Ultra-Low Frequency Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain Modulation in a Rat Model with Myogenous Temporomandibular Dysfunction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of ULF-TENS on Electrophysiology of Masseter Muscle after MMP Induction
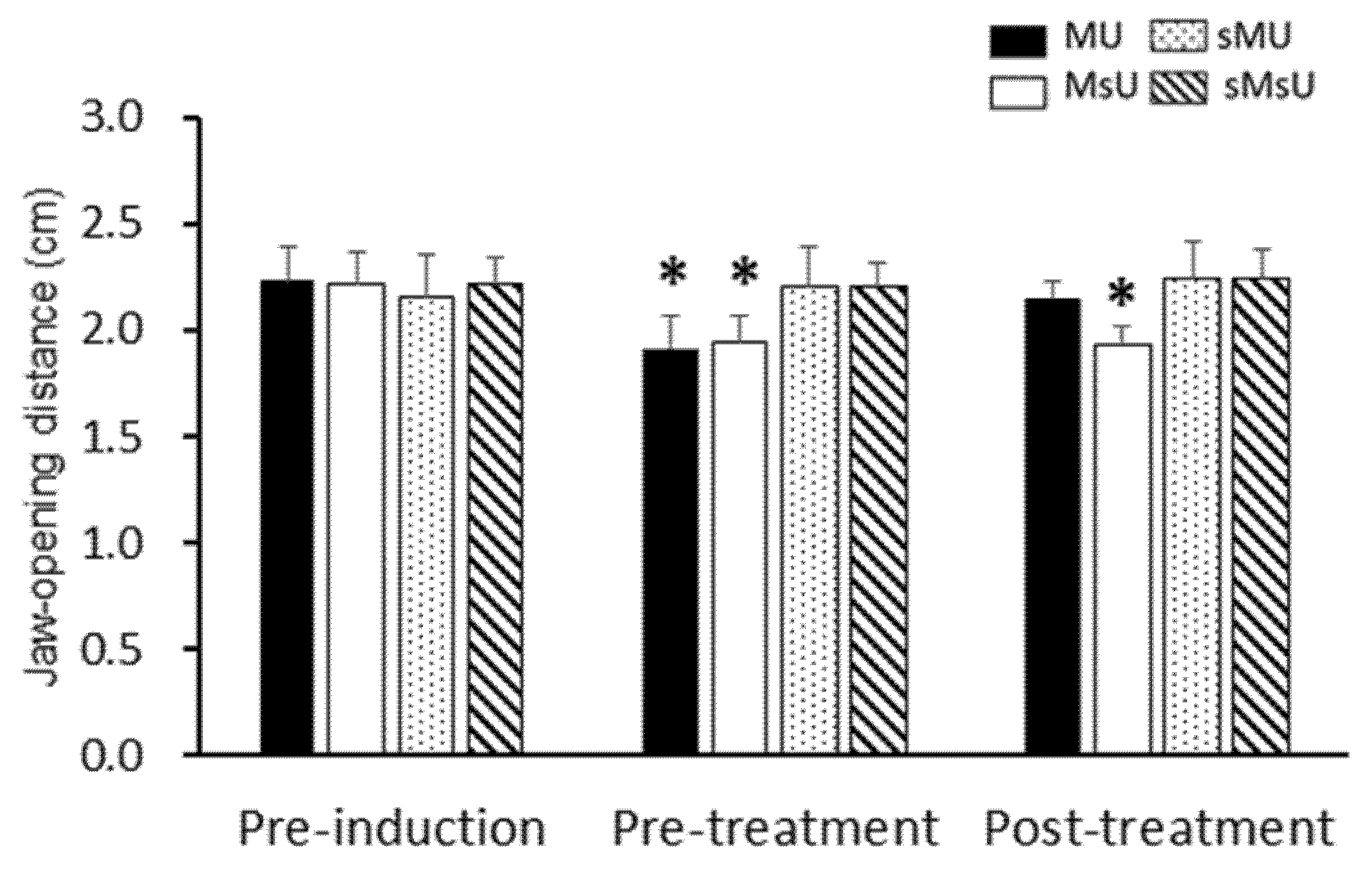
2.2. Effects of ULF-TENS on Maximal Jaw-Opening Distance after MMP Induction
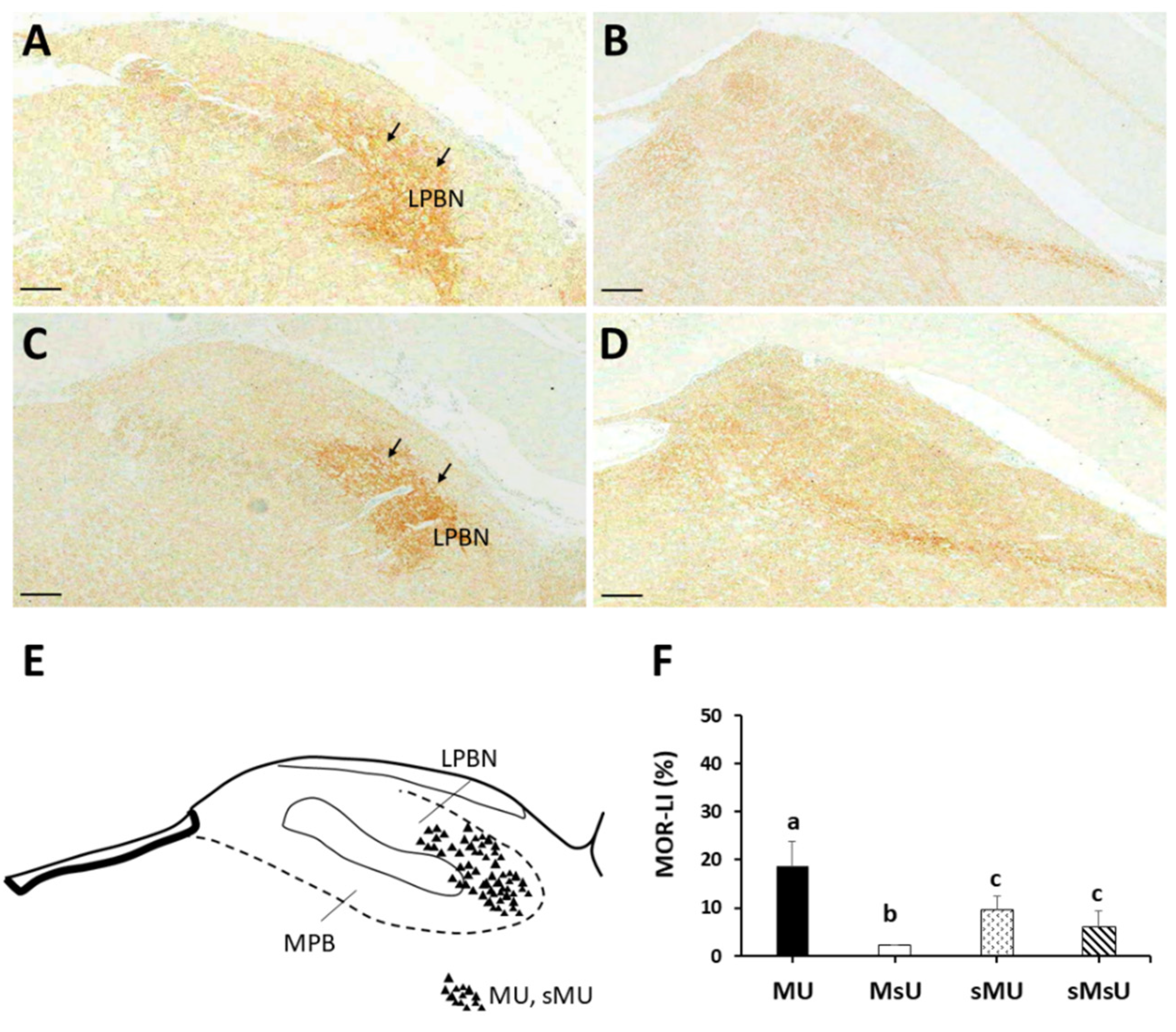
2.3. Expressions of SP-like and MOR-like Immunoreactivity in Parabrachial Nuclei
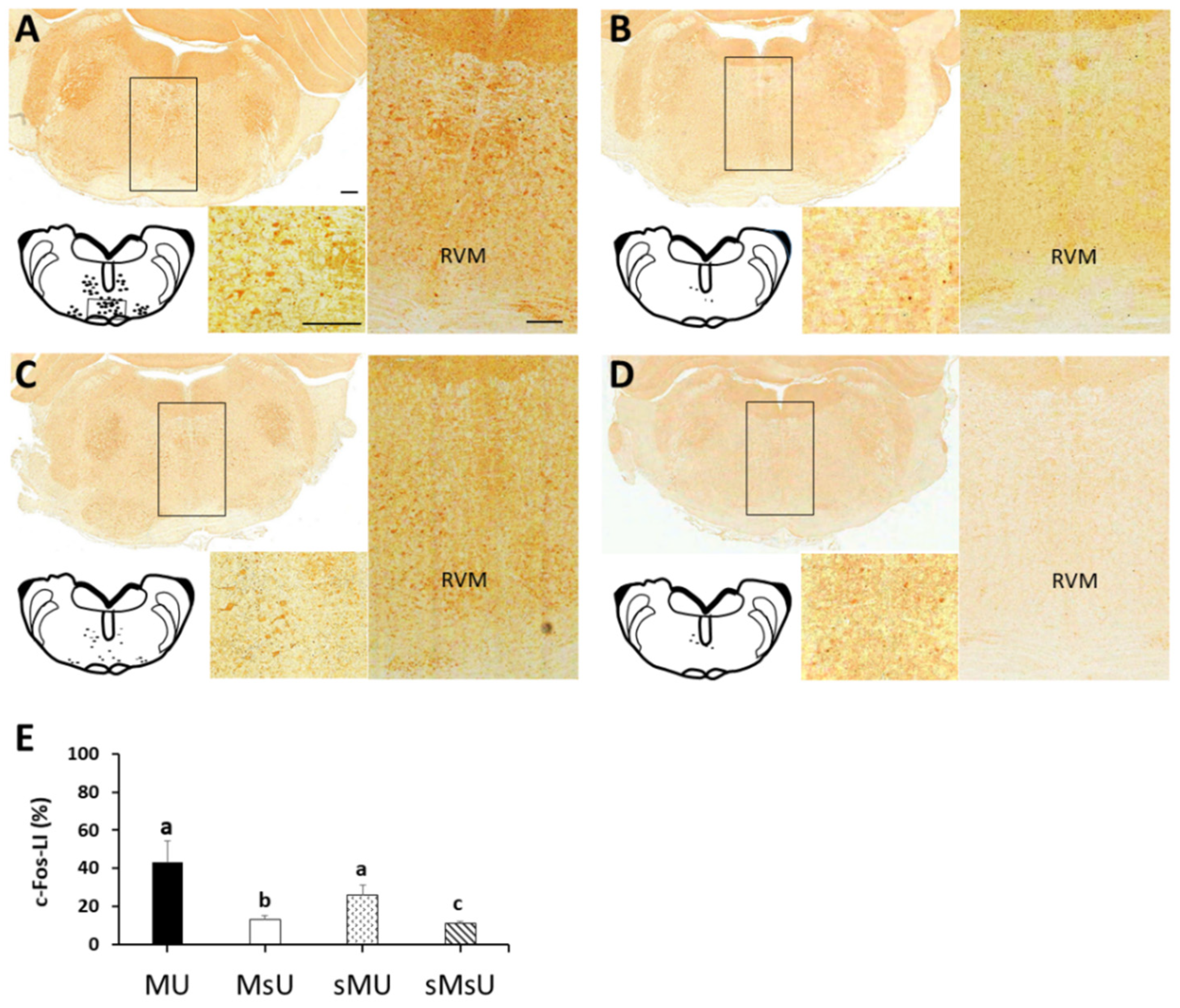
2.4. Expressions of c-Fos-like Immunoreactivity in Rostral Ventromedial Medulla
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Design
4.2. Animal Care and Ethical Approval
4.3. Induction and Identification of Masticatory Myofascial Pain
4.4. Ultra-Low Frequency Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
4.5. Ultrasound-Guided Electrophysiological Recording of Endplate Noise
4.6. Maximum Jaw-Opening Distance
4.7. Quantitative Analysis for SP, MOR, and c-Fos Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chou, L.W.; Hsieh, Y.L.; Kuan, T.S.; Hong, C.Z. Needling therapy for myofascial pain: Recommended technique with multiple rapid needle insertion. Biomedicine 2014, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Winocur, E.; Piccotti, F.; Ahlberg, J.; Lobbezoo, F. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review of axis I epidemiologic findings. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2011, 112, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Martínez, A.; Paris-Alemany, A.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I.; La Touche, R. Management of pain in patients with temporomandibular disorder (TMD): Challenges and solutions. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooper, B.C. Temporomandibular disorders: A position paper of the International College of Cranio-Mandibular Orthopedics (ICCMO). Cranio 2011, 29, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzotti, L. Electromyography tension and frequency spectrum analysis at rest of some masticatory muscles, before and after TENS. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 37, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, B.C.; Kleinberg, I. Establishment of a temporomandibular physiological state with neuromuscular orthosis treatment affects reduction of TMD symptoms in 313 patients. Cranio 2008, 26, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyszek, G.; Ketcham, R.; Garcia, R., Jr.; Radke, J. Electromyographic evidence of reduced muscle activity when ULF-TENS is applied to the Vth and VIIth cranial nerves. Cranio 2001, 19, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, A.; Sgolastra, F.; Ciarrocchi, I.; Cattaneo, R. Effects of transcutaneous electrical nervous stimulation on electromyographic and kinesiographic activity of patients with temporomandibular disorders: A placebo-controlled study. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipaila, N.; Sgolastra, F.; Spadaro, A.; Pietropaoli, D.; Masci, C.; Cattaneo, R.; Monaco, A. The effects of ULF-TENS stimulation on gnathology: The state of the art. Cranio 2014, 32, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konchak, P.A.; Thomas, N.R.; Lanigan, D.T.; Devon, R.M. Freeway space measurement using mandibular kinesiograph and EMG before and after TENS. Angle Orthod. 1988, 58, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- De Rossi, S.S.; Stern, I.; Sollecito, T.P. Disorders of the masticatory muscles. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 57, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.V.; Barbrick, B.; Esser, M.J. Trigeminal-parabrachial connections: Possible pathway for nociception-induced cardiovascular reflex responses. Brain Res. 1996, 715, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauriau, C.; Bernard, J.F. Pain pathways and parabrachial circuits in the rat. Exp. Physiol. 2002, 87, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Roeder, Z.; Li, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Ingram, S.L.; Heinricher, M.M. Optogenetic evidence for a direct circuit linking nociceptive transmission through the parabrachial complex with pain-modulating neurons of the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM). eNeuro 2017, 4, e0202-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ossipov, M.H.; Dussor, G.O.; Porreca, F. Central modulation of pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nomura, H.; Konno, H.; Takase, S.; Saito, H. Decrease of substance P in the parabrachial nucleus of multiple system atrophy. Auton. Neurosci. 2001, 92, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.M.; Kombian, S.B.; Zidichouski, J.A.; Pittman, Q.J. Peptidergic modulation of synaptic transmission in the parabrachial nucleus in vitro: Importance of degradative enzymes in regulating synaptic efficacy. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 6046–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aicher, S.A.; Punnoose, A.; Goldberg, A. Mu-Opioid receptors often colocalize with the substance P receptor (NK1) in the trigeminal dorsal horn. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 4345–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, Y.L.; Wu, B.T.; Yang, C.C. Increased substance P-like immunoreactivities in parabrachial and amygdaloid nuclei in a rat model with masticatory myofascial pain. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, B.; Ahmed, J.; Shenoy, N.; Ongole, R.; Sujir, N.; Natarajan, S. Comparison of transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (tens) and microcurrent nerve stimulation (mens) in the management of masticatory muscle pain: A comparative study. Pain Res. Manag. 2019, 2019, 8291624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, S.; Miyagi, A.; Yoshinaga, K.; Matsuka, Y.; Matsumoto, F.; Uyama, E.; Suzuki, Y.; Oshima, M.; Okura, K.; Tanaka, E. Immediate effect of masticatory muscle activity with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in muscle pain of temporomandibular disorders patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.; Siriani, A.O.; Bérzin, F. Effect of conventional TENS on pain and electromyographic activity of masticatory muscles in TMD patients. Braz. Oral Res. 2004, 18, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Svensson, P. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on jaw movement-evoked pain in patients with TMJ disc displacement without reduction and healthy controls. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2020, 78, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummolo, S.; Nota, A.; Tecco, S.; Caruso, S.; Marchetti, E.; Marzo, G.; Cutilli, T. Ultra-low-frequency transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (ULF-TENS) in subjects with craniofacial pain: A retrospective study. Cranio 2020, 38, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashani, O.; Johnson, M. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (tens) a possible aid for pain relief in developing countries? Libyan J. Med. 2009, 4, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sluka, K.A.; Walsh, D. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: Basic science mechanisms and clinical effectiveness. J. Pain 2003, 4, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.; Sgolastra, F.; Pietropaoli, D.; Giannoni, M.; Cattaneo, R. Comparison between sensory and motor transcutaneous electrical nervous stimulation on electromyographic and kinesiographic activity of patients with temporomandibular disorder: A controlled clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasmin, L.; Burkey, A.R.; Card, J.P.; Basbaum, A.I. Transneuronal labeling of a nociceptive pathway, the spino-(trigemino-)parabrachio-amygdaloid, in the rat. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 3751–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, F.; Sugimura, Y.K.; Takahashi, Y. Pain-associated neural plasticity in the parabrachial to central amygdala circuit: Pain changes the brain, and the brain changes the pain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1099, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Roeder, Z.; Chen, Q.; Davis, S.; Carlson, J.D.; Tupone, D.; Heinricher, M.M. Parabrachial complex links pain transmission to descending pain modulation. Pain 2016, 157, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagley, E.E.; Ingram, S.L. Endogenous opioid peptides in the descending pain modulatory circuit. Neuropharmacology 2020, 173, 108131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, M.; Gorcs, T.J.; Palkovits, M. Immunohistochemical study on the distribution of neuropeptides within the pontine tegmentum—Particularly the parabrachial nuclei and the locus coeruleus of the human brain. Neuroscience 1992, 46, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderah, T.W. Pathophysiology of pain. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 91, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.L.; Silverman, M.B.; Aicher, S.A. Rat trigeminal lamina I neurons that project to thalamic or parabrachial nuclei contain the mu-opioid receptor. Neuroscience 2004, 128, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwell, T.N.; Martin-Schild, S.; Inglis, F.M.; Zadina, J.E. Colocalization and shared distribution of endomorphins with substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and the mu opioid receptor. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 503, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroń, A.; Jedliński, M.; Grzywacz, E.; Mazur, M.; Trybek, G. Kinesiology Taping as an Innovative Measure against Post-Operative Complications after Third Molar Extraction-Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, L.; Budelier, K.; Clinesmith, M.; Fiedler, A.; Landstrom, R.; Leeper, B.J.; Moeller, L.; Mutch, S.; O’Dell, K.; Ross, J.; et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) reduces chronic hyperalgesia induced by muscle inflammation. Pain 2006, 120, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantana, J.M.; Da Silva, L.F.; De Resende, M.A.; Sluka, K.A. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation at both high and low frequencies activates ventrolateral periaqueductal grey to decrease mechanical hyperalgesia in arthritic rats. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalra, A.; Urban, M.O.; Sluka, K.A. Blockade of opioid receptors in rostral ventral medulla prevents antihyperalgesia produced by transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 298, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, J.D.; Craft, R.M.; LeResche, L.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Berkley, K.J.; Fillingim, R.B.; Gold, M.S.; Holdcroft, A.; Lautenbacher, S.; Mayer, E.A.; et al. Consensus Working Group of the Sex, Gender, and Pain SIG of the IASP. Studying sex and gender differences in pain and analgesia: A consensus report. Pain 2007, 132 (Suppl. 1), S26–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M. Ethical considerations in relation to pain in animal experimentation. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1986, 554, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 1983, 16, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, M.O.; Skjonsby, H.S.; Brazeau, G.A.; Parikh, U.K.; Jenkins, R.M. Weakness in mouse masticatory muscles by repetitive contractions with forced lengthening. J. Dent. Res. 1995, 74, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.Z.; Simons, D.G. Pathophysiologic and electrophysiologic mechanisms of myofascial trigger points. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1998, 79, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.L.; Chou, L.W.; Joe, Y.S.; Hong, C.Z. Spinal cord mechanism involving the remote effects of dry needling on the irritability of myofascial trigger spots in rabbit skeletal muscle. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Pre-Induction | Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | 2 Differences among Timepoints, p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPN prevalence | MU | 27.30 ± 5.68 | 52.60 ± 4.77 *†§ | 28.10 ± 6.03 ‡ | 0.00037 |
| (%) | MsU | 29.40 ± 7.07 | 51.20 ± 8.94 *†§ | 54.50 ± 6.17 *†§|| | 0.00038 |
| sMU | 22.70 ± 4.64 | 25.30 ± 6.00 | 24.80 ± 4.52 | 0.04214 (NS) | |
| sMsU | 28.10 ± 4.01 | 27.4 ± 4.76 | 28.20 ± 2.53 | 0.86687 (NS) | |
| 1 Differences among groups, p value | 0.0623 (NS) | 1.87 × 10−6 | 1.02 × 10−5 | ||
| Jaw-opening distance | MU | 2.23 ± 0.16 | 1.92 ± 0.16 *†§ | 2.15 ± 0.08 ‡ | 0.00183 |
| (cm) | MsU | 2.21 ± 0.15 | 1.95 ± 0.12 *†§ | 1.93 ± 0.09 *†§|| | 0.00037 |
| sMU | 2.16 ± 0.19 | 2.20 ± 0.19 | 2.24 ± 0.18 | 0.13904 (NS) | |
| sMsU | 2.22 ± 0.12 | 2.20 ± 0.11 | 2.26 ± 0.15 | 0.04436 (NS) | |
| 1 Differences among groups, p value | 0.88 (NS) | 3.03 × 10−5 | 1.61 × 10−4 | ||
| MU | MsU | sMU | sMsU | 1 Differences among Groups, p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parabrachial nucleus (%) | |||||
| SP | 21.18 ± 2.19 *†‡ | 49.33 ± 11.42 †‡ | 9.89 ± 0.35 | 8.49 ± 2.63 | p < 0.0001 |
| MOR | 18.63 ± 5.15 *†‡ | 2.10 ± 0.11 †‡ | 9.43 ± 2.85 | 6.09 ± 3.18 | p < 0.0001 |
| Rostral ventromedial medulla (%) | |||||
| c-Fos | 43.39 ± 10.73 *‡ | 13.19 ± 2.04 †‡ | 26.33 ± 5.08 ‡ | 10.97 ± 1.15 | p < 0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, Y.-L.; Yang, C.-C.; Yang, N.-P. Ultra-Low Frequency Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain Modulation in a Rat Model with Myogenous Temporomandibular Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189906
Hsieh Y-L, Yang C-C, Yang N-P. Ultra-Low Frequency Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain Modulation in a Rat Model with Myogenous Temporomandibular Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189906
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Yueh-Ling, Chen-Chia Yang, and Nian-Pu Yang. 2021. "Ultra-Low Frequency Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain Modulation in a Rat Model with Myogenous Temporomandibular Dysfunction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189906
APA StyleHsieh, Y.-L., Yang, C.-C., & Yang, N.-P. (2021). Ultra-Low Frequency Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain Modulation in a Rat Model with Myogenous Temporomandibular Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189906







