Mesenchymal Stem Cell: A Friend or Foe in Anti-Tumor Immunity
Abstract
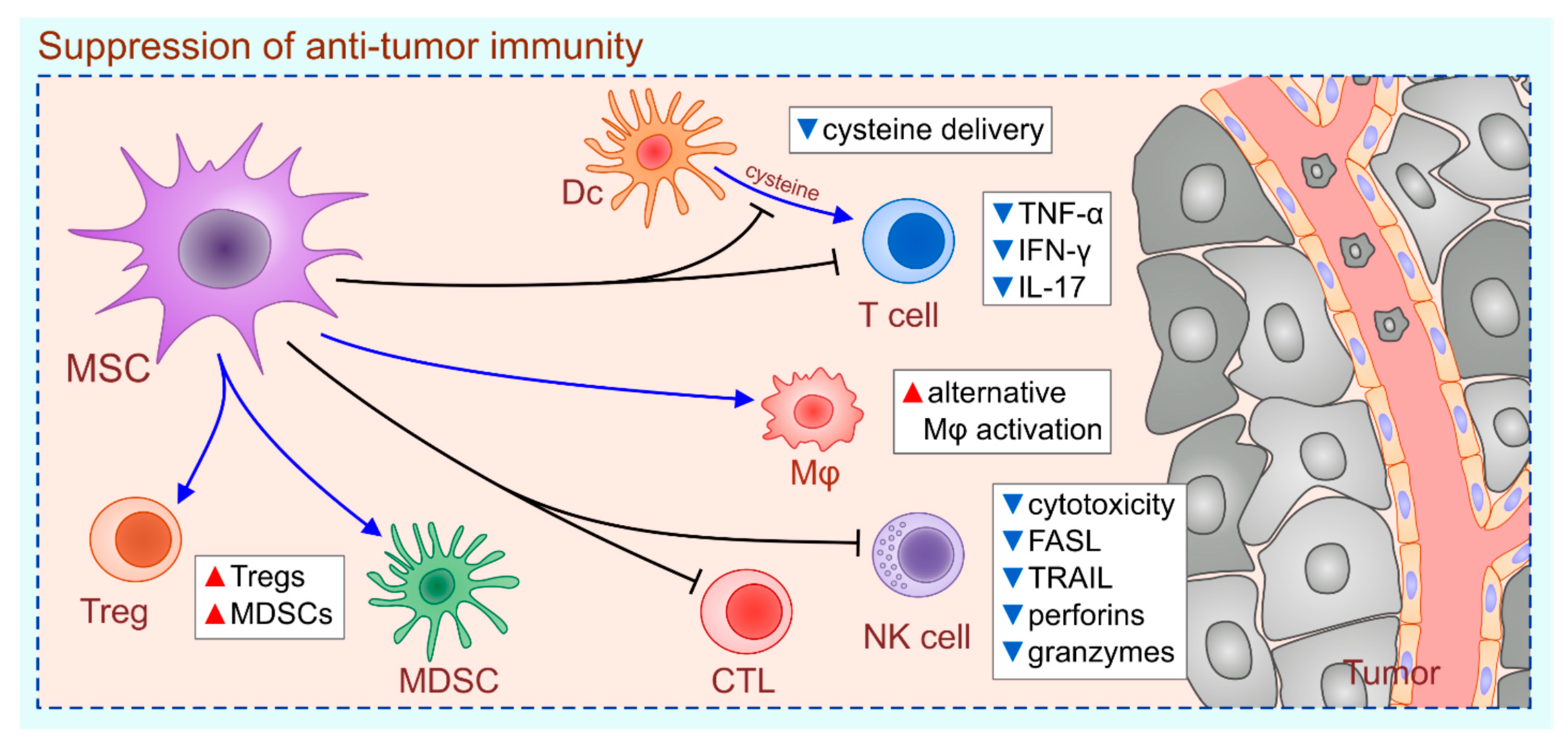
:1. Introduction
2. MSC-Dependent Suppression of Anti-Tumor Immunity
3. Immunoregulatory Effects of Exogenously Injected MSCs Depend on the Time of Their Administration
4. MSCs as Potentially New Therapeutic Agents in Immunotherapy of Cancer
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, X. The Mechanism of Stimulating and Mobilizing the Immune System Enhancing the Anti-Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 682435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, F.; Ho, P.C.; Lo, W.L. DCision-making in tumors governs T cell anti-tumor immunity. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5253–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Chen, T.; Hu, R.; Zhu, R.; Li, C.; Ruan, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, Y. Next frontier in tumor immunotherapy: Macrophage-mediated immune evasion. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaschek, L.; Zöphel, S.; Knörck, A.; Hoth, M. A calcium optimum for cytotoxic T lymphocyte and natural killer cell cytotoxicity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 115, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, G.; Plangger, A. The Impact of NK Cell-Based Therapeutics for the Treatment of Lung Cancer for Biologics: Targets and Therapy. Biologics 2021, 15, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Contribution of regulatory T cells to cancer: A review. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 7983–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jankovic, M.G.; Fellabaum, C.; Volarevic, A.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, A.; Volarevic, V. Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Factors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1084, 187–206. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, C.R.; Djonov, V.; Volarevic, V. The Cross-Talk between Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Immune Cells in Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wei, Z.; Xu, X.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Cai, X.; Mao, F. The Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell on Colorectal Cancer. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 9136583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Yu, F.; Han, B.; Li, B.; Li, L. Therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghian, E.; Margiana, R.; Chupradit, S.; Bokov, D.O.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Marofi, F.; Shariatzadeh, S.; Tosan, F.; Jarahian, M. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells as a Vehicle for Cytokine Delivery: An Emerging Approach for Tumor Immunotherapy. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 721174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh, A.; Altajer, A.H.; Rahman, H.S.; Saleh, M.M.; Bokov, D.O.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Marofi, F.; Zamani, M.; Yaghoubi, Y.; Yazdanifar, M.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Based Delivery: A Rapidly Evolving Strategy for Cancer Therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 686453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Ge, J.; Wu, P.; You, B.; Qian, H. Roles of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cancer Development and Targeted Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 9962194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Barik, S.; Bhuniya, A.; Dhar, J.; Dasgupta, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, M.; Guha, I.; Sarkar, K.; Chakrabarti, P.; et al. Tumor-associated mesenchymal stem cells inhibit naïve T cell expansion by blocking cysteine export from dendritic cells. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2068–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, M.K.; Sinha, P.; Clements, V.K.; Rodriguez, P.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit T-cell activation by depleting cystine and cysteine. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, X.H.; Feng, G.W.; Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Shen, C.; Hui, H.; Peng, D.; Li, Z.; Kong, D.L.; Tian, J. Activation of mesenchymal stem cells by macrophages promotes tumor progression through immune suppressive effects. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20934–20944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathew, E.; Brannon, A.L.; Del Vecchio, A.; Garcia, P.E.; Penny, M.K.; Kane, K.T.; Vinta, A.; Buckanovich, R.J.; di Magliano, M.P. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Pancreatic Tumor Growth by Inducing Alternative Polarization of Macrophages. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Lourdes Mora-García, M.; García-Rocha, R.; Morales-Ramírez, O.; Montesinos, J.J.; Weiss-Steider, B.; Hernández-Montes, J.; Ávila-Ibarra, L.R.; Don-López, C.A.; Velasco-Velázquez, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Serrano, V.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from cervical cancer produce high amounts of adenosine to suppress cytotoxic T lymphocyte functions. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Mi, F.; Han, M.; Tian, M.; Deng, L.; Meng, N.; Luo, J.; Fu, R. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit CD8+ T cell immune responses via PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in multiple myeloma. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Huang, C.; Han, F.; Chen, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wen, S.; Wang, M.; Shen, B.; et al. Gastric Cancer Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit NK Cell Function through mTOR Signalling to Promote Tumour Growth. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 9989790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, S.; Vuille, J.; Martin, P.; Letovanec, I.; Caignard, A.; Fregni, G.; Stamenkovic, I. Tumor-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Use Distinct Mechanisms to Block the Activity of Natural Killer Cell Subsets. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2891–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, J.H.; Eum, D.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Jin, Y.H.; Shim, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.-Y.; Park, S.J.; Heo, K.; Choi, Y.J. Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on cancer stemness and mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. PLoS ONE. 2020, 15, e0240533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhan, D.; Wang, J.; Arvindam, U.S.; Hallstrom, C.; Verneris, M.R.; Grzywacz, B.; Warlick, E.; Blazar, B.R.; Miller, J.S. Mesenchymal stromal cells shape the MDS microenvironment by inducing suppressive monocytes that dampen NK cell function. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e130155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vladimirovna, I.L.; Sosunova, E.; Nikolaev, A.; Nenasheva, T. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells: Common Traits in Immune Regulation. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 7121580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatzioannou, A.; Boumpas, A.; Papadopoulou, M.; Papafragkos, I.; Varveri, A.; Alissafi, T.; Verginis, P. Regulatory T Cells in Autoimmunity and Cancer: A Duplicitous Lifestyle. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 731947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Ren, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Rabson, A.B.; Roberts, A.I.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Mesenchymal stem cells use IDO to regulate immunity in tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidari, F.; Razmkhah, M.; Razban, V.; Erfani, N. Effects of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) silencing on immunomodulatory function and cancer-promoting characteristic of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs). Cell Biol. Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, F.; Razmkhah, M.; Rezaeifard, S.; Bagheri, M.; Talei, A.R.; Khalatbari, B.; Ghaderi, A. Mesenchymal stem cells induced anti-inflammatory features in B cells from breast tumor draining lymph nodes. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1658–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazdic, M.; Markovic, B.S.; Jovicic, N.; Misirkic-Marjanovic, M.; Djonov, V.; Jakovljevic, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cells by Downregulating Systemic Antitumor Immune Response. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 6294717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Mesenchymal stem cells: A friend or foe in immune-mediated diseases. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.C.; Heldring, N.; Kadri, N.; Le Blanc, K. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretion of Programmed Death-1 Ligands Regulates T Cell Mediated Immunosuppression. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloradovic, D.; Miloradovic, D.; Markovic, B.S.; Acovic, A.; Harrell, C.R.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. The Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Antimelanoma Immunity Depend on the Timing of Their Administration. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 8842659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Ljujic, B.; Stojkovic, P.; Lukic, A.; Arsenijevic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Human stem cell research and regenerative medicine—Present and future. Br. Med. Bull. 2011, 99, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szoor, A.; Vaidya, A.; Velasquez, M.P.; Mei, Z.; Galvan, D.L.; Torres, D.; Gee, A.; Heczey, A.; Gottschalk, S. T Cell-Activating Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Biotherapeutic for HCC. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2017, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magistri, P.; Leonard, S.Y.; Tang, C.M.; Chan, J.C.; Lee, T.E.; Sicklick, J.K. The glypican 3 hepatocellular carcinoma marker regulates human hepatic stellate cells via Hedgehog signaling. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 187, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Zhao, J.K.; Schiergens, T.S.; Wang, P.X.; Ou, B.C.; Al-Sayegh, R.; Li, M.L.; Lu, A.G.; Yin, S.; Thasler, W.E. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells promote colorectal cancer cell death under low-dose irradiation. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Volarevic, V. Therapeutic Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: From Basic Science to Clinics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles as New Remedies in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Wan, X.; Ouyang, M. microRNA-16-5p-containing exosomes derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion, while promoting apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating ITGA2. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 21380–21394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wan, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, J.; Han, M.; Zhou, C. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-3940-5p Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Integrin α6. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Li, J.J.; Jiang, F.; Shi, W.J.; Chang, G.Y. MicroRNA-4461 derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes inhibits tumorigenesis by downregulating COPB2 expression in colorectal cancer. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, T.; Jin, Y.; Mai, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, C. MicroRNA-15a Carried by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inhibits the Immune Evasion of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Regulating the KDM4B/HOXC4/PD-L1 Axis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 629893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, K.; Babashah, S.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Mowla, S.J.; Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M.; Ataei, F.; Dana, N.; Javan, M. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 2017, 40, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babajani, A.; Soltani, P.; Jamshidi, E.; Farjoo, M.H.; Niknejad, H. Recent Advances on Drug-Loaded Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Anti-neoplastic Agents for Targeted Treatment of Cancer. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layek, B.; Sadhukha, T.; Prabha, S. Glycoengineered mesenchymal stem cells as an enabling platform for two-step targeting of solid tumors. Biomaterials 2016, 88, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, B.; Sadhukha, T.; Panyam, J.; Prabha, S. Nano-Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase Therapeutic Efficacy of Anticancer Drug Through True Active Tumor Targeting. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Layek, B.; Shetty, M.; Nethi, S.K.; Sehgal, D.; Starr, T.K.; Prabha, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Guideposts for Nanoparticle-Mediated Targeted Drug Delivery in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Type of MSCs | Route of Injection | Tumor Type/Disease | Clinical Trial ID | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-β-expressing MSCs | intraperitoneal | ovarian cancer | NCT02530047 | Completed |
| AT-MSCs | submandibular | radiation-induced xerostomia in previous head and neck cancer patients | NCT02513238 | Completed |
| MSCs + UC-HSCs | intra-osseous | hematological malignancies | NCT02181478 | Completed |
| BM-MSCs infected with an oncolytic adenovirus, ICOVIR-5 (CELYVIR) | intravenous | metastatic and refractory tumors | NCT01844661 | Completed |
| BM-MSCs | intravenous | ARDS in patients with malignancies | NCT02804945 | Completed |
| MV-NIS-infected MSC | intraperitoneal | recurrent ovarian, primary peritoneal, fallopian tube cancer | NCT02068794 | Recruiting |
| TRAIL-expressing MSCs + cisplatin/pemetrexed | intravenous | metastatic NSCLC | NCT03298763 | Recruiting |
| BM-MSCs infected with an oncolytic adenovirus, ICOVIR-5 (CELYVIR) | intravenous | DIPG medulloblastoma | NCT04758533 | Recruiting |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harrell, C.R.; Volarevic, A.; Djonov, V.G.; Jovicic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell: A Friend or Foe in Anti-Tumor Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212429
Harrell CR, Volarevic A, Djonov VG, Jovicic N, Volarevic V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell: A Friend or Foe in Anti-Tumor Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212429
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarrell, Carl Randall, Ana Volarevic, Valentin G. Djonov, Nemanja Jovicic, and Vladislav Volarevic. 2021. "Mesenchymal Stem Cell: A Friend or Foe in Anti-Tumor Immunity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212429
APA StyleHarrell, C. R., Volarevic, A., Djonov, V. G., Jovicic, N., & Volarevic, V. (2021). Mesenchymal Stem Cell: A Friend or Foe in Anti-Tumor Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212429








