Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
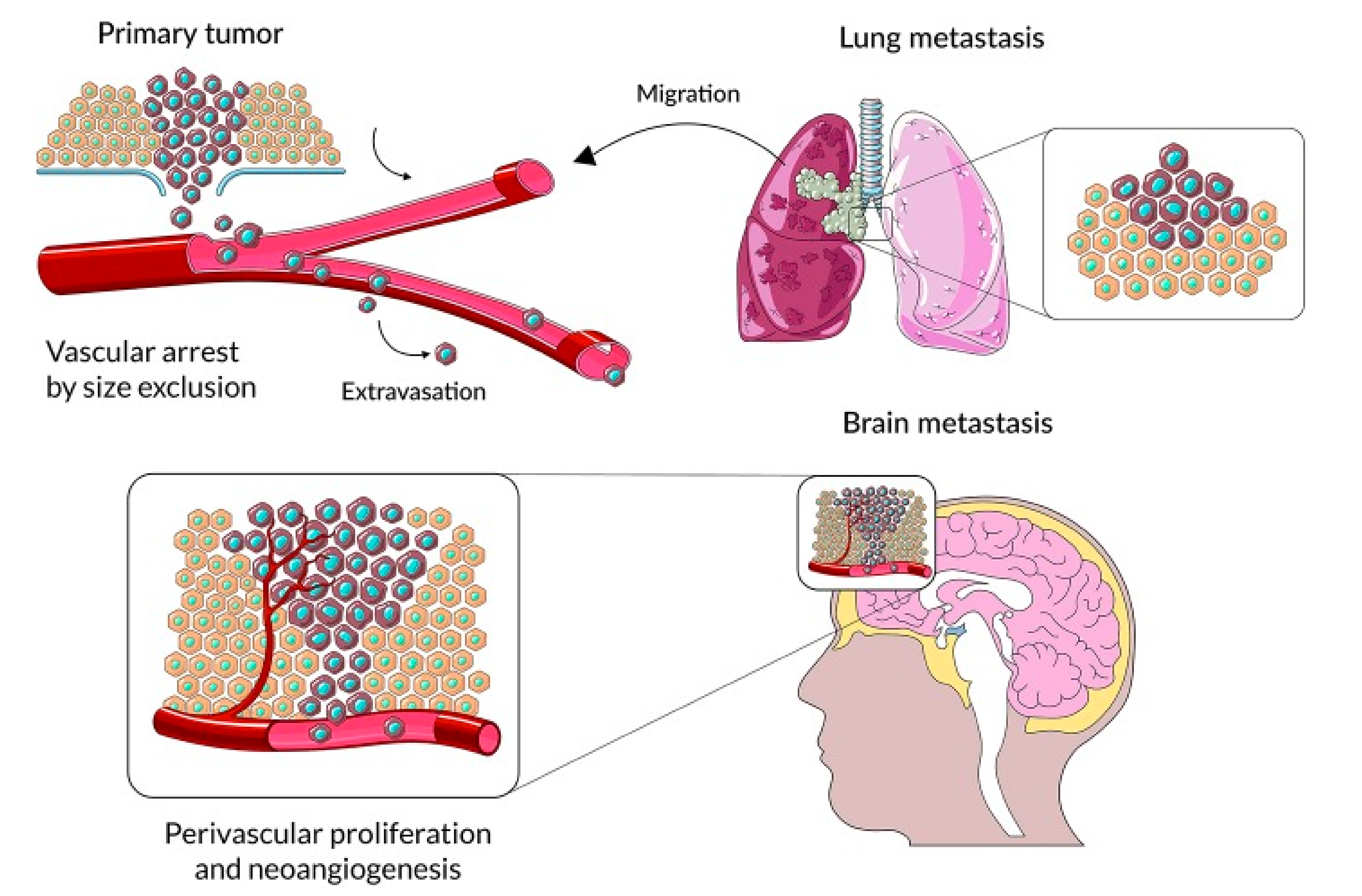
2. The Mechanism of Brain Metastasis Formation Is Similar to Other Organ Locations
3. Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma without Activating the Mutation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) or Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)
4. Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma with Present Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutation and ALK Rearrangement
5. Simultaneous CNS Radiotherapy and TKI Therapy
6. Immunotherapy of Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Didkowska, J.; Wojciechowska, U. Cancer in Poland in 2017; The Maria Sklodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Center: Warsaw, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chason, J.L.; Walker, F.B.; Landers, J.W. Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer 1963, 16, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, E.S.; Djalilian, H.R.; Cho, K.H.; Hall, W.A. Brain metastases. Histology, multiplicity, surgery, and survival. Cancer 1996, 78, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimm, S.; Wampler, G.L.; Stablein, D.; Hazra, T.; Young, H.F. Intracerebral metastases in solid-tumor patients: Natural history and results of treatment. Cancer 1981, 48, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagney, D.N.; Martin, A.M.; Catalano, P.J.; Redig, A.J.; Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q. Incidence and prognosis of patients with brain metastases at diagnosis of systemic malignancy: A population-based study. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Varambally, S.; Creighton, C.J. Molecular correlates of metastasis by systematic pan-cancer analysis across the cancer genome atlas. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 17, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, C.G.; Pricola, K.; Sarmiento, J.M.; Garg, S.K.; Bryant, A.; Black, K.L. Whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) alone versus WBRT and radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 9, CD006121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Baluszek, S.; Kamiska, B. Immune microenvironment of brain metastases–are microglia and other brain macrophages little helpers? Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muliaditan, T.; Caron, J.; Okesola, M.; Opzoomer, J.W.; Kosti, P.; Georgouli, M.; Gordon, P.; Lall, S.; Kuzeva, D.M.; Pedro, L.; et al. Macrophages are exploited from an innate wound healing response to facilitate cancer metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lassman, A.B.; De Angelis, L.M. Brain metastases. Neurol. Clin. 2007, 25, 1173–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, F.J.; Yu, D. Brain metastasis: Unique challenges and open opportunities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2017, 1867, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, D.W.; Scott, C.B.; Sperduto, P.W.; Flanders, A.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schell, M.C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Demas, W.; Ryu, J.; Bahary, J.-P. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: Phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, Y.Y.; Tham, I.W.; Lim, K.H.; Koh, W.Y.; Lu, J.J. Surgery or radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus surgery or radiosurgery alone for brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, CD009454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahgal, A.; Aoyama, H.; Kocher, M.; Neupane, B.; Collette, S.; Tago, M.; Shaw, P.; Beyene, J.; Chang, E.L. Phase 3 trials of stereotactic radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiation therapy for 1 to 4 brain metastases: Individual patient data meta-analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulvena, P.M.; Nankivell, M.G.; Barton, R. Whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases from non-small lung cancer: Quality of life (QoL) and overall survival (OS) results from the UK Medical Research Council (QUARTZ) randomised clinical trial (ISRCTN 3826061). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. 20), 8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.; Gondi, V.; Takakura, K.; Saeki, N.; Kunieda, E. Recent advances in managing brain metastasis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsao, M.N.; Lloyd, N.; Wong, R.K. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 4, CD003869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Um, S.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.S.; et al. A randomized phase III trial of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) versus observation for patients with asymptomatic cerebral oligo-metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 62–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinet, G.; Thomas, P.; Breton, J.L.; Lena, H.; Gouva, S.; Dabouis, G.; Bennouna, J.; Souquet, P.J.; Balmes, P.; Thiberville, L.; et al. Results of a phase III study of early versus delayed whole brain radiotherapy with concurrent cisplatin and vinorelbine combination in inoperable brain metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Groupe Francais de Pneumo- Cancerologie (GFPC) Protocol 95-1. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecht, C.J.; Hovestadt, A.; Verbiest, H.B.; van Vliet, J.J.; van Putten, W.L. Dose-effect relationship of dexamethasone on Karnofsky performance in metastatic brain tumors: A randomized study of doses of 4.8 and 16mg per day. Neurology 1994, 44, 65–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Novello, S.; Barlesi, F.; Califano, R.; Cufer, T.; Ekman, S.; Giaj Levra, M.; Kerr, K.; Popat, S.; Reck, M.; Senan, S.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. 5), V1–V27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): A rising star in the era of precision medicine of lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50209–50220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J., Jr.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Zhou, Y.; Ozawa, T.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W. Ligand-activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling governs endocytic trafficking of unliganded receptor monomers by non-canonical phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sooro, M.A.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, P. Targeting EGFR-mediated autophagy as a potential strategy for cancer therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppel, T.R.; Sarpong, K.; Murray, E.M.; Monsey, J.; Zhu, J.; Bose, R. Biophysical Evidence for Intrinsic Disorder in the C-terminal tails of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and HER3 Receptor tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 597610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, R.; Srivastava, S.; Katreddy, R.R.; Sobieski, J.; Zhang, W. Kinase-inactivated EGFR is required for the survival of wild-type EGFR-expressing cancer cells treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, E.; Feld, E.; Horn, L. Driven by mutations: The predictive value of mutation subtype in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Yu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, P. Uncommon mutation types of epidermal growth factor receptor and response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Son, J.; Park, E.; Kosaka, T.; Saxon, J.A.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Choi, H.G.; Tanizaki, J.; Eck, M.J.; Janne, P.A.; et al. Discovery of a highly potent and broadly effective epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 exon20 insertion mutant inhibitor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 7, 11629–11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, T.; Tanizaki, J.; Paranal, R.M.; Endoh, H.; Lydon, C.H.; Capelletti, M.; Repellin, C.E.; Choi, J.; Ogino, A.; Calles, A.; et al. Response heterogeneity of EGFR and HER2 Exon 20 insertions to covalent EGFR and HER2 inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Yang, T.J. Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: An update of the Graded Prognostic Assessment for Lung Cancer Using Molecular Markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. North- East Japan Study Group. Gefitinib or chemiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Maemondo, M. Updated overall survival results from a randomized phase III trial comparing gefitinib with carboplatin-paclitaxel for chemo-naive non-small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR gene mutations (NEJ002). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Park, K.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.T.; Ahn, M.J.; Yun, T.; Ahn, J.S.; Suh, C.H.; et al. First-SIGNAL: First-line single-agent iressa versus gemcitabine and cisplatin trial in never-smokers with adenocarcinoma of the lung. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G. Final overall survival results from a randomised phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heon, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Britt, J.; Costa, D.B.; Rabin, M.S.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E. Development of Central Nervous System Metastases in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and somatic EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Cancer Therapy. 2010, 16, 5873–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haaland, B.; Tan, P.S.; De Castro, G., Jr.; Lopes, G. Meta-Analysis of First-Line Therapies in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR-Activating Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Togashi, Y.; Masago, K.; Fukudo, M.; Tsuchido, Y.; Okuda, C.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Ikemi, Y.; Sakamori, Y.; Mio, T.; Katsuta, T.; et al. Efficacy of increased-dose erlotinib for central nervous system metastases in non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gromes, C.; Oxnard, G.R.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Pao, W.; Holodny, A.I.; Clarke, J.L.; Lassman, A.B. Pulsatile high-dose weekly erlotinib for CNS metastases from EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, J.L.; Pao, W.; Wu, N. High dose weekly erlotinib achieves therapeutic concentrations in CSF and is effective in leptomeningeal metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung cancer. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 99, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, C.R.; Janne, P.A. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackman, D.; Pao, W.; Riely, G.J.; Engelman, J.A.; Kris, M.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lynch, T.; Johnson, B.E.; Miller, V.A. Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Sequist, L.V.; Geater, S.L.; Tsai, C.H.-M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Schuler, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yu, C.-J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Zhou, C.; et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: A combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, Lux-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung 6. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P. LUX-Lung 6: A randomized, open-label, phase III study of afatinib (A) versus gemcitabine/cisplatin (GC) as first-line treatment for Asian patients with EGFR mutation-positive (EGFR M+) advanced adenocarcinoma for the lung. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, A.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Jassem, J. Management of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 71, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Sequist, L.V.; Zhhou, C.; Schuler, M.; Geater, S.L.; Mok, T.; Hu, C.-P.; Yamamoto, N.; Feng, J.; Byrne, K.O.; et al. Effect of dose adjustment on the safety and efficacy of afatinib for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma: Post hoc analyses of the randomized LUX-Lung 3 and 6 trials. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.; Hirsh, V.; Cadranel, J. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): A phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Schuler, M.; Sebastian, M.; Popat, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.-P.; O’Byrne, K.; Feng, J.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): Analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. Febr. 2015, 16, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.-P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX_Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Wu, Y.L.; Hirsh, V.; O’Byrne, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Mok, T.; Popat, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Massey, D.; Zazulina, V.; et al. First-line afatinib versus chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and common epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and brain metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckl, W.M.; Laack, E.; Reck, M.; Griesinger, F.; Schafer, H.; Kortsik, C.; Gaska, T.; Rawluk, J.; Kruger, S. Effectiveness of afatinib in clinical practice—First results of the GIDEON trial: A prospective non-interventional study in EGFR-mutated NSCLC in Germany. ESMO 2018, 19, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Odogwu, L.; Mathieu, L.; Goldberg, K.B.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Larkins, E.; Fiero, M.H.; Rodriguez, L.; Bijwaard, K.; Lee, E.Y.; Philip, R.; et al. FDA Benefit-Risk Assessment of Osimertinib for the Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor T790M Mutation. Oncologist 2018, 23, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, D.A.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, R.V.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291 an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Su, W.-C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor- resistant non-small-cell lung cancer AURA 2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Marcello, T. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, G.; Tsai, C.M.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bazhenova, L.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, G.-C.; Crino, L.; Satouchi, M.; Chu, Q.; Hida, T.; et al. Osimertinib for pretreated EFGR Thr 790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Su, W.-C.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; et al. Osimertinib in pretreated T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, S.M.E.; et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirashima, T.; Satouchi, M.; Hida, T.; Nishio, M.; Kato, T.; Sakai, H.; Imamura, F.; Kiura, K.; Okamoto, I.; Kasahara, K.; et al. Osimertinib for Japanese patients with T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A pooled subgroup analysis. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2884–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, M.J.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Cho, B.C.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Mitsudomi, T.; Lee, J.S. Osimertinib in Patients with T790M-Positive Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Korean Subgroup Analysis from Phase II Studies. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 52, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteekiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced Non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassunke, J.; Muller, F.; Keul, M.; Michels, S.; Dammert, M.A.; Schmitt, A.; Plenker, D.; Lategahn, J.; Heydt, C.; Bragelmann, J.; et al. Overcoming EGFRG724S-mediated osimertinib resistance through unique binding characteristics of second-generation EGFR inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Brown, K.H.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Ohe, Y.; Felip, E.; Leese, P.; Cantarini, M.; Vishwanathan, K.; Janne, P.A.; et al. Osimertinib Western and Asian clinical pharmacokinetics in patients and healthy volunteers: Implications for formulation, dose, and dosing frequency in pivotal clinical studies. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Okamoto, I.; Sriuranpong, V.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Imamura, F.; Lee, J.S.; Pang, Y.-K.; Cobo, M.; Kasahara, K.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Tissue and plasma EGFR mutation analysis in the FLAURA trial: Osimertinib versus comparator EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor as first-line treatment in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6644–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlisle, J.W.; Ramalingam, S.S. Improving outcomes for brain metastases in EGFR mutated NSCLC. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8 (Suppl. 4), S355–S359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Okamoto, I.; Kurata, T.; Kato, T.; Sugawara, S.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Uchida, H.; Hodge, R.; et al. Osimertinib versus standard-of-care EGFR-TKI as first line treatment for EGFRm advanced NSCLC FLAURA Japanese subset. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakai, H.; Hayashi, H.; Iwasa, T. Successful osimertinib treatment for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from lung adenocarcinoma with the T790M mutation of EGFR. ESMO Open 2017, 2 (Suppl. 1), e000104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; Hassan, O.U.; Yang, Y.-W.; Buchanan, P. Lung cancer: Biology and treatment options. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.-I.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK Fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Riely, G.J.; Shaw, A.T. Targeting ALK: Precision medicine takes on drug resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noe, J.; Lovejoy, A.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Yaung, S.J.; Bordogna, W.; Klass, D.M.; Cummings, C.A.; Shaw, A.T. ALK mutation status before and after alectinib treatment in locally advanced or metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC: Pooled analysis of two prospective trials. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metro, G.; Lunardi, G.; Floridi, P.; Pascali, J.P.; Marcomigni, L.; Chiari, R.; Ludovini, V.; Crino, L.; Gori, S. CSF concentration of crizotinib in two ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer patients with CNS metastases deriving clinical benefit from treatment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, e26–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, B.J.; Cappuzzo, F.; Felip, E.; Blackhall, F.H.; Costa, D.B.; Kim, D.-W.; Nakagawa, K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Mekhail, T.; Paolini, J.; et al. Intracranial efficacy of crizotinib versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced alk-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from Profiel 1014. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blackhall, F.; Cappuzzo, F. Crizotinib: From discovery to accelerated development to front-line treatment. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. 3), i35–i41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.H.; Janne, P.A.; Bartlett, C.H.; Tang, Y.; Kim, D.W.; Otterson, G.A.; Crino, L.; Selaru, P.; Cohen, D.P.; Clark, J.W.; et al. Clinical benefit of continuing ALK inhibition with crizotinib beyond initial disease progression in patients with advanced ALK- positive NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, N.; Ohe, Y.; Gemma, A.; Kusumoto, M.; Yamada, I.; Ishii, T.; Yamamoto, N. Safety and effectiveness of alectinib in a real-world surveillance study in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in Japan. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novello, S.; Mazieres, J.; Oh, I.J.; Castro, J.; de Migliorino, M.R.; Helland, A.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus chemotherapy in crizotinib-pretreated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from the phase III ALUR study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachaliou, N.; Bruno MFBracht, J.W.P.; Rosell, R. Profile of alectinib for the treatment of ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Patient selection and perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 4567–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, A.; Gandhi, L.; Gadgeel, S.; Riely, G.J.; Cetnar, J.; West, H.; Camidge, D.R.; Socinski, M.A.; Chiappori, A.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Alectinib in ALK-positive, crisotinib resistant, non-small-cell lung cancer: A single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishio, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kuriki, H.; Zeaiter, A.; Tamura, T. Analysis of central nervous system efficacy in the J-ALEX study of alectinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 121, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camidge, D.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Noe, J.; Nowicka, M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Cheema, P.; Pavlakis, N.; De Marinis, F.; et al. Efficacy and safety data and impact of the EML4-ALK Fusion variant of the efficacy of alectinib in untreated ALK-positive advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Global Phase III ALEX Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasini, P.; Egea, J.; Souquet-Bressand, M.; Greillier, L.; Barlesi, F. Alectinib in the treatment of ALK-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical trial evidence and experience with a focus on brain metastases. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2019, 13, 1753466619831906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.-J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum- based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND -4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Araki, M.; Sakashita, T.; Ma, B.; Kanada, R.; Yanagitani, N.; Horiike, A.; Koike, S.; Watanabe, K.; Tamai, K.; et al. Prediction of ALK mutations mediating ALK-TKIs resistance and drug re-purposing to overcome the resistance. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrows, S.T.; Wright, K.; Copley-Merriman, C.; Kaye, J.A.; Chioda, M.; Wiltshire, R.; Torgersen, K.M.; Masters, E. Systematic review of sequencing of ALK inhibitors in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer Targets Ther. 2019, 10, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-W.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Felip, E.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Camidge, D.R.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; De Pas, T.; Riely, G.J.; et al. Activity and safety of ceritinib in patients with ALK- rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEDN-1): Updated results from the multicentre, open- label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felip, E.; Crino, L.; Kim, D.W.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Felip, E. Whole body and intracranial efficacy of ceritinib in patients (pts) with crizotinib CRZ) pretreated, ALK-rearranged (ALK+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and baseline brain metastases (BM): Results from ASCEND-1 and ASCEND-2 trials. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, S118–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, E.; Orlov, S.; Park, K.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Wolf, J. ASCEND-3: A single- arm, open- label, multicenter phase II study of ceritinib in ALK- naive adult patients (pts) with ALK-rearranged (ALK+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Zhu, V.W.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Yeap, B.Y.; Saxena, A.; Ferris, L.A.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Farago, A.F.; Taber, A.; Traynor, A.; et al. Brigatinib in Patients with Alectinib- Refractory ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Hochmar, M.J.; Li, J.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 397, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Tiseo, M.; Ahn, M.J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Hansen, K.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Huber, R.M.; West, H.L.; Groen, H.J.M.; Hochmair, M.J.; et al. Brigatinib in patients with crizotinib-refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase- positive non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.H.; Tiseo, M.; Camidge, D.R. Brigatinib (BRG) in Patients (pts) with Crizotinib (CRZ)-Refractory ALK+ Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Brain Metastases in the Pivotal Randomized Phase 2 ALTA Trial; Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- LORBRENA (Lorlatinib). U.S. Prescribing Information; Pfizer Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Soo, R.A.; Riely, G.J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Clancy, J.S.; Li, S.; et al. ALK resistance mutations and efficacy of lorlatinib in advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.Y.; Friboulet, L.; Kodack, D.P.; Engstrom, L.D.; Li, Q.; West, M.; Tang, R.W.; Wang, H.; Tsaparikos, K.; Wang, J.; et al. PF-06463922, an ALK/ROS1 inhibitor, overcomes resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in pre-clinical models. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaw, A.T.; Felip, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Navarro, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Johnson, M.; Dietrich, J.; James, L.P.; et al. Loratynib in non-small cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: An international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Besse, B.; James, L.P. Safety and efficacy of loratynib from the dose escalation component of a study in patients with advanced ALK+ or ROS+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomo, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.-C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Mak, R.H.; Oxnard, G.R. Targed therapy as an alternative to whole-brain radiotherapy in EGFR-mutant or ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1274–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Lu, Z.; Bi, N.; Wang, L. Comparison of up-front radiotherapy and TKI with TKI alone for NSCLC with brain metastases and EGFR mutation: A meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2018, 122, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, F.; Ren, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J. EGFR TKI plus WBRT demonstrated no survival benefit other than that of TKI alone in patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutation and brain metastases. J. Thotacic. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Hasan, B.; De Maio, E.; Berghoff, A.S.; Girard, N.; Greillier, L.; Lantuejoul, S.; Obrien, M.; Reck, M.; et al. Young Investigators EORTC Lung Cancer Group. Diversity of brain metastases screening and management in non-small cell lung cancer in Europe: Results of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer lung Cancer group survey. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 93, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hiu, R.; Csoszi, T.; Fulop, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.-W.; Felip, E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.-J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESMO Guidelines Committee. Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/lung-and-chest-tumours/clinical-practice-living-guidelines-metastatic-non-small-cell-lung-cancer (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crino, L.; Bronte, G.; Bidoli, P.; Cravero, P.; Mineza, E.; Cortesi, E.; Garassino, M.C.; Proto, C.; Cappuzzo, F.; Grossi, F.; et al. Nivolumab and brain metastases in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 129, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]










| Prognostic Class | Characteristic | Median Survival (Months) |
|---|---|---|
| I | KPS ≥ 70, < 65 years, controlled primary tumor and no extracranial metastases | 7.1 |
| II | KPS ≥ 70, primary tumor not controlled | 4.2 |
| KPS ≥ 70, controlled primary tumor ≥ 65 years | ||
| KPS ≥ 70, controlled primary tumor | ||
| <65 years and extracranial metastases | ||
| III | KPS < 70 | 2.3 |
| Prognostic Factor | Age (Years) | KPS | Extracranial Metastases | Number of BM | Gene Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ≥70 | <70 | Present | >4 | EGFR neg/unk and ALK neg/unk |
| 0.5 | <70 | 70–80 | - | 1–4 | NA |
| 1 | - | 90–100 | Absent | NA | EGFR-pos or ALK-pos |
| Compound | CSF Penetration Rate (%) | CSF Concentration ng/mL or nM/L |
|---|---|---|
| Gefitinib | 1.13 ± 0.36% | 3.7 ± 1.9 ng/mL |
| 8.2 ± 4.3 nM/L | ||
| Erlotinib | 2.8–5.1% | 28.7 ± 16.8 ng/mL |
| 66.9 ± 39.0 nM/L | ||
| Afatynib | <1% | 0.464 ng/mL |
| Crizotinib | 0.26% | 0.616 ng/mL |
| Alectinib | 0.86 | 2.69 nM/L |
| Ceritinib | 0.15 | not reported |
| Lorlatinib | 20–30% | not reported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rybarczyk-Kasiuchnicz, A.; Ramlau, R.; Stencel, K. Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020593
Rybarczyk-Kasiuchnicz A, Ramlau R, Stencel K. Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020593
Chicago/Turabian StyleRybarczyk-Kasiuchnicz, Agnieszka, Rodryg Ramlau, and Katarzyna Stencel. 2021. "Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020593





