Mechanism of Phosgene-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Treatment Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Toxicology Studies
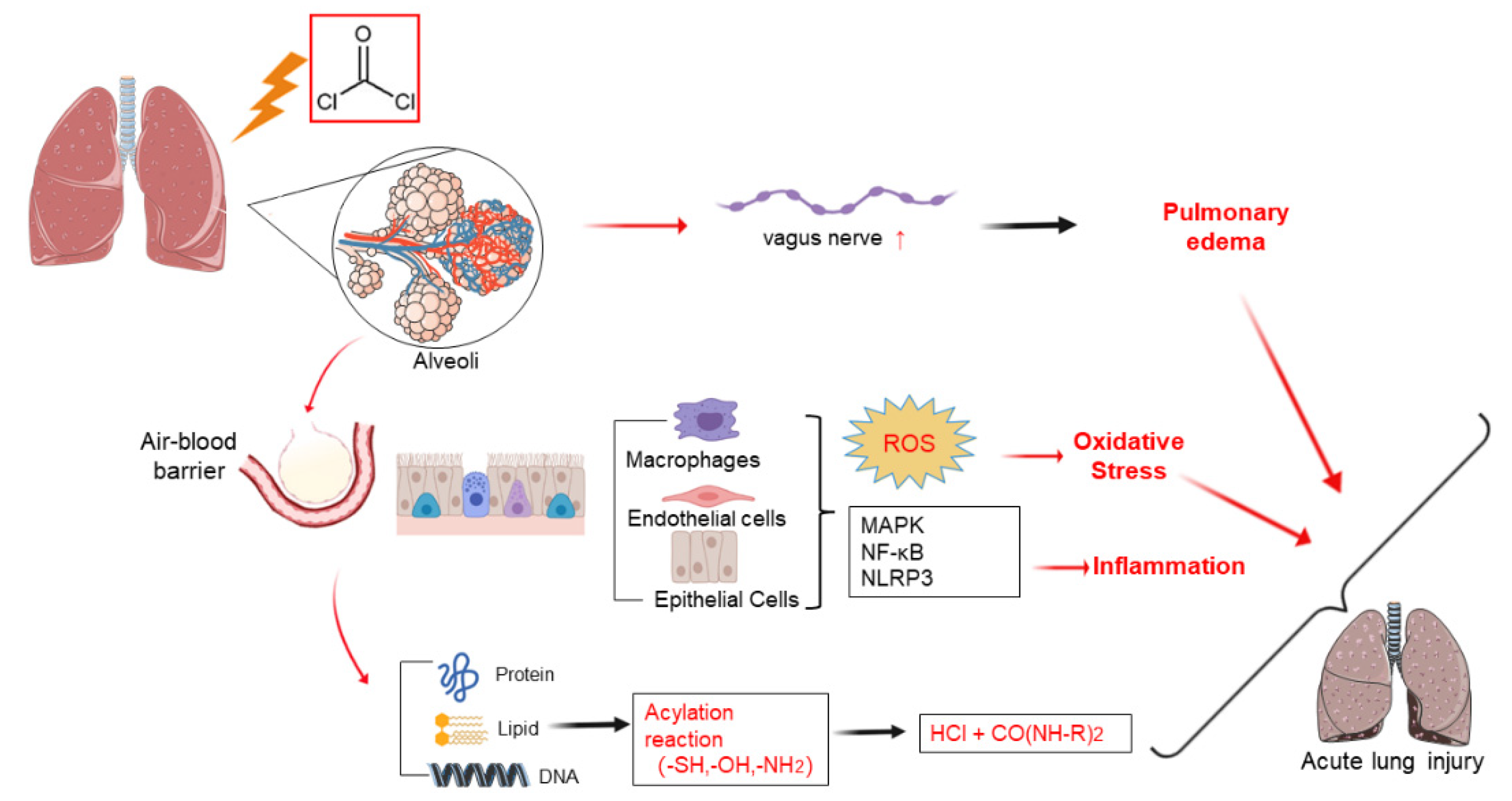
3. Pathophysiology Mechanisms
4. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms
4.1. Plasma Membrane Impairment
4.2. Inflammation
4.3. Oxidative Stress
5. Medical Treatments
5.1. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
5.1.1. Glucocorticoids
5.1.2. Ulinastatin
5.1.3. NOS-2 Inhibitors
5.1.4. Melatonin
5.1.5. Angiopoietin-1
5.2. Antioxidant Drugs
5.2.1. N-Acetylcysteine
5.2.2. Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester
5.2.3. Ibuprofen
5.2.4. Bio300
5.2.5. 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraynoic acid
5.3. Others
5.3.1. TRP Channel Inhibitors
5.3.2. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
5.3.3. FV-HSP72
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholson-Roberts, T.C. Phosgene use in World War 1 and early evaluations of pathophysiology. J. R. Army Med. Corps 2019, 165, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E. Terror weapons: The British experience of gas and its treatment in the First World War. War Hist. 2014, 21, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, G.J. Chemical warfare and medical response during World War I. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Chauhan, S.; D’Cruz, R.; Faruqi, S.; Singh, K.K.; Varma, S.; Singh, M.; Karthik, V. Chemical warfare agents. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, T.; Mori, W.; Ogawa, M.; Fujinaga, M.; Zhang, M.R. [(11)C]phosgene: Synthesis and application for development of PET radiotracers. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 92, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Yoon, J. Recent advances in the development of chromophore-based chemosensors for nerve agents and phosgene. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bessac, B.F.; Jordt, S.E. Sensory detection and responses to toxic gases: Mechanisms, health effects, and countermeasures. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2010, 7, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardison, L.S., Jr.; Wright, E.; Pizon, A.F. Phosgene exposure: A case of accidental industrial exposure. J. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Rosenbruch, M.; Pauluhn, J. Effect of PEEP on phosgene-induced lung edema: Pilot study on dogs using protective ventilation strategies. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 67, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainge, C.; Jugg, B.J.; Smith, A.J.; Brown, R.F.; Jenner, J.; Parkhouse, D.A.; Rice, P. Delayed low-dose supplemental oxygen improves survival following phosgene-induced acute lung injury. Inhal. Toxicol. 2010, 22, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Fairhall, S.; Rutter, S.; Auton, P.; Rendell, R.; Smith, A.; Perrott, R.; Roberts, T.N.; Jugg, B. Continuous positive airway pressure: An early intervention to prevent phosgene-induced acute lung injury. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 293, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauluhn, J. Concentration x time analyses of sensory irritants revisited: Weight of evidence or the toxic load approach. That is the question. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Pauluhn, J. Phosgene-induced lung edema: Comparison of clinical criteria for increased extravascular lung water content with postmortem lung gravimetry and lavage-protein in rats and dogs. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 305, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghio, A.J.; Kennedy, T.P.; Hatch, G.E.; Tepper, J.S. Reduction of neutrophil influx diminishes lung injury and mortality following phosgene inhalation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 71, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.; Blain, P.G.; Rice, P. Clinical management of casualties exposed to lung damaging agents: A critical review. Emerg. Med. J. 2006, 23, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, W.F. Pathogenesis of phosgene poisoning. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1985, 1, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borak, J.; Diller, W.F. Phosgene exposure: Mechanisms of injury and treatment strategies. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2001, 43, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.Y. Respiratory sensations evoked by activation of bronchopulmonary C-fibers. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009, 167, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Truebel, H.; Pauluhn, J. Novel insights into phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats: Role of dysregulated cardiopulmonary reflexes and nitric oxide in lung edema pathogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanhoe, F.; Meyers, F.H. Phosgene poisoning as an example of neuroparalytic acute pulmonary edema: The sympathetic vasomotor reflex involved. Dis. Chest 1964, 46, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauluhn, J. Phosgene inhalation toxicity: Update on mechanisms and mechanism-based treatment strategies. Toxicology 2021, 450, 152682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugg, B.; Jenner, J.; Rice, P. The effect of perfluoroisobutene and phosgene on rat lavage fluid surfactant phospholipids. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1999, 18, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, A.P.; Bernard, G.R. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: A clinical review. Lancet 2007, 369, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuto, A.M.; Clapp, D.L.; Hess, Z.A.; Moran, T.S. The temporal profile of cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in mice exposed to the industrial gas phosgene. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.K.; Shao, Y.R.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Significance of the NLRP3 inflammasome expression in rats with acute lung injury induced by phosgene. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2017, 35, 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, F.; Deng, J.; Wang, G.; Ye, R.D.; Christman, J.W. Pivotal role of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 in inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2016, 17, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-κB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.K.; Shao, Y.R.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, G. Adenovirus-delivered angiopoietin-1 suppresses NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK and attenuates inflammatory responses in phosgene-induced acute lung injury. Inhal. Toxicol. 2014, 26, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, J.A.; Riestra, A.M.; Gao, N.J.; LaRock, C.N.; Gupta, N.; Ali, S.R.; Hoffman, H.M.; Ghosh, P.; Nizet, V. Group A streptococcal M protein activates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, D.K.; Chen, J.F.; Shao, Y.R.; Zhou, F.Q.; Shen, J. Adenovirus-delivered angiopoietin-1 ameliorates phosgene-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.K.; Xu, N.; Shao, Y.R.; Shen, J. NLRP3 gene silencing ameliorates phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and proinflammatory factors, but not anti-inflammatory factors. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 45, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegman, C.H.; Li, F.; Ryffel, B.; Togbe, D.; Chung, K.F. Oxidative stress in ozone-induced chronic lung inflammation and emphysema: A facet of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendell, R.; Fairhall, S.; Graham, S.; Rutter, S.; Auton, P.; Smith, A.; Perrott, R.; Jugg, B. Assessment of N-acetylcysteine as a therapy for phosgene-induced acute lung injury. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 290, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ye, X.L.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.L.; Liang, X.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Qin, X.J.; Bai, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. Mechanism of acute lung injury due to phosgene exposition and its protection by cafeic acid phenethyl ester in the rat. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciuto, A.M.; Cascio, M.B.; Moran, T.S.; Forster, J.S. The fate of antioxidant enzymes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid over 7 days in mice with acute lung injury. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadimajd, S.; Khazaei, M. Oxidative stress and cancer: The role of Nrf2. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskot, R.H.; Grose, E.C.; Richards, J.H.; Doerfler, D.L. Effects of inhaled phosgene on rat lung antioxidant systems. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1991, 17, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, C. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by acute phosgene poisoning: A report of 4 cases. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2019, 31, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.B.; Hu, Y.T.; He, Q.; Zhu, R.K. Investigation and analysis of 7 cases of acute lung injury caused by a welding operation. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2019, 37, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Vandewalle, J.; Luypaert, A.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. Therapeutic mechanisms of glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, S.J.; De Bosscher, K. Glucocorticoid receptors: Finding the middle ground. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.K.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.B. Effects of dexamethasone pretreatment on expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in rats with acute lung injury induced by phosgene. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2011, 29, 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.Q.; He, D.K.; Shao, Y.R.; Shen, J. The effects of methylprednisolone on NLRP3 inflammasome in rats with acute lung injury Induced by Phosgene. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2018, 36, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.; Brown, R.; Jugg, B.; Platt, J.; Mann, T.; Masey, C.; Jenner, J.; Rice, P. The effect of steroid treatment with inhaled budesonide or intravenous methylprednisolone on phosgene-induced acute lung injury in a porcine model. Mil. Med. 2009, 174, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Pauluhn, J.; Trubel, H.; Wang, C. Single high-dose dexamethasone and sodium salicylate failed to attenuate phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats. Toxicology 2014, 315, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Pauluhn, J.; Trubel, H.; Wang, C. Corticosteroids found ineffective for phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Z.; Hai, C.X.; Li, W.L. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of acute phosgene poisoning and its research progress. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2020, 38, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, S.T.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Yu, Q.Q.; Tan, F.; Lu, S.H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.W.; Huang, H.Q.; et al. Ulinastatin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the JNK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway and activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Liu, S.; Luo, L.; Gu, N.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, D. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of ulinastatin: Inhibiting the hyperpermeability of vascular endothelial cells induced by TNF-alpha via the RhoA/ROCK signal pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 46, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Gan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, G. Ulinastatin reduces pathogenesis of phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2014, 30, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Z.; He, D.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J. Dynamic changes of a group of cytokines in phosgene-induced lung injury and the function of ulinastatin. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2014, 32, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, W.; Pauluhn, J.; Trubel, H.; Wang, C. Rat models of acute lung injury: Exhaled nitric oxide as a sensitive, noninvasive real-time biomarker of prognosis and efficacy of intervention. Toxicology 2013, 310, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liang, W.; He, W.; Huang, C.; Chen, Q.; Yi, H.; Long, L.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, M. Ghrelin attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the NF-kappaB, iNOS, and Akt signaling in alveolar macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2019, 317, L381–L391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Mo, S.; Yi, Q.; Lai, J.; Liu, H.; Shi, Z. Role and mechanism of maresin-1 in acute lung injury induced by trauma-hemorrhagic shock. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e923518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Trubel, H.; Wang, C.; Pauluhn, J. Phosgene- and chlorine-induced acute lung injury in rats: Comparison of cardiopulmonary function and biomarkers in exhaled breath. Toxicology 2014, 326, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.L.; Bai, H.; Xi, M.M.; Liu, R.; Qin, X.J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, W.L.; Hai, C.X. Ethyl pyruvate protects rats from phosgene-induced pulmonary edema by inhibiting cyclooxygenase2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipczak, P.T.; Senft, A.P.; Seagrave, J.; Weber, W.; Kuehl, P.J.; Fredenburgh, L.E.; McDonald, J.D.; Baron, R.M. NOS-2 inhibition in phosgene-induced acute lung injury. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cipolla-Neto, J.; Amaral, F.G.D. Melatonin as a hormone: New physiological and clinical insights. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 990–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Grailer, J.J.; Wang, N.; Wang, M.; Yao, J.; Zhong, R.; Gao, G.F.; Ward, P.A.; Tan, D.X.; et al. Melatonin alleviates acute lung injury through inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliasgharzadeh, A.; Farhood, B.; Amini, P.; Saffar, H.; Motevaseli, E.; Rezapoor, S.; Nouruzi, F.; Shabeeb, D.H.; Eleojo Musa, A.; Mohseni, M.; et al. Melatonin attenuates upregulation of Duox1 and Duox2 and protects against lung injury following chest irradiation in rats. Cell J. 2019, 21, 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; He, D.; Xu, D.; Zhong, Z.; Shen, J. Melatonin attenuates phosgene-induced acute lung injury via the upregulation Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 11281–11287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, D.; Shao, Y.; Xu, D.; Shen, J. Effect of melatonin on p38MAPKsignaling pathway in rats with phosgene-induced lung injury. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2014, 32, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; Gan, Z.Y.; He, D.K.; Zhong, Z.Y. Protective effect of melatonin in rats with phosgene-induced lung injury. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2012, 30, 834–838. [Google Scholar]
- Gutbier, B.; Neuhauss, A.K.; Reppe, K.; Ehrler, C.; Santel, A.; Kaufmann, J.; Scholz, M.; Weissmann, N.; Morawietz, L.; Mitchell, T.J.; et al. Prognostic and pathogenic role of angiopoietin-1 and -2 in pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Ryczko, M.; Xie, X.; Baardsnes, J.; Lord-Dufour, S.; Duroche, Y.; Hicks, E.A.; Taiyab, A.; Sheardown, H.; Quaggin, S.E.; et al. New soluble angiopoietin analog of Hepta-ANG1 prevents pathological vascular leakage. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.R.; Lee, K.S.; Park, S.J.; Min, K.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Choe, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Koh, G.Y.; Lee, Y.C. Angiopoietin-1 variant, COMP-Ang1 attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced acute lung injury. Exp. Mol. Med. 2008, 40, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.H.; McCarter, S.D.; Deng, Y.; Parker, C.H.; Liles, W.C.; Stewart, D.J. Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Shen, J. The changes of the ratio of angiopoietin-2 to angiopoietin-1 in the acute lung injury induced by phosgene in rats. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2011, 29, 608–610. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Wang, J.; Shao, Y.R.; He, D.K.; Zhang, L.; Nadeem, L.; Xu, G. Adenovirus-delivered angiopoietin-1 treatment for phosgene-induced acute lung injury. Inhal. Toxicol. 2013, 25, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H.; Li, C.H.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, M.J.; Xu, T.; Wei, D.; Liu, B.J.; Wang, G.H.; Tian, S.F. N-acetyl-l-cystine (NAC) protects against H9N2 swine influenza virus-induced acute lung injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, W.G.; Guo, X.C.; Wu, M.J.; Xu, Z.Y.; Jiang, J.F.; Shen, C.; Liu, H.Q. N-acetylcysteine-pretreated human embryonic mesenchymal stem cell administration protects against bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 346, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.D.; Chen, H.L.; Bai, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.L.; Liang, X.; Hai, C.X. N-acetylcysteine attenuates phosgene-induced acute lung injury via up-regulation of Nrf2 expression. Inhal. Toxicol. 2010, 22, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, Y.; Li, N.G.; Zhu, Y.; Duan, J.A. Bioactivity and chemical synthesis of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 16458–16476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainsford, K.D. Ibuprofen: Pharmacology, efficacy and safety. Inflammopharmacology 2009, 17, 275–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, T.G. Ibuprofen. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 91, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuto, A.M.; Stotts, R.R.; Hurt, H.H. Efficacy of ibuprofen and pentoxifylline in the treatment of phosgene-induced acute lung injury. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1996, 16, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.P.; Rao, N.V.; Noah, W.; Michael, J.R.; Jafri, M.H., Jr.; Gurtner, G.H.; Hoidal, J.R. Ibuprofen prevents oxidant lung injury and in vitro lipid peroxidation by chelating iron. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, W.W.; Keyser, B.M.; Paradiso, D.C.; Ray, R.; Andres, D.K.; Benton, B.J.; Rothwell, C.C.; Hoard-Fruchey, H.M.; Dillman, J.F.; Sciuto, A.M.; et al. Conceptual approaches for treatment of phosgene inhalation-induced lung injury. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 244, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tobias, L.D.; Hamilton, J.G. The effect of 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid on lipid metabolism. Lipids 1979, 14, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciuto, A.M. Posttreatment with ETYA protects against phosgene-induced lung injury by amplifying the glutathione to lipid peroxidation ratio. Inhal. Toxicol. 2000, 12, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banner, K.H.; Igney, F.; Poll, C. TRP channels: Emerging targets for respiratory disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 130, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandini, P.; De Logu, F.; Fusi, C.; Provezza, L.; Nassini, R.; Montagner, G.; Materazzi, S.; Munari, S.; Gilioli, E.; Bezzerri, V.; et al. Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 channels modulate inflammatory response in respiratory cells from patients with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, S.; Brayden, J.E. Transient receptor potential channels in the vasculature. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 645–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andres, D.; Keyser, B.; Benton, B.; Melber, A.; Olivera, D.; Holmes, W.; Paradiso, D.; Anderson, D.; Ray, R. Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels as a therapeutic target for intervention of respiratory effects and lethality from phosgene. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 244, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, D.C.; Shyu, W.C.; Lin, S.Z. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Fang, X.; Krasnodembskaya, A.; Howard, J.P.; Matthay, M.A. Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells for acute lung injury: Role of paracrine soluble factors. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, V.; Sengupta, S.; Lazo, A.; Woods, P.; Nolan, A.; Bremer, N. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as treatment for severe COVID-19. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Frassoni, F.; Ball, L.; Locatelli, F.; Roelofs, H.; Lewis, I.; Lanino, E.; Sundberg, B.; Bernardo, M.E.; Remberger, M.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase II study. Lancet 2008, 371, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Huang, H.; Lu, X.; Yan, X.; Jiang, X.; Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Xu, Z.; et al. Effect of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on lung damage in severe COVID-19 patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.G.; Liu, K.D.; Zhuo, H.; Caballero, L.; McMillan, M.; Fang, X.; Cosgrove, K.; Vojnik, R.; Calfee, C.S.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Mesenchymal stem (stromal) cells for treatment of ARDS: A phase 1 clinical trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Shao, Y.; Xu, G.; Lim, C.; Li, J.; Xu, D.; Shen, J. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2015, 27, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, Y.; He, D.; Zhang, L.; Xu, G.; Shen, J. Evidence that bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce epithelial permeability following phosgene-induced acute lung injury via activation of wnt3a protein-induced canonical wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Inhal. Toxicol. 2016, 28, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepp, J.A.; Zacharias, W.J.; Frank, D.B.; Cavanaugh, C.A.; Zhou, S.; Morley, M.P.; Morrisey, E.E. Distinct mesenchymal lineages and niches promote epithelial self-renewal and myofibrogenesis in the lung. Cell 2017, 170, 1134–1148.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, K.; He, D.; Shao, Y.; Xu, N.; Jin, C.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J. Exogenous mesenchymal stem cells affect the function of endogenous lung stem cells (club cells) in phosgene-induced lung injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 514, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szydlak, R. Mesenchymal stem cells’ homing and cardiac tissue repair. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, C.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J. Overexpression of heat shock protein 70 enhanced mesenchymal stem cell treatment efficacy in phosgene-induced acute lung injury. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, U.; Cameroni, E.; Pruenster, M.; Mahabaleshwar, H.; Raz, E.; Zerwes, H.G.; Rot, A.; Thelen, M. CXCR7 functions as a scavenger for CXCL12 and CXCL11. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Zhou, F.; He, D.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J. Overexpression of CXCR7 promotes mesenchymal stem cells to repair phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, J.; Lee, J.W. Therapeutic use of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in acute lung injury. Transfusion 2019, 59, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Shao, Y.; Ye, K.; Qu, Y.; Memet, O.; He, D.; Shen, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2019, 31, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; He, D.; Shao, Y.; Qu, Y.; Ye, K.; Memet, O.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J. Lung-derived exosomes in phosgene-induced acute lung injury regulate the functions of mesenchymal stem cells partially via miR-28–5p. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parseghian, M.H.; Hobson, S.T.; Richieri, R.A. Targeted heat shock protein 72 for pulmonary cytoprotection. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1374, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hobson, S.T.; Richieri, R.A.; Parseghian, M.H. Phosgene: Toxicology, animal models, and medical countermeasures. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2021, 31, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beere, H.M.; Wolf, B.B.; Cain, K.; Mosser, D.D.; Mahboubi, A.; Kuwana, T.; Tailor, P.; Morimoto, R.I.; Cohen, G.M.; Green, D.R. Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Kim, J.Y.; Ma, H.; Lee, J.E.; Yenari, M.A. Anti-inflammatory effects of the 70 kDa heat shock protein in experimental stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanimoto, T.; Parseghian, M.H.; Nakahara, T.; Kawai, H.; Narula, N.; Kim, D.; Nishimura, R.; Weisbart, R.H.; Chan, G.; Richieri, R.A.; et al. Cardioprotective Effects of HSP72 administration on ischemia-reperfusion Injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Wei, Y.; Song, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Feng, Q.; Xu, G. Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 818, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Garcia, J.; Osca-Verdegal, R.; Pallardo, F.V.; Ferreres, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Mulet, S.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Carbonell, N.; Garcia-Gimenez, J.L. Oxidative stress and inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: The potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, F.O.; Felipe, F.A.; de Melo Costa, A.C.; Teixeira, L.G.; Silva, E.R.; Nunes, P.S.; Shanmugam, S.; de Lucca Junior, W.; Quintans, J.S.; de Souza Araujo, A.A. Inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress in animals subjected to smoke inhalation: A systematic review. Lung 2016, 194, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Fang, L.E.; Liu, Z.; Xia, B.; Fan, X.; Li, C.; Lu, Q.; et al. NF-kappaB and FosB mediate inflammation and oxidative stress in the blast lung injury of rats exposed to shock waves. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Shen, J.; Mehra, R.; Kallianpur, A.; Culver, D.A.; Gack, M.U.; Farha, S.; Zein, J.; Comhair, S.; et al. A network medicine approach to investigation and population-based validation of disease manifestations and drug repurposing for COVID-19. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Q.; Huang, S.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Shi, M.; Fan, H.; Zhao, Y. Mechanism of Phosgene-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Treatment Strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010933
Lu Q, Huang S, Meng X, Zhang J, Yu S, Li J, Shi M, Fan H, Zhao Y. Mechanism of Phosgene-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Treatment Strategy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(20):10933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010933
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Qianying, Siyu Huang, Xiangyan Meng, Jianfeng Zhang, Sifan Yu, Junfeng Li, Mingyu Shi, Haojun Fan, and Yanmei Zhao. 2021. "Mechanism of Phosgene-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Treatment Strategy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 20: 10933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010933
APA StyleLu, Q., Huang, S., Meng, X., Zhang, J., Yu, S., Li, J., Shi, M., Fan, H., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Mechanism of Phosgene-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Treatment Strategy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(20), 10933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010933





