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirasaki, T.; Honda, M.; Mizuno, H.; Shimakami, T.; Okada, H.; Sakai, Y.; Murakami, S.; Wakita, T.; Kaneko, S. La protein required for internal ribosome entry site-directed translation is a potential therapeutic target for hepatitis C virus replication. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, S. Mapping of secondary structure of the spacer region within the 5′-untranslated region of the coxsackievirus B3 RNA: Possible role of an apical GAGA loop in binding La protein and influencing internal initiation of translation. Virus Res. 2005, 108, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nova-Ocampo, M.; Villegas-Sepúlveda, N.; del Angel, R.M. Translation elongation factor-1alpha, La, and PTB interact with the 3′ untranslated region of dengue 4 virus RNA. Virology 2002, 295, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.N.; Kenan, D.J.; Keene, J.D.; Gatignol, A.; Jeang, K.T. Direct interactions between autoantigen La and human immunodeficiency virus leader RNA. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 7008–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duncan, R.C.; Nakhasi, H.L. La autoantigen binding to a 5′ cis-element of rubella virus RNA correlates with element function in vivo. Gene 1997, 201, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Escolano, A.L.; Vázquez-Ochoa, M.; Escobar-Herrera, J.; Hernández-Acosta, J. La, PTB, and PAB proteins bind to the 3(′) untranslated region of Norwalk virus genomic RNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 311, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.; Bhullar, D.; Vrati, S. La protein can simultaneously bind to both 3′- and 5′-noncoding regions of Japanese encephalitis virus genome. DNA Cell Biol. 2011, 30, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Jang, S.K. La protein is required for efficient translation driven by encephalomyocarditis virus internal ribosomal entry site. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Back, S.H.; Rho, J.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, S.K. La autoantigen enhances translation of BiP mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 5009–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Li, Q.; Zhu, R.; Jin, J. La Autoantigen Induces Ribosome Binding Protein 1 (RRBP1) Expression through Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES)-Mediated Translation during Cellular Stress Condition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tan, J.; Qiao, W. Identification of the internal ribosome entry sites in the 5′-untranslated region of the c-fos gene. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.; Sella, O.; Le, S.Y.; Elroy-Stein, O. PDGF2/c-sis mRNA leader contains a differentiation-linked internal ribosomal entry site (D-IRES). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9356–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanbru, C.; Lafon, I.; Audigier, S.; Gensac, M.C.; Vagner, S.; Huez, G.; Prats, A.C. Alternative translation of the proto-oncogene c-myc by an internal ribosome entry site. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32061–32066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gan, W.; Rhoads, R.E. Internal initiation of translation directed by the 5′-untranslated region of the mRNA for eIF4G, a factor in-volved in the picornavirus-induced switch from cap-dependent to internal initiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huez, I.; Créancier, L.; Audigier, S.; Gensac, M.C.; Prats, A.C.; Prats, H. Two independent internal ribosome entry sites are involved in translation initiation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 6178–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacks, A.; Babon, J.; Kelly, G.; Manolaridis, I.; Cary, P.D.; Curry, S.; Conte, M.R. Structure of the C-terminal domain of human La protein reveals a novel RNA recognition motif coupled to a helical nuclear retention element. Structure 2003, 11, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cartellieri, M.; Koristka, S.; Arndt, C.; Feldmann, A.; Stamova, S.; von Bonin, M.; Töpfer, K.; Krüger, T.; Geib, M.; Michalk, I.; et al. A novel ex vivo isolation and expansion procedure for chimeric antigen receptor engrafted human T cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, C.; Bachmann, M.; Bergmann, R.; Berndt, N.; Feldmann, A.; Koristka, S. Theranostic CAR T cell targeting: A brief review. J. Label Comp. Radiopharm. 2019, 62, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jureczek, J.; Bergmann, R.; Berndt, N.; Koristka, S.; Kegler, A.; Puentes-Cala, E.; Soto, J.A.; Arndt, C.; Bachmann, M.; Feldmann, A. An oligo-His-tag of a targeting module does not influence its biodistribution and the retargeting capabilities of UniCAR T cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, S.; Arndt, C.; Feldmann, A.; Bergmann, R.; Bachmann, D.; Koristka, S.; Ludwig, F.; Ziller-Walter, P.; Kegler, A.; Gärtner, S.; et al. A novel nanobody-based target module for retargeting of T lymphocytes to EGFR-expressing cancer cells via the modular UniCAR platform. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1287246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, A.; Hoffmann, A.; Bergmann, R.; Koristka, S.; Berndt, N.; Arndt, C.; Loureiro, L.R.; Kittel-Boselli, E.; Mitwasi, N.; Kegler, A.; et al. Versatile chimeric antigen receptor platform for controllable and combinatorial T cell therapy. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1785608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, C.; Fasslrinner, F.; Loureiro, L.R.; Koristka, S.; Feldmann, A.; Bachmann, M. Adaptor CAR Platforms-Next Generation of T Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koristka, S.; Cartellieri, M.; Feldmann, A.; Arndt, C.; Loff, S.; Michalk, I.; Aliperta, R.; von Bonin, M.; Bornhäuser, M.; Ehninger, A.; et al. Flexible antigen-specific redirection of human regulatory T cells via a novel universal chimeric antigen receptor system. Blood 2014, 124, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartellieri, M.; Loff, S.; von Bonin, M.; Bejestani, E.P.; Ehninger, A.; Feldmann, A.; Koristka, S.; Arndt, C.; Ehninger, G.; Bachmann, M.P. Unicar: A novel modular retargeting platform technology for CAR T cells. Blood 2015, 126, 5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koristka, S.; Kegler, A.; Bergmann, R.; Arndt, C.; Feldmann, A.; Albert, S.; Cartellieri, M.; Ehninger, A.; Ehninger, G.; Middeke, J.M.; et al. Engrafting human regulatory T cells with a flexible modular chimeric antigen receptor technology. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 90, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, A.; Arndt, C.; Bergmann, R.; Loff, S.; Cartellieri, M.; Bachmann, D.; Aliperta, R.; Hetzenecker, M.; Ludwig, F.; Albert, S.; et al. Retargeting of T lymphocytes to PSCA- or PSMA positive prostate cancer cells using the novel modular chimeric antigen receptor platform technology “UniCAR”. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31368–31385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arndt, C.; Feldmann, A.; Koristka, S.; Schäfer, M.; Bergmann, R.; Mitwasi, N.; Berndt, N.; Bachmann, D.; Kegler, A.; Schmitz, M.; et al. A theranostic PSMA ligand for PET imaging and retargeting of T cells expressing the universal chimeric antigen receptor UniCAR. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1659095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jureczek, J.; Feldmann, A.; Bergmann, R.; Arndt, C.; Berndt, N.; Koristka, S.; Loureiro, L.R.; Mitwasi, N.; Hoffmann, A.; Kegler, A.; et al. Highly Efficient Targeting of EGFR-Expressing Tumor Cells with UniCAR T Cells via Target Modules Based on CetuximAb. Onco. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 5515–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, D.; Aliperta, R.; Bergmann, R.; Feldmann, A.; Koristka, S.; Arndt, C.; Loff, S.; Welzel, P.; Albert, S.; Kegler, A.; et al. Retargeting of UniCAR T cells with an in vivo synthesized target module directed against CD19 positive tumor cells. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7487–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loureiro, L.R.; Feldmann, A.; Bergmann, R.; Koristka, S.; Berndt, N.; Arndt, C.; Pietzsch, J.; Novo, C.; Videira, P.; Bachmann, M. Development of a novel target module redirecting UniCAR T cells to Sialyl Tn-expressing tumor cells. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 22, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, L.R.; Feldmann, A.; Bergmann, R.; Koristka, S.; Berndt, N.; Máthé, D.; Hegedüs, N.; Szigeti, K.; Videira, P.A.; Bachmann, M.; et al. Extended half-life target module for sustainable UniCAR T-cell treatment of STn-expressing cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitwasi, N.; Feldmann, A.; Arndt, C.; Koristka, S.; Berndt, N.; Jureczek, J.; Loureiro, L.R.; Bergmann, R.; Máthé, D.; Hegedüs, N.; et al. “UniCAR”-modified off-the-shelf NK-92 cells for targeting of GD2-expressing tumour cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cartellieri, M.; Feldmann, A.; Koristka, S.; Arndt, C.; Loff, S.; Ehninger, A.; von Bonin, M.; Bejestani, E.P.; Ehninger, G.; Bachmann, M.P. Switching CAR T cells on and off: A novel modular platform for retargeting of T cells to AML blasts. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feldmann, A.; Arndt, C.; Koristka, S.; Berndt, N.; Bergmann, R.; Bachmann, M.P. Conventional CARs versus modular CARs. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koristka, S.; Ziller-Walter, P.; Bergmann, R.; Arndt, C.; Feldmann, A.; Kegler, A.; Cartellieri, M.; Ehninger, A.; Ehninger, G.; Bornhäuser, M.; et al. Anti-CAR-engineered T cells for epitope-based elimination of autologous CAR T cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arndt, C.; Loureiro, L.R.; Feldmann, A.; Jureczek, J.; Bergmann, R.; Máthé, D.; Hegedüs, N.; Berndt, N.; Koristka, S.; Mitwasi, N.; et al. UniCAR T cell immunotherapy enables efficient elimination of radioresistant cancer cells. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1743036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaieni, S.H.; Derakhshan, Z.; Sariri, R. Alternations of salivary antioxidant enzymes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2015, 24, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scofield, R.H.; Kurien, B.T.; Ganick, S.; McClain, M.T.; Pye, Q.; James, J.A. Modification of lupus-associated 60-kDa Ro protein with the lipid oxidation product 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal increases antigenicity and facilitates epitope spreading. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurien, B.T.; Scofield, R.H. Free radical mediated peroxidative damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurien, B.T.; Hensley, K.; Bachmann, M.; Scofield, R.H. Oxidatively modified autoantigens in autoimmune diseas-es. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallwood, M.J.; Nissim, A.; Knight, A.R.; Whiteman, M.; Haigh, R.; Winyard, P.G. Oxidative stress in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.C.; Kim, S.J.; Sung, M.K. Impaired antioxidant status and decreased dietary intake of antioxidants in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2002, 22, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grölz, D.; Laubinger, J.; Wilmer, F.; Tröster, H.; Bachmann, M. Transfection analysis of expression of mRNA isoforms encoding the nuclear autoantigen La/SS-B. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12076–12082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, M.; Grölz, D.; Bartsch, H.; Klein, R.R.; Tröster, H. Analysis of expression of an alternative La (SS-B) cDNA and localization of the encoded N- and C-terminal peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1356, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feldmann, A.; Arndt, C.; Töpfer, K.; Stamova, S.; Krone, F.; Cartellieri, M.; Koristka, S.; Michalk, I.; Lindemann, D.; Schmitz, M.; et al. Novel humanized and highly efficient bispecific antibodies mediated killing of prostate stem cell antigen-expressing tumor cells by CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hauptmann, N.; Pion, M.; Wehner, R.; Munoz-Fernández, M.-Á.; Schmitz, M.; Voit, B.; Appelhans, D. Potential of Ni(II)-NTA-modified poly(ethylen imine) glycopolymers as carrier systems for future dendritic cell-based immunotherapy. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.R.; Williams, D.G.; Venables, P.J.; Maini, R.N. Monoclonal antibodies to the Sjögren’s syndrome associated antigen SS-B (La). J. Immunol. Methods 1985, 77, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijn, G.J.; Thijssen, J.P.; Smith, P.R.; Williams, D.G.; van Venrooij, W.J. Anti-La monoclonal antibodies recognizing epitopes within the RNA-binding domain of the La protein show differential capacities to immunoprecipitate RNA-associated La protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, A.; Stamova, S.; Bippes, C.C.; Bartsch, H.; Wehner, R.; Schmitz, M.; Temme, A.; Cartellieri, M.; Bachmann, M. Retargeting of T cells to prostate stem cell antigen expressing tumor cells: Comparison of different antibody formats. Prostate 2011, 71, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, C.; Koristka, S.; Feldmann, A.; Bachmann, M. Native Polyacrylamide Gels. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1855, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berndt, N.; Bippes, C.C.; Michalk, I.; Bartsch, T.; Arndt, C.; Puentes-Cala, E.; Soto, J.A.; Loureiro, L.R.; Kegler, A.; Bachmann, D.; et al. And Yet It Moves: Oxidation of the Nuclear Autoantigen La/SS-B Is the Driving Force for Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189699
Berndt N, Bippes CC, Michalk I, Bartsch T, Arndt C, Puentes-Cala E, Soto JA, Loureiro LR, Kegler A, Bachmann D, et al. And Yet It Moves: Oxidation of the Nuclear Autoantigen La/SS-B Is the Driving Force for Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189699
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerndt, Nicole, Claudia C. Bippes, Irene Michalk, Tabea Bartsch, Claudia Arndt, Edinson Puentes-Cala, Javier Andrés Soto, Liliana R. Loureiro, Alexandra Kegler, Dominik Bachmann, and et al. 2021. "And Yet It Moves: Oxidation of the Nuclear Autoantigen La/SS-B Is the Driving Force for Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189699
APA StyleBerndt, N., Bippes, C. C., Michalk, I., Bartsch, T., Arndt, C., Puentes-Cala, E., Soto, J. A., Loureiro, L. R., Kegler, A., Bachmann, D., Gross, J. K., Gross, T., Kurien, B. T., Scofield, R. H., Farris, A. D., James, J. A., Bergmann, R., Schmitz, M., Feldmann, A., & Bachmann, M. P. (2021). And Yet It Moves: Oxidation of the Nuclear Autoantigen La/SS-B Is the Driving Force for Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189699







