Potential Role of Insulin Growth-Factor-Binding Protein 2 as Therapeutic Target for Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
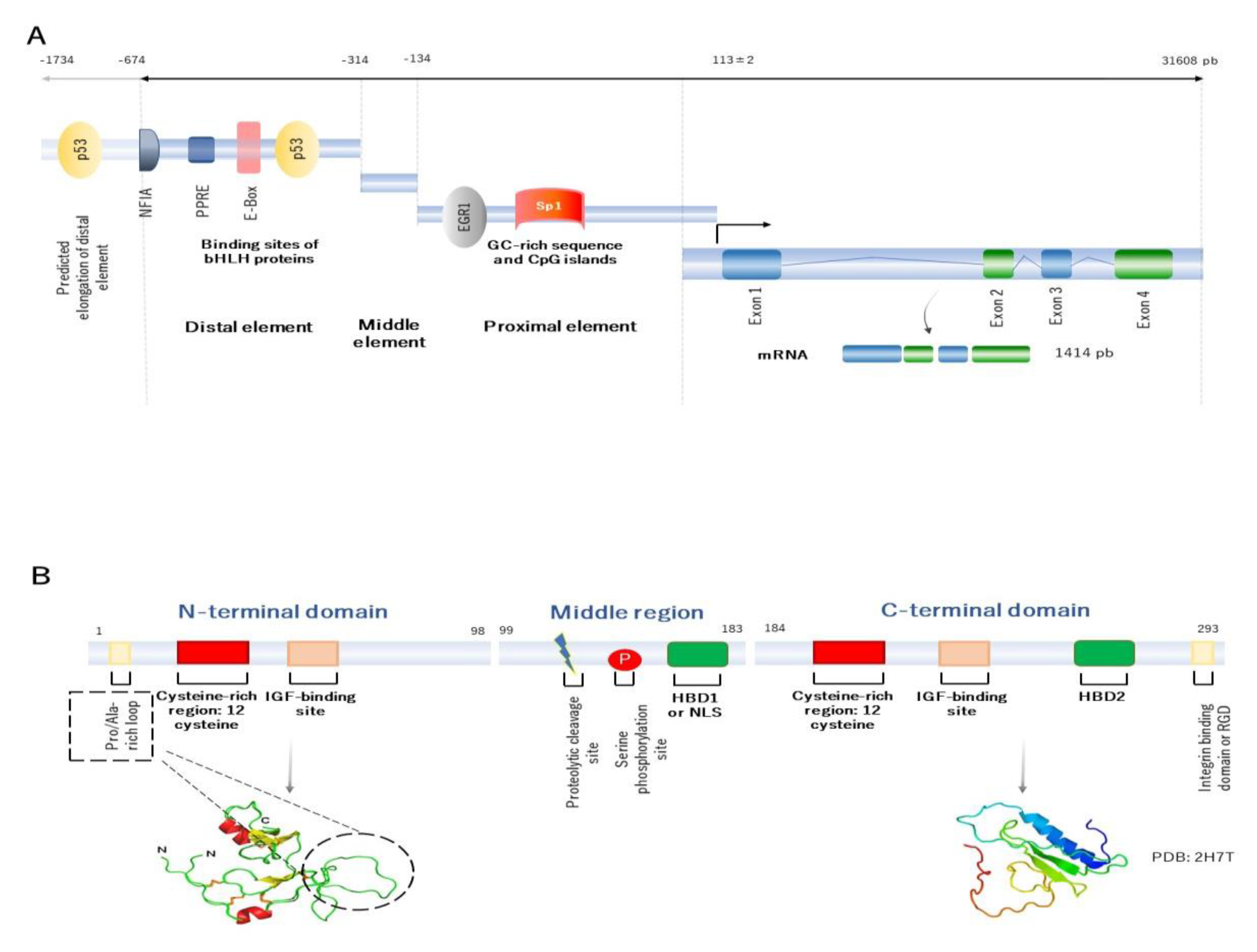
2. Building the Molecular Structure of IGFBP2
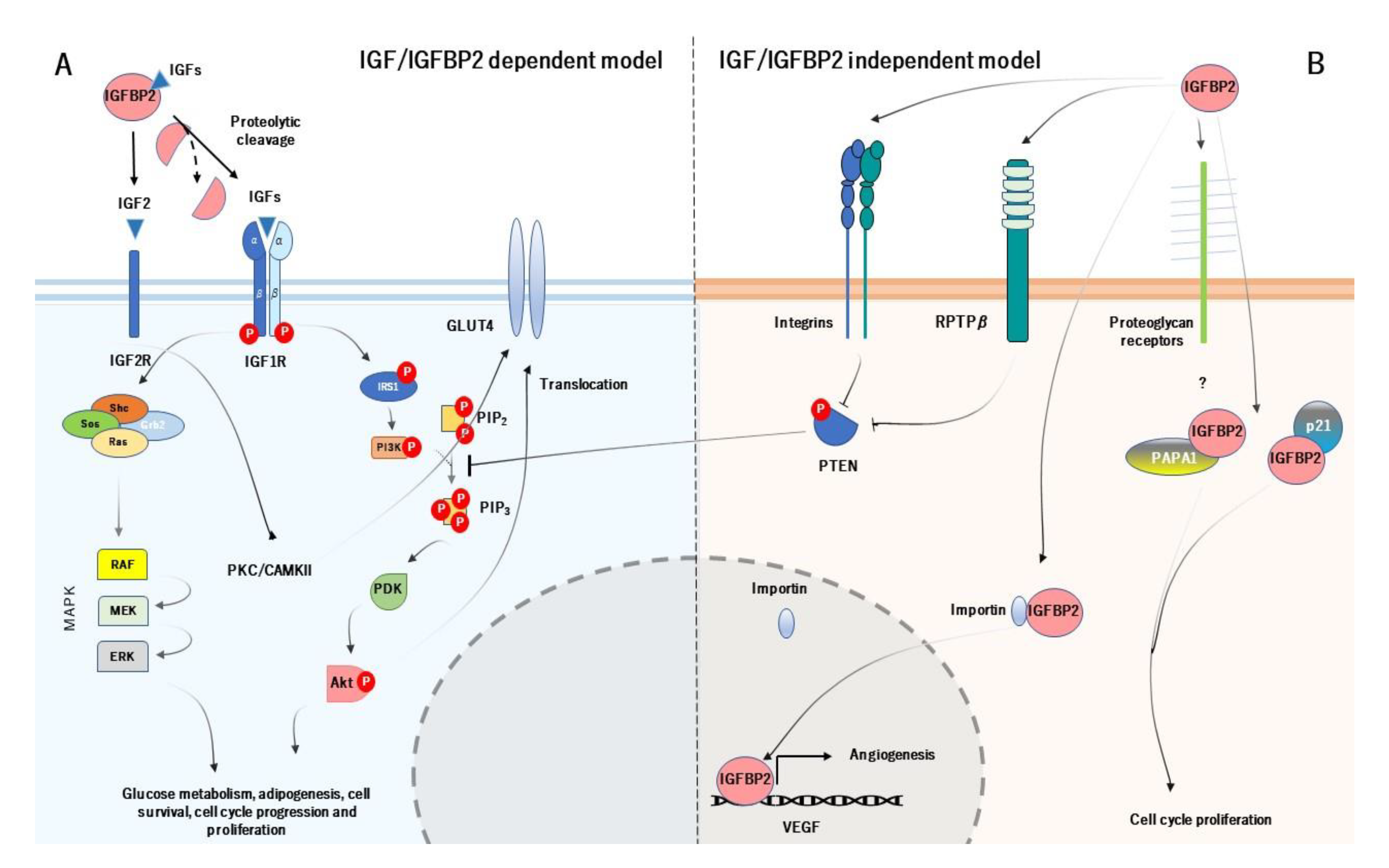
3. Mechanism of Action of IGFBP2 and its Physiological Role
4. IGFBP2 and Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance
4.1. The Suggested Role of IGFBP2 in the Development of Obesity
4.2. The Mechanisms of IGFBP2 in Insulin Sensitivity
4.3. The Association of IGFBP2 and Type 2 Diabetes
4.4. IGFBP2 Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome
4.5. Proposed Mechanisms of IGFBP2 in Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance
5. Diverse Strategies to Modify Serum IGFBP2 in a Prevention Context
5.1. Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
5.2. The Effect of Physical Activity on Serum IGFBP2
5.3. Epigenetic Regulation also Influences IGFBP2
6. Preclinical Pharmacology Studies of IGFBP2
7. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| p53 | transformation-related protein 53 |
| NFIA | nuclear factor IA |
| PPRE | peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor responsive element |
| E-Box | enhancer box |
| bHLH | Basic helix-loop-helix |
| EGFR1 | epidermal growth factor receptor 1 |
| Sp1 | specificity protein 1 |
| IGF1 | insulin growth factor type 1 |
| HBD1 | heparin binding domain 1 |
| NLS | nuclear localization sequence; |
| HBD2 | heparin binding domain |
| RGD | tripeptide Arg-Gly-Asp |
| PDB | Protein data bank |
| IGFBP2 | insulin growth factor binding protein 2. |
| IGF2 | Insulin growth factor 2; |
| IGF2R | Insulin growth factor receptor type 2 |
| IGF1R | Insulin growth factor receptor type 1 |
| Shc | SHC Adaptor Protein |
| SOS | Son of Sevenless |
| Ras | rat sarcoma |
| Grb2 | growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| IRS1 | Insulin receptor substrate 1 |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PIP3 | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate |
| GLU4 | glucose receptor type 4 |
| MAPK | mitogen activated protein kinase |
| RAF | Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| PKC/CAMKII | protein kinase C/calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II |
| PDK | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase |
| Akt | alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| RPTPβ | tyrosine phosphatase β |
| PAPA1 | Pim-1-associated protein-1 |
| P21 | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3 β |
References
- Rosenfeld, R.G. Insulin-like Growth Factors and the Basis of Growth. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2184–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedemann, J.; Macaulay, V.M. IGF1R signalling and its inhibition. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, S33–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, J.B.; Duan, C. IGF-Binding Proteins: Why Do They Exist and Why Are There So Many? Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heald, A.H.; Kaushal, K.; Siddals, K.W.; Rudenski, A.S.; Anderson, S.G.; Gibson, J.M. Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 (IGFBP-2) is a Marker for the Metabolic Syndrome. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2006, 114, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binkert, C.; Margot, J.B.; Landwehr, J.; Heinrich, G.; Schwander, J. Structure of the human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992, 6, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapf, J.; Schmid, C.; Guler, H.P.; Waldvogel, M.; Hauri, C.; Futo, E.; Hossenlopp, P.; Binoux, M.; Froesch, E.R. Regulation of binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in humans. Increased expression of IGF binding protein 2 during IGF I treatment of healthy adults and in patients with extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, F.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Boddu, S.; et al. Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D745–D751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, H.; Yazawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Shimoyamada, H.; Okudela, K.; Ikeda, M.; Hamada, K.; Yamada-Okabe, H.; Yao, M.; Kubota, Y.; et al. Growth Regulation via Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-4 and −2 in Association with Mutant K-ras in Lung Epithelia. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1550–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galea, C.A.; Mobli, M.; McNeil, K.A.; Mulhern, T.D.; Wallace, J.C.; King, G.F.; Forbes, B.E.; Norton, R.S. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2: NMR analysis and structural characterization of the N-terminal domain. Biochimie 2012, 94, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimberg, A.; Coleman, C.M.; Shi, Z.; Burns, T.F.; MacLachlan, T.K.; Wang, W.; El-Deiry, W.S. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 is a novel mediator of p53 inhibition of insulin-like growth factor signaling. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yazawa, T.; Sato, H.; Shimoyamada, H.; Okudela, K.; Woo, T.; Tajiri, M.; Ogura, T.; Ogawa, N.; Suzuki, T.; Mitsui, H.; et al. Neuroendocrine Cancer-Specific Up-Regulating Mechanism of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mireuta, M.; Darnel, A.; Pollak, M. IGFBP-2 expression in MCF-7 cells is regulated by the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through Sp1-induced increase in transcription. Growth Factors 2010, 28, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chen, P.-H.; Ho, K.-H.; Shih, C.-M.; Cheng, C.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Cheng, K.-T.; Liu, A.-J.; Chen, K.-C. The microRNA-302b-inhibited insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 signaling pathway induces glioma cell apoptosis by targeting nuclear factor IA. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughanem, H.; Cabrera-Mulero, A.; Millán-Gómez, M.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Cardona, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Santos, I.; Macías-González, M.; Mulero, C.-; Millán-Gómez, M.; et al. Transcriptional Analysis of FOXO1, C/EBP- and PPAR-2 Genes and Their association with Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Genes 2019, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badinga, L.; Song, S.; Simmen, R.C.M.; A Simmen, F. A Distal Regulatory Region of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 (IGFBP-2) Gene Interacts with the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor, AP-4. Endocrine 1998, 8, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, S.M.; Baxter, R.C. Cellular Actions of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 824–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.E.; Kilby, D.M.; Firth, S.M.; Robinson, P.J.; Baxter, R.C. Thein VivoPhosphorylation and Glycosylation of Human Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-5. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1392–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Xi, G.; Maile, L.A.; Wai, C.; Rosen, C.J.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein 2 Functions Coordinately with Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase and the IGF-I Receptor To Regulate IGF-I-Stimulated Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4116–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azar, W.J.; Zivkovic, S.; A Werther, G.; Russo, V.C. IGFBP-2 nuclear translocation is mediated by a functional NLS sequence and is essential for its pro-tumorigenic actions in cancer cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sala, A.; Capaldi, S.; Campagnoli, M.; Faggion, B.; Labò, S.; Perduca, M.; Romano, A.; Carrizo, M.E.; Valli, M.; Visai, L.; et al. Structure and Properties of the C-terminal Domain of Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-1 Isolated from Human Amniotic Fluid. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29812–29819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mark, S.; Kübler, B.; Höning, S.; Oesterreicher, S.; John, H.; Braulke, T.; Forssmann, W.-G.; Ständker, L.; Kuebler, B. Diversity of Human Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein-2 Fragments in Plasma: Primary Structure, IGF-Binding Properties, and Disulfide Bonding Pattern†. Biochemie 2005, 44, 3644–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.; Yao, S.; Keizer, D.W.; Wang, C.C.; Leon, B.; Forbes, B.E.; Wallace, J.C.; Norton, R.S. Structure, Dynamics and Heparin Binding of the C-terminal Domain of Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-2 (IGFBP-2). J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 364, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.S.; Gokulnath, P.; Bashir, M.; Shwetha, S.D.; Jaiswal, J.; Shastry, A.H.; Arimappamagan, A.; Santosh, V.; Kondaiah, P. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 regulates β-catenin signaling pathway in glioma cells and together contributes to poor patient prognosis. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, now053-1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo, V.C.; Schutt, B.S.; Andaloro, E.; Ymer, S.I.; Hoeflich, A.; Ranke, M.B.; Bach, L.A.; Werther, G.A. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 Binding to Extracellular Matrix Plays a Critical Role in Neuroblastoma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 4445–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, S.B.; Kearney, M.T. IGF-dependent and IGF-independent actions of IGF-binding protein-1 and -2: Implications for metabolic homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, R.G.; Pham, H.; Conover, C.A.; Hintz, R.L.; Baxter, R.C. Structural and Immunological Comparison of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins of Cerebrospinal and Amniotic Fluids. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1989, 68, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkharobi, H.; Alhodhodi, A.; Hawsawi, Y.; Alkafaji, H.; Devine, D.; El-Gendy, R.; Beattie, J. IGFBP-2 and -3 co-ordinately regulate IGF1 induced matrix mineralisation of differentiating human dental pulp cells. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 17, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lund, J.; Søndergaard, M.T.; Conover, C.A.; Overgaard, M.T. Heparin-binding mechanism of the IGF2/IGF-binding protein 2 complex. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 52, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-S. Role of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in glucose and lipid metabolism. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 18, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollak, M. The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: An update. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Cho, H.-Y.; Hoyt, K.R.; Naegele, J.R.; Obrietan, K. IGF-1 receptor-mediated ERK/MAPK signaling couples status epilepticus to progenitor cell proliferation in the subgranular layer of the dentate gyrus. Glia 2008, 56, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, P.; Dahms, N.M.; Kornfeld, S. Mannose 6-phosphate receptors: New twists in the tale. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.-H.; Tzang, B.-S.; Chen, L.-M.; Kuo, C.-H.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chen, L.-Y.; Tsai, F.-J.; Tsai, C.-H.; Kuo, W.; Huang, C.-Y. IGF-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptor signaling induced cell hypertrophy and atrial natriuretic peptide/BNP expression via Gαq interaction and protein kinase C-α/CaMKII activation in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 197, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappel, V.D.; Zanatta, L.; Postal, B.G.; Silva, F.R.M.B. Rutin potentiates calcium uptake via voltage-dependent calcium channel associated with stimulation of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 532, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoslahti, E. RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996, 12, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perks, C.M.; Vernon, E.G.; Rosendahl, A.H.; Tonge, D.; Holly, J.M.P. IGF-II and IGFBP-2 differentially regulate PTEN in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5966–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, V.C. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 Binds to Cell Surface Proteoglycans in the Rat Brain Olfactory Bulb. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 4858–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Wai, C.; DeMambro, V.; Rosen, C.J.; Clemmons, D.R. IGFBP-2 Directly Stimulates Osteoblast Differentiation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrien, X.; Bonvin, E.; Corroyer, S.; Tabary, O.; Clément, A.; Henrion-Caude, A. Intracellular colocalization and interaction of IGF-binding protein-2 with the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21CIP1/WAF1 during growth inhibition. Biochem. J. 2005, 392, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyako, K.; Cobb, L.J.; Francis, M.; Huang, A.; Peng, B.; Pintar, J.E.; Ariga, H.; Cohen, P. PAPA-1 Is a Nuclear Binding Partner of IGFBP-2 and Modulates Its Growth-Promoting Actions. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, S.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, K.R.; Cha, B.S.; Song, Y.D.; Lim, S.K.; Lee, H.C.; Huh, K.B. Effect of obesity on total and free insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, and their relationship to IGF-binding protein (BP)-1, IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, insulin, and growth hormone. Int. J. Obes. 1997, 21, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballerini, M.G.; Ropelato, M.G.; Domené, H.M.; A Pennisi, P.; Heinrich, J.J.; Jasper, H.G. Differential Impact of Simple Childhood Obesity on the Components of the Growth Hormone-Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-IGF Binding Proteins Axis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 17, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.W.; E Harcourt, B.; Kao, K.-T.; Alexander, E.J.; Russo, V.C.; Werther, G.A.; Sabin, M.A. Serum IGFBP-2 levels are associated with reduced insulin sensitivity in obese children. Clin. Obes. 2018, 8, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Pawlikowska, L.; Kanaya, A.; Hsueh, W.-C.; Colbert, L.; Newman, A.B.; Satterfield, S.; Rosen, C.; Cummings, S.R.; Harris, T.B.; et al. Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Binding Proteins 1 and 2 and Mortality in Older Adults: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffeis, C.; Benjamim, F.; Riccardo, B.; Massimiliano, C.; Francesco, B.; Luciano, C. Adipocytes IGFBP-2 Expression in Prepubertal Obese Children. Obesesity 2010, 18, 2055–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarini, G.; Pelosini, C.; Ferrari, F.; Magno, S.; Vitti, J.; Salvetti, G.; Moretto, C.; Marioni, A.; Buccianti, P.; Piaggi, P.; et al. Serum IGF-binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) concentrations change early after gastric bypass bariatric surgery revealing a possible marker of leptin sensitivity in obese subjects. Endocrine 2019, 65, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Regaiey, K.; Alshubrami, S.; Al-Beeshi, I.; Alnasser, T.; Alwabel, A.; Al-Beladi, H.; Al-Tujjar, O.; Alnasser, A.; Alfadda, A.A.; Iqbal, M. Effects of gastric sleeve surgery on the serum levels of GH, IGF-1 and IGF-binding protein 2 in healthy obese patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, S.B.; Kearney, M.T.; Shah, A.M.; Ezzat, V.A.; Miell, J.R.; Modo, M.; Williams, S.C.; Cawthorn, W.P.; Medina-Gomez, G.; Vidal-Puig, A.; et al. IGF-Binding Protein-2 Protects Against the Development of Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, G.; Solum, M.A.; Wai, C.; Maile, L.A.; Rosen, C.J.; Clemmons, D.R. The Heparin-Binding Domains of IGFBP-2 Mediate Its Inhibitory Effect on Preadipocyte Differentiation and Fat Development in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4146–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, H.F.; Frystyk, J.; Efendic, S.; Brismar, K.; Thorell, A. Analyses of IGFBP2 DNA methylation and mRNA expression in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2019, 45, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedbacker, K.; Birsoy, K.; Wysocki, R.W.; Asilmaz, E.; Ahima, R.S.; Farooqi, I.S.; Friedman, J.M. Antidiabetic Effects of IGFBP2, a Leptin-Regulated Gene. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yau, S.W.; A Henry, B.; Russo, V.C.; McConell, G.K.; Clarke, I.J.; A Werther, G.; Sabin, M.A. Leptin Enhances Insulin Sensitivity by Direct and Sympathetic Nervous System Regulation of Muscle IGFBP-2 Expression: Evidence From Nonrodent Models. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neumann, U.H.; Chen, S.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Baker, R.K.; Covey, S.D.; Cullis, P.R.; Kieffer, T.J. IGFBP2 Is Neither Sufficient nor Necessary for the Physiological Actions of Leptin on Glucose Homeostasis in Male ob/ob Mice. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemmons, D.R.; Snyder, D.K.; Busby, W.H. Variables Controlling the Secretion of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 in Normal Human Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 73, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, A.M.; Weickert, M.O.; Frystyk, J.; Spranger, J.; Schöfl, C.; Mohlig, M.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. The Role of Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein-2 in the Insulin-Mediated Decrease in IGF-I Bioactivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5093–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Santos, I.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Lara, M.F.; Fernández-García, J.C.; Tinahones, F.J.; Macias-Gonzalez, M. IGFBP-3 Interacts with the Vitamin D Receptor in Insulin Signaling Associated with Obesity in Visceral Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beld, A.W.V.D.; Carlson, O.D.; E Doyle, M.; Rizopoulos, D.; Ferrucci, L.; Van Der Lely, A.J.; Egan, J.M. IGFBP-2 and aging: A 20-year longitudinal study on IGFBP-2, IGF-I, BMI, insulin sensitivity and mortality in an aging population. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Miard, S.; Laplante, M.; Sonenberg, N.; Picard, F. Insulin stimulates IGFBP-2 expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through the PI3K/mTOR pathway. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 358, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, F.; Kässner, F.; Schmid, G.; Kratzsch, J.; Laner, A.; Wabitsch, M.; Körner, A.; Kiess, W.; Garten, A. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signalling regulates insulin-like-growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) production in human adipocytes. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2015, 25, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, B.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Spranger, J.; Arafat, A.M. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein-2, Independently of IGF-1, Induces GLUT-4 Translocation and Glucose Uptake in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpathak, S.N.; He, M.; Sun, Q.; Kaplan, R.C.; Muzumdar, R.; Rohan, T.E.; Gunter, M.J.; Pollak, M.; Kim, M.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Women. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lappas, M.; Jinks, D.; Shub, A.; Willcox, J.; Georgiou, H.M.; Permezel, M. Postpartum IGF-I and IGFBP-2 levels are prospectively associated with the development of type 2 diabetes in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. 2016, 42, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Mendola, P.; Albert, P.S.; Bao, W.; Hinkle, S.N.; Tsai, M.Y.; Zhang, C. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Longitudinal Study in a Multiracial Cohort. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3495–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.-R.; Wang, W.-J.; Yu, X.; Hua, X.; Ouyang, F.; Luo, Z.-C. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis Biomarkers and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenbecher, C.; Ouni, M.; Kuxhaus, O.; Jähnert, M.; Gottmann, P.; Teichmann, A.; Meidtner, K.; Kriebel, J.; Grallert, H.; Pischon, T.; et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 (IGFBP-2) and the Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2018, 68, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noordam, R.; Van Heemst, D.; Suhre, K.; Krumsiek, J.; Mook-Kanamori, D.O. Proteome-wide assessment of diabetes mellitus in Qatari identifies IGFBP-2 as a risk factor already with early glycaemic disturbances. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 689, 108476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, Y.; Miyake, K.; Yasuda, K.; Enya, M.; Hirota, Y.; Yamagata, K.; Hinokio, Y.; Oka, Y.; Iwasaki, N.; Iwamoto, Y.; et al. Replication of Genome-Wide Association Studies of Type 2 Diabetes Susceptibility in Japan. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3136–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauchi, S.; Meyre, D.; Durand, E.; Proença, C.; Marre, M.; Hadjadj, S.; Choquet, H.; De Graeve, F.; Gaget, S.; Allegaert, F.; et al. Post Genome-Wide Association Studies of Novel Genes Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Show Gene-Gene Interaction and High Predictive Value. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yin, J.-Y.; Dai, X.-P.; Pei, Q.; Dong, M.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, X.; Yu, M.; Zhou, H.-H.; Liu, Z.-Q. IGF2BP2 variations influence repaglinide response and risk of type 2 diabetes in Chinese population. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesing, K.; Fatemifar, G.; Charpentier, G.; Marre, M.; Tichet, J.; Hercberg, S.; Balkau, B.; Froguel, P.; Gibson, F. Evaluation of the Association of IGF2BP2 Variants With Type 2 Diabetes in French Caucasians. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1992–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, S.; Li, Z.; Lemieux, I.; Alméras, N.; Tremblay, A.; Bergeron, J.; Poirier, P.; Deshaies, Y.; Després, J.-P.; Picard, F. Circulating IGFBP-2 levels are incrementally linked to correlates of the metabolic syndrome and independently associated with VLDL triglycerides. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olszanecka, A.; Dragan, A.; Kawecka-Jaszcz, K.; Fedak, D.; Czarnecka, D. Relationships of insulin-like growth factor-1, its binding proteins, and cardiometabolic risk in hypertensive perimenopausal women. Metabolism 2017, 69, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouriamehr, S.; Barmaki, H.; Rastegary, M.; Lotfi, F.; Afjadi, M.N. Investigation of insulin-like growth factors/insulin-like growth factor binding proteins regulation in metabolic syndrome patients. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, R.V.; Hwang, S.-J.; Yeri, A.; Tanriverdi, K.; Pico, A.R.; Yao, C.; Murthy, V.L.; Ho, J.; Vitseva, O.; Demarco, D.; et al. Proteins Altered by Surgical Weight Loss Highlight Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance in the Community. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekimoto, H.; Boney, C.M. C-Terminal Src Kinase (CSK) Modulates Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Signaling through Src in 3T3-L1 Differentiation. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2546–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volloch, V.; Olsen, B.R. Why cellular stress suppresses adipogenesis in skeletal tissue, but is ineffective in adipose tissue: Control of mesenchymal cell differentiation via integrin binding sites in extracellular matrices. Matrix Biol. 2013, 32, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, E.M.; Verstappen, R.; Zwierzina, M.E.; Geley, S.; Pierer, G.; Ploner, C. ITGAV and ITGA5 diversely regulate proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pucilowska, J.B.; Davenport, M.L.; Kabir, I.; Clemmons, D.R.; Thissen, J.P.; Butler, T.; E Underwood, L. The effect of dietary protein supplementation on insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding proteins in children with shigellosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 77, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, D.; Le Bouc, Y.; Laville, M.; Combarnous, F.; O Joly, M.; Raton, P.; Zech, P. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and its binding proteins during a low-protein diet in chronic renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 6, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Vrieling, A.; Voskuil, D.W.; Bonfrer, J.M.; Korse, C.M.; Van Doorn, J.; Cats, A.; Depla, A.C.; Timmer, R.; Witteman, B.J.; E Van Leeuwen, F.; et al. Lycopene supplementation elevates circulating insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 and -2 concentrations in persons at greater risk of colorectal cancer. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowe, F.L.; Key, T.J.; Allen, N.E.; Appleby, P.N.; Roddam, A.; Overvad, K.; Grønbaek, H.; Tjønneland, A.; Halkjaer, J.; Dossus, L.; et al. The Association between Diet and Serum Concentrations of IGF-I, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2, and IGFBP-3 in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, N.J.; Metcalfe, C.; Gunnell, D.; Rowlands, M.-A.; Lane, J.A.; Gilbert, R.; Avery, K.N.L.; Davis, M.; Neal, D.E.; Hamdy, F.C.; et al. A cross-sectional analysis of the association between diet and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-II, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-2, and IGFBP-3 in men in the United Kingdom. Cancer Causes Control. 2012, 23, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupp, D.; Remer, T.; Penczynski, K.J.; Bolzenius, K.; Wudy, S.A.; Buyken, A.E. Relevance of fruits, vegetables and flavonoids from fruits and vegetables during early life, mid-childhood and adolescence for levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and its binding proteins IGFBP-2 and IGFBP-3 in young adulthood. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 115, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Manousopoulou, A.; Alokail, M.S.; Yakout, S.; Alenad, A.; Garay-Baquero, D.J.; Fotopoulos, M.; Teng, J.; Al-Attas, O.; Al-Saleh, Y.; et al. Sex-specific correlation of IGFBP-2 and IGFBP-3 with vitamin D status in adults with obesity: A cross-sectional serum proteomics study. Nutr. Diabetes 2018, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boisclair, Y.R.; Yang, Y.W.; Stewart, J.M.; Rechler, M.M. Insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin stimulate the synthesis of IGF-binding protein-2 in a human embryonic kidney cell line. Growth Regul. 1994, 4, 136–146. [Google Scholar]
- Bostedt, K.T.; Schmid, C.; Ghirlanda-Keller, C.; Olie, R.; Winterhalter, K.H.; Zapf, J. Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) I Down-Regulates Type 1 IGF Receptor (IGF 1R) and Reduces the IGF I Response in A549 Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Saos-2/B-10 Osteoblastic Osteosarcoma Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 271, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrailkill, K. Dual Hormonal Replacement Therapy with Insulin and Recombinant Human Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF)-I in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus: Effects on the Growth Hormone/IGF/IGF-Binding Protein System. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, E.; Krämer, R.; Blum, W.F.; Föll, J.; Brem, G. Consequences of postnatally elevated insulin-like growth factor-II in transgenic mice: Endocrine changes and effects on body and organ growth. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blum, W.F.; Horn, N.; Kratzsch, J.; O Jørgensen, J.; Juul, A.; Teale, D.; Mohnike, K.; Ranke, M.B. Clinical studies of IGFBP-2 by radioimmunoassay. Growth Regul. 1993, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Elmlinger, M.W.; Bell, M.; Schüett, B.S.; Langkamp, M.; Kutoh, E.; Ranke, M.B. Transactivation of the IGFBP-2 promoter in human tumor cell lines. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 175, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, U.; Enqvist, J.K.; Mattsson, C.M.; Carlsson-Skwirut, C.; Sundberg, C.J.; Ekblom, B.; Bang, P. Lack of sex differences in the IGF-IGFBP response to ultra endurance exercise. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2008, 18, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, S.M.; Spiering, B.A.; Alemany, J.A.; Tuckow, A.P.; Rarick, K.R.; Staab, J.S.; Hatfield, D.L.; Kraemer, W.J.; Maresh, C.M.; Nindl, B.C. Exercise-Induced Insulin-Like Growth Factor I System Concentrations after Training in Women. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, N.E.; Appleby, P.N.; Davey, G.K.; Kaaks, R.; Rinaldi, S.; Key, T.J. The associations of diet with serum insulin-like growth factor I and its main binding proteins in 292 women meat-eaters, vegetarians, and vegans. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2002, 11, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Espelund, U.; Bruun, J.M.; Richelsen, B.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Frystyk, J. Pro- and mature IGF-II during diet-induced weight loss in obese subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 153, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touskova, V.; Trachta, P.; Kavalkova, P.; Drapalova, J.; Haluzikova, D.; Mraz, M.; Lacinova, Z.; Marek, J.; Haluzík, M. Serum concentrations and tissue expression of components of insulin-like growth factor-axis in females with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: The influence of very-low-calorie diet. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 361, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.; Lemieux, I.; Li, Z.; Alméras, N.; Tremblay, A.; Bergeron, J.; Poirier, P.; Després, J.-P.; Picard, F. Changes in IGFBP-2 levels following a one-year lifestyle modification program are independently related to improvements in plasma apo B and LDL apo B levels. Atherosclerosis 2019, 281, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopple, J.D.; Cohen, A.H.; Wang, H.; Qing, D.; Tang, Z.; Fournier, M.; Lewis, M.; Casaburi, R.; Storer, T. Effect of Exercise on mRNA Levels for Growth Factors in Skeletal Muscle of Hemodialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2006, 16, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeo, C.; Ikeda, K.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Inoue, S. Identification of Igf2, Igfbp2 and Enpp2 as Estrogen-Responsive Genes in Rat Hippocampus. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, E.B.; Fisher, G.; Sartin, J.L.; Elsasser, T.H.; Wu, G.; Cowan, W.; Pascoe, D.D. Acute regulation of IGF-I by alterations in post-exercise macronutrients. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindl, B.C.; Alemany, J.A.; Rarick, K.R.; Eagle, S.R.; Darnell, M.E.; Allison, K.F.; A Harman, E. Differential basal and exercise-induced IGF-I system responses to resistance vs. calisthenic-based military readiness training programs. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2017, 32, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirna, M.; Lichtenauer, M.; Wernly, B.; Paar, V.; Jung, C.; Kretzschmar, D.; Uhlemann, M.; Franz, M.; Hoppe, U.C.; Schulze, P.C.; et al. Novel cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with cardiovascular diseases undergoing intensive physical exercise. Panminerva Med. 2020, 62, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, T.; Yokosuka, O.; Fukai, K.; Hirasawa, Y.; Tada, M.; Mikata, R.; Imazeki, F.; Taniguchi, H.; Iwama, A.; Miyazaki, M.; et al. Identification and investigation of methylated genes in hepatoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Houseman, E.A.; Morrison, Z.; Wrensch, M.R.; Patoka, J.S.; Ramos, C.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; McBride, S.; Marsit, C.; Christensen, B.C.; et al. DNA hypermethylation profiles associated with glioma subtypes and EZH2 and IGFBP2 mRNA expression. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; Von Schönfels, W.; Kolarova, J.; Bens, S.; Itzel, T.; Teufel, A.; Herrmann, A.; Brosch, M.; Hinrichsen, H.; et al. DNA Methylation Analysis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Suggests Distinct Disease-Specific and Remodeling Signatures after Bariatric Surgery. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nawathe, A.; Christian, M.; Kim, S.H.; Johnson, M.R.; Savvidou, M.D.; Terzidou, V. Insulin-like growth factor axis in pregnancies affected by fetal growth disorders. Clin. Epigenetics 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.; Gillatt, D.; Rowe, E.; Koupparis, A.; Holly, J.M.; Perks, C.M. IGFBP-2 acts as a tumour suppressor and plays a role in determining chemosensitivity in bladder cancer cells. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 7043–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacka, K.M.; Uzoh, C.C.; Zeng, L.; Persad, R.A.; Bahl, A.; Gillatt, D.; Perks, C.M.; Holly, J.M.P. Hyperglycaemia-induced chemoresistance of prostate cancer cells due to IGFBP2. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickard, A.; McDade, S.S.; McFarland, M.; McCluggage, W.G.; Wheeler, C.M.; McCance, D.J. HPV16 Down-Regulates the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 to Promote Epithelial Invasion in Organotypic Cultures. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, L.M.; Zhou, X.; Cogdell, D.E.; Chua, C.Y.; Huisinga, A.; Hess, K.R.; Fuller, G.N.; Zhang, W. Glioma progression is mediated by an addiction to aberrant IGFBP2 expression and can be blocked using anti-IGFBP2 strategies. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasinghe, I.R.; Woster, P.M. Cyclic peptide inhibitors of lysine-specific demethylase 1 with improved potency identified by alanine scanning mutagenesis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 148, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strub, T.; Ghiraldini, F.G.; Carcamo, S.; Li, M.; Wroblewska, A.; Singh, R.; Goldberg, M.S.; Hasson, D.; Wang, Z.; Gallagher, S.J.; et al. SIRT6 haploinsufficiency induces BRAFV600E melanoma cell resistance to MAPK inhibitors via IGF signalling. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Groups | Effectors | Effects of IGFBP2 | Physiological Context | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients | Vitamin D | ↑ | Men with obesity with high vitamin D had increased IGFBP2 levels than lower vitamin D subjects | [84] |
| Protein | ↓ | High protein diet was associated with decreased serum IGFBP2 levels | [81] | |
| Calcium | ↓ | High calcium diet was associated with decreased serum IGFBP2 levels | [81] | |
| Carbohydrates | ↑ | High carbohydrates diet was associated with increased serum IGFBP2 levels | [81] | |
| Monounsaturated fat | ↑ | High monounsaturated diet was associated with increased serum IGFBP2 circulating levels | [81] | |
| Lycopene and green tea | ↑ | A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded crossover study showed that lycopene and green tea supplements were associated with increased serum IGFBP2 | [80] | |
| Fruits and flavonoid intake | ↑ | High fruits and flavonoid intake was associated with increased serum IGFBP2 circulating | [83] | |
| Growth factors | Insulin | ↑ | Insulin increased IGFBP2 in cultured embryonic kidney cell line | [85] |
| IGF1, IGF2 and IGF analogues | ↑ | IGF1, IGF2 and IGF analogues increase IGFBP2 levels in human subjects and different cell models | [6,85,86,87,88,89,90] | |
| Leptin | ↑ | Leptin stimulates expression of IGFBP2 and increases protein levels in human skeletal muscle cells | [52] | |
| Physical activity | Endurance and resistance exercises | ↑ | Physical activity was associated with increased serum IGFBP2 | [91], [92] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boughanem, H.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; López-Miranda, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; Macias-Gonzalez, M. Potential Role of Insulin Growth-Factor-Binding Protein 2 as Therapeutic Target for Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031133
Boughanem H, Yubero-Serrano EM, López-Miranda J, Tinahones FJ, Macias-Gonzalez M. Potential Role of Insulin Growth-Factor-Binding Protein 2 as Therapeutic Target for Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031133
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoughanem, Hatim, Elena M. Yubero-Serrano, José López-Miranda, Francisco J. Tinahones, and Manuel Macias-Gonzalez. 2021. "Potential Role of Insulin Growth-Factor-Binding Protein 2 as Therapeutic Target for Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031133
APA StyleBoughanem, H., Yubero-Serrano, E. M., López-Miranda, J., Tinahones, F. J., & Macias-Gonzalez, M. (2021). Potential Role of Insulin Growth-Factor-Binding Protein 2 as Therapeutic Target for Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031133






