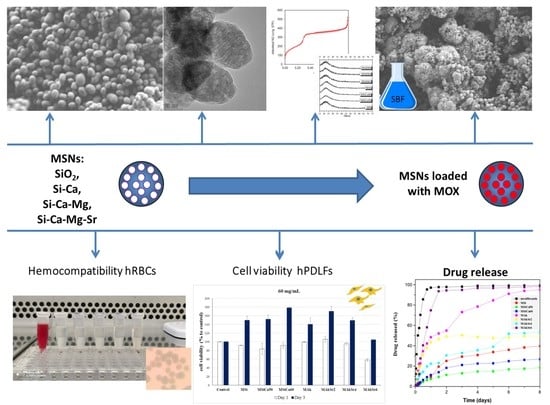
Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Mg- and Sr-Doped Nanoparticles for Moxifloxacin Drug Delivery in Promising Tissue Engineering Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
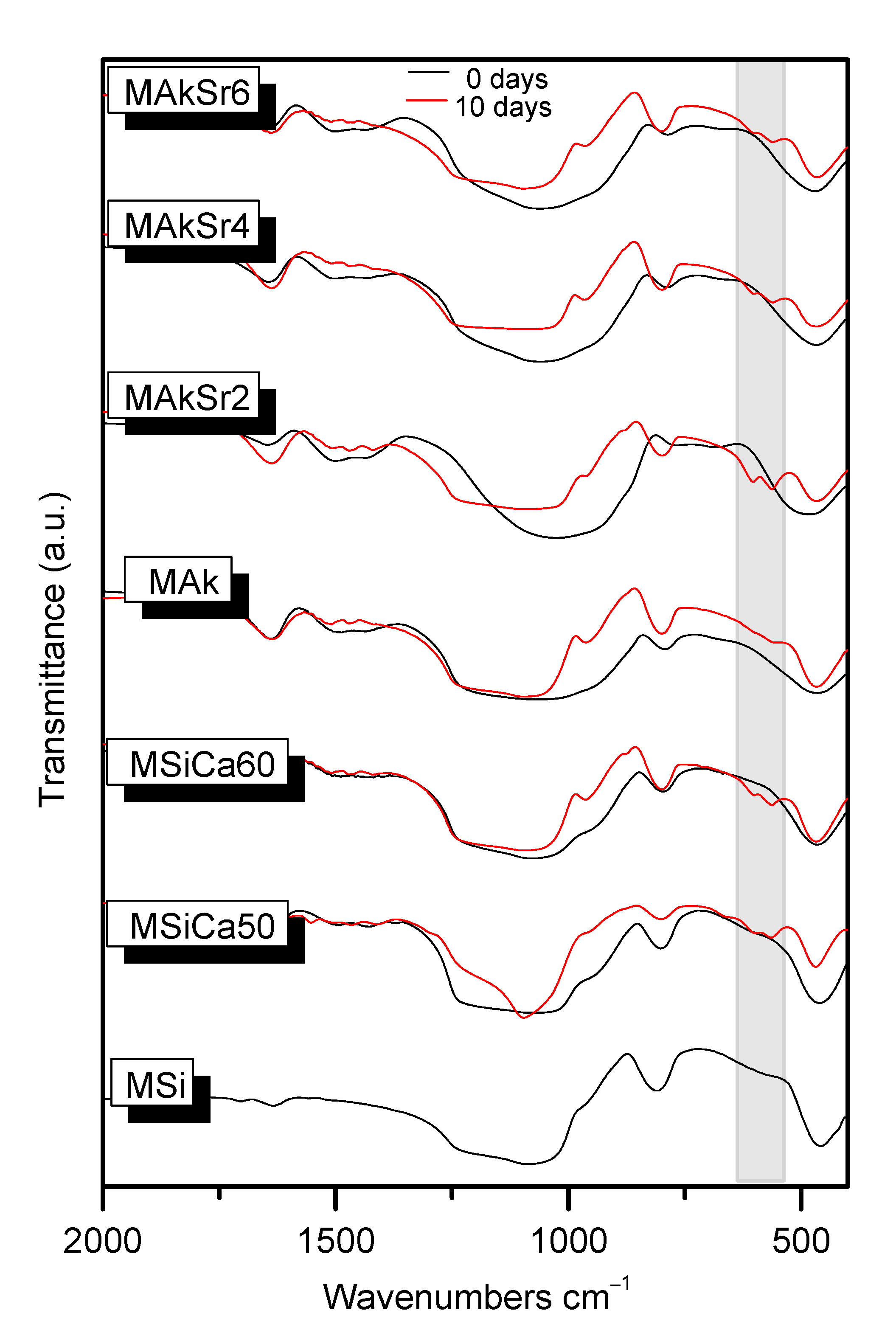
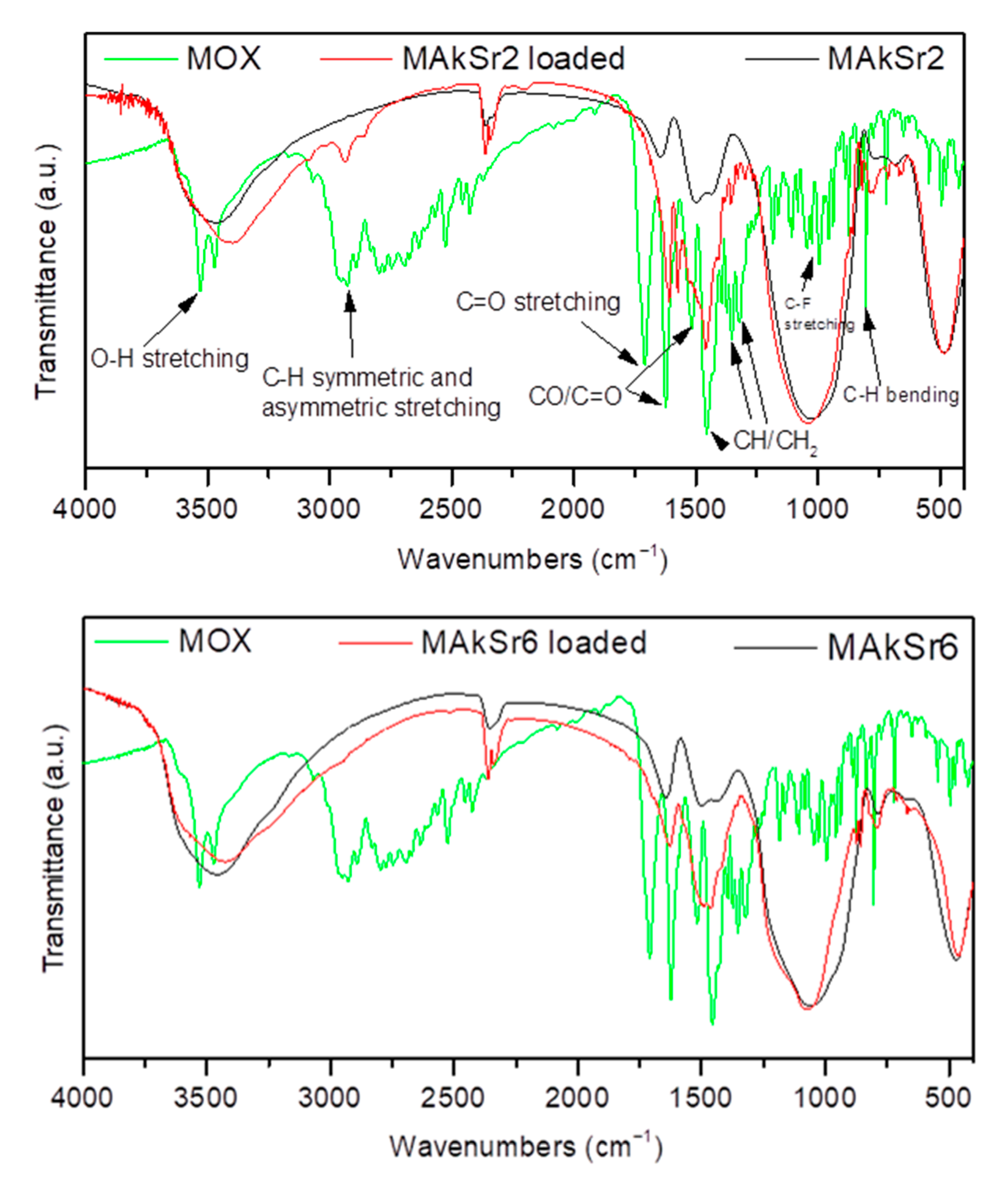
2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
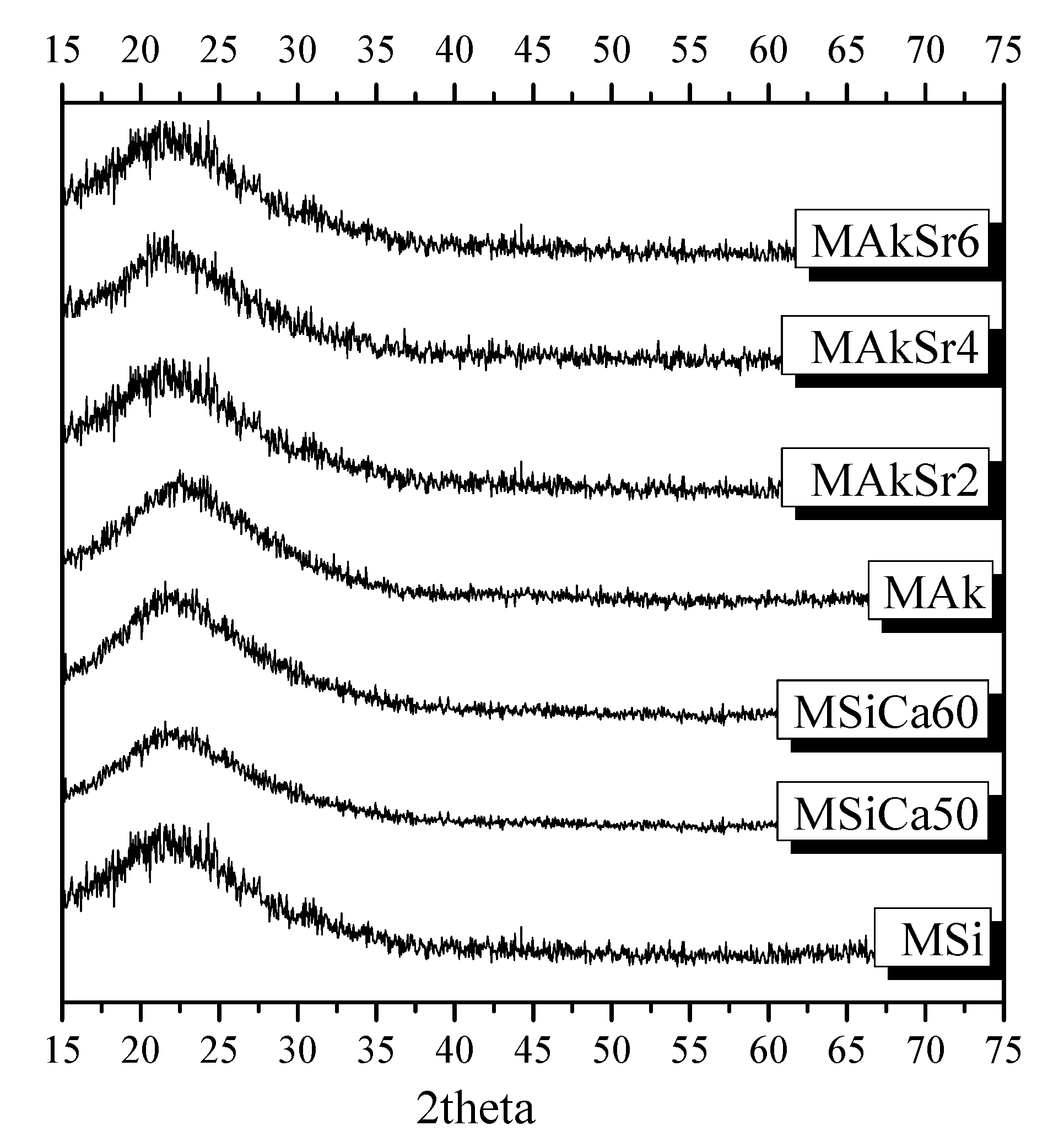
2.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
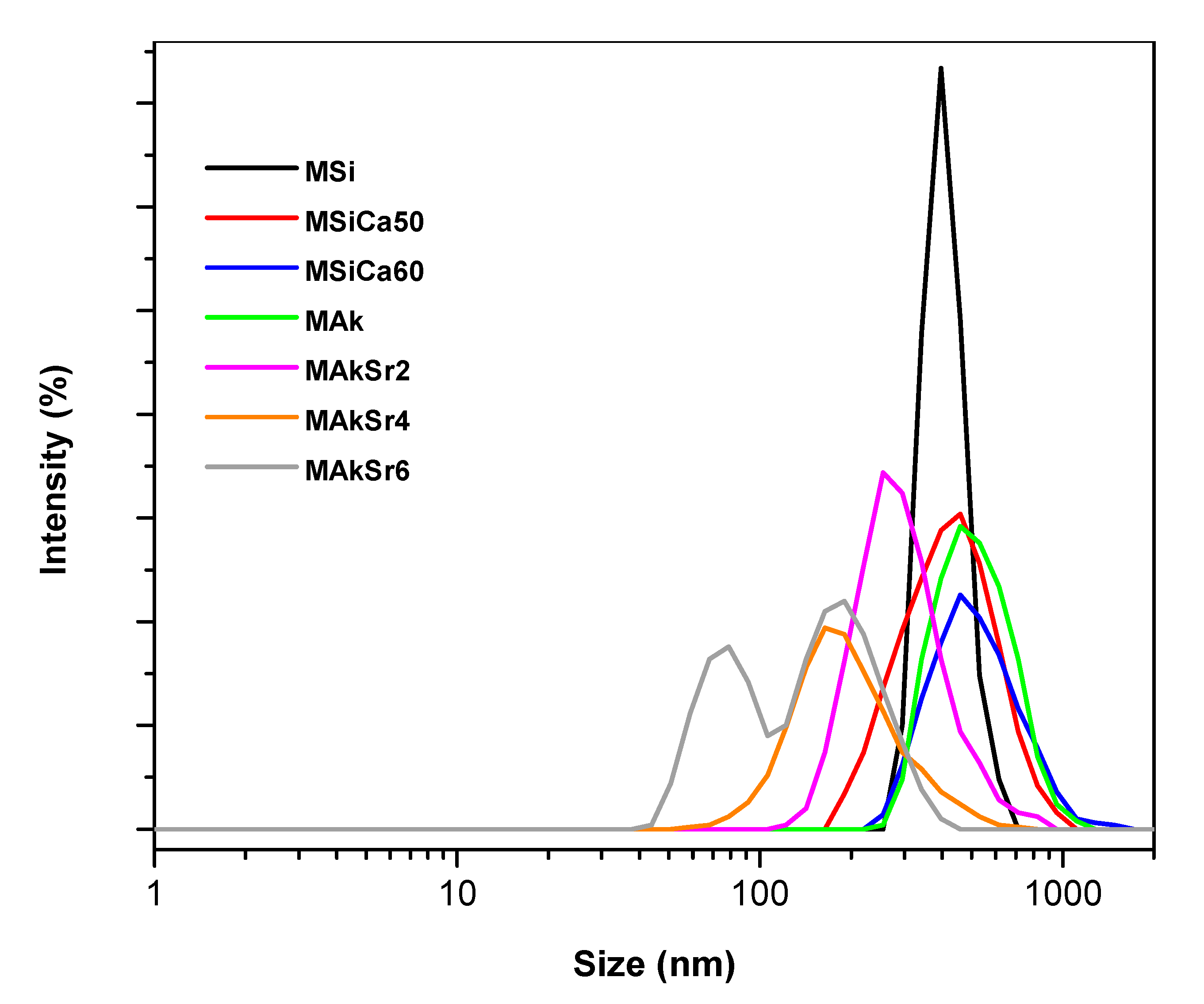
2.3. Particle Size Distribution and Z-potential Measurements by Laser Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.4. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) and Brunauer–Joyner–Halenda (BJH)
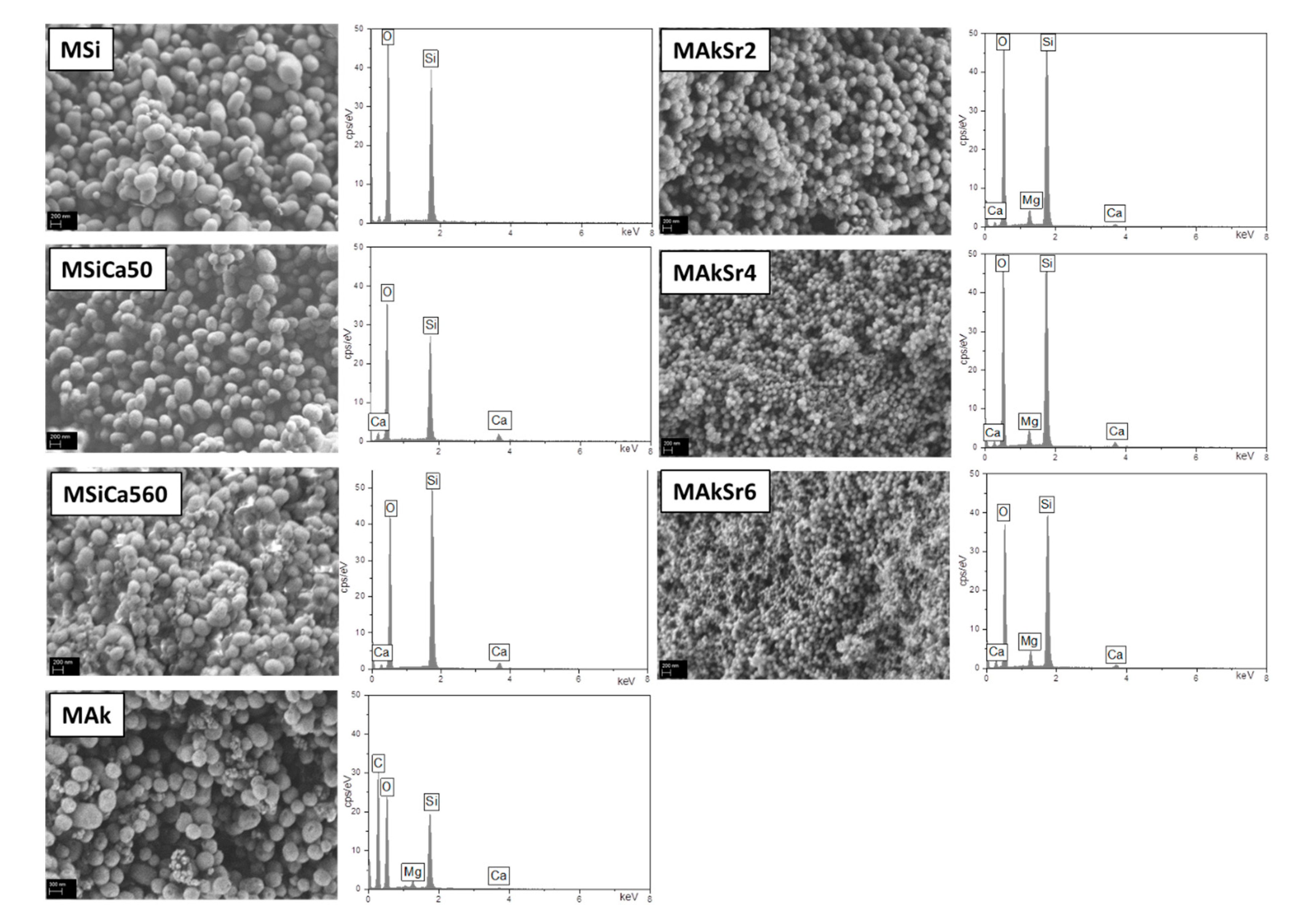
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX)
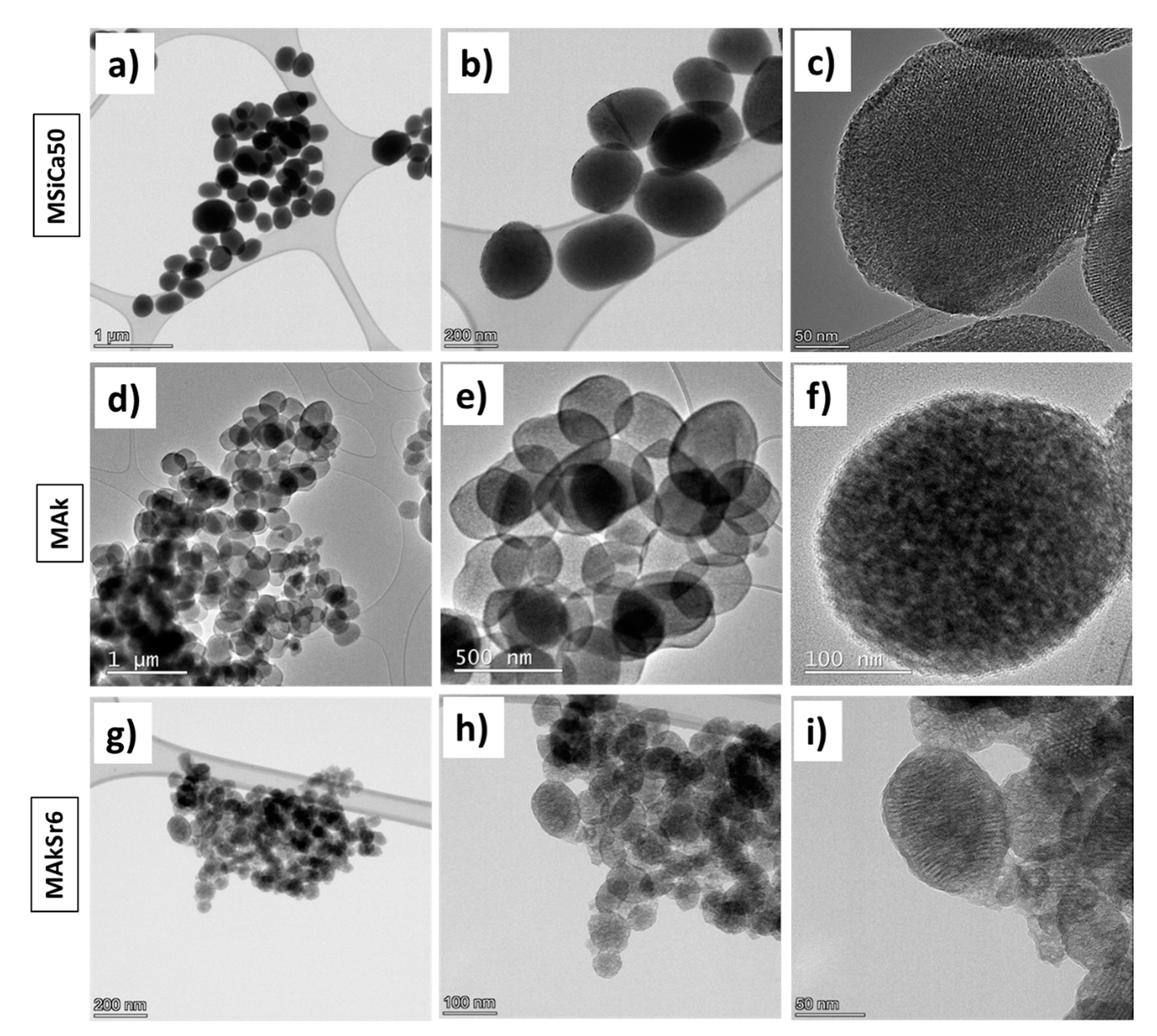
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.7. X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (XRF)
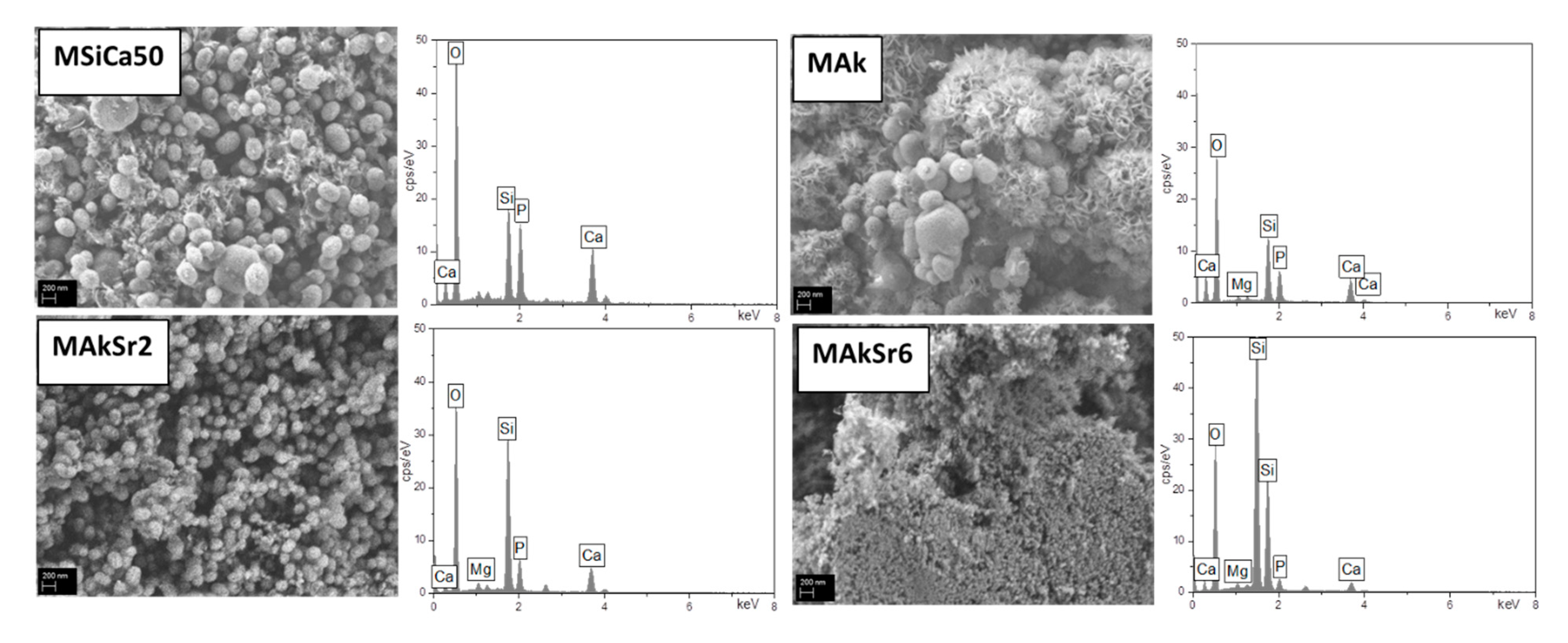
2.8. Apatite Forming Ability in c-SBF
2.9. Drug Loading and Release
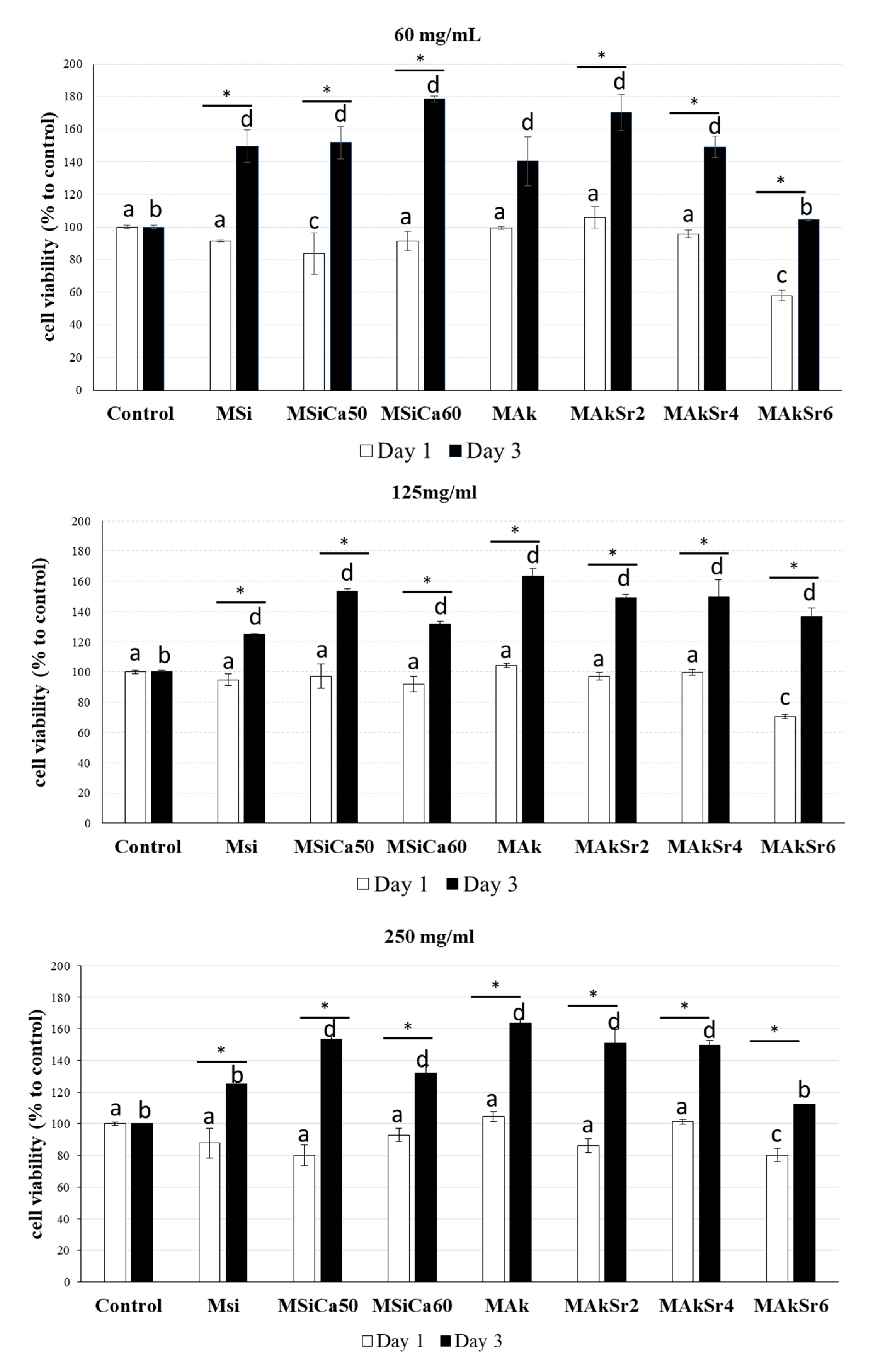
2.10. In Vitro Biocompatibility Assay
2.11. Hemolysis Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of MSNs
4.2. Physico-Chemical Characterization
4.2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.2.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.2.3. Particle Size and Z-Potential Measurements by Laser Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4.2.4. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) and Brunauer–Joyner–Halenda (BJH)
4.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX)
4.2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
4.2.7. X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (XRF)
4.2.8. Apatite Forming Ability in c-SBF
4.2.9. Evaluation of Drug Loading
4.2.10. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
4.3. Biological Properties Evaluation
4.3.1. In Vitro Biocompatibility Assay
4.3.2. Hemocompatibility Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSNs | Mesoporous Silica-based Νanoparticles |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| EDX | Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| XRF | X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy |
| BET/BJH | Brunauer Emmett Teller and Brunauer Joyner Halenda |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| BG | Bioactive Glasses |
| MBGs | Mesoporous bioactive glasses |
| MOX | Moxifloxacin |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol–2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| RBCs | Red Blood Cells |
| BO | Bridging Oxygens |
| NBO | Non Bridging Oxygens |
| HCAp | Hydroxycarbonate Apatite |
| hPDLFs | Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl Orthosilicate |
| DL | Drug Loading |
| SBF | Simulated Body Fluid |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
References
- Seftel, A. Treatment of Infections Associated with Surgical Implants. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okike, K.; Bhattacharyya, T. Trends in the Management of Open Fractures: A Critical Analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2006, 88, 2739–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, G. Biomaterials with antibacterial and osteoinductive properties to repair infected bone defects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothe, R.; Hauser, S.; Neuber, C.; Laube, M.; Schulze, S.; Rammelt, S.; Pietzsch, J. Adjuvant drug-assisted bone healing: Advances and challenges in drug delivery approaches. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Current insights. Molecules 2018, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharti, C.; Gulati, N.; Nagaich, U.; Pal, A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in target drug delivery system: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, S.; Singh, R.K.; Perez, R.A.; Neel, E.A.A.; Kim, H.W.; Chrzanowski, W. Silica-based mesoporous nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Tissue Eng. 2013, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baino, F.; Hamzehlou, S.; Kargozar, S. Bioactive glasses: Where are we and where are we going? J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.R.; Brauer, D.S.; Hupa, L.; Greenspan, D.C. Bioglass and Bioactive Glasses and Their Impact on Healthcare. Int. J. Appl. Glas. Sci. 2016, 7, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profeta, A.C.; Prucher, G.M. Bioactive-glass in periodontal surgery and implant dentistry. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saravanapavan, P.; Jones, J.R.; Pryce, R.S.; Hench, L.L. Bioactivity of gel-glass powders in the CaO-SiO2 system: A comparison with ternary (CaO-P2O5-SiO2) and quaternary glasses (SiO2-CaO-P2O5-Na 2O). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2003, 66, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Lim, D.K.; Kim, S. Calcium-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a lysosomolytic nanocarrier for amine-free loading and cytosolic delivery of siRNA. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 81, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Huang, T.H.; Kao, C.T.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, W.C.; Shie, M.Y. Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Nanoparticles with Drug Delivery and Odontogenesis Properties. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J.; Fan, W. Bioactive mesoporous calcium-silicate nanoparticles with excellent mineralization ability, osteostimulation, drug-delivery and antibacterial properties for filling apex roots of teeth. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 16801–16809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neščáková, Z.; Zheng, K.; Liverani, L.; Nawaz, Q.; Galusková, D.; Kaňková, H.; Michálek, M.; Galusek, D.; Boccaccini, A.R. Multifunctional zinc ion doped sol–gel derived mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciraldo, F.E.; Liverani, L.; Gritsch, L.; Goldmann, W.H.; Boccaccini, A.R. Synthesis and characterization of silver-doped mesoporous bioactive glass and its applications in conjunction with electrospinning. Materials 2018, 11, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bari, A.; Bloise, N.; Fiorilli, S.; Novajra, G.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Bruni, G.; Torres-Pardo, A.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Visai, L.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles as multifunctional agent for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaei, A.H.; Danaeifar, F.; Gammer, C.; Eckert, J.; Khosravimelal, S.; Gholipourmalekabadi, M. Synthesis and characterization of novel mesoporous strontium-modified bioactive glass nanospheres for bone tissue engineering applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 294, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalampounias, A.G. IR and Raman spectroscopic studies of sol-gel derived alkaline-earth silicate glasses. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2011, 34, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabia, Z.; El Mabrouk, K.; Bricha, M.; Nouneh, K. Mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles doped with magnesium: Drug delivery and acellular: In vitro bioactivity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12232–12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorilli, S.; Molino, G.; Pontremoli, C.; Iviglia, G.; Torre, E.; Cassinelli, C.; Morra, M.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. The incorporation of strontium to improve bone-regeneration ability of mesoporous bioactive glasses. Materials 2018, 11, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallach, S. Effects of magnesium on skeletal metabolism. Magnes. Trace Elem. 1990, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diba, M.; Tapia, F.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Strobel, L.A. Magnesium-Containing Bioactive Glasses for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Appl. Glas. Sci. 2012, 3, 221–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudouri, O.M.O.-M.; Kontonasaki, E.; Chrissafis, K.; Zinn, K.; Hoppe, A.; Detsch, R.; Paraskevopoulos, K.M.K.M.; Boccaccini, A.R.A.R. Towards the synthesis of an Mg-containing silicate glass-ceramic to be used as a scaffold for cementum/alveolar bone regeneration. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 16287–16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ke, J.; Prasadam, I.; Miron, R.J.; Lin, S.; Xiao, Y.; Chang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. A comparative study of Sr-incorporated mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds for regeneration of osteopenic bone defects. Osteoporos. Int. 2014, 25, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellberg, B.; Lipsky, B.A. Systemic antibiotic therapy for chronic osteomyelitis in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Shao, J.; Fu, J.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F.; Hooijmans, C.R.; Van Luijk, J.; Yang, F. Topical Host-Modulating Therapy for Periodontal Regeneration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2019, 25, 526–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Tarafder, S. Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1401–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thabit, A.K.; Fatani, D.F.; Bamakhrama, M.S.; Barnawi, O.A.; Basudan, L.O.; Alhejaili, S.F. Antibiotic penetration into bone and joints: An updated review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 81, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Long, T.; Yu, X.B.; Tang, T.T.; Dai, K.R.; Tian, B.; Guo, Y.P.; Zhu, Z.A. Mesoporous bioactive glass as a drug delivery system: Fabrication, bactericidal properties and biocompatibility. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landersdorfer, C.B.; Kinzig, M.; Hennig, F.F.; Bulitta, J.B.; Holzgrabe, U.; Drusano, G.L.; Sörgel, F.; Gusinde, J. Penetration of moxifloxacin into bone evaluated by Monte Carlo simulation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dajcs, J.J.; Thibodeaux, B.A.; Marquart, M.E.; Girgis, D.O.; Traidej, M.; Callaghan, R.J.O. Effectiveness of Cipro oxacin, Levo oxacin, or Moxi oxacin for Treatment of Experimental. Microbiology 2004, 48, 1948–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Theodorou, G.S.; Kontonasaki, E.; Tsamesidis, I.; Pantaleo, A.; Patsiaoura, D.; Papadopoulou, L.; Rhoades, J.; Likotrafiti, E.; Lioutas, C.B.; et al. Effect of ethanol/TEOS ratios and amount of ammonia on the properties of copper-doped calcium silicate nanoceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Dong, P.; Yang, G.H. The size dependence of growth rate of monodisperse silica particles from tetraalkoxysilane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 189, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Bowen, B.; Epstein, N. Production of Monodisperse Colloidal Silica Spheres: Effect of Temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 118, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riti, P.I.; Vulpoi, A.; Ponta, O.; Simon, V. The effect of synthesis route and magnesium addition on structure and bioactivity of sol-gel derived calcium-silicate glasses. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 14741–14748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.; González, P.; Liste, S.; Chiussi, S.; León, B.; Pérez-Amor, M.; Ylänen, H.O.; Hupa, M. Influence of the non-bridging oxygen groups on the bioactivity of silicate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, N.; Strnad, Z.; Šesták, J.; Strnad, J. Thermodynamics of non-bridging oxygen in silica bio-compatible glass-ceramics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 71, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, A. Infrared spectroscopy of micas. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 46, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.R.; Mortuza, M.G. Infrared spectra of xCaO(1-X-z)SiO2zP2O 5 glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2005, 351, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Chem. Int. 2016, 38, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cychosz, K.A.; Thommes, M. Progress in the Physisorption Characterization of Nanoporous Gas Storage Materials. Engineering 2018, 4, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B. Infrared Spectral Interpretation: A System Approach; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; ISBN 0849324637. [Google Scholar]
- Ogino, M.; Ohuchi, F.; Hench, L.L. Compositional dependence of the formation of calcium phosphate films on bioglass. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1980, 14, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filgueiras, M.R.T.; La Torre, G.; Hench, L.L. Solution effects on the surface reactions of three bioactive glass compositions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1993, 27, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Omari, M.M.H.; Jaafari, D.S.; Al-Sou’od, K.A.; Badwan, A.A. Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride. In Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 39, pp. 299–431. ISBN 9780128001738. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, S.; Chakraborti, C.K.; Mishra, S.C.; Nanda, U.N.; Naik, S. FTIR and XRD investigations of some fluoroquinolones. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaith, E.S.; Connolly, S. Evaluation of mesoporous SBA-15 for the controlled delivery of ciprofoxacin hydrochloride. Bioinspired Biomim. Nanobiomater. 2014, 3, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.U.; Ihsan, A.; Sarwar, Y.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Bano, K.; Tehseen, B.; Zeb, N.; Hussain, I.; Ansari, M.T.; Saeed, M.; et al. Hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanostructures; smart nanocarriers with high drug loading and controlled releasing features. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamesidis, I.; Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Lymperaki, E.; Kazeli, K.; Lioutas, C.B.; Christodoulou, E.; Perio, P.; Reybier, K.; Pantaleo, A.; Kontonasaki, E. Effect of ion doping in silica-based nanoparticles on the hemolytic and oxidative activity in contact with human erythrocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 318, 108974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanapavan, P.; Hench, L.L. Mesoporous calcium silicate glasses. II. Textural characterisation. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2003, 318, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.S.; Chicatun, F.; Stähli, C.; Muja, N.; Bureau, M.N.; Nazhat, S.N. Osteoblastic differentiation under controlled bioactive ion release by silica and titania doped sodium-free calcium phosphate-based glass. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, S.; Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S.A.; Bigham, A. The effect of synthesis medium on structure and drug delivery behavior of CTAB-assisted sol–gel derived nanoporous calcium–magnesium–silicate. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 83, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Xia, L.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Pan, H.; Xu, Y.; Lu, W.W.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, J. Biomaterials Enhanced osteoporotic bone regeneration by strontium-substituted calcium silicate bioactive ceramics. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 10028–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgo, D.; Mysen, B.O.; Kushiro, I. Anionic constitution of 1-atmosphere silicate melts: Implications for the structure of igneous melts. Science (80-) 1980, 208, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüssel, C. Introduction to Glass Science and Technology; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 1999; Volume 208. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.M.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Shuva, M.A.H.; Brooks, G.A. Study of the Structure of FeOx-CaO-SiO2-MgO and FeOx-CaO-SiO2-MgO-Cu2O-PdO Slags Relevant to Urban Ores Processing through Cu Smelting. Metals 2020, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, K.; Taccardi, N.; Beltrán, A.M.; Sui, B.; Zhou, T.; Marthala, V.R.R.; Hartmann, M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Timing of calcium nitrate addition affects morphology, dispersity and composition of bioactive glass nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 95101–95111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greasley, S.L.; Page, S.J.; Sirovica, S.; Chen, S.; Martin, R.A.; Riveiro, A.; Hanna, J.V.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Controlling particle size in the Stöber process and incorporation of calcium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basso, A.M.; Nicola, B.P.; Bernardo-Gusmão, K.; Pergher, S.B.C. Tunable Effect of the Calcination of the Silanol Groups of KIT-6 and SBA-15 Mesoporous Materials. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naruphontjirakul, P.; Greasley, S.L.; Chen, S.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Monodispersed strontium containing bioactive glass nanoparticles and MC3T3-E1 cellular response. Biomed. Glas. 2016, 2, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. An Introduction to Bioceramics; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liverani, L.; Boccardi, E.; Beltran, A.M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Incorporation of calcium containing mesoporous (MCM-41-type) particles in electrospun PCL fibers by using benign solvents. Polymers 2017, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, G.X.; Shu, B.; Huang, G.; Lu, W.W.; Pan, H.B. The effect of strontium incorporation into hydroxyapatites on their physical and biological properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Jiang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, Q. The effects of Sr concentration on physicochemical properties, bioactivity and biocompatibility of sub-micron bioactive glasses spheres. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesaraki, S.; Gholami, M.; Vazehrad, S.; Shahrabi, S. The effect of Sr concentration on bioactivity and biocompatibility of sol-gel derived glasses based on CaO-SrO-SiO2-P2O5 quaternary system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Pan, H.; Xu, X.; Tang, R. Toward a detailed understanding of magnesium ions on hydroxyapatite crystallization inhibition. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reviakine, I.; Jung, F.; Braune, S.; Brash, J.L.; Latour, R.; Gorbet, M.; van Oeveren, W. Stirred, shaken, or stagnant: What goes on at the blood–biomaterial interface. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.; McNeil, S. Understanding the correlation between in vitro and in vivo immunotoxicity tests for nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A. Handbook of Immunological Properties of Engineered Nanomaterials; World Scientific: Singapore, 2013; ISBN 9814390259. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Malugin, A.; Ghandehari, H. Impact of silica nanoparticle design on cellular toxicity and hemolytic activity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5717–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.Y.; Duan, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, Z. Oxidative Damage and Energy Metabolism Disorder Contribute to the Hemolytic Effect of Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Bai, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X. Impact of shape and pore size of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on serum protein adsorption and RBCS hemolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Haynes, C.L. Supporting Information: Impacts of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Size, Pore Ordering, and Pore Integrity on Hemolytic Activity. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4834–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, G.; Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.I.; Lin, V.S.Y. Interaction of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with human red blood cell membranes: Size and surface effects. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slowing, I.I.; Wu, C.W.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Lin, V.S.Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for reducing hemolytic activity towards mammalian red blood cells. Small 2009, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, C.; Tomatis, M.; Ghiazza, M.; Rabolli, V.; Bolis, V.; Lison, D.; Fubini, B. In search of the chemical basis of the hemolytic potential of silicas. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerashchenko, B.I.; Gunko, V.M.; Gerashchenko, I.I.; Mironyuk, I.F.; Leboda, R.; Hosoya, H. Probing the silica surfaces by red blood cells. Cytometry 2002, 49, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, D.S.T.; Paula, A.J.; Fonseca, L.C.; Luna, L.A.V.; Silveira, C.P.; Durán, N.; Alves, O.L. Monitoring the Hemolytic Effect of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles after Human Blood Protein Corona Formation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4595–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglekar, M.; Roggers, R.A.; Zhao, Y.; Trewyn, B.G. Interaction effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with different morphologies on human red blood cells. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2454–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, D.V.; Park, J.-K.; Kim, J.-K.; Elineema, G.; Shao, G.N.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.T. Characterization of Calcium-doped Silica Gel Prepared in an Aqueous Solution. Resour. Process. 2012, 59, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, V.G.; Owyoung, J.B.; Saiz, E.; Marshall, S.J.; Marshall, G.W.; Loomer, P.M. The ionic products of bioactive glass particle dissolution enhance periodontal ligament fibroblast osteocalcin expression and enhance early mineralized tissue development. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 98 A, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlstrom, B.L.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Johnson, N.W. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005, 366, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iviglia, G.; Kargozar, S.; Baino, F. Biomaterials, Current Strategies, and Novel Nano-Technological Approaches for Periodontal Regeneration. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarjuna, R.Y.V.; Deepika, P.C.; Venkatesh, M.P.; Rajeshwari, K.G. Evaluation of moxifloxacin-hydroxyapatite composite graft in the regeneration of intrabony defects: A clinical, radiographic, and microbiological study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2016, 7, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemmig, T.F.; Petersilka, G.; Völp, A.; Gravemeier, M.; Zilly, M.; Mross, D.; Prior, K.; Yamamoto, J.; Beikler, T. Efficacy and Safety of Adjunctive Local Moxifloxacin Delivery in the Treatment of Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, M.; Gilani, K.; Mortazavi, S.A. Preparation and characterization of rifampin loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a potential system for pulmonary drug delivery. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Clemens, D.L.; Lee, B.Y.; Dillon, B.J.; Horwitz, M.A.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with pH-Sensitive Nanovalves for Delivery of Moxifloxacin Provide Improved Treatment of Lethal Pneumonic Tularemia. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10778–10789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.Y.; Li, Z.; Clemens, D.L.; Dillon, B.J.; Hwang, A.A.; Zink, J.I.; Horwitz, M.A. Redox-Triggered Release of Moxifloxacin from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Disulfide Snap-Tops Enhances Efficacy Against Pneumonic Tularemia in Mice. Small 2016, 12, 3690–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigham, A.; Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S.A.; Khamsehashari, A.; Chami, A. Surfactant-assisted sol–gel synthesis and characterization of hierarchical nanoporous merwinite with controllable drug release. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florek, J.; Caillard, R.; Kleitz, F. Evaluation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for oral drug delivery-current status and perspective of MSNs drug carriers. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15252–15277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.; Dehghannejad, N.; Hashemikia, S.; Ghasemnejad, M.; Tabebordbar, H. Synthesis and surface modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and its application as carriers for sustained drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Kaur, P.; Bernela, M.; Thakur, R. Synthesis and Optimization of Streptomycin Loaded Chitosan-Alginate Nanoparticles. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 1, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kotcherlakota, R.; Barui, A.K.; Prashar, S.; Fajardo, M.; Briones, D.; Rodríguez-Diéguez, A.; Patra, C.R.; Gómez-Ruiz, S. Curcumin loaded mesoporous silica: An effective drug delivery system for cancer treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Lin, W.; Scholes, P.; Li, M. Investigating the effects of loading factors on the in vitro pharmaceutical performance of mesoporous materials as drug carriers for Ibuprofen. Materials (Basel) 2017, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Mizuno, M.; Yanagisawa, M.; Takadama, H. Bioactive behaviors of porous apatite- and wollastonite-containing glass-ceramic in two kinds of simulated body fluid. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 18, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Kushitani, H.; Sakka, S.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamum, T. Surface-Structure Changes in Bioactive. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemmar, A.; Beegam, S.; Yuvaraju, P.; Yasin, J.; Shahin, A.; Ali, B.H. Interaction of amorphous silica nanoparticles with erythrocytes in vitro: Role of oxidative stress. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Silica-Based Mesoporous Nanoparticles (MSNs), mol% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Surface Area (m2/g) SBET | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Size (nm) | ζ-Potential | PDI |
| MSi | 1279 | 1.003 | 2.4 | 408.8 | −26.700 | 0.362 |
| MSiCa50 | 726 | 0.753 | 2.7 | 437.9 | −22.100 | 0.436 |
| MSiCa60 | 741 | 0.805 | 2.7 | 534.7 | −19.300 | 0.507 |
| MAk | 757 | 0.989 | 3.0 | 522.9 | −20.800 | 0.426 |
| MAkSr2 | 700 | 1.618 | 3.0 | 304.9 | −21.700 | 0.674 |
| MAkSr4 | 737 | 1.994 | 3.0 | 207.4 | −16.000 | 0.699 |
| MAkSr6 | 668 | 1.812 | 3.1 | 151.9 | −15.700 | 0.708 |
| Sample | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | SrO | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N 1 | XRF | N1 | XRF | N 1 | XRF | N1 | XRF | ||
| MSi | 100 | 100.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 |
| MSiCa50 | 50 | 81.57 | 50 | 18.43 | - | - | - | - | 100 |
| MSiCa60 | 60 | 80.69 | 40 | 19.31 | - | - | - | - | 100 |
| MAk | 40 | 66.12 | 40 | 18.41 | 20 | 15.46 | - | - | 100 |
| MAkSr2 | 40 | 58.74 | 40 | 27.04 | 18 | 13.19 | 2 | 1.03 | 100 |
| MAkSr4 | 40 | 64.45 | 40 | 23.34 | 16 | 10.46 | 4 | 1.74 | 100 |
| MAkSr6 | 40 | 72.93 | 40 | 15.95 | 14 | 8.70 | 6 | 2.42 | 100 |
| Sample | % MOX Loading in the MSNs |
|---|---|
| MSi | 15 ± 2 |
| MSiCa50 | 38 ± 1 |
| MSiCa60 | 21 ± 1 |
| MAk | 11 ± 3 |
| MAkSr2 | 12 ± 1 |
| MAkSr4 | 14 ± 1 |
| MAkSr6 | 2 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pouroutzidou, G.K.; Liverani, L.; Theocharidou, A.; Tsamesidis, I.; Lazaridou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Beketova, A.; Pappa, C.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Anastasiou, A.D.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Mg- and Sr-Doped Nanoparticles for Moxifloxacin Drug Delivery in Promising Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020577
Pouroutzidou GK, Liverani L, Theocharidou A, Tsamesidis I, Lazaridou M, Christodoulou E, Beketova A, Pappa C, Triantafyllidis KS, Anastasiou AD, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Mg- and Sr-Doped Nanoparticles for Moxifloxacin Drug Delivery in Promising Tissue Engineering Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020577
Chicago/Turabian StylePouroutzidou, Georgia K., Liliana Liverani, Anna Theocharidou, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Maria Lazaridou, Evi Christodoulou, Anastasia Beketova, Christina Pappa, Konstantinos S. Triantafyllidis, Antonios D. Anastasiou, and et al. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Mg- and Sr-Doped Nanoparticles for Moxifloxacin Drug Delivery in Promising Tissue Engineering Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020577
APA StylePouroutzidou, G. K., Liverani, L., Theocharidou, A., Tsamesidis, I., Lazaridou, M., Christodoulou, E., Beketova, A., Pappa, C., Triantafyllidis, K. S., Anastasiou, A. D., Papadopoulou, L., Bikiaris, D. N., Boccaccini, A. R., & Kontonasaki, E. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Mg- and Sr-Doped Nanoparticles for Moxifloxacin Drug Delivery in Promising Tissue Engineering Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020577