Integrated Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome on Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Four Developmental Stages of Cerasus humilis Peel Coloration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
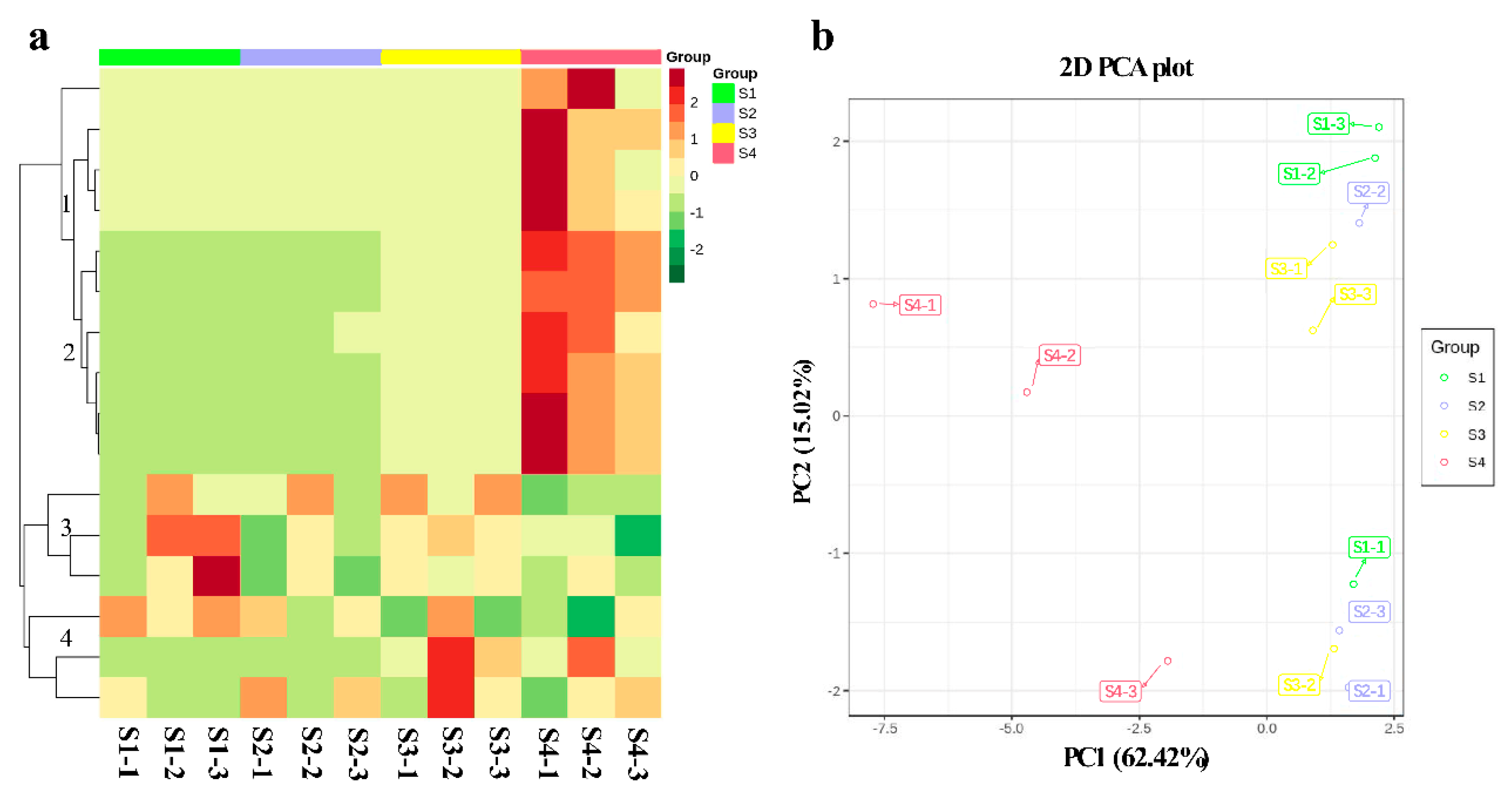
2.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Reveals Differences in Anthocyanin Metabolite Profiles
2.2. Overview of Transcriptome Sequencing
2.3. Annotation and Identification of Unigenes
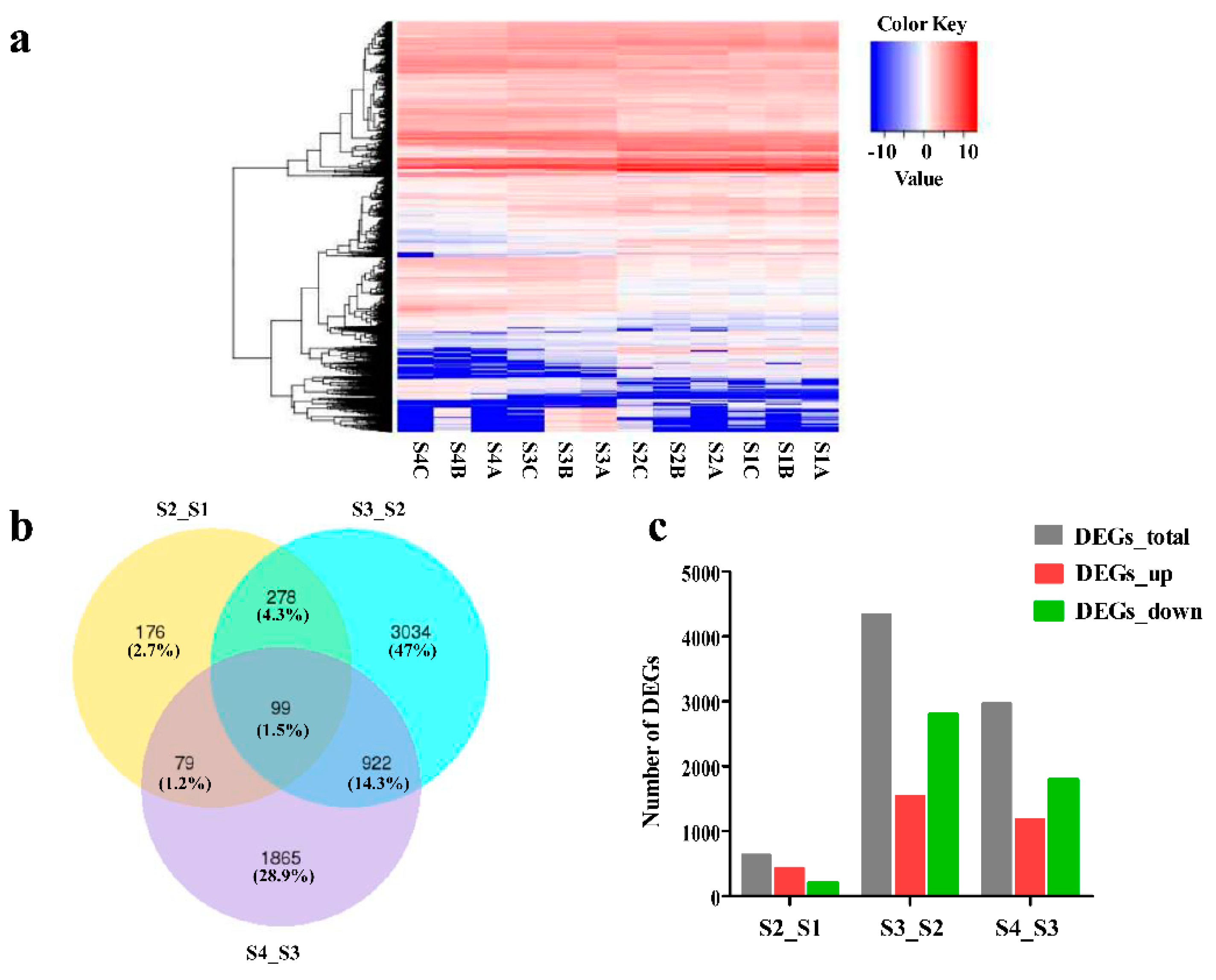
2.4. GO Enrichment and KEGG Pathway Analyses of DEGs
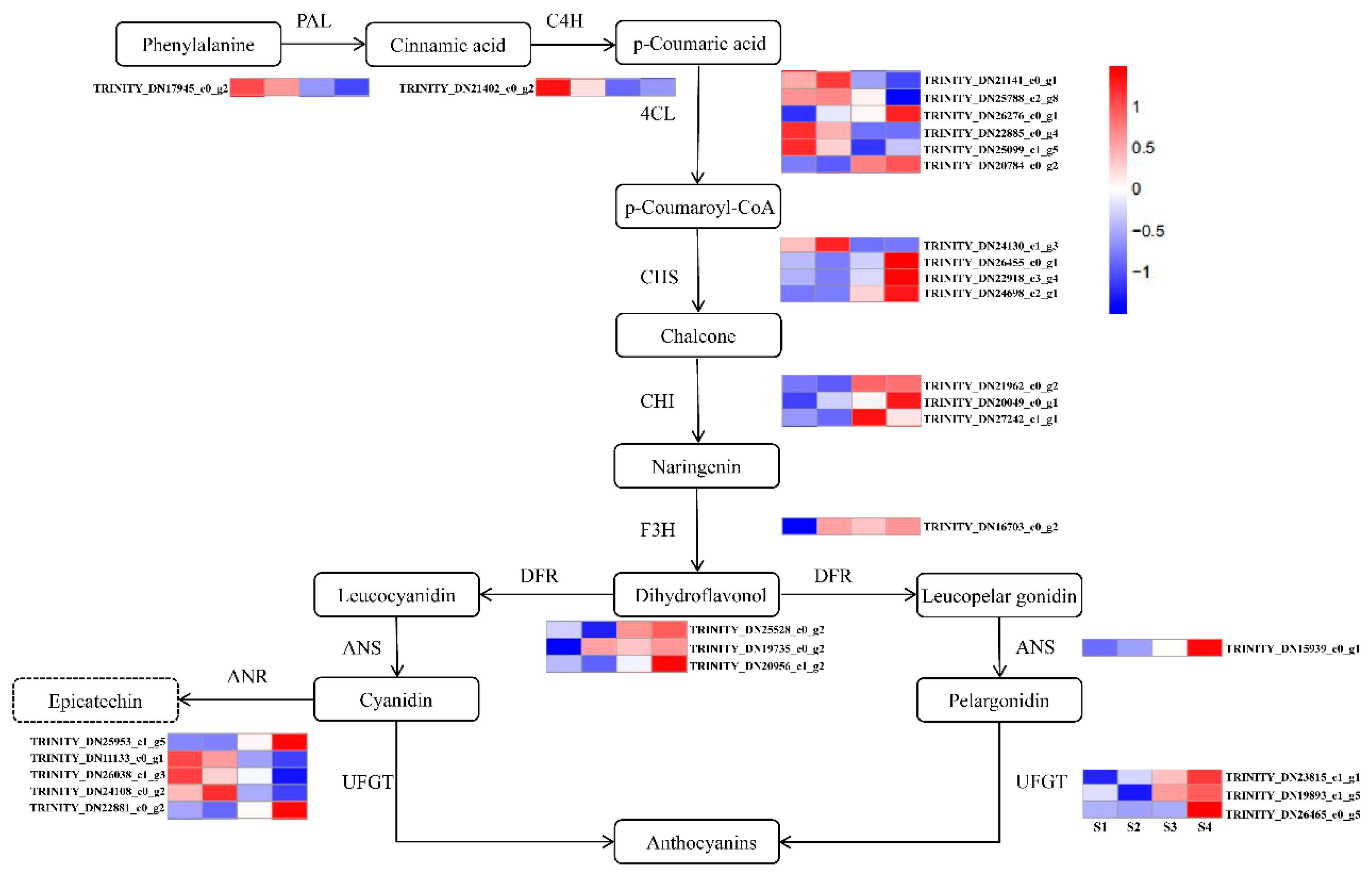
2.5. Analysis of Unigenes Related to Anthocyanidin Biosynthetic Pathways in the Fruit Peel
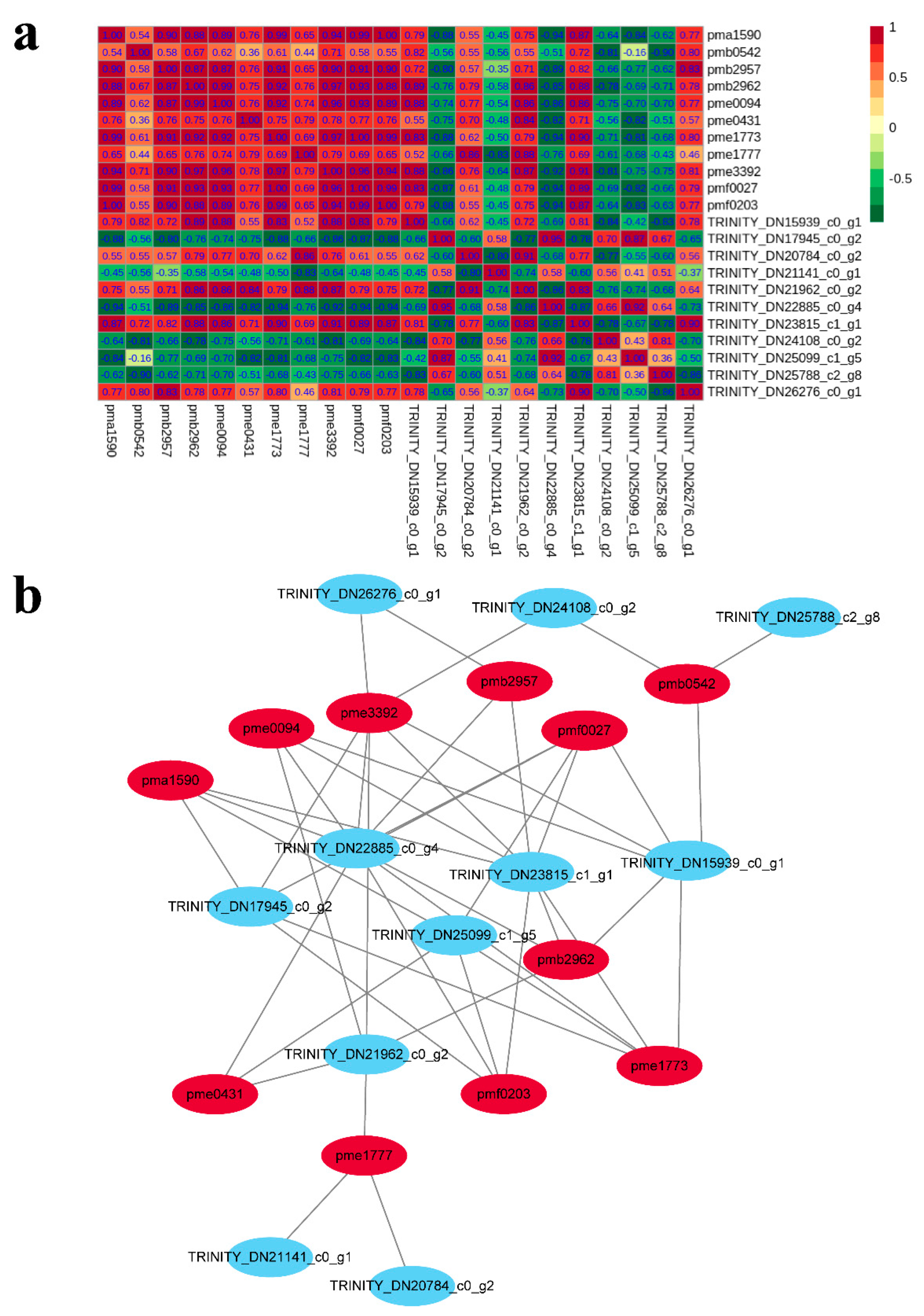
2.6. Integrated Analysis of the Transcriptome and Metabolome
2.7. The Changes of Transcription Factor in the Process of Peel Coloring
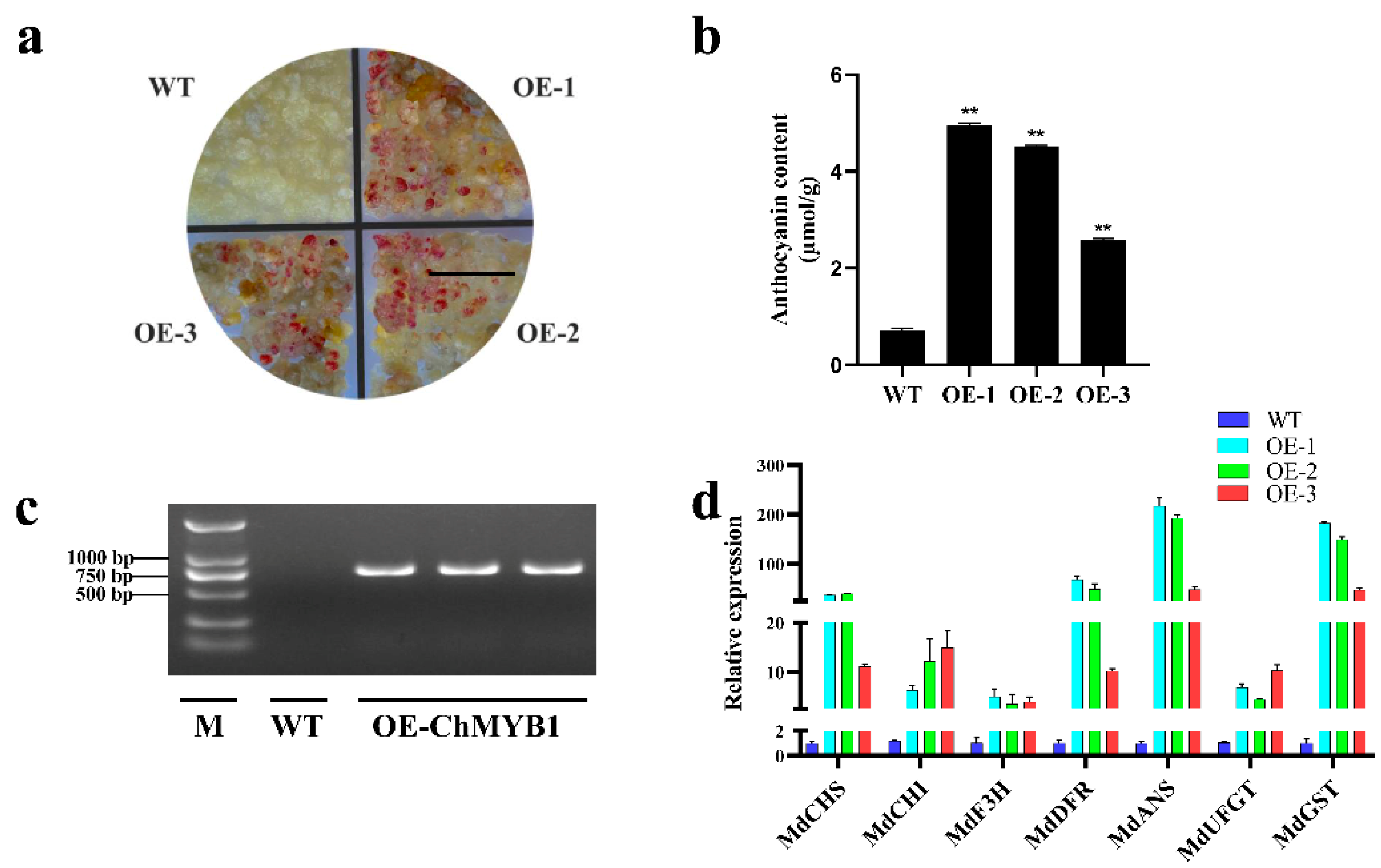
2.8. Heterologous Expression of ChMYB1 in Apple Calli
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
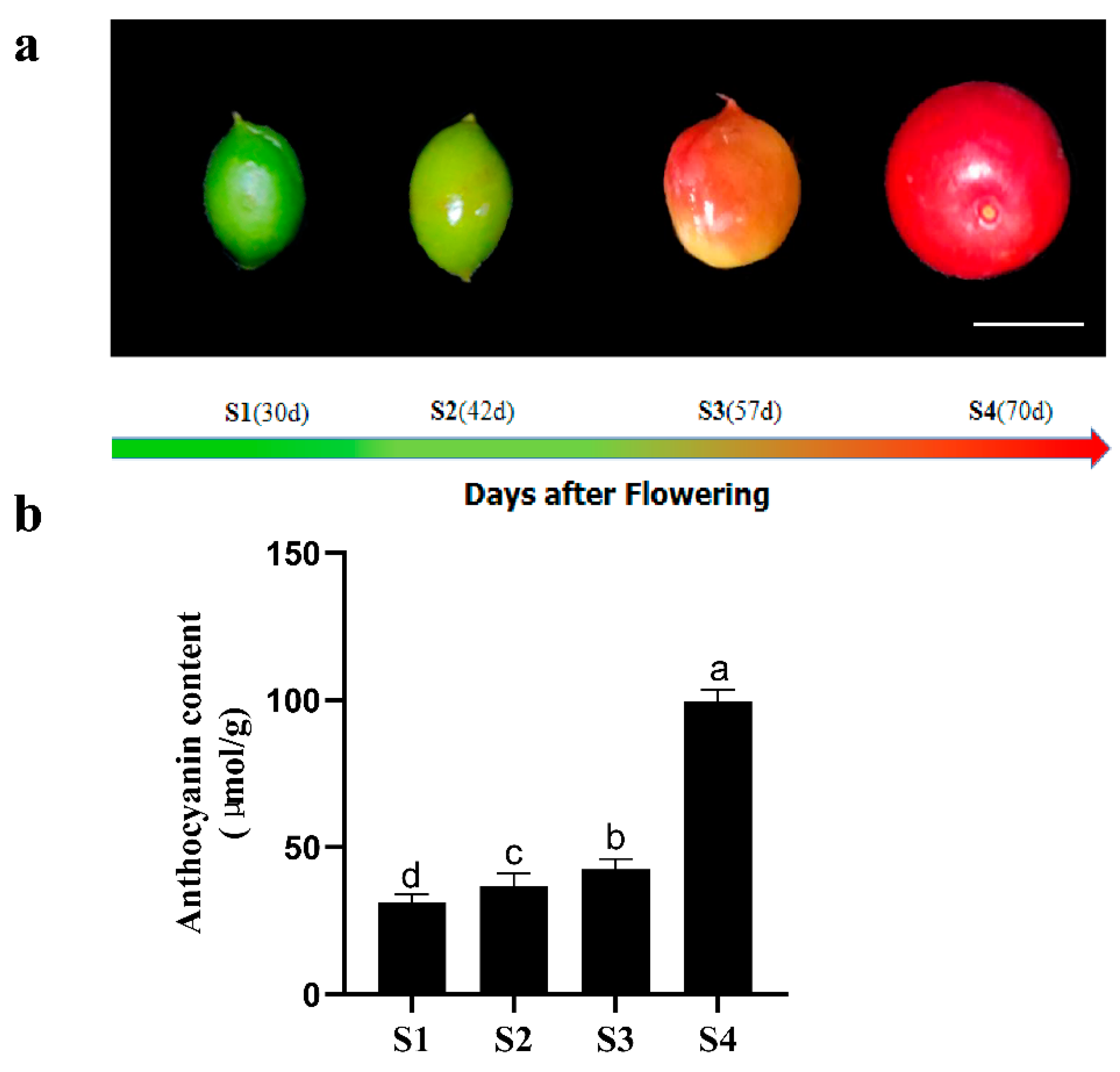
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Metabolome Analysis
4.3. RNA Isolation and Illumina Sequencing
4.4. Transcriptome Data Analysis
4.5. QRT-PCR and Expression Validation
4.6. Molecular Cloning of ChMYB1
4.7. Transformation of Apple Calli
4.8. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.F.; Yi, S.K.; Mu, X.P.; Zhang, J.C.; Du, J.J. Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of Cerasus humilis Using PacBio and Hi-C Technologies. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.P.; Wang, P.F.; Du, J.J.; Gao, Y.G.; Zhang, J.C. Comparison of fruit organic acids and metabolism-related gene expression between Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok and Cerasus glandulosa (Thunb.) Lois. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.P.; Ren, J.; Zhou, L.J.; Sun, L.N.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, Y.L.; Song, X.S. Water deficit mechanisms in perennial shrubs Cerasus humilis leaves revealed by physiological and proteomic analyses. Proteome Sci. 2016, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.P.; Shang, Z.W.; Wei, C.; Ren, J.; Song, X.S. Foliar Sprays of Photosynthetic Bacteria Improve the Growth and Anti-Oxidative Capability on Chinese Dwarf Cherry Seedlings. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.W.; Sun, L.J.; Song, X.S. The molecular cloning and functional characterization of ChNAC1, a NAC transcription factor in Cerasus humilis. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 89, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.Q.; Yang, C.X.; Li, W.D.; Hao, J.B.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhang, Z.S. Evaluation of volatile compounds from Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok.) germplasms by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.F.; Mu, X.P.; Du, J.J.; Gao, Y.G.; Bai, D.H.; Jia, L.T.; Zhang, J.C.; Ren, H.Y.; Xue, X.F. Flavonoid content and radical scavenging activity in fruits of Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis) genotypes. J. For. Res. 2017, 29, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Mu, X.P.; Gao, Y.G.; Zhang, J.C.; Du, J.J. Successful induction and the systematic characterization of tetraploids in cerasus humilis for subsequent breeding. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 265, 109216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.F.; Wu, S.H. The development of regulations of Chinese herbal medicines for both medicinal and food uses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Dubos, C.; Lepiniec, L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.G.; Wu, Q.Y.; Ye, N.H.; Liu, R.; Shi, L.; Xu, W.F.; Zhi, H.; Rahman, A.N.; Xia, Y.J.; Zhang, J.H. Proanthocyanidins inhibit seed germination by maintaining a high level of abscisic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.T.; Han, R.P.; Yu, J.W.; Zhu, M.K.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.Y. Anthocyanins accumulation and molecular analysis of correlated genes by metabolome and transcriptome in green and purple asparaguses (Asparagus officinalis L.). Food Chem. 2019, 271, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfanelli, C.; Poggi, A.; Loreti, E.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Sucrose-specific induction of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takos, A.M.; Jaffe, F.W.; Jacob, S.R.; Bogs, J.; Robinson, S.P.; Walker, A.R. Light-induced expression of a MYB gene regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in red apples. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1216–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colanero, S.; Tagliani, A.; Perata, P.; Gonzali, S. Alternative Splicing in the Anthocyanin Fruit Gene Encoding an R2R3 MYB Transcription Factor Affects Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Tomato Fruits. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.L.; Tao, R.Y.; Tang, Y.X.; Yin, L.; Ma, Y.J.; Ni, J.B.; Yan, X.H.; Yang, Q.S.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zeng, Y.L.; et al. BBX16, a B-box protein, positively regulates light-induced anthocyanin accumulation by activating MYB10 in red pear. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.B.; Liu, C.J. Multifaceted regulations of gateway enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids. Mol. Plant. 2015, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.Y.; Yu, H.N.; Gao, S.; Wu, Y.F.; Cheng, A.X.; Lou, H.X. The isolation and functional characterization of three liverwort genes encoding cinnamate 4-hydroxylase. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 117, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kim, J.I.; Pysh, L.; Chapple, C. Four Isoforms of Arabidopsis 4-Coumarate:CoA Ligase Have Overlapping yet Distinct Roles in Phenylpropanoid Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Meng, X.Y.; Liang, L.J.; Jiang, W.S.; Huang, Y.F.; He, J.; Hu, H.Y.; Almqvist, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, L. Molecular and Biochemical Analysis of Chalcone Synthase from Freesia hybrid in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.H.; McRoberts, J.; Shi, F.; Moreno, J.E.; Jones, A.D.; Howe, G.A. The flavonoid biosynthetic enzyme chalcone isomerase modulates terpenoid production in glandular trichomes of tomato. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flachowsky, H.; Halbwirth, H.; Treutter, D.; Richter, K.; Hanke, M.V.; Szankowski, I.; Gosch, C.; Stich, K.; Fischer, T.C. Silencing of flavanone-3-hydroxylase in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) leads to accumulation of flavanones, but not to reduced fire blight susceptibility. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 51, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Ning, G.G.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.X.; Jin, H.N.; Li, P.H.; Huang, S.S.; Zhao, J.; Bao, M.Z. Disequilibrium of Flavonol Synthase and Dihydroflavonol-4-Reductase Expression Associated Tightly to White vs. Red Color Flower Formation in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Maximova, S.; Payne, M.J.; Guiltinan, M.J. Proanthocyanidin synthesis in Theobroma cacao: Genes encoding anthocyanidin synthase, anthocyanidin reductase, and leucoanthocyanidin reductase. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin-Wang, K.; Micheletti, D.; Palmer, J.; Volz, R.; Lozano, L.; Espley, R.; Hellens, R.P.; Chagne, D.; Rowan, D.D.; Troggio, M.; et al. High temperature reduces apple fruit colour via modulation of the anthocyanin regulatory complex. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lin-Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Gu, C.; Dare, A.P.; Espley, R.V.; He, H.; Allan, A.C.; Han, Y. Molecular genetics of blood-fleshed peach reveals activation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by NAC transcription factors. Plant J. 2015, 82, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tan, H.J.; Ma, Z.X.; Huang, J.R. DELLA Proteins Promote Anthocyanin Biosynthesis via Sequestering MYBL2 and JAZ Suppressors of the MYB/bHLH/WD40 Complex in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant. 2016, 9, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, J.P.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, X.W.; Xu, H.F.; Bi, S.Q.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. An apple MYB transcription factor regulates cold tolerance and anthocyanin accumulation and undergoes MIEL1-mediated degradation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.K.; Fang, J.B.; Qi, X.J.; Lin, M.M.; Zhong, Y.P.; Sun, L.M.; Cui, W. Combined Analysis of the Fruit Metabolome and Transcriptome Reveals Candidate Genes Involved in Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Actinidia arguta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illa, E.; Eduardo, I.; Audergon, J.M.; Barale, F.; Dirlewanger, E.; Li, X.; Moing, A.; Lambert, P.; Le Dantec, L.; Gao, Z.; et al. Saturating the Prunus (stone fruits) genome with candidate genes for fruit quality. Mol. Breed. 2010, 28, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.L.; Sun, Y.W.; Qian, M.J.; Yang, F.X.; Ni, J.B.; Tao, R.Y.; Li, L.; Shu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Teng, Y.W. Transcriptome analysis of bagging-treated red Chinese sand pear peels reveals light-responsive pathway functions in anthocyanin accumulation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, H.M.; Lou, Q.; Liu, H.F.; Han, H.W.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.H.; Ma, Y.M.; Wang, H. Differential Regulation of Anthocyanins in Green and Purple Turnips Revealed by Combined De Novo Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, Q.Q.; Zhang, X.R.; Yang, H.; Li, H.D.; Lv, Y.Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.G.; Liu, F.Z.; Wan, Y.S. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Unveil Anthocyanin Metabolism in Pink and Red Testa of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Int. J. Genom. 2021, 2021, 5883901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.T.; Zhou, G.F.; Liu, P.; Liu, M.J. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling unveil the mechanisms of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. peel coloration. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 125903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Tu, H.; Wan, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.Q.; Luo, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.Y. Spatio-temporal distribution and natural variation of metabolites in citrus fruits. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wang, G.B.; Wang, T.L.; Cao, F.L. Integrated analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome in young and mature leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 143, 111906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Ren, J.; Lang, S.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhu, L.W.; Song, X.S. Differential Regulation of Anthocyanins in Cerasus humilis Fruit Color Revealed by Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis. Forests 2020, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.H.; Guo, H.X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z.M.; Yu, X.M.; Wu, J.F.; Zeng, F.C. Metabolome and Transcriptome Association Analysis Reveals Dynamic Regulation of Purine Metabolism and Flavonoid Synthesis in Transdifferentiation during Somatic Embryogenesis in Cotton. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, D.B.; Zhang, H.N.; Lai, B.; Liu, L.Q.; Pan, X.L.; Ma, Z.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Xie, J.H.; Shi, S.Y.; Wei, Y.Z. Integrative Analysis of the Coloring Mechanism of Red Longan Pericarp through Metabolome and Transcriptome Analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.B.; Mei, X.; Rothenberg, D.O.; Yang, Z.B.; Zhang, W.T.; Wan, S.H.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, L.Y. Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Putative Genes Involved in Anthocyanin Accumulation and Coloration in White and Pink Tea (Camellia sinensis) Flower. Molecules 2020, 25, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.D.; Li, Y.L.; Lu, Q.W.; Lu, H.F.; Li, J.M. Combined Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome Identified Candidate Genes Involved in Phenolic Acid Biosynthesis in the Leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaakola, L. New insights into the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in fruits. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steyn, W.J.; Holcroft, D.M.; Wand, S.J.E.; Jacobs, G. Regulation of pear color development in relation to activity of flavonoid enzymes. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2004, 129, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, F.; Cai, J.H.; Kong, X.M.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.B.; Ji, S.J. Transcriptome profiling reveals the roles of pigment mechanisms in postharvest broccoli yellowing. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Y.; Osbourn, A.; Ma, P.D. MYB Transcription Factors as Regulators of Phenylpropanoid Metabolism in Plants. Mol. Plant. 2015, 8, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, L.G.; Seal, A.G.; Montefiori, M.; McGhie, T.K.; Tsang, G.K.; Datson, P.M.; Hilario, E.; Marsh, H.E.; Dunn, J.K.; Hellens, R.P.; et al. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor determines red petal colour in an Actinidia (kiwifruit) hybrid population. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, T.T.; Wan, H.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Yao, Y.C. McMYB10 regulates coloration via activating McF3’H and later structural genes in ever-red leaf crabapple. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, C.M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Song, T.; Yu, M.W.; Yu, W.C.; Qu, S.C. The R2R3-type MYB transcription factor MdMYB90-like is responsible for the enhanced skin color of an apple bud sport mutant. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.F.; Zou, Q.; Yang, G.X.; Jiang, S.H.; Fang, H.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.S. MdMYB6 regulates anthocyanin formation in apple both through direct inhibition of the biosynthesis pathway and through substrate removal. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.Z.; Zou, Z.W.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Fang, W.P.; Zhu, X.J. Metabolic analyses reveal different mechanisms of leaf color change in two purple-leaf tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.) cultivars. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.L.; Wang, W.S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Yu, S.B.; Xiong, L.Z.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Schultz, A.W.; Wang, J.; Johnson, C.H.; Yannone, S.M.; Patti, G.J.; Siuzdak, G. Liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry characterization of metabolites guided by the METLIN database. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.X.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Tian, J.; Yao, Y.C. MdMYB8 is associated with flavonol biosynthesis via the activation of the MdFLS promoter in the fruits of Malus crabapple. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| DEG Set | TF Family | Number of DEGs | Up | Down | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2_S1 | ARF/ERF | 20 | 12 | 8 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor |
| B3 | 12 | 7 | 5 | B3 DNA-binding domain | |
| bHLH | 22 | 11 | 11 | basic helix-loop helix | |
| bzip | 8 | 5 | 3 | Basic region leucine zipper | |
| C2H2 | 8 | 5 | 3 | Zinc finger C2H2 domain-containing protein | |
| C3H | 9 | 7 | 2 | Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein | |
| DBB | 8 | 7 | 1 | double B-box zinc finger protein | |
| G2-like | 11 | 5 | 6 | Golden2-Like protein | |
| GRAS | 8 | 7 | 1 | C-terminal GRAS domain | |
| HSF | 22 | 18 | 4 | Heat stress transcription factor | |
| MYB | 28 | 20 | 8 | MYB-related protein | |
| NAC | 15 | 14 | 1 | NAC domain-containing protein | |
| S1Fa-like | 12 | 6 | 6 | Leucine-rich repeat protein | |
| other TFs | 104 | 56 | 48 | ||
| total | 287 | 180 | 107 | ||
| S3_S2 | ARF/ERF | 98 | 24 | 74 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor |
| B3 | 121 | 27 | 94 | B3 DNA-binding domain | |
| bHLH | 152 | 53 | 99 | basic helix-loop helix | |
| bzip | 62 | 25 | 37 | Basic region leucine zipper | |
| C2H2 | 76 | 27 | 49 | Zinc finger C2H2 domain-containing protein | |
| C3H | 52 | 17 | 35 | Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein | |
| DBB | 17 | 3 | 14 | double B-box zinc finger protein | |
| G2-like | 67 | 22 | 45 | Golden2-Like protein | |
| GRAS | 47 | 14 | 33 | C-terminal GRAS domain | |
| HSF | 64 | 14 | 50 | Heat stress transcription factor | |
| MYB | 159 | 48 | 111 | MYB-related protein | |
| NAC | 92 | 25 | 67 | NAC domain-containing protein | |
| S1Fa-like | 32 | 7 | 25 | Leucine-rich repeat protein | |
| other TFs | 717 | 252 | 465 | ||
| total | 1756 | 558 | 1198 | ||
| S4_S3 | ARF/ERF | 78 | 25 | 53 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor |
| B3 | 91 | 32 | 59 | B3 DNA-binding domain | |
| bHLH | 116 | 33 | 83 | basic helix-loop helix | |
| bzip | 55 | 17 | 38 | Basic region leucine zipper | |
| C2H2 | 47 | 13 | 34 | Zinc finger C2H2 domain-containing protein | |
| C3H | 39 | 13 | 26 | Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein | |
| DBB | 6 | 3 | 3 | double B-box zinc finger protein | |
| G2-like | 40 | 17 | 23 | Golden2-Like protein | |
| GRAS | 30 | 15 | 15 | C-terminal GRAS domain | |
| HSF | 39 | 25 | 14 | Heat stress transcription factor | |
| MYB | 112 | 32 | 80 | MYB-related protein | |
| NAC | 74 | 32 | 42 | NAC domain-containing protein | |
| S1Fa-like | 43 | 4 | 39 | Leucine-rich repeat protein | |
| other TFs | 484 | 160 | 324 | ||
| total | 1254 | 421 | 833 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lang, S.; Wang, D.; Song, X. Integrated Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome on Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Four Developmental Stages of Cerasus humilis Peel Coloration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111880
Ji X, Ren J, Zhang Y, Lang S, Wang D, Song X. Integrated Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome on Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Four Developmental Stages of Cerasus humilis Peel Coloration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111880
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiaolong, Jing Ren, Yixin Zhang, Shaoyu Lang, Di Wang, and Xingshun Song. 2021. "Integrated Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome on Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Four Developmental Stages of Cerasus humilis Peel Coloration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111880
APA StyleJi, X., Ren, J., Zhang, Y., Lang, S., Wang, D., & Song, X. (2021). Integrated Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome on Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Four Developmental Stages of Cerasus humilis Peel Coloration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(21), 11880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111880






