SB203580—A Potent p38 MAPK Inhibitor Reduces the Profibrotic Bronchial Fibroblasts Transition Associated with Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
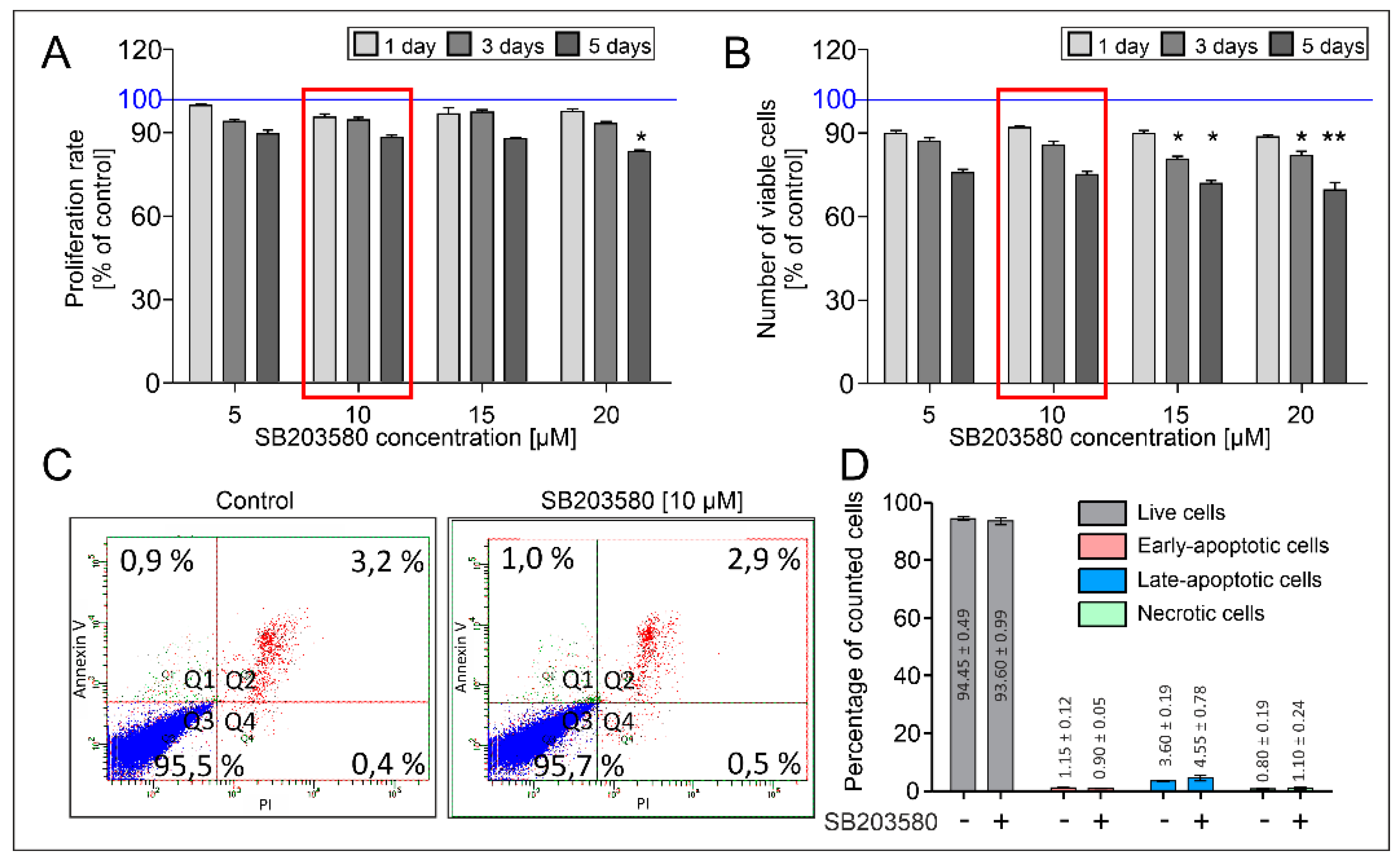
2.1. The TGF-β1-Induced Myofibroblastic Transition of HBFs AS Is Diminished in Response to the Administration of the p38 MAPK Inhibitor
2.2. Actin Cytoskeleton Architecture Is Rearranged in TGF-β1-Treated HBFs AS after the Administration of SB203580
2.3. SB203580 Diminishes the Levels of Cx43 in TGF-β1-Treated HBFs AS in a Smad-Dependent Manner
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Analysis of Viability, Proliferation and Apoptosis of HBFs
4.3. Immunofluorescence Studies
4.4. In-Cell ELISA Assay
4.5. Immunoblotting
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fehrenbach, H.; Wagner, C.; Wegmann, M. Airway remodeling in asthma: What really matters. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.J.; Van Winkle, L.S.; Fanucchi, M.V.; Plopper, C.G. The attenuated fibroblast sheath of the respiratory tract epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 21, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T.; Holloway, J.; Wilson, S.; Bucchieri, F.; Puddicombe, S.; Davies, D.E. Epithelial-mesenchymal communication in the pathogenesis of chronic asthma. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2004, 1, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgate, S.T.; Davies, D.E.; Lackie, P.M.; Wilson, S.J.; Puddicombe, S.M.; Lordan, J.L. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the pathogenesis of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paw, M.; Wnuk, D.; Jakieła, B.; Bochenek, G.; Sładek, K.; Madeja, Z.; Michalik, M. Responsiveness of human bronchial fibroblasts and epithelial cells from asthmatic and non-asthmatic donors to the transforming growth factor-β(1) in epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit model. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, M.; Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Paw, M.; Wnuk, D.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Sanak, M.; Pękala, E.; Madeja, Z. Fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition in bronchial asthma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3943–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalik, M.; Pierzchalska, M.; Legutko, A.; Ura, M.; Ostaszewska, A.; Soja, J.; Sanak, M. Asthmatic bronchial fibroblasts demonstrate enhanced potential to differentiate into myofibroblasts in culture. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Michalik, M.; Pierzchalska, M.; Wlodarczyk, A.; Wojcik, K.A.; Czyz, J.; Sanak, M.; Madeja, Z. Transition of asthmatic bronchial fibroblasts to myofibroblasts is inhibited by cell-cell contacts. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paw, M.; Borek, I.; Wnuk, D.; Ryszawy, D.; Piwowarczyk, K.; Kmiotek, K.; Wojcik-Pszczoła, K.A.; Pierzchalska, M.; Madeja, Z.; Sanak, M.; et al. Connexin43 controls the myofibroblastic differentiation of bronchial fibroblasts from patients with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, D.; Paw, M.; Ryczek, K.; Bochenek, G.; Sładek, K.; Madeja, Z.; Michalik, M. Enhanced asthma-related fibroblast to myofibroblast transition is the result of profibrotic TGF-β/Smad2/3 pathway intensification and antifibrotic TGF-β/Smad1/5/(8)9 pathway impairment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, D.; Lasota, S.; Paw, M.; Madeja, Z.; Michalik, M. Asthma-derived fibroblast to myofibroblast transition is enhanced in comparison to fibroblasts derived from non-asthmatic patients in 3D in vitro culture due to Smad2/3 signalling. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2020, 67, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paw, M.; Wnuk, D.; Kadziołka, D.; Sęk, A.; Lasota, S.; Czyż, J.; Madeja, Z.; Michalik, M. Fenofibrate reduces the asthma-related fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition by TGF-B/Smad2/3 signaling attenuation and connexin 43-dependent phenotype destabilization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Yoon, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, B. Effects of geniposide on hepatocytes undergoing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatic fibrosis by targeting TGFβ/Smad and ERK-MAPK signaling pathways. Biochimie 2015, 113, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Cong, S.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, Y.-X.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, L.-L.; Zhao, X.-K.; Mu, M.; Zhang, B.-F.; Fan, L.; et al. Platycodin D alleviates liver fibrosis and activation of hepatic stellate cells by regulating JNK/c-JUN signal pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 876, 172946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.-H.; Li, Y.-J.; Wu, H.-H.; Liu, S.-H.; Hsu, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-W.; Chu, P.-H.; Tian, Y.-C. Interleukin-17A induces renal fibrosis through the ERK and Smad signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.Y.; Flanc, R.S.; Tesch, G.H.; Han, Y.; Atkins, R.C.; Bennett, B.L.; Friedman, G.C.; Fan, J.-H.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. A pathogenic role for c-Jun amino-terminal kinase signaling in renal fibrosis and tubular cell apoptosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Hou, Y. Valproic acid regulates Ang II-induced pericyte-myofibroblast trans-differentiation via MAPK/ERK pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1976–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara, S.; Li, P.; Mise, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Izuoka, K.; Nakajima, T.; Gonzalez, F.; Ichihara, G. Ablation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis through enhanced c-Jun/HIF-1α signaling. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madala, S.K.; Schmidt, S.; Davidson, C.; Ikegami, M.; Wert, S.; Hardie, W.D. MEK-ERK pathway modulation ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis associated with epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S.; Gon, Y.; Takeshita, I.; Matsumoto, K.; Maruoka, S.; Horie, T. Transforming growth Factor-beta1 induces phenotypic modulation of human lung fibroblasts to myofibroblast through a c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Ying, W.; Yao, X.-X. Interleukin-1β upregulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression via c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 MAPK pathways in rat hepatic stellate cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 1861–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambe, C.; Atkins, R.C.; Tesch, G.H.; Masaki, T.; Schreiner, G.F.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. The role of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in renal fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, N.; Kohno, M.; Yokoyama, T. Inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway ameliorates renal fibrosis in an NPHP2 mouse model. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2012, 27, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molkentin, J.D.; Bugg, D.; Ghearing, N.; Dorn, L.E.; Kim, P.; Sargent, M.A.; Gunaje, J.; Otsu, K.; Davis, J. Fibroblast-Specific Genetic Manipulation of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase In Vivo Reveals Its Central Regulatory Role in Fibrosis. Circulation 2017, 136, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.A.; Blythe, N.M. Cardiac Fibroblast p38 MAPK: A Critical Regulator of Myocardial Remodeling. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Shi, Y.; Yang, J. Roles of p38 MAPK and JNK in TGF-β1-induced human alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Arch. Med. Res. 2013, 44, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southworth, T.; Mason, S.; Bell, A.; Ramis, I.; Calbet, M.; Domenech, A.; Prats, N.; Miralpeix, M.; Singh, D. PI3K, p38 and JAK/STAT signalling in bronchial tissue from patients with asthma following allergen challenge. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallese, D.; Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; Gnemmi, I.; Casolari, P.; Brun, P.; Sorbello, V.; Capelli, A.; Cappello, F.; Cavallesco, G.N.; Papi, A.; et al. Phospho-p38 MAPK expression in COPD patients and asthmatics and in challenged bronchial epithelium. Respiration 2015, 89, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, K.J.; Fricker, M.; McDonald, V.M.; Simpson, J.L.; Wood, L.G.; Wark, P.A.B.; Macdonald, H.E.; Reid, A.; Gibson, P.G. Sputum transcriptomics implicates increased p38 signalling activity in severe asthma. Respirology 2020, 25, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B.; Gabbiani, G. Cell-matrix and cell-cell contacts of myofibroblasts: Role in connective tissue remodeling. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 90, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, N.N.; Eming, S.A. Skin fibrosis: Models and mechanisms. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2016, 64, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; López de Juan Abad, B.; Cheng, K. Cardiac fibrosis: Myofibroblast-mediated pathological regulation and drug delivery strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppe, C.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Kranz, J.; Zhang, X.; Ziegler, S.; Perales-Patón, J.; Jansen, J.; Reimer, K.C.; Smith, J.R.; Dobie, R.; et al. Decoding myofibroblast origins in human kidney fibrosis. Nature 2021, 589, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eapen, M.S.; Lu, W.; Hackett, T.L.; Singhera, G.K.; Mahmood, M.Q.; Hardikar, A.; Ward, C.; Walters, E.H.; Sohal, S.S. Increased myofibroblasts in the small airways, and relationship to remodelling and functional changes in smokers and COPD patients: Potential role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00876-2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Kim, J.-D.; Ugai, K.; Matsuda, S.; Mikami, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Ikari, J.; Hatano, M.; Fukamizu, A.; Tatsumi, K.; et al. Transcriptomic changes involved in the dedifferentiation of myofibroblasts derived from the lung of a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuyakorn, W.; Smart, D.E.; Noto, A.; Bucchieri, F.; Haitchi, H.M.; Holgate, S.T.; Howarth, P.H.; Davies, D.E. Mechanical Strain Causes Adaptive Change in Bronchial Fibroblasts Enhancing Profibrotic and Inflammatory Responses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerati, P.C.; Mitchel, J.A.; Reid, A.T.; Knight, D.A.; Bartlett, N.W.; Park, J.-A.; Grainge, C.L. Airway mechanical compression: Its role in asthma pathogenesis and progression. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2020, 29, 190123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, M.J.; Phung, T.-K.N.; Park, J.-A. Bronchoconstriction: A potential missing link in airway remodelling. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, J.T.; Lourenço, J.D.; Righetti, R.F.; Tibério, I.F.L.C.; Prado, C.M.; Lopes, F.D.T.Q.S. Extracellular Matrix Component Remodeling in Respiratory Diseases: What Has Been Found in Clinical and Experimental Studies? Cells 2019, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-H.; Chen, D.-Q.; Wang, Y.-N.; Feng, Y.-L.; Cao, G.; Vaziri, N.D.; Zhao, Y.-Y. New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 292, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, P.; Khorasani, N.; Hew, M.; Johnson, M.; Chung, K.F. Effect of p38 MAPK inhibition on corticosteroid suppression of cytokine release in severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, S.; Harbron, C.; Khan, N.; Booth, G.; Armstrong, J.; Singh, D. Corticosteroid insensitive alveolar macrophages from asthma patients; synergistic interaction with a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.F. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in asthma and COPD. Chest 2011, 139, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Ter-Vehn, T.; Gebhardt, S.; Sebald, W.; Buttmann, M.; Grehn, F.; Schlunck, G.; Knaus, P. p38 inhibitors prevent TGF-beta-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation in human tenon fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.-Y.; Wu, S.-B.; Kau, H.-C.; Tsai, C.-C. JNK and p38 Inhibitors Prevent Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Induced Myofibroblast Transdifferentiation in Human Graves’ Orbital Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-M.; Park, I.-H.; Cho, J.-S.; Um, J.-Y.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.-M. Berberine inhibits myofibroblast differentiation in nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts via the p38 pathway. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, F.; Luppi, F.; Petecchia, L.; Di Stefano, A.; Longo, A.M.; Eva, A.; Vanni, C.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Sterk, P.J.; Sorbello, V.; et al. Bradykinin-induced asthmatic fibroblast/myofibroblast activities via bradykinin B2 receptor and different MAPK pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 710, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, A.; Shi, C.; Li, B. Curcumin suppresses transforming growth factor-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast differentiation via inhibition of Smad-2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Campanale, N.V.; Liang, R.J.; Deane, J.A.; Bertram, J.F.; Ricardo, S.D. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and transforming growth factor-beta1/Smad signaling pathways modulates the development of fibrosis in adriamycin-induced nephropathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, H.; Arai, T.; Mori, M.; Goya, S.; Kida, H.; Morishita, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Tachibana, I.; Osaki, T.; Hayashi, S. A p38 MAPK inhibitor, FR-167653, ameliorates murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2002, 283, L103–L112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, D.C.; Osborn, R.R.; Bochnowicz, S.; Webb, E.F.; Rieman, D.J.; Lee, J.C.; Romanic, A.M.; Adams, J.L.; Hay, D.W.; Griswold, D.E. SB 239063, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, reduces neutrophilia, inflammatory cytokines, MMP-9, and fibrosis in lung. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L895–L902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Medicherla, S.; Kerr, I.; Mangadu, R.; Protter, A.A.; Higgins, L.S. Selective p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor attenuates lung inflammation and fibrosis in IL-13 transgenic mouse model of asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2008, 1, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ko, J.-A.; Yanai, R.; Morishige, N.; Takezawa, T.; Nishida, T. Upregulation of connexin43 expression in corneal fibroblasts by corneal epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-S.; Zheng, H.; Xu, D.; Liu, P.-P.; Li, B.; Cao, Z.-M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of zymosan on the expression and function of the gap-junction protein connexin 43 in human corneal fibroblasts. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, L.; Riddell, A.; Chilton, L.; Smith, G.L.; Nicklin, S.A. Regulation of connexin 43 by interleukin 1β in adult rat cardiac fibroblasts and effects in an adult rat cardiac myocyte: Fibroblast co-culture model. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Gillespie, S.R.; Wolosin, J.M.; Bernstein, A.M.; Reinach, P.S. TRPV1 potentiates TGFβ-induction of corneal myofibroblast development through an oxidative stress-mediated p38-SMAD2 signaling loop. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, A.; Kan, H.; Wu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, S.; Yang, Y. MAPK inhibitors differently modulate TGF-β/Smad signaling in HepG2 cells. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 3643–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, F.; Matsuzaki, K.; Mori, S.; Tahashi, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Sugano, Y.; Yamagata, H.; Matsushita, M.; Seki, T.; Inagaki, Y.; et al. p38 MAPK mediates fibrogenic signal through Smad3 phosphorylation in rat myofibroblasts. Hepatology 2003, 38, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue-Mochita, M.; Inoue, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Kameda, T.; Awai-Kasaoka, N.; Ohtsu, N.; Kimoto, K.; Tanihara, H. p38 MAP kinase inhibitor suppresses transforming growth factor-β2-induced type 1 collagen production in trabecular meshwork cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, M.; Wojcik, K.A.; Hermanowicz, P.; Wnuk, D.; Burda, K.; Sanak, M.; Czyz, J.; Michalik, M. Undifferentiated bronchial fibroblasts derived from asthmatic patients display higher elastic modulus than their non-asthmatic counterparts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.; Jensen, C.C.; Yoshigi, M.; Beckerle, M. Mechanical signals activate p38 MAPK pathway-dependent reinforcement of actin via mechanosensitive HspB1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 2661–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, T.; Guo, T.; Zhu, L.; Sun, Z. Mechanical stress influences the morphology and function of human uterosacral ligament fibroblasts and activates the p38 MAPK pathway. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratyn-Schaus, Y.; Gardel, M.L. Transient frictional slip between integrin and the ECM in focal adhesions under myosin II tension. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Cusachs, P.; del Rio, A.; Puklin-Faucher, E.; Gauthier, N.C.; Biais, N.; Sheetz, M.P. Integrin-dependent force transmission to the extracellular matrix by α-actinin triggers adhesion maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1361–E1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, S.; Torisu, T.; Esaki, M.; Torisu, K.; Matsuno, Y.; Kitazono, T. Autophagy promotes degradation of internalized collagen and regulates distribution of focal adhesions to suppress cell adhesion. Biol. Open 2017, 6, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riquelme, M.A.; Gu, S.; Hua, R.; Jiang, J.X. Mechanotransduction via the coordinated actions of integrins, PI3K signaling and Connexin hemichannels. Bone Res. 2021, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, N.; Burra, S.; Siller-Jackson, A.J.; Gu, S.; Xia, X.; Weber, G.F.; DeSimone, D.; Bonewald, L.F.; Lafer, E.M.; Sprague, E.; et al. Mechanical stress-activated integrin α5β1 induces opening of connexin 43 hemichannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3359–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, A.I.; Rannels, D.E. Extracellular matrix fibronectin alters connexin43 expression by alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 280, L680–L688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarzemany, R.; Jiang, G.; Jiang, J.X.; Larjava, H.; Häkkinen, L. Connexin 43 Hemichannels Regulate the Expression of Wound Healing-Associated Genes in Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, J.A.; Price, G.W.; Cliff, C.L.; Green, C.R.; Squires, P.E.; Hills, C.E. Collagen I Modifies Connexin-43 Hemichannel Activity via Integrin α2β1 Binding in TGFβ1-Evoked Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meens, M.J.; Pfenniger, A.; Kwak, B.R.; Delmar, M. Regulation of cardiovascular connexins by mechanical forces and junctions. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Gene | Protein | Sequence 5′–3′ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| F’ | R’ | ||
| ACTA2 | α-SMA | CTGTTCCAGCCATCCTTCAT | CCGTGATCTCCTTCTGCATT |
| B2M | β2-microglobulin | AATGCGGCATCTTCAAACCT | TGACTTTGTCACAGCCCAAGATA |
| COL1A1 | Collagen 1A1 | CTTTGCATTCATCTCTCAAACTTAGTTTT | CCCCGCATGGGTCTTCA |
| COL1A2 | Collagen 1A2 | TGCTGCTGGTCAACCTGGTGC | ACTTCCAGCAGGACCGGGGG |
| FN1 | Fibronectin | TGTGGTTGCCTTGCACGAT | GCTTGTGGGTGTGACCTGAGT |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGT | GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC |
| GJA1 | Connexin 43 | AGGAGTTCAATCACTTGGCG | GAGTTTGCCTAAGGCGCTC |
| ITGA5 | Integrin αV | CCGTGTGGTTTTAGGTGGAC | TTGATCAGGTACTCGGGGTAA |
| TAGLN | Transgelin | CGTGGAGATCCCAACTGGTT | AAGGCCAATGACATGCTTTCC |
| 18S | 18S rRNA | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT | CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paw, M.; Wnuk, D.; Nit, K.; Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Szychowski, R.; Ślusarczyk, A.; Madeja, Z.; Michalik, M. SB203580—A Potent p38 MAPK Inhibitor Reduces the Profibrotic Bronchial Fibroblasts Transition Associated with Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312790
Paw M, Wnuk D, Nit K, Bobis-Wozowicz S, Szychowski R, Ślusarczyk A, Madeja Z, Michalik M. SB203580—A Potent p38 MAPK Inhibitor Reduces the Profibrotic Bronchial Fibroblasts Transition Associated with Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312790
Chicago/Turabian StylePaw, Milena, Dawid Wnuk, Kinga Nit, Sylwia Bobis-Wozowicz, Rafał Szychowski, Alicja Ślusarczyk, Zbigniew Madeja, and Marta Michalik. 2021. "SB203580—A Potent p38 MAPK Inhibitor Reduces the Profibrotic Bronchial Fibroblasts Transition Associated with Asthma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312790
APA StylePaw, M., Wnuk, D., Nit, K., Bobis-Wozowicz, S., Szychowski, R., Ślusarczyk, A., Madeja, Z., & Michalik, M. (2021). SB203580—A Potent p38 MAPK Inhibitor Reduces the Profibrotic Bronchial Fibroblasts Transition Associated with Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312790








