Abstract
This review addresses the molecular mechanisms of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) regulation in the hypothalamus under stress and stress resilience. CRF in the hypothalamus plays a central role in regulating the stress response. CRF stimulates adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) release from the anterior pituitary. ACTH stimulates glucocorticoid secretion from the adrenal glands. Glucocorticoids are essential for stress coping, stress resilience, and homeostasis. The activated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is suppressed by the negative feedback from glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoid-dependent repression of cAMP-stimulated Crf promoter activity is mediated by both the negative glucocorticoid response element and the serum response element. Conversely, the inducible cAMP-early repressor can suppress the stress response via inhibition of the cAMP-dependent Crf gene, as can the suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in the hypothalamus. CRF receptor type 1 is mainly involved in a stress response, depression, anorexia, and seizure, while CRF receptor type 2 mediates “stress coping” mechanisms such as anxiolysis in the brain. Differential effects of FK506-binding immunophilins, FKBP4 and FKBP5, contribute to the efficiency of glucocorticoids under stress resilience. Together, a variety of factors contribute to stress resilience. All these factors would have the differential roles under stress resilience.
1. Introduction
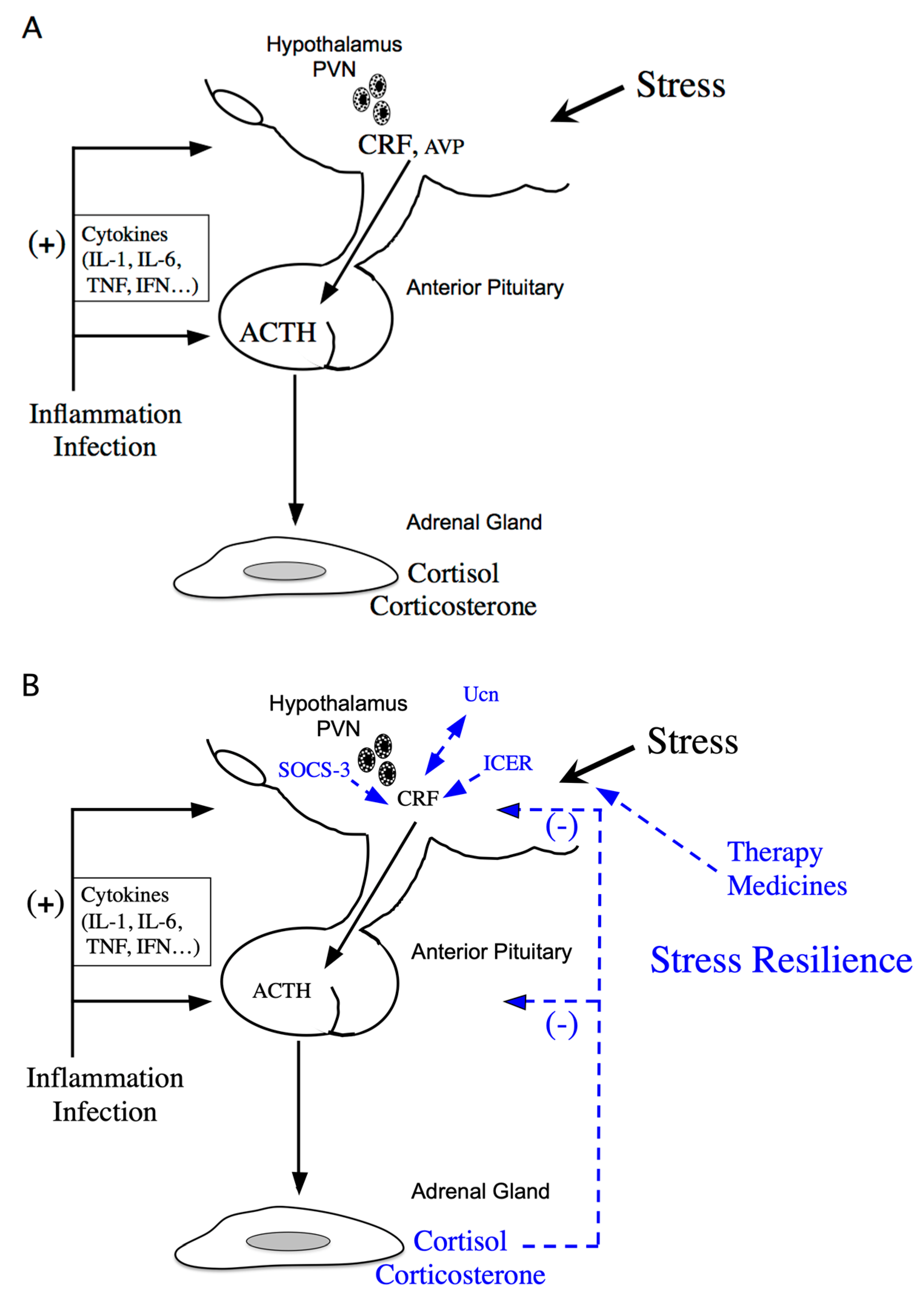
Stress response is considered the physiological and behavioral response to internal or external stimulus. The stress response is adaptive, and stress resilience is regarded as the result of the adaptive response to a stressor [1,2]. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is activated under various stressors (Figure 1A). Limbic structures, such as the central amygdala, bed nuclei of the stria terminalis, and nucleus accumbens shell of the extended amygdala, and the hippocampus, play an important role in stress responses. In parallel, stress responses also activate a physiological system for stress adaptation (Figure 1B).
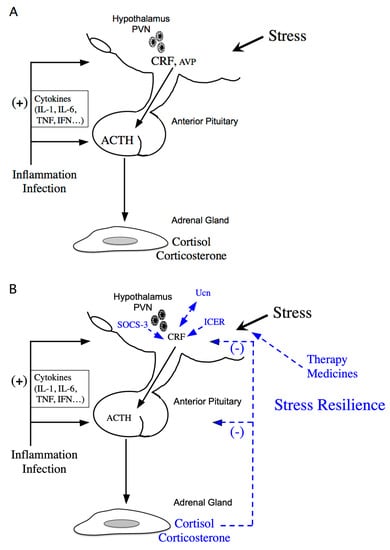
Figure 1.
Schematic model of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis regulation. (A) Activation of the HPA axis under stress. Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) plays a central role in controlling stress responses. Cytokines also stimulate CRF production under inflammation or infection. CRF, produced in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN), stimulates adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) production from the corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary (AP). ACTH then stimulates corticosterone and cortisol release, the principal glucocorticoids in rodents and human, respectively, from the adrenal glands. (B) Regulation of the HPA axis under stress resilience. Glucocorticoids are produced by ACTH in the adrenal glands. Circulating glucocorticoids are critical for recovery from stress conditions. Both inducible cAMP-early repressor (ICER) and suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS-3) contribute to the negative regulation of CRF synthesis in the hypothalamus. The urocortin (Ucn)-CRF receptor type 2 mediates “stress coping” responses. Therapy or medicines also target this to alleviate stressed states.
Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) is a key hormone regulating the stress response, as it modulates the HPA axis [3]. CRF is produced in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) in response to stress and plays an important role in the stress response as an initial activator of the HPA axis. CRF neurons in the PVN partially co-express arginine vasopressin (AVP), oxytocin, neurotensin, enkephalin, and cholecystokinin, and are primarily glutamatergic but partially gamma-aminobutyric acidergic (GABAergic) [4]: norepinephrine and glutamate stimulate CRF release under stress [5], while CRF is regulated by GABAergic inputs that inhibit its release [6]. CRF and AVP neurons in the parvocellular region of the PVN projecting to the external zone of the median eminence stimulate adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion from the anterior pituitary (AP) [7,8]. The CRF and AVP exert synergistic effects on ACTH secretion from the AP. CRF stimulates the synthesis and secretion of ACTH, encoded by the propiomelanocortin (Pomc) gene, in the AP [3] (Figure 1A). ACTH stimulates the secretion of corticosterone and cortisol, the main glucocorticoids in rodents and human, respectively, from the adrenal glands [9] (Figure 1A).
In Crf knockout (KO) mice, impaired adrenal responses have been shown in response to acute various stressors such as restraint, ether, and fasting [10,11,12]. The ACTH response to pain stress in Crf KO mice was also smaller than that in wild-type (WT) mice [13], suggesting a role of CRF on the increased ACTH release from the pituitary in response to stress. Two types of prohormone convertases contribute to Pomc processing. Pomc is cleaved to β-lipotropic hormone (β-LPH) and ACTH by the processing enzyme prohormone convertase-1. β-LPH and ACTH are then cleaved to β-endorphin (β-EP) and α-melanocyte stimulating hormone by the prohormone convertase-2, respectively. Pituitary Pomc mRNA levels are not attenuated [11,12]; however, ACTH contents are decreased in the AP of Crf KO mice [14], suggesting a role of CRF in Pomc processing. Immature Pomc is biologically inactive, and cannot stimulate cortisol production in the adrenal glands. Immunoreactive (ir) β-EP contents in the AP of Crf KO mice do not differ from those of WT mice. To determine the different molecular profile of Pomc-related peptides between WT mice and Crf KO mice, ir β-EP contents extracted from the AP of WT mice and Crf KO mice were assayed by gel filtration chromatography Gel filtration analyses, which revealed that a higher molecular weight form of ir β-EP, putative Pomc, increased in Crf KO mice, but the β-EP peak level was small and similar between the two groups [11]. These results suggest that CRF affects Prohormone convertase-1 gene expression levels in the AP, thus modulating Pomc processing.
Cytokines are important mediators of the interaction between the neuroendocrine and immune systems, and inflammatory stress positively affects the HPA axis at multiple levels via cytokines. Following inflammatory challenges, interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and interferon (IFN) stimulate CRF in the hypothalamus [15] (Figure 1A). For example, IL-6, a single 21- to 28-kDa glycoprotein produced in response to both immune activation and non-immune stress [16,17], increases Crf gene expression and secretion in the PVN [18,19]. Endogenous IL-1β and TNF-α productions are also involved in the stimulation of autocrine CRF production in hypothalamus [20,21]. HPA activation results in secretion of glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids have pleiotropic effects on the immune system. Glucocorticoids inhibit inflammation, lymphocyte activation, and the production of B cells, T cells, and cytokines. Therefore, the bilateral interaction between the immune and endocrine system exists under in vivo stress response.
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus acts as the central circadian pacemaker. SCN neurons negatively regulate activity in CRF neurons in the PVN. As an additional role of CRF in the PVN, CRF neurons positively regulate orexin neurons, which promote wakefulness [22]. Therefore, circadian pacemaker regulates wakefulness via CRF neurons in the PVN. Stress may impair the circadian rhythmicity. Additionally, circadian clock disruption is also observed in many psychiatric disorders [23]. The disorders are accompanied by a reduced amplitude or altered phase in a wide range of rhythms, including cortisol, melatonin, and circadian clock genes. Dysfunction of the CRF system may contribute to the circadian clock disruption. On the other hand, disruption of the circadian clock is observed in obese mice [24]. Among the variety of factors contributing to stress resilience, ghrelin, an important regulator of metabolism or energy homeostasis, improves the disruption of the circadian rhythm in steatotic liver.
2. Molecular Mechanisms of CRF Regulation in the Hypothalamus
Many neurotransmitters and neuropeptides are involved in activation of CRF neurons in the hypothalamus. Serotonin, noradrenaline, neuromedin C, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone affect intracellular Ca2+ concentration in CRF neurons of the PVN [4] and activate CRF neurons. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP), a member of the secretin/glucagon/vasoactive intestinal peptide family, and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1) also stimulate Crf gene activity in hypothalamic cells [25,26]. PACAP can contribute to CRF activation in the hypothalamus under emotional stress. In fact, the extended amygdala and the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis are identified as innervation sites of PACAP neurons. Both PACAP and the PACAP-selective PACAP receptor type 1 are highly expressed in the hypothalamus and the supraoptic nucleus [27,28]. PACAP increases Crf mRNA levels in the parvocellular region of the PVN, suggesting its involvement in the positive regulation of Crf gene expression [29]. The cyclic AMP (cAMP)-protein kinase A (PKA) pathway is involved in CRF synthesis by PACAP [25]. GLP1 also stimulates the activities of both Crf and Avp promoters in hypothalamic cells [26]. Basal promoter activities of Crf and Avp are increased in high glucose medium [26], while Crf and Avp promoter activities are increased by GLP1 in standard or low glucose medium but not in high. Hyperglycemia is, therefore, a stressor increasing the synthesis of CRF and AVP in the hypothalamus.
Ghrelin stimulates CRF release from rat hypothalamus explants, and ghrelin expression has been found in the rat hypothalamus [30]. Previous studies showed that ghrelin activated the HPA axis via CRF neurons of the PVN [30,31]. Glucocorticoids also stimulated the ghrelin-growth hormone-releasing peptide receptor type 1a (GHSR1a) system in hypothalamic cells. Dexamethasone increased Ghrelin mRNA levels, and Ghsr1a mRNA and protein levels. Finally, ghrelin increased Crf mRNA levels, as did dexamethasone, and both dexamethasone and ghrelin had an additive effect on Crf and Ghrelin mRNA levels [31,32].
Pyroglutamylated RFamide peptide (QRFP), an important regulator of metabolism and energy homeostasis, has orexigenic effects. QRFP acts via a specific receptor, G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 103. QRFP might be related to stress behavior, because intense grooming is observed in response to acute QRFP administration in mice. Gpr103 mRNA is expressed in the rat PVN. QRFP stimulates the HPA axis in vivo, and the Crf gene in hypothalamic cells [33]. QRFP stimulates the release of glucocorticoids, a representative orexigenic hormone, via CRF. Heat shock protein 70, a molecular chaperone produced under physical and environmental stress, also stimulates CRF in the hypothalamus, resulting in activation of the HPA axis [34].
The proximal Crf promoter shows several possible binding sites for transcriptional factors such as cAMP-response element (CRE), activator protein-1 (AP-1) protein binding sites, half glucocorticoid regulatory element (GRE), and half estrogen-responsive element (ERE) [35,36]. Forskolin or PACAP stimulates adenylate cyclase and then intracellular cAMP levels in hypothalamic cells [25]. Forskolin increases Crf transcriptional activity in hypothalamic and other cells [37,38,39]. Forskolin-induced Crf gene transcription is reduced in hypothalamic cells transfected with a mutant construct where the CRE element is mutated [40].
AP-1 proteins such as Fos and Jun are immediate-early gene products. The Fos protein family can dimerize with a Jun protein (Fos/Jun heterodimers), which binds to the regulatory sequences of target genes. FosB and cJun mRNA levels are regulated via PKA, protein kinase C (PKC), and Ca2+-dependent pathways. FosB or cJun overexpression potently increase Crf mRNA levels in hypothalamic cells, while their downregulation suppresses the stimulus-induced activation of Crf mRNA. Therefore, endogenous FosB and cJun are necessary for stimulus-induced Crf gene expression in hypothalamic cells [41]. The Fos/Jun heterodimer is involved in regulation of Crf gene expression. A truncated splice variant of FosB, FosB/ΔFosB was induced in the rat hypothalamus by surgical stress, and its expression upregulated by glucocorticoid removal. Induced FosB/ΔFosB expression was identified in CRH neurons of the PVN and AVP neurons of the supraoptic nucleus. In addition, forskolin-induced upregulation of FosB promoter activity was suppressed by glucocorticoids in the homologous hypothalamic cells. These results imply that glucocorticoids may be potent regulators of stress-induced FosB expression in hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons [42].
The PKA pathway is mainly involved in cAMP-dependent CRF synthesis in the hypothalamus [43,44]. Activation of the PKA pathway leads to binding of CRE-binding protein (CREB) to the CRE on the Crf promoter in hypothalamic cells [45]. PKC and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase are also partially involved in the positive regulation of Crf gene expression in hypothalamic cells [40]. Thus, the PKA, PKC, and p38 MAP kinase pathways are all involved in Crf activation in hypothalamic cells. Meanwhile, glucocorticoids suppress cAMP-dependent increase in Fos B gene promoter activity [41].
Estrogen regulates the HPA axis by stimulating Crf gene expression in the hypothalamus, as shown when high levels of estrogen replacement increased basal Crf mRNA levels in the PVN of ovariectomized rats [46]. A physiologically relevant dose (10 nM) of estradiol (E2) stimulates both Crf gene transcription and mRNA expression in hypothalamic 4B cells [47]. This result suggests that the direct effect of E2 in increasing CRF in the PVN may contribute to the enhanced ACTH and cortisol levels observed in the midluteal phase. CRF neuron activation, in turn, may affect gonadal function in a bidirectional manner, because estrogens activate the HPA axis, while the estrogen-induced activation of CRF neurons would suppress gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Moreover, E2 and diarylpropionitrile, an estrogen receptor β agonist, increase Crf transcriptional activity. Therefore, estrogen receptor β activation by estrogens induces Crf gene transcription in hypothalamic cells. Furthermore, treatment with both E2 and forskolin, a ubiquitous activator of adenylyl cyclase and cAMP, shows additive effects on Crf promoter activity [47]. Therefore, estrogens enhance Crf gene activation by cAMP under stress. Estrogen activates the HPA axis, and then activation of the HPA axis may suppress gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
As mentioned previously, stress resilience is considered the result of the adaptive response to a stressor. Circulating glucocorticoids are critical for recovery from stress conditions and essential for stress resilience (Figure 1B). Treatment with glucocorticoids in adrenalectomized rats does not perfectly prevent the increase in stress-induced Crf heteronuclear RNA [48]. Therefore, factors other than glucocorticoids might be involved in limiting CRF activation during stress. Inducible cAMP-early repressor (ICER), a cAMP-inducible member of the CRE modulator (CREM) family and a CREM repressor isoform, are such candidates [49,50]. CREM, CREB, and AP-1 bind to CRE promoter elements to stimulate transcription [51], while ICER acts as a competitive inhibitor of such CRE-dependent transcription [49]. Therefore, ICER can suppress the stress response via inhibition of the cAMP-dependent Crf gene [36] (Figure 1B). Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-3 acts as a potent negative regulator of cytokine signaling [52]. SOCS-3 suppresses cytokine-induced ACTH production in corticotrophs [53]. IL-6 stimulates Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of the transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling, while IL-6-induced SOCS-3 acts as a negative regulator and inhibits STAT phosphorylation by JAK at the receptor complex [54,55]. SOCS-3 is stimulated by IL-6 and cAMP, while SOCS-3 knockdown increases IL-6- or forskolin-induced Crf gene transcription, thereby contributing to the negative regulation of CRF synthesis in the hypothalamus [56] (Figure 1B).
3. Roles of the CRF Peptide Family and Stress-Related Peptides and Their Receptors under Stress
Urocortins (Ucns) are members of the CRF peptide family. Three Ucns have been found in mammals. Ucn1 has potent effects including appetite suppression and modulation of the cardiovascular system [57,58,59]. Ucn2 has more potent vasodilatory and cardiac inotropic effects than CRF and shows suppression of host resistance to infection via IL-10 upregulation [60]. Ucn3 modulates insulin secretion and Ca2+ influx in pancreatic β-cells [61] and improves cellular stress responses and glucose uptake [62].
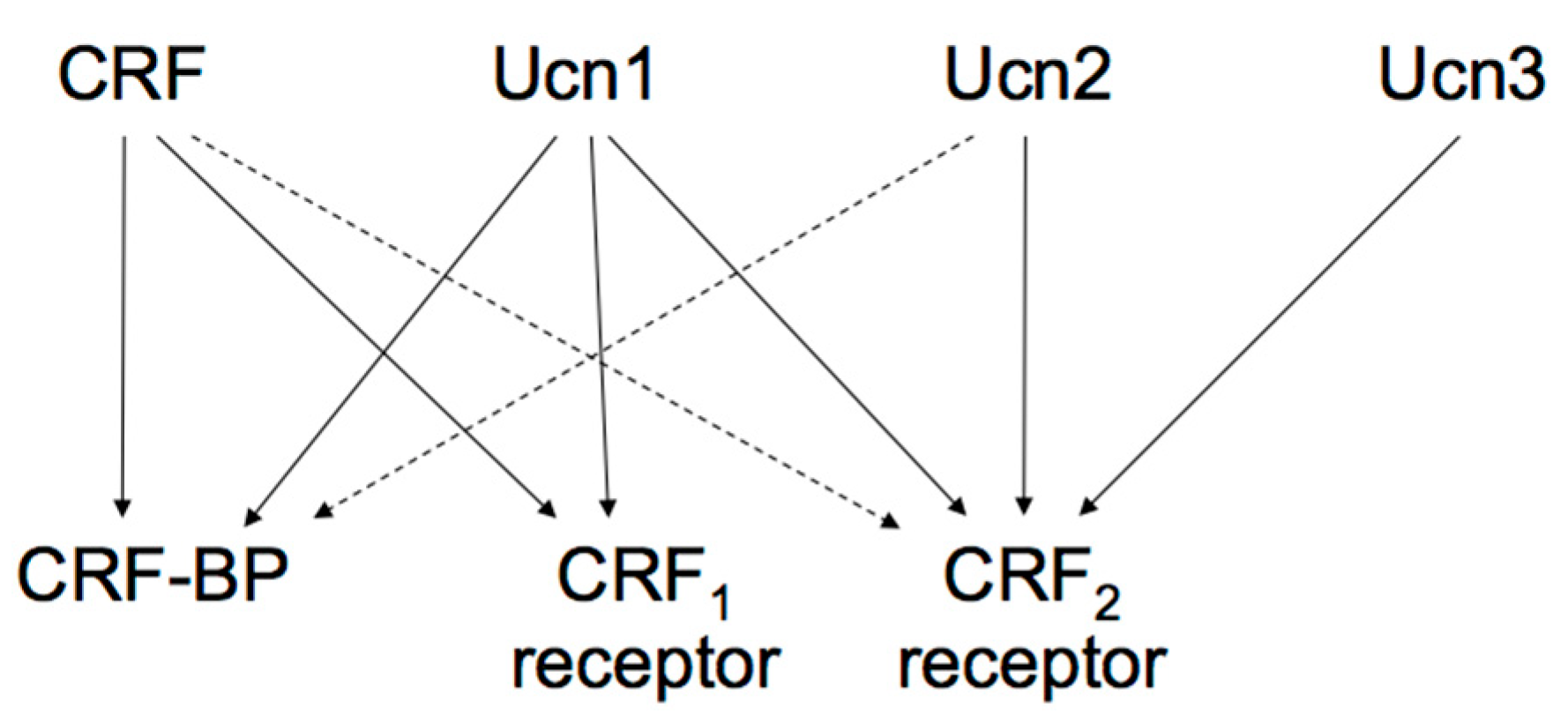
The actions of the CRF family peptides are mediated by ≥ 2 distinct G protein-coupled receptors, namely the CRF receptor type 1 (CRF1 receptor) [63,64,65] and CRF receptor type 2 (CRF2 receptor) [66,67,68]. CRF has a higher affinity for the CRF1 receptor than for the CRF2 receptor (Figure 2) [69]. Ucn1 binds to both the CRF1 and CRF2 receptors, while Ucn2 and Ucn3 are highly selective for the CRF2 receptor, with little affinity for the CRF1 receptor (Figure 2) [57,70,71,72].
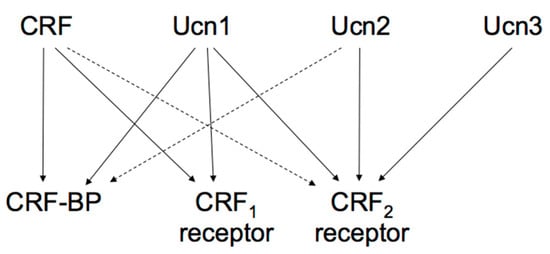
Figure 2.
Proposed signaling mechanisms of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), urocortins (Ucns) and CRF receptors. CRF-BP, CRF-binding protein. Solid lines represent a high affinity binding, and dashed lines a low affinity binding.
These two receptors share 69% amino acid homology [67] but have different tissue distributions and pharmacological properties with respect to ligands [69]. CRF1 receptor is mainly expressed in the pituitary, the brain, and various peripheral tissues. In pituitary corticotrophs, CRF1 receptor is the major subtype responsible for regulating ACTH synthesis and secretion. CRF2 receptor is located in different brain areas than the CRF1 receptor and is also abundant in the periphery. The CRF2 receptor has ≥ 3 alternative splice variants, CRF2a receptor, CRF2b receptor, and CRF2g receptor. In the rat, CRF2a receptor mRNA was found primarily in the brain and the pituitary [73,74]. In contrast, the CRF2b receptor was predominantly expressed in peripheral sites such as the heart, gastrointestinal tract, and vascular smooth muscles [74]. CRF receptors primarily activate adenylyl cyclase and cAMP pathways through Gsα activation. In addition, CRF receptors can activate other types of Gα [75].
The CRF1 receptor is mainly involved in stress responses, depression, anorexia, and seizure, while the CRF2 receptor mediates “stress coping” responses such as anxiolysis in the brain [69], as shown by mice deficient in CRF2 receptor and the use of a CRF2 receptor antagonist, which display increased anxiety-like behaviors and a hypersensitive stress response [76]. Our previous findings also show that the intracellular signals mediated by the CRF2 receptor have an antagonistic effect to the CRF1 receptor. Therefore, specific CRF receptor subtypes may contribute to different stress responses and homeostasis. The lateral septum contributes to the control of stress response and anxiety. Activation of CRF2 receptor in the lateral septum and septohypothalamic circuits are reported to be involved in stress-induced persistent anxiety [77].
Hypothalamic CRF stimulates synthesis and secretion of ACTH via the CRF1 receptor in the anterior pituitary gland. CRF1 receptor mRNA levels are down-regulated by CRF via the cAMP-protein kinase A (PKA) pathway or by mRNA degradation via PKA [78]. Prolonged agonist activation of receptors leads to a loss of responsiveness or receptor desensitization. After agonist-activated stimulation of receptor signaling, the CRF1 receptor is down-regulated and desensitized in the pituitary corticotrophs. Generally, GPRs are desensitized by GPR kinases (GRKs). CRF desensitize the cAMP-dependent response by CRF1 receptors. GRK2 is involved in CRF-induced desensitization of the CRF1 receptor in corticotrophs, where the protein kinase A pathway plays an important role [79]. Intracellular molecules, such as β-arrestins, contribute to membrane receptor phosphorylation, desensitization, and trafficking of GPRs, thereby modulating ligand activated-receptor responses [80].
CRF-binding protein (CRF-BP), a 37-kDa secreted glycoprotein, binds to CRF and Ucn1 with an affinity equal to or greater than CRF receptors, suggesting its role as an important modulator of CRF, Ucns, and their receptors. CRF-BP inhibits CRF-induced ACTH secretion from pituitary corticotrophs and may show a similar CRF release action in the hypothalamus [81]. Potential CRF-BP roles might be modulating energy balance and feeding behavior. Additionally, changes in CRF-BP would relieve the action of CRF under stress. In humans, depression, Alzheimer’s disease, and inflammatory diseases have been related to CRF-BP dysregulation [81]. Investigating the potential roles and pathophysiology of CRF-BP may help elucidate the etiology of said diseases.
4. CRF Dysregulation and Therapy
CRF dysregulation in the hypothalamus and the HPA axis is associated with diseases related to stress and brain and inflammatory diseases. Hyperactivity of the HPA axis is found in patients with anxiety and mood disorders. Patients with posttraumatic stress disorder have decreased activity of the pituitary-adrenal axis, presumably due to exaggerated negative feedback or CRF hypersecretion with the subsequent down-regulation of the anterior pituitary CRF receptors [82]. Additionally, differences in CRF and the CRF1 receptor regulation may cause inherent differences in stress reactivity, which predicts susceptibility and resilience to a depressive phenotype [83,84].
The stressed state may be relieved or reduced via the HPA axis and other hormones by therapy, medicines or natural stimulation (Figure 1B). Successful therapy results in normal regulation of the HPA axis. For example, benzodiazepines reduce the activity of CRF neurons in the hypothalamus [85], tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors partially act by modulating the HPA axis, while escitalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, inhibits CRF expression in the hypothalamus and hippocampus, increasing their glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression. Both mineralocorticoid receptors and GRs in the PVN are involved in the regulation of depressive and anxiety-like behaviors [86]. The simultaneous restoration of both receptors and CRF in the PVN might help in the treatment of depression and anxiety. Nature, forests, urban green space, plants, and wooden materials reduce sympathetic nervous system activation and lower the blood pressure [87], and probably normalize the HPA axis. Oxytocin in the hypothalamus has been shown to facilitate affiliative social behaviors and to induce anxiolytic actions. For instance, post-weaning stroking procedures induce affiliative responses via activation of oxytocin neurons in the caudal PVN [88].
5. Negative CRF Feedback Mechanisms in the Hypothalamus
Glucocorticoids inhibit CRF production in the hypothalamic PVN and ACTH production in the AP, modulating its own production (Figure 1B). Simultaneously, glucocorticoids inhibit CRF neurons in the PVN by binding to GRs in the hippocampus [86].
The HPA axis is regulated by a negative feedback mechanism (Figure 1B). In fact, hypothalamic parvocellular neurons express GRs, and glucocorticoids negatively regulate Crf gene expression directly in the hypothalamus. The Crf promoter region contributes to inhibition by glucocorticoids by acting as a negative GRE (nGRE) (Figure 3), even though the Crf promoter does not contain a classical consensus GRE, there are several regions GRs can bind to [89,90]. Glucocorticoids can inhibit CREB and cFos in the PVN [91,92,93].

Figure 3.
Schematic model of transcriptional regulation of the corticotropin-releasing factor (Crf) promoter. Possible binding sites for transcriptional factors such as the cAMP-response element (CRE), activator protein 1 (AP-1) protein (Fos/Jun) binding sites, the half glucocorticoid regulatory element (GRE), and the half estrogen-responsive element (ERE) in the proximal Crf promoter. The Crf promoter region also contributes to glucocorticoid inhibition as a negative GRE (nGRE), as it includes a serum response element (SRE).
Additionally, other promoter regions are involved in the inhibition of Crf gene expression in hypothalamic cells (Figure 3). Crf promoter sequences between –248 and –233 bp are also involved in the glucocorticoid suppression of cAMP-stimulated Crf promoter activity (Figure 3), including a serum response element (SRE) [94], which contributes to the negative response to glucocorticoids, because the GR can bind to SRE and inhibit promoter activation by antagonizing positive transcription [94]. Therefore, in addition to nGRE, the glucocorticoid suppression of cAMP stimulated CRF promoter activity may also be caused by SRE in hypothalamic cells.
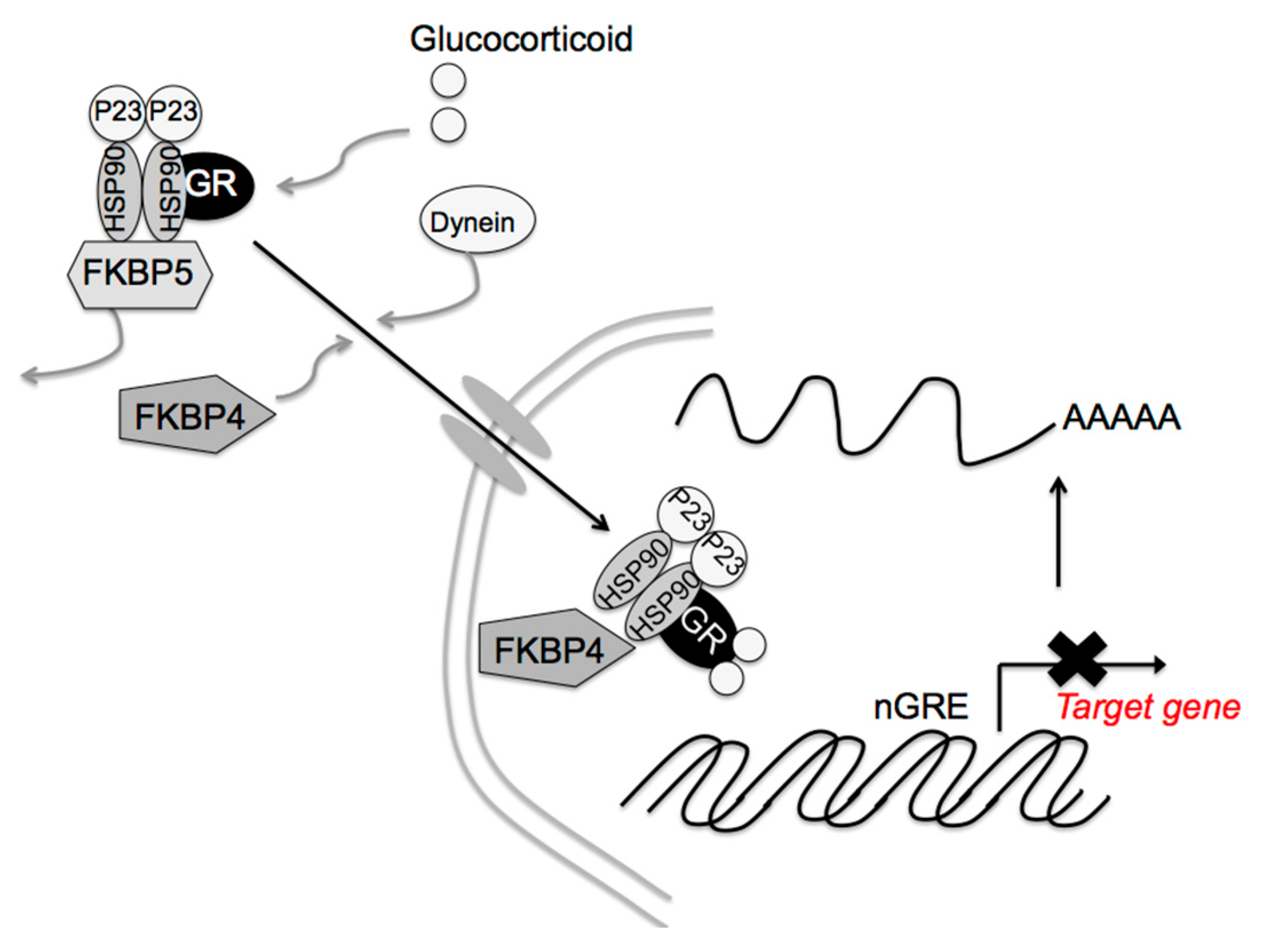
Glucocorticoid signaling is mediated via the GR, 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, and the FK506-binding immunophilins, FKBP52 (FKBP4) and FKBP51 (FKBP5) [95,96,97]. FKBP4 and FKBP5 differentially regulate dynein interactions and GR nuclear translocation, respectively [98]. In the absence of corticosterone, the GR is retained in the cytoplasm as a complex containing one GR molecule, heat shock protein (HSP) 90 dimer, HSP90-binding protein P23, and FKBP5 [99,100]. After glucocorticoid binding to the GR, FKBP5 is replaced by FKBP4, resulting in complex translocation to the nucleus (Figure 4). The GR then acts on Crf gene expression. Thus, FKBP4 contributes to the negative feedback effect of glucocorticoids. GR activity also stimulates Fkbp5 gene transcription [100,101], the higher FKBP5 levels in turn inhibit GR translocation to the nucleus, diminishing the effects on glucocorticoids’ target genes. In fact, Fkbp4 contributes to the negative feedback of glucocorticoids, and Fkbp5 reduces the efficiency of the glucocorticoid effect on Pomc gene expression in pituitary corticotrophic cells [102]. Fkbp5 deletion in the PVN dampens the acute stress response and increases GR sensitivity [103], while its overexpression in the PVN produces chronic overactivation of the HPA axis [103]. That way, the differential effects of FKBP4 and FKBP5 in the PVN contribute to glucocorticoid efficiency and stress resilience. Other molecules, such as HSP90, HSP90-binding protein P23, and GR itself may be involved in these glucocorticoid effects. Post-translational regulation of these molecules, such as protein phosphorylation, acetylation, and SUMOylation, as well as expression regulation, may also contribute to said effects.
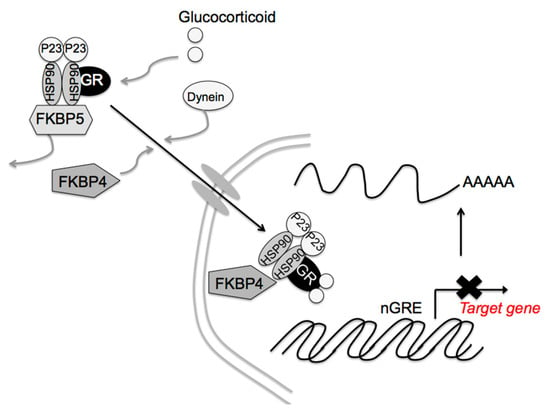
Figure 4.
Proposed FK506-binding immunophilin 4 (FKBP4) and FKBP5 signaling mechanisms by glucocorticoids. After cortisol binding to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), FKBP5 is replaced by FKBP4, resulting in complex translocation to the nucleus. Newly formed GR/heat shock protein 90 (HSP90)/FKBP4 complexes generally accumulate in the nucleus. The GR then modulates the target gene expression. [Modified from Ref. ([102], Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5724.) with permission of the publisher.] Copyright 2021, MDPI.
Additionally, Itoi et al. performed genome-wide analysis of glucocorticoid-response transcripts in the PVN of male rats after long term high-dose corticosterone exposure and found suppression of Crf and Avp gene expression, downregulation of the apelin receptor, and upregulation of dual-specificity protein phopsphatase 1 (Dusp1). These changes may contribute to the suppression of Crf and Avp gene expression [104]. In particular, Dusp1 encodes a phosphatase that inactivates the MAPK. Glucocorticoids-induced Dusp1 upregulation might counteract MAMP-mediated Crf gene expression. Immediate early genes, such as the brain-specific homeobox protein homolog, early growth-response protein 1, Fos, Fosb, Junb, and nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 3, were transiently upregulated by acute corticosterone administration, and may participate in transcriptional modulation of glucocorticoids target genes.
6. Conclusions
In summary, various stressors can activate the HPA axis. CRF, a key player in stress responses, is produced in the PVN in response to stress and plays an important role in the stress response as main initiator of the HPA axis. The stress response also activates a physiological system for stress adaptation. The activated the HPA axis is suppressed by the negative feedback effect of glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids are essential for stress resilience. ICER can suppress the stress response via inhibition of the cAMP-dependent CRF gene. SOCS-3, stimulated by IL-6 and cAMP, is also involved in the negative regulation of Crf gene expression in the hypothalamus. The CRF1 receptor is mainly involved in stress responses, while the CRF2 receptor mediates “stress coping”, for which glucocorticoids are essential. The differential effects of FKBP4 and FKBP5 further contribute to glucocorticoid efficiency under stress resilience. Altogether, a variety of factors contribute to stress resilience. Importance of each factor, however, remains to be explored. The differential roles of all these factors under stress resilience would be elucidated in the future.
Author Contributions
K.K. conceived and designed the experiments; K.K. analyzed the data; K.K. and M.D. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; K.K. wrote the paper; Y.I. and M.D. reviewed the paper; and M.D. is a supervisor of the department. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Oken, B.S.; Chamine, I.; Wakeland, W. A systems approach to stress, stressors and resilience in humans. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 282, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, M.A.G.; Pérez-Mármol, J.M.; Gonzalez-Pérez, R.; García-Ríos, M.D.C.; Peralta-Ramírez, M.I. Relationship between resilience and stress: Perceived stress, stressful life events, HPA axis response during a stressful task and hair cortisol. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 202, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, W.; Spiess, J.; Rivier, C.; Rivier, J. Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science 1981, 213, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Nagayama, A.; Itoi, K.; Yamanaka, A. Identification of substances which regulate activity of corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.P.; Tasker, J.; Ziegler, D.R.; Cullinan, W.E. Local circuit regulation of paraventricular nucleus stress integration: Glutamate–GABA connections. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 71, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, J.G.; Boudaba, C.; Schrader, L.A. Local glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic circuits and metabotropic glutamate receptors in the hypothalamic paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 449, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, G.E.; Linton, E.A.; Lowry, P.J. Corticotropin releasing activity of the new CRF is potentiated several times by vasopressin. Nat. Cell Biol. 1982, 299, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouri, T.; Itoi, K.; Takahashi, K.; Suda, T.; Murakami, O.; Yoshinaga, K.; Andoh, N.; Ohtani, H.; Masuda, T.; Sasano, N. Colocalization of corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin in the paraventricular nucleus of the human hypothalamus. Neuroendocrinology 1993, 57, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitnall, M.H. Regulation of the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone neurosecretory system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1993, 40, 573–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muglia, L.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Gilbert, D.J.; Copeland, N.G.; Majzoub, A.J. Expression of the mouse corticotropin-releasing hormone gene in vivo and targeted inactivation in embryonic stem cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muglia, L.J.; Jacobson, L.; Dikkes, P.; Majzoub, J.A. Corticotropin-releasing hormone deficiency reveals major fetal but not adult glucocorticoid need. Nat. Cell Biol. 1995, 373, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muglia, L.J.; Jacobson, L.; Weninger, S.C.; Luedke, C.E.; Bae, D.S.; Jeong, K.H.; Majzoub, J.A. Impaired diurnal adrenal rhythmicity restored by constant infusion of corticotropin-releasing hormone in corticotropin-releasing hormone-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2923–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Kageyama, K.; Nigawara, T.; Kasagi, Y.; Suda, T. Effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) on the synthesis and secretion of proopiomelanocortin-related peptides in the anterior pituitary: A study using CRH-deficient mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 367, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muglia, L.J.; Jacobson, L.; Luedke, C.; Vogt, S.K.; Schaefer, M.L.; Dikkes, P.; Fukuda, S.; Sakai, Y.; Suda, T.; Majzoub, J.A. Corticotropin-releasing hormone links pituitary adrenocorticotropin gene expression and release during adrenal insufficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Kagaya, S.; Takayasu, S.; Hanada, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Suda, T. Cytokines induce NF-ĸB, Nurr1 and corticotropin-releasing factor gene transcription in hypothalamic 4B cells. Neuroimmunomodulation 2010, 17, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, A.; Huang, Q.H.; Somogyvári-Vigh, A.; Arimura, A. Immobilization stress may increase plasma interleukin-6 via central and peripheral catecholamines. Neuroimmunomodulation 1994, 1, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Kusnecov, A.W.; Shurin, M.R.; DePaoli, M.; Rabin, B.S. Exposure to physical and psychological stressors elevates plasma interleukin 6: Relationship to the activation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, P.; Tsagarakis, S.; Faria, M.S.; Rees, L.H.; Besser, G.M.; Grossman, A.B. Interleukins-1 and -6 stimulate the release of corticotropin-releasing Hormone-41 from rat hypothalamus in vitro via the eicosanoid cyclooxygenase pathway. Endocrinology 1991, 128, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallieres, L.; Rivest, S. Interleukin-6 is a needed proinflammatory cytokine in the prolonged neural activity and transcriptional activation of corticotropin-releasing factor during endotoxemia1. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 3890–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalis, K.; Muglia, L.J.; Bae, D.; Hilderbrand, H.; Majzoub, J.A. CRH and the immune system. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 72, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, A.V.; Rivier, C.L. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by cytokines: Actions and mechanisms of action. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, D.; Mukai, Y.; Hung, C.J.; Chowdhury, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamanaka, A. The mammalian circadian pacemaker regulates wakefulness via CRFneurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd0384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allada, R.; Bass, J. Circadian mechanisms in medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, W. Ghrelin restores the disruption of the circadian clock in steatotic liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, K.; Hanada, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Sakihara, S.; Nigawara, T.; Kasckow, J.; Suda, T. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide stimulates corticotropin-releasing factor, vasopressin and interleukin-6 gene transcription in hypothalamic 4B cells. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 195, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Yamagata, S.; Akimoto, K.; Sugiyama, A.; Murasawa, S.; Suda, T. Action of glucagon-like peptide 1 and glucose levels on corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin gene expression in rat hypothalamic 4B cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 362, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Ueta, Y.; Serino, R.; Kabashima, N.; Shibuya, I.; Yamashita, H. PACAP type I receptor gene expression in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of rats. NeuroReport 1996, 8, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioda, S.; Shuto, Y.; Somogyvári-Vigh, A.; Legradi, G.; Onda, H.; Coy, D.H.; Nakajo, S.; Arimura, A. Localization and gene expression of the receptor for pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide in the rat brain. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 28, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinevich, V.; Fournier, A.; Pelletier, G. Effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) on corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) gene expression in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res. 1997, 773, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozid, A.M.; Tringali, G.; Forsling, M.L.; Hendricks, M.S.; Ajodha, S.; Edwards, R.; Navarra, P.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. Ghrelin is released from rat hypothalamic explants and stimulates corticotrophin-releasing hormone and arginine-vasopressin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2003, 35, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Kumata, Y.; Akimoto, K.; Takayasu, S.; Tamasawa, N.; Suda, T. Ghrelin stimulates corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin gene expression in rat hypothalamic 4B cells. Stress 2011, 14, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Akimoto, K.; Yamagata, S.; Sugiyama, A.; Murasawa, S.; Watanuki, Y.; Tamasawa, N.; Suda, T. Dexamethasone stimulates the expression of ghrelin and its receptor in rat hypothalamic 4B cells. Regul. Pept. 2012, 174, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigame, N.; Kageyama, K.; Takayasu, S.; Furumai, K.; Nakada, Y.; Daimon, M. Regulation of the expression of corticotropin-releasing factor gene by pyroglutamylated RFamide peptide in rat hypothalamic 4B cells. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchimura, T.; Hara, S.; Yazawa, T.; Kamei, Y.; Kitano, T. Involvement of heat shock proteins on the transcriptional regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone in medaka. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Denver, R.J. Regulation of vertebrate corticotropin-releasing factor genes. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 153, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, K.; Tamasawa, N.; Suda, T. Signal transduction in the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor system and its clinical implications. Stress 2011, 14, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seasholtz, A.F.; Thompson, R.C.; Douglass, J.O. Identification of a cyclic adenosine monophosphate-responsive element in the rat corticotropin-releasing hormone gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 1988, 2, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, D.; Rupprecht, R.; Van, L.P.; Holsboer, F. Identification and characterization of a 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-responsive element in the human corticotropin-releasing hormone gene promoter. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992, 6, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamamori, E.; Asai, M.; Yoshida, M.; Takano, K.; Itoi, K.; Oiso, Y.; Iwasaki, Y. Calcium/calmodulin kinase IV pathway is involved in the transcriptional regulation of the corticotropin-releasing hormone gene promoter in neuronal cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 33, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Hanada, K.; Takayasu, S.; Iwasaki, Y.; Sakihara, S.; Nigawara, T.; Suda, T. Involvement of regulatory elements on corticotropin-releasing factor gene promoter in hypothalamic 4B cells. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2008, 31, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Itoi, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Niioka, K.; Watanuki, Y.; Yamagata, S.; Nakada, Y.; Das, G.; Suda, T.; Daimon, M. Stimulation of corticotropin-releasing factor gene expression by FosB in rat hypothalamic 4B cells. Peptides 2013, 51, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Uchida, K.; Kageyama, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Suda, T.; Itoi, K. Glucocorticoid dependency of surgical stress-induced FosB/DeltaFosB expression in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the rathypothalamus. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2009, 21, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, T.; Yajima, F.; Tomori, N.; Demura, H.; Shizume, K. In vitro study of immunoreactive corticotropin-releasing factor release from the rat hypothalamus. Life Sci. 1985, 37, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Halvorson, L.M.; Legradi, G. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) mimics neuroendocrine and behavioral manifestations of stress: Evidence for PKA-mediated expression of the corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) gene. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 138, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Nicholson, R.C.; King, B.; Chan, E.C.; Fitter, J.T.; Smith, R. glucocorticoid stimulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression requires a cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate regulatory element in human primary placental cytotrophoblast cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ochedalski, T.; Subburaju, S.; Wynn, P.C.; Aguilera, G. Interaction between oestrogen and oxytocin on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity. J. Neuroendocr. 2007, 19, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, E.; Kageyama, K.; Hanada, K.; Kasckow, J.; Suda, T. Effects of estradiol on regulation of corticotropin-releasing factor gene and interleukin-6 production via estrogen receptor type beta in hypothalamic 4B cells. Peptides 2008, 29, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.M.; Aguilera, G. Differential regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone and vasopressin transcription by glucocorticoids. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 5642–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Foulkes, N.S.; Borrelli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P. CREM gene: Use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell 1991, 64, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.A.; Foulkes, N.S.; Lalli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Inducibility and negative autoregulation of CREM: An alternative promoter directs the expression of ICER, an early response repressor. Cell 1993, 75, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Signal transduction and gene regulation: The nuclear response to cAMP. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17359–17362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, D.; Hilton, D. SOCS: Physiological suppressors of cytokine signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 2813–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auernhammer, C.J.; Bousquet, C.; Melmed, S. Autoregulation of pituitary corticotroph SOCS-3 expression: Characterization of the murine SOCS-3 promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6964–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, P.A.; Waxman, D. SOCS/CIS protein inhibition of growth hormone-stimulated STAT5 signaling by multiple mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35553–35561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Weissenbach, M.; Haan, S.; Heinrich, P.C.; Schaper, F. SOCS3 exerts its inhibitory function on interleukin-6 signal transduction through the SHP2 recruitment site of gp130. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12848–12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, K.; Hanada, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Suda, T. Regulation and role of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in hypothalamic 4B cells. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 201, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Donaldson, C.J.; Bittencourt, J.; Perrin, M.H.; Lewis, A.K.; Sutton, S.; Chan, R.; Turnbull, A.V.; Lovejoy, D.; Rivier, C.; et al. Urocortin, a mammalian neuropeptide related to fish urotensin I and to corticotropin-releasing factor. Nat. Cell Biol. 1995, 378, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, M.; Merlo-Pich, E.; Chan, R.K.W.; Basso, A.M.; Rivier, J.; Vale, W.; Koob, G.F. Appetite-suppressing effects of urocortin, a CRF-related neuropeptide. Science 1996, 273, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, D.G.; Vaughan, J.; Rivier, J.; Vale, W.; May, C.N. Cardiac inotropic actions of urocortin in conscious sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1997, 272, H2115–H2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashinami, H.; Kageyama, K.; Suda, T.; Nakane, A. Urocortin 2 suppresses host resistance to Listeria monocytogenes infection via up-regulation of interleukin-10. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5003–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Kimura, R.; Suga, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Suda, T.; Wakui, M. Modulation of Ca2+ influx by corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) family of peptides via CRF receptors in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Peptides 2006, 27, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavalakatt, S.; Khadir, A.; Madhu, D.; Koistinen, H.A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Tuomilehto, J.; Abubaker, J.; Tiss, A. Urocortin 3 overexpression reduces ER stress and heat shock response in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Pearse, R.; O’Connell, S.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Identification of a seven transmembrane helix receptor for corticotropin-releasing factor and sauvagine in mammalian brain. Neuron 1993, 11, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lewis, K.A.; Perrin, M.H.; Vale, W.W. Expression cloning of a human corticotropin-releasing-factor receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8967–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, N.; Laurent, P.; Lefort, S.; Chalon, P.; Lelias, J.-M.; Kaghad, M.; Le Fur, G.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P. Primary structure and functional expression of mouse pituitary and human brain corticotrophin releasing factor receptors. FEBS Lett. 1993, 335, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Liaw, C.W.; Grigoriadis, D.E.; Clevenger, W.; Chalmers, D.T.; De Souza, E.B.; Oltersdorf, T. Cloning and characterization of a functionally distinct corticotropin-releasing factor receptor subtype from rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, M.; Donaldson, C.; Chen, R.; Blount, A.; Berggren, T.; Bilezikjian, L.; Sawchenko, P.; Vale, W. Identification of a second corticotropin-releasing factor receptor gene and characterization of a cDNA expressed in heart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2969–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenzel, P.; Kesterson, R.; Yeung, W.; Cone, R.D.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P.; Rittenberg, M.B. Identification of a novel murine receptor for corticotropin-releasing hormone expressed in the heart. Mol. Endocrinol. 1995, 9, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Suda, T.; Kageyama, K.; Sakihara, S.; Nigawara, T. Physiological roles of urocortins, human homologues of fish urotensin I, and their receptors. Peptides 2004, 25, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.Y.; Hsueh, A.J. Human stresscopin and stresscopin-related peptide are selective ligands for the type 2 corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Li, C.; Perrin, M.H.; Blount, A.; Kunitake, K.; Donaldson, C.; Vaughan, J.; Reyes, T.M.; Gulyas, J.; Fischer, W.; et al. Identification of urocortin III, an additional member of the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) family with high affinity for the CRF2 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7570–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, T.M.; Lewis, K.; Perrin, M.H.; Kunitake, K.S.; Vaughan, J.; Arias, C.A.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Gulyas, J.; Rivier, J.; Vale, W.W.; et al. Urocortin II: A member of the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) neuropeptide family that is selectively bound by type 2 CRF receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, K.; Li, C.; Vale, W.W. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 2 messenger ribonucleic acid in rat pituitary: Localization and regulation by immune challenge, restraint stress, and glucocorticoids. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Chalmers, D.T.; Liu, C.; De Souza, E.B. CRF2 alpha and CRF2 beta receptor mRNAs are differentially distributed between the rat central nervous system and peripheral tissues. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 4139–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, M.; Stein, D.J.; Gallas-Lopes, M.; Landau, L.; De Almeida, R.M.M. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor signaling and modulation: Implications for stress response and resilience. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2020, 42, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, T.L.; Contarino, A.; Smith, G.W.; Chan, R.; Gold, L.H.; Sawchenko, P.E.; Koob, G.F.; Vale, W.W.; Lee, K.-F. Mice deficient for corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2 display anxiety-like behaviour and are hypersensitive to stress. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, T.E.; Dee, N.; Bernard, A.; Lerchner, W.; Heintz, N.; Anderson, D.J. Control of stress-induced persistent anxiety by an extra-amygdala septohypothalamic circuit. Cell 2014, 156, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T.; Kageyama, K.; Kasagi, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Nigawara, T.; Sakihara, S.; Suda, T. Differential regulation of corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 1 (CRF1 receptor) mRNA via protein kinase A and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in rat anterior pituitary cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2005, 243, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, K.; Hanada, K.; Moriyama, T.; Nigawara, T.; Sakihara, S.; Suda, T. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 involvement in desensitization of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) receptor type 1 by CRF in murine corticotrophs. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gatto, F.; Feelders, R.; Van Der Pas, R.; Kros, J.M.; Dogan, F.; Van Koetsveld, P.M.; Van Der Lelij, A.-J.; Neggers, S.J.C.M.M.; Minuto, F.; De Herder, W.; et al. β-Arrestin 1 and 2 and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 expression in pituitary adenomas: Role in the regulation of response to somatostatin analogue treatment in patients with acromegaly. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4715–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Westphal, N.J.; Seasholtz, A.F. CRH-BP: The regulation and function of a phylogenetically conservedbinding protein. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehuda, R.; Golier, J.A.; Halligan, S.; Meaney, M.; Bierer, L.M. The ACTH response to dexamethasone in PTSD. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.K.; Walker, H.E.; Valentino, R.J.; Bhatnagar, S. Individual differences in reactivity to social stress predict susceptibility and resilience to a depressive phenotype: Role of corticotropin-releasing factor. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, D.; Sokolowski, M.; Wasserman, J. Genetics of HPA-axis, depression and suicidality. Eur. Psychiatry 2010, 25, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafet, G.E.; Nemeroff, C.B. Pharmacological treatment of anxiety disorders: The role of the HPA Axis. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Cui, S.Y.; Cui, X.Y.; Liu, Y.T.; Hu, X.; Zhao, H.L.; Qin, Y.; Kurban, N.; Zhang, Y.H. Anti-stress effects of combined block of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3696–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ikei, H.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of nature therapy: A review of the research in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, S.; Takayanagi, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Onaka, T. Gentle stroking stimuli induce affiliative responsiveness to humans in male rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardiola-Diaz, H.M.; Kolinske, J.S.; Gates, L.H.; Seasholtz, A.F. Negative glucorticoid regulation of cyclic adenosine 3’, 5’-monophosphate-stimulated corticotropin-releasing hormone-reporter expression in AtT-20 cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1996, 10, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Malkoski, S.P.; Dorin, R.I. Composite glucocorticoid regulation at a functionally defined negative glucocorticoid response element of the human corticotropin-releasing hormone gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 1629–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- King, B.R.; Smith, R.; Nicholson, R.C. Novel glucocorticoid and cAMP interactions on the CRH gene promoter. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 194, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, L.; Sharp, F.R.; Dallman, M.F. Induction of fos-like immunoreactivity in hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor neurons after adrenalectomy in the rat. Endocrinology 1990, 126, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Légrádi, G.; Holzer, D.; Kapcala, L.P.; Lechan, R.M. Glucocorticoids inhibit stress-induced phosphorylation of CREB in corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Neuroendocrinology 1997, 66, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagianni, N.; Tsawdaroglou, N. The c-fos serum response element (SRE) confers negative response to glucocorticoids. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Conca, M.; Gardela, J.; Martinez, A.C.; Wright, D.; López-Bejar, M.; Rodríguez-Martínez, H.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, M.; Ruiz-Conca, M. Natural mating differentially triggers expression of glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1)-related genes in the preovulatory porcine female reproductive tract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrka, A.R.; Ridout, K.K.; Parade, S.H. Childhood adversity and epigenetic regulation of glucocorticoidsignaling genes: Associations in children and adults. Dev. Psychopathol. 2016, 28, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitellius, G.; Lombes, M. Genetics in endocrinology: Glucocorticoid resistance syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 182, R15–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wochnik, G.M.; Rüegg, J.; Abel, G.A.; Schmidt, U.; Holsboer, F.; Rein, T. FK506-binding proteins 51 and 52 differentially regulate dynein interaction and nuclear translocation of the glucocorticoid receptor in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 4609–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.D.; Ozsan, I.; Ospina, S.R.; Gulick, D.; Blair, L.J. Hsp90 Heterocomplexes regulate steroid hormone receptors: From stress response to psychiatric disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkulov, V.M.; Merkulova, T.I.; Bondar, N.P. Mechanisms of brain glucocorticoid resistance in stress-induced psychopathologies. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatro, E.T.; Everall, I.P.; Kaul, M.; Achim, C.L. Modulation of glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation in neurons by immunophilins FKBP51 and FKBP52: Implications for major depressive disorder. Brain Res. 2009, 1286, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Watanuki, Y.; Niioka, K.; Daimon, M. Differential effects of Fkbp4 and Fkbp5 on regulation of the Proopiomelanocortin Gene in murine AtT-20 corticotroph cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häusl, A.S.; Brix, L.M.; Hartmann, J.; Pöhlmann, M.L.; Lopez, J.-P.; Menegaz, D.; Brivio, E.; Engelhardt, C.; Roeh, S.; Bajaj, T.; et al. The co-chaperone Fkbp5 shapes the acute stress response in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3060–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoi, K.; Motoike, I.; Liu, Y.; Clokie, S.; Iwasaki, Y.; Uchida, K.; Sato, T.; Aguilera, G. Genome-wide analysis of glucocorticoid-responsive transcripts in the hypothalamic paraventricular region of male rats. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).