Establishment of Intestinal Organoid from Rousettus leschenaultii and the Susceptibility to Bat-Associated Viruses, SARS-CoV-2 and Pteropine Orthoreovirus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
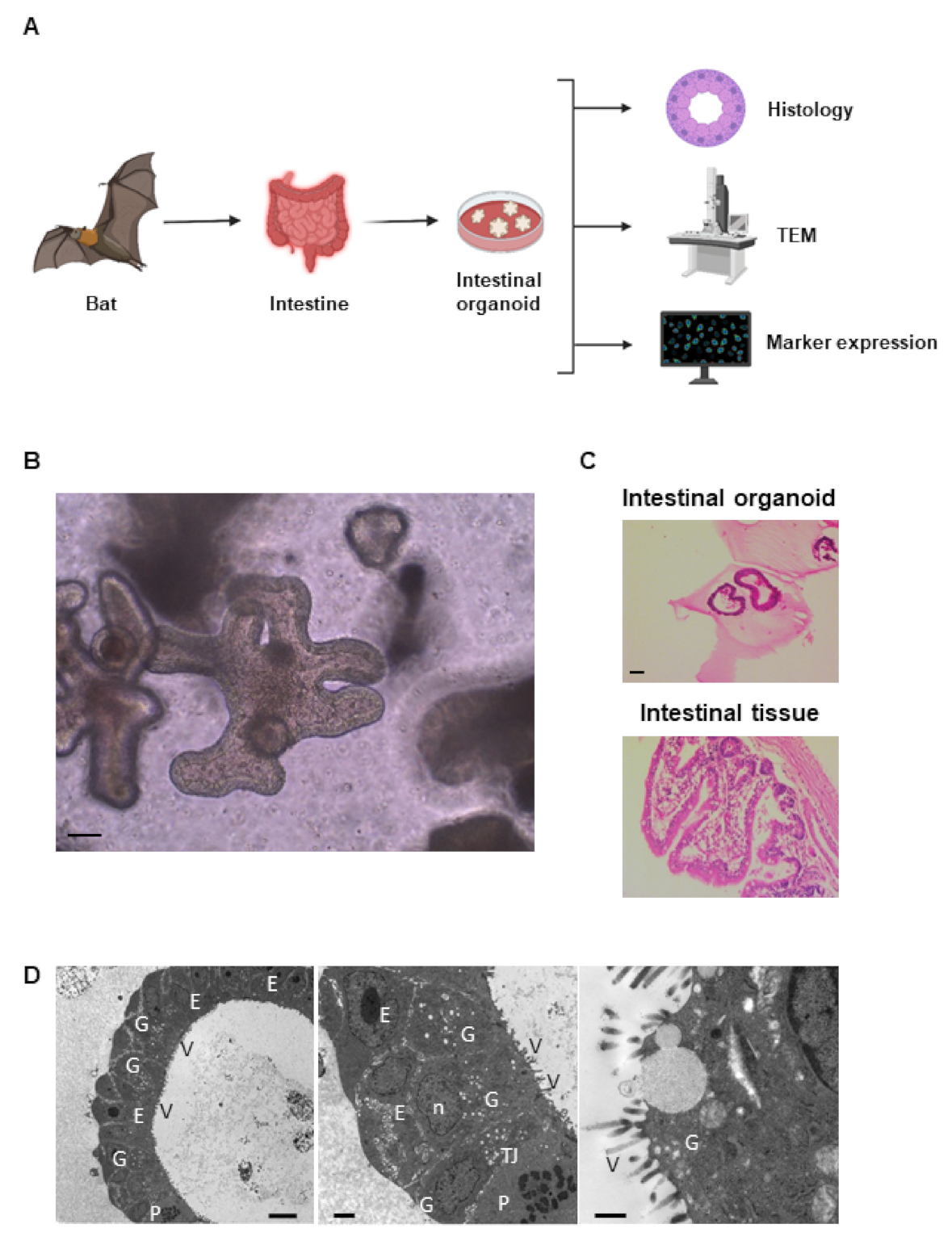
2.1. Establishment of Intestinal Organoid from Rousettus leschenaultii
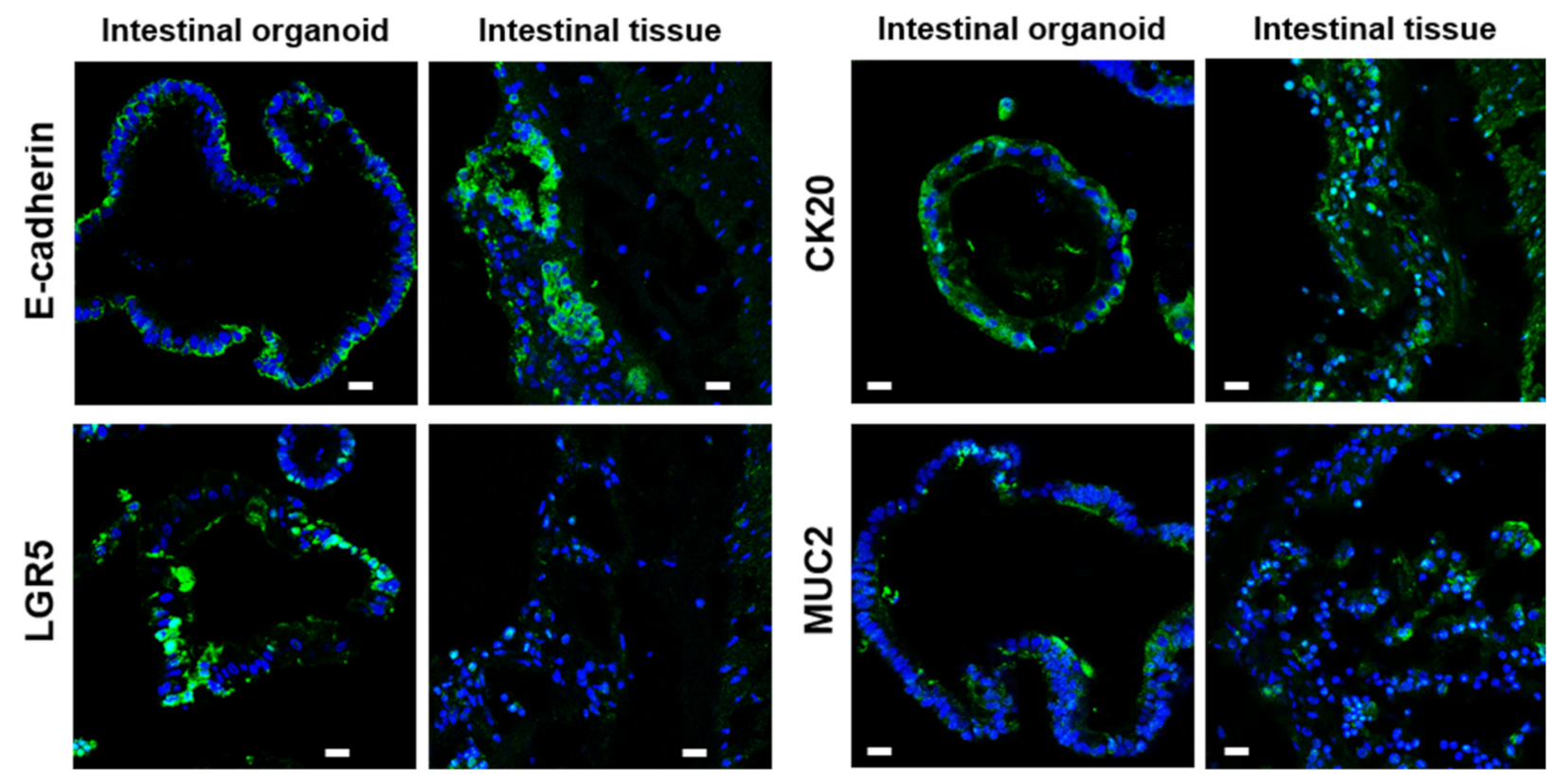
2.2. Characterization of Bat Organoid
2.3. Evaluation of Appropriate Growth and Maintenance Media for Rousette Bat Organoids
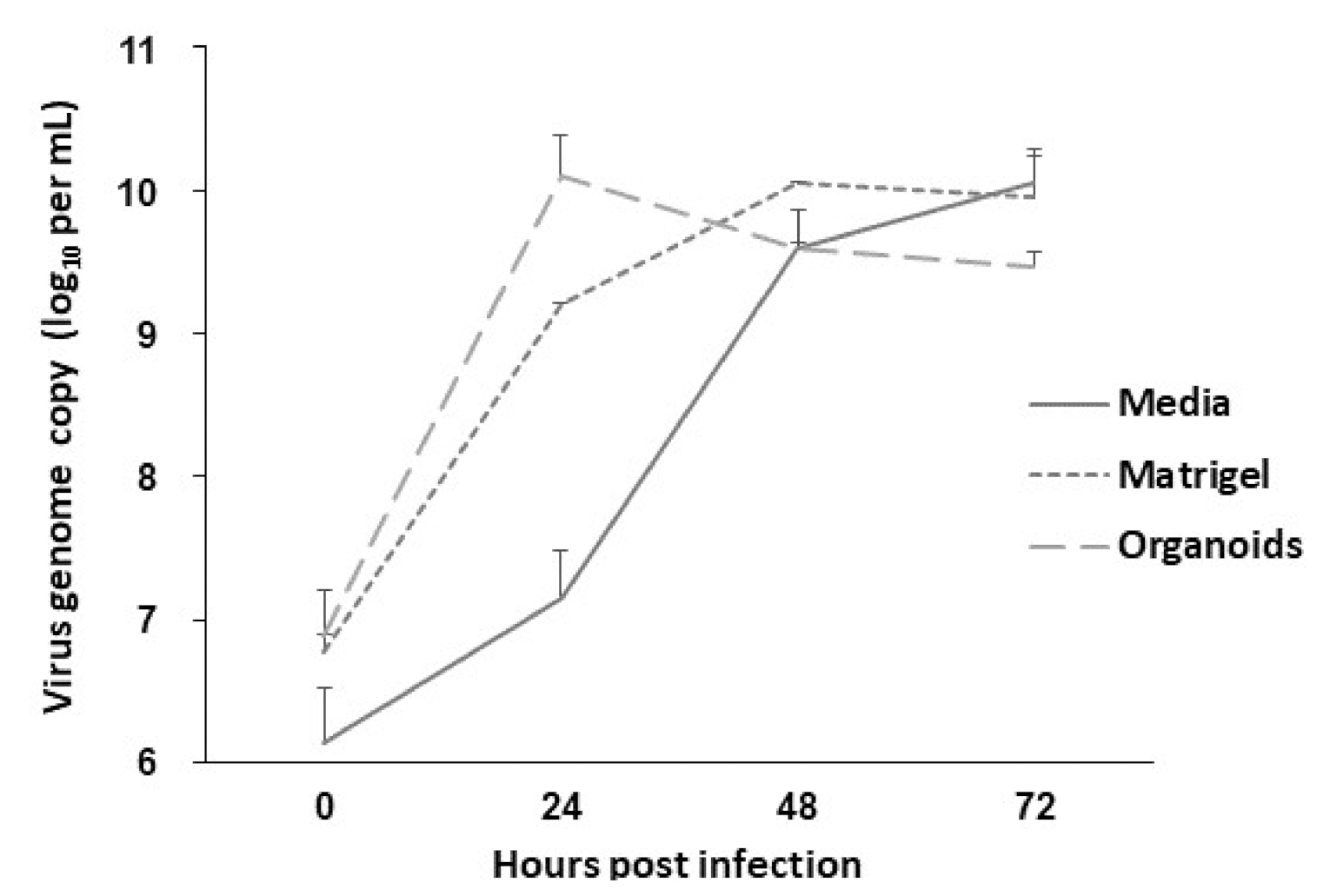
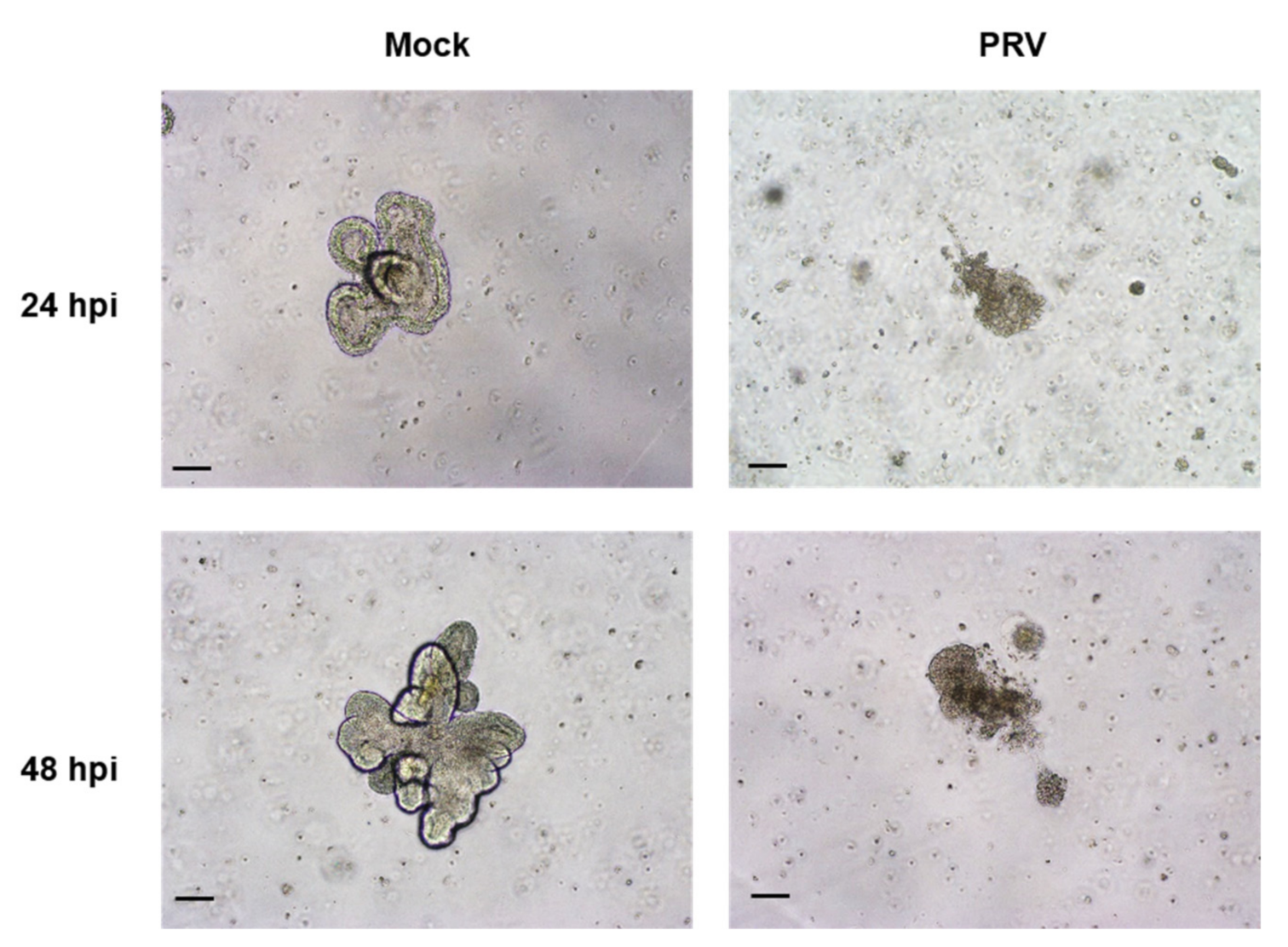
2.4. Susceptibility of the Organoids to SARS-CoV-2 and PRV
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Rousette Bat Tissues
4.2. Establishment of Bat Intestinal Organoid
4.3. Investigation of Suitable Supplementation for Organoid Culture
4.4. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Examination
4.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.6. Sensitivity of Organoid to SARS-CoV-2 and Pteropine Orthoreovirus
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munster, V.J.; Adney, D.R.; van Doremalen, N.; Brown, V.R.; Miazgowicz, K.L.; Milne-Price, S.; Bushmaker, T.; Rosenke, R.; Scott, D.; Hawkinson, A.; et al. Replication and shedding of MERS-CoV in Jamaican fruit bats (Artibeus jamaicensis). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosten, C.; Gunther, S.; Preiser, W.; van der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.R.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.F.; Anderson, D.E. Viruses in bats and potential spillover to animals and humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coltart, C.E.; Lindsey, B.; Ghinai, I.; Johnson, A.M.; Heymann, D.L. The Ebola outbreak, 2013–2016: Old lessons for new epidemics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigott, D.M.; Golding, N.; Mylne, A.; Huang, Z.; Weiss, D.J.; Brady, O.J.; Kraemer, M.U.; Hay, S.I. Mapping the zoonotic niche of Marburg virus disease in Africa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muzeniek, T.; Perera, T.; Siriwardana, S.; Bas, D.; Kaplan, F.; Öruc, M.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Schwarz, F.; Premawansa, G.; Premawansa, S.; et al. Detection of Alpha- and Betacoronaviruses in Miniopterus fuliginosus and Rousettus leschenaultii, two species of Sri Lankan Bats. Vaccines 2021, 9, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, A.; Vidal, N.; Keita, A.K.; Thaurignac, G.; Esteban, A.; De Nys, H.; Diallo, R.; Toure, A.; Goumou, S.; Soumah, A.K.; et al. Wide Diversity of Coronaviruses in Frugivorous and Insectivorous Bat Species: A Pilot Study in Guinea, West Africa. Viruses 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.D.; Shete-Aich, A.; Nyayanit, D.A.; Pardeshi, P.; Majumdar, T.; Balasubramanian, R.; Ullas, P.T.; Mohandas, S.; Dighe, H.; Sawant, P.; et al. Detection of coronaviruses in Pteropus & Rousettus species of bats from different States of India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Schlottau, K.; Rissmann, M.; Graaf, A.; Schön, J.; Sehl, J.; Wylezich, C.; Höper, D.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; Harder, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 in fruit bats, ferrets, pigs, and chickens: An experimental transmission study. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e218–e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrut, X.; Souris, M.; Towner, J.S.; Rollin, P.E.; Nichol, S.T.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Leroy, E. Large serological survey showing cocirculation of Ebola and Marburg viruses in Gabonese bat populations, and a high seroprevalence of both viruses in Rousettus aegyptiacus. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Masangkay, J.S.; Omatsu, T.; Ikegami, T.; Alviola, P.; Ueda, N.; Iha, K.; Fujii, H.; Ishii, Y.; et al. Reston Ebolavirus antibodies in bats, the Philippines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1559–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.F.; Shi, Z. Serological evidence of ebolavirus infection in bats, China. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paweska, J.T.; Jansen van Vuren, P.; Masumu, J.; Leman, P.A.; Grobbelaar, A.A.; Birkhead, M.; Clift, S.; Swanepoel, R.; Kemp, A. Virological and serological findings in Rousettus aegyptiacus experimentally inoculated with vero cells-adapted hogan strain of Marburg virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gard, G.P.; Marshall, I.D. Nelson Bay virus. A novel reovirus. Archiv fur die gesamte Virusforschung 1973, 43, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.B.; Crameri, G.; Hyatt, A.; Yu, M.; Tompang, M.R.; Rosli, J.; McEachern, J.; Crameri, S.; Kumarasamy, V.; Eaton, B.T.; et al. A previously unknown reovirus of bat origin is associated with an acute respiratory disease in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11424–11429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voon, K.; Chua, K.B.; Yu, M.; Crameri, G.; Barr, J.A.; Malik, Y.; Wang, L.F. Evolutionary relationship of the L- and M-class genome segments of bat-borne fusogenic orthoreoviruses in Malaysia and Australia. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92 Pt 12, 2930–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Qiu, W.; He, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Characterization of a novel orthoreovirus isolated from fruit bat, China. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, H.; Shimojima, M.; Ngoc, T.C.; Quoc Huy, N.V.; Chuong, T.X.; Le Van, A.; Saijo, M.; Yang, M.; Sugamata, M. Serological evidence of human infection with Pteropine orthoreovirus in Central Vietnam. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, S.; Maeda, K.; Horimoto, T.; Masangkay, J.S.; Puentespina, R., Jr.; Alvarez, J.; Eres, E.; Cosico, E.; Nagata, N.; Egawa, K.; et al. First isolation and characterization of pteropine orthoreoviruses in fruit bats in the Philippines. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middendorp, S.; Schneeberger, K.; Wiegerinck, C.L.; Mokry, M.; Akkerman, R.D.; van Wijngaarden, S.; Clevers, H.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E. Adult stem cells in the small intestine are intrinsically programmed with their location-specific function. Stem. Cells 2014, 32, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovbasnjuk, O.; Zachos, N.C.; In, J.; Foulke-Abel, J.; Ettayebi, K.; Hyser, J.M.; Broughman, J.R.; Zeng, X.L.; Middendorp, S.; de Jonge, H.R.; et al. Human enteroids: Preclinical models of non-inflammatory diarrhea. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4 (Suppl. 1), S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saxena, K.; Blutt, S.E.; Ettayebi, K.; Zeng, X.L.; Broughman, J.R.; Crawford, S.E.; Karandikar, U.C.; Sastri, N.P.; Conner, M.E.; Opekun, A.R.; et al. Human Intestinal Enteroids: A New Model To Study Human Rotavirus Infection, Host Restriction, and Pathophysiology. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abugomaa, A.; Elbadawy, M. Patient-derived organoid analysis of drug resistance in precision medicine: Is there a value? Expert Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2020, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abugomaa, A.; Elbadawy, M.; Yamanaka, M.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Mori, T.; Uchide, T.; Azakami, D.; Fukushima, R.; Yoshida, T.; et al. Establishment of 2.5D organoid culture model using 3D bladder cancer organoid culture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawy, M.; Sato, Y.; Mori, T.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Yamanaka, M.; Azakami, D.; Uchide, T.; Fukushima, R.; Yoshida, T.; et al. Anti-tumor effect of trametinib in bladder cancer organoid and the underlying mechanism. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2021, 22, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbadawy, M.; Abugomaa, A.; Yamawaki, H.; Usui, T.; Sasaki, K. Development of prostate cancer organoid culture models in basic medicine and translational research. Cancers 2020, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbadawy, M.; Usui, T.; Yamawaki, H.; Sasaki, K. Development of an experimental model for analyzing drug resistance in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Doremalen, N.; Schäfer, A.; Menachery, V.D.; Letko, M.; Bushmaker, T.; Fischer, R.J.; Figueroa, D.M.; Hanley, P.W.; Saturday, G.; Baric, R.S.; et al. SARS-Like Coronavirus WIV1-CoV Does Not Replicate in Egyptian Fruit Bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus). Viruses 2018, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Chiu, M.C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Wei, Y.; Lee, A.; Zhang, A.J.; Chu, H.; et al. Infection of bat and human intestinal organoids by SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onozato, D.; Yamashita, M.; Nakanishi, A.; Akagawa, T.; Kida, Y.; Ogawa, I.; Hashita, T.; Iwao, T.; Matsunaga, T. Generation of Intestinal Organoids Suitable for Pharmacokinetic Studies from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnert, F.; Davis, C.R.; Wang, H.T.; Chu, P.; Lee, M.; Yuan, J.; Nusse, R.; Kuo, C.J. Essential requirement for Wnt signaling in proliferation of adult small intestine and colon revealed by adenoviral expression of Dickkopf-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bongers, G.; Muniz, L.R.; Pacer, M.E.; Iuga, A.C.; Thirunarayanan, N.; Slinger, E.; Smit, M.J.; Reddy, E.P.; Mayer, L.; Furtado, G.C.; et al. A role for the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in development of intestinal serrated polyps in mice and humans. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juul, A.; Bang, P.; Hertel, N.T.; Main, K.; Dalgaard, P.; Jorgensen, K.; Muller, J.; Hall, K.; Skakkebaek, N.E. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I in 1030 healthy children, adolescents, and adults: Relation to age, sex, stage of puberty, testicular size, and body mass index. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 78, 744–752. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, A.T.; Van Landeghem, L.; Gavin, H.E.; Magness, S.T.; Lund, P.K. Impact of diet-induced obesity on intestinal stem cells: Hyperproliferation but impaired intrinsic function that requires insulin/IGF1. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3302–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Landeghem, L.; Santoro, M.A.; Mah, A.T.; Krebs, A.E.; Dehmer, J.J.; McNaughton, K.K.; Helmrath, M.A.; Magness, S.T.; Lund, P.K. IGF1 stimulates crypt expansion via differential activation of 2 intestinal stem cell populations. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2828–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Dai, D.; He, X.; Zhu, S.; Yao, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Qu, F.; Qiu, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Growth Factor FGF2 Cooperates with Interleukin-17 to Repair Intestinal Epithelial Damage. Immunity 2015, 43, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akram, K.M.; Patel, N.; Spiteri, M.A.; Forsyth, N.R. Lung Regeneration: Endogenous and Exogenous Stem Cell Mediated Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nogawa, H.; Ito, T. Branching morphogenesis of embryonic mouse lung epithelium in mesenchyme-free culture. Development 1995, 121, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, W.V.; Itoh, A.; Nogawa, H.; Mason, I.; Brody, J.S. FGF-1 and FGF-7 induce distinct patterns of growth and differentiation in embryonic lung epithelium. Dev. Dyn. 1997, 208, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, J.M.; Gebb, S.A.; Nielsen, L.D. Induction of alveolar type II cell differentiation in embryonic tracheal epithelium in mesenchyme-free culture. Development 1999, 126, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfhagen, T.R.; Swantz, R.J.; Wert, S.E.; McCarty, J.M.; Kerlakian, C.B.; Glasser, S.W.; Whitsett, J.A. Respiratory epithelial cell expression of human transforming growth factor-alpha induces lung fibrosis in transgenic mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, P.; Zeeh, J.M.; Lakshmanan, J.; Wu, V.S.; Procaccino, F.; Reinshagen, M.; McRoberts, J.A.; Eysselein, V.E. Increased expression of transforming growth factor alpha precursors in acute experimental colitis in rats. Gut 1997, 41, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Coffey, R.J. From wavy hair to naked proteins: The role of transforming growth factor alpha in health and disease. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, T.; van Es, J.H.; Snippert, H.J.; Stange, D.E.; Vries, R.G.; van den Born, M.; Barker, N.; Shroyer, N.F.; van de Wetering, M.; Clevers, H. Paneth cells constitute the niche for Lgr5 stem cells in intestinal crypts. Nature 2011, 469, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sannes, P.L.; Burch, K.K.; Khosla, J. Immunohistochemical localization of epidermal growth factor and acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors in postnatal developing and adult rat lungs. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 7, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.; Seth, R.; Shum, L.; Horcher, P.G.; Hall, F.L.; Werb, Z.; Slavkin, H.C. Epigenetic role of epidermal growth factor expression and signalling in embryonic mouse lung morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 1992, 149, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Jiao, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, B.J.; Wang, X.; Guo, M.; Wang, L.F.; Lan, K.; et al. ACE2 receptor usage reveals variation in susceptibility to SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 infection among bat species. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Pan, X.; Li, L.; Yu, F.; Zheng, A.; Du, P.; Han, P.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. Binding and molecular basis of the bat coronavirus RaTG13 virus to ACE2 in humans and other species. Cell 2021, 184, 3438–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.F.; Teng, C.L.; Chua, K.B.; Voon, K. Pteropine orthoreovirus: An important emerging virus causing infectious disease in the tropics? J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, L.I.; Chua, K.B.; Cummins, D.; Hyatt, A.; Crameri, G.; Eaton, B.T.; Wang, L.F. Pulau virus; a new member of the Nelson Bay orthoreovirus species isolated from fruit bats in Malaysia. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawy, M.; Usui, T.; Mori, T.; Tsunedomi, R.; Hazama, S.; Nabeta, R.; Uchide, T.; Fukushima, R.; Yoshida, T.; Shibutani, M.; et al. Establishment of a novel experimental model for muscle-invasive bladder cancer using a dog bladder cancer organoid culture. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2806–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawy, M.; Yamanaka, M.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Tsunedomi, R.; Hazama, S.; Nagano, H.; Yoshida, T.; Shibutani, M.; Ichikawa, R.; et al. Efficacy of primary liver organoid culture from different stages of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) mouse model. Biomaterials 2020, 237, 119823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbadawy, M.; Hayashi, K.; Ayame, H.; Ishihara, Y.; Abugomaa, A.; Shibutani, M.; Hayashi, S.M.; Hazama, S.; Takenouchi, H.; Nakajima, M.; et al. Anti-cancer activity of amorphous curcumin preparation in patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Hibino, M.; Hase, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Kasamatsu, Y.; Hirose, M.; Mutoh, Y.; Homma, Y.; Terada, M.; Ogawa, T.; et al. A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label Trial of Early versus Late Favipiravir Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01897–e01920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, K.; Shimojima, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Nagata, N.; Tani, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Watanabe, S.; Fukushi, S.; Saijo, M. Virulence, pathology, and pathogenesis of Pteropine orthoreovirus (PRV) in BALB/c mice: Development of an animal infection model for PRV. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbadawy, M.; Kato, Y.; Saito, N.; Hayashi, K.; Abugomaa, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoshida, T.; Shibutani, M.; Kaneda, M.; Yamawaki, H.; et al. Establishment of Intestinal Organoid from Rousettus leschenaultii and the Susceptibility to Bat-Associated Viruses, SARS-CoV-2 and Pteropine Orthoreovirus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910763
Elbadawy M, Kato Y, Saito N, Hayashi K, Abugomaa A, Kobayashi M, Yoshida T, Shibutani M, Kaneda M, Yamawaki H, et al. Establishment of Intestinal Organoid from Rousettus leschenaultii and the Susceptibility to Bat-Associated Viruses, SARS-CoV-2 and Pteropine Orthoreovirus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910763
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbadawy, Mohamed, Yuki Kato, Nagisa Saito, Kimika Hayashi, Amira Abugomaa, Mio Kobayashi, Toshinori Yoshida, Makoto Shibutani, Masahiro Kaneda, Hideyuki Yamawaki, and et al. 2021. "Establishment of Intestinal Organoid from Rousettus leschenaultii and the Susceptibility to Bat-Associated Viruses, SARS-CoV-2 and Pteropine Orthoreovirus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910763
APA StyleElbadawy, M., Kato, Y., Saito, N., Hayashi, K., Abugomaa, A., Kobayashi, M., Yoshida, T., Shibutani, M., Kaneda, M., Yamawaki, H., Mizutani, T., Lim, C.-K., Saijo, M., Sasaki, K., Usui, T., & Omatsu, T. (2021). Establishment of Intestinal Organoid from Rousettus leschenaultii and the Susceptibility to Bat-Associated Viruses, SARS-CoV-2 and Pteropine Orthoreovirus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910763







