Crabp1 Modulates HPA Axis Homeostasis and Anxiety-like Behaviors by Altering FKBP5 Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Crabp1 Knockout (CKO) Mice Were Less Anxious
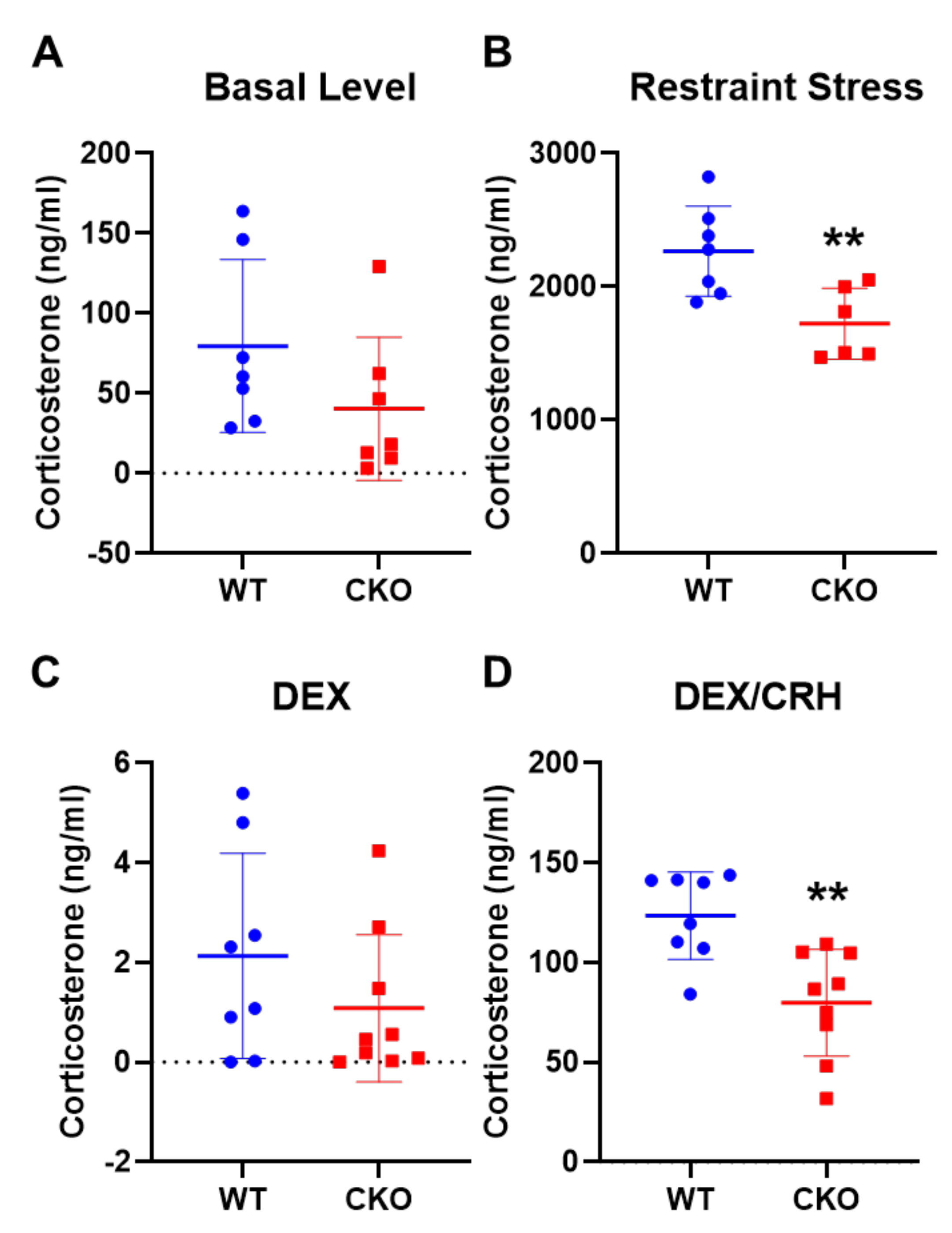
2.2. Deleting Crabp1 Enhanced Feedback Inhibition of HPA Axis
2.3. Deleting Crabp1 Reduced the Expression of FKBP5 in Hypothalamus and Pituitary Glands
2.4. Altering Crabp1 Level Changed the Expression of FKBP5 in a Pituitary Gland Cell Line AtT20
2.5. DEX and atRA Increased Crabp1 Expression in AtT20 Cell
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Behavioral Assessments
4.2.1. Open Field Test
4.2.2. Elevated plus Maze Test
4.3. Corticosterone Level
4.3.1. Acute Restraint Test
4.3.2. Combined DEX/CRH Test
4.4. Tissue Sample Collection
4.5. AtT20 Cell Culture, Crabp1 Overexpression and Crabp1 Silencing
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. RT-qPCR
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, P.; van Dam, A.M.; Wang, Y.; Lucassen, P.J.; Zhou, J.N. Retinoic acid and depressive disorders: Evidence and possible neurobiological mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 112, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D.; McCaffery, P. The neurobiology of retinoic acid in affective disorders. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D.; Shearer, K.D.; McCaffery, P.J. Retinoic acid and affective disorders: The evidence for an association. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2012, 73, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Yan, X.B.; Chen, X.N.; Meng, Q.Y.; Zhou, J.N. Chronic all-trans retinoic acid administration induced hyperactivity of HPA axis and behavioral changes in young rats. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, L.D.; Rossignoli, M.T.; Delfino-Pereira, P.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; de Lima Umeoka, E.H. A comprehensive overview on stress neurobiology: Basic concepts and clinical implications. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, M.A.C.; Wand, G. Stress and the HPA axis: Role of glucocorticoids in alcohol dependence. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2012, 34, 468–483. [Google Scholar]
- De Kloet, C.S.; Vermetten, E.; Geuze, E.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J.; Westenberg, H.G.M. Assessment of HPA-axis function in posttraumatic stress disorder: Pharmacological and non-pharmacological challenge tests, a review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2006, 40, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.; Newport, D.J.; Mletzko, T.; Miller, A.H.; Nemeroff, C.B. The link between childhood trauma and depression: Insights from HPA axis studies in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannas, A.S.; Wiechmann, T.; Gassen, N.C.; Binder, E.B. Gene-Stress-Epigenetic Regulation of FKBP5: Clinical and Translational Implications. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hähle, A.; Merz, S.; Meyners, C.; Hausch, F. The many faces of FKBP51. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, I.; Wei, L.N. All-trans retinoic acid as a versatile cytosolic signal modulator mediated by CRABP1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, S.D.; Lin, Y.-W.; Wu, C.-Y.; Kagechika, H.; Wei, L.-N. Cellular retinoic acid binding protein I mediates rapid non-canonical activation of ERK1/2 by all-trans retinoic acid. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Persaud, S.D.; Ogokeh, S.; Meyers, T.A.; Townsend, D.W.; Wei, L.N. CRABP1 protects the heart from isoproterenol-induced acute and chronic remodeling. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Nhieu, J.; Lin, Y.W.; Wei, L.N. All-trans retinoic acid attenuates isoproterenol-induced cardiac dysfunction through Crabp1 to dampen CaMKII activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 858, 172485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, P.R.; Tanaka-Sahker, M.; Chan, A.C.; Jellison, S.S.; Klisares, M.J.; Hing, B.W.; Shabbir, Y.; Gaul, L.N.; Nagahama, Y.; Robles, J.; et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation investigation of glucocorticoid exposure within buccal samples. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano-Ortiz, A.L.; Salcedo-Vargas, M.; Vargas-Requena, C.L.; López-Díaz, J.A.; De la Mora-Covarrubias, A.; Silva-Espinoza, J.C.; Jiménez-Vega, F. DNA methylation of cellular retinoic acid-binding proteins in cervical cancer. Genet. Epigenet. 2016, 8, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.L.; Lin, Y.W.; Nhieu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, L.N. Sonic hedgehog-gli1 signaling and cellular retinoic acid binding protein 1 gene regulation in motor neuron differentiation and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhieu, J.; Lin, Y.L.; Wei, L.N. Noncanonical retinoic acid signaling. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 637, pp. 261–281. ISBN 978-0-12820-144-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.L.; Persaud, S.D.; Nhieu, J.; Wei, L.N. Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 1 modulates stem cell proliferation to affect learning and memory in male mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3004–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.N.; Lee, C.H.; Filipcik, P.; Chang, L. Regulation of the mouse cellular retinoic acid-binding protein-I gene by thyroid hormone and retinoids in transgenic mouse embryos and P19 cells. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 155, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, J.; Wagner, K.V.; Gaali, S.; Kirschner, A.; Kozany, C.; Rühter, G.; Dedic, N.; Häusl, A.S.; Hoeijmakers, L.; Westerholz, S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the psychiatric risk factor FKBP51 has anxiolytic properties. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, G.R.; Gassen, N.C.; Rein, T. The FKBP51 glucocorticoid receptor co-chaperone: Regulation, function, and implications in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häusl, A.S.; Brix, L.M.; Hartmann, J.; Pöhlmann, M.L.; Lopez, J.P.; Menegaz, D.; Brivio, E.; Engelhardt, C.; Roeh, S.; Bajaj, T.; et al. The co-chaperone Fkbp5 shapes the acute stress response in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3060–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glad, C.A.M.; Andersson-Assarsson, J.C.; Berglund, P.; Bergthorsdottir, R.; Ragnarsson, O.; Johannsson, G. Reduced DNA methylation and psychopathology following endogenous hypercortisolism—A genome-wide study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.S.; Tamashiro, K.L.K.; Yang, X.; Purcell, R.H.; Huo, Y.; Rongione, M.; Potash, J.B.; Wand, G.S. A measure of glucocorticoid load provided by DNA methylation of Fkbp5 in mice. Psychopharmacology 2011, 218, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.S.; Tamashiro, K.L.K.; Yang, X.; Purcell, R.H.; Harvey, A.; Willour, V.L.; Huo, Y.; Rongione, M.; Wand, G.S.; Potash, J.B. Chronic corticosterone exposure increases expression and decreases deoxyribonucleic acid methylation of Fkbp5 in mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4332–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.N.; Meng, Q.Y.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F.; Wang, G.H.; Zhou, J.N. The Involvement of Retinoic Acid Receptor-α in Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Gene Expression and Affective Disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Huang, W.H.; Persaud, S.D.; Wei, L.N. RIP140 in thyroid hormone-repression and chromatin remodeling of Crabp1 gene during adipocyte differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Park, S.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Burton, F.H.; Wei, L.N. Cellular retinoic acid binding protein 1 protects mice from high-fat diet-induced obesity by decreasing adipocyte hypertrophy. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, S.D.; Huang, W.H.; Park, S.W.; Wei, L.N. Gene repressive activity of RIP140 through direct interaction with CDK8. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Di Martino, O.; Welch, J.S. Retinoic acid receptors in acute myeloid leukemia therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, S.D.; Park, S.W.; Ishigami-Yuasa, M.; Koyano-Nakagawa, N.; Kagechika, H.; Wei, L.N. All trans-retinoic acid analogs promote cancer cell apoptosis through non-genomic Crabp1 mediating ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wook Park, S.; Nhieu, J.; Persaud, S.D.; Miller, M.C.; Xia, Y.; Lin, Y.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Kagechika, H.; Mayo, K.H.; Wei, L.N. A new regulatory mechanism for Raf kinase activation, retinoic acid-bound Crabp1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Imoto, I.; Inoue, J.; Kozaki, K.; Tsuda, H.; Shimada, Y.; Aiko, S.; Yoshizumi, Y.; Iwai, T.; Kawano, T.; et al. Frequent methylation-associated silencing of a candidate tumor-suppressor, CRABP1, in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6456–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellow, S.; Chopin, P.; File, S.E.; Briley, M. Validation of open: Closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1985, 14, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touma, C.; Gassen, N.C.; Herrmann, L.; Cheung-Flynn, J.; Bll, D.R.; Ionescu, I.A.; Heinzmann, J.M.; Knapman, A.; Siebertz, A.; Depping, A.M.; et al. FK506 binding protein 5 shapes stress responsiveness: Modulation of neuroendocrine reactivity and coping behavior. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| CRH | GGAATCTCAACAGAAGTCCCGC | CTGCAGCAACACGCGGAAAAAG |
| AVP | GCTACTTCCAGAACTGCCCAAG | CAGCAGATGCTTGGTCCGAAGC |
| POMC | CCATAGATGTGTGGAGCTGGTG | CATCTCCGTTGCCAGGAAACAC |
| CRHR1 | CGCAAGTGGATGTTCGTCTGCA | TCCAGGACGTTTGCCAAACCAG |
| GR (Nr3c1) | TGGAGAGGACAACCTGACTTCC | ACGGAGGAGAACTCACATCTGG |
| FKBP5 | GATTGCCGAGATGTGGTGTTCG | GGCTTCTCCAAAACCATAGCGTG |
| Crabp1 | CGGAGATCAACTTCAAGGTCGG | CCCTCAAGAAGTGTCTGTGTGC |
| GAPDH | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-L.; Wei, C.-W.; Lerdall, T.A.; Nhieu, J.; Wei, L.-N. Crabp1 Modulates HPA Axis Homeostasis and Anxiety-like Behaviors by Altering FKBP5 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212240
Lin Y-L, Wei C-W, Lerdall TA, Nhieu J, Wei L-N. Crabp1 Modulates HPA Axis Homeostasis and Anxiety-like Behaviors by Altering FKBP5 Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212240
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yu-Lung, Chin-Wen Wei, Thomas A. Lerdall, Jennifer Nhieu, and Li-Na Wei. 2021. "Crabp1 Modulates HPA Axis Homeostasis and Anxiety-like Behaviors by Altering FKBP5 Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212240
APA StyleLin, Y.-L., Wei, C.-W., Lerdall, T. A., Nhieu, J., & Wei, L.-N. (2021). Crabp1 Modulates HPA Axis Homeostasis and Anxiety-like Behaviors by Altering FKBP5 Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212240






