Lamotrigine Attenuates Neuronal Excitability, Depresses GABA Synaptic Inhibition, and Modulates Theta Rhythms in Rat Hippocampus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of LTG on Spontaneous GABAergic Synaptic Activity in CA3c Pyramidal Cells
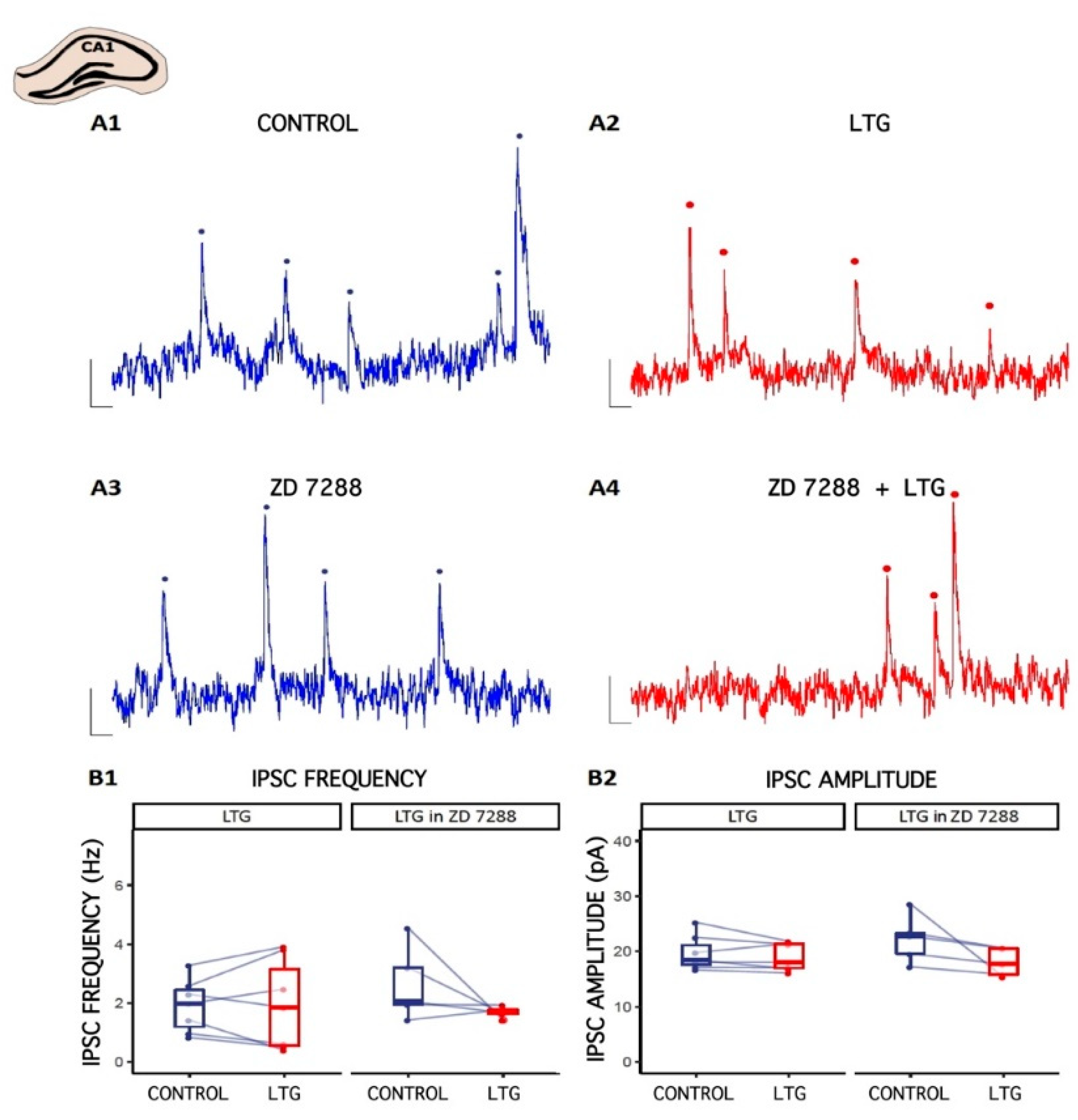
2.2. Effect of LTG on Spontaneous GABAergic Synaptic Activity in CA1 Pyramidal Cells
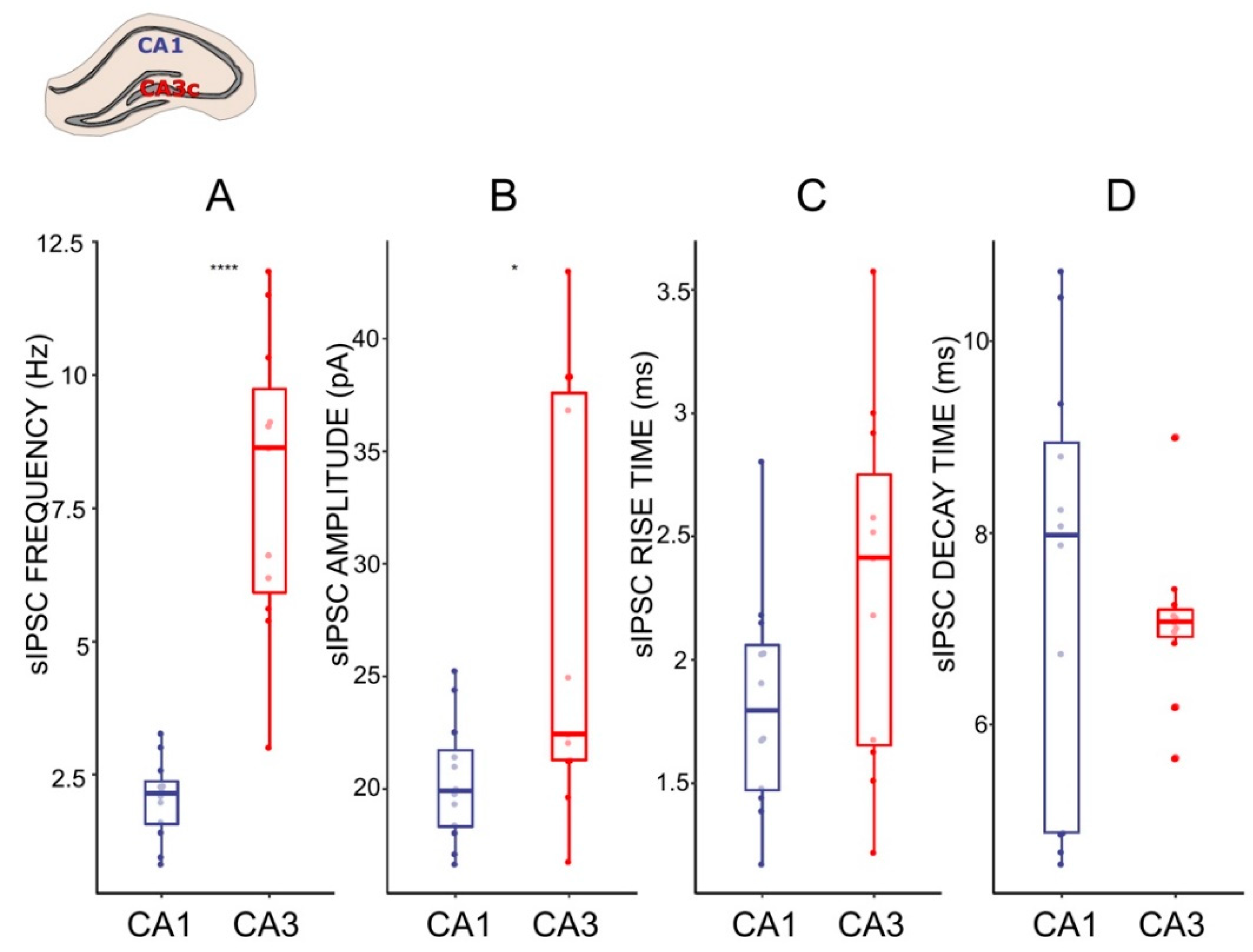
2.3. GABAergic Transmission Differs between CA1 and CA3c Hippocampal Neurons
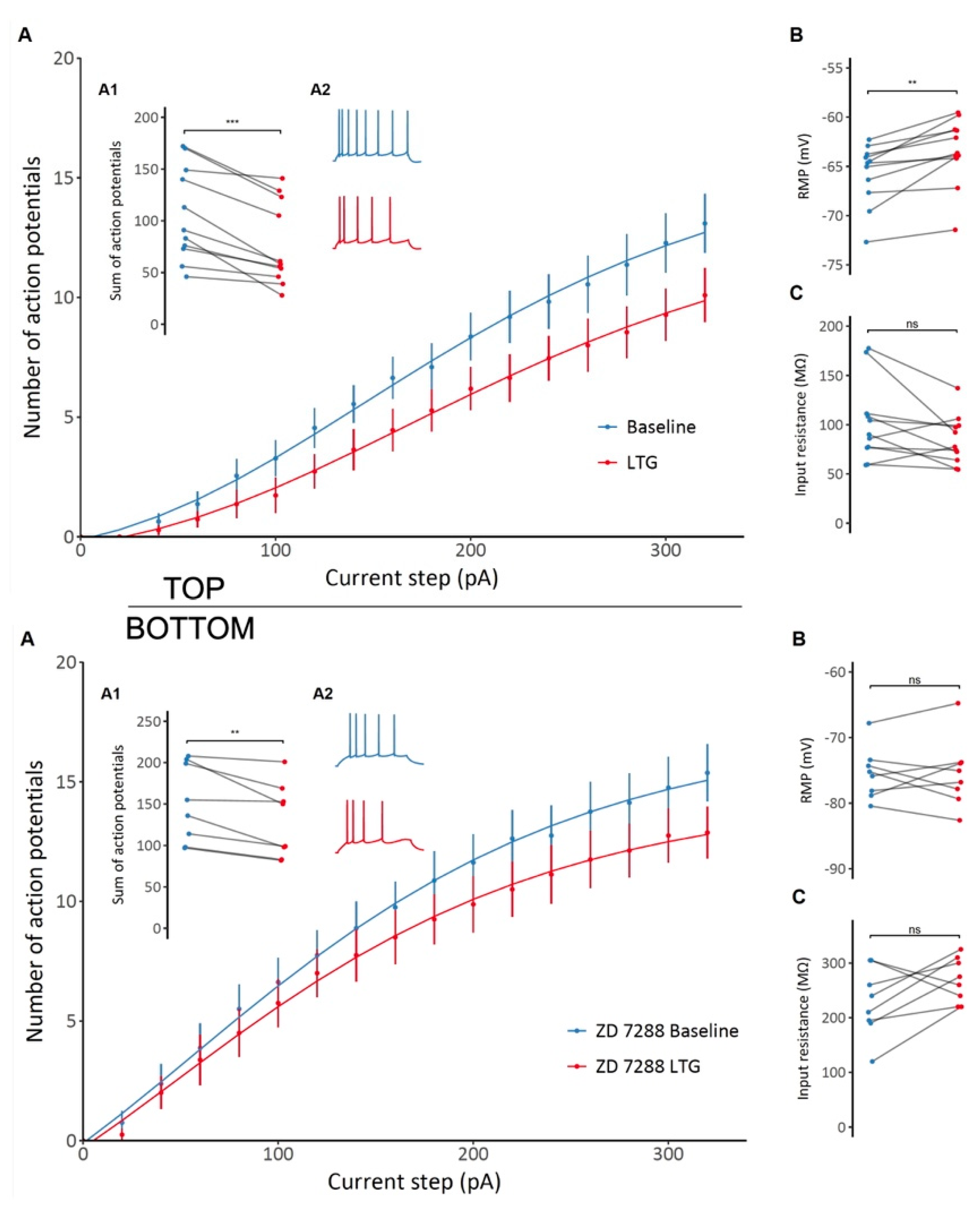
2.4. Effects of LTG on CA1 Pyramidal Neuron Excitability and Passive Membrane Properties
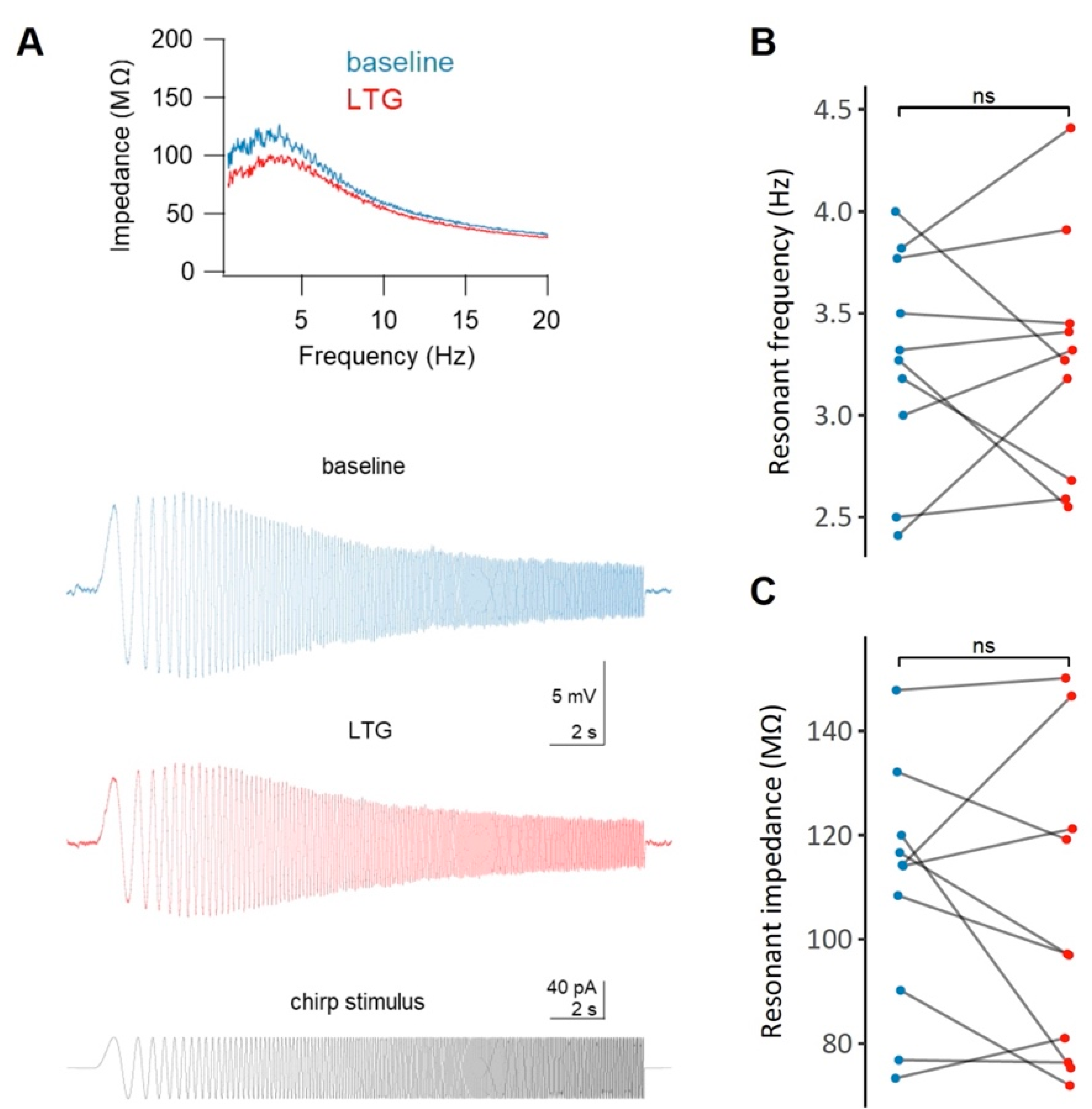
2.5. Effects of LTG on the Resonant Properties of CA1 Neurons
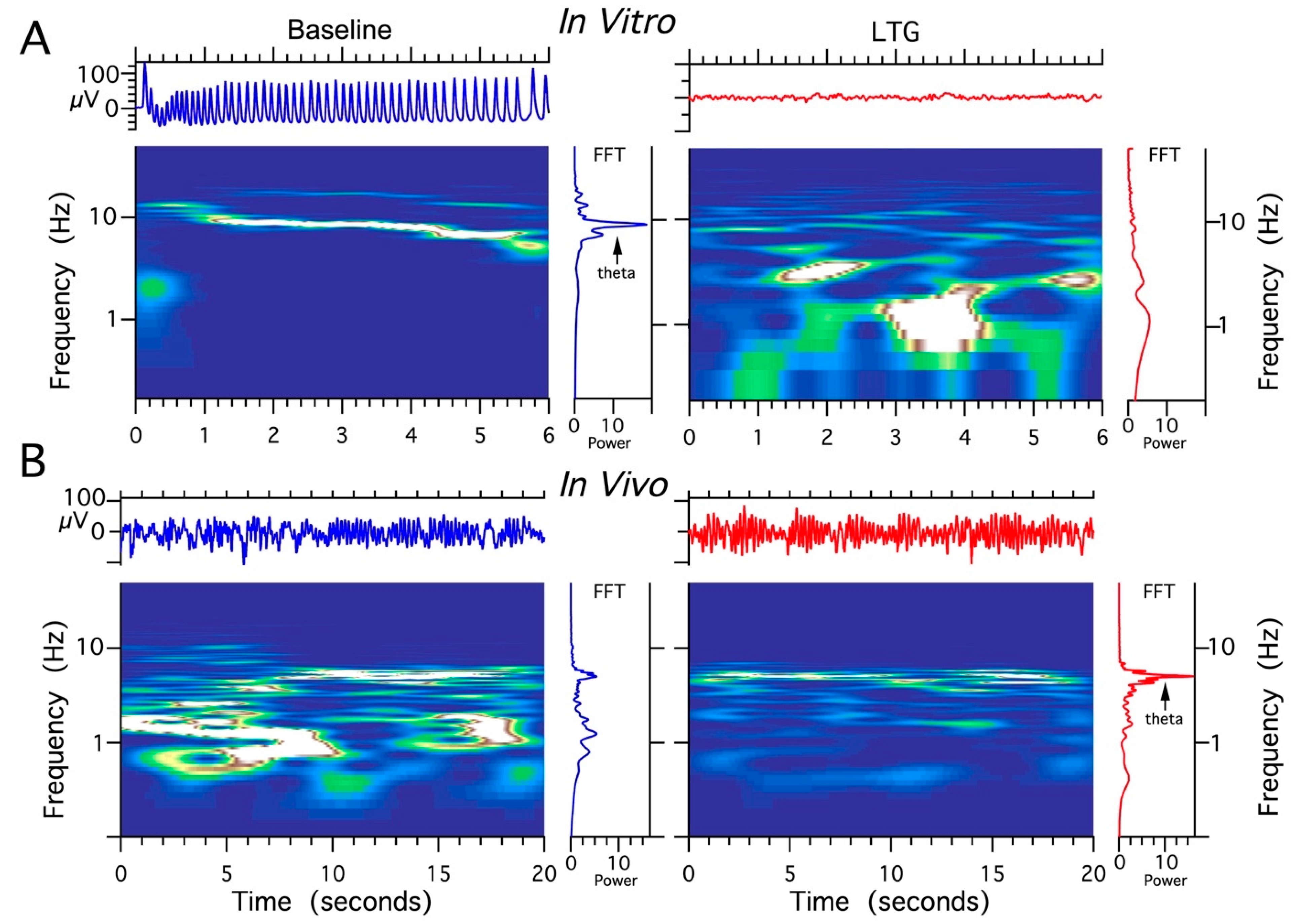
2.6. Effect of LTG, ZD 7288, and the Combined Infusion on Cholinergically Induced Hippocampal Theta Oscillations In Vitro
2.7. Effect of LTG, ZD 7288, and a Combined Infusion on Spontaneous Hippocampal THETA Rhythm Recorded In Vivo
3. Discussion
3.1. LTG Reduces Spontaneous GABAergic Synaptic Activity in CA3c, with No Effect on CA1
Pyramidal Cells
3.2. LTG Attenuates Membrane Excitability and Depolarizes the Resting Membrane Potential of CA1 Pyramidal Neurons with No Effect on Membrane Resonant Properties
3.3. LTG at a Concentration of 4 μg/μL Enhances Hippocampal Theta Oscillations In Vivo
3.4. LTG Diminishes Hippocampal Theta Oscillations In Vitro
3.5. Summary Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patch Clamp Electrophysiology
4.1.1. Tissue Preparation for Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Recordings
4.1.2. Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Recordings
4.1.3. Recording and Detection of Spontaneous Inhibitory Postsynaptic Currents
4.1.4. Whole-Cell Current-Clamp Recordings of CA1 Pyramidal Neurons
Synaptic Blockers
Excitability and Passive Membrane Properties
Membrane Potential Resonance
4.1.5. Patch Clamp Data Analysis and Statistics
4.2. In Vitro Local Field Potentials (LFPs) Recordings
4.2.1. Subjects and Procedure
4.2.2. Recording Technique, Data Acquisition and Data Analysis
4.3. In Vivo Local Field Potentials (LFPs) Recordings
4.3.1. Subjects and Surgical Procedure
4.3.2. Hippocampal Electrode Implantation and Local Field Potential Recording
4.3.3. Hippocampal Cannula Implantation and Injections
4.3.4. Experimental Procedure
4.3.5. Recording Procedure and Data Analysis
4.3.6. Histological Procedure
4.3.7. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bland, B.H.; Colom, L.V. Extrinsic and intrinsic properties underlying oscillation and synchrony in limbic cortex. Prog. Neurobiol. 1993, 41, 157–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, B.H.; Oddie, S.D. Theta band oscillation and synchrony in the hippocampal formation and associated structures: The case for its role in sensorimotor integration. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 127, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsáki, G. Theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Neuron 2002, 33, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Bocian, R.; Konopacki, J. The generation of theta rhythm in hippocampal formation maintained in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 679–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNaughton, N.; Kocsis, B.; Hajós, M. Elicited hippocampal theta rhythm: A screen for anxiolytic and procognitive drugs through changes in hippocampal function? Behav. Pharmacol. 2007, 18, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Kandel, E.R. Theta frequency stimulation induces a local form of late phase LTP in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Learn. Mem. 2005, 12, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekstrom, A.D.; Caplan, J.B.; Ho, E.; Shattuck, K.; Fred, I.; Kahana, M.J. Human hippocampal theta activity during virtual navigation. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.M.; Lucchi, C.; Simonini, C.; Rosal Lustosa, Í.; Biagini, G. Status Epilepticus Dynamics Predicts Latency to Spontaneous Seizures in the Kainic Acid Model. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 54, 493–507. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, B.H.; Konopacki, J.; Dyck, R. Heterogeneity among hippocampal pyramidal neurons revealed by their relation to theta-band oscillation and synchrony. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 195, 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, B.H.; Konopacki, J.; Dyck, R.H. Relationship between membrane potential oscillations and rhythmic discharges in identified hippocampal theta-related cells. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 3046–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colgin, L.L. Mechanisms and functions of theta rhythms. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 36, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Chen, F.; Li, B.; Hu, Z. Neurophysiology of HCN channels: From cellular functions to multiple regulations. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 112, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Li, S. In vivo contribution of h-channels in the septal pacemaker to theta rhythm generation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, R.B.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents: From molecules to physiological function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Núñez, A.; García-Austt, E.; Buño, W. Synaptic contributions to theta rhythm genesis in rat CA1-CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vivo. Brain Res. 1990, 533, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltesz, I.; Deschênes, M. Low- and high-frequency membrane potential oscillations during theta activity in CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons of the rat hippocampus under ketamine-xylazine anesthesia. J. Neurophysiol. 1993, 70, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylinen, A.; Soltész, I.; Bragin, A.; Penttonen, M.; Sik, A.; Buzsáki, G. Intracellular correlates of hippocampal theta rhythm in identified pyramidal cells, granule cells, and basket cells. Hippocampus 1995, 5, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.D.; Núñez, A.; García-Austt, E. In vivo intracellular analysis of rat dentate granule cells. Brain Res. 1990, 509, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukatch, H.S.; MacIver, M.B. Physiology, pharmacology, and topography of cholinergic neocortical oscillations in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 77, 2427–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.; Stieber, J.; Ludwig, A. Pathophysiology of HCN channels. Pflug. Arch. 2007, 454, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupica, C.R.; Bell, J.A.; Hoffman, A.F.; Watson, P.L. Contribution of the hyperpolarization-activated current (I(h)) to membrane potential and GABA release in hippocampal interneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postea, O.; Biel, M. Exploring HCN channels as novel drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poller, W.C.; Bernard, R.; Derst, C.; Weiss, T.; Madai, V.I.; Veh, R.W. Lateral habenular neurons projecting to reward-processing monoaminergic nuclei express hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotid-gated cation channels. Neuroscience 2011, 193, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, S.A.; Kempadoo, K.A.; Thuault, S.J.; Siegelbaum, S.A.; Kandel, E.R. Increased size and stability of CA1 and CA3 place fields in HCN1 knockout mice. Neuron 2011, 72, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nolan, M.F.; Malleret, G.; Dudman, J.T.; Buhl, D.L.; Santoro, B.; Gibbs, E.; Vronskaya, S.; Buzsáki, G.; Siegelbaum, S.A.; Kandel, E.R.; et al. A behavioral role for dendritic integration: HCN1 channels constrain spatial memory and plasticity at inputs to distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Cell 2004, 119, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varga, V.; Hangya, B.; Kránitz, K.; Ludányi, A.; Zemankovics, R.; Katona, I.; Shigemoto, R.; Freund, T.F.; Borhegyi, Z. The presence of pacemaker HCN channels identifies theta rhythmic GABAergic neurons in the medial septum. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 3893–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, R.A.; Soleymani, S.V.; Brewster, A.L.; Nguyen, S.T.; Bec, H.; Mathern, G.W.; Baram, T.Z. Enhanced expression of a specific hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel (HCN) in surviving dentate gyrus granule cells of human and experimental epileptic hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6826–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.M.; Ridsdale, L.; Richardson, M.P.; Ashworth, M.; Gulliford, M.C. Trends in antiepileptic drug utilisation in UK primary care 1993–2008: Cohort study using the General Practice Research Database. Seizure 2012, 21, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Premoli, I.; Costantini, A.; Rivolta, D.; Biondi, A.; Richardson, M.P. The effect of lamotrigine and levetiracetam on TMS-Evoked EEG responses depends on stimulation intensity. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, H.; Kamp, D.; Harris, E. An in vitro investigation of the action of lamotrigine on neuronal voltage-activated sodium channels. Epilepsy Res. 1992, 13, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poolos, N.P.; Migliore, M.; Johnston, D. Pharmacological upregulation of h-channels reduces the excitability of pyramidal neuron dendrites. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, A.; Stewart, H.; Schulzer, M.; Cameron, D. Anti-glutamate therapy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A trial using lamotrigine. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 20, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, S.; Aykut-Bingöl, C.; Tanridağ, T.; Aktan, S. Antiglutamatergic therapy in Alzheimer’s disease—Effects of lamotrigine. Short communication. J. Neural Transm. 1998, 105, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.M.; Kim, T.; Vargas, E.; Petrou, S.; Reid, C.A. Spike-and-wave discharge mediated reduction in hippocampal HCN1 channel function associates with learning deficits in a genetic mouse model of epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 64, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omrani, A.; van der Vaart, T.; Mientjes, E.; van Woerden, G.M.; Hojjati, M.R.; Li, K.W.; Gutmann, D.H.; Levelt, C.N.; Smit, A.B.; Silva, A.J.; et al. HCN channels are a novel therapeutic target for cognitive dysfunction in Neurofibromatosis type 1. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, S.W.; Jia, F.; Abbas, S.Y.; Hofmann, F.; Ludwig, A.; Goldstein, P.A. Dendritic HCN2 channels constrain glutamate-driven excitability in reticular thalamic neurons. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8719–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Lee, C.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, M.L.; Yang, Y.P.; Chang, K.Y.; Chiou, S.H. Revisiting the lamotrigine-mediated effect on hippocampal GABAergic transmission. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zemankovics, R.; Káli, S.; Paulsen, O.; Freund, T.F.; Hájos, N. Differences in subthreshold resonance of hippocampal pyramidal cells and interneurons: The role of h-current and passive membrane characteristics. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 2109–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Yi, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, K.; Kang, S.J.; Shin, K.S. HCN channel activity-dependent modulation of inhibitory synaptic transmission in the rat basolateral amygdala. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.N.; Wang, Y.; He, S.M.; Wang, X.L.; Zhu, J.L.; Gao, G.D. SK- and h-current contribute to the generation of theta-like resonance of rat substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons at hyperpolarized membrane potentials. Brain Struct. Funct. 2012, 217, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.W.; Chapman, C.A. Contribution of Ih to the relative facilitation of synaptic responses induced by carbachol in the entorhinal cortex during repetitive stimulation of the parasubiculum. Neuroscience 2014, 278, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raus Balind, S.; Magó, Á.; Ahmadi, M.; Kis, N.; Varga-Németh, Z.; Lőrincz, A.; Makara, J.K. Diverse synaptic and dendritic mechanisms of complex spike burst generation in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strange, B.A.; Witter, M.P.; Lein, E.S.; Moser, E.I. Functional organization of the hippocampal longitudinal axis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Netsyk, O.; Hammoud, H.; Korol, S.V.; Jin, Z.; Tafreshiha, A.S.; Birnir, B. Tonic GABA-activated synaptic and extrasynaptic currents in dentate gyrus granule cells and CA3 pyramidal neurons along the mouse hippocampal dorsoventral axis. Hippocampus 2020, 30, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIver, M.B.; Harris, D.P.; Konopacki, J.; Roth, S.H.; Bland, B.H. Carbachol induced rhythmical slow wave activity recorded from dentate granule neurons in vitro. Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. 1986, 29, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konopacki, J.; Gołębiewski, H.; Eckersdorf, B.; Kowalczyk, T.; Bocian, R. In vitro recorded theta-like activity in the limbic cortex: Comparison with spontaneous theta and epileptiform discharges. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2000, 60, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, B.H.; Bland, C.E.; MacIver, M.B. Median raphe stimulation-induced motor inhibition concurrent with suppression of type 1 and type 2 hippocampal theta. Hippocampus 2016, 26, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sceniak, M.P.; Maciver, M.B. Cellular actions of urethane on rat visual cortical neurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papatheodoropoulos, C.; Asprodini, E.; Nikita, I.; Koutsona, C.; Kostopoulos, G. Weaker synaptic inhibition in CA1 region of ventral compared to dorsal rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 2002, 948, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, R.A.; Brewster, A.; Santoro, B.; Ludwig, A.; Hofmann, F.; Biel, M.; Baram, T.Z. Differential and age-dependent expression of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel isoforms 1-4 suggests evolving roles in the developing rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2001, 106, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brewster, A.; Bender, R.A.; Chen, Y.; Dube, C.; Eghbal-Ahmadi, M.; Baram, T.Z. Developmental febrile seizures modulate hippocampal gene expression of hyperpo-larization-activated channels in an isoform- and cell-specific manner. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 4591–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, B.; Chen, S.; Luthi, A.; Pavlidis, P.; Shumyatsky, G.P.; Tibbs, G.R.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Molecular and functional heterogeneity of hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channels in the mouse CNS. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 5264–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Antuono, M.; Benini, R.; Biagini, G.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Barbarosie, M.; Tancredi, V.; Avoli, M. Limbic network interactions leading to hyperexcitability in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuccio, G.; D’Antuono, M.; de Guzman, P.; De Lannoy, L.; Biagini, G.; Avoli, M. In vitro ictogenesis and parahippocampal networks in a rodent model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 39, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, B.W.; Justice, J.A.; Zhang, K.; He, X.H.; Sanchez, R.M. Increased basal synaptic inhibition of hippocampal area CA1 pyramidal neurons by an antiepileptic drug that enhances I(h). Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, H.; Seol, M.J.; Lee, K. Differential expression of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel subunits during hippocampal development in the mouse. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasilyev, D.V.; Barish, M.E. Postnatal development of the hyperpolarization-activated excitatory current Ih in mouse hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8992–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, M.J.; Marden, C.M.; Miller, A.A. Pharmacological studies on lamotrigine, a novel potential antiepileptic drug: II. Neurochemical studies on the mechanism of action. Epilepsia 1986, 27, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossel, K.A.; Beagle, A.J.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Shu, H.; Lee, S.E.; Naasan, G.; Hegde, M.; Cornes, S.B.; Henry, M.L.; Nelson, A.B.; et al. Seizures and epileptiform activity in the early stages of Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K. Mechanisms for the resonant property in rodent neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 156, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopacki, J.; Gołębiewski, H. Theta-like activity in hippocampal formation slices: Cholinergic–GABAergic interaction. Neuroreport 1993, 4, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopacki, J.; Gołębiewski, H.; Eckersdorf, B.; Błaszczyk, M.; Grabowski, R. Theta-like activity in hippocampal formation slices: The effect of strong disinhibition of GABAA and GABAB receptors. Brain Res. 1997, 775, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, V.H.; Bland, B.H. The role of the septohippocampal pathway in the regulation of hippocampal field activity and behavior: Analysis by the intraseptal microinfusion of carbachol, atropine, and procaine. Exp. Neurol. 1993, 120, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.G.; Chrobak, J.J.; Sik, A.; Wiley, R.G.; Buzsáki, G. Hippocampal theta activity following selective lesion of the septal cholinergic system. Neuroscience 1994, 62, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smythe, J.W.; Colom, L.V.; Bland, B.H. The extrinsic modulation of hippocampal theta depends on the coactivation of cholinergic and GABA-ergic medial septal inputs. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1992, 16, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Bragin, A.; Buzsáki, G. Interdependence of multiple theta generators in the hippocampus: A partial coherence analysis. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6200–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Gołebiewski, H.; Konopacki, J. Is the dentate gyrus an independent generator of in vitro recorded theta rhythm? Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemond, P.; Epstein, D.; Boley, A.; Migliore, M.; Ascoli, G.A.; Jaffe, D.B. Distinct classes of pyramidal cells exhibit mutually exclusive firing patterns in hippocampal area CA3b. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Aradi, I.; Thon, N.; Eghbal-Ahmadi, M.; Baram, T.Z.; Soltesz, I. Persistently modified h-channels after complex febrile seizures convert the seizure-induced enhancement of inhibition to hyperexcitability. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.S.; Chetkovich, D.M. HCN channels in behavior and neurological disease: Too hyper or not active enough? Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2011, 46, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, C.T.; Magistretti, J.; Shalinsky, M.H.; Fransén, E.O.; Hasselmo, M.E.; Alonso, A. Properties and role of I(h) in the pacing of subthreshold oscillations in entorhinal cortex layer II neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 2562–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maccaferri, G.; McBain, C.J. The hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) and its contribution to pacemaker activity in rat CA1 hippocampal stratum oriens-alveus interneurones. J. Physiol. 1996, 497, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Aihara, T.; Tsukada, M. Phase shift of subthreshold theta oscillation in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell membrane by excitatory synaptic inputs. Neuroscience 2006, 140, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.; Narayanan, R. HCN channels enhance spike phase coherence and regulate the phase of spikes and LFPs in the theta-frequency range. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2207–E2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, S.P.; Johnston, D. Temporal synchrony and gamma-to-theta power conversion in the dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1812–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahnsen, H.; Llinas, R. Ionic basis for the electro-responsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones in vitro. J. Physiol. 1984, 349, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotty, F.; Danik, M.; Manseau, F.; Laplante, F.; Quirion, R.; Williams, S. Distinct electrophysiological properties of glutamatergic, cholinergic and GABAergic rat septohippocampal neurons: Novel implications for hippocampal rhythmicity. J. Physiol. 2003, 551, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Vervaeke, K.; Storm, J.F. Two forms of electrical resonance at theta frequencies, generated by M-current, h-current and persistent Na+ current in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J. Physiol. 2002, 545, 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, F.G.; Goddard, R.S.; Suckling, J.M.; Ganter, P.; Kasthuri, N.; Paulsen, O. Distinct frequency preferences of different types of rat hippocampal neurones in response to oscillatory input currents. J. Physiol. 2000, 529, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, W.H. Membrane properties of cell types within guinea pig basal forebrain nuclei in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 1988, 59, 1590–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, N.P.; Harris, S.J.; Henderson, Z. Parvalbumin-immunoreactive, fast spiking neurons in the medial septum⁄diagonal band complex of the rat: Intracellular recordings in vitro. Neuroscience 1999, 92, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Datta, S.; Wu, M.; Alreja, M. Hippocampal theta rhythm is reduced by suppression of the H-current in septohippocampal GABAergic neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antuono, M.; Inaba, Y.; Biagini, G.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Tancredi, V.; Avoli, M. Synaptic hyperexcitability of deep layer neocortical cells in a genetic model of absence seizures. Genes Brain Behav. 2006, 5, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inaba, Y.; Biagini, G.; Avoli, M. The H current blocker ZD7288 decreases epileptiform hyperexcitability in the rat neocortex by depressing synaptic transmission. Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, M.F.; Dudman, J.T.; Dodson, P.D.; Santoro, B. HCN1 channels control resting and active integrative properties of stellate cells from layer II of the entorhinal cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12440–12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.Y.; Fu, W.M.; Chen, C.C.; Su, M.J.; Liou, H.H. Lamotrigine inhibits postsynaptic AMPA receptor and glutamate release in the dentate gyrus. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierska, P.; Konopacki, J. Development of NMDA-induced theta rhythm in hippocampal formation slices. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 98, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, B.E.; Reid, C.A.; Myers, D.; Ng, C.; Powell, K.; Phillips, A.M.; Zheng, T.; O’Brien, T.J.; Williams, D.A. Excitotoxic-mediated transcriptional decreases in HCN2 channel function increase network excitability in CA1. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 219, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorincz, A.; Notomi, T.; Tamas, G.; Shigemoto, R.; Nusser, Z. Polarized and compartment-dependent distribution of HCN1 in pyramidal cell dendrites. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, J.C. Dendritic lh normalizes temporal summation in hippocampal CA1. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.R.; Stuart, G.J. Site independence of EPSP time course is mediated by dendritic I(h) in neocortical pyramidal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 3177–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodin, E.A.; Rim, C.S.; Kitano, H.; Lewis, R.; Rennick, P.M. A comparison of the effectiveness of primidone versus carbamazepine in epileptic outpatients. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1976, 163, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilifar, M.; Yadollahpour, A.; Moazedi, A.A.; Ghotbeddin, Z. Quantitative analysis of the antiepileptogenic effects of low frequency stimulation applied prior or after kindling stimulation in rats. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paxinos, C.; Watson, G. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D. Ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggplot2 (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. Dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Ritz, C.; Strebig, J.C. Drc: Analysis of Dose-Response Curves. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=drc (accessed on 12 January 2021).

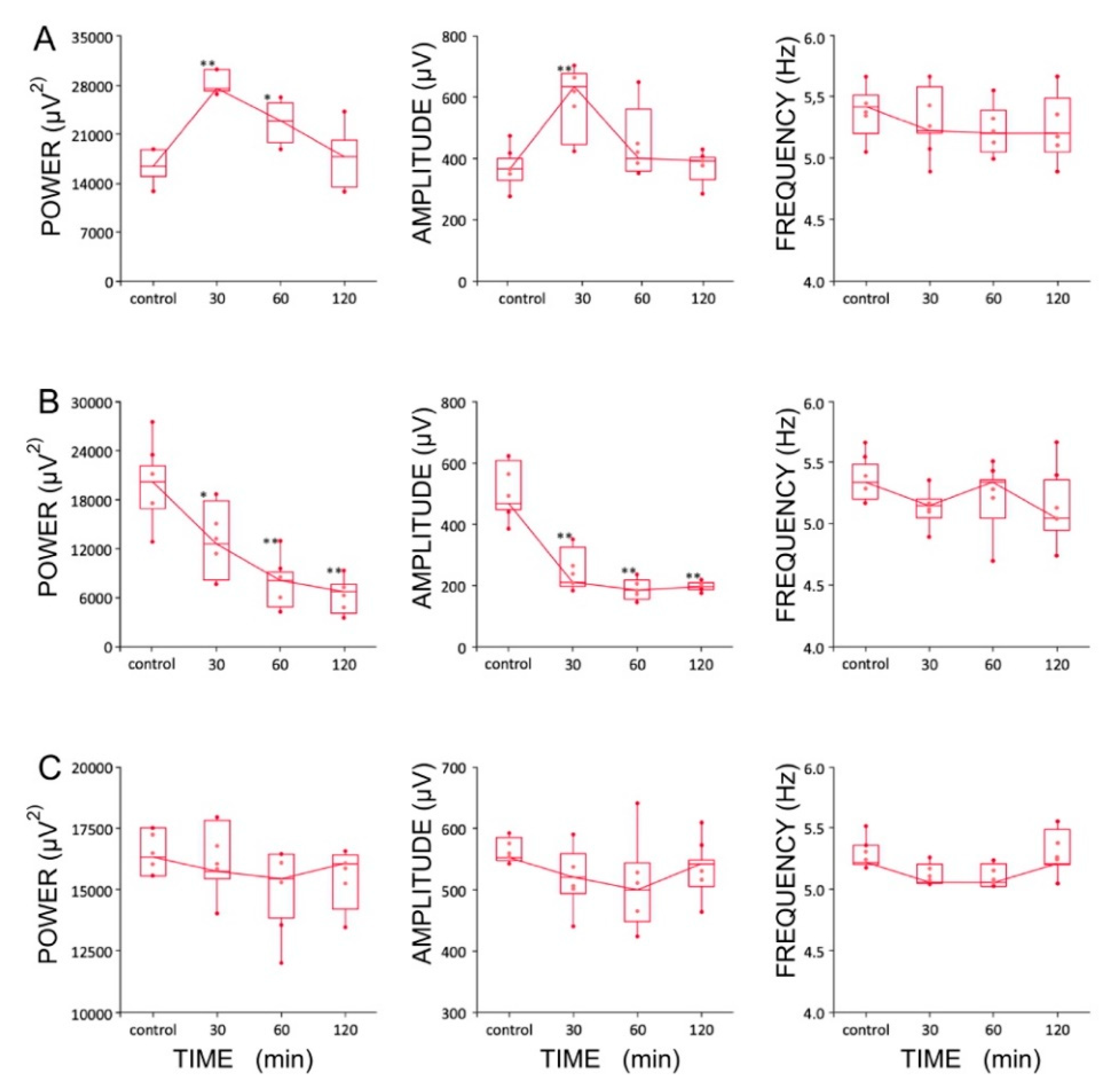
| Parameters of Theta Rhythm | Groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I LTG 4 µg/1 µL | Group II LTG 6 µg/1 µL | Group III ZD7288 4 µg/1 µL | Group IV ZD7288 4 µg/1 µL + LTG 4 µg/ 1 µL | |||
| preinjection | (control) | power (μV2) | 16,396.2 (14,969.0, 18,789.1) | 17,233.2 (15,846.6, 23,448.4) | 20,023.1 (16,914.2, 22,104.3) | 16,334.5 (15,567.1, 17,532.8) |
| amplitude (μV) | 565.5 (527.2, 598.3) | 554.6 (487.2, 602.4) | 468.8 (449.6, 609.1) | 552.2 (547.6, 585,1) | ||
| frequency (Hz) | 5.4 (5.2, 5.5) | 5.2 (5.1, 5.2) | 5.3 (5.2, 5.5) | 5.2 (5.2, 5.4) | ||
| postinjection | 30 min | power (μV2) | 27,502.8 (27,215.2, 30,145.6) p < 0.001 | 5125.5 (4264.8, 5383.1) p < 0.001 | 12,604.7 (8150.6, 17,800.0) p < 0.01 | 15,752.3 (15,444.6, 17,843.5) |
| amplitude (μV) | 833.2 (646.0, 874.6) p < 0.001 | 299.3 (287.2, 310.6) p < 0.001 | 210.4 (197.6, 325.5) p < 0.001 | 520.4 (493.3, 559.1) | ||
| frequency (Hz) | 5.2 (5.2, 5.6) | 5.1 (5.1, 5.2) | 5.1 (5.0, 5.2) | 5,1 (5.1, 5.2) | ||
| 60 min | power (μV2) | 22,903.4 (19,791.6, 25,458.7) p < 0.01 | 4854.2 (4684.6, 4978.5) p < 0.001 | 8160.7 (4880.0, 9121.9) p < 0.001 | 15,461.6 (13,852.4, 16,455.2) | |
| amplitude (μV) | 598.6 (557.4, 760.1) | 275.4 (258.2, 280.7) p < 0.001 | 186.6 (155.4, 218.6) p < 0.001 | 500.2 (448.1, 554.0) | ||
| frequency (Hz) | 5.2 (5.1, 5.4) | 5.2 (5.1, 5.2) | 5.3 (5.0, 5.4) | 5,1 (5.0, 5.2) | ||
| 120 min | power (μV2) | 17,755.4 (13,413.3, 20,123.1) | 4807.6 (3988.4, 4993.8) p < 0.001 | 6802.0 (4134.1, 7634.5) p < 0.001 | 16,075.3 (14,224.8, 16,413.0) | |
| amplitude (μV) | 591.2 (530.0, 602.5) | 253.8 (242.6, 306.7) p < 0.001 | 197.3 (187.1, 209.2) p < 0.001 | 542.3 (505.4, 549.6) | ||
| frequency (Hz) | 5.2 (5.1, 5.5) | 5.2 (5.1, 5.4) | 5.0 (4.8, 5.4) | 5,2 (5.2, 5.5) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazmierska-Grebowska, P.; Siwiec, M.; Sowa, J.E.; Caban, B.; Kowalczyk, T.; Bocian, R.; MacIver, M.B. Lamotrigine Attenuates Neuronal Excitability, Depresses GABA Synaptic Inhibition, and Modulates Theta Rhythms in Rat Hippocampus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413604
Kazmierska-Grebowska P, Siwiec M, Sowa JE, Caban B, Kowalczyk T, Bocian R, MacIver MB. Lamotrigine Attenuates Neuronal Excitability, Depresses GABA Synaptic Inhibition, and Modulates Theta Rhythms in Rat Hippocampus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(24):13604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413604
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazmierska-Grebowska, Paulina, Marcin Siwiec, Joanna Ewa Sowa, Bartosz Caban, Tomasz Kowalczyk, Renata Bocian, and M. Bruce MacIver. 2021. "Lamotrigine Attenuates Neuronal Excitability, Depresses GABA Synaptic Inhibition, and Modulates Theta Rhythms in Rat Hippocampus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 24: 13604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413604
APA StyleKazmierska-Grebowska, P., Siwiec, M., Sowa, J. E., Caban, B., Kowalczyk, T., Bocian, R., & MacIver, M. B. (2021). Lamotrigine Attenuates Neuronal Excitability, Depresses GABA Synaptic Inhibition, and Modulates Theta Rhythms in Rat Hippocampus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(24), 13604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413604







