Mode of Action of Neonicotinoid Insecticides Imidacloprid and Thiacloprid to the Cockroach Pameα7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
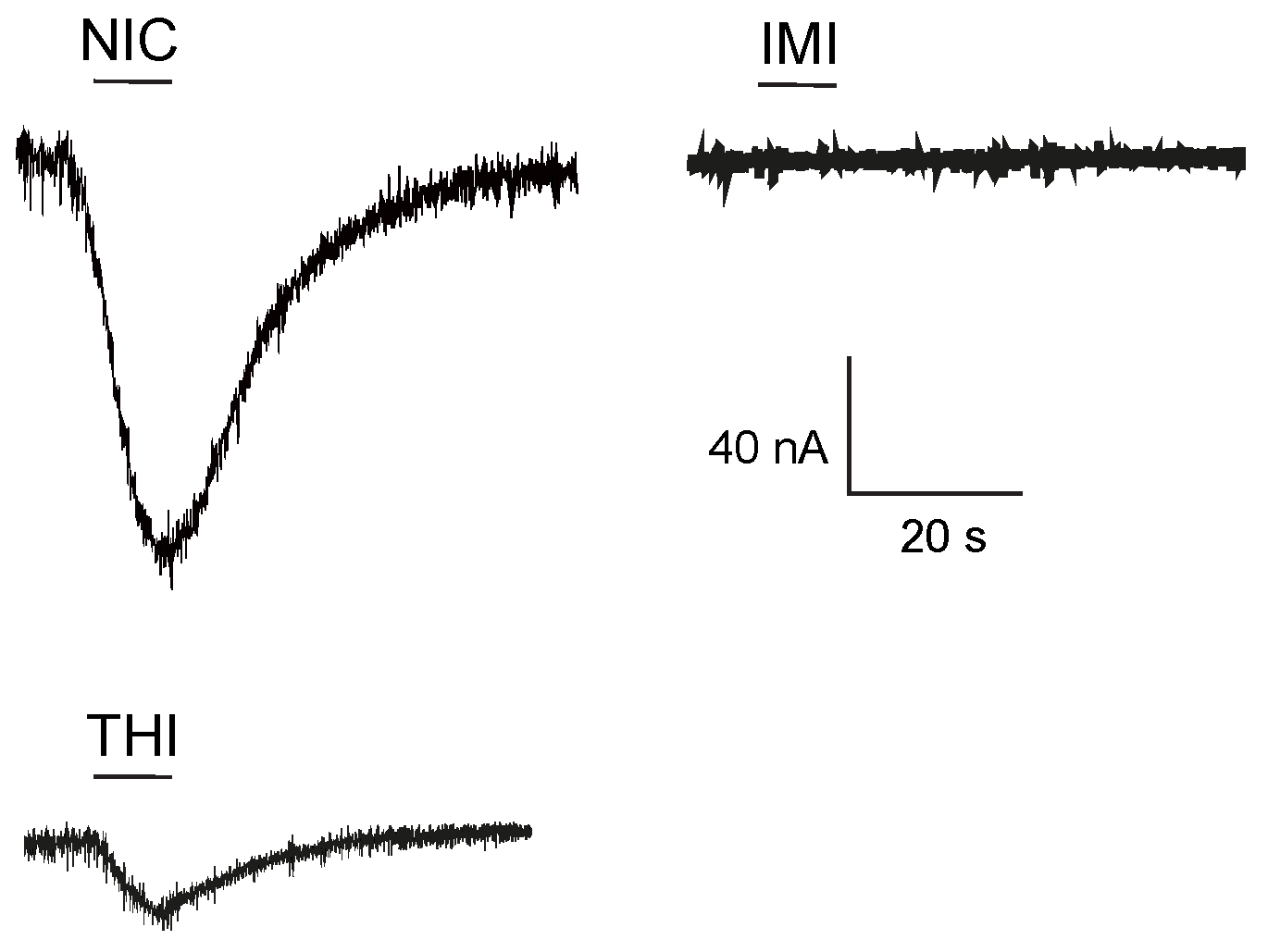
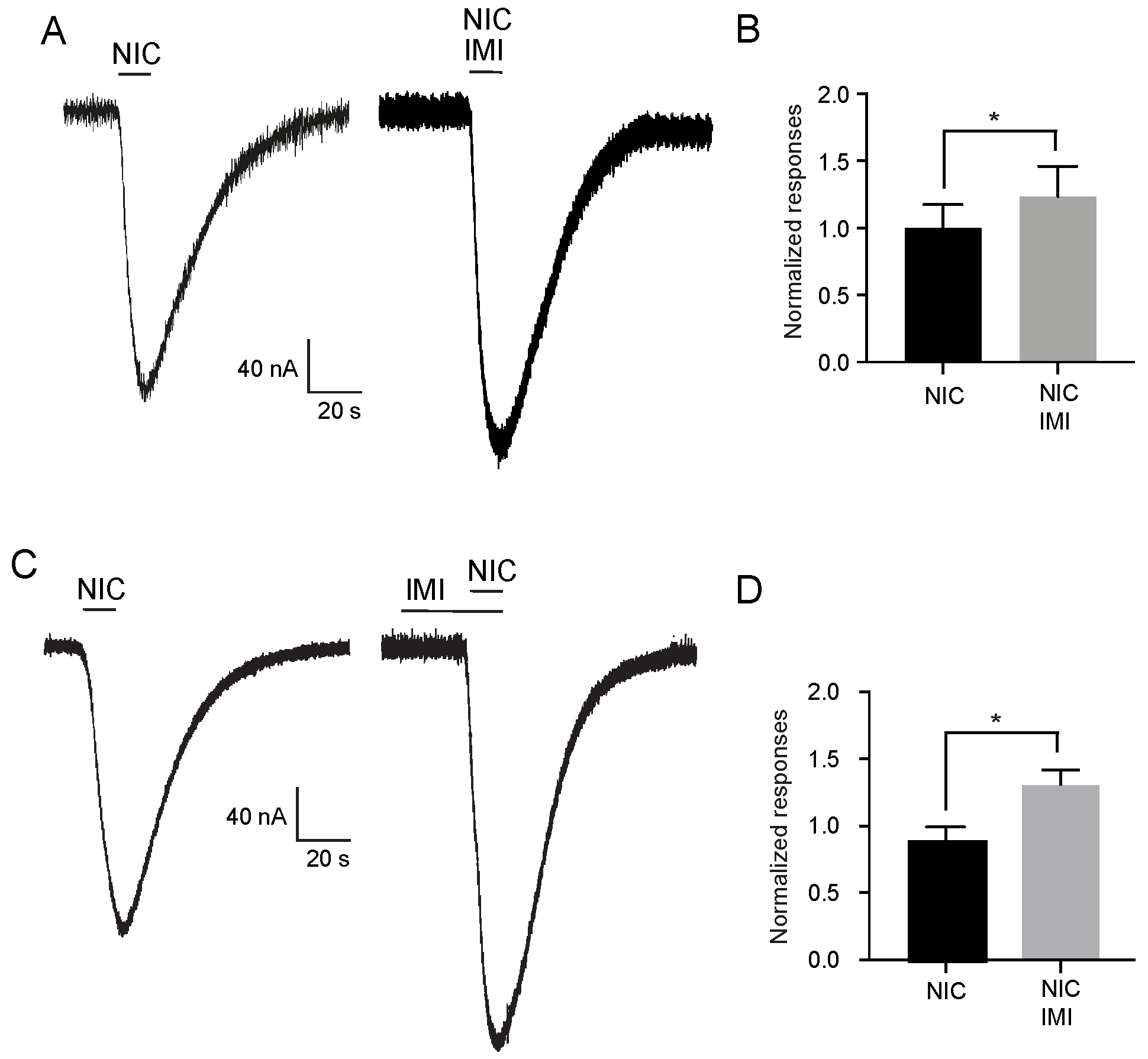
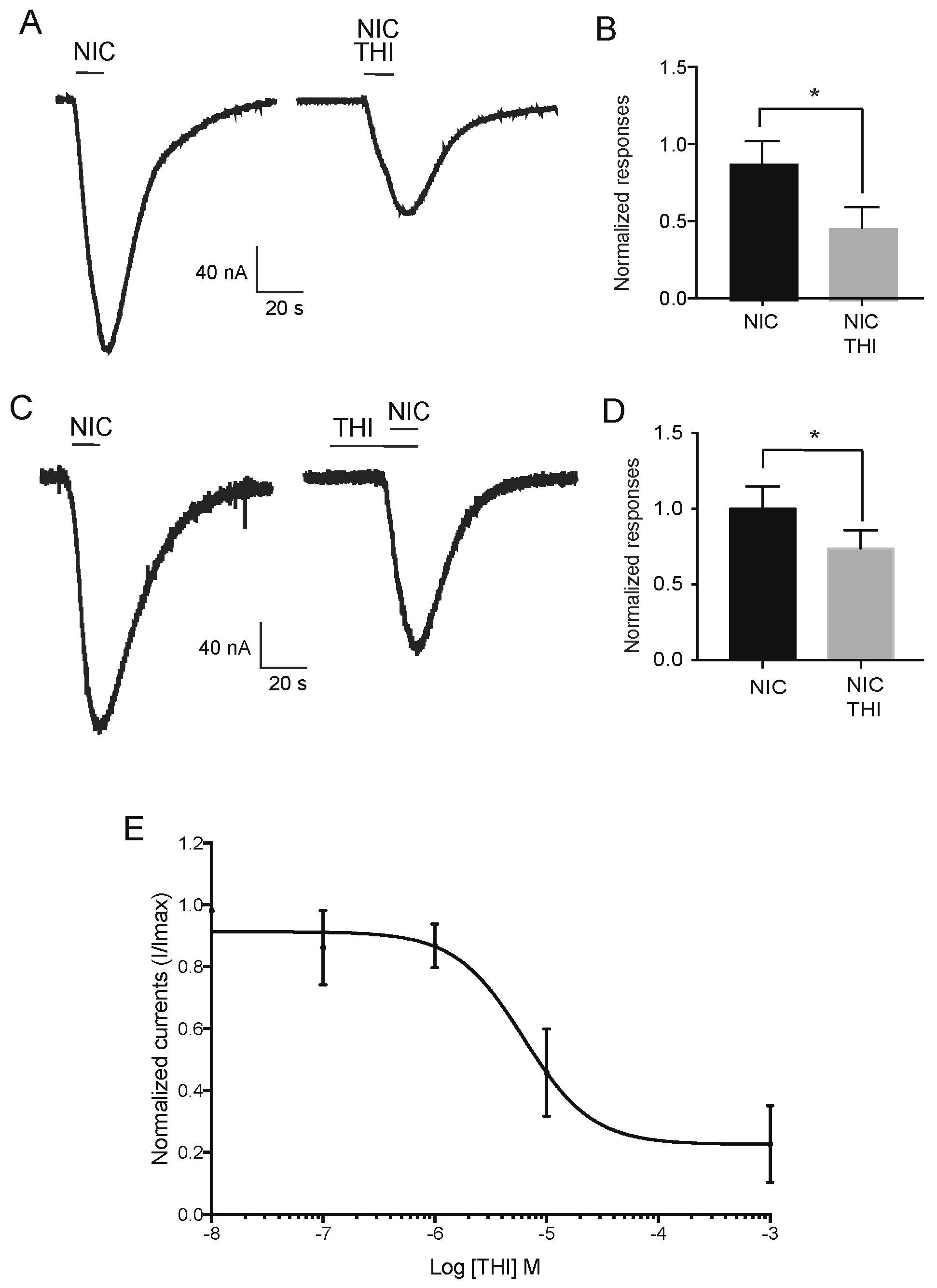
2.1. Effect of Neonicotinoid Insecticides on Nicotine-Induced Currents
2.2. Sequence Alignments and Homology Modeling
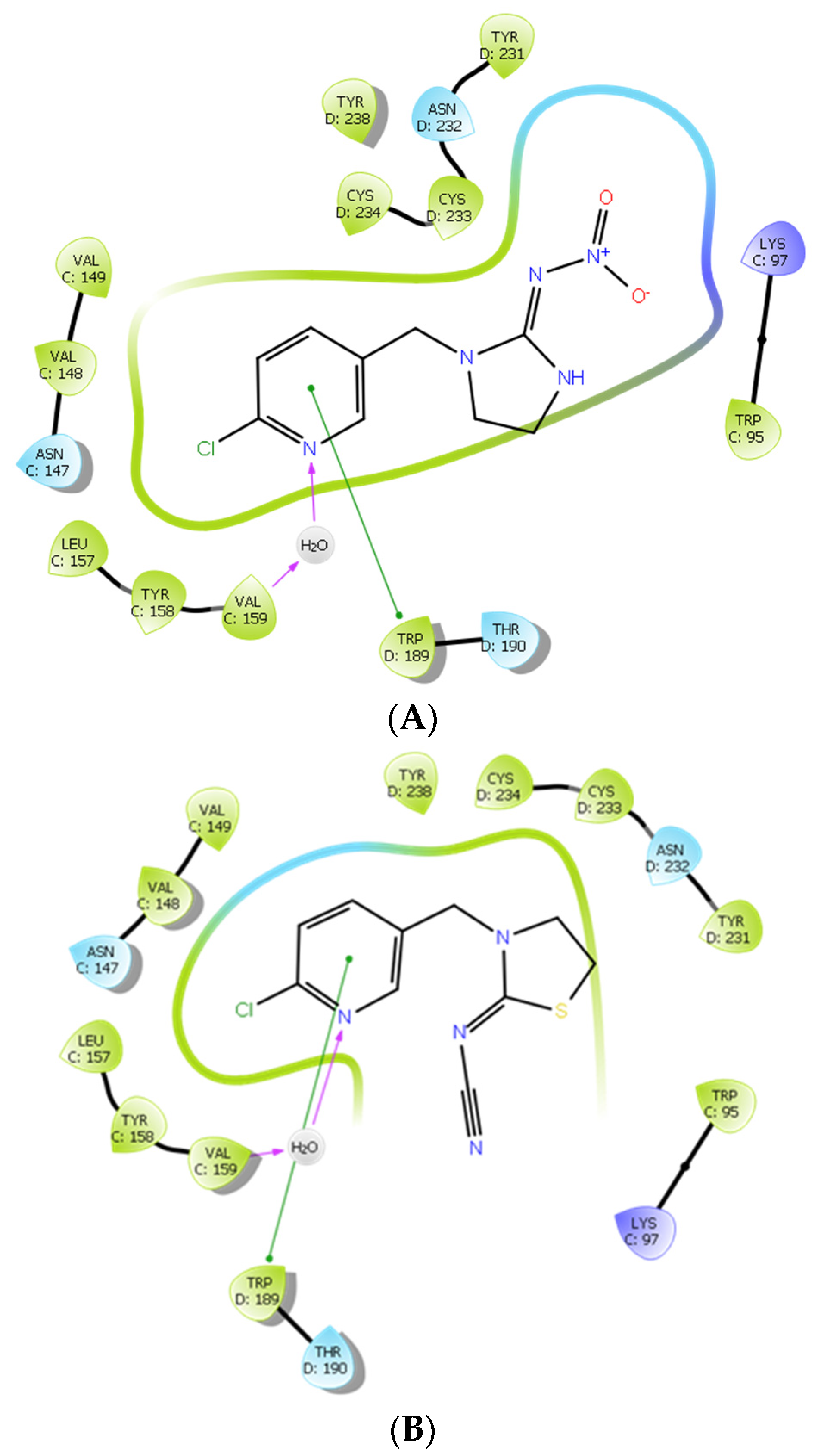
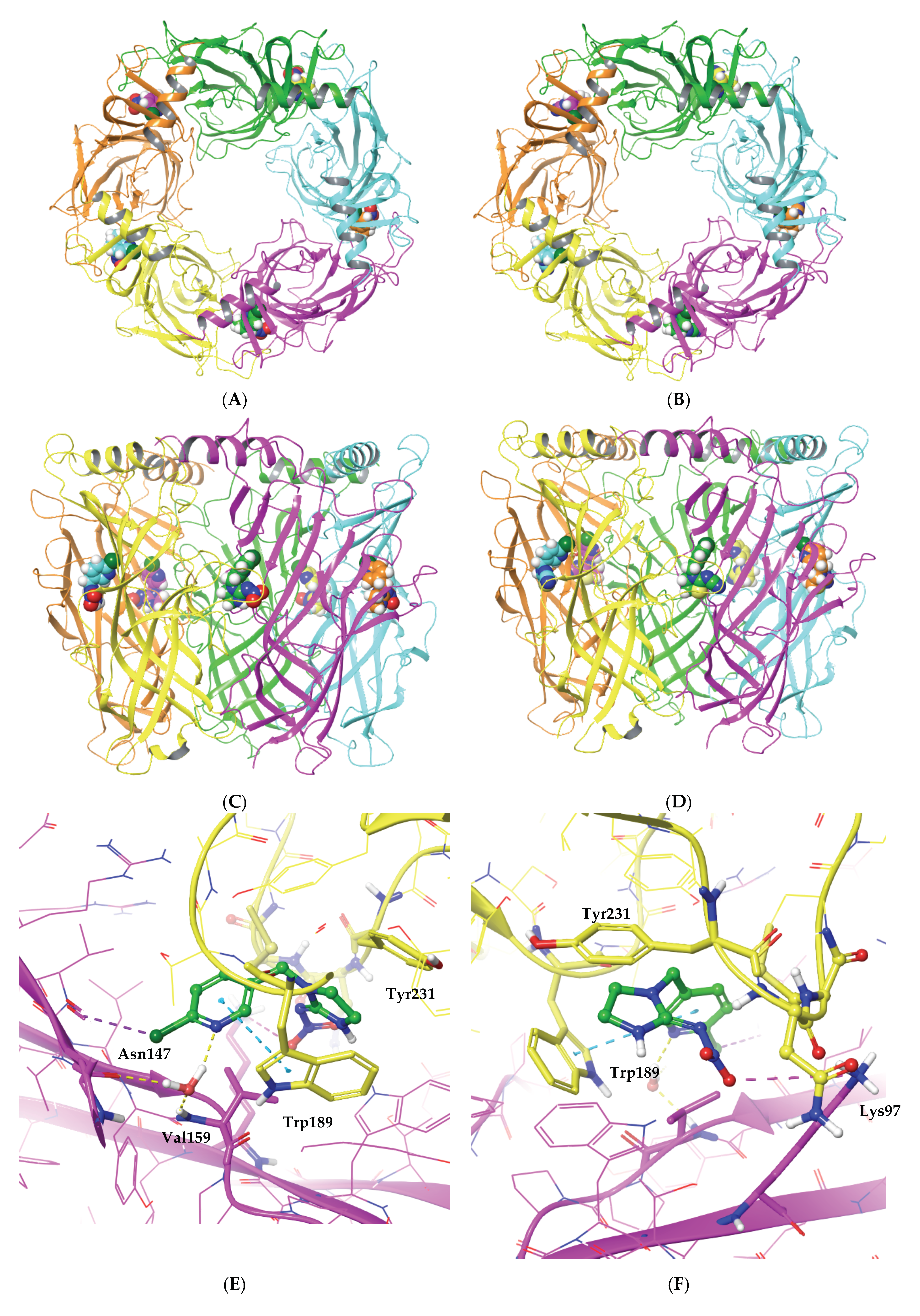
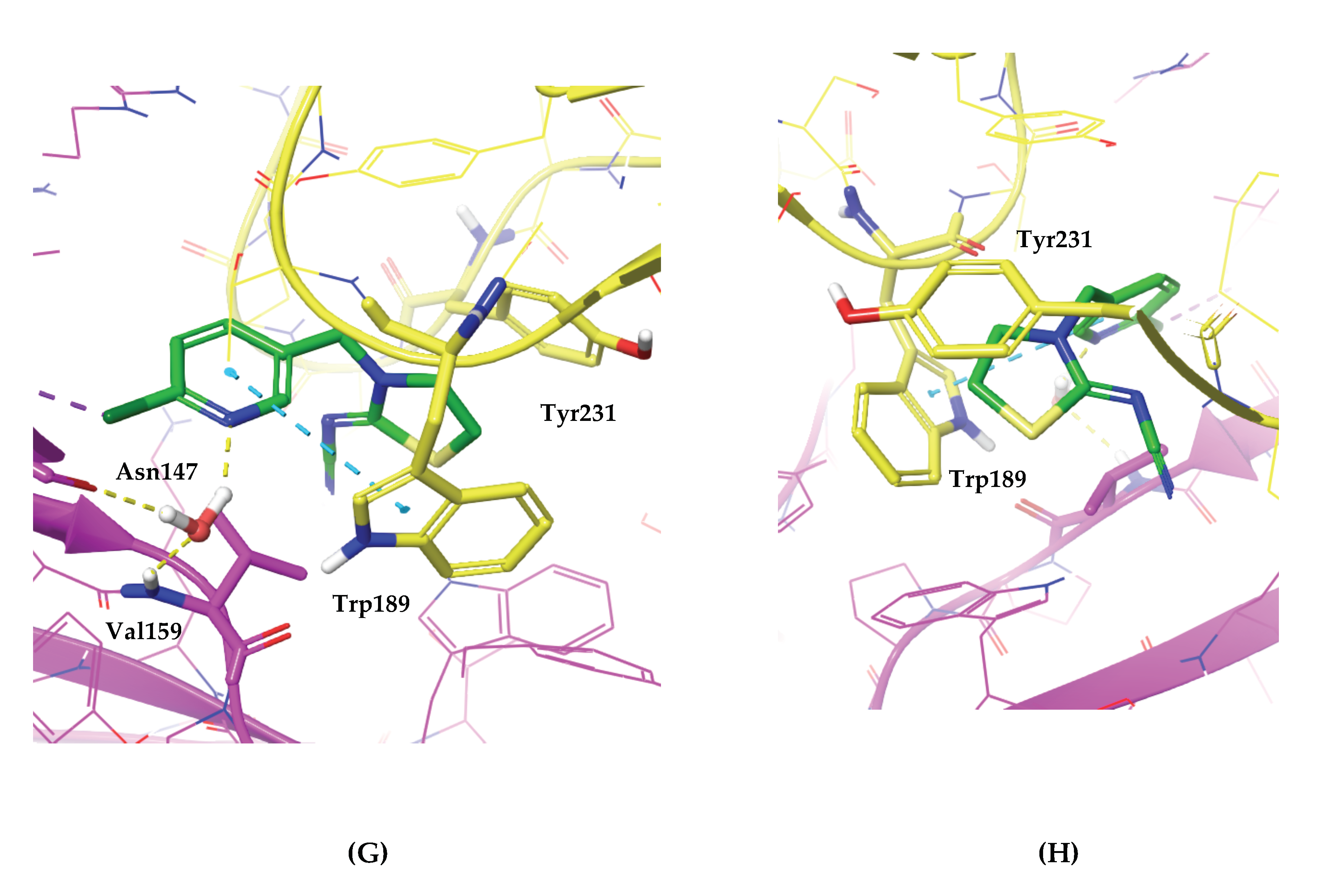
2.3. Investigating the Binding of Imidacloprid and Thiacloprid to the Cockroach Pameα7nAChR through Molecular Docking Studies
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
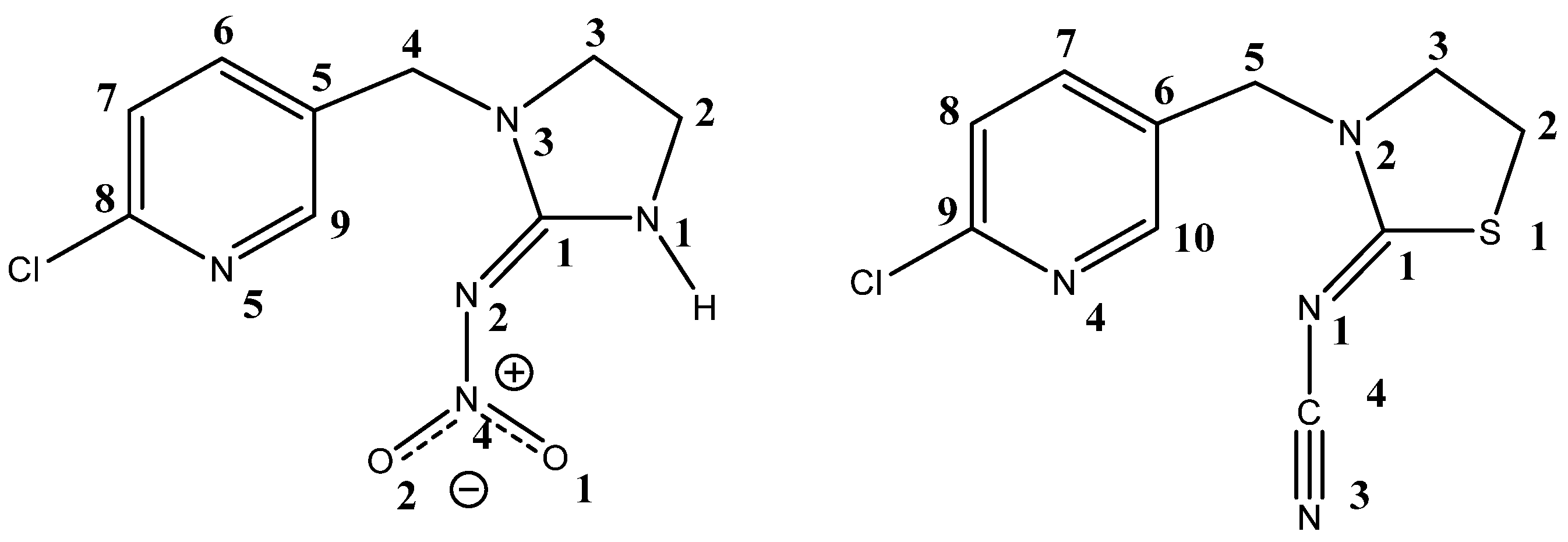
4.1. Compounds
4.2. Oocytes Injection
4.3. Voltage-Clamp Recordings
4.4. Homology Modeling
4.5. Docking
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corringer, P.J.; Le Novere, N.; Changeux, J.P. Nicotinic receptors at the amino acid level. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 40, 431–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changeux, J.P. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: A typical ‘allosteric machine’. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, D.; Terry, A.V., Jr. The wonderland of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thany, S.H.; Lenaers, G.; Raymond-Delpech, V.; Sattelle, D.B.; Lapied, B. Exploring the pharmacological properties of insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Buckingham, S.D.; Matsuda, K.; Sattelle, D.B. Modes of Action, Resistance and Toxicity of Insecticides Targeting Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillebois, E.; Cartereau, A.; Jones, A.K.; Thany, S.H. Neonicotinoid insecticides mode of action on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors using binding studies. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 151, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casida, J.E. Pest toxicology: The primary mechanisms of pesticide action. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Schindler, M.; Elbert, A. Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Beck, M.E. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists: A milestone for modern crop protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9464–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, V.L.; Saar, R. Desensitizing and non-desensitizing subtypes of alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cockroach neurons. J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 50, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Galligan, J.J.; Hollingworth, R.M. Agonist actions of neonicotinoids on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed by cockroach neurons. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houchat, J.N.; Dissanamossi, B.M.; Landagaray, E.; Mathe-Allainmat, M.; Cartereau, A.; Graton, J.; Lebreton, J.; Le Questel, J.Y.; Thany, S.H. Mode of action of sulfoxaflor on alpha-bungarotoxin-insensitive nAChR1 and nAChR2 subtypes: Inhibitory effect of imidacloprid. Neurotoxicology 2019, 74, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courjaret, R.; Grolleau, F.; Lapied, B. Two distinct calcium-sensitive and -insensitive PKC up- and down-regulate an alpha-bungarotoxin-resistant nAChR1 in insect neurosecretory cells (DUM neurons). Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, V.L. Antagonist pharmacology of desensitizing and non-desensitizing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cockroach neurons. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courjaret, R.; Lapied, B. Complex intracellular messenger pathways regulate one type of neuronal alpha-bungarotoxin-resistant nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in insect neurosecretory cells (dorsal unpaired median neurons). Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodereau-Dubois, B.; List, O.; Calas-List, D.; Marques, O.; Communal, P.Y.; Thany, S.H.; Lapied, B. Transmembrane potential polarization, calcium influx, and receptor conformational state modulate the sensitivity of the imidacloprid-insensitive neuronal insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptor to neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thany, S.H.; Courjaret, R.; Lapied, B. Effect of calcium on nicotine-induced current expressed by an atypical alpha-bungarotoxin-insensitive nAChR2. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 438, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillebois, E.; Thany, S.H. Characterization of nicotine acetylcholine receptor subunits in the cockroach Periplaneta americana mushroom bodies reveals a strong expression of beta1 subunit: Involvement in nicotine-induced currents. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 93, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattelle, D.B.; Jones, A.K.; Sattelle, B.M.; Matsuda, K.; Reenan, R.; Biggin, P.C. Edit, cut and paste in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Bioessays 2005, 27, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.K.; Raymond-Delpech, V.; Thany, S.H.; Gauthier, M.; Sattelle, D.B. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family of the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.K.; Grauso, M.; Sattelle, D.B. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family of the malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Genomics 2005, 85, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.P.; Jones, A.K.; Tamborindeguy, C.; Davies, T.G.; Amey, J.S.; Williamson, S.; Wolstenholme, A.; Field, L.M.; Williamson, M.S.; Walsh, T.K.; et al. Identification of ion channel genes in the Acyrthosiphon pisum genome. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19 (Suppl. 2), 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillebois, E.; Beloula, A.; Quinchard, S.; Jaubert-Possamai, S.; Daguin, A.; Servent, D.; Tagu, D.; Thany, S.H.; Tricoire-Leignel, H. Neonicotinoid Binding, Toxicity and Expression of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunits in the Aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Cang, X.; Bao, H.; Liu, Z. The potential subunits involved in two subtypes of alpha-Bgt-resistant nAChRs in cockroach dorsal unpaired median (DUM) neurons. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phulera, S.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J.; Claxton, D.P.; Yoder, N.; Yoshioka, C.; Gouaux, E. Cryo-EM structure of the benzodiazepine-sensitive alpha1beta1gamma2S tri-heteromeric GABAA receptor in complex with GABA. Elife 2018, 7, e39383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartereau, A.; Taillebois, E.; Selvam, B.; Martin, C.; Graton, J.; Le Questel, J.Y.; Thany, S.H. Cloning and Expression of Cockroach alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunit. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thany, S.H. Agonist actions of clothianidin on synaptic and extrasynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on cockroach sixth abdominal ganglion. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Deglise, P.; Grunewald, B.; Gauthier, M. The insecticide imidacloprid is a partial agonist of the nicotinic receptor of honeybee Kenyon cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 321, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, T.T.; Harel, M.; Hibbs, R.E.; Radic, Z.; Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E.; Taylor, P. Atomic interactions of neonicotinoid agonists with AChBP: Molecular recognition of the distinctive electronegative pharmacophore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7606–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2014-1: Prime, version 3.5, Schrödinger, LLC, New York,NY, 2014. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2014-1, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., 3rd; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, G.N.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Sasisekharan, V. Stereochemistry of polypeptide chain configurations. J. Mol. Biol. 1963, 7, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Molecular recognition of neonicotinoid insecticides: The determinants of life or death. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sixma, T.K.; Smit, A.B. Acetylcholine binding protein (AChBP): A secreted glial protein that provides a high-resolution model for the extracellular domain of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2003, 32, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celie, P.H.; van Rossum-Fikkert, S.E.; van Dijk, W.J.; Brejc, K.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Nicotine and carbamylcholine binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as studied in AChBP crystal structures. Neuron 2004, 41, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celie, P.H.; Klaassen, R.V.; van Rossum-Fikkert, S.E.; van Elk, R.; van Nierop, P.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Crystal structure of acetylcholine-binding protein from Bulinus truncatus reveals the conserved structural scaffold and sites of variation in nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26457–26466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.B.; Sulzenbacher, G.; Huxford, T.; Marchot, P.; Taylor, P.; Bourne, Y. Structures of Aplysia AChBP complexes with nicotinic agonists and antagonists reveal distinctive binding interfaces and conformations. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3635–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Okajima, T.; Yamashita, A.; Oda, T.; Hirata, K.; Nishiwaki, H.; Morimoto, T.; Akamatsu, M.; Ashikawa, Y.; Kuroda, S.; et al. Crystal structures of Lymnaea stagnalis AChBP in complex with neonicotinoid insecticides imidacloprid and clothianidin. Invert. Neurosci. 2008, 8, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucktooa, P.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Insight in nAChR subtype selectivity from AChBP crystal structures. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulens, C.; Akdemir, A.; Jongejan, A.; van Elk, R.; Bertrand, S.; Perrakis, A.; Leurs, R.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K.; Bertrand, D.; et al. Use of acetylcholine binding protein in the search for novel alpha7 nicotinic receptor ligands. In silico docking, pharmacological screening, and X-ray analysis. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, D.; Ballivet, M.; Gomez, M.; Bertrand, S.; Phannavong, B.; Gundelfinger, E.D. Physiological properties of neuronal nicotinic receptors reconstituted from the vertebrate beta 2 subunit and Drosophila alpha subunits. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Matsuda, K.; Otake, M.; Kuwamura, M.; Shimomura, M.; Komai, K.; Akamatsu, M.; Raymond, V.; Sattelle, D.B. Diverse actions of neonicotinoids on chicken alpha7, alpha4beta2 and Drosophila-chicken SADbeta2 and ALSbeta2 hybrid nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, S.; Bertrand, D.; Matter, J.M.; Hernandez, M.C.; Bertrand, S.; Millar, N.; Valera, S.; Barkas, T.; Ballivet, M. A neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit (alpha 7) is developmentally regulated and forms a homo-oligomeric channel blocked by alpha-BTX. Neuron 1990, 5, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Wells, J.; Hawkins, J.; Colombo, C.; Bermudez, I.; Jones, A.K. Cloning and functional expression of intracellular loop variants of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) RDL GABA receptor. Neurotoxicology 2017, 60, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Buckingham, S.D.; Freeman, J.C.; Squire, M.D.; Baylis, H.A.; Sattelle, D.B. Effects of the alpha subunit on imidacloprid sensitivity of recombinant nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Shimomura, M.; Kondo, Y.; Ihara, M.; Hashigami, K.; Yoshida, N.; Raymond, V.; Mongan, N.P.; Freeman, J.C.; Komai, K.; et al. Role of loop D of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in its interaction with the insecticide imidacloprid and related neonicotinoids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, B.; Graton, J.; Laurent, A.D.; Alamiddine, Z.; Mathe-Allainmat, M.; Lebreton, J.; Coqueret, O.; Olivier, C.; Thany, S.H.; Le Questel, J.Y. Imidacloprid and thiacloprid neonicotinoids bind more favourably to cockroach than to honeybee alpha6 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: Insights from computational studies. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2015, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cartereau, A.; Taillebois, E.; Le Questel, J.-Y.; Thany, S.H. Mode of Action of Neonicotinoid Insecticides Imidacloprid and Thiacloprid to the Cockroach Pameα7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189880
Cartereau A, Taillebois E, Le Questel J-Y, Thany SH. Mode of Action of Neonicotinoid Insecticides Imidacloprid and Thiacloprid to the Cockroach Pameα7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189880
Chicago/Turabian StyleCartereau, Alison, Emiliane Taillebois, Jean-Yves Le Questel, and Steeve H. Thany. 2021. "Mode of Action of Neonicotinoid Insecticides Imidacloprid and Thiacloprid to the Cockroach Pameα7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189880
APA StyleCartereau, A., Taillebois, E., Le Questel, J.-Y., & Thany, S. H. (2021). Mode of Action of Neonicotinoid Insecticides Imidacloprid and Thiacloprid to the Cockroach Pameα7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189880





