Tetraoctylammonium, a Long Chain Quaternary Ammonium Blocker, Promotes a Noncollapsed, Resting-Like Inactivated State in KcsA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
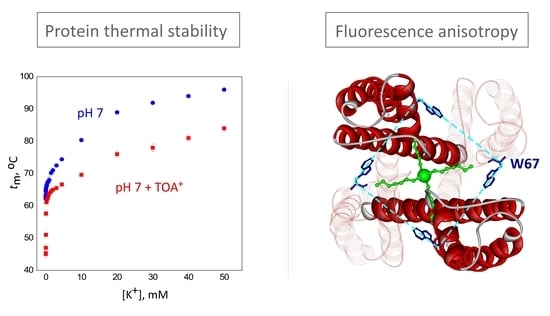
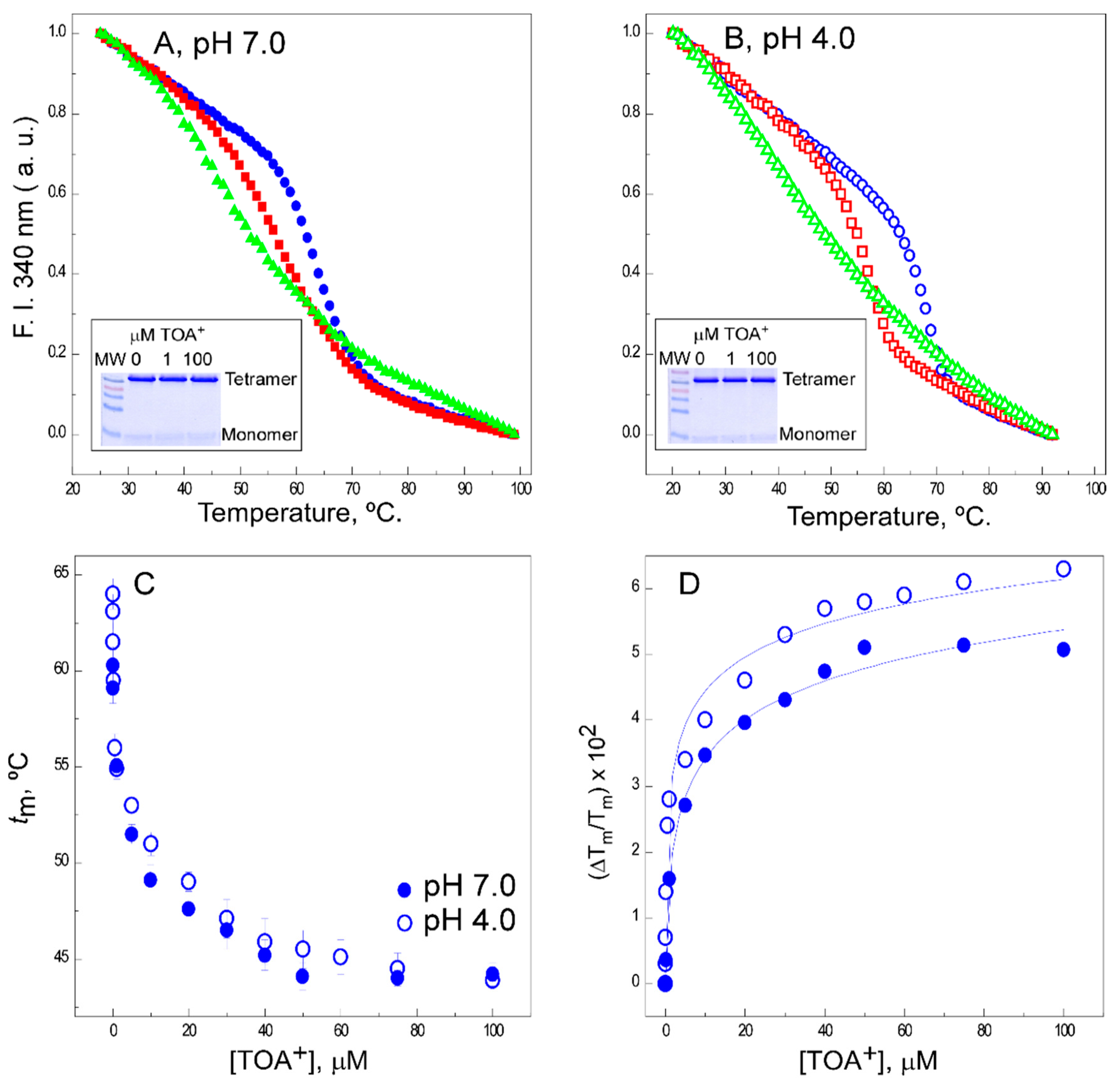
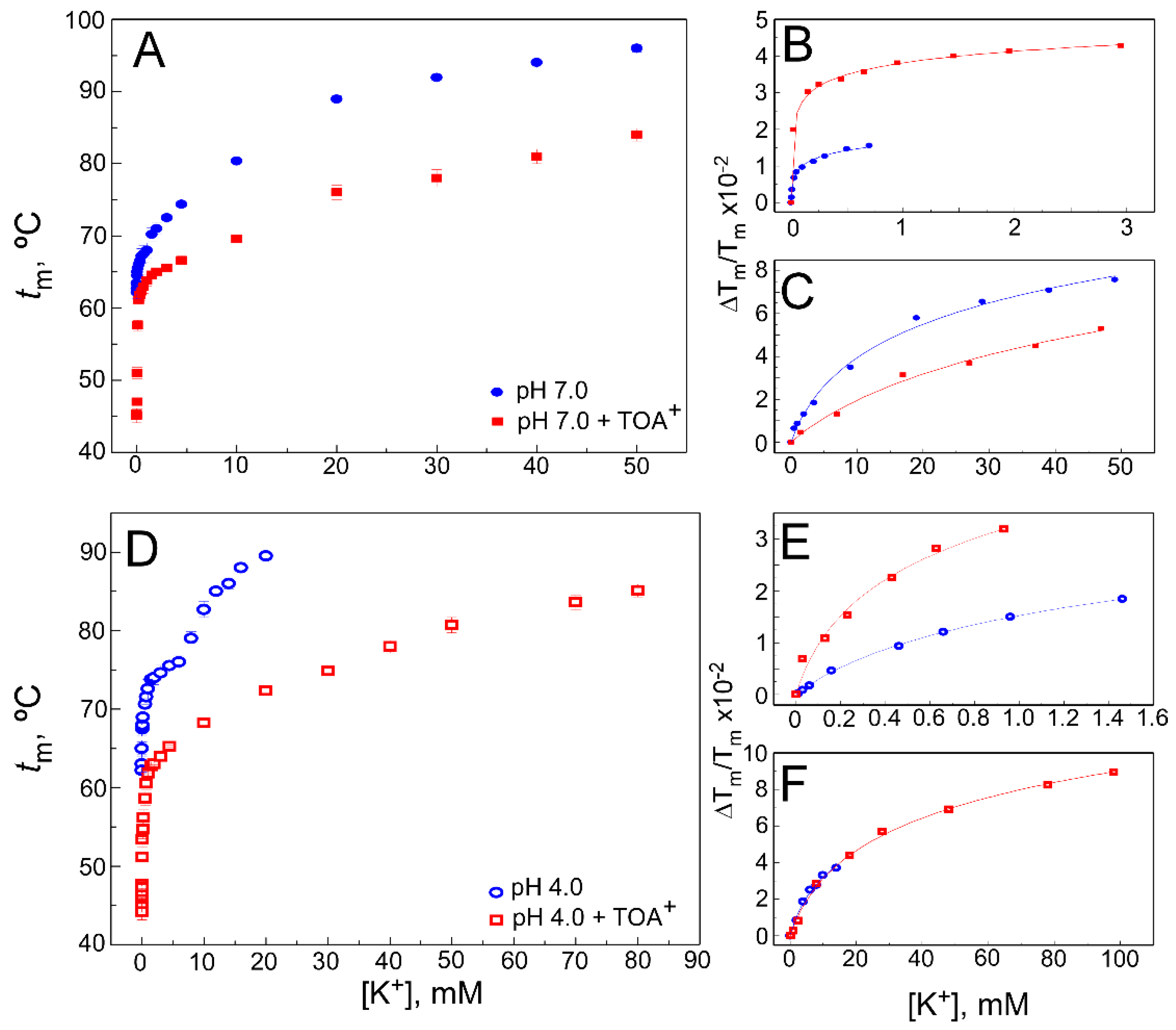
2.1. TOA+ Binds to Wild-Type KcsA with High Affinity and Diminishes the Thermal Stability of the Channel
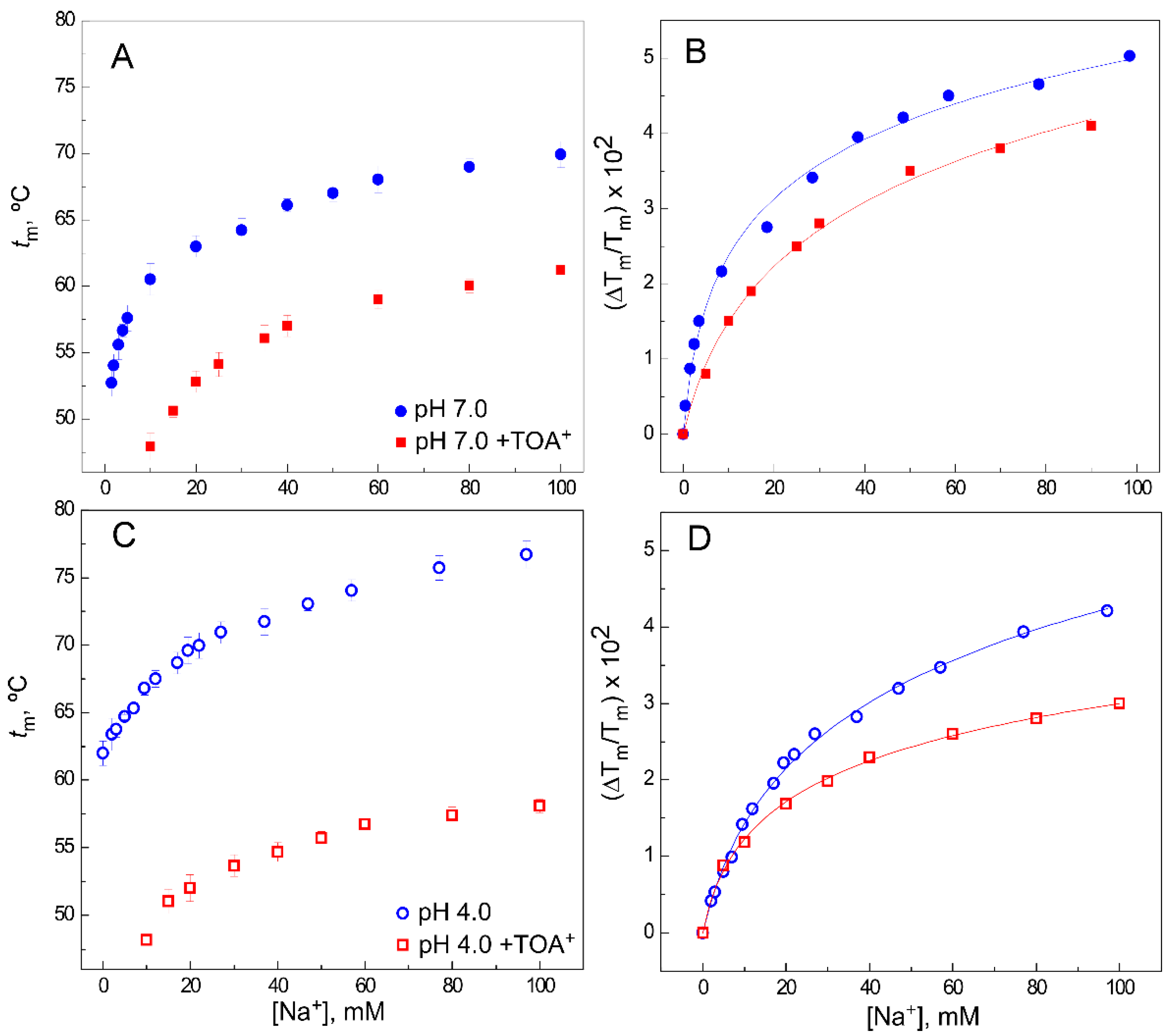
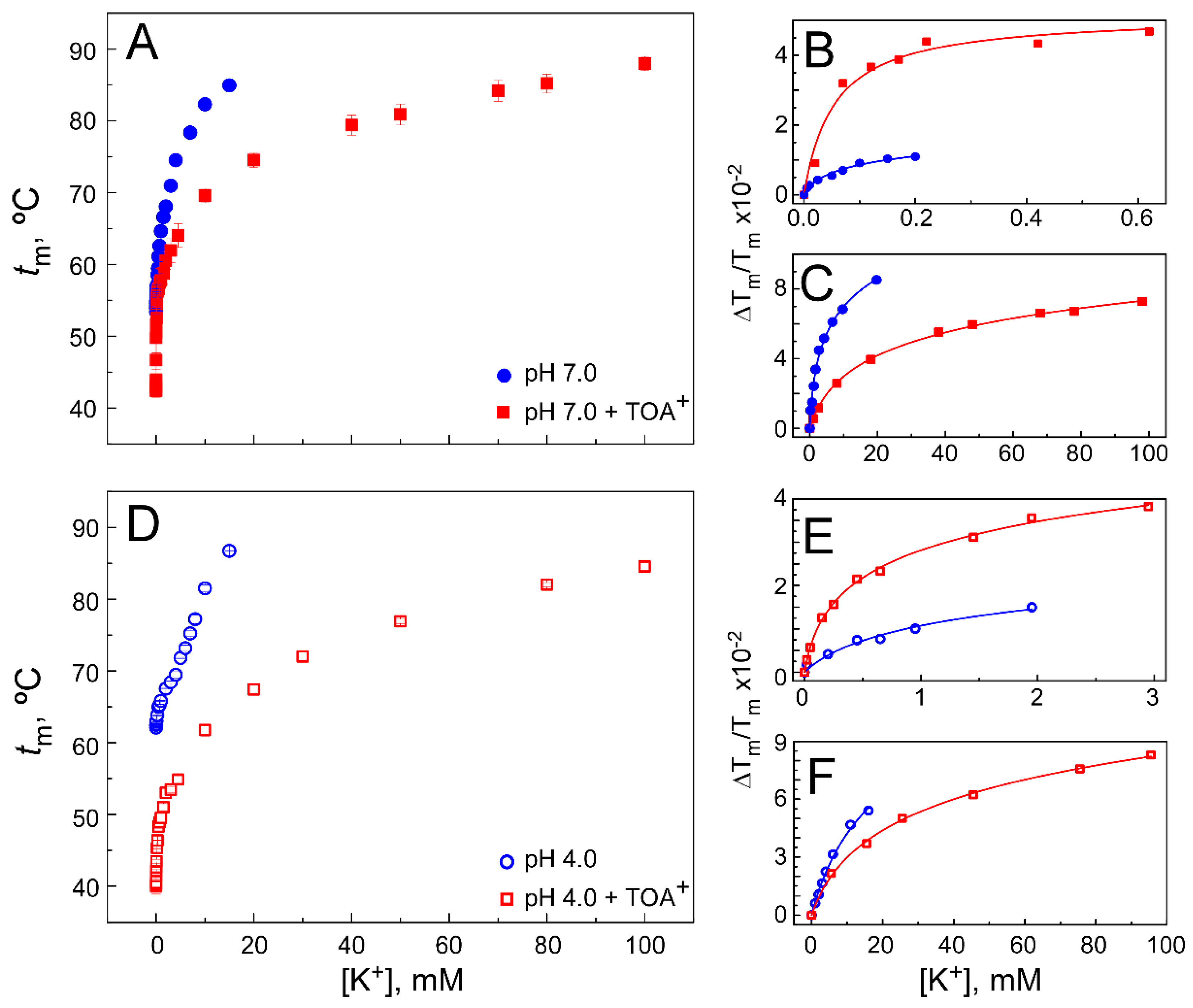
2.2. The Presence of TOA+ in the Cavity Diminishes the Affinity of WT KcsA to Bind K+ in the Closed Channel State
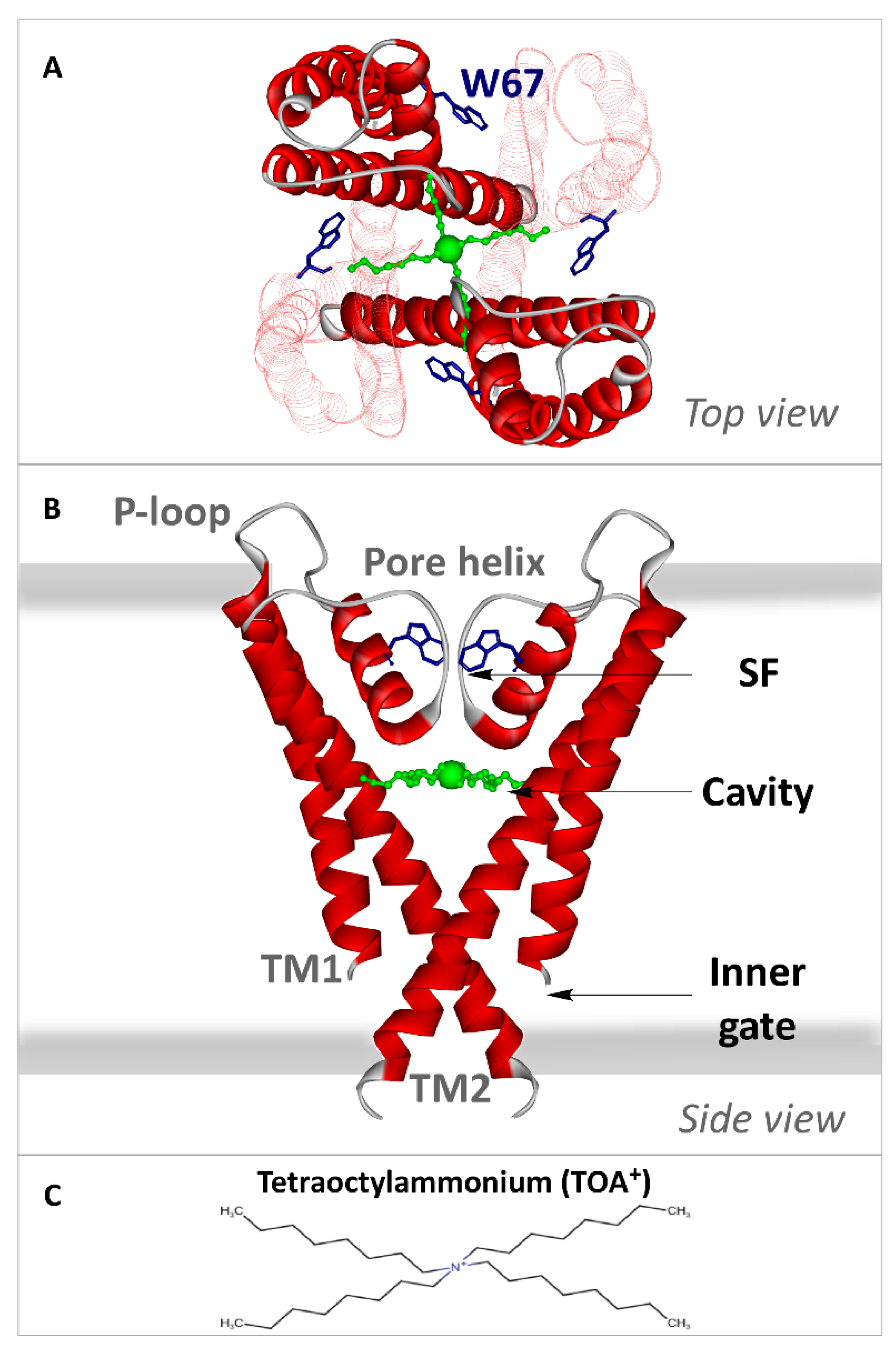
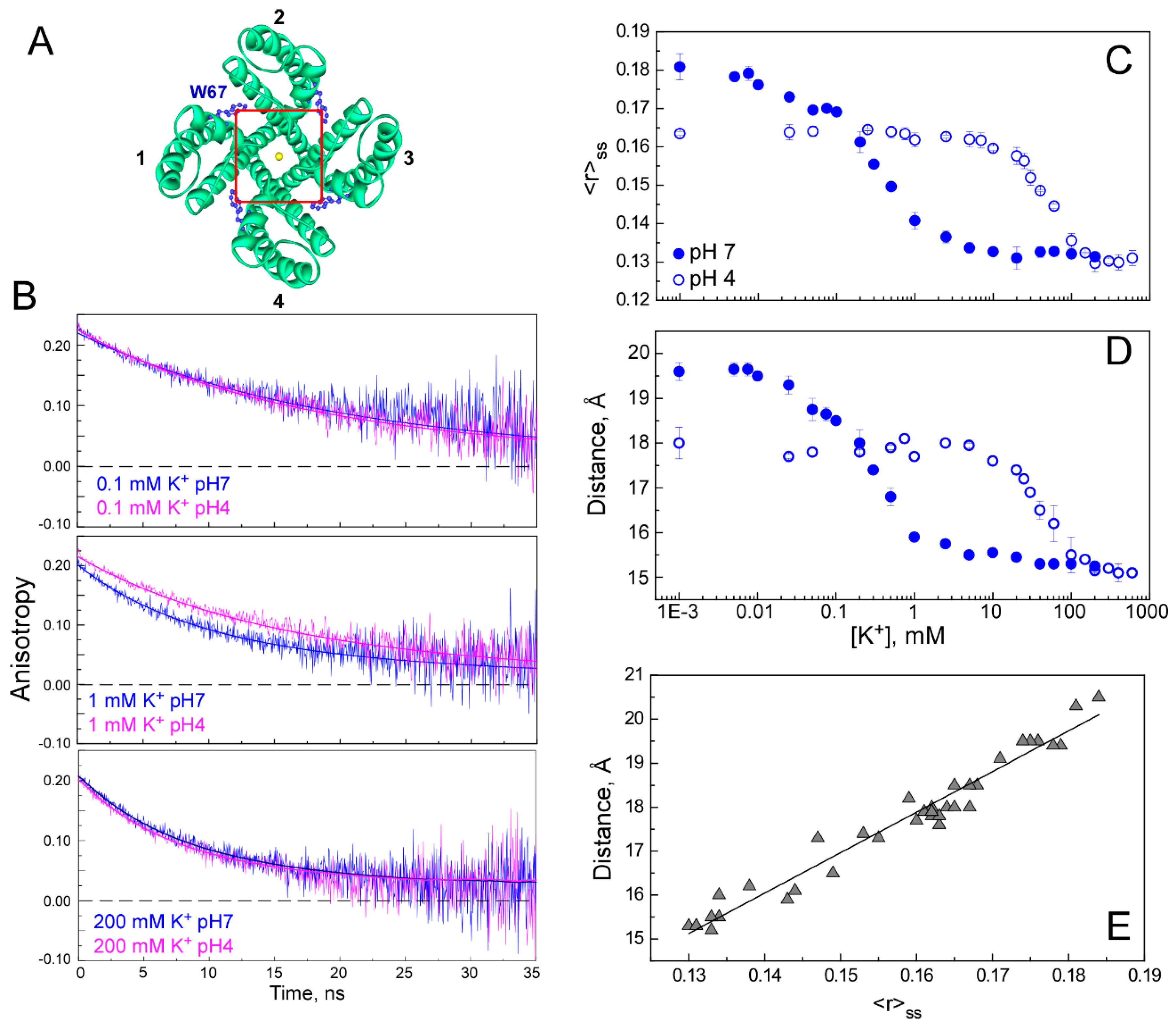
2.3. The Homo-FRET Process in the W67 KcsA Mutant Reports Differences between the Nonconductive, Conductive, and Inactivated Conformations of the Selectivity Filter
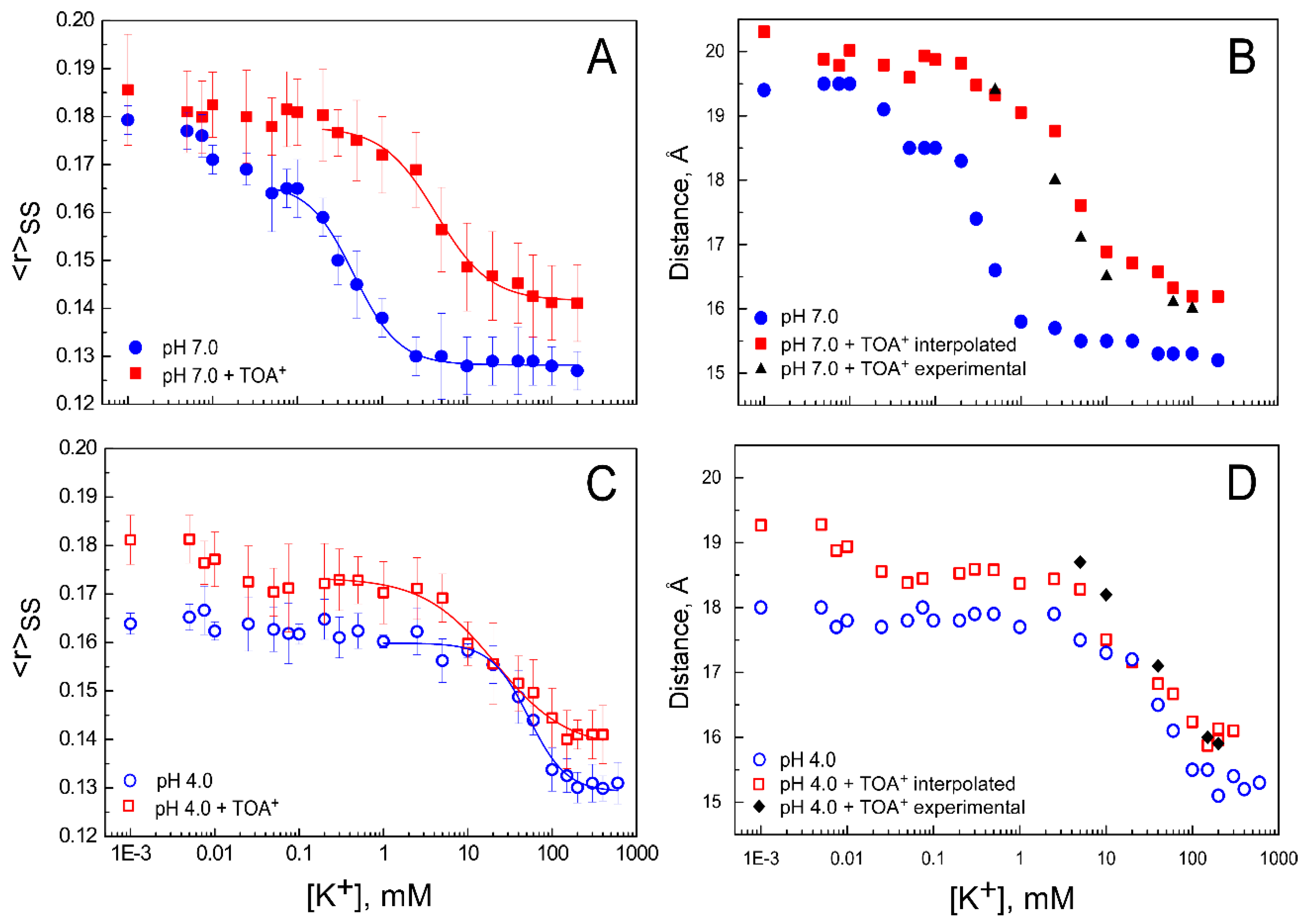
2.4. The Presence of TOA+ Bound at the Cavity Promotes the Inactivated State of the Selectivity Filter and Allosterically Changes the Pore Helix Conformation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. KcsA Heterologous Expression and Purification
4.3. Thermal Denaturation Assay and Cation Binding Analysis
4.4. Steady-State Fluorescence Measurements
4.5. Time-Resolved Fluorescence Measurements and Intersubunit Distance Calculations
4.6. Calculation of the K+ Binding Affinity to KcsA from Changes in the Steady-State Anisotropy Values
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yellen, G. The moving parts of voltage-gated ion channels. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1998, 31, 239–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes; Mass Sinauer Assoc. Inc.: Sunderland, UK, 2001; p. 5. ISBN 0-87893-321-2. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, C.M.; Binstock, L. Anomalous rectification in the squid giant axon injected with tetraethylammonium chloride. J. Gen. Physiol. 1965, 48, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J. Gen. Physiol. 1967, 50, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, C.M. Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injection in squid axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 1969, 54, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, C.M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 1971, 58, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.L.; Aldrich, R.W.; Yellen, G. Tetraethylammonium blockade distinguishes two inactivation mechanisms in voltage-activated K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5092–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heginbotham, L.; MacKinnon, R. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron 1992, 8, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.L.; Mossman, C.; Aubé, J.; Yellen, G. The internal quaternary ammonium receptor site of Shaker potassium channels. Neuron 1993, 10, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, S.; Vasquez, V.; Tereshko, V.; Esaki, K.; Fellouse, F.A.; Sidhu, S.S.; Koide, S.; Perozo, E.; Kossiakoff, A. Crystal structure of full-length KcsA in its closed conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6644–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, D.A.; Morais, C.J.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Kuo, A.; Gulbis, J.M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. The structure of the potassium channel: Molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 1998, 280, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Morais-Cabral, J.H.; Kaufman, A.; MacKinnon, R. Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel-Fab complex at 2.0 Å resolution. Nature 2001, 414, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais-Cabral, J.H.; Zhou, Y.; MacKinnon, R. Energetic optimization of ion conduction rate by the K+ selectivity filter. Nature 2001, 414, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, B.J.; Bhate, M.P.; McDermott, A.E. Transmembrane allosteric coupling of the gates in a potassium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; MacKinnon, R. The occupancy of ions in the K+ selectivity filter: Charge balance and coupling of ion binding to a protein conformational change underlie high conduction rates. J.Mol.Biol. 2003, 333, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chill, J.H. NMR study of the tetrameric KcsA potassium channel in detergent micelles. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Morales, J.F.; Cuello, L.G.; Zhao, Y.; Jogini, V.; Cortes, D.M.; Roux, B.; Perozo, E. Molecular determinants of gating at the potassium-channel selectivity filter. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.A.; Tzitzilonis, C.; Kwiatkowski, W.; Choe, S.; Riek, R. Conformational dynamics of the KcsA potassium channel governs gating properties. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ader, C.; Schneider, R.; Hornig, S.; Velisetty, P.; Vardanyan, V.; Giller, K.; Ohmert, I.; Becker, S.; Pongs, O.; Baldus, M. Coupling of activation and inactivation gate in a K-channel: Potassium and ligand sensitivity. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2825–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhate, M.P.; Wylie, B.J.; Tian, L.; McDermott, A.E. Conformational dynamics in the selectivity filter of KcsA in response to potassium ion concentration. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 401, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Osawa, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Shimada, I. Structural basis underlying the dual gate properties of KcsA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6216–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.W.L.; McCoy, J.G.; Thompson, A.N.; Nichols, C.G.; Nimigean, C.M. Mechanism for selectivity-inactivation coupling in KcsA potassium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5272–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockless, S.W.; Zhou, M.; MacKinnon, R. Structural and thermodynamic properties of selective ion binding in a K+ channel. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuello, L.G.; Cortes, D.M.; Jogini, V.; Sompornpisut, A.; Perozo, E. A molecular mechanism for proton-dependent gating in KcsA. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, M.; Onishi, Y.; Yanagida, T.; Ide, T. Role of the KcsA channel cytoplasmic domain in pH-dependent gating. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posson, D.J.; Thompson, A.N.; McCoy, J.G.; Nimigean, C.M. Molecular interactions involved in proton-dependent gating in KcsA potassium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2013, 142, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, T.; Zagotta, W.N.; Aldrich, R.W. Two types of inactivation in Shaker K+ channels: Effects of alterations in the carboxy-terminal region. Neuron 1991, 7, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jurman, M.E.; Yellen, G. Dynamic rearrangement of the outer mouth of a K+ channel during gating. Neuron 1996, 16, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Mi, X.; Paajanen, V.; Wang, K.; Fan, Z. Activation-coupled inactivation in the bacterial potassium channel KcsA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17630–17635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ostmeyer, J.; Cuello, L.G.; Perozo, E.; Roux, B. Rapid constriction of the selectivity filter underlies C-type inactivation in the KcsA potassium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2018, 150, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello, L.G.; Cortes, D.M.; Perozo, E. The gating cycle of a K+ channel at atomic resolution. Elife 2017, 6, e28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannan, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Crystallographic Study of the Tetrabutylammonium Block to the KcsA K+ Channel. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenaeus, M.J.; Burdette, D.; Wagner, T.; Focia, P.J.; Gross, A. Structures of KcsA in complex with symmetrical quaternary ammonium compounds reveal a hydrophobic binding site. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 5365–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renart, M.L.; Giudici, A.M.; Poveda, J.A.; Fedorov, A.; Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Prieto, M.; Díaz-García, C.; González-Ros, J.M.; Coutinho, A. Conformational plasticity in the KcsA potassium channel pore helix revealed by homo-FRET studies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6215–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudici, A.M.; Renart, M.L.; Díaz-García, C.; Morales, A.; Poveda, J.A.; González-Ros, J.M. Accessibility of cations to the selectivity filter of KcsA in the inactivated state: An equilibrium binding study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraneni, P.K.; Komarov, A.G.; Costantino, C.A.; Devereaux, J.J.; Matulef, K.; Valiyaveetil, F.I. Semisynthetic K+ channels show that the constricted conformation of the selectivity filter is not the C-type inactivated state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15698–15703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renart, M.L.; Triano, I.; Poveda, J.A.; Encinar, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.V.; Gómez, J.; González Ros, J.M. Ion binding to KcsA: Implications in ion selectivity and channel gating. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9480–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triano, I.; Barrera, F.N.; Renart, M.L.; Molina, M.L.; Fernandez-Ballester, G.; Poveda, J.A.; Fernandez, A.M.; Encinar, J.A.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.V.; Otzen, D.; et al. Occupancy of nonannular lipid binding sites on KcsA greatly increases the stability of the tetrameric protein. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5397–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renart, M.L.; Montoya, E.; Giudici, A.M.; Poveda, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Morales, A.; González-Ros, J.M. Selective exclusion and selective binding both contribute to ion selectivity in KcsA, a model potassium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15552–15560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, E.; Lourdes Renart, M.; Marcela Giudici, A.; Poveda, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Morales, A.; González-Ros, J.M. Differential binding of monovalent cations to KcsA: Deciphering the mechanisms of potassium channel selectivity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraldo-Gómez, J.D.; Kutluay, E.; Jogini, V.; Zhao, Y.; Heginbotham, L.; Roux, B. Mechanism of Intracellular Block of the KcsA K+ Channel by Tetrabutylammonium: Insights from X-ray Crystallography, Electrophysiology and Replica-exchange Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 365, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozo, E.; Marien Cortes, D.; Cuello, L.G. Three-dimensional architecture and gating mechanism of a K+ channel studied by EPR spectroscopy. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perozo, E.; Cortes, D.M.; Cuello, L.G. Structural rearrangements underlying K+-channel activation gating. Science 1999, 285, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Shimizu, H.; Inoue, F.; Konno, T.; Sasaki, Y.C.; Oiki, S. Surface structure and its dynamic rearrangements of the KcsA potassium channel upon gating and tetrabutylammonium blocking. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28379–28386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renart, M.L.; Montoya, E.; Fernandez, A.M.; Molina, M.L.; Poveda, J.A.; Encinar, J.A.; Ayala, J.L.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.V.; Gomez, J.; Morales, A.; et al. Contribution of ion binding affinity to ion selectivity and permeation in KcsA, a model potassium channel. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 3891–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello, L.G.; Jogini, V.; Cortes, D.M.; Pan, A.C.; Gagnon, D.G.; Dalmas, O.; Cordero-Morales, J.F.; Chakrapani, S.; Roux, B.; Perozo, E. Structural basis for the coupling between activation and inactivation gates in K+ channels. Nature 2010, 466, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello, L.G.; Jogini, V.; Cortes, D.M.; Perozo, E. Structural mechanism of C-type inactivation in K+ channels. Nature 2010, 466, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.C.; Cuello, L.G.; Perozo, E.; Roux, B. Thermodynamic coupling between activation and inactivation gating in potassium channels revealed by free energy molecular dynamics simulations. J. Gen. Physiol. 2011, 138, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, S.; Cuello, L.G.; Cortes, D.M.; Koide, S.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Perozo, E. Mechanism of activation gating in the full-length KcsA K+ channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11896–11899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Morais-Cabral, J.H.; Mann, S.; MacKinnon, R. Potassium channel receptor site for the inactivation gate and quaternary amine inhibitors. Nature 2001, 411, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulef, K.; Komarov, A.G.; Costantino, C.A.; Valiyaveetil, F.I. Using protein backbone mutagenesis to dissect the link between ion occupancy and C-Type inactivation in K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17886–17891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulef, K.; Annen, A.W.; Nix, J.C.; Valiyaveetil, F.I. Individual Ion Binding Sites in the K+ Channel Play Distinct Roles in C-type Inactivation and in Recovery from Inactivation. Structure 2016, 24, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baukrowitz, T.; Yellen, G. Modulation of K+ current by frequency and external [K+]: A tale of two inactivation mechanisms. Neuron 1995, 15, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bhate, M.P.; McDermott, A.E. Transmembrane allosteric energetics characterization for strong coupling between proton and potassium ion binding in the KcsA channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8788–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, R.P.; Armstrong, C.M. K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+. Nature 1981, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmusson, R.L.; Morales, M.J.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Campbell, D.L.; Brahmajothi, M.V.; Strauss, H.C. Inactivation of voltage-gated cardiac K+ channels. Circ. Res. 1998, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.S.; Syeda, R.; Montal, M. Stabilization of the conductive conformation of a voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channel: The lid mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 16619–16628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, F.N.; Renart, M.L.; Molina, M.L.; Poveda, J.A.; Encinar, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Neira, J.L.; González-Ros, J.M. Unfolding and refolding in vitro of a tetrameric, alpha-helical membrane protein: The prokaryotic potassium channel KcsA. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 14344–14352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.L.; Encinar, J.A.; Barrera, F.N.; Fernández-Ballester, G.; Riquelme, G.; Gonzalez-Ros, J.M. Influence of C-terminal protein domains and protein-lipid interactions on tetramerization and stability of the potassium channel KcsA. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 14924–14931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.A.; Prieto, M.; Encinar, J.A.; González-Ros, J.M.; Mateo, C.R. Intrinsic tyrosine fluorescence as a tool to study the interaction of the Shaker B “ball” peptide with anionic membranes. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 7124–7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy. In Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 372–374. [Google Scholar]
| Tested Cation | Sets of Binding Sites Detected | WT KcsA, pH 7.0 | WT KcsA, pH 4.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Added TOA+ | +100 µM TOA+ | No Added TOA+ | +100 µM TOA+ | ||||||
| KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD (M) from Tm | 95% CI | ||
| Na+ | 1 | 3.3 × 10−3 | (2.5−4.3) × 10−3 b | 1.4 × 10−2 | (0.9–2.1) × 10−2 a,b | 7.7 × 10−3 | (6.6–8.9) × 10−3 | 1.3 × 10−2 | (0.9–1.8) × 10−2 a,b |
| K+ | 2 | 2.8 × 10−7 | (2.0–3.9) × 10−7 b | 5.0 × 10−5 | (3.3–7.5) × 10−5 a,b | 3.8 × 10−4 | (2.1–6.9) × 10−4 | 1.9 × 10−4 | (0.9–4.9) × 10−4 |
| 4.2 × 10−3 | (3.2–5.4) × 10−3 b | 1.6 × 10−3 | (1.2–2.1) × 10−2 a,b | 1.1 × 10−1 | (0.7–1.5) × 10−1 | 1.0 × 10−1 | (0.8−1.4) × 10−1 | ||
| W67 KcsA, pH 7.0 | W67 KcsA, pH 4.0 | ||||||||
| KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | KD(M) from Tm | 95% CI | ||
| K+ | 2 | 1.0 × 10−5 | (0.7–1.5) × 10−5 b | 3.2 × 10−5 | (1.2–8.6) × 10−5 b | 4.8 × 10−4 | (2.7–8.7) × 10−4 | 1.2 × 10−4 | (1.0−1.4) × 10−4 a,b |
| 9.4 × 10−4 | (5.8–14.0) × 10−4 b | 5.2 × 10−3 | (3.3–8.1) × 10−3 a,b | 1.4 × 10−2 | (1.1–1.7) × 10−2 | 8.6 × 10−3 | (7.1–10.4) × 10−3 a,b | ||
| KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | KD(M) from <r>SS | 95% CI | ||
| K+ | 1 | 4.5 × 10−4 | (3.6–5.4) × 10−4 b | 4.3 × 10−3 | (3.4–5.2) × 10−3 a,b | 4.4 × 10−2 | (4.3–4.6) × 10−2 | 1.9 × 10−2 | (1.2–2.5) × 10−2 a,b |
| Inner Gate Conformation | Ionic Condition | Intersubunit Distances (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(δ2)-C(ε2) Inter-Tryptophan Lateral Distances from X-ray Structures (a) | Homo-FRET Analysis (b) | |||
| Extracellular Fab, 1–125 KcsA | Intracellular Fab, full-length KcsA | |||
| Closed | Low K+ | 17.8 (1K4D) | n.a. (c) | 18.5 ± 0.2 |
| High K+ | 17.3 (1K4C) | 15.9 (3EFF) | 15.4 ± 0.2 | |
| Low K+ + TOA+ | n.a. | n.a. | 19.1 ± 0.3 | |
| High K+ + TOA+ | 17.6 (2W0F) | n.a. | 16.1 ± 0.2 | |
| Open | Low K+ | n.a. | n.a. | 17.9 ± 0.2 (e) |
| High K+ | 17.7 (d) (3F5W) | 15.2 (d) (3PJS) | 15.3 ± 0.1 (e) | |
| Low K+ + TOA+ | n.a. | n.a. | 18.4 ± 0.2 (e) | |
| High K+ + TOA+ | n.a. | n.a. | 16.2 ± 0.3 (e) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giudici, A.M.; Díaz-García, C.; Renart, M.L.; Coutinho, A.; Prieto, M.; González-Ros, J.M.; Poveda, J.A. Tetraoctylammonium, a Long Chain Quaternary Ammonium Blocker, Promotes a Noncollapsed, Resting-Like Inactivated State in KcsA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020490
Giudici AM, Díaz-García C, Renart ML, Coutinho A, Prieto M, González-Ros JM, Poveda JA. Tetraoctylammonium, a Long Chain Quaternary Ammonium Blocker, Promotes a Noncollapsed, Resting-Like Inactivated State in KcsA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020490
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiudici, Ana Marcela, Clara Díaz-García, Maria Lourdes Renart, Ana Coutinho, Manuel Prieto, José M. González-Ros, and José Antonio Poveda. 2021. "Tetraoctylammonium, a Long Chain Quaternary Ammonium Blocker, Promotes a Noncollapsed, Resting-Like Inactivated State in KcsA" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020490
APA StyleGiudici, A. M., Díaz-García, C., Renart, M. L., Coutinho, A., Prieto, M., González-Ros, J. M., & Poveda, J. A. (2021). Tetraoctylammonium, a Long Chain Quaternary Ammonium Blocker, Promotes a Noncollapsed, Resting-Like Inactivated State in KcsA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020490