Effectiveness of Columbianadin, a Bioactive Coumarin Derivative, in Perturbing Transient and Persistent INa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
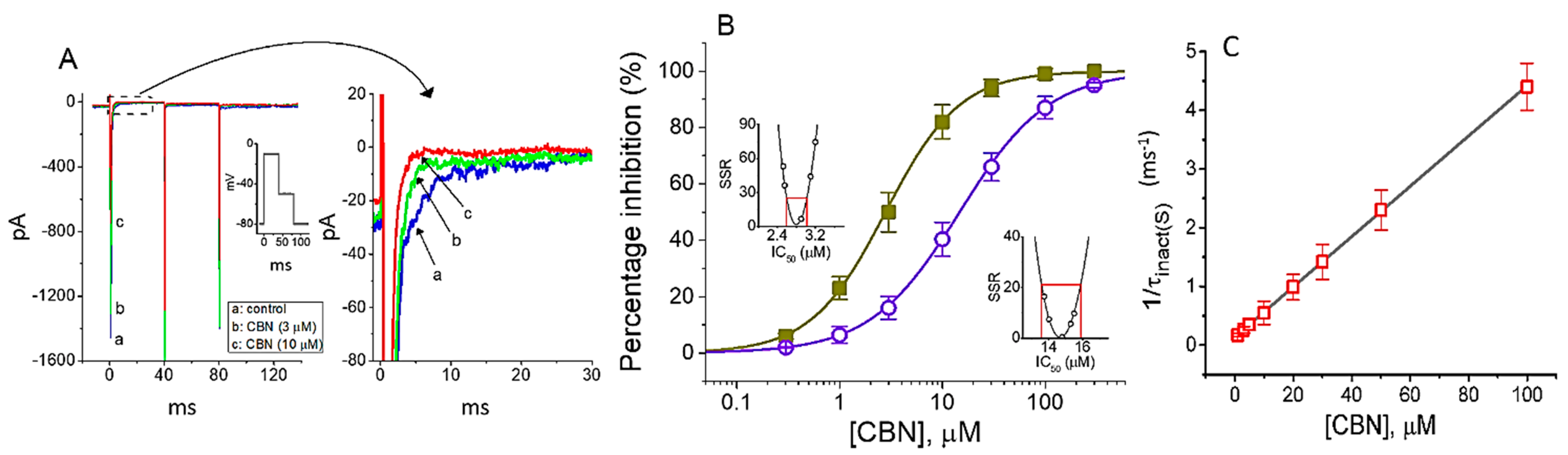
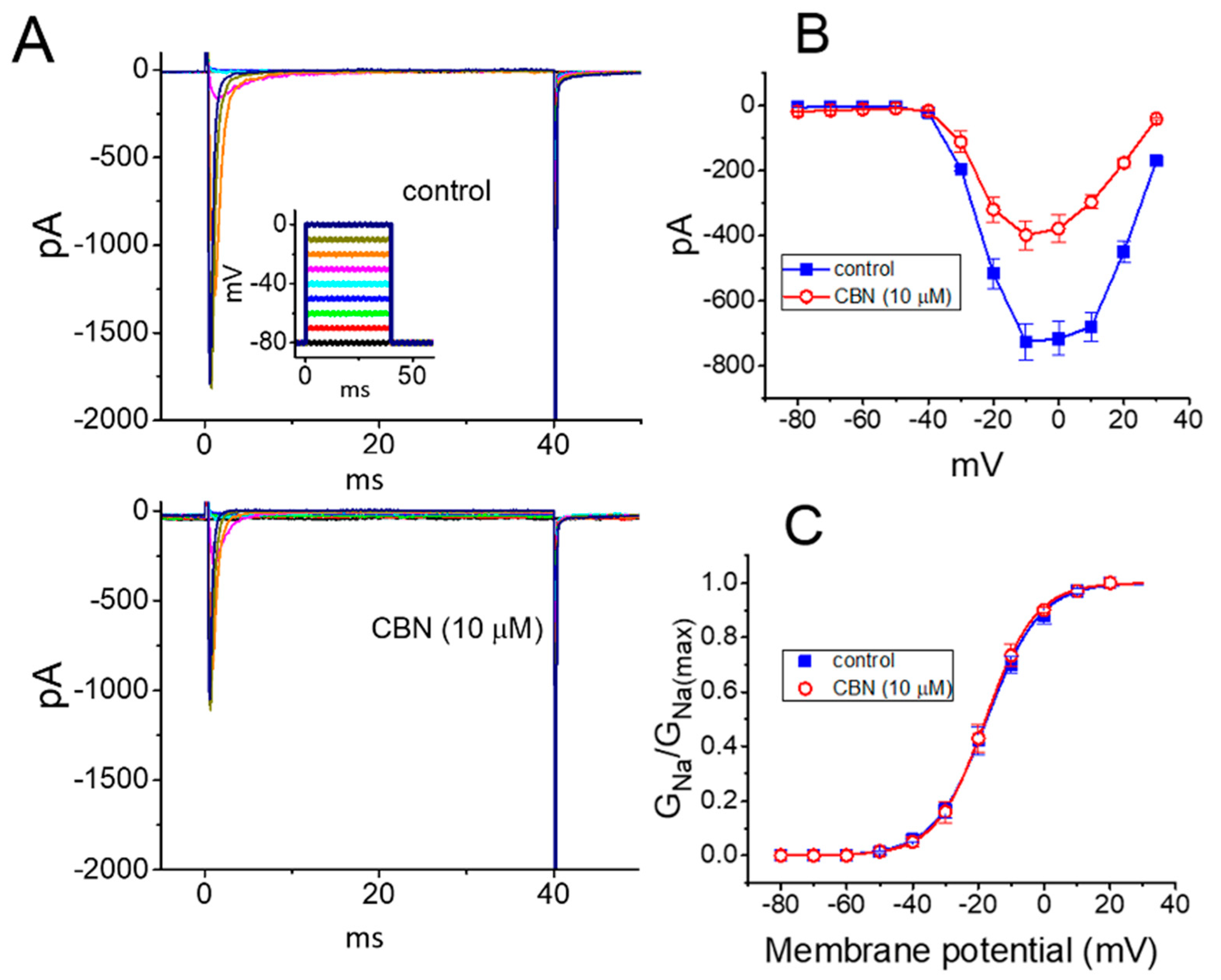
2.1. Effect of Columbianadin (CBN) on Voltage-Gated Na+ Current (INa) Recorded from GH3 Cells
2.2. Kinetic Study of CBN Action on INa
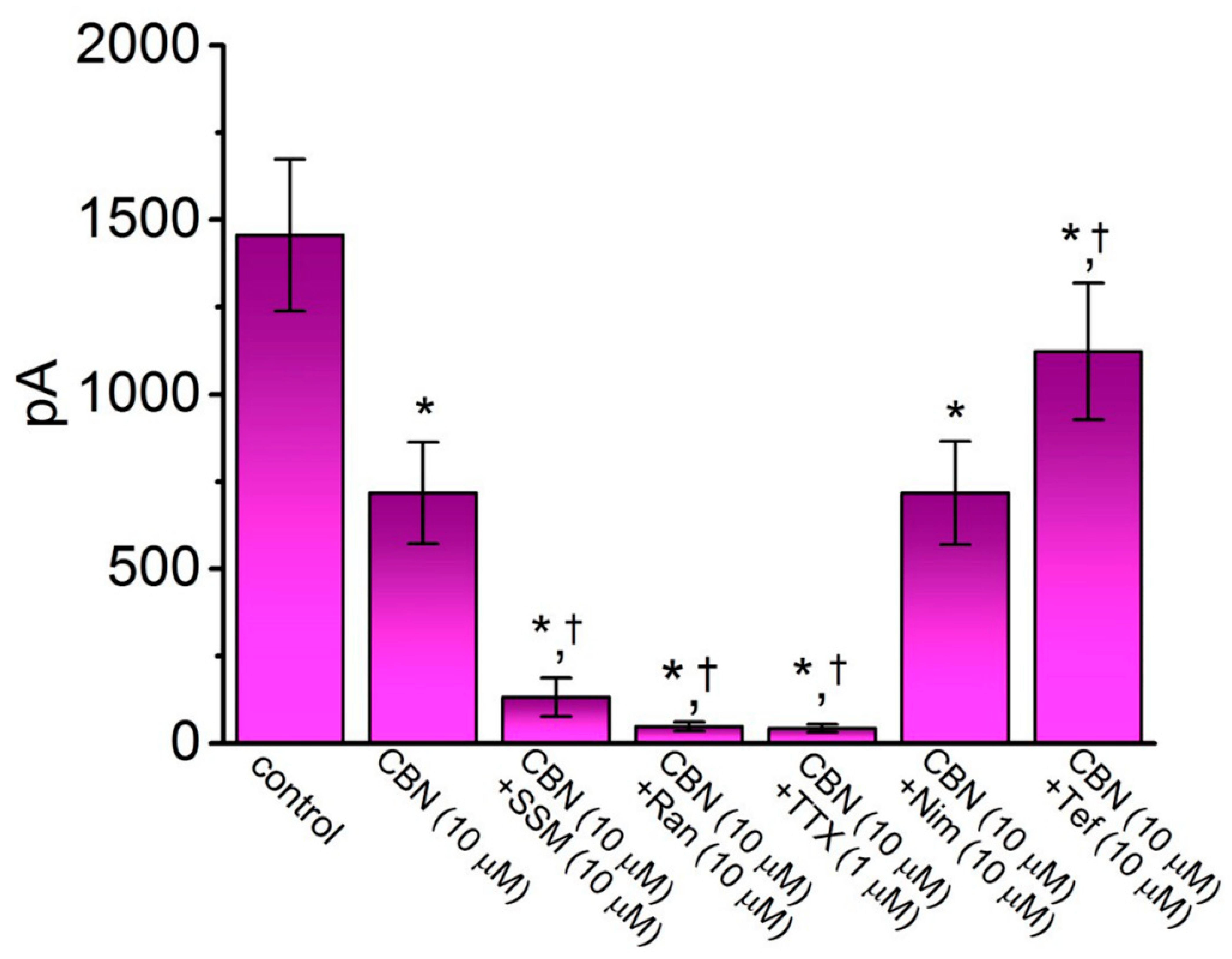
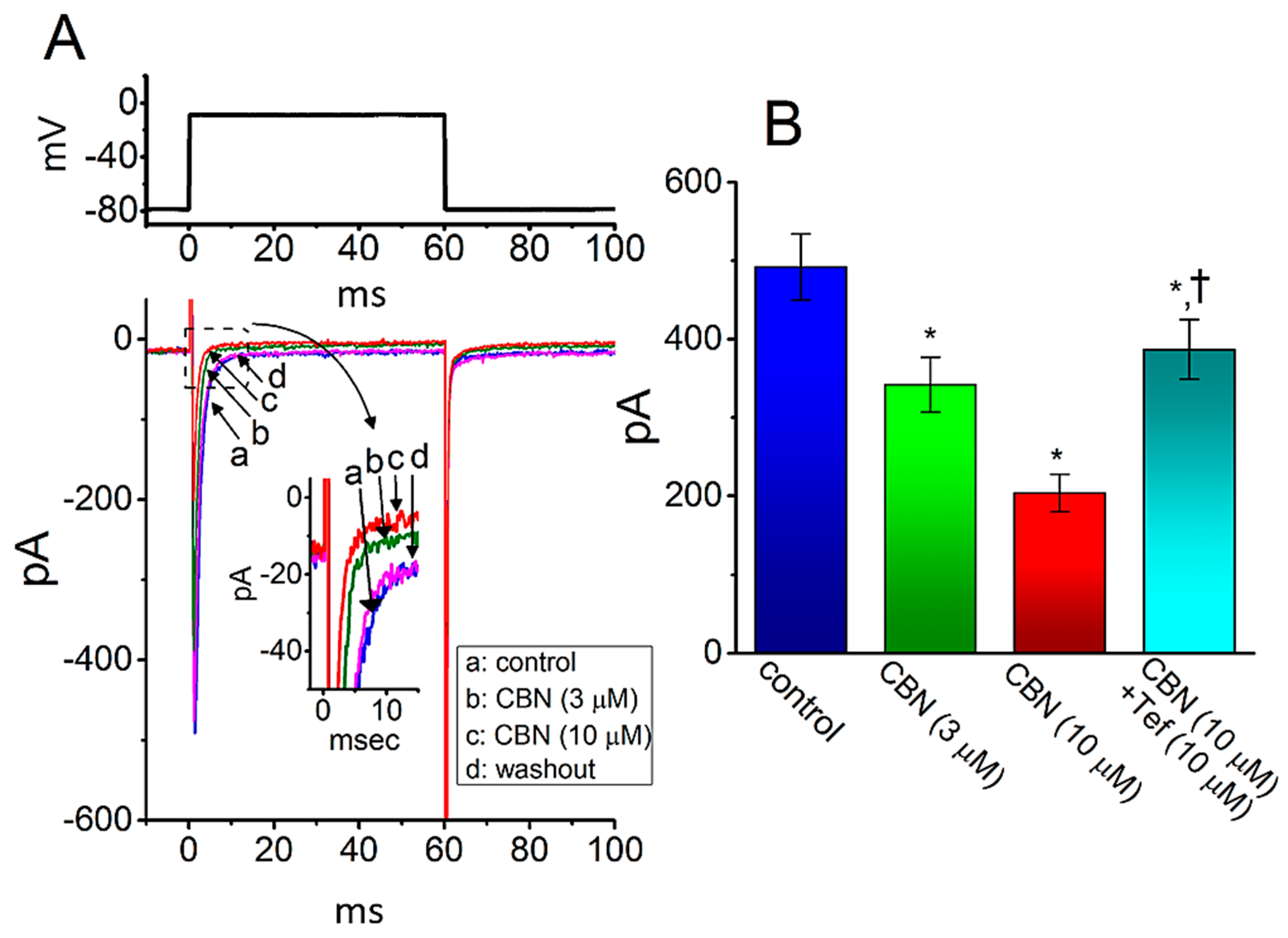
2.3. Comparison among Effects of CBN, CBN Plus Sesamin (SSM), CBN Plus Ranolazine (Ran), CBN Plus Tetrodotoxin (TTX), CBN Plus Nimodipine (Nim), and CBN Plus Tefluthrin (Tef) on Peak INa Recorded from GH3 Cells
2.4. Lack of Effect of CBN on the Steady-State Activation Curve of INa
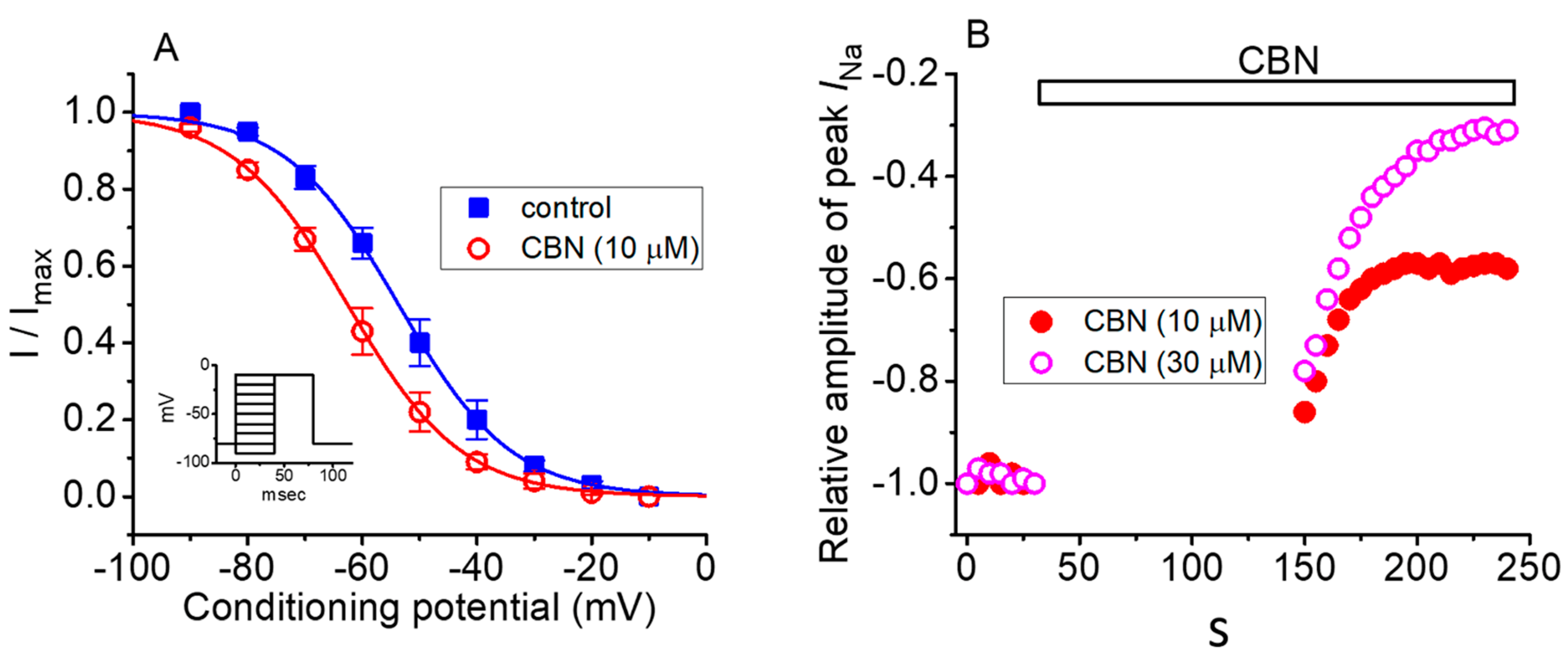
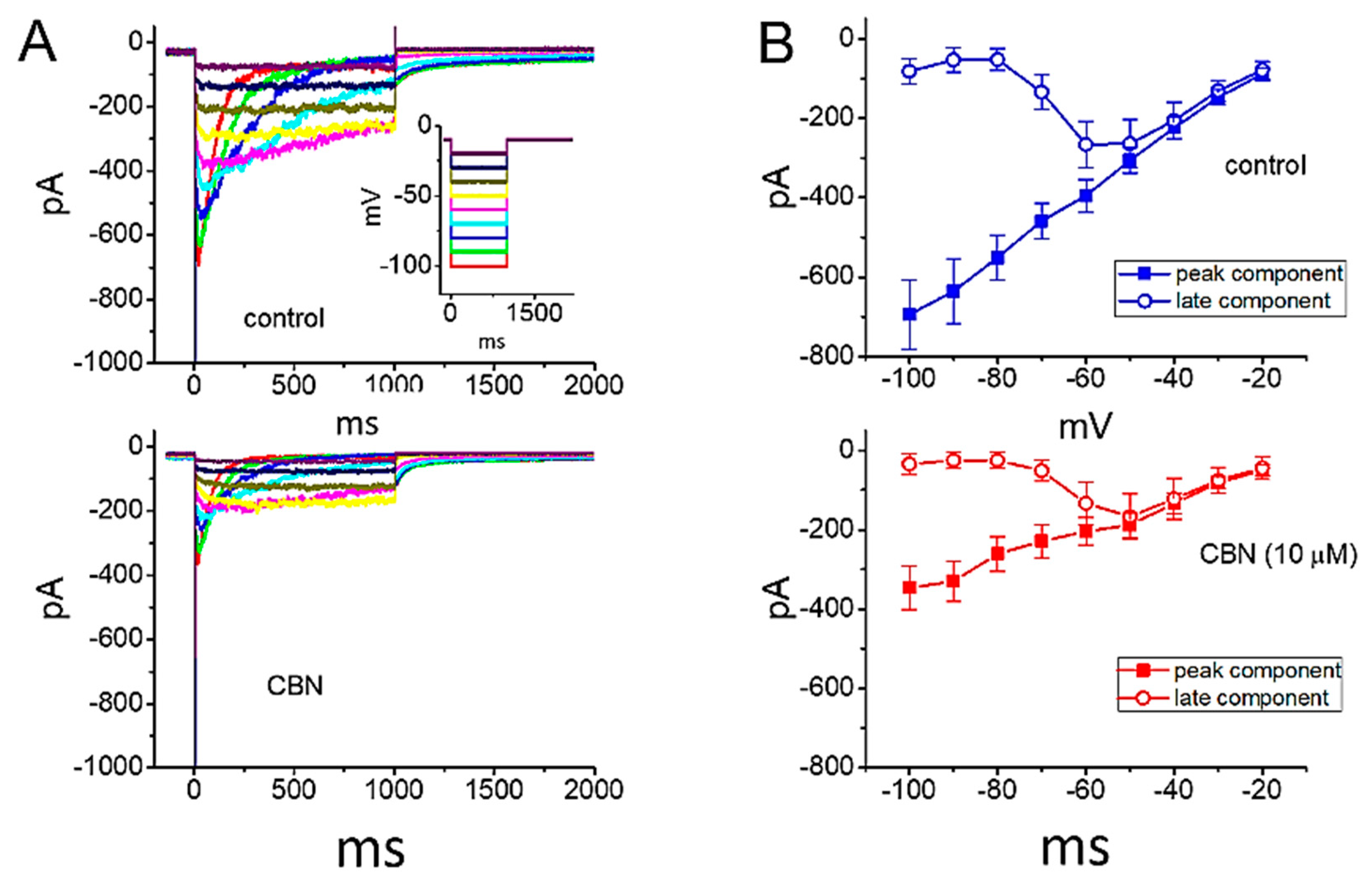
2.5. Steady-State Inactivation Curve of Peak INa Obtained in the Absence or Presence of CBN
2.6. Use-Dependence of CBN-induced Inhibition of Peak INa
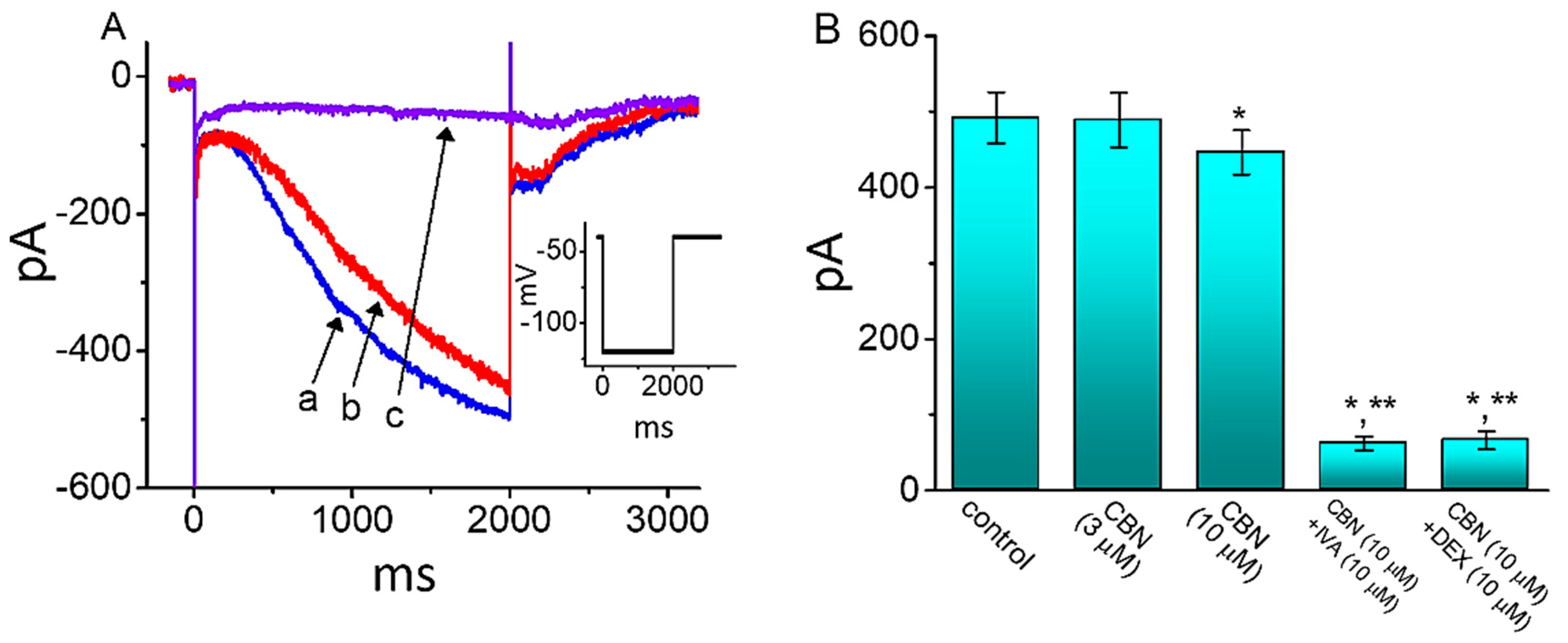
2.7. The Enhanced Amplitude by Tef of Persistent Na+ Current (INa(P)) Attenuated by CBN
2.8. Effect of CBN on erg-Mediated K+ Current (IK(erg)) in GH3 Cells
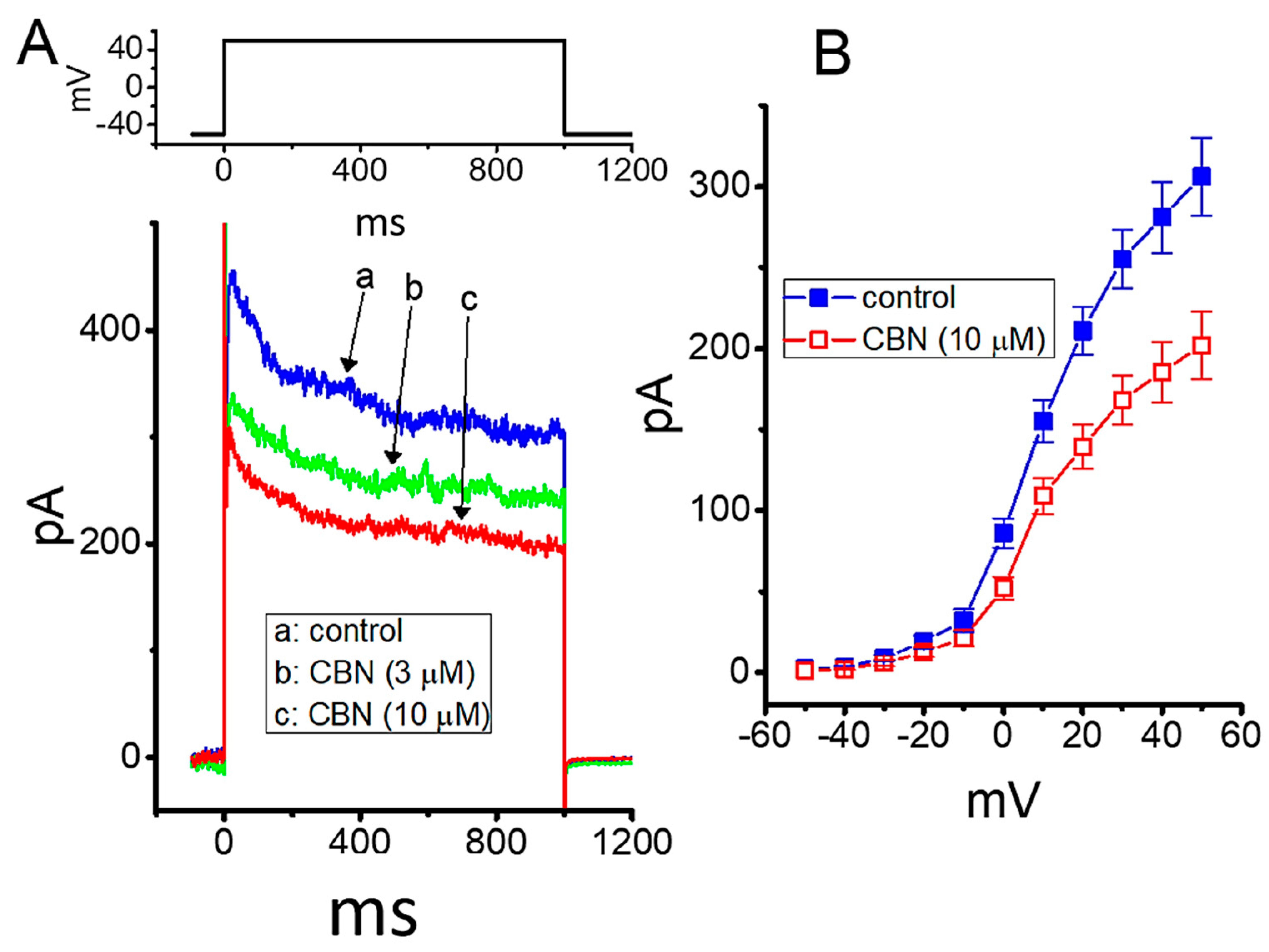
2.9. Effect of CBN on Delayed-Rectifier K+ Current (IK(DR)) in GH3 Cells
2.10. Effect of CBN on Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Current (Ih) in GH3 Cells
2.11. Inhibitory Effect of CBN on INa Identified from HL-1 Cardiomyocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Solutions Used in this Work
4.2. Cell Preparations
4.3. Electrophysiological Measurements
4.4. Curve-Fitting Procedures and Statistical Analyses
4.5. Data Recordings
4.6. Data Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| CBN | columbianadin |
| DEX | dexmedetomidine |
| GNa | Na+-current conductance |
| I-V | current versus voltage |
| IC50 | half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| Ih | hyperpolarization-activated cation current |
| IK(erg) | erg-mediated K+ current |
| INa | voltage-gated Na+ current |
| IVA | ivabradine |
| KD | dissociation constant |
| NaV channel | voltage-gated Na+ channel |
| Nim | nimodipine |
| Ran | ranolazine |
| SEM | standard error of mean |
| SSM | sesamin |
| SSR | sum of the squared residuals |
| τinact(S) | time constant for the slow component of INa inactivation |
| Tef | tefluthrin |
| TEA | tetraethylammonium chloride |
| TTX | tetrodotoxin |
References
- Chen, Y.F.; Tsai, H.Y.; Wu, T.S. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities from roots of Angelica pubescens. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Hsu, A.C.; Pan, H.; Gu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Dong, B.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Zheng, R.; et al. Columbianadin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis through the NOD1 Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Li, W.; Yang, X.W. Biotransformation of columbianadin by rat hepatic microsomes and inhibition of biotransformation products on NO production in RAW 264.7 cells in vitro. Phytochemistry 2012, 81, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. Inhibition of airway inflammation by the roots of Angelica decursiva and its constituent, columbianadin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.M.; Hsia, C.W.; Tsai, C.L.; Hsia, C.H.; Jayakumar, T.; Velusamy, M.; Sheu, J.R. Modulation of human platelet activation and in vivo vascular thrombosis by columbianadin: Regulation by integrin alphaIIbbeta3 inside-out but not outside-in signals. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Hua, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Dong, L.; Gao, Q.; Fu, X. The ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Angelica biserrata—A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y. Separation and Enrichment of Three Coumarins from Angelicae Pubescentis Radix by Macroporous Resin with Preparative HPLC and Evaluation of Their Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.L.; Lu, T.J.; Wu, S.N. Effectiveness in Block by Dexmedetomidine of Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Current, Independent of Its Agonistic Effect on alpha2-Adrenergic Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhao, C.; Yao, M.; Song, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wen, A. Analgesic effect of coumarins from Radix angelicae pubescentis is mediated by inflammatory factors and TRPV1 in a spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 195, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wu, B.; Zhang, W.; Ji, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Z.Y. Inhibitory Effects of Columbianadin on Nociceptive Behaviors in a Neuropathic Pain Model, and on Voltage-Gated Calcium Currents in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, T.X.; Yang, Y.F.; Jia, L.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.B. Systematic analysis of the metabolites of Angelicae Pubescentis Radix by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with metabonomics approaches after oral administration to rats. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 188, 113445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhong, B.; Xiao, Q.; Du, L.; Hou, Y.; Sun, H.S.; Lu, J.J.; Chen, X. Induction of programmed necrosis: A novel anti-cancer strategy for natural compounds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 214, 107593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerer, M.B.; Dayan, S.; Han, M.I.; Sharma, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K. Nanoformulations of Coumarins and the Hybrid Molecules of Coumarins with Potential Anticancer Effects. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1797–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.I.; Hong, J.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.K. Columbianadin Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Inducing Apoptosis and Necroptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, H.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z. Traditional Chinese Medicine of Angelicae Pubescentis Radix: A Review of Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorela, H.; Vuorela, P.; Tornquist, K.; Alaranta, S. Calcium channel blocking activity: Screening methods for plant derived compounds. Phytomedicine 1997, 4, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornquist, K.; Vuorela, H. The furanocoumarin columbianadin inhibits depolarization induced Ca2+ uptake in rat pituitary GH3 cells. Planta Med. 1990, 56, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.H.; Catterall, W.A. Overview of the voltage-gated sodium channel family. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Goldin, A.L.; Waxman, S.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojilkovic, S.S.; Tabak, J.; Bertram, R. Ion channels and signaling in the pituitary gland. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 845–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Lo, Y.C.; Peng, H.; Hsu, T.I.; Wu, S.N. Effects of ranolazine, a novel anti-anginal drug, on ion currents and membrane potential in pituitary tumor GH(3) cells and NG108-15 neuronal cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 110, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.C.; Tseng, Y.T.; Liu, C.M.; Wu, B.N.; Wu, S.N. Actions of KMUP-1, a xanthine and piperazine derivative, on voltage-gated Na(+) and Ca(2+) -activated K(+) currents in GH3 pituitary tumour cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 5110–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simasko, S.M. A background sodium conductance is necessary for spontaneous depolarizations in rat pituitary cell line GH3. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, C709–C719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, A.D. Nonlinear temperature modulation of sodium channel kinetics in GH(3) cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1511, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.C.; Kao, Z.H.; Lee, S.W.; Wu, S.N. Effects of Sesamin, the Major Furofuran Lignan of Sesame Oil, on the Amplitude and Gating of Voltage-Gated Na(+) and K(+) Currents. Molecules 2020, 25, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.N.; Lo, Y.K.; Li, H.F.; Shen, A.Y. Functional coupling of voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ current to Ca2+-activated K+ current in pituitary GH3 cells. Chin. J. Physiol. 2001, 44, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, B.S.; Lo, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C. Underlying mechanism of actions of tefluthrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, on voltage-gated ion currents and on action currents in pituitary tumor (GH3) cells and GnRH-secreting (GT1-7) neurons. Toxicology 2009, 258, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, E.C.; Wu, S.N.; Lo, Y.C.; Su, K. Differential regulation of tefluthrin and telmisartan on the gating charges of INa activation and inactivation as well as on resurgent and persistent INa in a pituitary cell line (GH3). Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 285, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simasko, S.M.; Sankaranarayanan, S. Characterization of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current in rat pituitary cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, E405–E414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wang, Q.; Han, J.; Goswamee, P.; Gupta, A.; McQuiston, A.R.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, L. Photodynamic Modification of Native HCN Channels Expressed in Thalamocortical Neurons. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Wu, S.N. Concerted suppression of Ih and activation of IK(M) by ivabradine, an HCN-channel inhibitor, in pituitary cells and hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 149, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, C.M.; Bezanilla, F. Currents related to movement of the gating particles of the sodium channels. Nature 1973, 242, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalba-Galea, C.A. Hysteresis in voltage-gated channels. Channels 2017, 11, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.W.; Guo, Q.M.; Wang, Y. [Absorption and transport of 6 coumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata in human Caco-2 cell monolayer model]. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2008, 6, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Yang, X.W. Tissue distribution study of columbianadin and its active metabolite columbianetin in rats. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Chen, S.; Luo, Q.; Wang, C.P.; Hao, J.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Chang, Y.X. The Tissue Distribution of Four Major Coumarins after Oral Administration of Angelicae Pubescentis Radix Extract to Rats Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 2365697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Luo, Q.; Wang, C.P.; He, J.; Pang, X.; Teye Azietaku, J.; Chang, Y.X. Simultaneous Determination of Columbianadin and Its Metabolite Columbianetin in Rat Plasma by LC-MS/MS: Application to Pharmacokinetics of Columbianadin after Oral Administration. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8568303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.X.; Wang, C.P.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Luo, Q.; He, J.; Lu, B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.L.; Gao, X.M. LC-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetic study of columbianadin in rat plasma after intravenous administration of pure columbianadin. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Damour, O.; Augustin, C.; Black, A.F. Applications of reconstructed skin models in pharmaco-toxicological trials. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1998, 36, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.P.; Joe, I.H.; George, V.; Nielsen, O.F.; Jayakumar, V.S. Vibrational spectroscopic studies on the natural product, columbianadin. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.N.; Chern, J.H.; Shen, S.; Chen, H.H.; Hsu, Y.T.; Lee, C.C.; Chan, M.H.; Lai, M.C.; Shie, F.S. Stimulatory actions of a novel thiourea derivative on large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 3409–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claycomb, W.C.; Lanson, N.A., Jr.; Stallworth, B.S.; Egeland, D.B.; Delcarpio, J.B.; Bahinski, A.; Izzo, N.J., Jr. HL-1 cells: A cardiac muscle cell line that contracts and retains phenotypic characteristics of the adult cardiomyocyte. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2979–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, R.L.; Caldwell, J.H. How do patch clamp seals form? A lipid bleb model. Pflügers Archiv 1990, 416, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmer, G.; Keller, S. Nonlinear least-squares data fitting in Excel spreadsheets. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, W.-T.; Wu, S.-N. Effectiveness of Columbianadin, a Bioactive Coumarin Derivative, in Perturbing Transient and Persistent INa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020621
Chang W-T, Wu S-N. Effectiveness of Columbianadin, a Bioactive Coumarin Derivative, in Perturbing Transient and Persistent INa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020621
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Wei-Ting, and Sheng-Nan Wu. 2021. "Effectiveness of Columbianadin, a Bioactive Coumarin Derivative, in Perturbing Transient and Persistent INa" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020621
APA StyleChang, W.-T., & Wu, S.-N. (2021). Effectiveness of Columbianadin, a Bioactive Coumarin Derivative, in Perturbing Transient and Persistent INa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020621



