FluCell-SELEX Aptamers as Specific Binding Molecules for Diagnostics of the Health Relevant Gut Bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
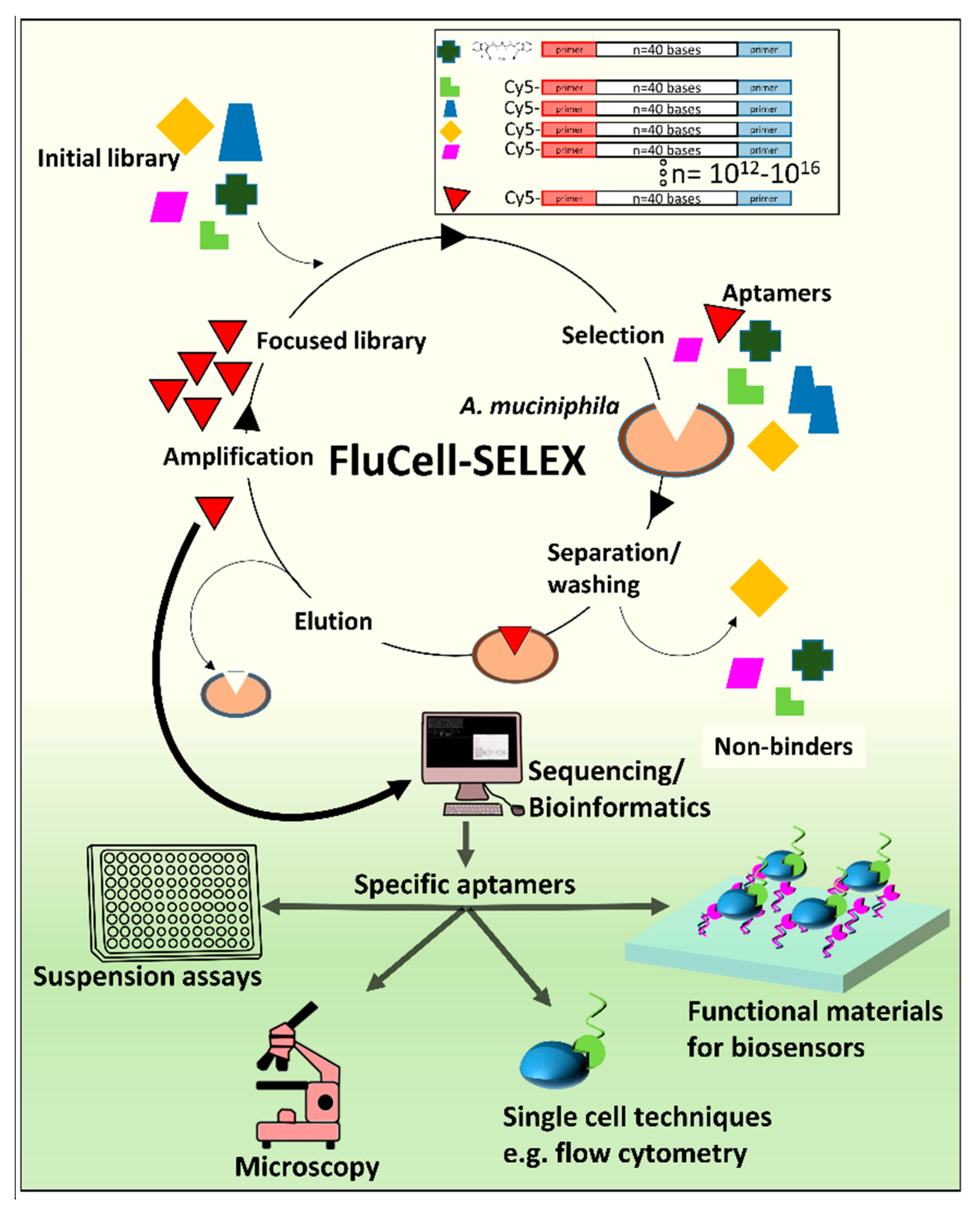
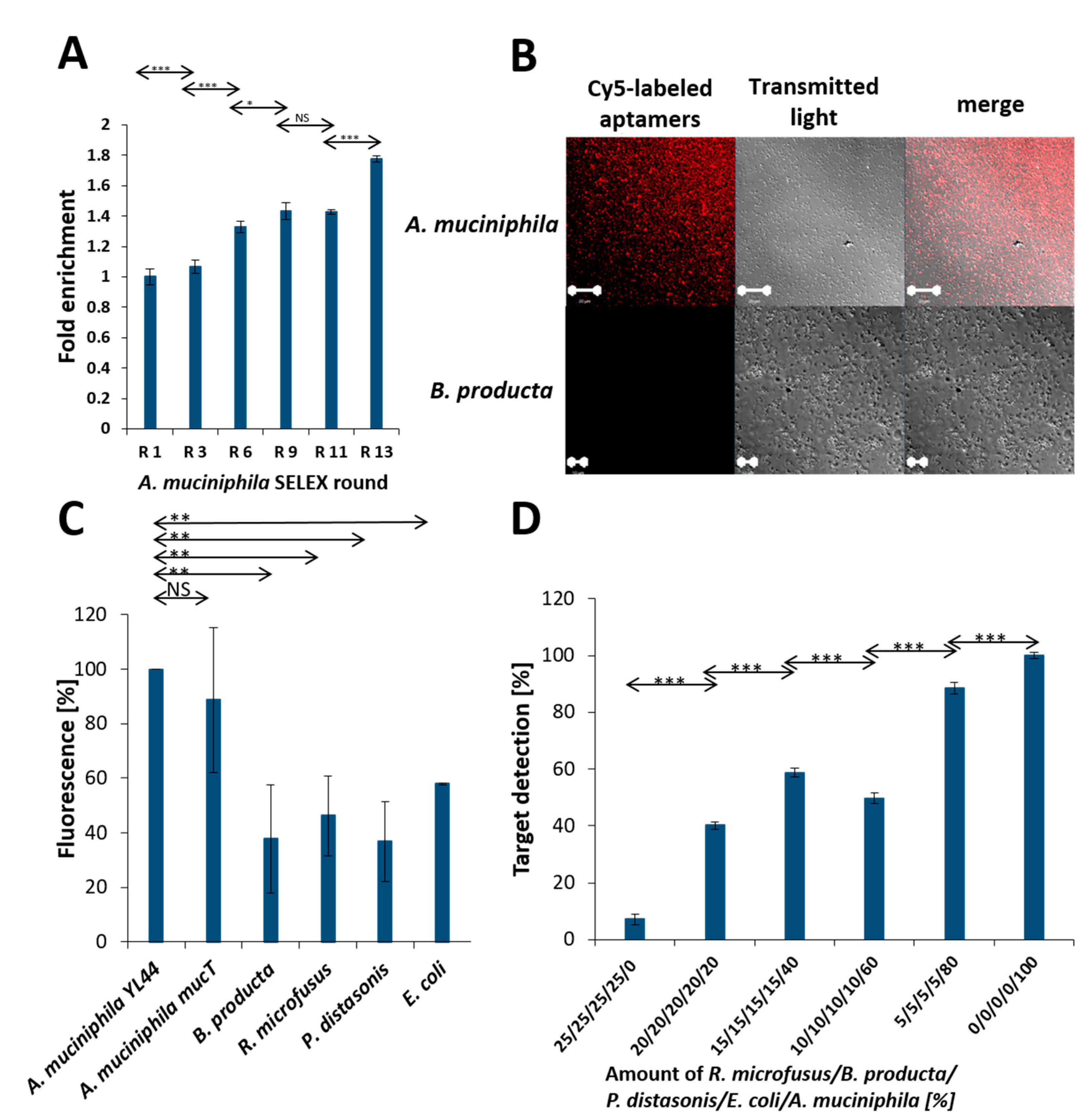
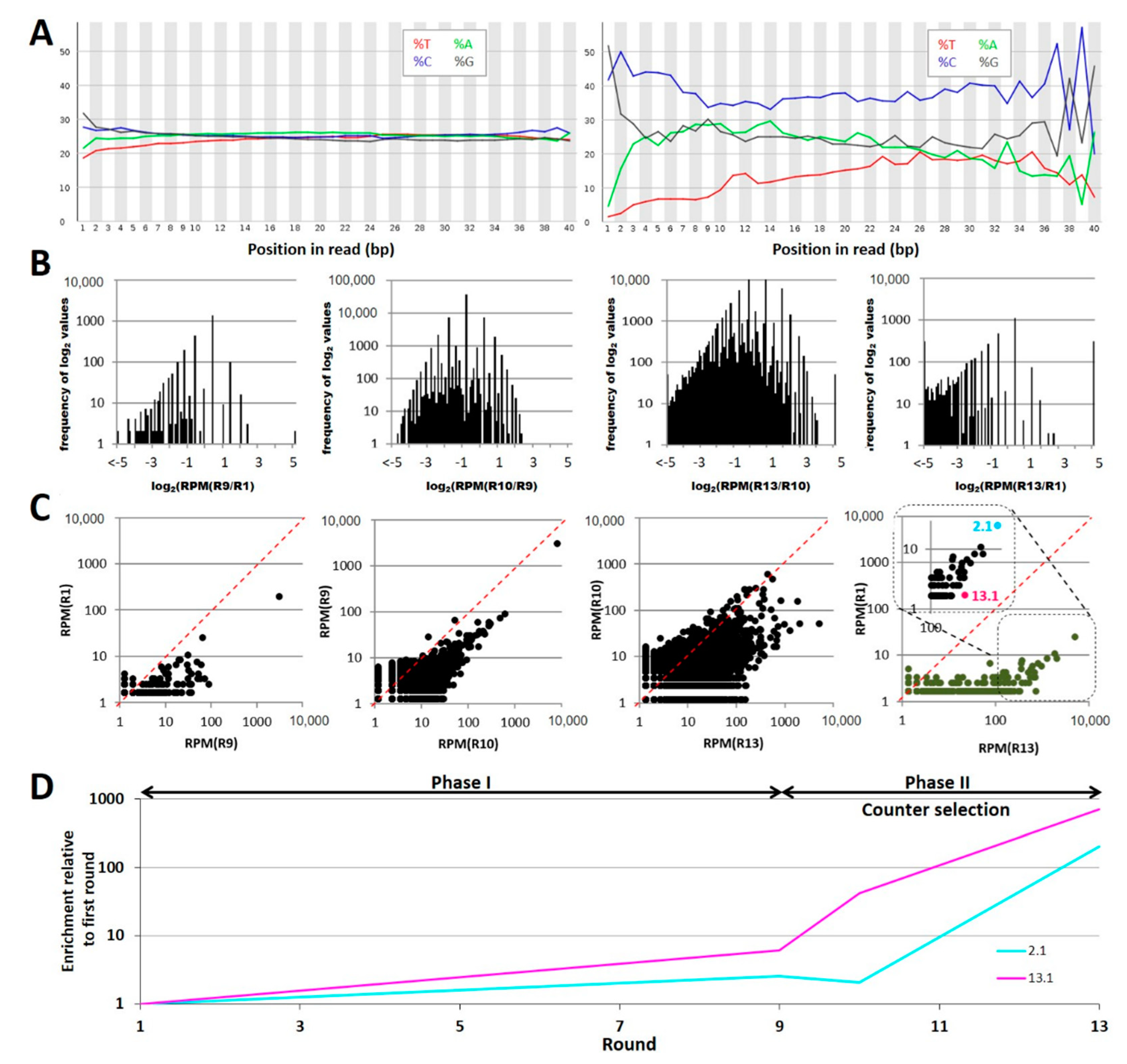
2.1. Evolution of the Focused Aptamer Library by FluCell-SELEX
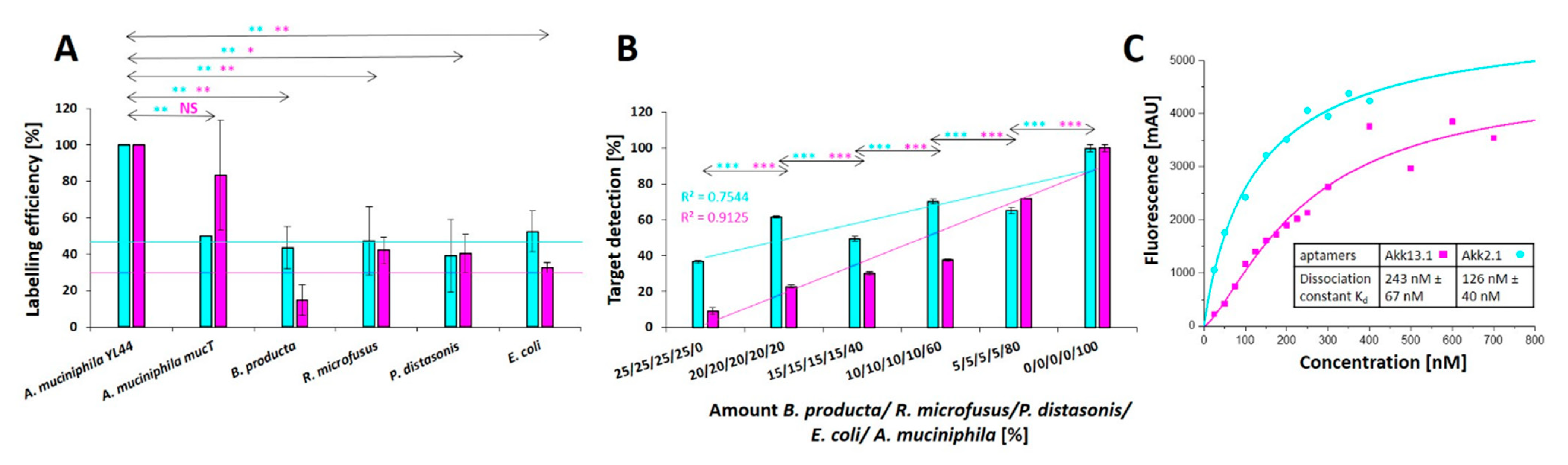
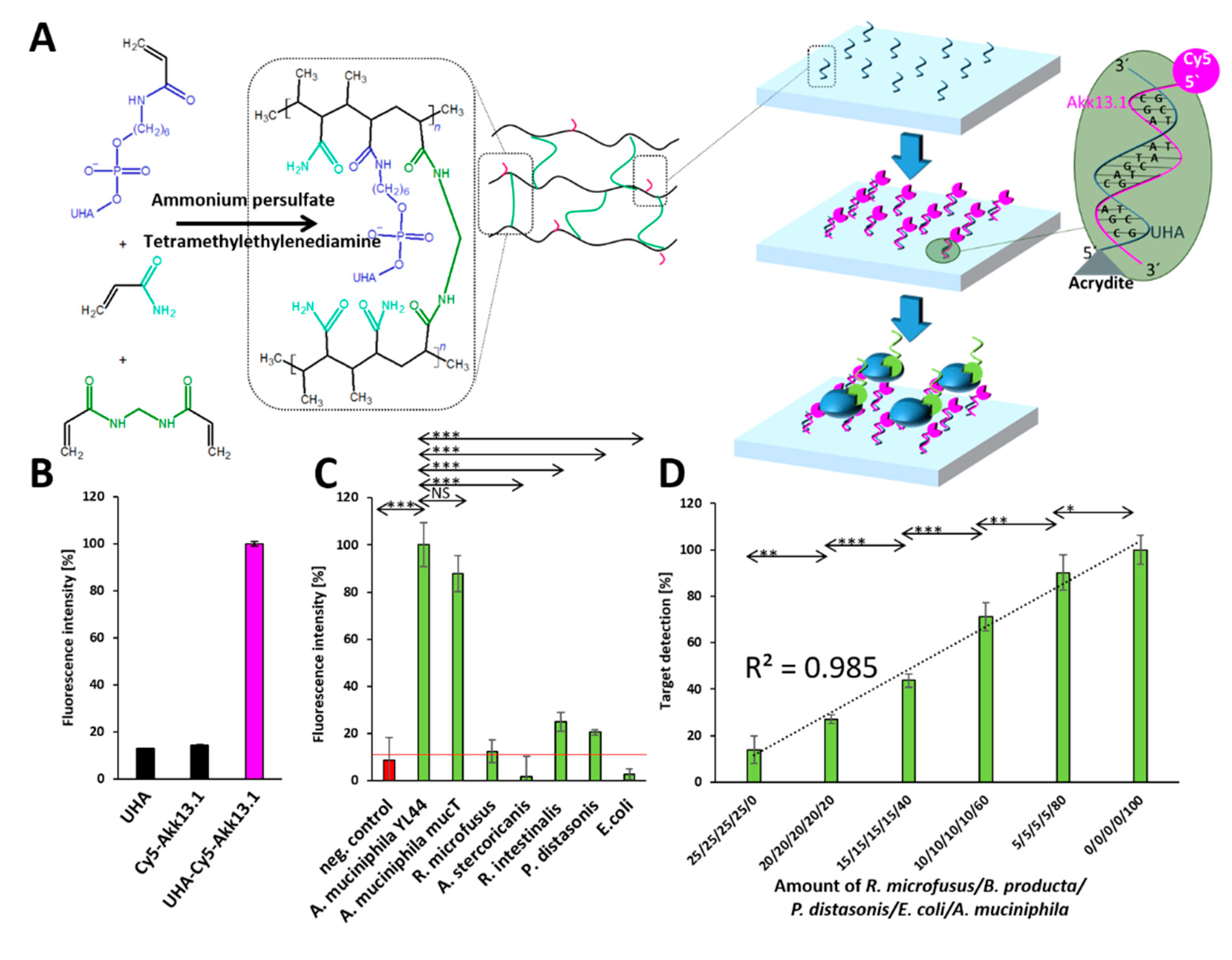
2.2. Selection of Individual Aptamers from the Library
2.3. Application Testing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cultivation of Bacteria
4.2. SELEX Procedure
4.3. Suspension Fluorimetric Labeling Assay
4.4. Next Generation Sequencing
4.5. Computational Analysis of NGS Data
4.6. Evaluation of Akk13.1 in Flow Cytometry
4.7. Evaluation of Akk13.1 in Microscopy
4.8. Evaluation of Akk13.1 for Biosensor Applications
4.9. Animal Housing and Breeding
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derrien, M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Plugge, C.M.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia municiphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; Van Den Berg, F.W.J.; Nielsen, D.S.; Andreasen, A.S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, L.H.; Jakobsen, M. Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chia, N.; Kalari, K.R.; Yao, J.Z.; Novotna, M.; Soldan, M.M.P.; Luckey, D.H.; Marietta, E.V.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Chen, X.; et al. Multiple sclerosis patients have a distinct gut microbiota compared to healthy controls. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Waubant, E.; Chehoud, C.; Kuczynski, J.; Desantis, T.Z.; Warrington, J.; Venkatesan, A.; Fraser, C.M.; Mowry, E.M. Gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis: Possible influence of immunomodulators. J. Investig. Med. 2015, 63, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z.; Deng, L.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, W.; Huang, D.; Peng, Y. Protective effects of Akkermansia muciniphila on cognitive deficits and amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harach, T.; Marungruang, N.; Duthilleul, N.; Cheatham, V.; Mc Coy, K.D.; Frisoni, G.; Neher, J.J.; Fåk, F.; Jucker, M.; Lasser, T.; et al. Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz-Buschart, A.; Pandey, U.; Wicke, T.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Janzen, A.; Sittig-Wiegand, E.; Trenkwalder, C.; Oertel, W.H.; Mollenhauer, B.; Wilmes, P. The nasal and gut microbiome in Parkinson’s disease and idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, K.R. An introduction to microbiome analysis for human biology applications. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, P. Beiträge zur Theorie und Praxis der histologischen Färbung. In The Collected Papers of Paul Ehrlich; Himmelweit, F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 29–64. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, A.; Markowitz, O. Introduction to reflectance confocal microscopy and its use in clinical practice. JAAD Case Rep. 2018, 4, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raoult, D.; Birg, M.L.; Scola, B.L.; Fournier, P.E.; Enea, M.; Lepidi, H.; Roux, V.; Piette, J.-C.; Vandenesch, F.; Vital-Durand, D.; et al. Cultivation of the Bacillus of Whipple’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renesto, P.; Crapoulet, N.; Ogata, H.; La Scola, B.; Vestris, G.; Claverie, J.M.; Raoult, D. Genome-based design of a cell-free culture medium for Tropheryma whipplei. Lancet 2003, 362, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E.; Drancourt, M. What does the future hold for clinical microbiology? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.C.; Lyons, C. Electrode Systems for Continuous Monitoring in Cardiovascular Surgery. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.H.; Lee, S.Y. Glucose biosensors: An overview of use in clinical practice. Sensors 2010, 10, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IUPAC Isotopomer. IUPAC Compend. Chem. Terminol. 2009, 31, 32–33. [CrossRef]
- Cross, G.H.; Reeves, A.A.; Brand, S.; Popplewell, J.F.; Peel, L.L.; Swann, M.J.; Freeman, N.J. A new quantitative optical biosensor for protein characterisation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMiguel-Ramos, M.; Díaz-Durán, B.; Escolano, J.M.; Barba, M.; Mirea, T.; Olivares, J.; Clement, M.; Iborra, E. Gravimetric biosensor based on a 1.3 GHz AlN shear-mode solidly mounted resonator. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casadio, S.; Lowdon, J.W.; Betlem, K.; Ueta, J.T.; Foster, C.W.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Development of a novel flexible polymer-based biosensor platform for the thermal detection of noradrenaline in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Clever, G.H.; Takezawa, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Tanaka, K.; Guo, X.; Shionoya, M. Direct conductance measurement of individual metallo-DNA duplexes within single-molecule break junctions. Angew. Chemie.-Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8886–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horáček, J.; Garrett, S.D.; Skládal, P.; Morgan, M.R.A. Characterization of the interactions between immobilized parathion and the corresponding recombinant scFv antibody using a piezoelectric biosensor. Food Agric. Immunol. 1998, 10, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassas, I.; Braiek, M.; Bonhomme, A.; Bessueille, F.; Rafin, G.; Majdoub, H.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Voltammetric glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase encapsulation in a chitosan-kappa-carrageenan polyelectrolyte complex. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 95, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Yang, S. Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiczek, D.; Raber, H.; Bodenberger, N.; Oswald, T.; Sahan, M.; Mayer, D.; Wiese, S.; Stenger, S.; Weil, T.; Rosenau, F. The Diversity of a Polyclonal FluCell-SELEX Library Outperforms Individual Aptamers as Emerging Diagnostic Tools for the Identification of Carbapenem Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Battig, M.R.; Wang, Y. Aptamer-based molecular recognition for biosensor development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, T. Aptamers and SELEX: The technology. World Pat. Inf. 2003, 25, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Finegold, S.M.; Song, Y.; Lawson, P.A. Reclassification of Clostridium coccoides, Ruminococcus hansenii, Ruminococcus hydrogenotrophicus, Ruminococcus luti, Ruminococcus productus and Ruminococcus schinkii as Blautia coccoides gen. nov., comb. nov., Blautia hansenii comb. nov., Blautia hydroge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, M. Next-generation analysis of deep sequencing data: Bringing light into the black box of SELEX experiments. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer Nature: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 1380, pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, K.K.; Chang, J.L.; Burke, D.H. FASTAptamer: A bioinformatic toolkit for high-throughput sequence analysis of combinatorial selections. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guilbault, G.G.; Hrabánková, E. Determination of urea in blood and urine with a ureasensitive electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1970, 52, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, N.; Gaddes, E.R.; Zhang, X.; Dong, C.; Wang, Y. A Drosera-bioinspired hydrogel for catching and killing cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domenyuk, V.; Gatalica, Z.; Santhanam, R.; Wei, X.; Stark, A.; Kennedy, P.; Toussaint, B.; Levenberg, S.; Wang, J.; Xiao, N.; et al. Poly-ligand profiling differentiates trastuzumab-treated breast cancer patients according to their outcomes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumstummler, A.; Lehmann, D.; Janjic, N.; Ochsner, U.A. Specific capture and detection of Staphylococcus aureus with high-affinity modified aptamers to cell surface components. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, S.H.; Jaykus, L.A. Nucleic acid aptamers for capture and detection of Listeria spp. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovskaya, O.S.; Savitskaya, A.G.; Zamay, T.N.; Reshetneva, I.T.; Zamay, G.S.; Erkaev, E.N.; Wang, X.; Wehbe, M.; Salmina, A.B.; Perianova, O.V.; et al. Development of bacteriostatic DNA aptamers for salmonella. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenyuk, V.; Zhong, Z.; Stark, A.; Xiao, N.; O’Neill, H.A.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Tinder, T.T.; Tonapi, S.; Duncan, J.; et al. Plasma Exosome Profiling of Cancer Patients by a Next Generation Systems Biology Approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, T.; O’Neill, H.A.; Logie, S.C.; Fowler, K.M.; Duncan, J.E.; Rosenow, M.; Bondre, A.S.; Tinder, T.; Maher, V.; Zarkovic, J.; et al. ADAPT identifies an ESCRT complex composition that discriminates VCaP from LNCaP prostate cancer cell exosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 4013–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiczek, D.; Bodenberger, N.; Rosenau, F. Aptamers as promising agents in diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Antimicrob. Res. Nov. Bioknowledge Educ. Programs 2017, 6, 368–378. [Google Scholar]
- Hahnke, R.L.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; García-López, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Huntemann, M.; Ivanova, N.N.; Woyke, T.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome-based taxonomic classification of Bacteroidetes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneuchi, C.; Mitsuoka, T. Bacteroides microfusus, a New Species from the Intestines of Calves, Chickens, and Japanese Quails. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1979, 29, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, M.D.; Shah, H.N.; Mitsuoka, T. Reclassification of Bacteroides microfusus (Kaneuchi and Mitsuoka) in a New Genus Rikenella, as Rikenella microfusus comb. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1985, 6, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, M.; Benno, Y. Reclassification of Bacteroides distasonis, Bacteroides goldsteinii and Bacteroides merdae as Parabacteroides distasonis gen. nov., comb. nov., Parabacteroides goldsteinii comb. nov and Parabacteroides merdae comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggerth, A.H.; Gagnon, B.H. The Bacteroides of Human Feces. J. Bacteriol. 1933, 25, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tolle, F.; Mayer, G. Preparation of SELEX samples for next-generation sequencing. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer Nature: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 1380, pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S. FastQC-A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Gordon, A.; Hannon, G.J. Gordon FASTX-Toolkit. 2014. Available online: http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Round | Index 5′ → 3′ | Forward Primer 5′ → 3′ | Reverse Primer 5′ → 3′ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ATC ACG | TCAGTCGTAT ATCACG ACGATGATACTC GGACTGTAGGGAAGAGAAGGACATATGAT | GCTATGTACT CGTGAT TCTCGTAGTTCA AGCGACTCAAGTGGTCATGTACTAGTCAA |
| 9 | CGA TGT | TCACTCGTAT CGATGT ACGATGATACTC GGACTGTAGGGAAGAGAAGGACATATGAT | GCTATGTACT ACATCG TCTCGTAGTTCA AGCGACTCAAGTGGTCATGTACTAGTCAA |
| 10 | TTA GGC | TCACTCGTAT TTAGGC ACGATGATACTC GGACTGTAGGGAAGAGAAGGACATATGAT | GCTATGTACT GCCTAA TCTCGTAGTTCA AGCGACTCAAGTGGTCATGTACTAGTCAA |
| 13 | TGA CCA | TCACTCGTAT TGAACCA ACGATGATACTC GGACTGTAGGGAAGAGAAGGACATATGAT | GCTATGTACT TGGTCA TCTCGTAGTTCA AGCGACTCAAGTGGTCATGTACTAGTCAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raber, H.F.; Kubiczek, D.H.; Bodenberger, N.; Kissmann, A.-K.; D’souza, D.; Xing, H.; Mayer, D.; Xu, P.; Knippschild, U.; Spellerberg, B.; et al. FluCell-SELEX Aptamers as Specific Binding Molecules for Diagnostics of the Health Relevant Gut Bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910425
Raber HF, Kubiczek DH, Bodenberger N, Kissmann A-K, D’souza D, Xing H, Mayer D, Xu P, Knippschild U, Spellerberg B, et al. FluCell-SELEX Aptamers as Specific Binding Molecules for Diagnostics of the Health Relevant Gut Bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910425
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaber, Heinz Fabian, Dennis Horst Kubiczek, Nicholas Bodenberger, Ann-Kathrin Kissmann, Deena D’souza, Hu Xing, Daniel Mayer, Pengfei Xu, Uwe Knippschild, Barbara Spellerberg, and et al. 2021. "FluCell-SELEX Aptamers as Specific Binding Molecules for Diagnostics of the Health Relevant Gut Bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910425
APA StyleRaber, H. F., Kubiczek, D. H., Bodenberger, N., Kissmann, A.-K., D’souza, D., Xing, H., Mayer, D., Xu, P., Knippschild, U., Spellerberg, B., Weil, T., & Rosenau, F. (2021). FluCell-SELEX Aptamers as Specific Binding Molecules for Diagnostics of the Health Relevant Gut Bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910425







