Pro-Apoptotic and Immunotherapeutic Effects of Carbon Nanotubes Functionalized with Recombinant Human Surfactant Protein D on Leukemic Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
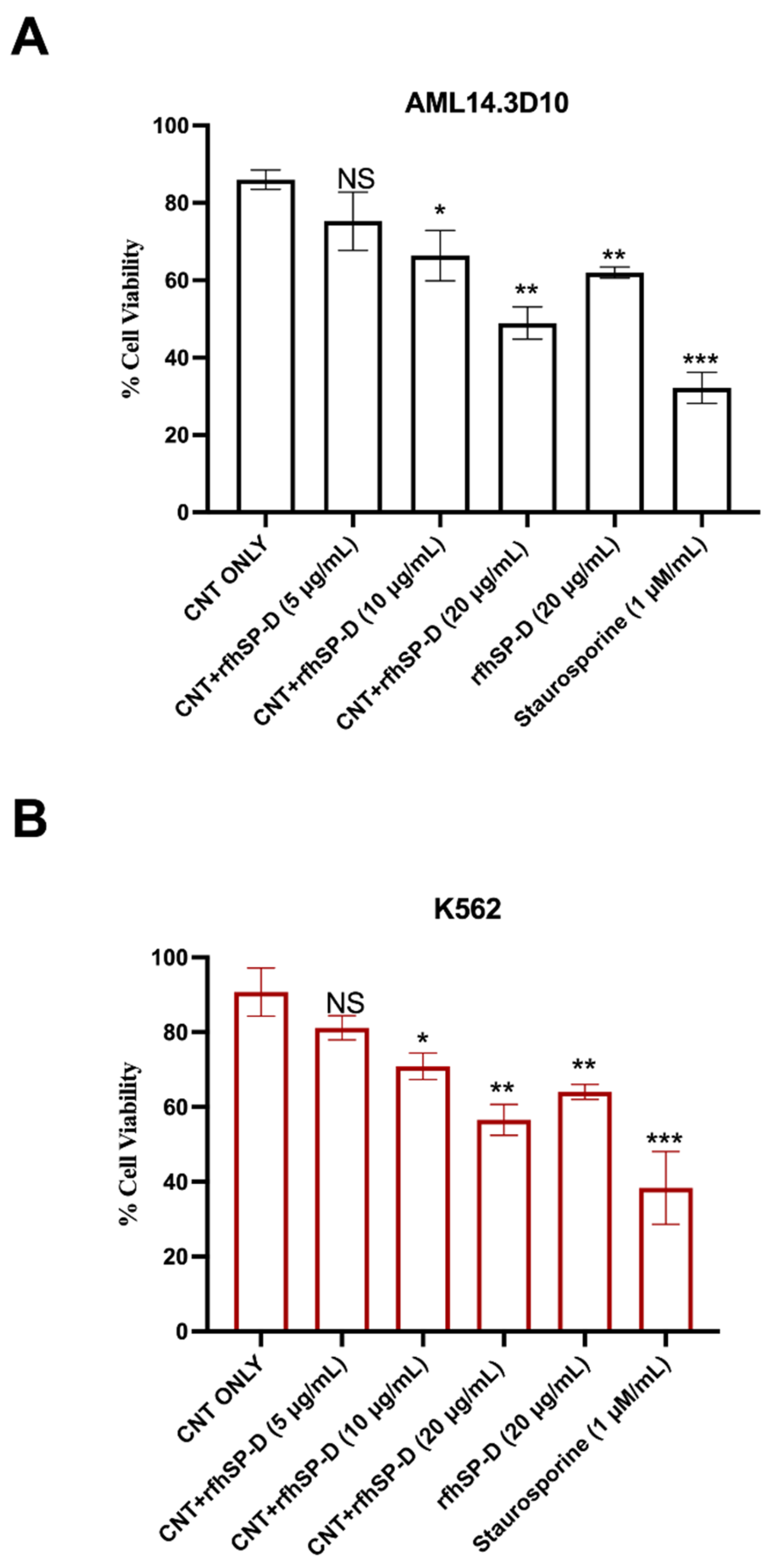
2.1. CNT + rfhSP-D Treatment Reduces Cell Viability of AML14.3D10 and K562 Leukemic Cell Lines
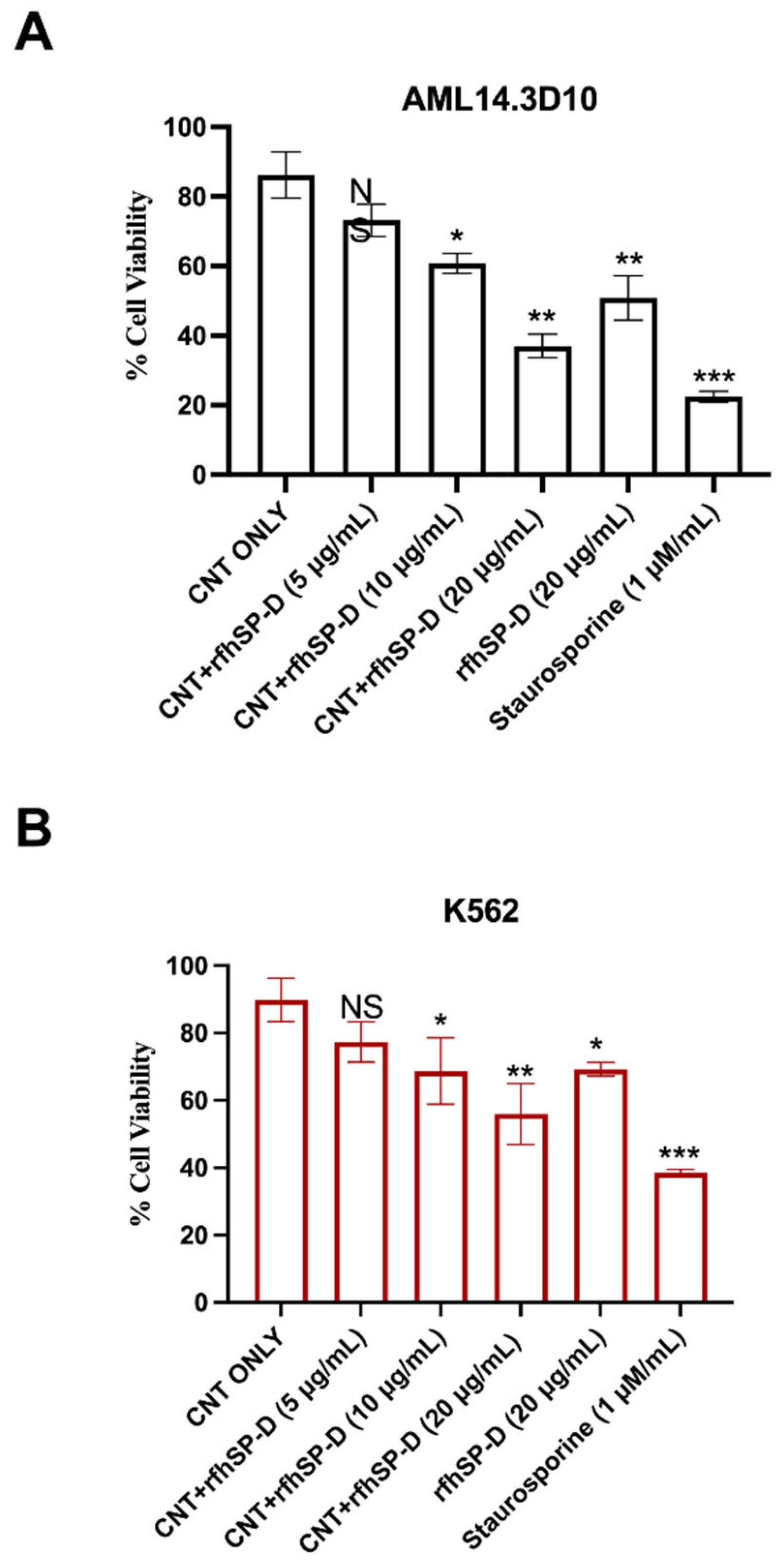
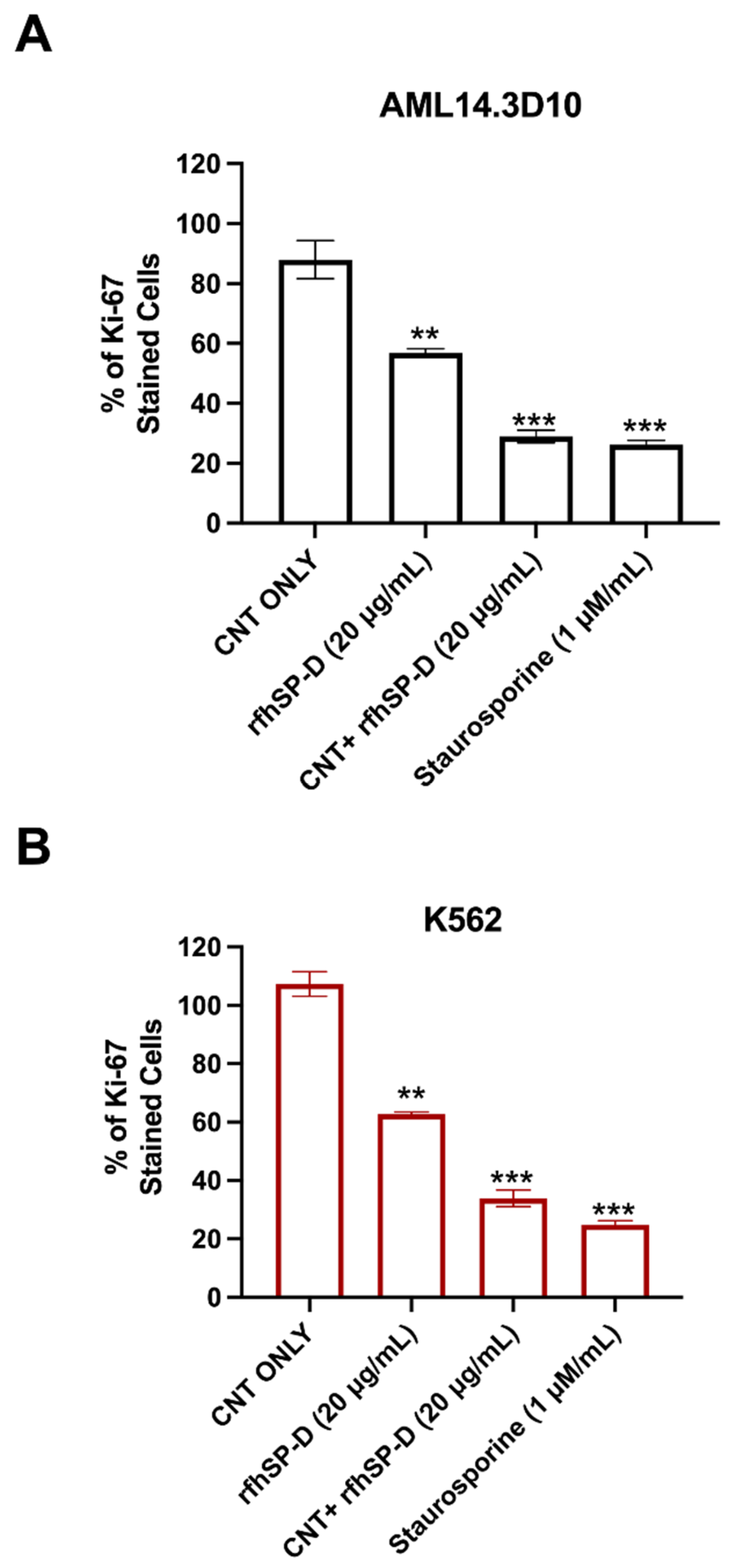
2.2. Proliferation of AML14.3D10 and K562 Cell Lines Is Reduced following CNT + rfhSP-D Treatment
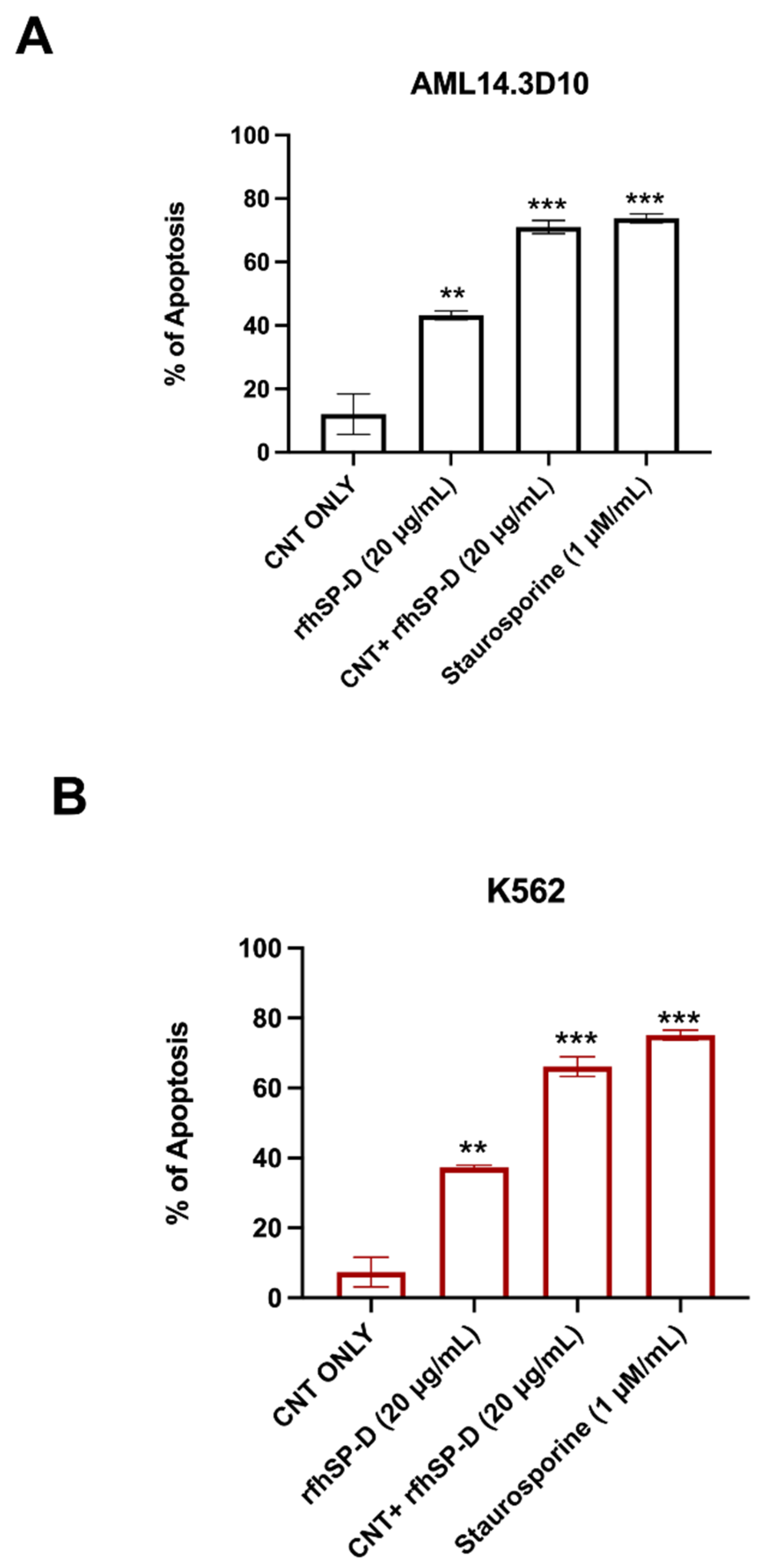
2.3. Apoptosis Induction by CNT + rfhSP-D in AML14.3D10 and K562 Cell Lines
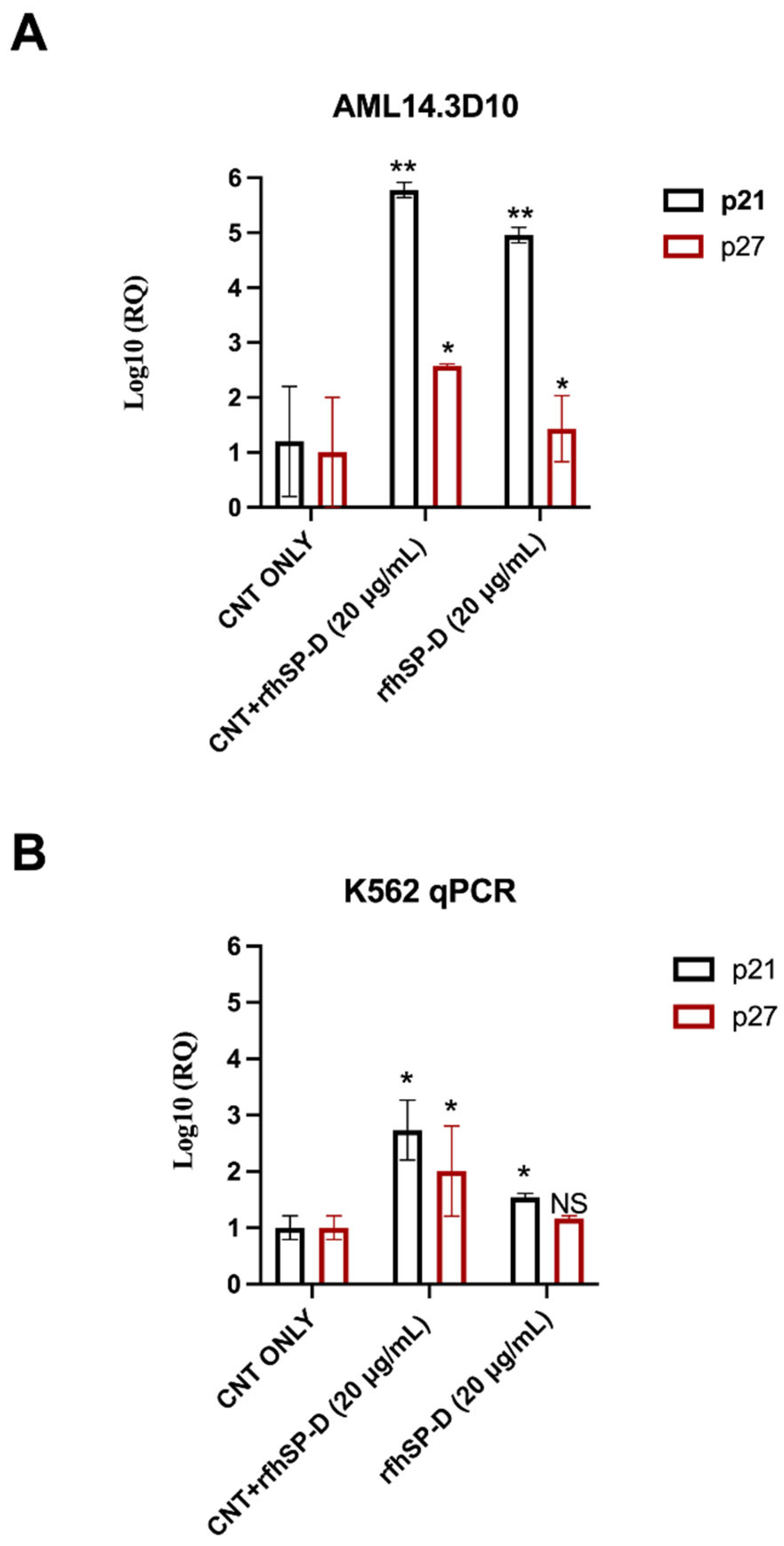
2.4. Up-Regulation of Cell-Cycle Inhibitors by CNT + rfhSP-D Treatment
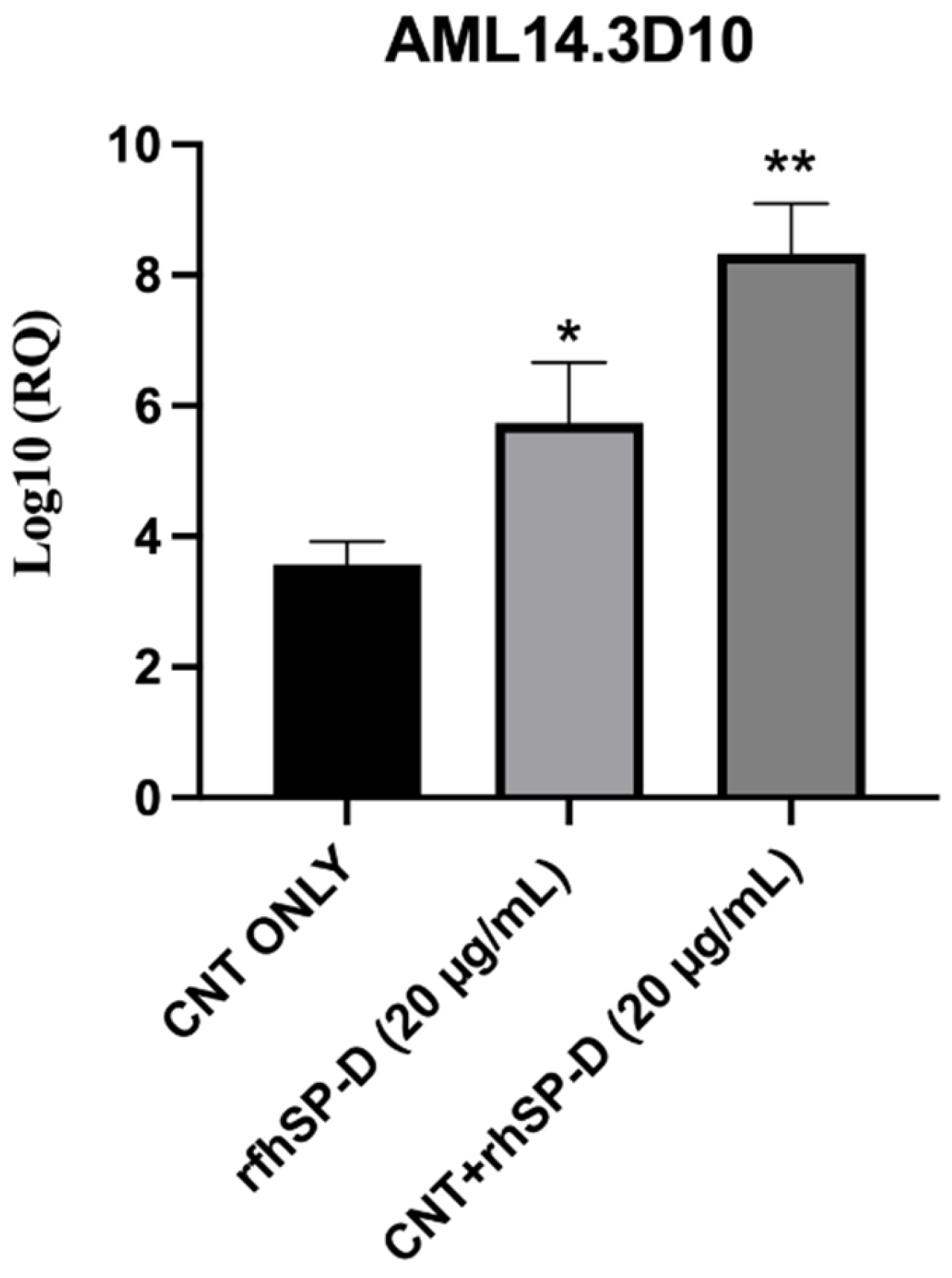
2.5. rfhSP-D Upregulates p53 Expression in AML14.3D10 Cell Line
2.6. Apoptosis Induction in AML14.3D10 and K562 Cells by rfhSP-D-CNT via Intrinsic Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Dispersion and Functionalization of CNTs
4.3. Expression and Purification of rfhSP-D
4.4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
4.5. Trypan-Blue-Dye Exclusion Assay
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Caspase-3/7 Analysis
4.9. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boraschi, D.; Castellano, L.R.C.; Italiani, P. Interaction of Nanomaterials with the Immune System: Role in Nanosafety and Nanomedicine. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvador-Morales, C.; Flahaut, E.; Sim, E.; Sloan, J.; Green, M.L.; Sim, R.B. Complement activation and protein adsorption by carbon nanotubes. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.H.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Nurunnabi, M.; Li, L.; Khan, H.A.; Cho, K.J.; Huh, K.M.; Lee, Y. Hybrid photoactive nanomaterial composed of gold nanoparticles, pheophorbide-A and hyaluronic acid as a targeted bimodal phototherapy. Macromol. Res. 2015, 23, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.E.; Bakhiet, A.O.; Khan, A.; Khan, H.A. Recent trends in biomedical applications of nanomaterials. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2018, 15, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafiujjaman, M.; Khan, H.A.; Lee, Y.K. Peptide-influenced graphene quantum dots on iron oxide nanoparticles for dual imaging of lung cancer cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Sakharkar, M.; Nayak, A.; Kishore, U.; Khan, A. Nanoparticles for biomedical applications. In Nanobiomaterials: Nanostructured Materials for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 357–384. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Hobson, D.; Hydbring, P. Nanoparticles for immune system targeting. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Kesharwani, P.; Jain, N.K. Biomedical Applications and Toxicological Aspects of Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2018, 35, 293–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardharajula, S.; Ali, S.Z.; Tiwari, P.M.; Eroglu, E.; Vig, K.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Functionalized carbon nanotubes: Biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5361–5374. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Tabakman, S.; Welsher, K.; Dai, H. Carbon Nanotubes in Biology and Medicine: In vitro and in vivo Detection, Imaging and Drug Delivery. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 85–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Tierce, N.T.; Bekyarova, E.; Bardeen, C.J. Protection of Molecular Microcrystals by Encapsulation under Single-Layer Graphene. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8129–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, E.; Wright, J.R. Surfactant proteins A and D and pulmonary host defense. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 521–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, E.C. Surfactant protein-D and pulmonary host defense. Respir. Res. 2000, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastva, A.M.; Wright, J.R.; Williams, K.L. Immunomodulatory roles of surfactant proteins A and D: Implications in lung disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2007, 4, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nayak, A.; Dodagatta-Marri, E.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Kishore, U. An insight into the diverse roles of surfactant proteins, SP-A and SP-D in innate and adaptive immunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murugaiah, V.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Kishore, U. Collectins: Innate Immune Pattern Recognition Molecules. Lectin Host Def. Microb. Infect. 2020, 1204, 75–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, A.; Riaz, M.S.; Murugaiah, V.; Varghese, P.M.; Singh, S.K.; Kishore, U. A recombinant fragment of human surfactant protein D induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cell lines via fas-mediated pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Riaz, M.S.; Singh, S.K.; Kishore, U. Human surfactant protein D suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating TGF-β. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.; Murugaiah, V.; Sotiriadis, G.; Kaur, A.; Jeyaneethi, J.; Sturniolo, I.; Alhamlan, F.; Chatterjee, J.; Hall, M.; Kishore, U. Surfactant protein D as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, G.; Prakash, G.; Murthy, V.; Sable, N.; Menon, S.; Alrokayan, S.; Khan, H.A.; Murugaiah, V.; Bakshi, G.; Kishore, U. Human SP-D acts as an innate immune surveillance molecule against androgen-responsive and androgen-resistant prostate cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, L.; Pandit, H.; Madan, T.; Gautam, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Warke, H.; Sundaram, C.S.; Sirdeshmukh, R.; Sarma, P.U.; Kishore, U.; et al. Human surfactant protein D alters oxidative stress and HMGA1 expression to induce p53 apoptotic pathway in eosinophil leukemic cell line. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ariki, S.; Asakawa, D.; Tajiri, M.; Wada, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nishitani, C.; Takamiya, R.; Saito, A. Surfactant protein D suppresses lung cancer progression by downregulation of epidermal growth factor signaling. Oncogene 2015, 34, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, M.; Ding, P.; Mackay, R.M.; Deb, R.; Mckenzie, Z.; Kendall, K.; Madsen, J.; Clark, H. Surfactant protein D (SP-D) alters cellular uptake of particles and nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruge, C.A.; Schaefer, U.F.; Herrmann, J.; Kirch, J.; Canadas, O.; Echaide, M.; Perez-Gil, J.; Casals, C.; Muller, R.; Lehr, C.M. The interplay of lung surfactant proteins and lipids assimilates the macrophage clearance of nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, G.; Hampel, S.; Klingeler, R.; Puoci, F.; Iemma, F.; Curcio, M.; Parisi, O.I.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Picci, N.; Leonhardt, A.; et al. Antioxidant multi-walled carbon nanotubes by free radical grafting of gallic acid: New materials for biomedical applications. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pondman, K.M.; Paudyal, B.; Sim, R.B.; Kaur, A.; Kouser, L.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Jones, L.A.; Salvador-Morales, C.; Khan, H.A.; Ten Haken, B.; et al. Pulmonary surfactant protein SP-D opsonises carbon nanotubes and augments their phagocytosis and subsequent pro-inflammatory immune response. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pondman, K.M.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Paudyal, B.; Shamji, M.H.; Switzer, A.; Pathan, A.A.; Abozaid, S.M.; Ten Haken, B.; Stenbeck, G.; Sim, R.B.; et al. Complement Deposition on Nanoparticles Can Modulate Immune Responses by Macrophage, B and T Cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.A.; Paul, C.C. The AML14 and AML14.3D10 cell lines: A long-overdue model for the study of eosinophils and more. Stem Cells 1998, 16, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palucka, A.K.; Coussens, L.M. The Basis of Oncoimmunology. Cell 2016, 164, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vesely, M.D.; Kershaw, M.H.; Schreiber, R.D.; Smyth, M.J. Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, A.G.; Janicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaiah, V.; Agostinis, C.; Varghese, P.M.; Belmonte, B.; Vieni, S.; Alaql, F.A.; Alrokayan, S.H.; Khan, H.A.; Kaur, A.; Roberts, T.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid Present in the Tumor Microenvironment Can Negate the Pro-apototic Effect of a Recombinant Fragment of Human Surfactant Protein D on Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, W.J.; Mcphillips, K.A.; Dickinson, M.G.; Linderman, D.J.; Morimoto, K.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Oldham, K.M.; Vandivier, R.W.; Henson, P.M.; Gardai, S.J. Surfactant proteins A and D suppress alveolar macrophage phagocytosis via interaction with SIRP alpha. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, G.; Sathe, G.; Kundu, I.; Biswas, B.; Gautam, P.; Alkahtani, S.; Idicula-Thomas, S.; Sirdeshmukh, R.; Kishore, U.; Madan, T. Membrane Interactome of a Recombinant Fragment of Human Surfactant Protein D Reveals GRP78 as a Novel Binding Partner in PC3, a Metastatic Prostate Cancer Cell Line. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| 18S | 5′-ATGGCCGTTCTTAGTTGGTG-3′ | 5′-CGCTGAGCCAGTCAGTGTAG-3′ |
| P53 | 5′-AGCACTGTCCAACAACACCA-3′ | 5′-CTTCAGGTGGCTGGAGTGAG-3′ |
| p21 | 5′-TGGAGACTCTCAGGGTCGAAA-3′ | 5′-CGGCGTTTGGAGTGGTAGAA-3′ |
| p27 | 5′-CCGGTGGACCACGAAGAGT-3′ | 5′-GCTCGCCTCTTCCATGTCTC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, H.A.; Kishore, U.; Alsulami, H.M.; Alrokayan, S.H. Pro-Apoptotic and Immunotherapeutic Effects of Carbon Nanotubes Functionalized with Recombinant Human Surfactant Protein D on Leukemic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910445
Khan HA, Kishore U, Alsulami HM, Alrokayan SH. Pro-Apoptotic and Immunotherapeutic Effects of Carbon Nanotubes Functionalized with Recombinant Human Surfactant Protein D on Leukemic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910445
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Haseeb A., Uday Kishore, Hamed M. Alsulami, and Salman H. Alrokayan. 2021. "Pro-Apoptotic and Immunotherapeutic Effects of Carbon Nanotubes Functionalized with Recombinant Human Surfactant Protein D on Leukemic Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910445
APA StyleKhan, H. A., Kishore, U., Alsulami, H. M., & Alrokayan, S. H. (2021). Pro-Apoptotic and Immunotherapeutic Effects of Carbon Nanotubes Functionalized with Recombinant Human Surfactant Protein D on Leukemic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910445







