Limitations and Possibilities of Transarterial Chemotherapeutic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Role of the Tumour Microenvironment
2.1. The Elusive Transition from Cirrhosis to Tumour
2.2. Cellular Interactions and Immunology
2.3. Vascularity and Penetrability
2.4. The Potential Role of Liver Lymphatics
3. Current Drug Performance
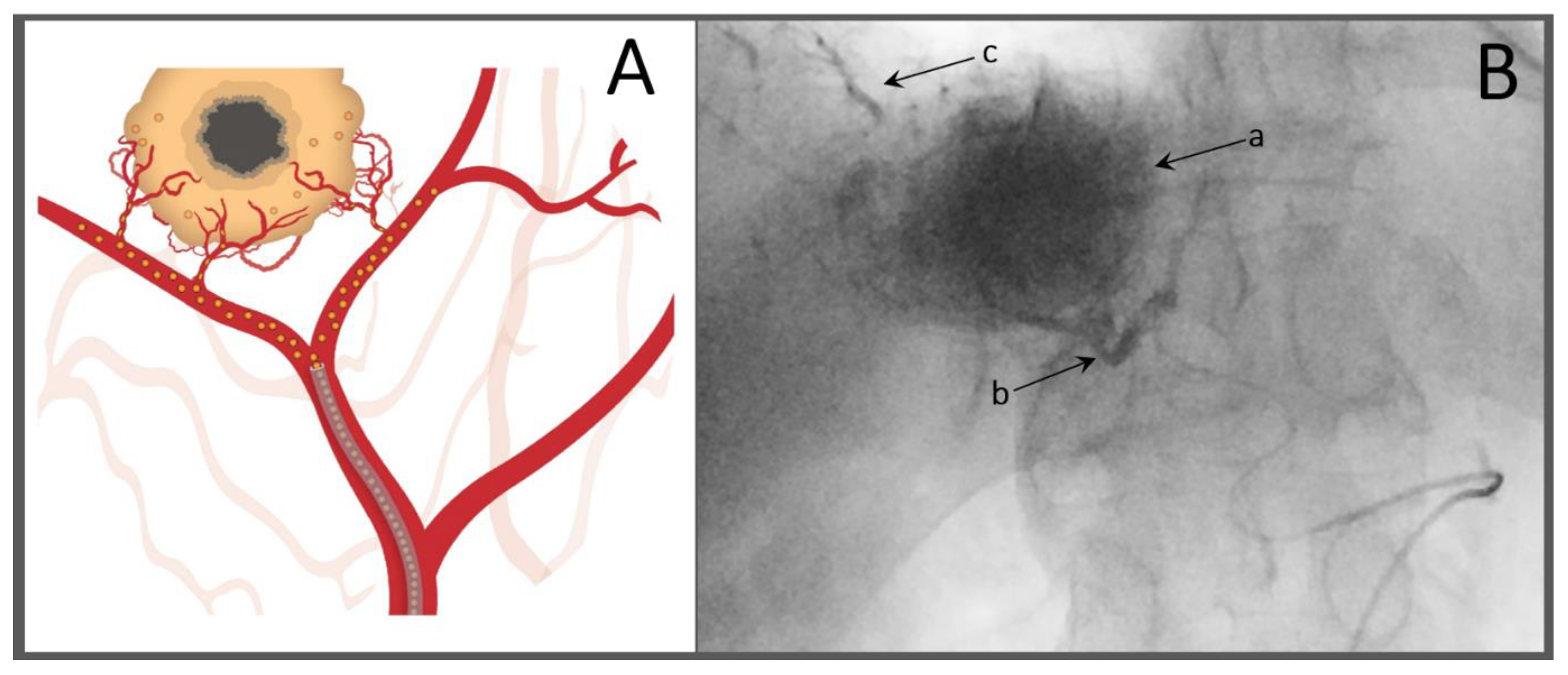
3.1. Conventional TACE (cTACE) with Chemotherapeutics in Lipiodol® Emulsions
3.2. Lipid Nano-Formulations with Anthracyclines
3.3. Hydrogel Microparticles (Microspheres) as Drug-Eluting Entities
4. The Future of TACE
4.1. Preclinical Studies
4.2. Clinical Studies
5. Expert Opinion (TBA)
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cTACE | conventional TACE |
| CTLA-4 | cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| DEM | drug-eluting microparticle |
| DEM-TACE | drug-eluting microparticle-TACE |
| DDS | drug-delivery systems |
| DSM | degradable starch microspheres |
| ECM | excess extracellular matrix |
| EPR | enhanced permeability and retention |
| etherPEs | alkylacylglycerophosphoethanolamines |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| IR | interventional radiology |
| ORR | objective response rate |
| OS | overall survival |
| PD-1 | the programmed death receptor 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed death ligand 1 |
| PPLE | peritumoral portal Lipiodol enhancement |
| PUFAs | polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| RCT | randomized control trials |
| RFA | radiofrequency ablation |
| TACE | transarterial chemoembolization |
| TIM-3 | T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 |
| TTP | time to progression |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factors |
References
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration; Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blachier, M.; Leleu, H.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Valla, D.C.; Roudot-Thoraval, F. The burden of liver disease in Europe: A review of available epidemiological data. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y. Deciphering hepatocellular carcinoma through metabolomics: From biomarker discovery to therapy evaluation. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maesaka, K.; Sakamori, R.; Yamada, R.; Tahata, Y.; Urabe, A.; Shigekawa, M.; Kodama, T.; Hikita, H.; Tatsumi, T.; Takehara, T. Hypovascular hepatic nodules as a predictive factor for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization refractoriness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Tovoli, F.; Foerster, F.; Worns, M.A.; Cucchetti, A.; Bolondi, L. The treatment of intermediate stage tumours beyond TACE: From surgery to systemic therapy. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nationellt Vårdprogram för Levercellscancer. Regionala Cancer Centrum i Samverkan. 2020. Available online: https://kunskapsbanken.cancercentrum.se/globalassets/cancerdiagnoser/lever-och-galla/vardprogram/nationellt-vardprogram-levercellscancer.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Inchingolo, R.; Posa, A.; Mariappan, M.; Spiliopoulos, S. Locoregional treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current evidence and future directions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4614–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aranda Aguilar, E.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; Bolondi, L.; Cheung, T.T.; Kloeckner, R.; de Baere, T. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 72, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, C.; Mahler, M.; Soulen, M.C. Liver-directed therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, T.D.; Rudolph, K.L.; Layer, G.; Chavan, A.; Greten, T.F.; Rosenthal, H.; Kubicka, S.; Galanski, M.; Manns, M.P.; Schild, H.; et al. Chemoocclusion vs. chemoperfusion for treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised trial. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 32, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusaka, T.; Kasugai, H.; Shioyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kudo, M.; Saisho, H.; Osaki, Y.; Sata, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Kumada, T.; et al. Transarterial chemotherapy alone versus transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized phase III trial. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Tu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yao, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Dou, C.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X. Hypoxia Accelerates Aggressiveness of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Involving Oxidative Stress, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Non-Canonical Hedgehog Signaling. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003, 37, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namur, J.; Wassef, M.; Millot, J.M.; Lewis, A.L.; Manfait, M.; Laurent, A. Drug-eluting beads for liver embolization: Concentration of doxorubicin in tissue and in beads in a pig model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, T.; Plotkin, S.; Yu, R.; Sutter, A.; Wu, Y.; Cruise, G.M. An In Vitro Evaluation of Four Types of Drug-Eluting Microspheres Loaded with Doxorubicin. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, O.; Denys, A.; de Baere, T.; Boulens, N.; Doelker, E. Comparative study of chemoembolization loadable beads: In vitro drug release and physical properties of DC bead and hepasphere loaded with doxorubicin and irinotecan. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Pan, K.T.; Chen, C.B.; Hung, C.F.; Chou, C.T. The short-term safety and efficacy of TANDEM microspheres of various sizes and doxorubicin loading concentrations for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.T.; Do, R.K.; Gonen, M.; Covey, A.M.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Jarnagin, W.R.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Allen, P.J.; Erinjeri, J.P.; et al. Randomized Trial of Hepatic Artery Embolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Doxorubicin-Eluting Microspheres Compared With Embolization With Microspheres Alone. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagari, K.; Pomoni, M.; Kelekis, A.; Pomoni, A.; Dourakis, S.; Spyridopoulos, T.; Moschouris, H.; Emmanouil, E.; Rizos, S.; Kelekis, D. Prospective randomized comparison of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads and bland embolization with BeadBlock for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.S.; Benhamou, M.; Teyssier, Y.; Seigneurin, A.; Abousalihac, M.; Sengel, C.; Seror, O.; Ghelfi, J.; Ganne-Carrie, N.; Blaise, L.; et al. Comparison of Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization and Bland Embolization for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbelboer, I.R.; Pavlovic, N.; Heindryckx, F.; Sjogren, E.; Lennernas, H. Liver Cancer Cell Lines Treated with Doxorubicin under Normoxia and Hypoxia: Cell Viability and Oncologic Protein Profile. Cancers 2019, 11, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Di Maso, M.; Muscatiello, N. Drug-eluting beads versus conventional chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golfieri, R.; Giampalma, E.; Renzulli, M.; Cioni, R.; Bargellini, I.; Bartolozzi, C.; Breatta, A.D.; Gandini, G.; Nani, R.; Gasparini, D.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs. conventional chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammer, J.; Malagari, K.; Vogl, T.; Pilleul, F.; Denys, A.; Watkinson, A.; Pitton, M.; Sergent, G.; Pfammatter, T.; Terraz, S.; et al. Prospective randomized study of doxorubicin-eluting-bead embolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of the PRECISION V study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, N.; Reyes, D.K.; Lin, M.; Kamel, I.; Pawlik, T.M.; Frangakis, C.; Geschwind, J.F. Phase II study of chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: High incidence of biliary injury. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiu, B.; Deschamps, F.; Aho, S.; Munck, F.; Dromain, C.; Boige, V.; Malka, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Ducreux, M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Liver/biliary injuries following chemoembolisation of endocrine tumours and hepatocellular carcinoma: Lipiodol vs. drug-eluting beads. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, A.; Guiu, B.; Duran, R.; Aho, S.; Bize, P.; Deltenre, P.; Dunet, V.; Denys, A. Liver and biliary damages following transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison between drug-eluting beads and lipiodol emulsion. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montana, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Sola, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarchoan, M.; Agarwal, P.; Villanueva, A.; Rao, S.; Dawson, L.A.; Llovet, J.M.; Finn, R.S.; Groopman, J.D.; El-Serag, H.B.; Monga, S.P.; et al. Recent Developments and Therapeutic Strategies against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4326–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienberg, E.; Dubbelboer, I.R.; Karalli, A.; Axelsson, R.; Brismar, T.B.; Ebeling Barbier, C.; Noren, A.; Duraj, F.; Hedeland, M.; Bondesson, U.; et al. In Vivo Drug Delivery Performance of Lipiodol-Based Emulsion or Drug-Eluting Beads in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, S.; Rimassa, L.; Finn, R.S. Molecular therapies for HCC: Looking outside the box. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi Birgani, M.; Carloni, V. Tumor Microenvironment, a Paradigm in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, M.S.; Xu, L.; Liang, H.H.; Lin, X.J.; Guo, R.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Lau, W.Y. Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Hur, Y.H.; Shin, S.S.; Heo, S.H.; Cho, S.B.; Kang, Y.J.; Lim, H.S.; Seon, H.J.; Jeong, Y.Y. Combined Therapy of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection for Single 2-3 cm Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score Matching Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1240–1247.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Salgado, O.C.; Singh, S.; Hippen, K.L.; Maynard, J.C.; Burlingame, A.L.; Ball, L.E.; Blazar, B.R.; Farrar, M.A.; Hogquist, K.A.; et al. The lineage stability and suppressive program of regulatory T cells require protein O-GlcNAcylation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Xiong, F.; Ge, J.; Xiang, B.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; et al. Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, N.; Calitz, C.; Thanapirom, K.; Mazza, G.; Rombouts, K.; Gerwins, P.; Heindryckx, F. Inhibiting IRE1α-endonuclease activity decreases tumor burden in a mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma. eLife 2020, 9, e55865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calitz, C.; Pavlović, N.; Rosenquist, J.; Zagami, C.; Samanta, A.; Heindryckx, F. A Biomimetic Model for Liver Cancer to Study Tumor-Stroma Interactions in a 3D Environment with Tunable Bio-Physical Properties. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, e61606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindryckx, F.; Gerwins, P. Targeting the tumor stroma in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Ding, S. The Crosstalk Between Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) and Tumor Cells and the Corresponding Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 590941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.T.; Song, K.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.H.; Liu, W.R.; Shi, G.M.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Ding, Z.B.; Fan, J. Tumor-associated macrophages modulate resistance to oxaliplatin via inducing autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucikova, J.; Kepp, O.; Kasikova, L.; Petroni, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Spisek, R.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumet, J.D.; Limagne, E.; Thibaudin, M.; Ghiringhelli, F. Immunogenic Cell Death and Elimination of Immunosuppressive Cells: A Double-Edged Sword of Chemotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Guo, J.; Hu, M.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L. Icaritin Exacerbates Mitophagy and Synergizes with Doxorubicin to Induce Immunogenic Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Nano. 2020, 14, 4816–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Jang, J.W.; Oh, B.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Chung, K.W.; Jung, H.S.; Jekarl, D.W.; Lee, S. Change in inflammatory cytokine profiles after transarterial chemotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cytokine 2013, 64, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, J.; Wong, J.S.L.; Kwok, G.G.W.; Li, B.C.W.; Leung, R.; Chiu, J.; Cheung, T.T.; Yau, T. Nivolumab + Ipilimumab for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with Sorafenib. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampaki, M.; Ionas, E.; Hadziyannis, E.; Deutsch, M.; Malagari, K.; Koskinas, J. Association of TIM-3 with BCLC Stage, Serum PD-L1 Detection, and Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Huang, T.; Wei, H.; Shen, L.; Zhu, D.; He, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; et al. The correlation and prognostic value of serum levels of soluble programmed death protein 1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, S.; Heindryckx, F.; Geerts, A.; van Steenkiste, C.; Colle, I.; van Vlierberghe, H. Angiogenesis in chronic liver disease and its complications. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, A.; Sporn, M.B. The tumour microenvironment as a target for chemoprevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Su, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, C. Remodeling the Tumor Microenvironment with Emerging Nanotherapeutics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Since the EPR effect fails in the clinic, what is the future of nanomedicine? J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, S.; Syed, A.M.; Ngai, J.; Kingston, B.R.; Maiorino, L.; Rothschild, J.; MacMillan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Rajesh, N.U.; Hoang, T.; et al. The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennernas, B.; Albertsson, P.; Lennernas, H.; Norrby, K. Chemotherapy and antiangiogenesis--drug-specific, dose-related effects. Acta Oncol. 2003, 42, 294–303. [Google Scholar]
- Heldin, C.H.; Rubin, K.; Pietras, K.; Ostman, A. High interstitial fluid pressure—An obstacle in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebied, O.M.; Federle, M.P.; Carr, B.I.; Pealer, K.M.; Li, W.; Amesur, N.; Zajko, A. Evaluation of responses to chemoembolization in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullenberg, F.; Degerstedt, O.; Calitz, C.; Pavlovic, N.; Balgoma, D.; Grasjo, J.; Sjogren, E.; Hedeland, M.; Heindryckx, F.; Lennernas, H. In Vitro Cell Toxicity and Intracellular Uptake of Doxorubicin Exposed as a Solution or Liposomes: Implications for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2021, 10, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbelboer, I.R.; Lilienberg, E.; Sjogren, E.; Lennernas, H. A Model-Based Approach to Assessing the Importance of Intracellular Binding Sites in Doxorubicin Disposition. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Tao, L.; Qian, Z.; Li, W. Microfluidic-enabled self-organized tumor model for in vitro cytotoxicity assessment of doxorubicin. Biomed. Microdevices 2020, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Iwakiri, Y. The Hepatic Lymphatic Vascular System: Structure, Function, Markers, and Lymphangiogenesis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Iwakiri, Y. Lymphatics in the liver. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataru, R.P.; Jung, K.; Jang, C.; Yang, H.; Schwendener, R.A.; Baik, J.E.; Han, S.H.; Alitalo, K.; Koh, G.Y. Critical role of CD11b+ macrophages and VEGF in inflammatory lymphangiogenesis, antigen clearance, and inflammation resolution. Blood 2009, 113, 5650–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburini, B.A.J.; Finlon, J.M.; Gillen, A.E.; Kriss, M.S.; Riemondy, K.A.; Fu, R.; Schuyler, R.P.; Hesselberth, J.R.; Rosen, H.R.; Burchill, M.A. Chronic Liver Disease in Humans Causes Expansion and Differentiation of Liver Lymphatic Endothelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugues, S.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Fernandez-Varo, G.; Ros, J.; Arteta, D.; Munoz-Luque, J.; Arroyo, V.; Rodes, J.; Jimenez, W. Microarray analysis of endothelial differentially expressed genes in liver of cirrhotic rats. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, D.N.; Perry, M.A.; Kvietys, P.R.; Taylor, A.E. Capillary and interstitial forces during fluid absorption in the cat small intestine. Gastroenterology 1984, 86, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; de Baere, T.; Soulen, M.C.; Rilling, W.S.; Geschwind, J.F. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology 2016, 64, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfieri, R.; Cappelli, A.; Cucchetti, A.; Piscaglia, F.; Carpenzano, M.; Peri, E.; Ravaioli, M.; D’Errico-Grigioni, A.; Pinna, A.D.; Bolondi, L. Efficacy of selective transarterial chemoembolization in inducing tumor necrosis in small (<5 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, K.; Maeda, H.; Konno, T. Use of oily contrast medium for selective drug targeting to tumor: Enhanced therapeutic effect and X-ray image. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kan, Z.; Sato, M.; Ivancev, K.; Uchida, B.; Hedgpeth, P.; Lunderquist, A.; Rosch, J.; Yamada, R. Distribution and effect of iodized poppyseed oil in the liver after hepatic artery embolization: Experimental study in several animal species. Radiology 1993, 186, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idee, J.M.; Guiu, B. Use of Lipiodol as a drug-delivery system for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 88, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi Varzaneh, F.; Pandey, A.; Aliyari Ghasabeh, M.; Shao, N.; Khoshpouri, P.; Pandey, P.; Zarghampour, M.; Fouladi, D.; Liddell, R.; Anders, R.A.; et al. Prediction of post-TACE necrosis of hepatocellular carcinoma usingvolumetric enhancement on MRI and volumetric oil deposition on CT, with pathological correlation. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3032–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liapi, E.; Geschwind, J.F. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for liver cancer: Is it time to distinguish conventional from drug-eluting chemoembolization? Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 34, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khaddari, S.; Gaudin, J.L.; Abidi, H.; Picaud, G.; Rode, A.; Souquet, J.C. Chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: Multivariate analysis of survival prognostic factors after the first session. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2002, 26, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.Y.; Ryu, H.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Ahn, S.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Han, K.H. Radiological response predicts survival following transarterial chemoembolisation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman Sennefelt, S.; Dimopoulou Creusen, A.; Johnson, U.; Rorsman, F.; Vessby, J.; Ebeling Barbier, C. Peritumoral portal enhancement during transarterial chemoembolization—A potential prognostic factor for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Radiol. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Miyayama, S.; Mitsui, T.; Zen, Y.; Sudo, Y.; Yamashiro, M.; Okuda, M.; Yoshie, Y.; Sanada, T.; Notsumata, K.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Histopathological findings after ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannangkoon, K.; Hongsakul, K.; Tubtawee, T.; Piratvisuth, T. Safety margin of embolized area can reduce local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after superselective transarterial chemoembolization. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Matsui, O.; Yamashiro, M.; Ryu, Y.; Kaito, K.; Ozaki, K.; Takeda, T.; Yoneda, N.; Notsumata, K.; Toya, D.; et al. Ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with a 2-f tip microcatheter for small hepatocellular carcinomas: Relationship between local tumor recurrence and visualization of the portal vein with iodized oil. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 18, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimitsu, K. Transarterial chemoembolization using iodized oil for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Perspective from multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepat. Med. 2014, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sia, D.; Villanueva, A.; Friedman, S.L.; Llovet, J.M. Liver Cancer Cell of Origin, Molecular Class, and Effects on Patient Prognosis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogacki, K.; Kasprzak, A.; Stepinski, A. Alterations of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinomas associated with hepatitis C virus. Pol. J. Pathol. 2015, 66, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, D.; Yuan, X.; Liu, L.I.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X.; Chen, S.; Ai, M.; Chen, B.O.; Shi, D. vbeta-Catenin Expression Correlates with Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayasu, K.; Arii, S.; Matsuo, N.; Yoshikawa, M.; Ryu, M.; Takasaki, K.; Sato, M.; Yamanaka, N.; Shimamura, Y.; Ohto, M. Comparison of CT findings with resected specimens after chemoembolization with iodized oil for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbelboer, I.R.; Lilienberg, E.; Ahnfelt, E.; Sjogren, E.; Axen, N.; Lennernas, H. Treatment of intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of intrahepatic doxorubicin drug-delivery systems. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallustio, B.C.; Boddy, A.V. Is there scope for better individualisation of anthracycline cancer chemotherapy? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Cho, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Baek, S.Y.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, D.D.; Kim, H.C. Comparison of drug release and pharmacokinetics after transarterial chemoembolization using diverse lipiodol emulsions and drug-eluting beads. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Oi, H.; Sawada, S. Transcatheter oily chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 1989, 170, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnfelt, E.D.O.; Lilienberg, E.; Sjögren, E.; Hansson, P.; Lennernäs, H. Lipiodol-based emulsions used for transarterial chemoembolization and drug delivery: Effects of composition on stability and product quality. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padia, S.A. Is Idarubicin the Future of TACE? Radiology 2019, 291, 809–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoulet, P.; Cercueil, J.P.; Faure, P.; Osmak, L.; Isambert, N.; Beltramo, J.L.; Cognet, F.; Krause, D.; Bedenne, L.; Chauffert, B. Increased cytotoxicity and stability of Lipiodol-pirarubicin emulsion compared to classical doxorubicin-Lipiodol: Potential advantage for chemoembolization of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs 2001, 12, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilienberg, E.; Ebeling Barbier, C.; Nyman, R.; Hedeland, M.; Bondesson, U.; Axen, N.; Lennernas, H. Investigation of hepatobiliary disposition of doxorubicin following intrahepatic delivery of different dosage forms. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulin, M.; Guiu, S.; Chauffert, B.; Aho, S.; Cercueil, J.P.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Krause, D.; Fagnoni, P.; Hillon, P.; Bedenne, L.; et al. Screening of anticancer drugs for chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs 2011, 22, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.S.; Teyssier, Y.; Abousalihac, M.; Seigneurin, A.; Ghelfi, J.; Sengel, C.; Decaens, T. Idarubicin vs. doxorubicin in transarterial chemoembolization of intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favelier, S.; Boulin, M.; Hamza, S.; Cercueil, J.P.; Cherblanc, V.; Lepage, C.; Hillon, P.; Chauffert, B.; Krause, D.; Guiu, B. Lipiodol trans-arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with idarubicin: First experience. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.; Zustovich, F.; Farinati, F.; Cillo, U.; Vitale, A.; Zanus, G.; Donach, M.; Farina, M.; Zovato, S.; Pastorelli, D. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and gemcitabine in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of a phase 2 study. Cancer 2011, 117, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhai, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneously overcome tumor vascular endothelium and extracellular matrix barriers via a non-destructive size-controlled nanomedicine. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosio, F.; Arpicco, S.; Stella, B.; Fattal, E. Hyaluronic acid for anticancer drug and nucleic acid delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 204–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, N.; Ishigami, M.; Ishizu, Y.; Kuzuya, T.; Honda, T.; Hayashi, K.; Hirooka, Y.; Goto, H. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of techniques. World J. Hepatol. 2014, 6, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiu, B.; Colombat, S.; Piron, L.; Hermida, M.; Allimant, C.; Pierredon-Foulongne, M.A.; Belgour, A.; Escal, L.; Cassinotto, C.; Boulin, M. Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Idarubicin-Loaded Tandem Drug-Eluting Embolics. Cancers 2019, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiu, B.; Chevallier, P.; Assenat, E.; Barbier, E.; Merle, P.; Bouvier, A.; Dumortier, J.; Nguyen-Khac, E.; Gugenheim, J.; Rode, A.; et al. Idarubicin-loaded Beads for Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The IDASPHERE II Single-Arm Phase II Trial. Radiology 2019, 291, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Anita, K. Angiogenesis in liver regeneration and fibrosis: “A double-edged sword”. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, H.J.; Xing, M.; Spivey, J.R.; Hanish, S.I.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Kauh, J.S.; Chen, Z.; Kim, H.S. Survival, efficacy, and safety of small versus large doxorubicin drug-eluting beads TACE chemoembolization in patients with unresectable HCC. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, W706–W714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.R.; Xiang, H.; Chan, M.V.; Chan, C. Survival, tumour response and safety of 70-150 mum versus 100-300 mum doxorubicin drug-eluting beads in transarterial chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 63, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, M.R.; Sharma, K.V.; Woods, D.L.; Reddy, G.; Tang, Y.; Pritchard, W.F.; Chiesa, O.A.; Karanian, J.W.; Esparza, J.A.; Donahue, D.; et al. Radiopaque drug-eluting beads for transcatheter embolotherapy: Experimental study of drug penetration and coverage in swine. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 257–264.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.L.; Taylor, R.R.; Hall, B.; Gonzalez, M.V.; Willis, S.L.; Stratford, P.W. Pharmacokinetic and safety study of doxorubicin-eluting beads in a porcine model of hepatic arterial embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 17, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeken, T.; Moussa, N.; Pernot, S.; Abed, A.; Dean, C.; Taieb, J.; Sapoval, M.; Pellerin, O. Does Bead Size Affect Patient Outcome in Irinotecan-Loaded Beads Chemoembolization Plus Systemic Chemotherapy Regimens for Liver-Dominant Colorectal Cancer? Results of an Observational Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindryckx, F.; Mertens, K.; Charette, N.; Vandeghinste, B.; Casteleyn, C.; van Steenkiste, C.; Slaets, D.; Libbrecht, L.; Staelens, S.; Starkel, P.; et al. Kinetics of angiogenic changes in a new mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabbaz, R.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Smith, A.A.; Garcia, K.D.; Lokken, R.P.; Gaba, R.C. Development and Angiographic Use of the Rabbit VX2 Model for Liver Cancer. J. Vis. Exp. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nass, N.; Streit, S.; Wybranski, C.; Jurgens, J.; Brauner, J.; Schulz, N.; Powerski, M.; Ricke, J.; Kalinski, T.; Dudeck, O.; et al. Validation of VX2 as a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model: Comparison of the Molecular Reaction of VX2 and HepG2 Tumor Cells to Sorafenib In Vitro. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.J.; Oppermann, E.; Qian, J.; Imlau, U.; Tran, A.; Hamidavi, Y.; Korkusuz, H.; Bechstein, W.O.; Nour-Eldin, N.E.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma in a rat model: The effect of additional injection of survivin siRNA to the treatment protocol. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, W.F.; Woods, D.L.; Esparza-Trujillo, J.A.; Starost, M.F.; Mauda-Havakuk, M.; Mikhail, A.S.; Bakhutashvili, I.; Leonard, S.; Jones, E.C.; Krishnasamy, V.; et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Woodchuck Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 812–819.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, H.; Seo, M.; Han, H.; Yoo, H.; Seo, H.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, P.; et al. Development and evaluation of an ultrasound-triggered microbubble combined transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) formulation on rabbit VX2 liver cancer model. Theranostics 2021, 11, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yu, P.; Chen, Y.; Sun, B.; Dong, P.; Zhu, T.; Meng, X. N-acetylgalactosamine-decorated nanoliposomes for targeted delivery of paclitaxel to hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 222, 113605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, L.; Stigliano, R.; Triantos, C.; Senzolo, M.; Cholongitas, E.; Davies, N.; Tibballs, J.; Meyer, T.; Patch, D.W.; Burroughs, A.K. Transarterial therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Which technique is more effective? A systematic review of cohort and randomized studies. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 30, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgoma, D.; Kullenberg, F.; Calitz, C.; Kopsida, M.; Heindryckx, F.; Lennernäs, H.; Hedeland, M. Anthracyclins Increase PUFAs: Potential Implications in ER Stress and Cell Death. Cells 2021, 10, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, N.; Heindryckx, F. Exploring the Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through mining of the Human Protein Atlas. Biology 2021, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, N.; Heindryckx, F. Targeting ER stress in the hepatic tumor microenvironment. FEBS J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindryckx, F.; Binet, F.; Ponticos, M.; Rombouts, K.; Lau, J.; Kreuger, J.; Gerwins, P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress enhances fibrosis through IRE1alpha-mediated degradation of miR-150 and XBP-1 splicing. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M.; Han, G.; Tak, W.Y.; Yang, J.; Guglielmi, A.; Paik, S.W.; Reig, M.; Kim, D.Y.; Chau, G.Y.; et al. Sorafenib or placebo plus TACE with doxorubicin-eluting beads for intermediate stage HCC: The SPACE trial. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Fox, R.; Ma, Y.T.; Ross, P.J.; James, M.W.; Sturgess, R.; Stubbs, C.; Stocken, D.D.; Wall, L.; Watkinson, A.; et al. Sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolisation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (TACE 2): A randomised placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Han, G.; Finn, R.S.; Poon, R.T.; Blanc, J.F.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.; Tak, W.Y.; Yu, X.; et al. Brivanib as adjuvant therapy to transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized phase III trial. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Park, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Liang, P.C.; Hidaka, H.; Izumi, N.; Heo, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Sheen, I.S.; et al. Orantinib versus placebo combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENTAL): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, phase 3 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Young Jang, J.; Jae Kim, Y. Recent Updates of Transarterial Chemoembolilzation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2020, 21, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. A New Treatment Option for Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma with High Tumor Burden: Initial Lenvatinib Therapy with Subsequent Selective TACE. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Chan, S.; Minami, T.; Chishina, H.; Aoki, T.; Takita, M.; Hagiwara, S.; Minami, Y.; Ida, H.; et al. Lenvatinib as an Initial Treatment in Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Beyond Up-To-Seven Criteria and Child-Pugh A Liver Function: A Proof-Of-Concept Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The ABC-HCC Trial: Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab vs. Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) in Intermediate-Stage HepatoCellular Carcinoma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04803994 (accessed on 10 November 2021).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebeling Barbier, C.; Heindryckx, F.; Lennernäs, H. Limitations and Possibilities of Transarterial Chemotherapeutic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313051
Ebeling Barbier C, Heindryckx F, Lennernäs H. Limitations and Possibilities of Transarterial Chemotherapeutic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):13051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313051
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbeling Barbier, Charlotte, Femke Heindryckx, and Hans Lennernäs. 2021. "Limitations and Possibilities of Transarterial Chemotherapeutic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 13051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313051
APA StyleEbeling Barbier, C., Heindryckx, F., & Lennernäs, H. (2021). Limitations and Possibilities of Transarterial Chemotherapeutic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 13051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313051






