Patidegib in Dermatology: A Current Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Study Design
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Phase I Trials
3.2. Phase II Trials
3.2.1. Completed
3.2.2. Uncompleted
3.3. Phase III Trials
4. Discussion
4.1. Histopathological Considerations
4.2. Inefficacy of Sequential Hp Inhibitors Therapy
4.3. Patients with Comorbidities
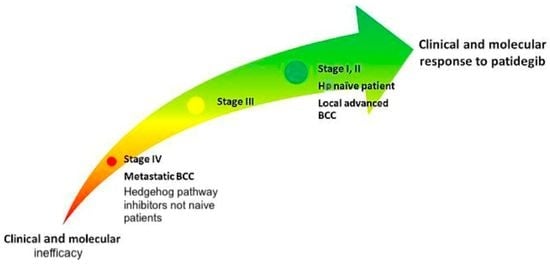
4.4. Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dika, E.; Scarfì, F.; Ferracin, M.; Broseghini, E.; Marcelli, E.; Bortolani, B.; Campione, E.; Riefolo, M.; Ricci, C.; Lambertini, M. Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.P.; Kus, K.J.B.; Ruiz, E. Basal Cell Carcinoma Review. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campione, E.; Di Prete, M.; Del Principe, I.; Diluvio, L.; Citarella, L.; Orlandi, A.; Chimenti, S.; Bianchi, L. Lack of efficacy of imiquimod in patients with basal cell carcinoma previously treated with rituximab for B cell lymphoma: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, L.; Orlandi, A.; Campione, E.; Angeloni, C.; Costanzo, A.; Spagnoli, L.G.; Chimenti, S. Topical treatment of basal cell carcinoma with tazarotene: A clinicopathological study on a large series of cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 151, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosio, T.; Di Prete, M.; Gaziano, R.; Lanna, C.; Orlandi, A.; Di Francesco, P.; Bianchi, L.; Campione, E. Trifarotene: A Current Review and Perspectives in Dermatology. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, K.; Campione, E.; Micantonio, T.; Marulli, G.C.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Chimenti, S. Imiquimod Treatment of Superficial and Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma: 12-Week Open-Label Trial. Dermatol. Surg. 2006, 31, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diluvio, L.; Bavetta, M.; Di Prete, M.; Orlandi, A.; Bianchi, L.; Campione, E. Dermoscopic monitoring of efficacy of ingenol mebutate in the treatment of pigmented and non-pigmented basal cell carcinomas. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campione, E.; Di Prete, M.; Lozzi, F.; Lanna, C.; Spallone, G.; Mazzeo, M.; Cosio, T.; Rapanotti, C.; Dika, E.; Gaziano, R.; et al. High-Risk Recurrence Basal Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors and Review of the Literature. Chemotherapy 2020, 65, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosio, T.; Di Prete, M.; Campione, E. Arsenic Trioxide, Itraconazole, All-Trans Retinoic Acid and Nicotinamide: A Proof of Concept for Combined Treatments with Hedgehog Inhibitors in Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesiak, A.; Czuwara, J.; Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Kiprian, D.; Maj, J.; Owczarek, W.; Placek, W.; Rudnicka, L.; Rutkowski, P.; Sobjanek, M.; et al. Basal cell carcinoma. Diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations of Polish Dermatological Society. Dermatol. Rev. 2019, 106, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.H.; Siebold, C.; Rohatgi, R. Biochemical mechanisms of vertebrate hedgehog signaling. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeng, K.-S.; Chang, C.-F.; Lin, S.-S. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Organogenesis, Tumors, and Tumor Microenvironments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorlin, R.J. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma (Gorlin) syndrome. Genet. Med. 2004, 6, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramyan, J. Hedgehog Signaling and Embryonic Craniofacial Disorders. J. Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robarge, K.D.; Brunton, S.A.; Castanedo, G.M.; Cui, Y.; Dina, M.S.; Goldsmith, R.; Gould, S.E.; Guichert, O.; Gunzner, J.L.; Halladay, J.; et al. GDC-0449—A potent inhibitor of the hedgehog pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5576–5581, Erratum in 2010, 20, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Wu, X.; Jiang, J.; Gao, W.; Wan, Y.; Cheng, D.; Han, D.; Liu, J.; Englund, N.P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a Potent and Selective Smoothened Antagonist. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Axelson, M.; Liu, K.; Jiang, X.; He, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Kufrin, D.; Palmby, T.; Dong, Z.; Russell, A.M.; et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approval: Vismodegib for Recurrent, Locally Advanced, or Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2289–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casey, D.; Demko, S.; Shord, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, H.; He, K.; Putman, A.; Helms, W.S.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Sonidegib for Locally Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Raimondo, C.; Mazzeo, M.; Di Prete, M.; Lombardo, P.; Silvaggio, D.; Del Duca, E.; Bianchi, L.; Spallone, G. Efficacy of Vismodegib in pigmented basal cell carcinoma: Appearances are deceiving. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzmer, R.; Solomon, J.A. Hedgehog Pathway Inhibition for the Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PellePharm. News. Available online: https://pellepharm.com/news/ (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- European Medicines Agency. EMA/116423/2018—Annual Report of the European Medicines Agency. 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/orphan-designation/eu/3/18/1998-public-summary-opinion-orphan-designation-patidegib-treatment-naevoid-basal-cell-carcinoma_en.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Jimeno, A.; Weiss, G.J.; Miller, W.H.; Gettinger, S.; Eigl, B.; Chang, A.L.S.; Dunbar, J.; Devens, S.; Faia, K.; Skliris, G.; et al. Phase I Study of the Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor IPI-926 in Adult Patients with Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogenet, A.; Greillier, L.; Tomasini, P. The Value of Population Screening in Advancing Personalized Medicine in the Field of Lung Cancer. Pharm. Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.A.; Li, A.S.; Chang, A.L.S. Patient with Gorlin Syndrome and Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Refractory to Smoothened Inhibitors. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Trial of Patidegib Gel 2%, 4%, and Vehicle to Decrease the Number of Surgically Eligible Basal Cell Carcinomas in Gorlin Syn-Drome Patients—Full Text View. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02762084 (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Clinical Trial of Patidegib Gel 2%, 4%, and Vehicle Applied Once or Twice Daily to Decrease the GLI1 Biomarker in Sporadic Nodular Basal Cell Carcinomas—Full Text View. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02828111 (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Study of Patidegib Topical Gel, 2%, for the Reduction of Disease Burden of Persistently Developing Basal Cell Carcinomas in Patients with Non-Gorlin High Frequency BCC—Full Text View. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04155190 (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Extension Study of Patidegib Topical Gel, 2% in Subjects with Gorlin Syndrome (Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome)—Full Text View. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04308395 (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Study of Patidegib Topical Gel, 2%, for the Reduction of Disease Burden of Persistently Developing Basal Cell Carcinomas (BCCs) in Subjects with Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome (Gorlin Syndrome)—Full Text View. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03703310 (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Sinha, N.; Chowdhury, S.; Sarkar, R.R. Molecular basis of drug resistance in smoothened receptor: An in silico study of protein resistivity and specificity. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2020, 88, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pricl, S.; Cortelazzi, B.; Dal Col, V.; Marson, D.; Laurini, E.; Fermeglia, M.; Licitra, L.; Pilotti, S.; Bossi, P.; Perrone, F. Smoothened (SMO) receptor mutations dictate resistance to vismodegib in basal cell carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, S.; Sarin, K.; Whitson, R.J.; Li, J.R.; Kim, G.; Rezaee, M.; Ally, M.S.; Kim, J.; Yao, C.; Chang, A.L.S.; et al. Smoothened Variants Explain the Majority of Drug Resistance in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Evron, T.; Vardy, E.; Han, G.W.; Huang, X.-P.; Hufeisen, S.J.; Mangano, T.J.; Urban, D.J.; Katritch, V.; et al. Structural basis for Smoothened receptor modulation and chemoresistance to anticancer drugs. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, H.J.; Pau, G.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Modrusan, Z.; Januario, T.; Tsui, V.; Durham, A.B.; Dlugosz, A.A.; Haverty, P.M.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Smoothened Inhibitor Resistance in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Huang, X.-P.; Liu, W.; Siu, F.Y.; Roth, B.L.; Cherezov, V.; Stevens, R.C. Structure of the human smoothened receptor bound to an antitumour agent. Nature 2013, 497, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danial, C.; Sarin, K.Y.; Oro, A.E.; Chang, A.L.S. An Investigator-Initiated Open-Label Trial of Sonidegib in Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma Patients Resistant to Vismodegib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahrokni, A.; Tin, A.; Alexander, K.; Sarraf, S.; Afonso, A.; Filippova, O.; Harris, J.; Downey, R.J.; Vickers, A.J.; Korc-Grodzicki, B. Development and Evaluation of a New Frailty Index for Older Surgical Patients with Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e193545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Lewis, L.D.; Lorusso, P.; Maitland, M.; Chandra, P.; Cheeti, S.; Colburn, D.; Williams, S.; Simmons, B.; Graham, R.A. Pharmacokinetics and safety of vismodegib in patients with advanced solid malignancies and hepatic impairment. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekulic, A.; Migden, M.R.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Garbe, C.; Gesierich, A.; Lao, C.D.; Miller, C.; Mortier, L.; Murrell, D.F.; Hamid, O.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of vismodegib in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma: Final update of the pivotal ERIVANCE BCC study. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelblinger, P.; Lang, R. New developments in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma: Update on current and emerging treatment options with a focus on vismodegib. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 8327–8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Einolf, H.J.; Zhou, J.; Won, C.; Wang, L.; Rebello, S. A Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach to Predict Drug–Drug Interactions of Sonidegib (LDE225) with Perpetrators of CYP3A in Cancer Patients. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, A.; Fabbrocini, G.; Costa, C.; Scalvenzi, M. Sonidegib: Safety and Efficacy in Treatment of Advanced Basal Cell Carci-noma. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 10, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.J.; Gardner, D.; Beachy, P.A. Arsenic antagonizes the Hedgehog pathway by preventing ciliary accumulation and reducing stability of the Gli2 transcriptional effector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13432–13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piaserico, S.; Michelotto, A.; Frigo, A.C.; Alaibac, M. TLR7 Gln11Leu single nucleotide polymorphism and response to treatment with imiquimod in patients with basal cell carcinoma: A pilot study. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Drug Formulation | Timing (Daily; Weeks) | Clinical Outcome | Molecular Outcome | ISGTA Scale | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT 02828111 | Patidegib 2% gel | Once; 12 | −56.15% (48.14) | −56.3% (99.59) | 42.9 |
| Twice; 12 | −17.01% (36.87) | −42.51% (55.64) | 20.0 | ||
| Patidegib 4% gel | Once; 12 | −8.73% (46.6) | −3.24% (69.03) | 0 | |
| Twice; 12 | −18.41% (60.59) | −28.85% (46.23) | 16.7 | ||
| NCT 02762084 | Patidegib 2% gel | Twice; 26 | −51.29% (41.78) | −53.83% (27.2) | 33.3 |
| Twice; 14 | N/A | N/A | 33.3 | ||
| Patidegib 4% gel | Twice; 26 | −26.63% (41.27) | −20.69% (34.73) | 30.0 | |
| Twice; 14 | N/A | N/A | 13.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cosio, T.; Di Prete, M.; Di Raimondo, C.; Garofalo, V.; Lozzi, F.; Lanna, C.; Dika, E.; Orlandi, A.; Rapanotti, M.C.; Bianchi, L.; et al. Patidegib in Dermatology: A Current Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910725
Cosio T, Di Prete M, Di Raimondo C, Garofalo V, Lozzi F, Lanna C, Dika E, Orlandi A, Rapanotti MC, Bianchi L, et al. Patidegib in Dermatology: A Current Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910725
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosio, Terenzio, Monia Di Prete, Cosimo Di Raimondo, Virginia Garofalo, Flavia Lozzi, Caterina Lanna, Emi Dika, Augusto Orlandi, Maria Cristina Rapanotti, Luca Bianchi, and et al. 2021. "Patidegib in Dermatology: A Current Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910725
APA StyleCosio, T., Di Prete, M., Di Raimondo, C., Garofalo, V., Lozzi, F., Lanna, C., Dika, E., Orlandi, A., Rapanotti, M. C., Bianchi, L., & Campione, E. (2021). Patidegib in Dermatology: A Current Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910725