Exercise Intervention Mitigates Pathological Liver Changes in NAFLD Zebrafish by Activating SIRT1/AMPK/NRF2 Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
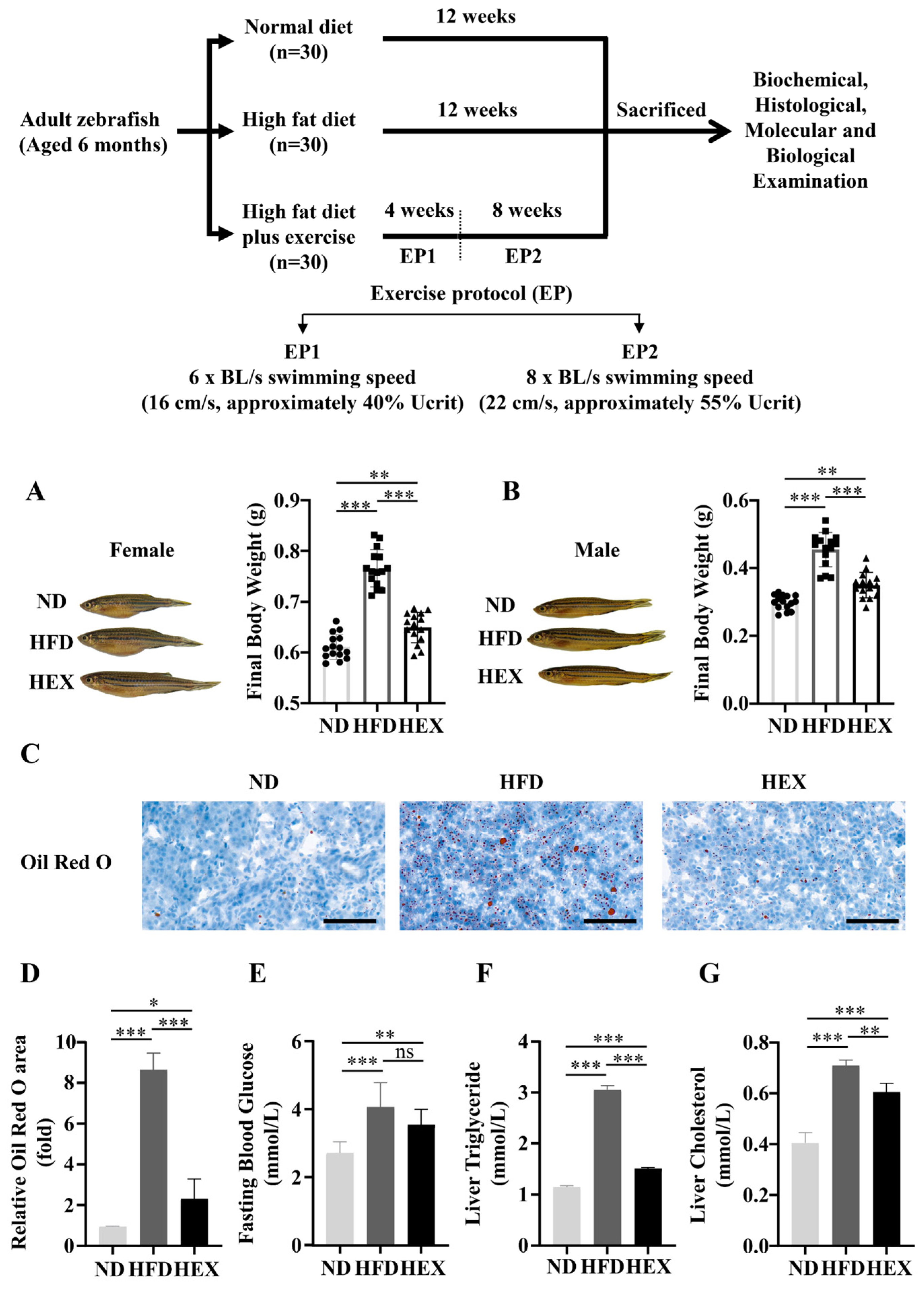
2.1. Swimming Exercise Reduces Body Weight Gain and Lipid Accumulation in HFD Zebrafish
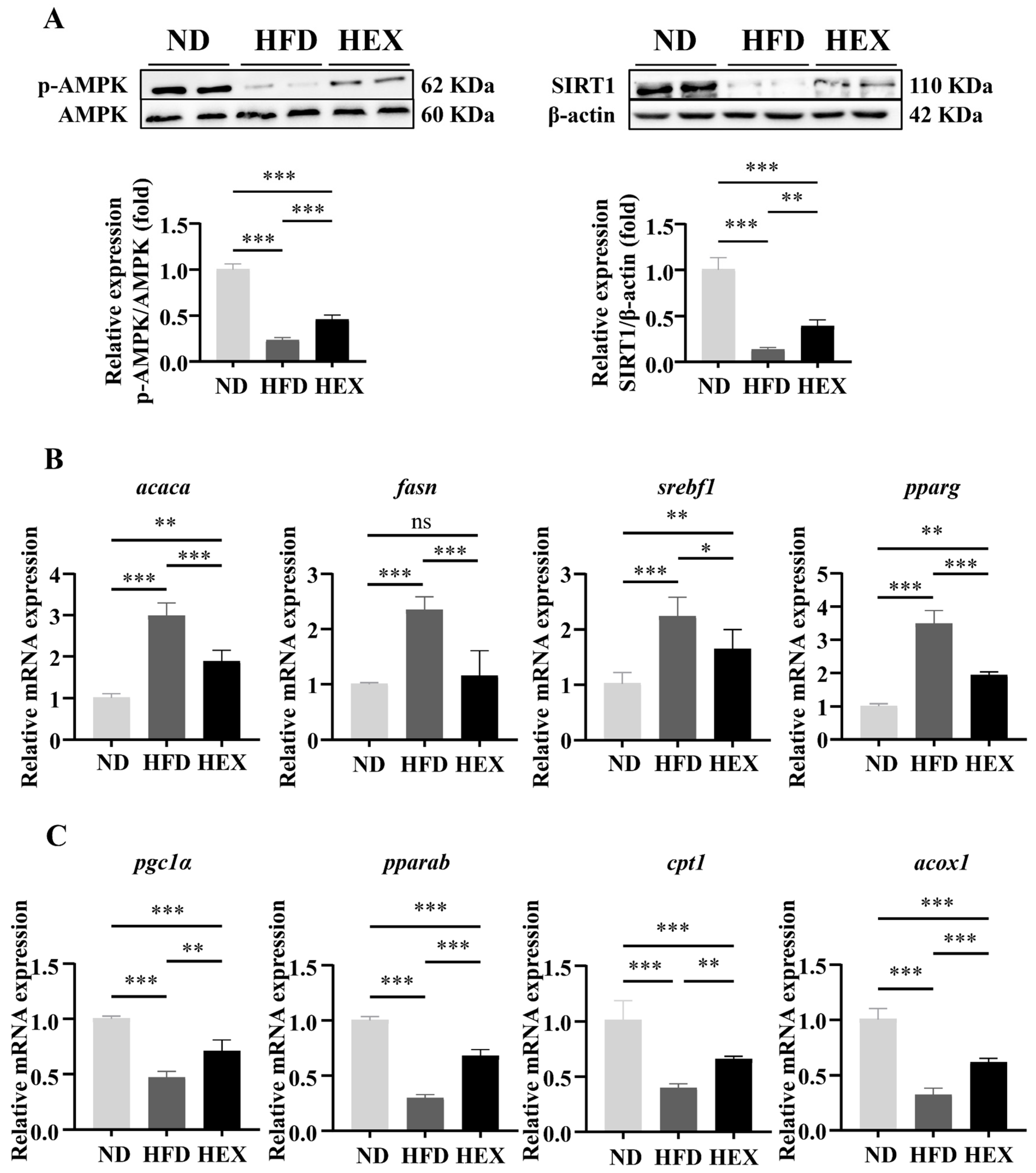
2.2. Swimming Exercise Activates SIRT1/AMPK Signaling and Improves Lipid Metabolism Disorders in HFD Zebrafish Livers
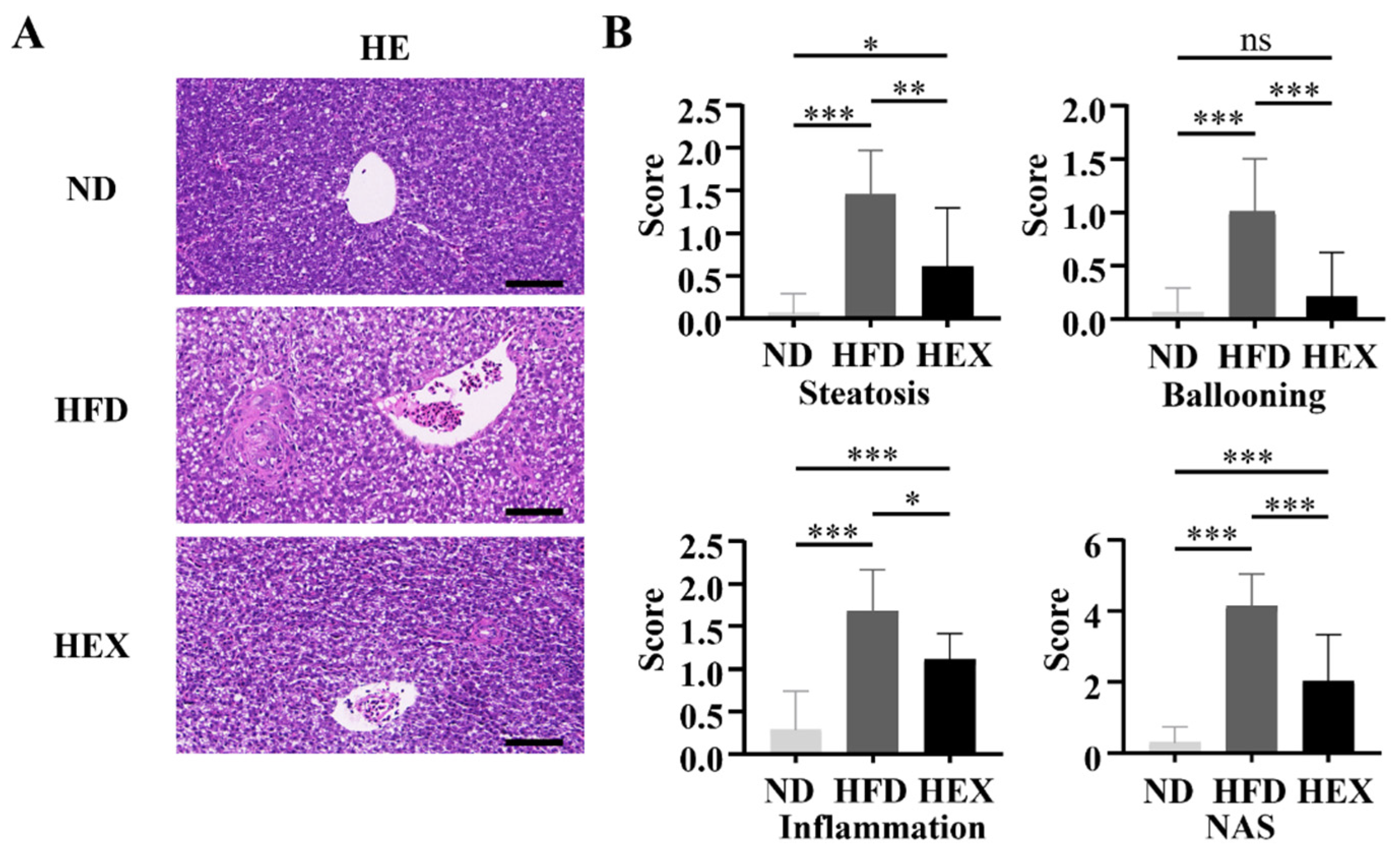
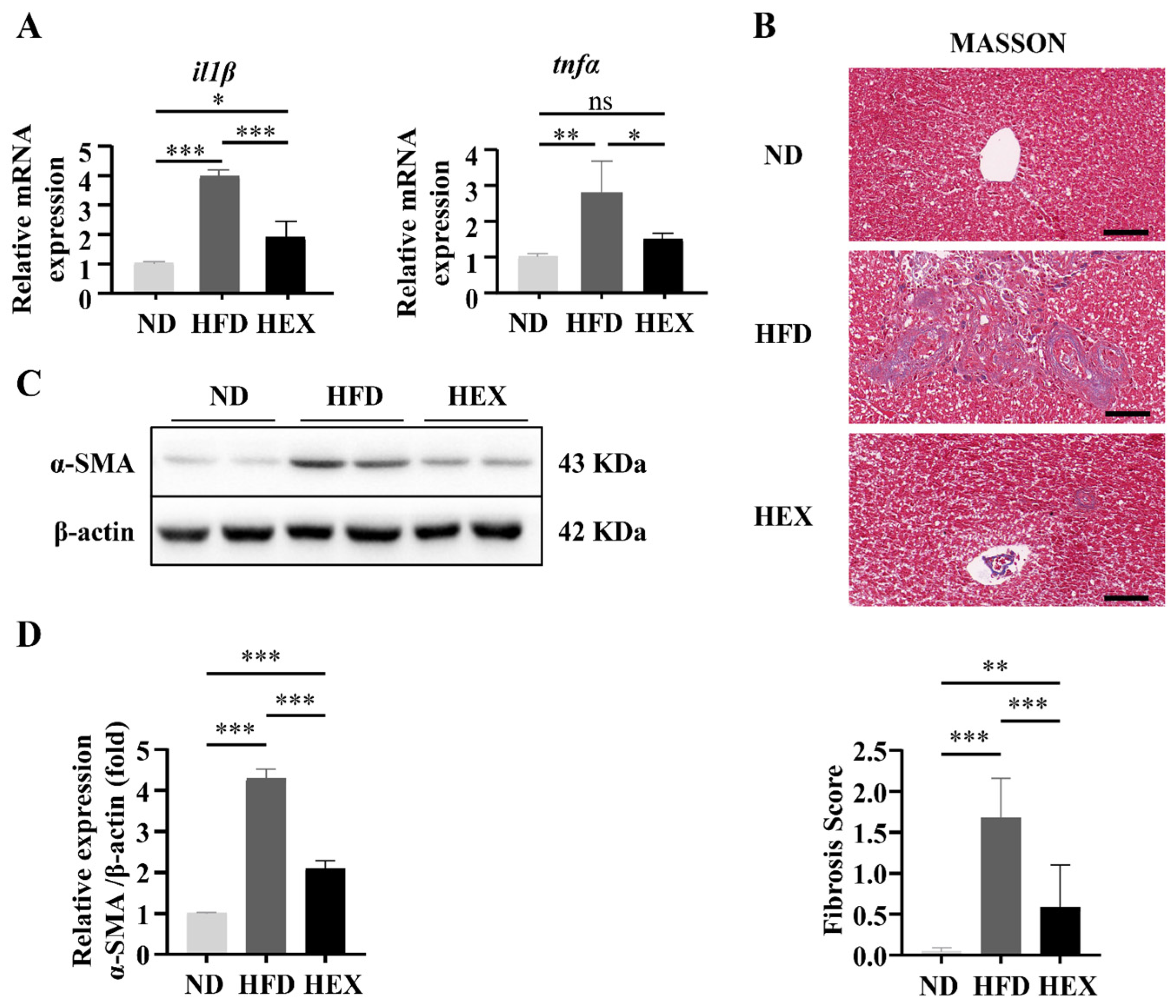
2.3. Swimming Exercise Ameliorates Liver Pathological Changes in HFD Zebrafish
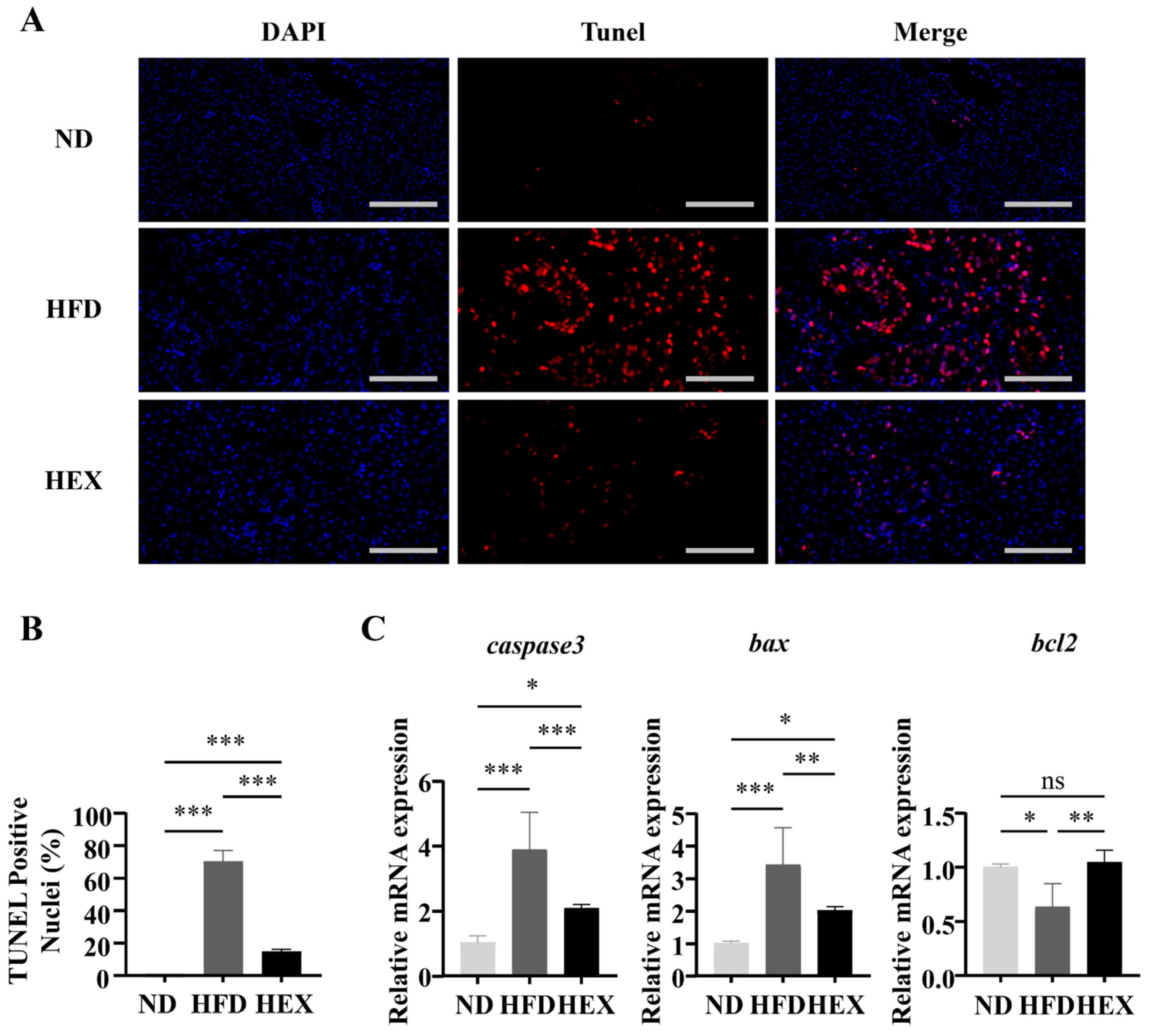
2.4. Swimming Exercise Attenuates Hepatocyte Apoptosis in HFD Zebrafish
2.5. Swimming Exercise Protects HFD Zebrafish Livers from Oxidative Stress
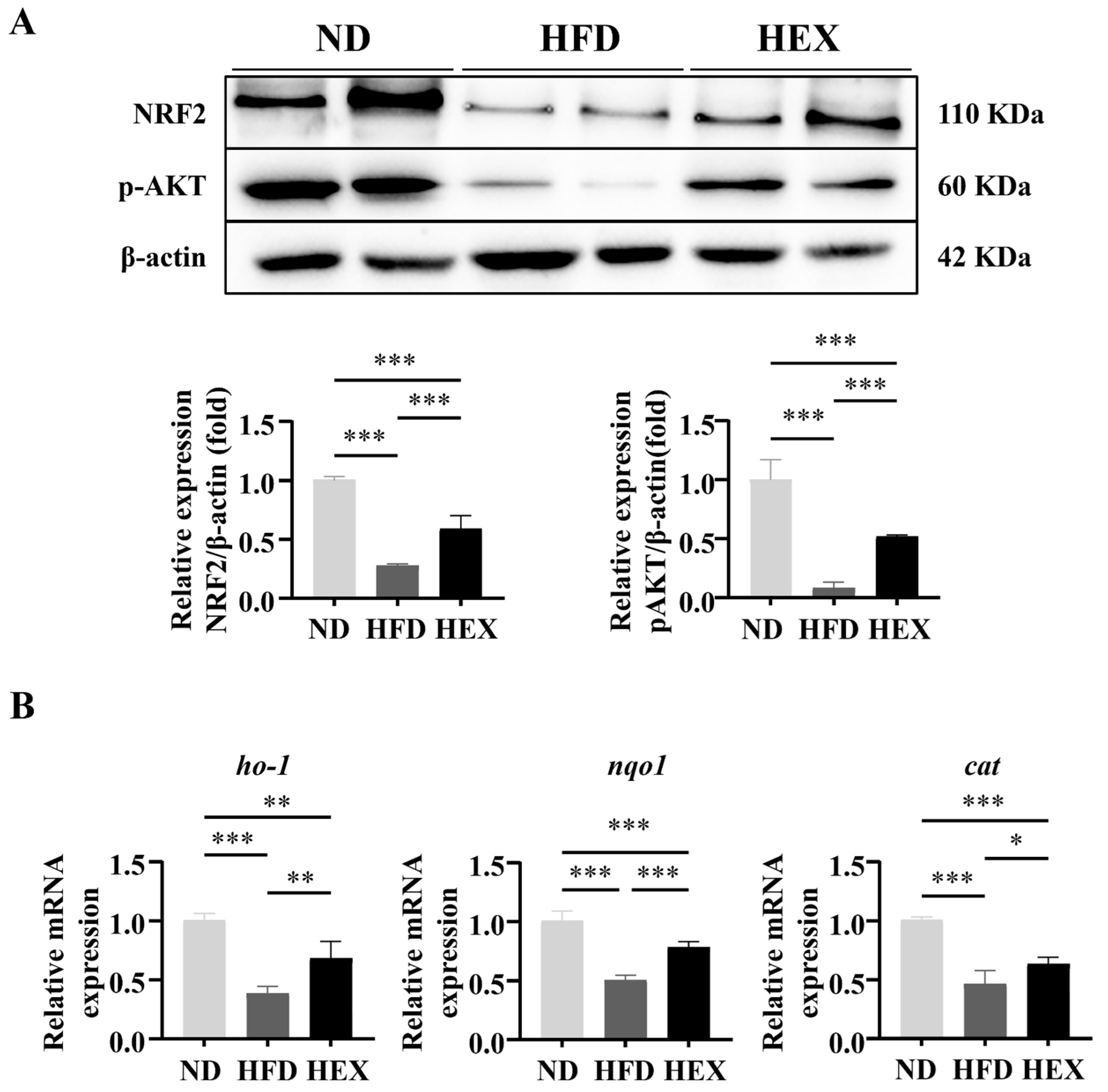
2.6. Swimming Exercise Upregulates the Expression and Function of NRF2 in HFD Zebrafish
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Models
4.2. Exercise Protocol
4.3. Blood Analysis
4.4. Liver Triglyceride (TG), Total Cholesterol TC, and Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels
4.5. Histological Analysis of Liver Sections
4.6. Apoptosis Assay
4.7. Determination of Liver ROS Production
4.8. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.9. Western Blotting Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neuman, M.G.; Cohen, L.B.; Nanau, R.M. Biomarkers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 28, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulai, P.S.; Singh, S.; Patel, J.; Soni, M.; Prokop, L.J.; Younossi, Z.; Sebastiani, G.; Ekstedt, M.; Hagstrom, H.; Nasr, P.; et al. Increased risk of mortality by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, H.H.; Feigh, M.; Veidal, S.S.; Rigbolt, K.T.; Vrang, N.; Fosgerau, K. Mouse models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in preclinical drug development. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Bian, F.; Xing, S.; Jin, S. Salidroside Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via AMPK-Dependent TXNIP/NLRP3 Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 8597897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, Y.; Kessoku, T.; Sumida, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Kato, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Imajo, K.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Efficacy of glutathione for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An open-label, single-arm, multicenter, pilot study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenhofer, S.; Kleikers, P.W.; Radermacher, K.A.; Scheurer, P.; Rob Hermans, J.J.; Schiffers, P.; Ho, H.; Wingler, K.; Schmidt, H.H. The NOX toolbox: Validating the role of NADPH oxidases in physiology and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 2327–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, S.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, G.; et al. Polydatin attenuates diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1411–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Fan, C.; Cai, Y.; Fang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.; Guan, M. Transplantation of brown adipose tissue up-regulates miR-99a to ameliorate liver metabolic disorders in diabetic mice by targeting NOX4. Adipocyte 2020, 9, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupte, A.A.; Lyon, C.J.; Hsueh, W.A. Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like-2 factor (Nrf2), a key regulator of the antioxidant response to protect against atherosclerosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Curr. Diabets Rep. 2013, 13, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jian, T.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Tong, B.; Li, J.; Meng, X.; Ren, B.; Chen, J. Chicoric Acid Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via the AMPK/Nrf2/NFkappaB Signaling Pathway and Restores Gut Microbiota in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9734560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, B.; Dong, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y. Effects of inflammatory responses, apoptosis, and STAT3/NF-kappaB- and Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress on benign prostatic hyperplasia induced by a high-fat diet. Aging 2019, 11, 5570–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Hou, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y. S-Propargyl-cysteine Exerts a Novel Protective Effect on Methionine and Choline Deficient Diet-Induced Fatty Liver via Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4690857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xue, H.; Fang, W.; Chen, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Shen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Ling, W. Adropin protects against liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via the Nrf2 mediated antioxidant capacity. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimozono, R.; Asaoka, Y.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Aoki, T.; Noda, H.; Yamada, M.; Kaino, M.; Mochizuki, H. Nrf2 activators attenuate the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-related fibrosis in a dietary rat model. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 84, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, O.; Filozof, C.; Noureddin, M.; Berner-Hansen, M.; Schabel, E.; Omokaro, S.O.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Barradas, K.; Miller, V.; Francque, S.; et al. Standardisation of diet and exercise in clinical trials of NAFLD-NASH: Recommendations from the Liver Forum. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirupathi, A.; de Souza, C.T. Multi-regulatory network of ROS: The interconnection of ROS, PGC-1 alpha, and AMPK-SIRT1 during exercise. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 73, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalafi, M.; Mohebbi, H.; Symonds, M.E.; Karimi, P.; Akbari, A.; Tabari, E.; Faridnia, M.; Moghaddami, K. The Impact of Moderate-Intensity Continuous or High-Intensity Interval Training on Adipogenesis and Browning of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Obese Male Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Dun, Y.; Zhang, W.; You, B.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, J.; Ripley-Gonzalez, J.W.; Liu, S. Exercise improves lipid droplet metabolism disorder through activation of AMPK-mediated lipophagy in NAFLD. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.W.; Kao, H.H.; Wu, C.H. Exercise training upregulates SIRT1 to attenuate inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in kidney and liver of diabetic db/db mice. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, T.; Xiao, H. The Implication of Oxidative Stress and AMPK-Nrf2 Antioxidative Signaling in Pneumonia Pathogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefont-Rousselot, D. Resveratrol and Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2016, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cai, L. Role of sirtuin-1 in diabetic nephropathy. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, T.; Peng, J. Liver development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Genet. Genom. 2009, 36, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessling, W.; Sadler, K.C. Zebrafish: An important tool for liver disease research. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palstra, A.P.; Tudorache, C.; Rovira, M.; Brittijn, S.A.; Burgerhout, E.; van den Thillart, G.E.; Spaink, H.P.; Planas, J.V. Establishing zebrafish as a novel exercise model: Swimming economy, swimming-enhanced growth and muscle growth marker gene expression. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palstra, A.P.; Rovira, M.; Rizo-Roca, D.; Torrella, J.R.; Spaink, H.P.; Planas, J.V. Swimming-induced exercise promotes hypertrophy and vascularization of fast skeletal muscle fibres and activation of myogenic and angiogenic transcriptional programs in adult zebrafish. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovira, M.; Arrey, G.; Planas, J.V. Exercise-Induced Hypertrophic and Oxidative Signaling Pathways and Myokine Expression in Fast Muscle of Adult Zebrafish. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rovira, M.; Borras, D.M.; Marques, I.J.; Puig, C.; Planas, J.V. Physiological Responses to Swimming-Induced Exercise in the Adult Zebrafish Regenerating Heart. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyau, C.C.; Wang, H.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, S.H.; Chang, C.C.; Peng, R.Y. Antrodan Alleviates High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Induced Fatty Liver Disease in C57BL/6 Mice Model via AMPK/Sirt1/SREBP-1c/PPARgamma Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Qiu, F.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Effects of Natural Products on Fructose-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Nutrients 2017, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaminskyy, V.O.; Zhivotovsky, B. Free radicals in cross talk between autophagy and apoptosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology 2010, 52, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, M.S.; Kim, W.D.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, S.G. AMPK Facilitates Nuclear Accumulation of Nrf2 by Phosphorylating at Serine 550. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; Cai, L. Sulforaphane prevents type 2 diabetes-induced nephropathy via AMPK-mediated activation of lipid metabolic pathways and Nrf2 antioxidative function. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 2469–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.B.; Bao, J.; Deng, C.X. Emerging roles of SIRT1 in fatty liver diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, N.B.; Xu, X.J.; Nelson, L.; Cacicedo, J.M.; Saha, A.K.; Lan, F.; Ido, Y. AMPK and SIRT1: A long-standing partnership? Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E751–E760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) controls the aging process via an integrated signaling network. Ageing Res. Rev. 2012, 11, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colak, Y.; Ozturk, O.; Senates, E.; Tuncer, I.; Yorulmaz, E.; Adali, G.; Doganay, L.; Enc, F.Y. SIRT1 as a potential therapeutic target for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, HY5–HY9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cetrullo, S.; D’Adamo, S.; Tantini, B.; Borzi, R.M.; Flamigni, F. mTOR, AMPK, and Sirt1: Key Players in Metabolic Stress Management. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2015, 25, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Li, H.; Feng, Y. Green Tea and Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) for the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases (NAFLD): Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Mechanism. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, P.; Pardo, V.; Mobasher, M.A.; Garcia-Martinez, I.; Ruiz, L.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.; Sanchez-Ramos, C.; Muntane, J.; Alemany, S.; James, L.P.; et al. SIRT1 Controls Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity by Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 1187–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simao, A.L.; Afonso, M.B.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Gama-Carvalho, M.; Machado, M.V.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Castro, R.E. Skeletal muscle miR-34a/SIRT1:AMPK axis is activated in experimental and human non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponugoti, B.; Kim, D.H.; Xiao, Z.; Smith, Z.; Miao, J.; Zang, M.; Wu, S.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Kemper, J.K. SIRT1 deacetylates and inhibits SREBP-1C activity in regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33959–33970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liou, C.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Ting, N.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Shen, S.C.; Wu, S.J.; Huang, W.C. Protective Effects of Licochalcone A Ameliorates Obesity and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Via Promotion of the Sirt-1/AMPK Pathway in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Cells 2019, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Rivera, C.A.; Yin, J.; Weng, J.; Ye, J. Lack of SIRT1 (Mammalian Sirtuin 1) activity leads to liver steatosis in the SIRT1+/- mice: A role of lipid mobilization and inflammation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Giles, A.; Nakamura, K.; Lee, J.W.; Hou, X.; Donmez, G.; Li, J.; Luo, Z.; Walsh, K.; et al. Hepatic overexpression of SIRT1 in mice attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin resistance in the liver. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1664–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radak, Z.; Suzuki, K.; Posa, A.; Petrovszky, Z.; Koltai, E.; Boldogh, I. The systemic role of SIRT1 in exercise mediated adaptation. Redox Biol. 2020, 35, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; Longo, M.; Rustichelli, A.; Dongiovanni, P. Nutrition and Genetics in NAFLD: The Perfect Binomium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, C.Y.; Zhai, Z.Z.; Li, Z.F.; Wang, L. High fat diet-triggered non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A review of proposed mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 330, 109199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Petta, S.; Dalle Grave, R. Diet, weight loss, and liver health in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathophysiology, evidence, and practice. Hepatology 2016, 63, 2032–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.T.; Kleiner, D.E. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farrell, G.C.; Larter, C.Z. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006, 43, S99–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mridha, A.R.; Wree, A.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Yeh, M.M.; Johnson, C.D.; Van Rooyen, D.M.; Haczeyni, F.; Teoh, N.C.; Savard, C.; Ioannou, G.N.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wree, A.; McGeough, M.D.; Pena, C.A.; Schlattjan, M.; Li, H.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Messer, K.; Canbay, A.; Hoffman, H.M.; Feldstein, A.E. NLRP3 inflammasome activation is required for fibrosis development in NAFLD. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaul, S.; Leszczynska, A.; Alegre, F.; Kaufmann, B.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, L.A.; Wree, A.; Damm, G.; Seehofer, D.; Calvente, C.J.; et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, D.; Thoma, C.; Hallsworth, K.; Cassidy, S.; Hardy, T.; Burt, A.D.; Tiniakos, D.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Taylor, R.; Day, C.P.; et al. Exercise Reduces Liver Lipids and Visceral Adiposity in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staels, B.; Rubenstrunk, A.; Noel, B.; Rigou, G.; Delataille, P.; Millatt, L.J.; Baron, M.; Lucas, A.; Tailleux, A.; Hum, D.W.; et al. Hepatoprotective effects of the dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/delta agonist, GFT505, in rodent models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Din, S.H.; Sabra, A.N.; Hammam, O.A.; Ebeid, F.A.; El-Lakkany, N.M. Pharmacological and antioxidant actions of garlic and.or onion in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in rats. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Viollet, B.; Terkeltaub, R.; Liu-Bryan, R. AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses urate crystal-induced inflammation and transduces colchicine effects in macrophages. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spahis, S.; Delvin, E.; Borys, J.M.; Levy, E. Oxidative Stress as a Critical Factor in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Pathogenesis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 519–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Cederbaum, A.I. Stimulation and proliferation of primary rat hepatic stellate cells by cytochrome P450 2E1-derived reactive oxygen species. Hepatology 2002, 35, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Valle, V.; Chavez-Tapia, N.C.; Uribe, M.; Mendez-Sanchez, N. Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: A review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4850–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbia, D.; Cannella, L.; De Martin, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in NAFLD-NASH-HCC Transition-Focus on NADPH Oxidases. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Zobeiri, M.; Parvizi, F.; El-Senduny, F.F.; Marmouzi, I.; Coy-Barrera, E.; Naseri, R.; Nabavi, S.M.; Rahimi, R.; Abdollahi, M. Curcumin in Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review of the Cellular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress and Clinical Perspective. Nutrients 2018, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Park, J.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, J.; Lee, D.K.; Kwon, S.W.; Han, D.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.H. SQSTM1/p62 activates NFE2L2/NRF2 via ULK1-mediated autophagic KEAP1 degradation and protects mouse liver from lipotoxicity. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1949–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, H.; Teimouri, M.; Shabani, M.; Koushki, M.; Babaei Khorzoughi, R.; Namvarjah, F.; Izadi, P.; Meshkani, R. Resveratrol alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through epigenetic modification of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 119, 105667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Feng, H.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Qin, H.; Liu, G. Geniposide alleviates non-alcohol fatty liver disease via regulating Nrf2/AMPK/mTOR signalling pathways. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5097–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.Y.; Jin, M.L.; Ko, M.J.; Park, G.; Choi, Y.W. Anti-neuroinflammatory Effect of Emodin in LPS-Stimulated Microglia: Involvement of AMPK/Nrf2 Activation. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2981–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ruan, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Saavedra, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Pang, T. A Dual AMPK/Nrf2 Activator Reduces Brain Inflammation After Stroke by Enhancing Microglia M2 Polarization. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzinger, M.; Fischhuber, K.; Poloske, D.; Mechtler, K.; Heiss, E.H. AMPK leads to phosphorylation of the transcription factor Nrf2, tuning transactivation of selected target genes. Redox Biol. 2020, 29, 101393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. GSK-3beta acts upstream of Fyn kinase in regulation of nuclear export and degradation of NF-E2 related factor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16502–16510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, H.; Liu, Q.; Wen, Z.; Feng, H.; Deng, X.; Ci, X. Xanthohumol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury via induction of AMPK/GSK3beta-Nrf2 signal axis. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.A.; Joyner, M.J.; Green, D.J. Mimicking exercise: What matters most and where to next? J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Zheng, L.; Tang, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, R.; Peng, X.; Wu, X.; Zhu, P. Identification of Potentially Relevant Genes for Excessive Exercise-Induced Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy in Zebrafish. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 565307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.C.; Zhang, C.Y.; Duan, J.X.; Guan, X.X.; Yang, H.H.; Jiang, H.L.; Hammock, B.D.; Hwang, S.H.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, C.X.; et al. PTUPB ameliorates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, C.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, X.; Zheng, L.; Tang, C. Exercise Intervention Mitigates Pathological Liver Changes in NAFLD Zebrafish by Activating SIRT1/AMPK/NRF2 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010940
Zou Y, Chen Z, Sun C, Yang D, Zhou Z, Peng X, Zheng L, Tang C. Exercise Intervention Mitigates Pathological Liver Changes in NAFLD Zebrafish by Activating SIRT1/AMPK/NRF2 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(20):10940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010940
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yunyi, Zhanglin Chen, Chenchen Sun, Dong Yang, Zuoqiong Zhou, Xiyang Peng, Lan Zheng, and Changfa Tang. 2021. "Exercise Intervention Mitigates Pathological Liver Changes in NAFLD Zebrafish by Activating SIRT1/AMPK/NRF2 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 20: 10940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010940
APA StyleZou, Y., Chen, Z., Sun, C., Yang, D., Zhou, Z., Peng, X., Zheng, L., & Tang, C. (2021). Exercise Intervention Mitigates Pathological Liver Changes in NAFLD Zebrafish by Activating SIRT1/AMPK/NRF2 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(20), 10940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222010940




