PEG Linker Length Strongly Affects Tumor Cell Killing by PEGylated Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors in Hypoxic Carcinomas Expressing Carbonic Anhydrase IX
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
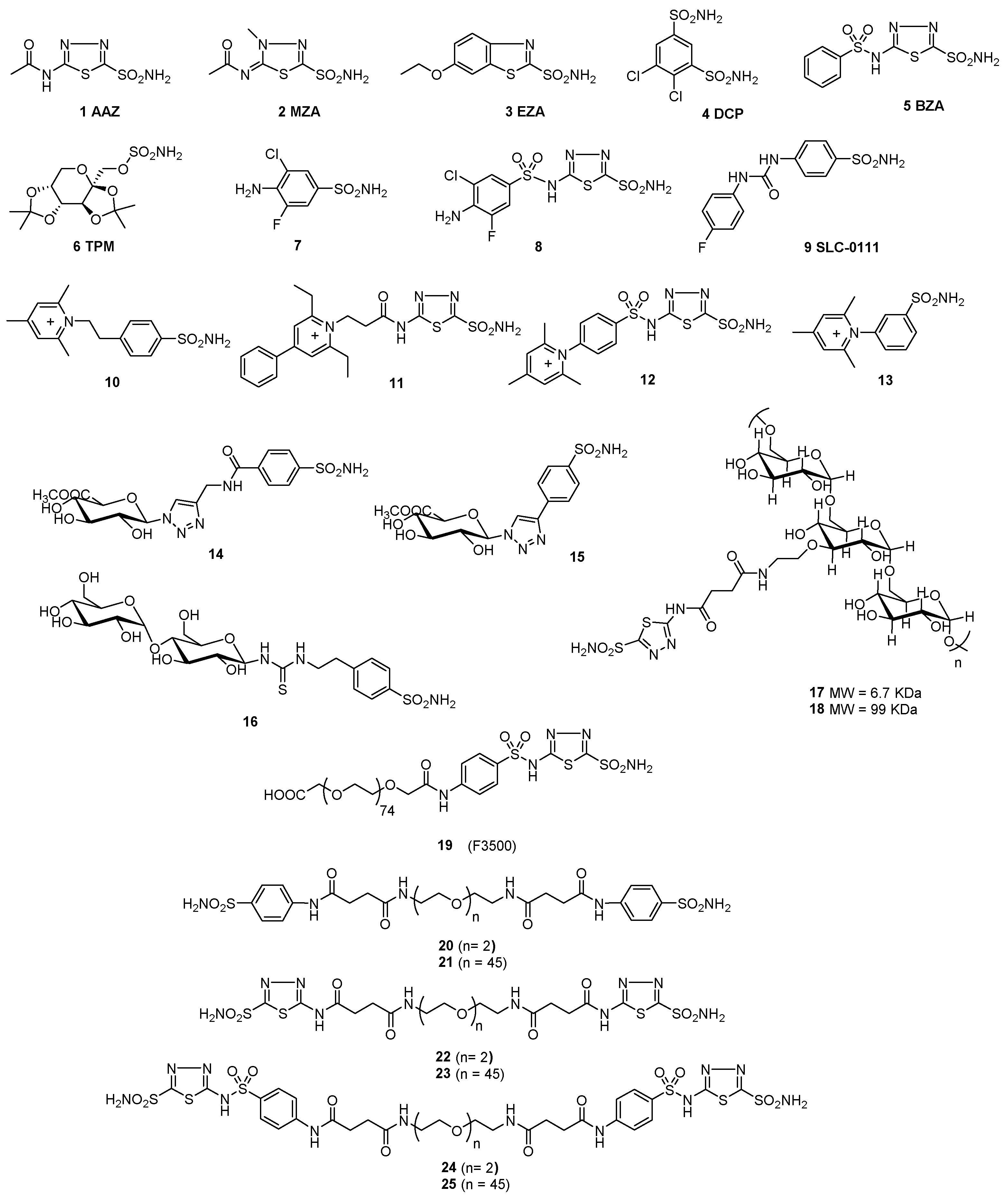
2.1. Synthesis of Polymeric CAIs
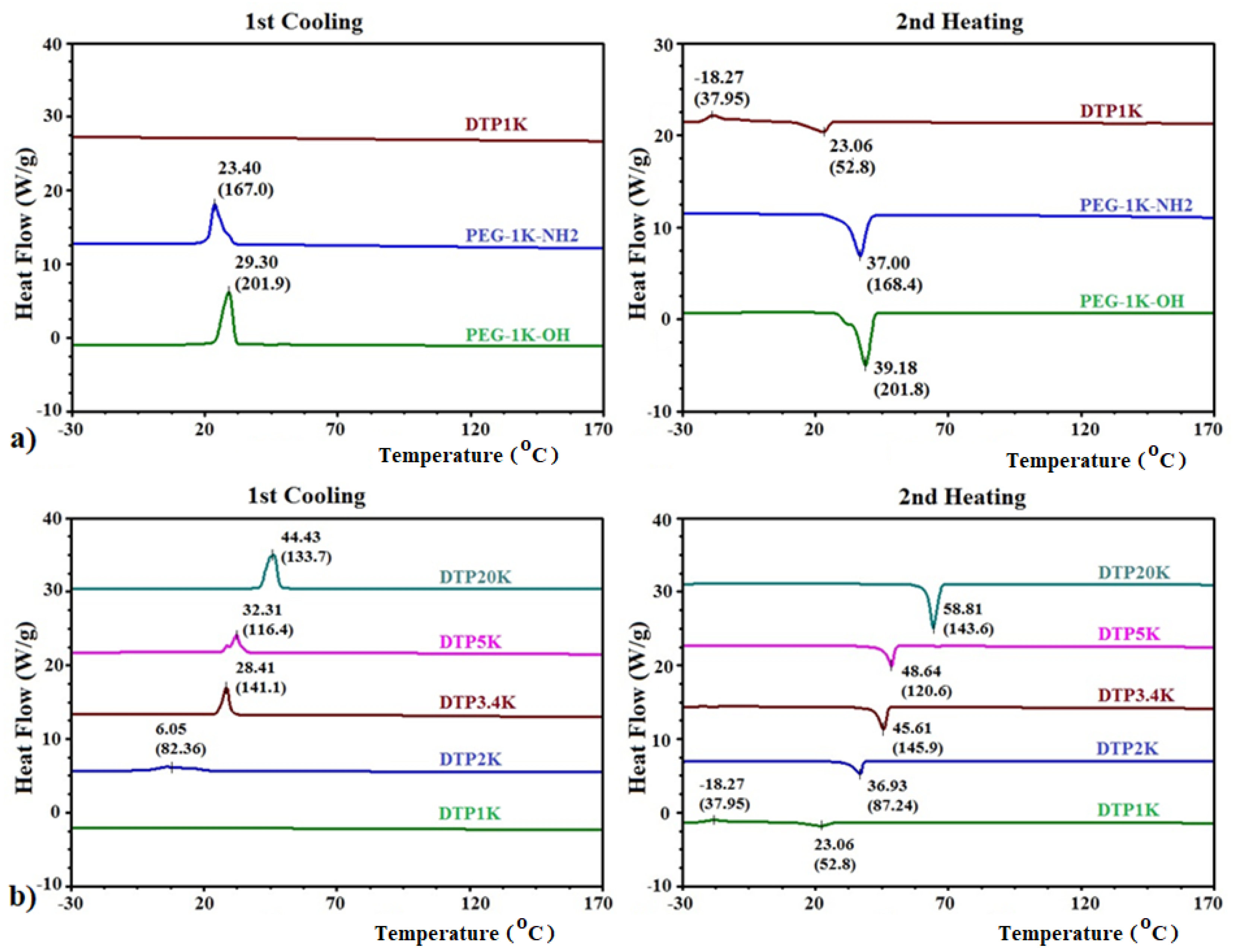
2.2. DSC Analysis of Polymeric CAIs
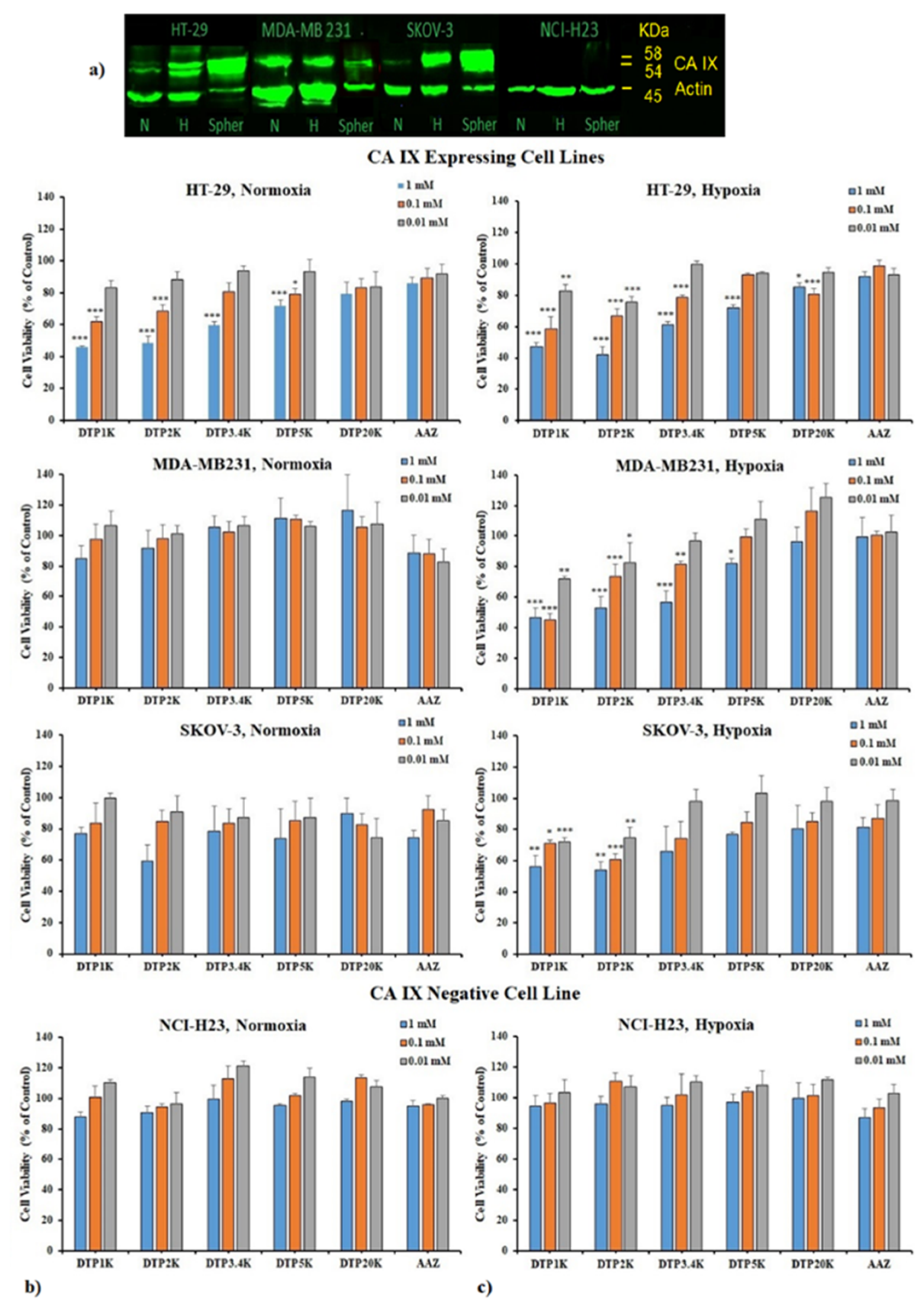
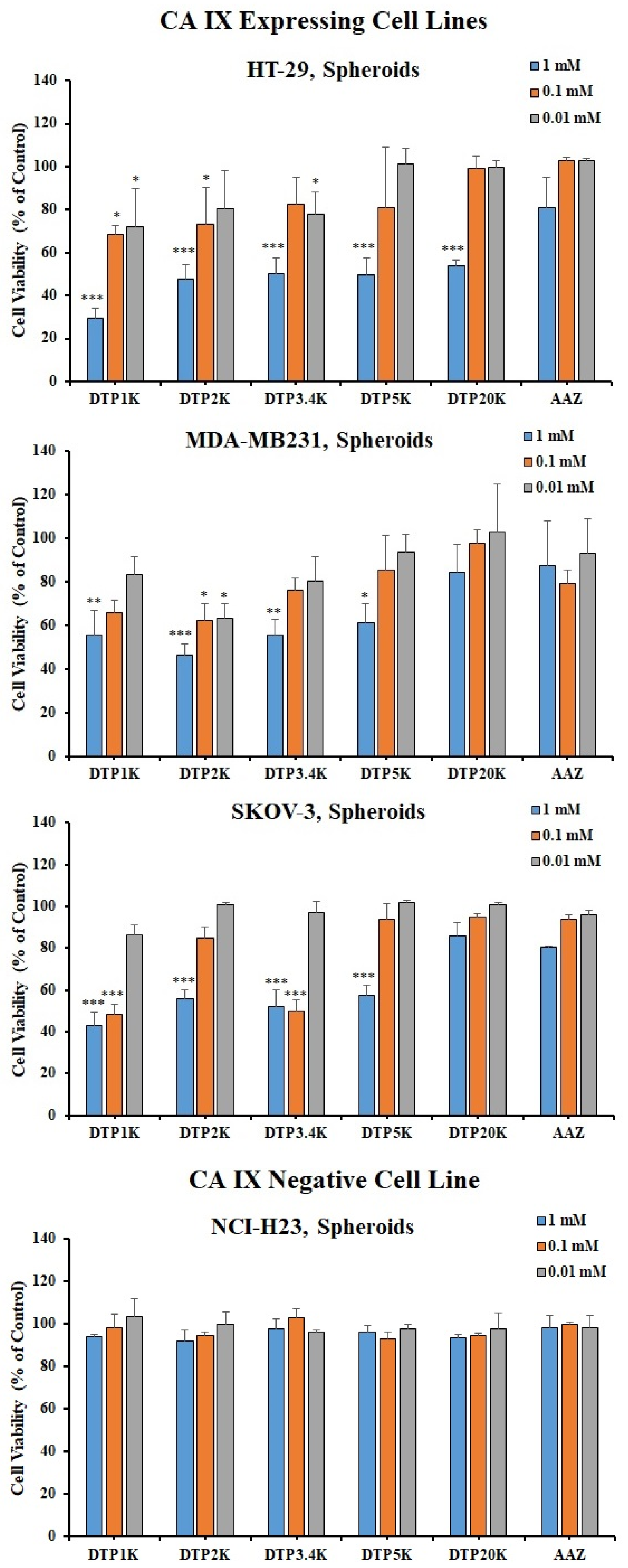
2.3. Biological Testing of Polymeric CAIs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of 4-oxo-4-((5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)Amino)Butanoic Acid 27
3.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of Bis-Sulfonamides 23 and 28–31
3.2.1. Bis-((5-Sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-amidosuccinyl)-polyethyleneglycol1000diamide (DTP1K) 28
3.2.2. Bis-(5-Sulfamoyl-(1,3,4)-thiadiazol-2-yl)-amidosuccinyl)-polyethyleneglycol2000diamide (DTP2K) 23
3.2.3. Bis-(5-Sulfamoyl-(1,3,4)-thiadiazol-2-yl)-amidosuccinyl)-polyethyleneglycol3400diamide (DTP3.4K) 29
3.2.4. Bis-(5-Sulfamoyl-(1,3,4)-thiadiazol-2-yl)-amidosuccinyl)-polyethyleneglycol5000diamide (DTP2K) 30
3.2.5. Bis-(5-Sulfamoyl-(1,3,4)-thiadiazol-2-yl)-amidosuccinyl)-polyethyleneglycol20000diamide (DTP2K) 31
3.3. Viability Evaluation in 2D Cell Cultures
3.4. Viability Evaluation in 3D Cell Cultures
3.5. CA IX Profiling Using Western Blotting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eales, K.L.; Hollinshead, K.E.; Tennant, D.A. Hypoxia and metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors: Mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia—A key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar]
- Neri, D.; Supuran, C.T. Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 767–777. [Google Scholar]
- Shabana, A.M.; Ilies, M.A. Drug Delivery to Hypoxic Tumors Targeting Carbonic Anhydrase IX. In Targeted Nanosystems for Therapeutic Applications: New Concepts, Dynamic Properties, Efficiency, and Toxicity; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 1309, pp. 223–252. [Google Scholar]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition and the Management of Hypoxic Tumors. Metabolites 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, R.A.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, U.K.; Ilies, M.A. Chapter 7—Efflux pumps, NHE1, monocarboxylate transporters, and ABC transporter subfamily inhibitors. In pH-Interfering Agents as Chemosensitizers in Cancer Therapy; Supuran, C.T., Carradori, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 10, pp. 95–120. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S. Hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX as a target for cancer therapy: From biology to clinical use. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, L.; Peeters, S.; Lieuwes, N.G.; Geusens, N.; Thiry, A.; Wigfield, S.; Carta, F.; McIntyre, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Dogne, J.M.; et al. Specific inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX activity enhances the in vivo therapeutic effect of tumor irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 99, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, B.P.; Pinard, M.A.; McKenna, R. Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX activity and expression. Molecules 2015, 20, 2323–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatovicova, M.; Jelenska, L.; Hulikova, A.; Csaderova, L.; Ditte, Z.; Ditte, P.; Goliasova, T.; Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S. Carbonic anhydrase IX as an anticancer therapy target: Preclinical evaluation of internalizing monoclonal antibody directed to catalytic domain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3255–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanova, S.; Shabana, A.M.; Mondal, U.K.; Ilies, M.A. Carbonic anhydrases as disease markers. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; McDonald, P.C.; Oloumi, A.; Chia, S.; Ostlund, C.; Ahmadi, A.; Kyle, A.; Auf dem Keller, U.; Leung, S.; Huntsman, D.; et al. Targeting tumor hypoxia: Suppression of breast tumor growth and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3364–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.C.; Winum, J.Y.; Supuran, C.T.; Dedhar, S. Recent developments in targeting carbonic anhydrase IX for cancer therapeutics. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Winum, J.-Y. Carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors in cancer therapy: An update. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, A.M.; Mondal, U.K.; Alam, M.R.; Spoon, T.; Ross, C.A.; Madesh, M.; Supuran, C.T.; Ilies, M.A. pH-Sensitive Multi-ligand Gold Nanoplatform Targeting Carbonic Anhydrase IX Enhances the Delivery of Doxorubicin to Hypoxic Tumor Spheroids and Overcomes the Hypoxia-Induced Chemoresistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17792–17808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mboge, M.Y.; Mahon, B.P.; McKenna, R.; Frost, S.C. Carbonic Anhydrases: Role in pH Control and Cancer. Metabolites 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilies, M.A.; Vullo, D.; Pastorek, J.; Scozzafava, A.; Ilies, M.; Caproiu, M.T.; Pastorekova, S.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of tumor-associated isozyme IX by halogenosulfanilamide and halogenophenylaminobenzolamide derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Di Fiore, A.; D’Ambrosio, K.; Supuran, C.T.; De Simone, G. Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases: How to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4421–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist? J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akocak, S.; Ilies, M.A. Next-generation primary sulfonamide carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. In Targeting Carbonic Anhydrases; Supuran, C.T., Capasso, C., Eds.; Future Science: London, UK, 2014; pp. 35–51. [Google Scholar]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, V.M.; Kaufman, G.K.; Urbach, A.R.; Gitlin, I.; Gudiksen, K.L.; Weibel, D.B.; Whitesides, G.M. Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 946–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Ilies, M.A.; Scozzafava, A. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors—Part 29 1: Interaction of isozymes I, II and IV with benzolamide-like derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 33, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A.; Ilies, M.A.; Iorga, B.; Cristea, T.; Briganti, F.; Chiraleu, F.; Banciu, M.D. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors—Part 53—Synthesis of substituted-pyridinium derivatives of aromatic sulfonamides: The first non-polymeric membrane-impermeable inhibitors with selectivity for isozyme IV. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 33, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Mincione, F.; Menabuoni, L.; Ilies, M.A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: Water-Soluble 4-Sulfamoylphenylthioureas as Topical Intraocular Pressure-Lowering Agents with Long-Lasting Effects. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4884–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scozzafava, A.; Briganti, F.; Ilies, M.A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis of membrane-impermeant low molecular weight sulfonamides possessing in vivo selectivity for the membrane-bound versus cytosolic isozymes. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.R.; Morgan, P.E.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Mastrolorenzo, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Design of Selective, Membrane-Impermeant Inhibitors Targeting the Human Tumor-Associated Isozyme IX. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akocak, S.; Güzel-Akdemir, Ö.; Kishore Kumar Sanku, R.; Russom, S.S.; Iorga, B.I.; Supuran, C.T.; Ilies, M.A. Pyridinium derivatives of 3-aminobenzenesulfonamide are nanomolar-potent inhibitors of tumor-expressed carbonic anhydrase isozymes CA IX and CA XII. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 103, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winum, J.Y.; Colinas, P.A.; Supuran, C.T. Glycosidic carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors: A sweet approach against cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, B.L.; Bornaghi, L.F.; Houston, T.A.; Innocenti, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Poulsen, S.A. A novel class of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Glycoconjugate benzene sulfonamides prepared by “click-tailing”. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6539–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaine, F.Z.; Winum, J.Y.; Montero, J.L.; Regainia, Z.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Selective inhibition of the extracellular, tumor-associated isoforms IX and XII over isozymes I and II with glycosyl-thioureido-sulfonamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5096–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, B.L.; Innocenti, A.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Poulsen, S.A. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrases with glycosyltriazole benzene sulfonamides. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C.; Chiche, J.; Grellier, C.; Lopez, M.; Bornaghi, L.F.; Maresca, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Pouyssegur, J.; Poulsen, S.A. Targeting hypoxic tumor cell viability with carbohydrate-based carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6905–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touisni, N.; Maresca, A.; McDonald, P.C.; Lou, Y.; Scozzafava, A.; Dedhar, S.; Winum, J.Y.; Supuran, C.T. Glycosyl coumarin carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors strongly attenuate the growth of primary breast tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8271–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanpure, R.P.; Ren, B.; Peat, T.S.; Bornaghi, L.F.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Poulsen, S.A. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors with dual-tail moieties to match the hydrophobic and hydrophilic halves of the carbonic anhydrase active site. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinker, J.P.; Coulson, R.; Weiner, I.M. Dextran-bound inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1981, 218, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maren, T.H.; Conroy, C.W.; Wynns, G.C.; Godman, D.R. Renal and Cerebrospinal Fluid Formation Pharmacology of a High Molecular Weight Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A.; Ilies, M.A.; Briganti, F. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: Synthesis of Sulfonamides Incorporating 2,4,6-Trisubstituted-Pyridinium-Ethylcarboxamido Moieties Possessing Membrane-Impermeability and in Vivo Selectivity for the Membrane-Bound (CA IV) Versus the Cytosolic (CA I and CA II) Isozymes. J. Enzym. Inhib. 2000, 15, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winum, J.-Y.; Casini, A.; Mincione, F.; Starnotti, M.; Montero, J.-L.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: N-(p-sulfamoylphenyl)-α-d-glycopyranosylamines as topically acting antiglaucoma agents in hypertensive rabbits. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilies, M.A.; Winum, J.-Y. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors for the treatment of tumors: Therapeutic, immunologic, and diagnostic tools targeting isoforms IX and XII. In Carbonic Anhydrases; Supuran, C.T., Nocentini, A., Eds.; Elsevier; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 331–365. [Google Scholar]
- Veronese, F.M.; Mero, A. The impact of PEGylation on biological therapies. BioDrugs Clin. Immunother. Biopharm. Gene Ther. 2008, 22, 315–329. [Google Scholar]
- Whittington, D.A.; Waheed, A.; Ulmasov, B.; Shah, G.N.; Grubb, J.H.; Sly, W.S.; Christianson, D.W. Crystal structure of the dimeric extracellular domain of human carbonic anhydrase XII, a bitopic membrane protein overexpressed in certain cancer tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9545–9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Hilvo, M.; Di Fiore, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Pan, P.; Parkkila, S.; Scaloni, A.; Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S.; Pedone, C.; et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the tumor-associated human carbonic anhydrase IX. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16233–16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akocak, S.; Alam, M.R.; Shabana, A.M.; Sanku, R.K.; Vullo, D.; Thompson, H.; Swenson, E.R.; Supuran, C.T.; Ilies, M.A. PEGylated Bis-Sulfonamide Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Can Efficiently Control the Growth of Several Carbonic Anhydrase IX-Expressing Carcinomas. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5077–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafreshi, N.K.; Lloyd, M.C.; Bui, M.M.; Gillies, R.J.; Morse, D.L. Carbonic anhydrase IX as an imaging and therapeutic target for tumors and metastases. Subcell. Biochem. 2014, 75, 221–254. [Google Scholar]
- Tafreshi, N.K.; Lloyd, M.C.; Proemsey, J.B.; Bui, M.M.; Kim, J.; Gillies, R.J.; Morse, D.L. Evaluation of CAIX and CAXII Expression in Breast Cancer at Varied O2 Levels: CAIX is the Superior Surrogate Imaging Biomarker of Tumor Hypoxia. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.L.; Chu, J.S.; Su, W.C.; Huang, S.C.; Lee, W.Y. Hypoxia and metabolic phenotypes during breast carcinogenesis: Expression of HIF-1alpha, GLUT1, and CAIX. Virchows Arch. 2010, 457, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Beasley, N.J.P.; Watson, P.H.; Turner, K.J.; Pastorek, J.; Sibtain, A.; Wilson, G.D.; Turley, H.; Talks, K.L.; Maxwell, P.H.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible Expression of Tumor-associated Carbonic Anhydrases. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 7075–7083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saarnio, J.; Parkkila, S.; Parkkila, A.K.; Haukipuro, K.; Pastorekova, S.; Pastorek, J.; Kairaluoma, M.I.; Karttunen, T.J. Immunohistochemical study of colorectal tumors for expression of a novel transmembrane carbonic anhydrase, MN/CA IX, with potential value as a marker of cell proliferation. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Douma, K.; Supuran, C.T.; Chiu, R.K.; van Zandvoort, M.A.M.J.; Pastoreková, S.; Scozzafava, A.; Wouters, B.G.; Lambin, P. Imaging the hypoxia surrogate marker CA IX requires expression and catalytic activity for binding fluorescent sulfonamide inhibitors. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 83, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.A.; Ganesan, R.; Reynolds, G.; Gross, L.; Stevens, A.; Pastorek, J.; Murray, P.G.; Perunovic, B.; Anwar, M.S.; Billingham, L.; et al. Hypoxia-regulated carbonic anhydrase IX expression is associated with poor survival in patients with invasive breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlskog, J.K.J.; Schliemann, C.; Mårlind, J.; Qureshi, U.; Ammar, A.; Pedley, R.B.; Neri, D. Human monoclonal antibodies targeting carbonic anhydrase IX for the molecular imaging of hypoxic regions in solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlin, S.; Khan, N.; Ku, T.; Longo, V.A.; Larson, S.M.; Smith-Jones, P.M. Molecular targeting of carbonic anhydrase IX in mice with hypoxic HT29 colorectal tumor xenografts. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choschzick, M.; Oosterwijk, E.; Muller, V.; Woelber, L.; Simon, R.; Moch, H.; Tennstedt, P. Overexpression of carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is an independent unfavorable prognostic marker in endometrioid ovarian cancer. Virchows Arch. 2011, 459, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynninen, P.; Vaskivuo, L.; Saarnio, J.; Haapasalo, H.; Kivela, J.; Pastorekova, S.; Pastorek, J.; Waheed, A.; Sly, W.S.; Puistola, U.; et al. Expression of transmembrane carbonic anhydrases IX and XII in ovarian tumours. Histopathology 2006, 49, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Palmer, D.H.; Ganesan, R.; Hiller, L.; Gregory, J.; Murray, P.G.; Pastorek, J.; Young, L.; James, N.D. Carbonic anhydrase IX, a marker of hypoxia: Correlation with clinical outcome in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 11, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukourakis, M.I.; Bentzen, S.M.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Wilson, G.D.; Daley, F.M.; Saunders, M.I.; Dische, S.; Sivridis, E.; Harris, A.L. Endogenous Markers of Two Separate Hypoxia Response Pathways (hypoxia inducible factor 2 alpha and carbonic anhydrase 9) Are Associated With Radiotherapy Failure in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Recruited in the CHART Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loncaster, J.A.; Harris, A.L.; Davidson, S.E.; Logue, J.P.; Hunter, R.D.; Wycoff, C.C.; Pastorek, J.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Stratford, I.J.; West, C.M.L. Carbonic Anhydrase (CA IX) Expression, a Potential New Intrinsic Marker of Hypoxia: Correlations with Tumor Oxygen Measurements and Prognosis in Locally Advanced Carcinoma of the Cervix. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6394–6399. [Google Scholar]
- Noordhuis, M.G.; Eijsink, J.J.H.; Roossink, F.; de Graeff, P.; Pras, E.; Schuuring, E.; Wisman, G.B.A.; de Bock, G.H.; van der Zee, A.G.J. Prognostic Cell Biological Markers in Cervical Cancer Patients Primarily Treated With (Chemo)radiation: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvelä, S.; Parkkila, S.; Bragge, H.; Kähkönen, M.; Parkkila, A.-K.; Soini, Y.; Pastorekova, S.; Pastorek, J.; Haapasalo, H. Carbonic anhydrase IX in oligodendroglial brain tumors. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrastina, A.; Závada, J.; Parkkila, S.; Kaluz, Š.; Kaluzová, M.; Rajčáni, J.; Pastorek, J.; Pastoreková, S. Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of 125I-labeled monoclonal antibody M75 specific for carbonic anhydrase IX, an intrinsic marker of hypoxia, in nude mice xenografted with human colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 105, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, F.; Dumy, P.; Supuran, C.T.; Winum, J.Y. Multivalent Carbonic Anhydrases Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, E.T.; Snyder, P.W.; Perez-Castillejos, R.; Bilgicer, B.; Moustakas, D.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Dependence of Avidity on Linker Length for a Bivalent Ligand-Bivalent Receptor Model System. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitianu, A.; Ilies Marc, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran Claudiu, T. Synthesis and Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitory Activity of 5-Benzoylamido- and 5-(3-Nitrobenzoylamido)- 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide and their Metal Complexes. Main Group Met. Chem. 1997, 20, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andring, J.T.; Fouch, M.; Akocak, S.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Ilies, M.A.; McKenna, R. Structural Basis of Nanomolar Inhibition of Tumor-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase IX: X-Ray Crystallographic and Inhibition Study of Lipophilic Inhibitors with Acetazolamide Backbone. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13064–13075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, Z.J.; Paneth, P.; Rudziński, J. A Study on the Activation of Carboxylic Acids by Means of 2-Chloro-4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine and 2-Chloro-4,6-diphenoxy-1,3,5-triazine. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 4248–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolak, N.; Akocak, S.; Bua, S.; Sanku, R.K.K.; Supuran, C.T. Discovery of new ureido benzenesulfonamides incorporating 1,3,5-triazine moieties as carbonic anhydrase I, II, IX and XII inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, M.H.; Prenner, E.J. Differential scanning calorimetry: An invaluable tool for a detailed thermodynamic characterization of macromolecules and their interactions. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahmady, Z.S.; Chaloin, O.; Kostarelos, K. Monoclonal antibody-targeted, temperature-sensitive liposomes: In vivo tumor chemotherapeutics in combination with mild hyperthermia. J. Control. Release 2014, 196, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, M.; Shiga, M.; Sasamoto, K.; Mizoguchi, M.; He, P.-G. A New Sulfonated Tetrazolium Salt That Produces a Highly Water-Soluble Formazan Dye. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Experimental Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hypoxic Tumors. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, A.; Carta, F.; Nocentini, A.; Winum, J.Y.; Zalubovskis, R.; Akdemir, A.; Onnis, V.; Eldehna, W.M.; Capasso, C.; Simone, G.; et al. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Targeting Metabolism and Tumor Microenvironment. Metabolites 2020, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| KI (nM) * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | EG Units | hCA I | hCA II | hCA IX | hCA XII |
| 20 | 3 | 221 ± 16 | 37.1 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 2.6 ± 0.2 |
| 21 | 46 | 272 ± 25 | 1764 ± 45 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.2 |
| 22 | 3 | 180 ± 12 | 8.7 ± 0.5 | 9.6 ± 0.1 | 5.9 ± 0.4 |
| 23 | 46 | 225 ± 21 | 66.6 ± 3.1 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 5.4 ± 0.3 |
| 24 | 3 | 192 ± 9 | 8.6 ± 0.4 | 24.1 ± 0.2 | 2.8 ± 0.1 |
| 25 | 46 | 181 ± 9 | 12.9 ± 1.0 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 |
| 1 | 250 ± 12 | 12 ± 0.8 | 25 ± 1.7 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mondal, U.K.; Doroba, K.; Shabana, A.M.; Adelberg, R.; Alam, M.R.; Supuran, C.T.; Ilies, M.A. PEG Linker Length Strongly Affects Tumor Cell Killing by PEGylated Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors in Hypoxic Carcinomas Expressing Carbonic Anhydrase IX. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031120
Mondal UK, Doroba K, Shabana AM, Adelberg R, Alam MR, Supuran CT, Ilies MA. PEG Linker Length Strongly Affects Tumor Cell Killing by PEGylated Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors in Hypoxic Carcinomas Expressing Carbonic Anhydrase IX. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031120
Chicago/Turabian StyleMondal, Utpal K., Kate Doroba, Ahmed M. Shabana, Rachel Adelberg, Md. Raqibul Alam, Claudiu T. Supuran, and Marc A. Ilies. 2021. "PEG Linker Length Strongly Affects Tumor Cell Killing by PEGylated Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors in Hypoxic Carcinomas Expressing Carbonic Anhydrase IX" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031120
APA StyleMondal, U. K., Doroba, K., Shabana, A. M., Adelberg, R., Alam, M. R., Supuran, C. T., & Ilies, M. A. (2021). PEG Linker Length Strongly Affects Tumor Cell Killing by PEGylated Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors in Hypoxic Carcinomas Expressing Carbonic Anhydrase IX. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031120








