Computationally Reconstructed Interactome of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 Reveals Novel Functional Modules and Protein Hubs for Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Protein Interactome
2.1.1. Interolog Method
2.1.2. Domain-Based Method
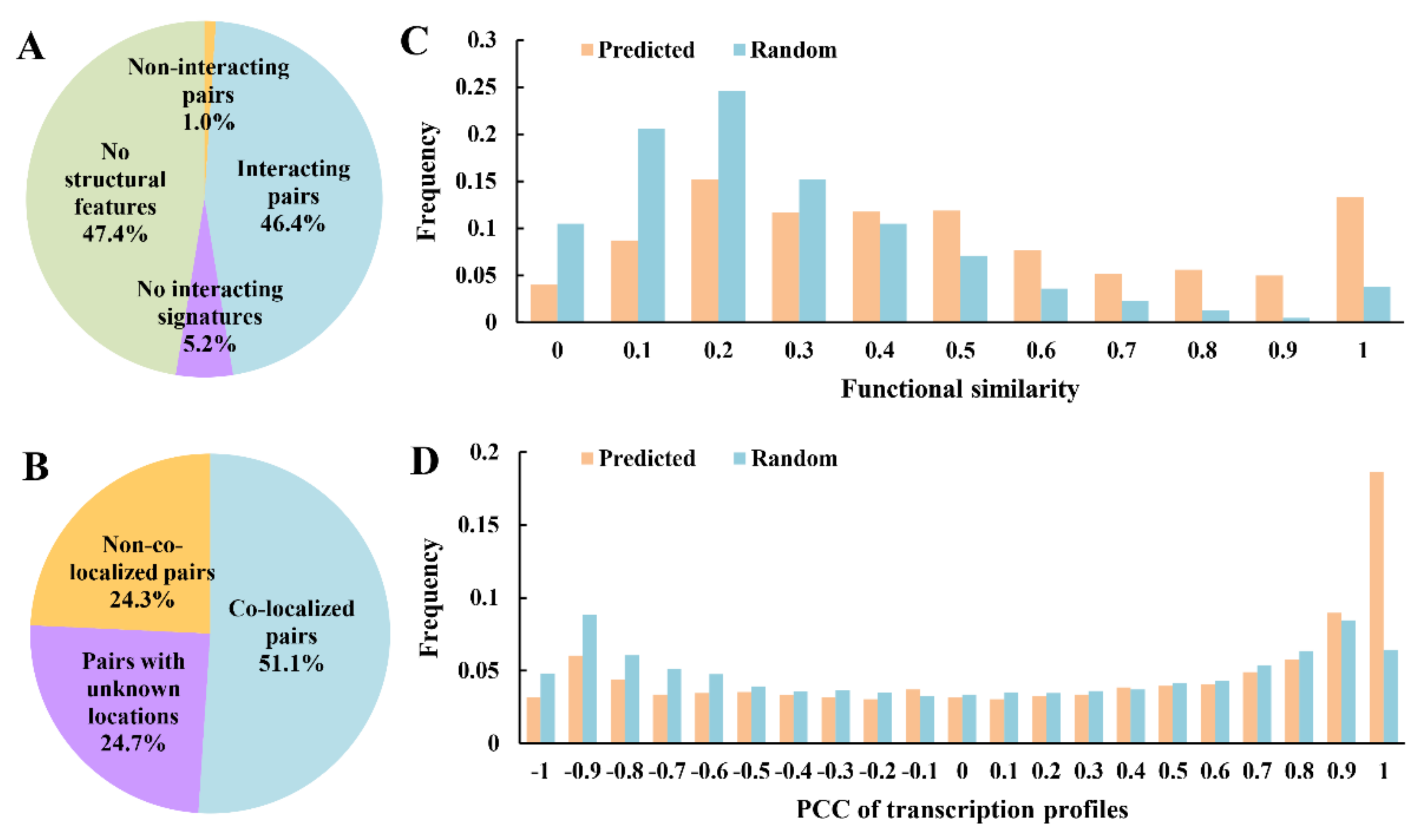
2.2. Quality Assessment of the Reconstructed PPI Network
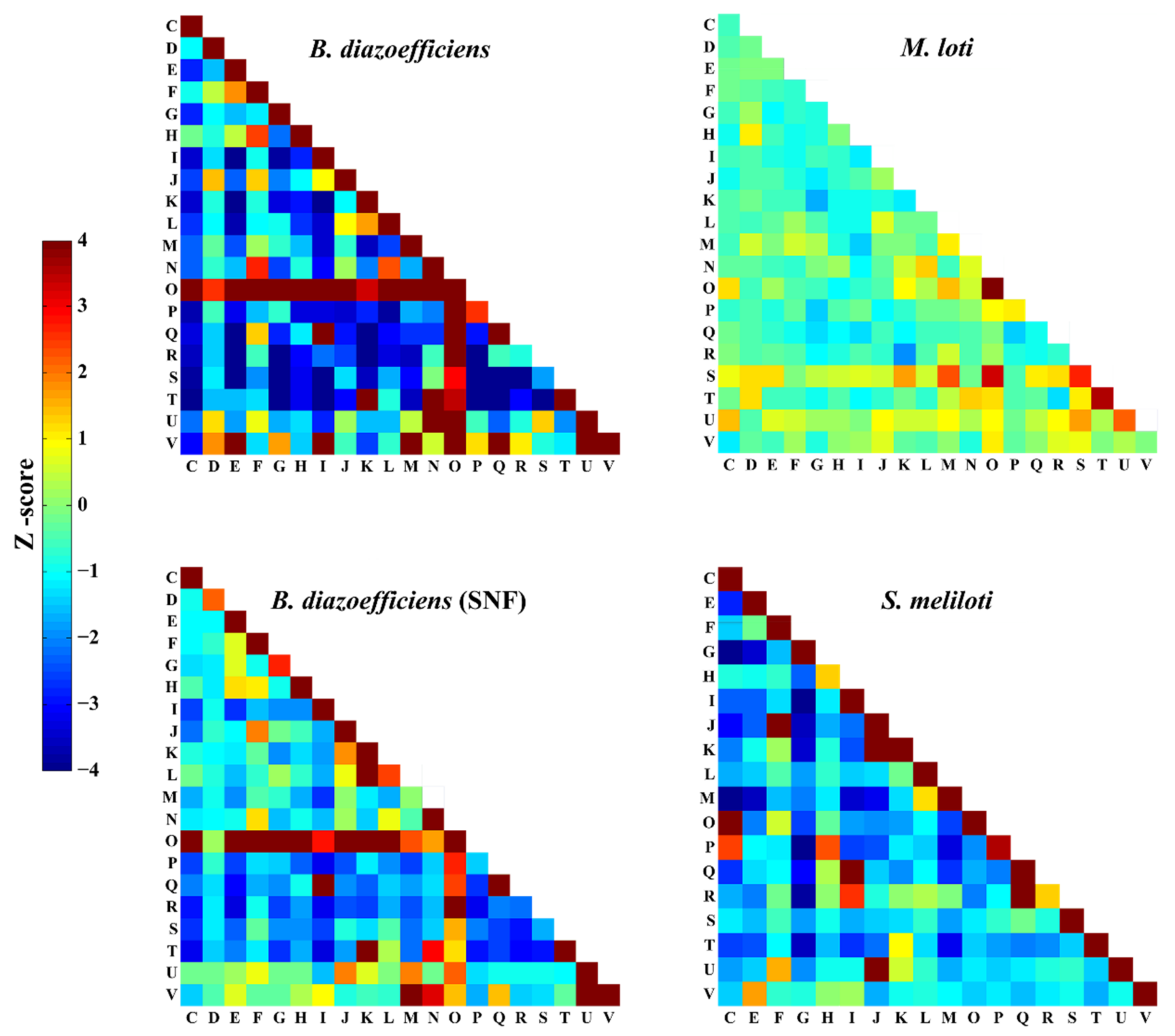
2.3. COG Function Enrichment Analysis of PPIs
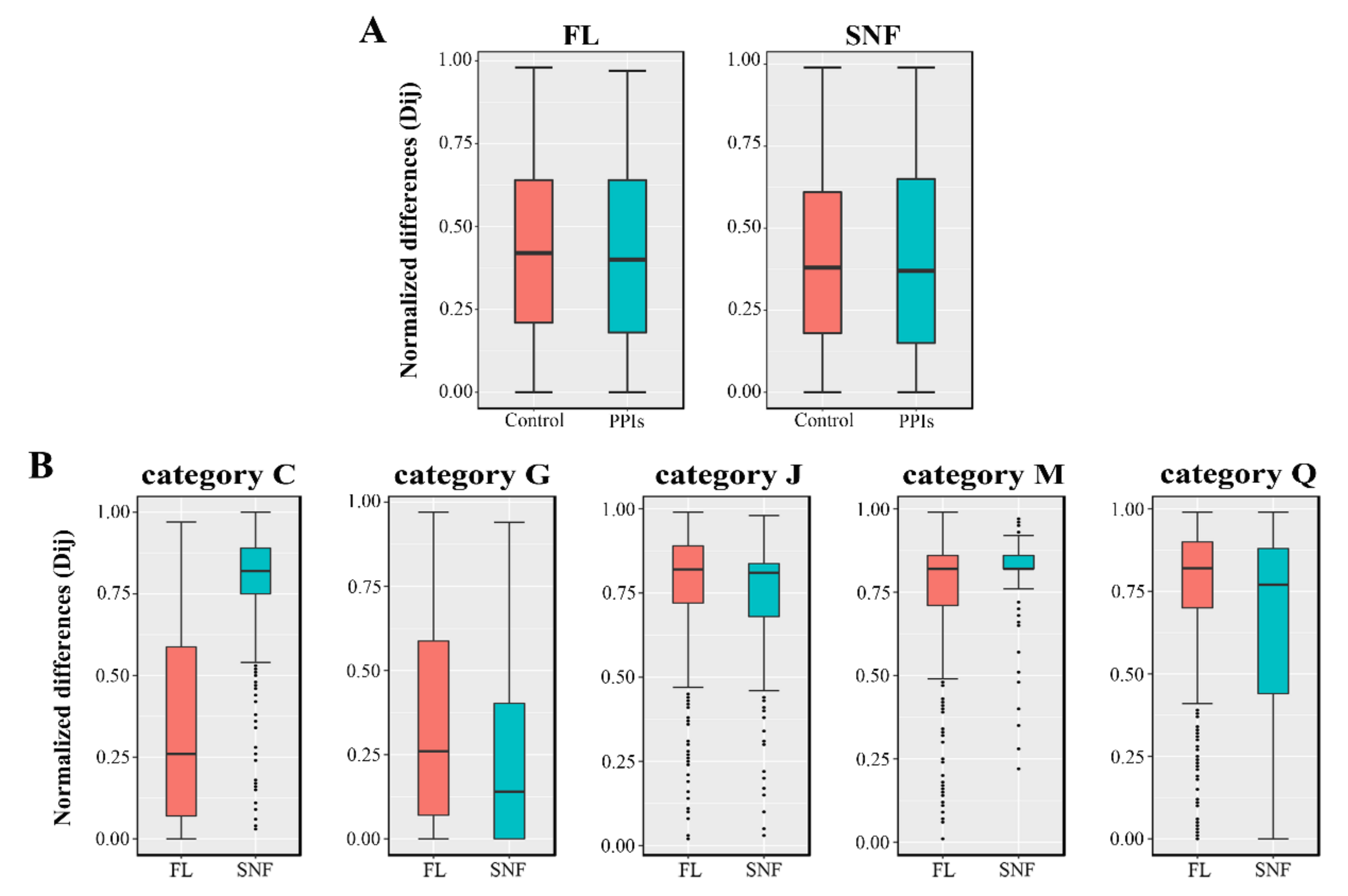
2.4. Reconstruction and Validation of the PPI Sub-Networks in FL and SNF Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reconstruction of the Genome-Scale PPI Network of B. diazoefficiens USDA110
3.2. Quality Assessment of the PPI Network
3.3. Properties of the Reconstructed PPI Network
3.4. Comparison of PPIs among Rhizobia
3.5. Analysis and Comparison of the PPI Networks under FL and SNF States
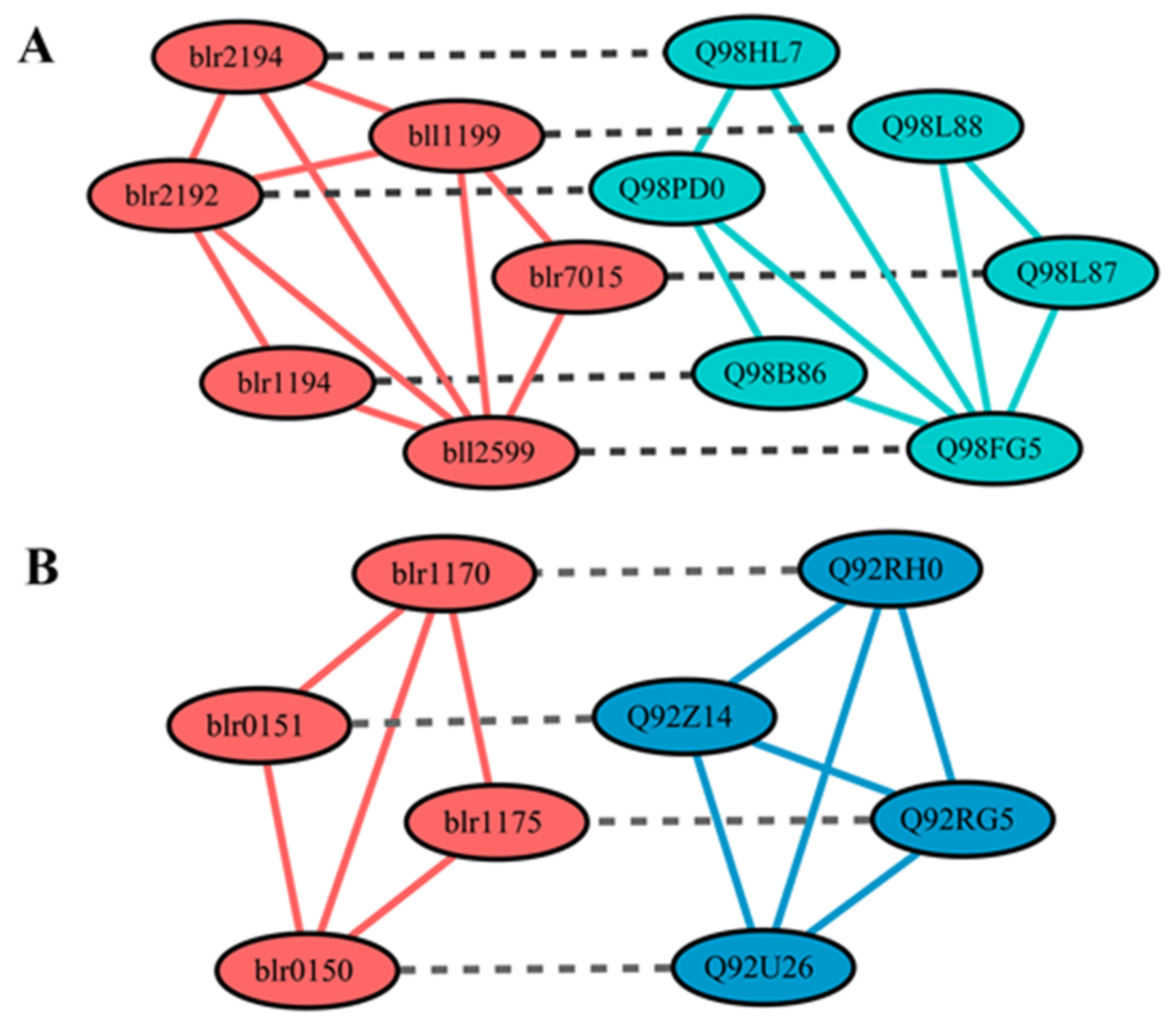
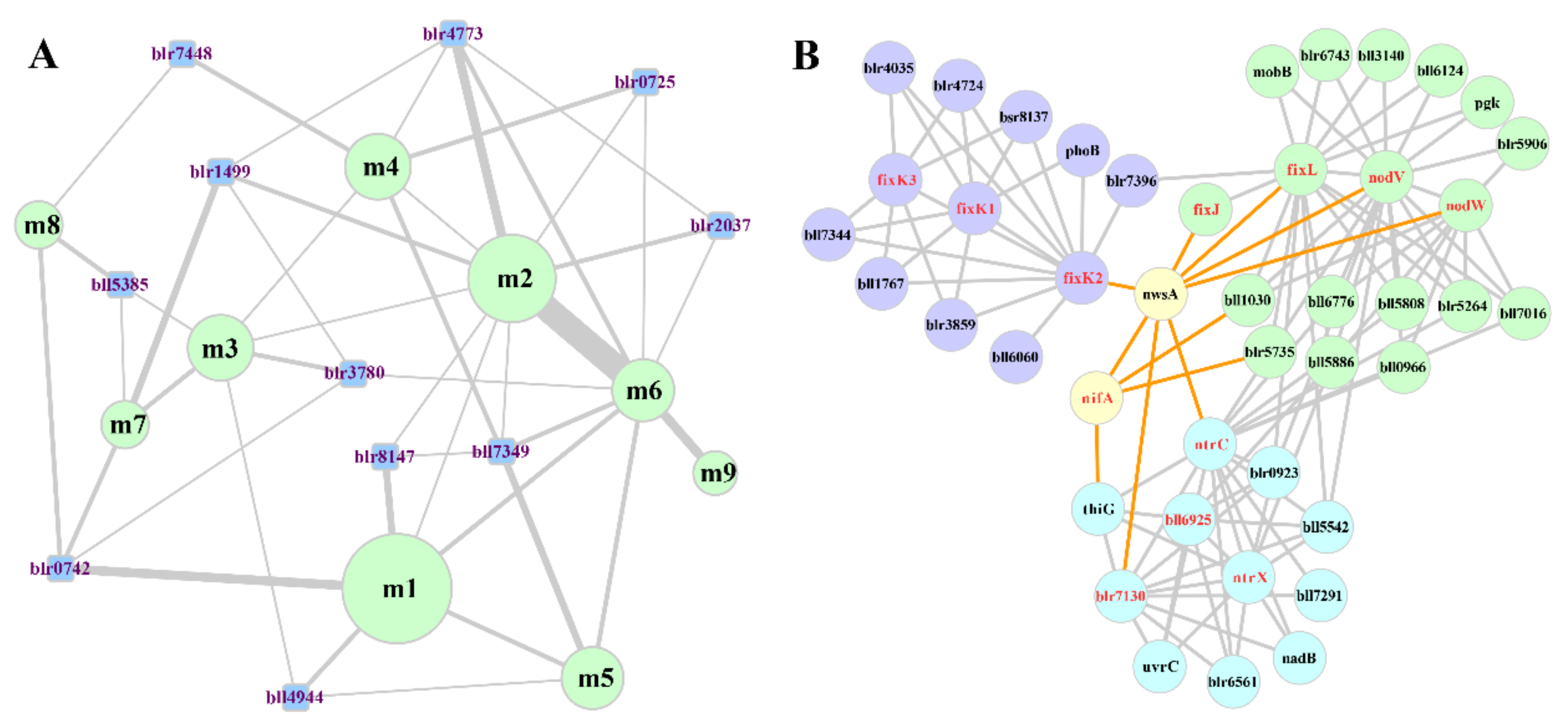
3.6. Analysis of the Core-Sub-PPI-Network for Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Galloway, J.N. An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 2008, 451, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Delamuta, J.R.M.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Ormeño-Orrillo, E.; Melo, I.S.; Martínez-Romero, E.; Hungria, M. Polyphasic evidence supporting the reclassification of Bradyrhizobium japonicum group Ia strains as Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 3342–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.; Hennecke, H. Mapping of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum DNA Region region carrying genes for symbiosis and an asymmetric accumulation of reiterated sequences. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillette, W.K.; Elkan, G.H. Bradyrhizobium (Arachis) sp. strain NC92 contains two nodD genes involved in the repression of nodA and a nolA gene required for the efficient nodulation of host plants. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 2757–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Israel, D.W. Cultivar and Rhizobium strain effects on nitrogen fixation and remobilization by soybeans. Agron. J. 1981, 73, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, W.J.; Kuykendall, L.D. Enhanced nodulation and nitrogen fixation by a revertant of a nodulation-defective Bradyrhizobium japonicum tryptophan auxotroph. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuykendall, L.D.; Hashem, F.M.; Hunter, W.J. Enhanced competitiveness of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum mutant strain improved for nodulation and nitrogen fixation. Plant Soil 1996, 186, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosslak, R.M.; Bookland, R.; Barkei, J.; Paaren, H.E.; Appelbaum, E.R. Induction of Bradyrhizobium japonicum common nod genes by isoflavones isolated from Glycine max. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7428–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, S.; Stacey, G.; Yu, O. Endogenous isoflavones are essential for the establishment of symbiosis between soybean and Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Plant J. 2006, 48, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Sato, S.; Minamisawa, K.; Uchiumi, T.; Sasamoto, S.; Watanabe, A.; Idesawa, K.; Iriguchi, M.; Kawashima, K.; et al. Complete genomic sequence of nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110 (Supplement). DNA Res. 2002, 9, 225–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pessi, G.; Ahrens, C.H.; Rehrauer, H.; Lindemann, A.; Hauser, F.; Fischer, H.M.; Hennecke, H. Genome-wide transcript analysis of Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroids in soybean root nodules. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarma, A.D.; Emerich, D.W. Global protein expression pattern of Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroids: A prelude to functional proteomics. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, A.D.; Emerich, D.W. A comparative proteomic evaluation of culture grown vs nodule isolated Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proteomics 2006, 6, 3008–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmotte, N.; Ahrens, C.H.; Knief, C.; Qeli, E.; Koch, M.; Fischer, H.M.; Vorholt, J.A.; Hennecke, H.; Pessi, G. An integrated proteomics and transcriptomics reference data set provides new insights into the Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroid metabolism in soybean root nodules. Proteomics 2010, 10, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelena, Č.; Hahn, J.; Imakaev, M.; Omasits, U.; Förstner, K.U.; Ljubimov, N.; Goebel, M.; Pessi, G.; Fischer, H.M.; Ahrens, C.H.; et al. Genome-wide transcription start site mapping of Bradyrhizobium japonicum grown free-living or in symbiosis—A rich resource to identify new transcripts, proteins and to study gene regulation. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 302. [Google Scholar]
- Lardi, M.; Murset, V.; Fischer, H.M.; Mesa, S.; Ahrens, C.H.; Zamboni, N.; Pessi, G. Metabolomic profiling of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens-induced root nodules reveals both host plant-specific and developmental signatures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Gu, H.; Du, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Dunwell, J.M.; Cao, Y.; et al. Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA 110-Glycine max interactome provides candidate proteins associated with symbiosis. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3061–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavin, A.C.; Supertifurga, G. Protein complexes and proteome organization from yeast to man. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Kuster, B. Affinity purification-mass spectrometry. Powerful tools for the characterization of protein complexes. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, R.; Pons, T.; Céol, A.; Valencia, A.; Aloy, P. Towards a detailed atlas of protein-protein interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, I.W.; Linding, R.; Farley, D.W.; Liu, Y.; Pesquita, C.; Faria, D.; Bull, S.; Pawson, T.; Morris, Q.; Wrana, J.L. Dynamic modularity in protein interaction networks predicts breast cancer outcome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.D.; Bertin, N.; Hao, T.; Goldberg, D.S.; Berriz, G.F.; Zhang, L.V.; Dupuy, D.; Walhout, A.J.; Cusick, M.E.; Roth, F.P.; et al. Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network. Nature 2004, 430, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuchty, S. Controllability in protein interaction networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwikowski, B.; Uetz, P.; Fields, S. A network of protein-protein interactions in yeast. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi, S.; Ray, D.; Warde-Farley, D.; Grouios, C.; Morris, Q. GeneMANIA: A real-time multiple association network integration algorithm for predicting gene function. Genome Biol. 2008, 9 (Suppl. 1), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giot, L.; Bader, J.S.; Brouwer, C.; Chaudhuri, A.; Kuang, B.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.L.; Ooi, C.E.; Godwin, B.; Vitols, E.; et al. A protein interaction map of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 2003, 302, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uetz, P.; Giot, L.; Cagney, G.; Mansfield, T.A.; Judson, R.S.; Knight, J.R.; Lockshon, D.; Narayan, V.; Srinivasan, M.; Pochart, P.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of protein-protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 2000, 403, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.; Peng, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Sun, J. Reconstruction and application of protein–protein interaction network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Mering, C.; Krause, R.; Snel, B.; Cornell, M.; Oliver, S.G.; Fields, S.; Bork, P. Comparative assessment of large-scale data sets of protein-protein interactions. Nature 2002, 417, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, M.P.H.; Thorne, T.; de Silva, E.; Stewart, R.; An, H.J.; Lappe, M.; Wiuf, C. Estimating the size of the human interactome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6959–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Guo, M.; Needham, C.J.; Huang, Y.; Cai, L.; Westhead, D.R. Simple sequence-based kernels do not predict protein–protein interactions. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2610–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, J.; Song, J.; Chang, S. Prediction of human protein–protein interaction by a domain-based approach. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 396, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlyar, M.; Aem, R.; Jurisica, I. Prediction of protein-protein interactions. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2017, 60, 8.2.1–8.2.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walhout, A.J.; Walhout, A.J.; Sordella, R.; Lu, X.; Hartley, J.L.; Temple, G.F.; Brasch, M.A.; Thierry-Mieg, N.; Vidal, M. Protein interaction mapping in C. elegans using proteins involved in vulval development. Science 2000, 287, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, L.R.; Vaglio, P.; Reboul, J.; Ge, H.; Davis, B.P.; Garrels, J.; Vincent, S.; Vidal, M. Identification of potential interaction networks using sequence-based searches for conserved protein-protein interactions or “interologs”. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 2120–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parrish, J.R.; Yu, J.; Liu, G.; Hines, J.A.; Chan, J.E.; Mangiola, B.A.; Zhang, H.; Pacifico, S.; Fotouhi, F.; DiRita, V.J.; et al. A proteome-wide protein interaction map for Campylobacter jejuni. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajagopala, S.V.; Sikorski, P.; Kumar, A.; Mosca, R.; Vlasblom, J.; Arnold, R.; Franca-Koh, J.; Pakala, S.B.; Phanse, S.; Ceol, A.; et al. The binary protein-protein interaction landscape of Escherichia coli. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Häuser, R.; Ceol, A.; Rajagopala, S.V.; Mosca, R.; Siszler, G.; Wermke, N.; Sikorski, P.; Schwarz, F.; Schick, M.; Wuchty, S.; et al. A second-generation protein–protein interaction network of Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimoda, Y.; Shinp, S.; Kohara, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Tabata, S.; Sato, S. A large scale analysis of protein-protein interactions in the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Mesorhizobium loti. DNA Res. 2008, 15, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Shimoda, Y.; Muraki, A.; Kohara, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Tabata, S. A large-scale protein protein interaction analysis in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. DNA Res. 2007, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Titz, B.; Rajagopala, S.V.; Goll, J.; Häuser, R.; McKevitt, M.T.; Palzkill, T.; Uetz, P. The binary protein interactome of Treponema pallidum-the syphilis spirochete. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Reguly, T.; Boucher, L.; Breitkreutz, A.; Tyers, M. BioGRID: A general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D535–D539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xenarios, I.; Rice, D.W.; Salwinski, L.; Baron, M.K.; Marcotte, E.M.; Eisenberg, D. DIP: The database of interacting proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orchard, S.; Ammari, M.; Aranda, B.; Breuza, L.; Briganti, L.; Broackes-Carter, F.; Campbell, N.H.; Chavali, G.; Chen, C.; del-Toro, N.; et al. The MIntAct project-IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D358–D363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peri, S.; Navarro, J.D.; Amanchy, R.; Kristiansen, T.Z.; Jonnalagadda, C.K.; Surendranath, V.; Niranjan, V.; Muthusamy, B.; Gandhi, T.K.; Gronborg, M.; et al. Development of human protein reference database as an initial platform for approaching systems biology in humans. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Remm, M.; Storm, C.E.V.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Automatic clustering of orthologs and in-paralogs from pairwise species comparisons. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 314, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosca, R.; Ceol, A.; Stein, A.; Olivella, R.; Aloy, P. 3did: A catalog of domain-based interactions of known three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D374–D379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planas-Iglesias, J.; Marin-Lopez, M.A.; Bonet, J.; Garcia-Garcia, J.; Oliva, B. iLoops: A protein-protein interaction prediction server based on structural features. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2360–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas-Iglesias, J.; Bonet, J.; García-García, J.; Marín-López, M.A.; Feliu, E.; Oliva, B. Understanding protein-protein interactions using local structural features. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.Y.; Wagner, J.R.; Laird, M.R.; Melli, G.; Rey, S.; Lo, R.; Dao, P.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Ester, M.; Foster, L.J.; et al. PSORTb 3.0: Improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Du, Z.; Payattakool, R.; Yu, P.S.; Chen, C.F. A new method to measure the semantic similarity of GO terms. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, R.; Greenbaum, D.; Gerstein, M. Relating whole-genome expression data with protein-protein interactions. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Koonin, E.V.; Lipman, D.J. A genomic perspective on protein families. Science 1997, 278, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehner, B.; Fraser, A.G. A first-draft human protein-interaction map. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, H.; Liu, Z.; Church, G.M.; Vidal, M. Correlation between transcriptome and interactome mapping data from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenov, Y.; Ramírez, F.; Schelhorn, S.E.; Lengauer, T.; Albrecht, M. Computing topological parameters of biological networks. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolf, Y.I.; Karev GKoonin, E.V. Scale-free networks in biology: New insights into the fundamentals of evolution? Bioessays 2002, 24, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmiran, A.; Desveaux, D.; Subramaniam, R. Building a protein-interaction network to study Fusarium graminearum pathogenesis. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 40, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, E.; Tan, T.; Lin, K. Promiscuous domains: Facilitating stability of the yeast protein-protein interaction network. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacher, J.C.; Akutsu, T. Dominating scale-free networks with variable scaling exponent: Heterogeneous networks are not difficult to control. N. J. Phys. 2012, 14, 073005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peregrínalvarez, J.M.; Xiong, X.; Chong, S.; Parkinson, J. The modular organization of protein interactions in Escherichia coli. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000523. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Llorente, I.; Caviedes, M.A.; Dary, M.; Palomares, A.J.; Cánovas, F.M.; Peregrín-Alvarez, J.M. The Symbiosis Interactome: A computational approach reveals novel components, functional interactions and modules in Sinorhizobium meliloti. BMC Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, M.F. Key roles of microsymbiont amino acid metabolism in rhizobia-legume interactions. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 411–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, R.; Suthram, S.; Kelley, R.M.; Kuhn, T.; McCuine, S.; Uetz, P.; Sittler, T.; Karp, R.M.; Ideker, T. Conserved patterns of protein interaction in multiple species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1974–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, D.; Yaveroğlu, Ö.N.; Malod-Dognin, N.; Stojmirovic, A.; Pržulj, N. Topology-function conservation in protein-protein interaction networks. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micale, G.; Pulvirenti, A.; Giugno, R.; Ferro, A. GASOLINE: A greedy and stochastic algorithm for optimal local multiple alignment of interaction networks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quelas, J.I.; Althabegoiti, M.J.; Jimenez-Sanchez, C.; Melgarejo, A.A.; Marconi, V.I.; Mongiardini, E.J.; Trejo, S.A.; Mengucci, F.; Ortega-Calvo, J.J.; Lodeiro, A.R. Swimming performance of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens is an emergent property of its two flagellar systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, K.; Mellaherrera, R.A.; Golden, J.W. Cyanobacterial heterocysts. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhargava, S.; Chouhan, S. Diazotrophic specific cytochrome c oxidase required to overcome light stress in the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Li, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, H.; Ge, J. Research progress of mitochondrial electron transport chain and its biological significance. Fudan Univ. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 42, 250–261. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, X.P.; Ma, B.G. Construction and simulation of the Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 metabolic network: A comparison between free-living and symbiotic states. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Lu, H. Correlation between gene expression profiles and protein–protein interactions within and across genomes. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, J.H.; Apeltsin, L.; Newman, A.M.; Baumbach, J.; Wittkop, T.; Su, G.; Bader, G.D.; Ferrin, T.E. ClusterMaker: A multi-algorithm clustering plugin for Cytoscape. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enright, A.J.; Van, D.S.; Ouzounis, C.A. An efficient algorithm for large-scale detection of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, P.; Michel, P.; Hennecke, H.; Göttfert, M. A novel response-regulator is able to suppress the nodulation defect of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum nodW mutant. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1993, 241, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.; Stacey, G. Nodulation gene regulation in Bradyrhizobium japonicum: A unique integration of global regulatory circuits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nellen-anthamatten, D.; Rossi, P.; Preisig, O.; Kullik, I.; Babst, M.; Fischer, H.M.; Hennecke, H. Bradyrhizobium japonicum FixK2, a crucial distributor in the FixLJ-dependent regulatory cascade for control of genes inducible by low oxygen levels. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5251–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dixon, R.; Kahn, D. Genetic regulation of biological nitrogen fixation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, S.; Hauser, F.; Friberg, M.; Malaguti, E.; Fischer, H.M.; Hennecke, H. Comprehensive assessment of the regulons controlled by the FixLJ-FixK2-FixK1 cascade in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6568–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindemann, A.; Moser, A.; Pessi, G.; Hauser, F.; Friberg, M.; Hennecke, H.; Fischer, H.M. New target genes controlled by the Bradyrhizobium japonicum two-component regulatory system RegSR. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, G.B.; Chapman, K.A.; Chelm, B.K. Role of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum ntrC gene product in differential regulation of the glutamine synthetase II gene (glnII). J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 5452–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franck, W.L.; Qiu, J.; Lee, H.I.; Chang, W.S.; Stacey, G. DNA microarray-based identification of genes regulated by NtrC in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 5299–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terpolilli, J.J.; Hood, G.A.; Poole, P.S. What determines the efficiency of N2-fixing Rhizobium-legume symbioses? Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2012, 60, 325. [Google Scholar]


| Degree | Closeness Centrality | Betweenness Centrality | Average Shortest Path Length | Clustering Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median for the FL network | 9 | 0.322 | 4.35 × 10−5 | 3.10 | 0.206 |
| Median for the SNF network | 7 | 0.328 | 7.54 × 10−5 | 3.02 | 0.211 |
| p-value | <2.2 × 10−16 | 2.87 × 10−4 | 3.69 × 10−5 | 6.01 × 10−6 | 1.81 × 10−2 |
| Modules | No. of Nodes | No. of PPIs | No. of SNF-Associated Proteins | Enriched COG Categories | Deduced Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m1 | 24 | 49 | 2 | O, K, E, F | Synthesis of symbiotic nitrogen fixation associated protein. |
| m2 | 18 | 40 | 4 | T | Oxygen concentration response and transcriptional regulation of downstream N2-fixing genes. |
| m3 | 12 | 29 | 3 | E, C | Serine metabolism, transformation of amino-containing metabolites. |
| m4 | 12 | 28 | 3 | T | Upstream regulation of nitrogenase and related transcription factors. |
| m5 | 11 | 33 | 7 | E, C | N2-fixing reaction, NH4+ transport and related regulation. |
| m6 | 11 | 32 | 4 | T | DNA damage repair, oxygen stress defense |
| m7 | 7 | 7 | 1 | E | Transformation of amino-containing metabolites. |
| m8 | 7 | 11 | 4 | C | Energy production, electron transfer. |
| m9 | 6 | 8 | 2 | C | Reduction of oxidative nitrogenase. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.-X.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Ma, B.-G. Computationally Reconstructed Interactome of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 Reveals Novel Functional Modules and Protein Hubs for Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111907
Ma J-X, Yang Y, Li G, Ma B-G. Computationally Reconstructed Interactome of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 Reveals Novel Functional Modules and Protein Hubs for Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111907
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jun-Xiao, Yi Yang, Guang Li, and Bin-Guang Ma. 2021. "Computationally Reconstructed Interactome of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 Reveals Novel Functional Modules and Protein Hubs for Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111907






