Abstract
The mechanisms of how obesity contributes to the development of cardio-metabolic diseases are not entirely understood. Obesity is frequently associated with adipose tissue dysfunction, characterized by, e.g., adipocyte hypertrophy, ectopic fat accumulation, immune cell infiltration, and the altered secretion of adipokines. Factors secreted from adipose tissue may induce and/or maintain a local and systemic low-grade activation of the innate immune system. Attraction of macrophages into adipose tissue and altered crosstalk between macrophages, adipocytes, and other cells of adipose tissue are symptoms of metabolic inflammation. Among several secreted factors attracting immune cells to adipose tissue, chemotactic C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) (also described as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)) has been shown to play a crucial role in adipose tissue macrophage infiltration. In this review, we aimed to summarize and discuss the current knowledge on CCL2 with a focus on its role in linking obesity to cardio-metabolic diseases.
1. Introduction
Accumulation of adipose tissue (AT) is the major symptom of obesity. Until about 25 years ago, AT was regarded as an energy storage organ that additionally acts as isolation for the inner organs [1]. Due to the discovery of its endocrine function in the late 1980s, our understanding of AT changed fundamentally [2]. Since then, hundreds of bioactive components secreted by AT have been found [3,4]. Those AT-derived secretory factors including leptin, adiponectin, adipsin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI1), complement components, or cytokines such as tumor necrosis factors (e.g., TNF-α) or chemokines (e.g., CCL2) have been described with the term “adipokines” [5].
In 1999, Funahashi et al. defined “biologically active molecules secreted from adipose tissue” as “adipocytokines” [6]. However, this term is potentially misleading because it suggests that all AT-secreted substances are cytokines. While this is true for some AT-secreted molecules (e.g., IL-6 or TNF-α), the majority is of non-cytokine origin. Although Trayhurn and Wood recommended to use the term “’adipokine’ […] to describe a protein that is secreted from […] adipocytes”, commonly all AT-produced and -secreted substances are named “adipokines”, independent of whether they are secreted primarily from adipocytes or other AT cell types [7].
Adipokines are a heterogenous group of peptides including hormones, growth factors, and cytokines which differ in their physiological functions. Adipokines play an important role in the regulation of energy homeostasis, appetite, satiety, lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis, blood pressure and vascular homeostasis, angiogenesis, and immune response [8]. Whereas adipocyte-secreted adiponectin and leptin circulate in the blood as endocrine factors, it was demonstrated that some adipokines mainly have a para or autocrine functions within AT without a contribution to inter-organ tissue crosstalk [9]. Serum concentrations of several adipokines reflect body energy stores, fat mass and distribution, systemic insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, a pro-inflammatory state, and other phenotype characteristics [4,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. As examples, leptin serum concentrations are proportionally secreted to body fat mass [17], where circulating adiponectin are typically lower in individuals with obesity compared to those who are lean [18]. Additionally, several immune-modulating adipokines, such as IL-6, IL-8, CXCL5, or CCL2, are elevated in the obese state [9,19]. These changes in adipokines’ secretion pattern can be explained by AT remodeling, a process in which quantitative and qualitive changes in the cellular composition of AT occur in response to excessive weight gain [20].
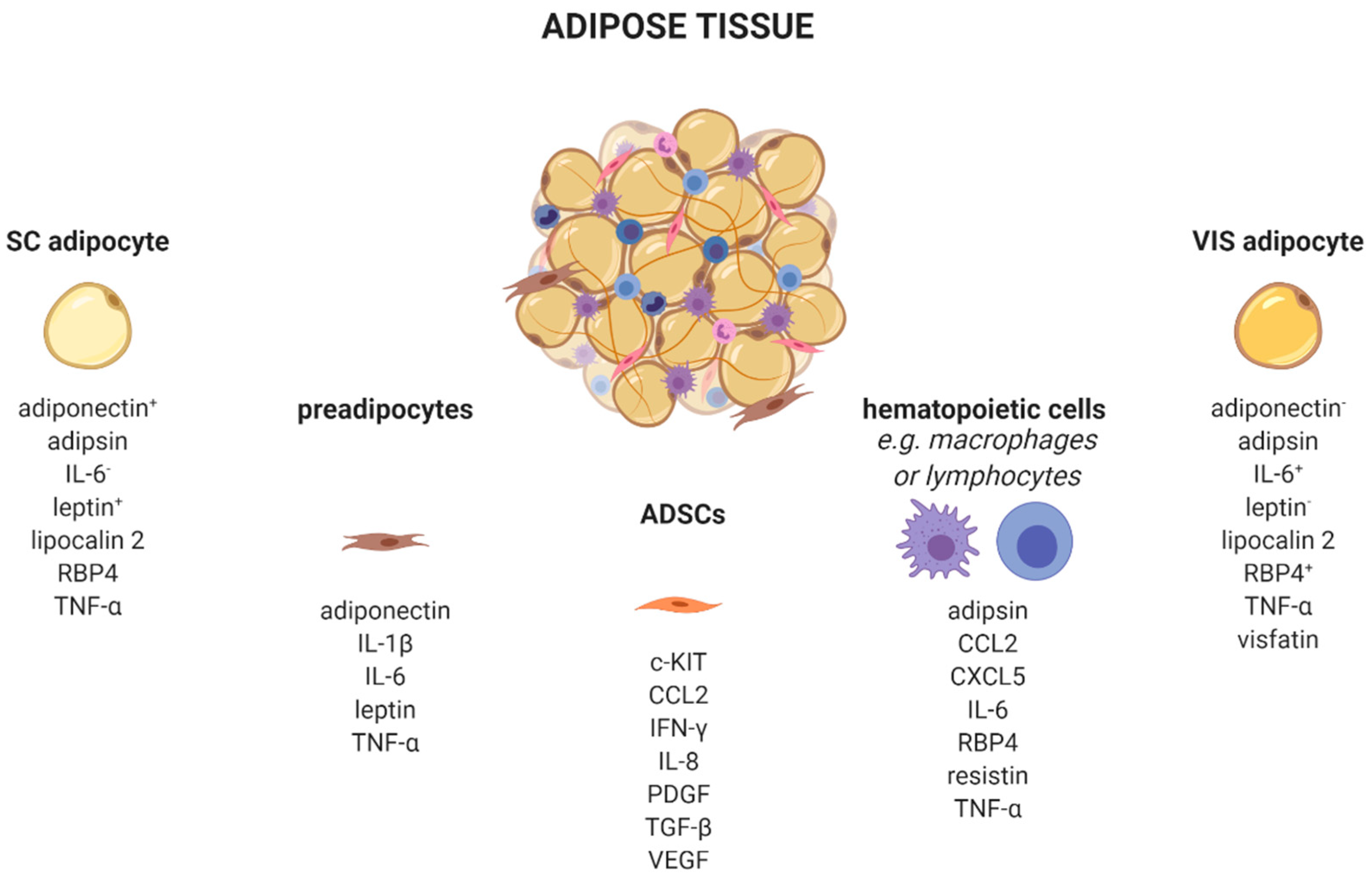
AT is a complex organ composed of several cell types (Figure 1). Adipocytes account for up to 80% of AT volume, but reflect only 20–40% of cell number. AT consists of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), preadipocytes, endothelial cells, and leukocytes [21,22]. Very recently, single-nucleus RNA-sequencing (snRNA-seq) analysis of mouse and human adipose tissue revealed a subpopulation of adipocytes that regulates thermogenesis [23]. Depending on their type, different AT-cells produce distinct adipokine patterns. Therefore, knowing the cellular origin for adipokine production is important to dissect which cell type might be enriched and/or activated in AT. For example, adipocytes exhibit a quantitatively distinct adipokine pattern in the function of the fat-depot (subcutaneous (sc) and visceral (vis)) origin. Adiponectin and leptin are predominantly expressed in sc AT [24]. In contrast, IL-6 [25], omentin [26], visfatin [27], and RBP4 exhibit higher vis than sc production [28]. Adipsin [29], lipocalin 2 [30], and TNF-α [31] are secreted in both depots in comparable amounts. Using single-cell or single nuclei transcriptomics, it is now possible to discriminate adipocyte subpopulations within one depot, as well as more than 10 different AT cell types which differ in their metabolic and transcriptional properties including the identification of differences in cellular adipokine sources [23,32,33,34].
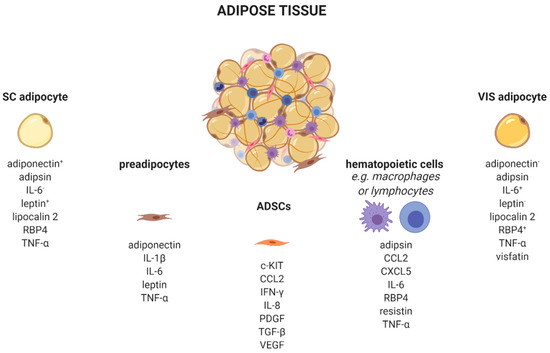
Figure 1.
Adipose tissue cells secrete distinct adipokines. Adipose tissue consists of a variety of cell types, such as adipocytes, preadipocytes, adipose tissue-derived stem cells, and several immune cells which produce and secrete cell-type-specific adipokines. +/−, higher/lower secreted in sc or vis. c-KIT, KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; CXCL5, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 5; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor; RBP4, retinol binding protein 4; SC, subcutaneous; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VIS, visceral. Created with BioRender.com.
Besides adipocytes, ADSCs produce a variety of chemokines and growth factors such as the pro-angiogenic CCL2, IL-8, vascular-endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [35], platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF) [36], or c-kit which induces endothelial cell proliferation [37]. Furthermore, ADSCs secrete immune-modulating substances like interferon-γ (IFN-γ) or transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) [38].
Depending on the fat depot, 15–50% of all resident AT-cells are preadipocytes [39]. Using a conditioned medium from obese murine epididymal AT, Renovato–Martins et al. demonstrated that 3T3-L1 preadipocytes secrete leptin and adiponectin as well as the pro-inflammatory factors IL-6, TNFα, and IL-1β [40].
In addition to those cell types of mesenchymal origin, there are various hematopoietic cells resident in AT. Nearly all known leukocytes such as macrophages, monocytes, dendritic, or natural killer cells, B-, and T-cells, as well as neutrophils or eosinophils, are of high importance in the adipokine context. The majority of immune cells express the leptin receptor on their cellular surface. Since circulating levels elevate proportional to the amount of white adipose tissue, leptin acts as a pro-inflammatory adipokine on immune cells. Subsequently, leptin receptor signaling via JAK2-STAT leads to a broad range production of pro-inflammatory adipokines, such as interleukins (IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, and IL-18), TNFα, or CCL2 [22,41]. Indeed, CCL2 (MCP-1) is a member of the small inducible gene family that plays a role in the recruitment of monocytes to sites of injury and infection, but also to AT under conditions of inflammation or adipocyte apoptosis [42,43,44]. Recently, CCL2 has been described as an important factor linking sc AT to altered glucose metabolism and body fat distribution [45].
In this review, we summarized recent data on the importance of C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) in the context of obesity.
2. C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2
2.1. Structure, Sources and Signaling
Chemokines are proteins with molecular weights ranging between 8 to 12 kDa that mediate cellular movement (chemotaxis), hematopoiesis, leukocyte degranulation, and angiogenesis [46]. Four chemokine subfamilies have been categorized based on the number and location of N-terminal cysteine residues: C, CC, CXC, and CX3C [47]. Chemokine sequences are highly conserved and share similar structures consisting of a flexible N-terminus followed by a loop containing three antiparallel β-sheets on to which is folded an α-helix [48]. Experiments which also defined the crystal structure of CCL2 revealed that it forms dimers in an anti-parallel β strand arrangement between the two flexible N-termini [49].
CCL2, also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), was the first discovered human CC-family chemokine [50,51]. The gene is located on chromosome 17 (q11.2) [52] and is produced by endothelial cells, fibroblasts, epithelial, smooth muscle, mesangial, astrocytic, monocytic, and microglial cells [53,54,55,56], whereas monocytes and macrophages are major sources of CCL2 [57,58]. Additionally, (pre-)adipocytes express CCL2 [59].
CCL2 expression is induced by inflammatory stimuli (IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)), transforming growth factor β (TGFβ), lipopolysaccharide (LPS), interferon γ (IFNγ), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) [60]. Human serum CCL2 has been associated with a chronic pro-inflammatory state and was suggested as a biomarker for malignant disease such as prostate and breast cancer [61,62]. High CCL2 expression in tissues indicates chemo-attraction of monocytes in the context of local defense mechanism activation and repair of tissue damage [63].
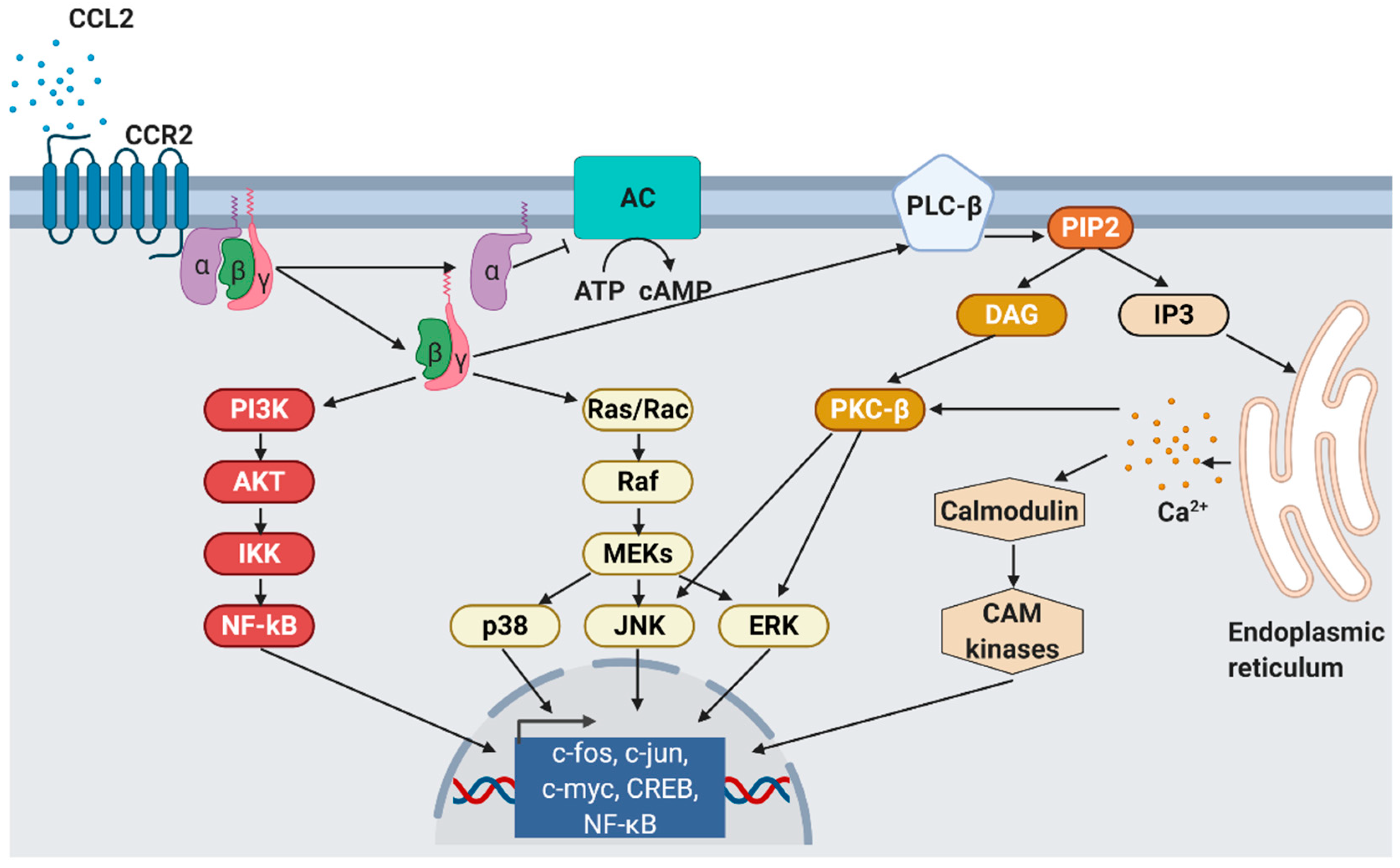
Chemokines are secreted in response to pro-inflammatory signals, such as cytokines, to selectively recruit immune cells including monocytes, neutrophils, or lymphocytes to sites of inflammation or injuries. For CCL2, there are two activation pathways described. During the canonical pathway, inflammatory substances such as tumor-necrosis factor α (TNFα) binds to its receptor, resulting in the activation of the inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase (IKK). Activated IKK then phosphorylates the NF-κB-bound inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB), whereby IκB is degraded. Consequently, released NF-κB homodimers translocate to the nucleus where they activate the transcription of inflammation-related genes e.g., CCL2, TNFα, and IL-6 [64]. Alternatively, CCL2 can be activated by the non-canonical pathway, i.e., NF-κB-independent CCL2 expression stimulated by PDGF [50] or insulin. In human aortic endothelial cells, physiological insulin concentrations were shown to suppress the expression of both NF-κB and CCL2 by more than 60% [65]. Nakatsumi et al. demonstrated that insulin activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway which leads to the inhibition mTORC1-repressor, the ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB). In turn, mTORC1 induces forkhead box K1 (FOXK1) dephosphorylation via protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), leading to CCL2 expression [66] (Figure 2).
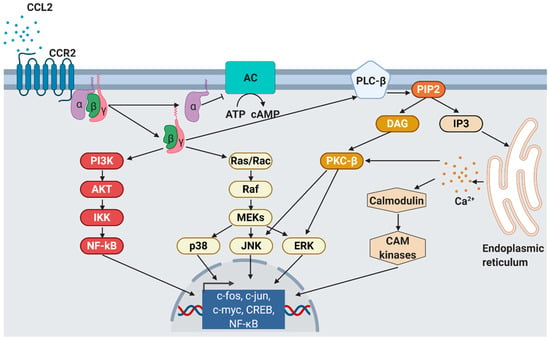
Figure 2.
CCL2 signaling. As response to CCL2 binding at the N-terminus, extracellular loops and transmembrane bundle of CCR2, the intracellular G-protein αi subunit dissociates from the CCR2 and the βγ subunit. The α subunit then inhibits adenylyl cyclase (AC) function resulting in decreased cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels. In contrast, the βγ subunit signaling induces gene expression via several pathways. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; IKK, inhibitor of NF-κB kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor of kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Ras, rat sarcoma; Rac, ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate; Raf, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; p38, mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK, c-jun N-terminal kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PLC-β, phospholipase C-β; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; PKC-β, protein kinase C-β; CAM, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; c-fos, proto-oncogene c-Fos; c-jun, proto-oncogene Jun; c-myc, proto-oncogene Myc; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein. Modified from Bose S. & Cho J. [75] using BioRender.com.
The effects of CCL2 on target cells are mediated by a specific chemokine receptor. Cells that express the distinct CC chemokine receptor (CCR) are able to migrate along the chemokine gradient upon CCL2 activation [67]. CCRs are G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) belonging to the rhodopsin or serpentine receptor family [68] which are expressed on different types of leukocytes such as eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells [69]. Human CC chemokines bind to at least two different CCRs.
CCL2 usually binds to CCR2 that exists in two different splice variants, CCR2A and CCR2B, which differ in their C-terminal tails [70]. In contrast to the widespread expression of CCL2, CCR2A is mainly expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells and mononuclear cells, whereas CCR2B is the predominant receptor on monocytes and natural killer cells [71]. In addition to CCL2, CCR2 binds another five pro-inflammatory cytokines, CCL7 [72], CCL8 [73], CCL12 [74], CCL13 [75], and CCL16 [76]. However, CCL2 has the highest activation potential that finally leads to monocyte migration into target tissues [77]. As a result of CCL2/CCR2 binding, cell migration is promoted by the activation of several signaling cascades such as JAK2/STAT3 [78], MAP kinase [79], and PI3K [80] pathways (Figure 3).
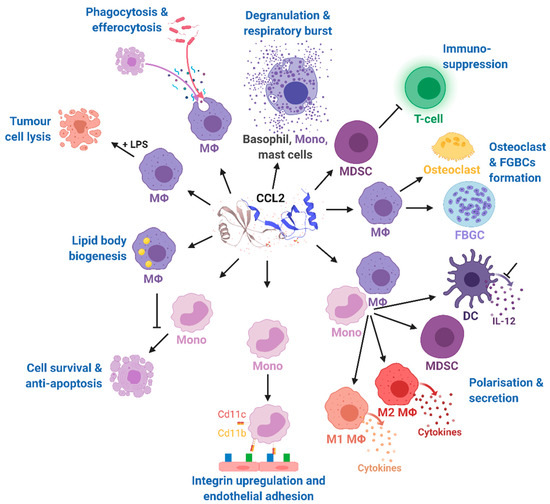
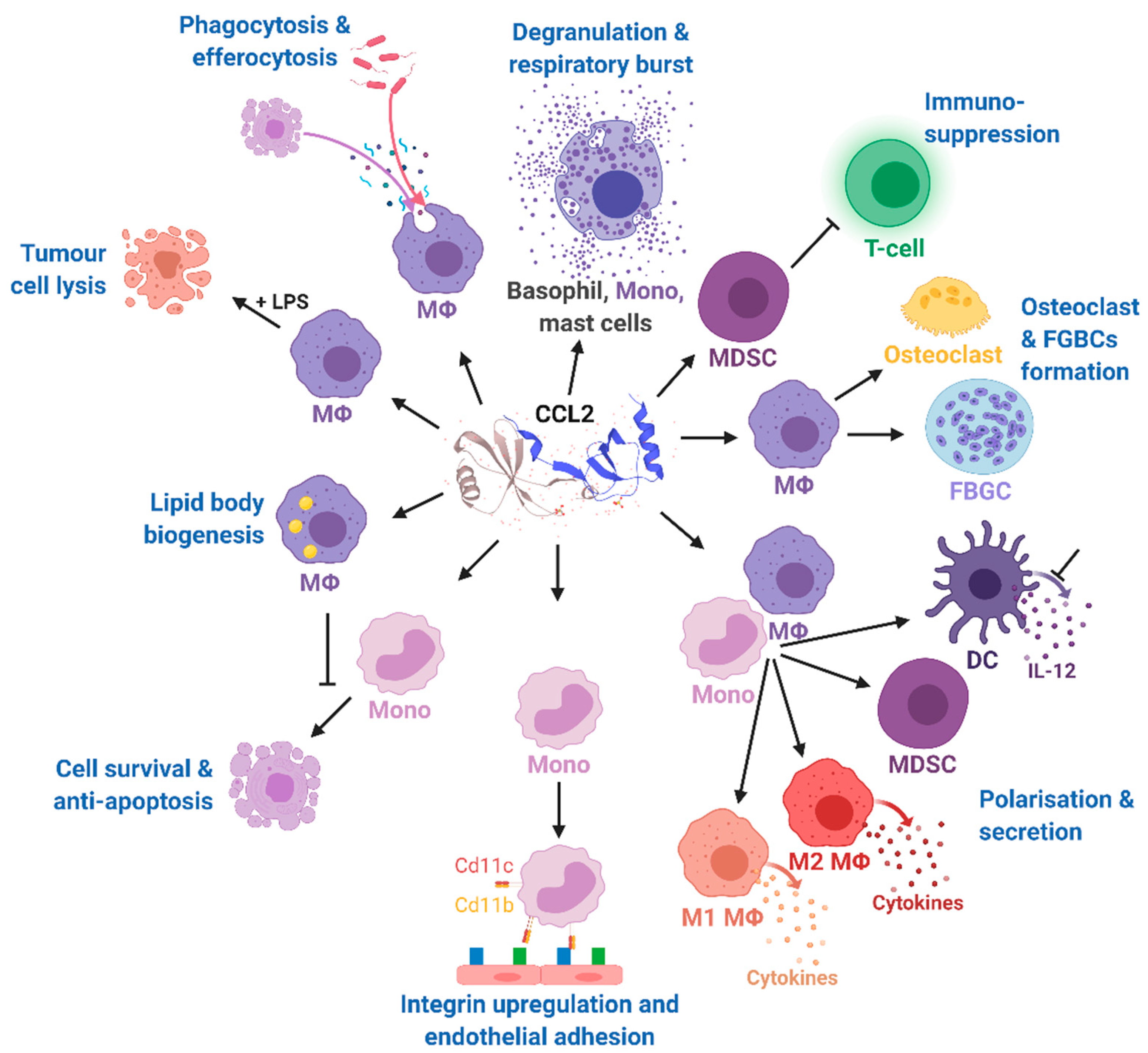
Figure 3.
Effects of CCL2 on different immune cell types. Mono, monocytes; MΦ, macrophages; DC, dendritic cells; FBGCs, foreign body giant cells; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; IL-12, interleukin 12; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; CD11b, cluster of differentiation molecule 11B; CD11c, cluster of differentiation molecule 11C. The CCL2 structure was taken from uniprot [86]. Modified from Gschwandtner M. et al. [60] using BioRender.com.
CCL2’s binding at CCR2 results in the dissociation of GDP from the Gαi subunit which associates with intracellular GTP and inhibits membrane-bound adenylyl cyclases, finally leading to decreased intracellular cAMP levels. In contrast, the released G-protein βγ heterodimer activates phospholipase C which then hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) [75]. IP3 diffuses in the cytosol and stimulates calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum [81]. The released Ca2+ is further bound by calmodulin (CaM), an essential modulator of various processes like immune response, inflammation [82], apoptosis, or metabolism [83]. Elevated Ca2+ levels as well as DAG activate protein kinase C-β (PKC-β) that mediates gene expression via c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) activation [84]. Monocyte migration is regulated via Gβγ activation of PI3K/Akt, which in turn polymerizes actin for pseudopod formation [85].
The multiple and pleiotropic effects of CCL2 on multiple cells of the myeloid lineage are summarized in Figure 4 and are more extensively discussed in a recent comprehensive review highlighting the role of CCL2 on immune cell behavior and tumor immunity [60]. In our review, we focused on the role of CCL2 in the context of obesity-related diseases.
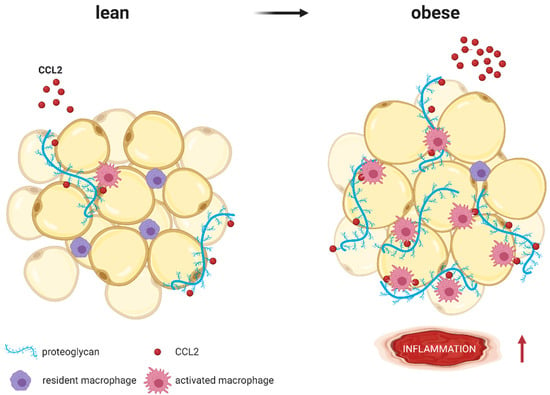
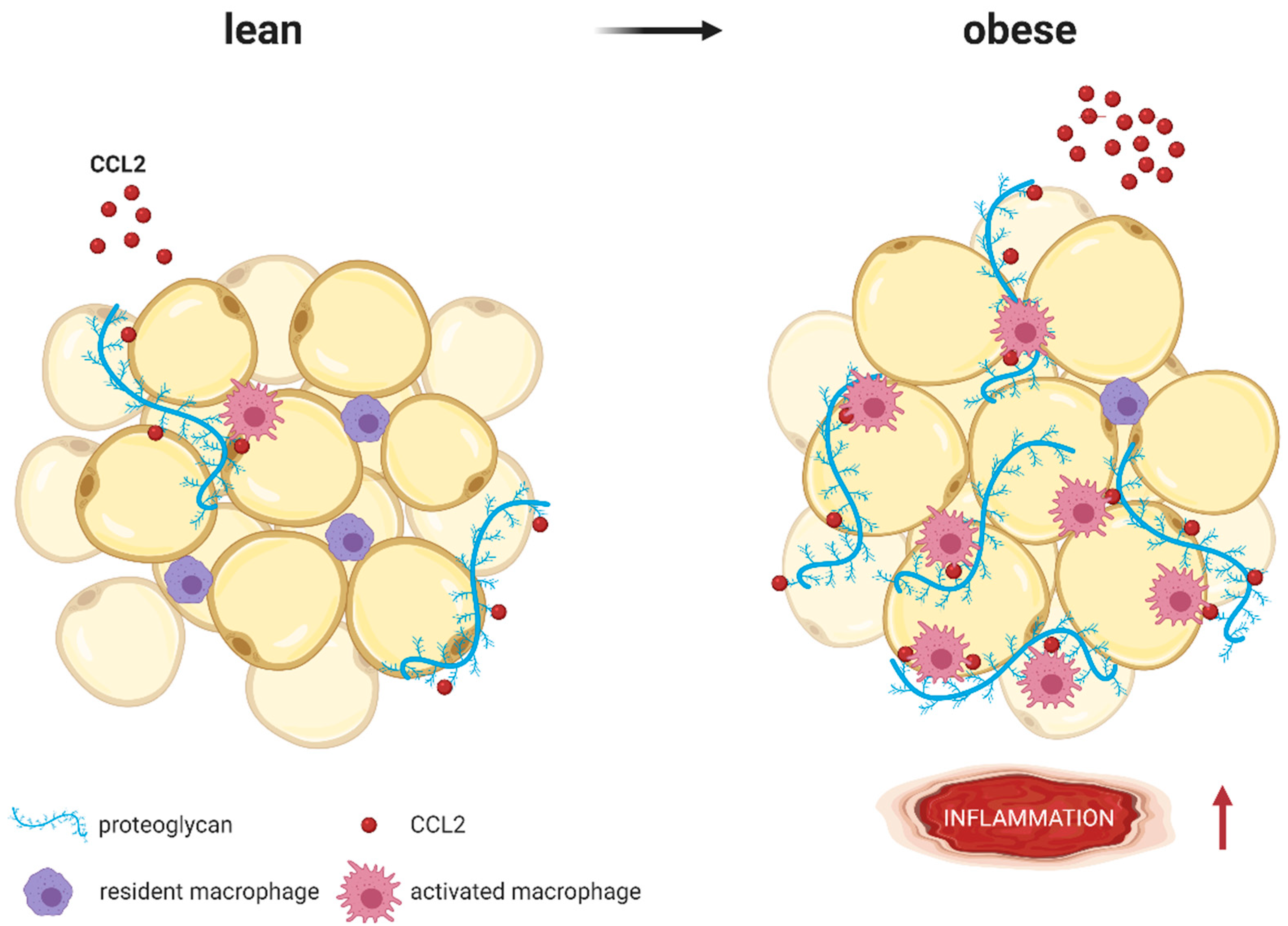
Figure 4.
CCL2 (red molecules) binds to proteoglycans (blue strands) such as heparan sulfate or heparin, which are part of the extracellular matrix surrounding adipocytes. Whereas lean AT expresses low proteoglycan levels, expression increases with obesity. As coreceptors, proteoglycans immobilize CCL2 and present it to macrophages, resulting in higher AT inflammation (represented by ↑). Modified from Pessentheiner A. et al. [140] using BioRender.com.
2.2. Animal Models
To study the physiological role of CCL2 and to investigate its signaling pathways, knockout mice were generated. Mice deficient in Ccl2 are viable, fertile, and reproduce with a normal litter size, sex distribution, development, and life span as expected from wild-type mice [42,87].
Mice with an ablation of Ccl2 develop severe defects in monocyte recruitment to sites of inflammatory damage or in response to immunological signaling [42]. When crossed with low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-deficient mice, CCL2 has been shown to reduce atherosclerosis upon high-cholesterol diets, suggesting an important role of CCL2 in the initiation of atherosclerosis [88].
Even though CCL2 has a central role in monocyte recruitment, there are several CC chemokines known that modulate chemotaxis in a similar manner, e.g., CCL7 (MCP3), CCL8 (MCP2), CCL12 (MCP5), or CCL14 (MCP4). Notwithstanding that Ccl2 mainly binds to Ccr2, this receptor can be further activated by Ccl7 and Ccl12 in mice [89,90,91]. In summary, this suggests that other chemokines potentially compensate for the loss of Ccl2 in knockout mice. Nevertheless, Ccl2−/− mice showed impaired monocyte trafficking and cytokine secretion. Apart from finding normal numbers of Kupffer cells and macrophages in Ccl2-deficient mice, these mice were not able to recruit monocytes or macrophages 72 h after thioglycolate administration [42], an agent that increases monocyte migration after intraperitoneal injection [92]. Splenocytes of Ccl2−/− mice were characterized by a significant reduction of IL-4 and IL-5 production and an about 50% reduced IFN-γ secretion [42].
In a model of myocardial infarction, Ccl2−/− mice were characterized by both a decreased and delayed macrophage infiltration and a delayed replacement of damaged cardiomyocytes [93]. Furthermore, these mice showed similar infarct sizes, an extended inflammation phase, and a lower post-infarction left ventricle remodeling [93].
Knockout mice were further used to validate the impact of Ccl2 in ulcerative colitis. Ccl2−/− mice exhibit lower macrophage and CD3+ T cell infiltration as well as reduced IL-1β, IL-12p40, and IFN-γ production, ultimately resulting in a reduced severity of colitis [94].
Targeting Ccl2 as a therapeutic strategy in kidney diseases was also analyzed using mice lacking Ccl2. Nephritis was induced with nephrotoxic serum, whereupon wild-type mice reacted with five times higher Ccl2 expression compared to unstimulated mice [95]. Around 90% of renal Ccl2 was localized within cortical tubules and most of them get damaged during induced nephritis. In contrast, Ccl2-deficient mice presented a ~40% reduction of tubular injury coming from a decreased macrophage recruitment to Ccl2 producing tubular endothelial cells [95].
Furthermore, Ccl2 plays an essential role in skeletal muscle regeneration. The comparison of wild-type and Ccl2−/− mice which underwent femoral artery excision (FAE) exposed a decreased, but longer lasting macrophage infiltration associated with residual necrotic tissue. The injured muscle was mostly regenerated 21 days after FAE in Ccl2−/− mice, but in contrast to wild-types they presented an enhanced adipocyte accumulation within the remodeled muscle tissue [96]. Both decreased macrophage infiltration and impaired muscle regeneration with increased adipocyte infiltration were also described for Ccr2-deficient mice [97].
2.3. Human Mutations in the CCL2 Pathway and Associated Diseases
Polymorphisms within the CCL2 gene are described in the context of several human diseases. Neural tube defects (NTD) such as spina bifida belong to the most common congenital malformations that can be well treated by maternal folic acid supplementation during pregnancy [98]. Nevertheless, a maternal polymorphism in the CCL2 promotor region is associated with a 1.5-fold increase of NTD in children [98]. Additionally, a chronic low folate status is a major factor to suffer from hyperhomocysteinemia which, in turn, is a risk marker for atherothrombotic diseases. During the development of atherosclerotic lesions, endothelial cells upregulate the expression of CCL2. Therefore, folate shortage results in increased CCL2 levels via augmented p38 expression [99]. Moreover, women carrying a 677C>T polymorphism in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, a key enzyme in the folate/homocysteine metabolism, showed strongly elevated CCL2 levels caused by enhanced homocysteine levels [100,101].
Two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) located in the CCL2 promotor region (-2136T) and in intron 1 (767G) are found strongly associated with an reduced susceptibility to human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) infection [102]. Because CCL2 is not able to bind the HIV-1 coreceptors CCR5 and CXCR4, the authors suggested that carriers of those SNPs potentially exhibit an differential immune response to HIV-1 infection [102].
Several SNPs in the CCL2 gene are associated with autoimmune diseases. As an example, the -2518A/G variation within the CCL2 promotor region has been shown to be associated with Crohn’s disease without affecting CCL2 plasma levels [103]. In contrast, ulcerative colitis presents raised CCL2 levels. Here, the -2518A/G SNP alone does not represent a genetic risk factor. However, in combination with a polymorphism within the interleukin-1β gene, the ulcerative colitis risk is increased significantly [104].
Polymorphisms concerning CCL2 are further associated with premature coronary artery disease [105], rheumatoid arthritis [106], sepsis [107], and lupus nephritis [108].
CCL2 has been shown to play an important role during development and progression of diabetic nephropathy (DN). In patients suffering from DN, microRNA miR-374a was found to be downregulated in nephropathic tissue. In cell culture, miR-374a can downregulate CCL2 expression, which suggests the miR-374a/CCL2 axis as potential target for DN treatment or therapy [109].
2.4. Effects of Antibody Administration Affecting CCL2/CCR2 Signaling
CCL2 regulates the monocyte and macrophage migration and infiltration into inflamed, but also tumor tissues. Therefore, a variety of cancers, e.g., glioma [110], breast tumors [111], or prostate cancer [112] are associated with increased serum concentrations of CCL2. Physiological anti-tumor responses can be inhibited by tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) or myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which promote tumor growth [110]. Systemic CCL2 blockade with anti-CCL2 antibodies (Ab) resulted in decreased TAMs and MDSCs as well as modestly prolonged survival both in mice bearing intracranial GL261 glioma or intracranial human U87 glioma xenografts. However, a combined treatment with the chemotherapeutic agent temozolomide and antibodies resulted in a significantly prolonged survival [110]. A combined treatment was also found to be beneficial for prostate cancer regression. The combination of anti-CCL2 Ab with docetaxel was shown to generate a more effective tumor regression than either Ab- or docetaxel-treatment alone [112]. Nevertheless, the use of CCL2 blockade as therapeutic is discussed controversially. In nude mice bearing MCF10CA1d breast tumor xenografts, continuous delivery of human CCL2-neutralizing Ab (0.3 mg/kg/day using osmotic pumps) was analyzed over 4 weeks. There, tumor growth, macrophage recruitment, and tumor angiogenesis were not affected by CCL2 blockade. Surprisingly, human CCL2 levels were significantly increased in both circulating blood and tumor interstitial fluid, whereas murine CCL2 levels were not affected [111].
Chronic inflammation is accompanied by elevated CCL2 levels as exemplified in hepatocellular carcinoma or rheumatoid arthritis. Mice carrying a miR-122 knockout displayed upregulated hepatic CCL2 expression leading to hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Treatment with neutralizing CCL2 Ab suppressed chronic liver inflammation, reduced liver damage and both liver carcinoma incidence and tumor burden by downregulating pro-inflammatory pSTAT3, c-MYC, and NF-κB signals. Tumorigenesis was inhibited by enhanced natural killer cell cytotoxicity and IFNγ secretion after CCL2 Ab administration [113]. However, in the context of rheumatoid arthritis, treatment with human anti-CCL2 monoclonal Ab does not have a benefit compared with placebo control [114]. There was an unexpected dose-related CCL2 increase, resulting in worsening rheumatoid arthritis in patients treated with high doses of the Ab [114]. In addition, the blockade of CCL2 receptor CCR2 via human CCR2 blocking antibodies displayed up to 94% reduction of free CCR2 on monocytes, but without an amelioration of synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis [115]. Taken together, these results did not support a beneficial role of CCL2 Ab treatment in the context of rheumatoid arthritis.
2.5. CCL2 in Obesity and Obesity Related Diseases
Obesity is a major risk factor to develop noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) such as hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and specific types of cancer. Worldwide, all NCDs together account for more than 70% of premature deaths, which in turn highlights the impact of obesity in the context of a global health burden (reviewed in [116]). In general, the BMI correlates with AT CCL2 expression, whereas weight loss reduces these levels [117]. CCL2 has been shown to play a unique role among several cytokines that may influence the function of adipocytes, recruitment of AT macrophages, and the link between AT inflammation and insulin resistance [117,118,119].
2.5.1. CCL2 Reflects a Pro-Inflammatory State
Obesity can contribute to local AT inflammation which most likely underlies a systemic chronic low-grade inflammation [120]. The typical symptoms of inflammation, heat, pain, redness, and swelling are caused by the effects of inflammatory regulators and mediators such as cytokines or chemokines [121].
The mechanisms of how obesity contribute to activation or maintenance of inflammation are not completely understood, but may include hypoxia in adipose tissue, increased adipocyte apoptosis, several stresses in AT, and others [120,122,123,124]. A permanent excess of nutrients can induce intracellular stress in adipocytes, leading to inflammation [125]. In addition, a systemic pro-inflammatory state is frequently induced by macrophage recruitment as a consequence of adipocyte apoptosis, AT-derived bacteria, accumulation of xenobiotics, altered fatty acid flux within AT, or others [126,127,128,129]. Cell culture experiments revealed the ability of macrophages to express higher levels of CCL2 mRNA after incubation with palmitic acid [130]. Elevated levels of free fatty acids can upregulate CCL2 expression through the toll-like receptor (TLR) 4/TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF)/interferon regulatory factor (IRF) 3 pathway [131]. Human monocytic cells undergoing a combined incubation with palmitate and TNF-α expressed significantly higher amounts of CCL2 as treated with one of these components alone [131]. The authors concluded that palmitate binding at TLR4 amplifies the TNF-α/NF-κB-induced CCL2 expression via downstream TRIF/IRF3 activation.
Moreover, in vitro experiments identified ten miRNAs dysregulated during obesity which are strongly associated with the secretion of CCL2 [132]. miR-193b was shown to modulate CCL2 expression indirectly by the downregulation of several transcription factors, e.g., NFKB1. In contrast, miR-126 can directly bind at the 3′-untranslated region of CCL2 mRNA and thereby regulate its expression [132].
Additionally, both adipocyte hyperplasia and hypertrophy cause local hypoxia within AT that triggers adipocyte death, inflammation, tissue fibrosis, and angiogenesis [133]. In murine 3T3-L1 cells as well as in human SW872 adipocytes cultured under intermittent hypoxia conditions, mRNA levels of CCL2, RETN, and TNFα were significantly increased without affecting promotor activity. All three genes exhibited a miR-452 target sequence and miR-452 levels were significantly decreased under hypoxia in these cells [134]. Hence, the authors summarized that hypoxia downregulates miR-452 which in turn increases the expression of CCL2, RETN, and TNFα, causing insulin resistance. In a comparison of age-, sex-, and BMI-matched patients with metabolically healthy obesity either with preserved insulin sensitivity or insulin resistance, we found that neither CCL2 serum concentrations nor AT expression are related to AT inflammation [14]. Despite that, CCL2 could represent one of the mechanistic links between obesity and related diseases which are at least in part mediated by a pro-inflammatory state.
Very recently, upregulation of CCL2 expression in human subcutaneous AT has been related to AT senescence in severely obese individuals [45]. Together with other factors, including senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal), insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and IL-6, CCL2 could thereby contribute to a higher number of senescent cells which may perpetuate AT inflammation and fibrosis as additional cellular sources of proinflammatory factors [45]. An intact remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), a network of different proteins and proteoglycans, is required for healthy adipose tissue expansion [135,136]. Through limiting the expansion of “metabolically safe” fat depots, altered extracellular matrix composition may indirectly contribute to metabolic diseases [137]. AT fibrosis maybe considered an end stage of ECM alterations, which has been associated with obesity comorbid disorders [138,139].
CCL2 binds to proteoglycans, which are part of the extracellular matrix surrounding adipocytes. Whereas lean AT expresses low proteoglycan levels, expression increases with obesity. Proteoglycans immobilize CCL2 and present it to macrophages resulting in higher AT inflammation [140,141,142] (Figure 3). Inhibition of NLRP3 and subsequent reduction of AT CCL2 expression has been shown to reduce fibrosis and related AT inflammation [143]. In addition to monocyte recruitment into AT, the CCL2-CCR2 axis has been identified as an important mechanism of how AT inflammation in visceral depots may recruit regulatory T cells in a sex hormone-dependent manner [144].
Stromal CCL2 signaling in AT may even play a role in promoting fibrosis of mammary tumors through the recruitment of myeloid-lineage cells [145]. This example demonstrates that increased CCL2 may link obesity, AT inflammation, and fibrosis to certain types of cancers.
2.5.2. CCL2 and Insulin Resistance
It is well established that chronic low-grade activation of the innate immune system caused by obesity leads to the manifestation of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Developing insulin resistance is closely related to adipocyte hypertrophy and following proinflammatory responses [146]. Using a 3T3-L1 cell model, it has been demonstrated that adipocytes treated with saturated fatty acids produced higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines, such as Ccl2, Tnf-α, or Il-6, than cells treated with monounsaturated fatty acids [146]. In contrast, Kim et al. showed that hypertrophic adipocytes became insulin resistant independently of proinflammatory responses through impaired Glut4 trafficking [146]. Furthermore, Kawano et al. found that the first organ expressing high levels of Ccl2 in response to a high-fat diet (HFD) is the colon. Higher Ccl2 levels recruit pro-inflammatory macrophages, resulting in increased gut permeability, activation of the inflammasome, and finally in inflammation and AT insulin resistance [147].
Rodent studies suggested that insulin resistance is caused by AT inflammation [44,148]. Indeed, immuno-compromised mice are not protected against HFD-induced insulin resistance. In particular, early onset of HFD-induced insulin resistance was independent of inflammation, whereas the chronic state during obesity was mediated by macrophages [149]. However, Ccr2 knockout mice showed improved insulin resistance and reduced macrophage infiltration under HFD [150].
During obesity, the number of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages is increased in white adipose tissue (WAT) [151]. This increase can be explained by at least two mechanisms. First, mature adipocytes secrete CCL2 which recruits circulating monocytes into AT where they differentiate into macrophages [151]. The second explanation is that CCL2 triggers resident AT macrophage proliferation during obesity [152]. To investigate the mechanisms by which Ccl2 is activated in adipocytes, insulin resistant, mTorc2-deficient AdRiKO mice have been generated. Ablation of insulin/mTorc2 signaling resulted in elevated Ccl2 expression exclusively in adipocytes, but not in fibroblasts or hepatocytes leading to AT inflammation. Based on these findings, the authors proposed that insulin resistance is the cause and not the result of AT inflammation [153].
2.5.3. CCL2 and Cardiovascular Diseases
Obesity is one of the major risk factors leading to the development of cardiovascular diseases. However, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood yet. Chemokines are of relevance in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (ASCVD) and act in a network instead of a single cytokine modality. CCL2 is able to recruit different cell types such as monocytes, memory T cells, or dendritic cells and is therefore associated with cardiac diseases like ischemia, reperfusion injury, or fibrosis heart failure [154]. Plasma levels of CCL2 were found to be significantly increased in patients with coronary heart disease compared to healthy individuals [155].
In a cohort of 2270 patients with acute coronary syndromes, increased CCL2 levels were found to be associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis and mortality of myocardial infarction [156]. In a study including 1411 patients with ASCVD over a median follow-up of 3.3 years, both lower and higher serum CCL2 levels were shown to be linked to a higher mortality [157]. Another study investigated the influence of the CCL2-2518 A/G SNP of circulating C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in patients with ASCVD. The highest CRP levels were found in patients homozygous for this GG polymorphism [158]. This SNP was further shown to be associated with higher CCL2 levels in patients with insulin resistance compared to those with insulin sensitivity [159]. However, studies investigating circulating CCL2 levels as predictors for ASCVD are not coherent. In a small group of 83 patients with acute myocardial infarction and 38 patients with stabile angina, both CCL2 and CC chemokine, regulated upon activation, normal T cell-expressed and presumably secreted (RANTES) serum levels were analyzed. Whereas CCL2 concentrations were observed as highly variable, the authors suggest RANTES serum levels as better reflectors for atherosclerotic lesions [160]. In summary, it remains controversial whether CCL2 plays a causative role in ASCVD.
2.6. CCL2 as Drug Target
CCL2 is a promising drug target for inflammatory, cardio-metabolic, and some malignant diseases (Table 1). CCL2 is implicated in pathogeneses of several diseases characterized by monocytic infiltrates, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and atherosclerosis. CCL2 is further involved in neuroinflammatory processes that mediate diseases of the central nervous system (CNS), which are characterized by neuronal degeneration. Indeed, CCL2 expression in glial cells is increased in epilepsy, brain ischemia, Alzheimer’s disease, and traumatic brain injury [161,162]. Especially, the reduction of monocyte migration to the site of inflammation by CCL2 inhibition has been shown to successfully reduce inflammation in mice [163]. In a mouse model of diabetes-associated periodontitis, oral administration of Bindarit, a CCL2 synthesis inhibitor, suppressed periodontal inflammation, resulting in reduced alveolar bone loss and increased periodontal epithelial thickness. Additionally, the monocyte infiltration into the periodontium was reduced after Bindarit treatment [163]. Patients with severe respiratory illness caused by seasonal influenza virus H7N9 show enhanced levels of pro-inflammatory factors including CCL2. In mice infected by H7N9 influenza virus, an anti-inflammatory therapy with Bindarit was demonstrated to be ineffective. Therefore, a Bindarit treatment for supportive influenza-therapy has not been pursued [164].

Table 1.
Potential for CCL2 as a drug target to treat inflammatory, cardio-metabolic, and distinct malignant disease in the future. As of January 2021, no specific CCL2-targeting treatment has been approved by responsible legal authorities.
CCL2 may contribute to tumor progression and the spread of metastasis and could therefore be an interesting target for anti-cancer drugs. However, the CCL2/CCR2 axis seems to play a dual role in early tumor immunosurveillance and progression. Whereas the use of an anti-CCL2 monoclonal antibody reduced both the growth of primary malignant lesions and the metastases number in an implantable tumor model, CCL2 or CCR2 knockout mice developed transgenic tumors and had an increased number of metastases [165]. In multiple myeloma, CCL2 can recruit macrophages to the bone marrow. Those myeloma-associated macrophages are an essential factor in drug resistance by interacting with myeloma cells and upregulating their CCL2 expression. In turn, CCL2 upregulates the expression of MCP-1-induced protein (MCPIP1) in macrophages which triggers their polarization into the M2 phenotype that protects the myeloma cells from drug-induced apoptosis. Therefore, therapeutic strategies targeting MCPIP1 could be promising to enhance the chemotherapeutic effect [166].
Another approach to inhibit CCL2-action is to target its receptor, CCR2, to reduce inflammation. In this context, an allosteric, noncompetitive, peptidic CCR2 inhibitor, ECL1i, d(LGTFLKC) was described to solely inhibit CCL2-induced events in vitro. In a model of peritonitis, ECL1i inhibited monocyte and macrophage recruitment and further limited leukocyte recruitment and therefore disease progression in a murine model of multiple sclerosis [167]. In mice, intraperitoneal injections of TAK-779, a dual CCR2/CCR5 inhibitor, have been shown to reduce retinal vascular permeability in diabetic animals [168]. Taken together, there are several pharmacotherapeutic strategies and compounds at early phases of clinical studies (Table 1), but so far, no specific CCL2-targeting treatment has been approved for the treatment of the many diseases associated with CCL2 activation. To date, there is only one small molecule (CCR2/CCR5 antagonist Cenicriviroc) that reached a clinical phase 3 trial targeting liver fibrosis in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NCT03028740). An antibody against CCL2 (CNTO888, Carlumab), investigated in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer and patients with solid tumors, or an antibody against CCR2 (MLN1202, Plozalizumab), investigated in patients with RA, was not successful in clinical trials to date [169].
3. Summary and Conclusions
CCL2 is one of the first studied chemokines which has been predominantly investigated for the role in attracting immune cells into target tissues. The effects CCL2 are multiple and include regulation of myeloid cell function, immune response, modulation of cell-killing properties of monocytes and macrophages, but also linking obesity to its related cardio-metabolic and malignant diseases. Importantly, CCL2 exerts immunosuppressive effects that have been found to reduce the defense against malignant diseases. Targeting CCL2 signaling has attracted a lot of attention for potential clinical applications in the treatment of various types of cancer, atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, and type 2 diabetes. However, so far modulation of CCL2 itself or the CCL2/CCR2 axis has not yet resulted in pharmacotherapies. Several clinical trials (www.clinicaltrials.gov) with anti-CCL2 antibodies or small molecule CCR2 receptor antagonists are running and have to prove whether CCL2 is indeed a future drug target.
Funding
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) through CRC 1052, project number 209933838, subproject B1 to M.B.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
S.D. does not have any conflicts of interest to declare. M.B. received honoraria as a consultant and speaker from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Sanofi.
Abbreviations
| Ab | Antibody |
| AdRiKO | Adipose-specific Rictor knockout |
| ADSCs | Adipose-derived stem cells |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| AT | Adipose tissue |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CaM | Calmodulin |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 |
| CCR | CC chemokine receptor |
| c-kit | KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| DN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FAE | Femoral artery excision |
| FOXK1 | Forkhead box K1 |
| GDP | Guanosine diphosphate |
| GLUT4 | Glucose transporter 4 |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| GTP | Guanosine triphosphate |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IKK | Inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IP3 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| IRF | Interferon regulatory factor |
| IκB | Inhibitor of NF-κB |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LDL | Low density lipoprotein |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAP | Mitogen-activated protein |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MCPIP1 | MCP-1-induced protein |
| M-CSF | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| MDSC | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| mTORC1 | Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 |
| NCD | Noncommunicable diseases |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| NTD | Neural tube defect |
| PAI1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PKC-β | Protein kinase C-β |
| PP2A | Protein phosphatase 2A |
| RANTES | Regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and presumably secreted |
| RBP4 | Retinol binding protein |
| RETN | Resistin |
| RHEB | Ras homolog enriched in brain |
| sc | Subcutaneous |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| snRNA-seq | Single-nucleus RNA sequencing |
| STAT | Signal transducers and activators of transcription |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| TGFβ | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TRIF | TIR-domain containing adapter-inducing interferon β |
| VEGF | Vascular-endothelial growth factor |
| vis | Visceral |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
References
- Obregon, M.-J. Adipose tissues and thyroid hormones. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehr, S.; Hartwig, S.; Lamers, D.; Famulla, S.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.-G.; Cuvelier, C.; Ruige, J.; Eckardt, K.; Ouwens, D.M.; et al. Identification and validation of novel adipokines released from primary human adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2012, 11, M111.010504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheja, L.; Heeren, J. The endocrine function of adipose tissues in health and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arner, P. Editorial: Visfatin—A True Or False Trail To Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Shimomura, I.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Takahashi, M.; Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Matsuzawa, Y. 3. Role of adipocytokines on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in visceral obesity. Intern. Med. 1999, 38, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wood, I.S. Adipokines: Inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Joseph, F. Adipose Tissue and Adipokines: The Association with and Application of Adipokines in Obesity. Scientifica 2014, 2014, 28592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; Madan, A.K.; Hiler, M.L.; Cheema, P.; Bahouth, S.W. Comparison of the release of adipokines by adipose tissue, adipose tissue matrix, and adipocytes from visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues of obese humans. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.; Gebhardt, C.; Scholz, M.; Wohland, T.; Schleinitz, D.; Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Kovacs, P.; Tönjes, A. Relationship between 12 adipocytokines and distinct components of the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flehmig, G.; Scholz, M.; Klöting, N.; Fasshauer, M.; Tönjes, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Youn, B.S.; Blüher, M. Identification of adipokine clusters related to parameters of fat mass, insulin sensitivity and inflammation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M. Adipokines in gestational diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöting, N.; Fasshauer, M.; Dietrich, A.; Kovacs, P.; Schön, M.R.; Kern, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Insulin-sensitive obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E506–E515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.; Roth, I.; Richter, J.; Tönjes, A.; Kralisch, S.; Lossner, U.; Kratzsch, J.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M. Different associations of adipokines in lean and healthy adults. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönjes, A.; Fasshauer, M.; Kratzsch, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokine pattern in subjects with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance in comparison to normal glucose tolerance and diabetes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S. Revisiting leptin’s role in obesity and weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2380–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, E.; Scudiero, O.; Monaco, M.L.; Palmieri, A.; Mazzarella, G.; Costagliola, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A. New insight into adiponectin role in obesity and obesity-related diseases. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 658913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, S.S.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, J.B. Adipose tissue remodeling: Its role in energy metabolism and metabolic disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve Ràfols, M. Adipose tissue: Cell heterogeneity and functional diversity. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2014, 61, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, P. The role of adipokines in chronic inflammation. Immunol. Targets Ther. 2016, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Dong, H.; Balaz, M.; Slyper, M.; Drokhlyansky, E.; Colleluori, G.; Giordano, A.; Kovanicova, Z.; Stefanicka, P.; Balazova, L.; et al. snRNA-seq reveals a subpopulation of adipocytes that regulates thermogenesis. Nature 2020, 587, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, H. Gene expression in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues. Ann. Med. 2001, 33, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, S.K.; Bunkin, D.A.; Greenberg, A.S. Omental and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissues of Obese Subjects Release Interleukin-6: Depot Difference and Regulation by Glucocorticoid 1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-Z.; Lee, M.-J.; Hu, H.; Pray, J.; Wu, H.-B.; Hansen, B.C.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Fried, S.K.; McLenithan, J.C.; Gong, D.-W. Identification of omentin as a novel depot-specific adipokine in human adipose tissue: Possible role in modulating insulin action. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E1253–E1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, Y.; He, W.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Li, L. Visfatin is regulated by interleukin-6 and affected by the PPAR-γ pathway in BeWo cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöting, N.; Graham, T.E.; Berndt, J.; Kralisch, S.; Kovacs, P.; Wason, C.J.; Fasshauer, M.; Schön, M.R.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M.; et al. Serum Retinol-Binding Protein Is More Highly Expressed in Visceral than in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue and Is a Marker of Intra-abdominal Fat Mass. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.C.; Ljubicic, S.; Leibiger, B.; Kern, M.; Leibiger, I.B.; Moede, T.; Kelly, M.E.; Chatterjee Bhowmick, D.; Murano, I.; Cohen, P.; et al. Adipsin Is an Adipokine that Improves β Cell Function in Diabetes. Cell 2014, 158, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguet, T.; Quintero, Y.; Terra, X.; Martínez, S.; Lucas, A.; Pellitero, S.; Aguilar, C.; Hernández, M.; Del Castillo, D.; Richart, C. Upregulation of Lipocalin 2 in Adipose Tissues of Severely Obese Women: Positive Relationship With Proinflammatory Cytokines. Obesity 2011, 19, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, G.; Kiss, S.; Keszthelyi, L.; Sápi, Z.; Ory, I.; Salamon, F.; Kovács, M.; Vargha, P.; Szekeres, O.; Speer, G.; et al. Expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha protein in the subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in correlation with adipocyte cell volume, serum TNF-alpha, soluble serum TNF-receptor-2 concentrations and C-peptide level. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Sharma, R.; Gase, G.; Ussar, S.; Li, Y.; Welch, L.; Berryman, D.E.; Kispert, A.; Blüher, M.; Kahn, C.R. Tbx15 Defines a Glycolytic Subpopulation and White Adipocyte Heterogeneity. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Luong, Q.; Sharma, R.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Ussar, S.; Kahn, C.R. Developmental and functional heterogeneity of white adipocytes within a single fat depot. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e99291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, A.K.; Dankel, S.N.; Rastegarpanah, B.; Cai, W.; Xue, R.; Crovella, M.; Tseng, Y.; Kahn, C.R.; Kasif, S. Single-cell transcriptional networks in differentiating preadipocytes suggest drivers associated with tissue heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preisner, F.; Leimer, U.; Sandmann, S.; Zoernig, I.; Germann, G.; Koellensperger, E. Impact of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells on Malignant Melanoma Cells in An In Vitro Co-culture Model. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2018, 14, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salha, S.; Gehmert, S.; Brébant, V.; Anker, A.; Loibl, M.; Prantl, L.; Gehmert, S. PDGF regulated migration of mesenchymal stem cells towards malignancy acts via the PI3K signaling pathway. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2019, 70, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, H.; Qian, C. c-Kit-Positive Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote the Growth and Angiogenesis of Breast Cancer. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7407168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerlin, L.; Park, T.S.; Zambidis, E.T.; Donnenberg, V.S.; Donnenberg, A.D. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome and regenerative therapy after cancer. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wong, S.; Xie, W.; Lei, T.; Luo, Z. Palmitate modulates intracellular signaling, induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, and causes apoptosis in mouse 3T3-L1 and rat primary preadipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renovato-Martins, M.; Moreira-Nunes, C.; Atella, G.C.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.; Moraes, J.A. de Obese Adipose Tissue Secretion Induces Inflammation in Preadipocytes: Role of Toll-Like Receptor-4. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Rutledge, B.J.; Gu, L.; Fiorillo, J.; Lukacs, N.W.; Kunkel, S.L.; North, R.; Gerard, C.; Rollins, B.J. Abnormalities in monocyte recruitment and cytokine expression in monocyte chemoattractant protein 1-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartipy, P.; Loskutoff, D.J. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7265–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, H.; Tateya, S.; Tamori, Y.; Kotani, K.; Hiasa, K.I.; Kitazawa, R.; Kitazawa, S.; Miyachi, H.; Maeda, S.; Egashira, K.; et al. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, C.; Marcelin, G.; Adriouch, S.; Rose, C.; Genser, L.; Ambrosini, M.; Bichet, J.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Marquet, F.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; et al. Senescence-associated β-galactosidase in subcutaneous adipose tissue associates with altered glycaemic status and truncal fat in severe obesity. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.C.; Mayo, K.H. Chemokines from a Structural Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, B.J. Chemokines. Blood 1997, 90, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clore, G.M.; Gronenborn, A.M. Three-dimensional structures of α and β chemokines. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.M.; Nelson, C.A.; Van Berkel, V.; Lau, E.K.; Studts, J.M.; Brett, T.J.; Speck, S.H.; Handel, T.M.; Virgin, H.W.; Fremont, D.H. Structural basis of chemokine sequestration by a herpesvirus decoy receptor. Cell 2002, 111, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, B.H.; Reffel, A.C.; Stiles, C.D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 1983, 33, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, B.J.; Morrison, E.D.; Stiles, C.D. Cloning and expression of JE, a gene inducible by platelet-derived growth factor and whose product has cytokine-like properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 3738–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabian, M.; Sparkes, R.S.; Mohandas, T.; Fogelman, A.M.; Lusis, A.J. Localization of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 gene (SCYA2) to human chromosome 17q11.2-q21.1. Genomics 1991, 9, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barna, B.P.; Pettay, J.; Barnett, G.H.; Zhou, P.; Iwasaki, K.; Estes, M.L. Regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in adult human non-neoplastic astrocytes is sensitive to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or antibody to the 55-kDa TNF receptor. J. Neuroimmunol. 1994, 50, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, S.D.; Berliner, J.A.; Valente, A.J.; Territo, M.C.; Navab, M.; Parhami, F.; Gerrity, R.; Schwartz, C.J.; Fogelman, A.M. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein induces monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in human endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5134–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, Z.; Strieter, R.M.; Neild, G.H.; Thompson, R.C.; Kunkel, S.L.; Westwick, J. IL-1 receptor antagonist inhibits monocyte chemotactic peptide 1 generation by human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992, 42, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standiford, T.J.; Kunkel, S.L.; Phan, S.H.; Rollins, B.J.; Strieter, R.M. Alveolar macrophage-derived cytokines induce monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression from human pulmonary type II-like epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9912–9918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Yuhki, N.; Moore, S.K.; Appella, E.; Lerman, M.I.; Leonard, E.J. Human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). Full-length cDNA cloning, expression in mitogen-stimulated blood mononuclear leukocytes, and sequence similarity to mouse competence gene JE. FEBS Lett. 1989, 244, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Robinson, E.A.; Tanaka, S.; Appella, E.; Kuratsu, J.I.; Leonard, E.J. Purification and amino acid analysis of two human glioma-derived monocyte chemoattractants. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 169, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, C.C.; Romero, I.A.; Cancello, R.; Camoin, L.; Strosberg, A.D. Chemokines control fat accumulation and leptin secretion by cultured human adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 175, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwandtner, M.; Derler, R.; Midwood, K.S. More Than Just Attractive: How CCL2 Influences Myeloid Cell Behavior Beyond Chemotaxis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaur, I.; Noack, A.; Makarevic, J.; Oppermann, E.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Gasser, M.; Borgmann, H.; Huesch, T.; Gust, K.M.; Reiter, M.; et al. CCL2 Chemokine as a Potential Biomarker for Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 47, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubowicka, E.; Przylipiak, A.; Zajkowska, M.; Piskór, B.M.; Malinowski, P.; Fiedorowicz, W.; Ławicki, S. Plasma Chemokine CCL2 and Its Receptor CCR2 Concentrations as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Patients. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2124390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljada, A.; Ghanim, H.; Saadeh, R.; Dandona, P. Insulin Inhibits NFκB and MCP-1 Expression in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsumi, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakayama, K.I. Noncanonical Pathway for Regulation of CCL2 Expression by an mTORC1-FOXK1 Axis Promotes Recruitment of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 2471–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callewaere, C.; Banisadr, G.; Rostène, W.; Parsadaniantz, S.M. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in the brain: Implication in neuroendocrine regulation. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 38, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettgen, H.; Broide, D.H. Introduction to mechanisms of allergic disease. In Allergy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Charo, I.F.; Myers, S.J.; Herman, A.; Franci, C.; Connolly, A.J.; Coughlin, S.R. Molecular cloning and functional expression of two monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 receptors reveals alternative splicing of the carboxyl-terminal tails. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, C.; Civatte, M.; Pellissier, J.; Figarella-Branger, D. CCR2A and CCR2B, the two isoforms of the monocytes chemoattractant protein-1 receptor are up-regulated and expressed by different cell subsets in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2001, 102, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, C.H.; Leary, J.A. A competitive binding study of chemokine, sulfated receptor, and glycosaminoglycan interactions by nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 407, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, R.S.; Kallenbach, J.G.; Bachman, J.F.; Mitchell, A.; Paris, N.D.; Chakkalakal, J.V. Inhibition of inflammatory CCR2 signaling promotes aged muscle regeneration and strength recovery after injury. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafi, M.N.; Garcia-Zepeda, E.A.; MacLean, J.A.; Charo, I.F.; Luster, A.D. Murine Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein (MCP)-5: A Novel CC Chemokine That Is a Structural and Functional Homologue of Human MCP-1. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Cho, J. Role of chemokine CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 in neurodegenerative diseases. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomiyama, H.; Hieshima, K.; Nakayama, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Fujisawa, R.; Tanase, S.; Nishiura, H.; Matsuno, K.; Takamori, H.; Tabira, Y.; et al. Human CC chemokine liver-expressed chemokine/CCL16 is a functional ligand for CCR1, CCR2 and CCR5, and constitutively expressed by hepatocytes. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzani, S.; Zhou, D.; Locati, M.; Rieppi, M.; Proost, P.; Magazin, M.; Vita, N.; van Damme, J.; Mantovani, A. Receptors and transduction pathways for monocyte chemotactic protein-2 and monocyte chemotactic protein-3. Similarities and differences with MCP-1. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 3615–3622. [Google Scholar]
- Mellado, M.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Aragay, A.; del Real, G.; Martín, A.M.; Vila-Coro, A.J.; Serrano, A.; Mayor, F.; Martínez-A, C. The chemokine monocyte chemotactic protein 1 triggers Janus kinase 2 activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of the CCR2B receptor. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- Cambien, B.; Pomeranz, M.; Millet, M.A.; Rossi, B.; Schmid-Alliana, A. Signal transduction involved in MCP-1-mediated monocytic transendothelial migration. Blood 2001, 97, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, J.H.; Kirby, J.A.; Ali, S. Leucocyte chemotaxis: Examination of mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation by Monocyte Chemoattractant Proteins-1, -2, -3 and -4. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 127, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, E.; Roest, G.; Vervliet, T.; Parys, J.B.; Bultynck, G. IP3 receptor-mediated calcium signaling and its role in autophagy in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racioppi, L.; Noeldner, P.K.; Lin, F.; Arvai, S.; Means, A.R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 regulates macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11579–11591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, F.; Eckard, L.; Chen, S.; Nutt, L.K. Metabolic regulation of apoptosis via Ca+/Calmodulin Kinase II (CaMKII). BMC Proc. 2012, 6, P36. [Google Scholar]
- Sriraman, V.; Modi, S.R.; Bodenburg, Y.; Denner, L.A.; Urban, R.J. Identification of ERK and JNK as signaling mediators on protein kinase C activation in cultured granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 294, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.; Miltz, W.; Mir, A.K.; Wiessner, C. Targeting monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 signalling in disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2003, 7, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, T.; Warr, G.; Loy, J.; Bravo, R. Defects in macrophage recruitment and host defense in mice lacking the CCR2 chemokine receptor. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Okada, Y.; Clinton, S.K.; Gerard, C.; Sukhova, G.K.; Libby, P.; Rollins, B.J. Absence of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 reduces atherosclerosis in low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combadiere, C.; Ahuja, S.K.; Murphy, P.M. Cloning and functional expression of a human eosinophil CC chemokine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16491–16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, C.; Proost, P.; Charo, I.F. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-3, but not monocyte chemoattractant protein-2, is a functional ligand of the human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 receptor. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 6511–6517. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, L.B.; Cerovic, V.; Milling, S.W.F.; Graham, G.J.; Hansell, C.A.H.; Nibbs, R.J.B. Characterization of Conventional and Atypical Receptors for the Chemokine CCL2 on Mouse Leukocytes. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Goncalves, R.; Mosser, D.M. The Isolation and Characterization of Murine Macrophages. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2008, 83, 14.1.1–14.1.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewald, O.; Zymek, P.; Winkelmann, K.; Koerting, A.; Ren, G.; Abou-Khamis, T.; Michael, L.H.; Rollins, B.J.; Entman, M.L.; Frangogiannis, N.G. CCL2/monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulates inflammatory responses critical to healing myocardial infarcts. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.I.; Motomura, Y.; Wang, H.; El-Sharkawy, R.T.; Verdu, E.F.; Verma-Gandhu, M.; Rollins, B.J.; Collins, S.M. Critical role of MCP-1 in the pathogenesis of experimental colitis in the context of immune and enterochromaffin cells. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G803–G811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesch, G.H.; Schwarting, A.; Kinoshita, K.; Lan, H.Y.; Rollins, B.J.; Kelley, V.R. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 promotes macrophage-mediated tubular injury, but not glomerular injury, in nephrotoxic serum nephritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shireman, P.K.; Contreras-Shannon, V.; Ochoa, O.; Karia, B.P.; Michalek, J.E.; McManus, L.M. MCP-1 deficiency causes altered inflammation with impaired skeletal muscle regeneration. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Shannon, V.; Ochoa, O.; Reyes-Reyna, S.M.; Sun, D.; Michalek, J.E.; Kuziel, W.A.; McManus, L.M.; Shireman, P.K. Fat accumulation with altered inflammation and regeneration in skeletal muscle of CCR2−/− mice following ischemic injury. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, 953–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.E.; Etheredge, A.J.; Brown, K.S.; Mitchell, L.E.; Whitehead, A.S. Maternal genotype for the monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 A(-2518)G promoter polymorphism is associated with the risk of spina bifida in offspring. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2006, 140, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Jensen, L.E.; Huang, Y.; Kealey, C.; Blair, I.A.; Whitehead, A.S. The up-regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in Ea.hy 926 endothelial cells under long-term low folate stress is mediated by the p38 MAPK pathway. Atherosclerosis 2009, 205, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammons, A.L.; Summers, C.M.; Woodside, J.V.; McNulty, H.; Strain, J.J.; Young, I.S.; Murray, L.; Boreham, C.A.; Scott, J.M.; Mitchell, L.E.; et al. Folate/homocysteine phenotypes and MTHFR 677C>T genotypes are associated with serum levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, F.L.; Siow, Y.L.; Wang, G.; Lynn, E.G.; Karmin, O. Homocysteine stimulates the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in endothelial cells leading to enhanced monocyte chemotaxis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 216, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, W.S.; Goedert, J.J.; Strathdee, S.; Buchbinder, S.; Detels, R.; Donfield, S.; O’Brien, S.J.; Winkler, C. MCP-1-MCP-3-Eotaxin gene cluster influences HIV-1 transmission. Aids 2003, 17, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, O.; Latiano, A.; Salvatori, E.; Valvano, M.R.; Bossa, F.; Latiano, T.; Corritore, G.; Di Mauro, L.; Andriulli, A.; Annesec, V. The A2518G polymorphism of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is associated with crohn’s disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Yao, S.P.; Guo, L.; Mao, D.W. The combination of polymorphisms within MCP-1 and IL-1β associated with ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2009, 36, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Martínez, J.; Posadas-Sánchez, R.; Álvarez-León, E.; Villarreal-Molina, T.; Cardoso-Saldaña, G.; Fragoso, J.M.; Juárez-Rojas, J.G.; Medina-Urrutia, A.; Posadas-Romero, C.; Vargas-Alarcón, G. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene (MCP-1) polymorphisms are associated with risk of premature coronary artery disease in Mexican patients from the Genetics of Atherosclerotic Disease (GEA) study. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 167, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Escribano, M.F.; Torres, B.; Aguilar, F.; Rodríguez, R.; García, A.; Valenzuela, Á.; Núñez-Roldán, A. MCP-1 promoter polymorphism in Spanish patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hum. Immunol. 2003, 64, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y.; Chen, F.; Liao, Q.; Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tao, S.; et al. Association study of MCP-1 promoter polymorphisms with the susceptibility and progression of sepsis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, G.-Y.; Meng, C.-R.; Hao, Y.-F.; Dai, J.-H. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)-2518 A/G polymorphism and lupus nephritis risk: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Dong, J.; Sheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, L. miR-374a Regulates Inflammatory Response in Diabetic Nephropathy by Targeting MCP-1 Expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Fujita, M.; Snyder, L.A.; Okada, H. Systemic delivery of neutralizing antibody targeting CCL2 for glioma therapy. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 104, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Smart, C.; Hu, Q.; Cheng, N. Continuous Delivery of Neutralizing Antibodies Elevate CCL2 Levels in Mice Bearing MCF10CA1d Breast Tumor Xenografts. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loberg, R.D.; Ying, C.; Craig, M.; Day, L.L.; Sargent, E.; Neeley, C.; Wojno, K.; Snyder, L.A.; Yan, L.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting CCL2 with systemic delivery of neutralizing antibodies induces prostate cancer tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9417–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, K.Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Hsu, S.H.; He, S.; Wani, N.A.; Barajas, J.M.; Snyder, L.A.; Frankel, W.L.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. Blocking the CCL2-CCR2 axis using CCL2-neutralizing antibody is an effective therapy for hepatocellular cancer in a mouse model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haringman, J.J.; Gerlag, D.M.; Smeets, T.J.M.; Baeten, D.; Van Den Bosch, F.; Bresnihan, B.; Breedveld, F.C.; Dinant, H.J.; Legay, F.; Gram, H.; et al. A randomized controlled trial with an anti-CCL2 (anti-monocyte chemotactic protein 1) monoclonal antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergunst, C.E.; Gerlag, D.M.; Lopatinskaya, L.; Klareskog, L.; Smith, M.D.; van den Bosch, F.; Dinant, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Wyant, T.; Jacobson, E.W.; et al. Modulation of CCR2 in rheumatoid arthritis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, T.; Richelsen, B.; Bruun, J.M. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is produced in isolated adipocytes, associated with adiposity and reduced after weight loss in morbid obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlman, I.; Kaaman, M.; Olsson, T.; Tan, G.D.; Bickerton, A.S.T.; Wåhlén, K.; Andersson, J.; Nordström, E.A.; Blomqvist, L.; Sjögren, A.; et al. A unique role of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 among chemokines in adipose tissue of obese subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 5834–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancello, R.; Henegar, C.; Viguerie, N.; Taleb, S.; Poitou, C.; Rouault, C.; Coupaye, M.; Pelloux, V.; Hugol, D.; Bouillot, J.L.; et al. Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, I.S.; Choue, R. Obesity, inflammation and diet. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2013, 16, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles A Janeway, J.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Principles of innate and adaptive immunity. In Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue remodeling and obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, M.W.; Scherer, P.E. Minireview: The adipocyte—At the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. The inflammatory process of adipose tissue. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2008, 6, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Surmi, B.K.; Hasty, A.H. Macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue: Initiation, propagation and remodeling. Future Lipidol. 2008, 3, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braune, J.; Lindhorst, A.; Fröba, J.; Hobusch, C.; Kovacs, P.; Blüher, M.; Eilers, J.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. Multinucleated Giant Cells in Adipose Tissue Are Specialized in Adipocyte Degradation. Diabetes 2021, 70, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massier, L.; Chakaroun, R.; Tabei, S.; Crane, A.; Didt, K.D.; Fallmann, J.; Von Bergen, M.; Haange, S.B.; Heyne, H.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Adipose tissue derived bacteria are associated with inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Gut 2020, 69, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; Gebauer, S.; Haange, S.-B.; Schubert, K.; Kern, M.; Moulla, Y.; Dietrich, A.; Schön, M.R.; Klöting, N.; von Bergen, M.; et al. Accumulation of distinct persistent organic pollutants is associated with adipose tissue inflammation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullberg, K.B.; Larsen, J.Ø.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Effects of LPS and dietary free fatty acids on MCP-1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and macrophages in vitro. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Al-Roub, A.; Kochumon, S.; Akther, N.; Thomas, R.; Kumari, M.; Koshy, M.S.; Tiss, A.; Hannun, Y.A.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. The Synergy between Palmitate and TNF-α for CCL2 Production Is Dependent on the TRIF/IRF3 Pathway: Implications for Metabolic Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3599–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, E.; Mejhert, N.; Kulyté, A.; Balwierz, P.J.; Pachkov, M.; Cormont, M.; Lorente-Cebrián, S.; Ehrlund, A.; Laurencikiene, J.; Hedén, P.; et al. Adipose tissue MicroRNAs as regulators of CCL2 production in human obesity. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, A.M.; Berbecaru-Iovan, A.; Din-Anghel, F.R.I.; Stanciulescu, C.E.; Berbecaru-Iovan, S.; Banita, I.M.; Pisoschi, C.G. Interplay between Hypoxia, Inflammation and Adipocyte Remodeling in the Metabolic Syndrome. In Hypoxia and Human Diseases; InTech: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama, T.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Yamauchi, A.; Makino, M.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Shobatake, R.; Ota, H.; Takeda, M.; Ohbayashi, C.; Takasawa, S. Intermittent Hypoxia Up-Regulates CCL2, RETN, and TNFα mRNAs in Adipocytes via Down-regulation of miR-452. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Méndez-Gutiérrez, A.; Aguilera, C.M.; Plaza-Díaz, J. Extracellular matrix remodeling of adipose tissue in obesity and metabolic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henegar, C.; Tordjman, J.; Achard, V.; Lacasa, D.; Cremer, I.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Poitou, C.; Basdevant, A.; Stich, V.; Viguerie, N.; et al. Adipose tissue transcriptomic signature highlights the pathological relevance of extracellular matrix in human obesity. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divoux, A.; Tordjman, J.; Lacasa, D.; Veyrie, N.; Hugol, D.; Aissat, A.; Basdevant, A.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Poitou, C.; Zucker, J.D.; et al. Fibrosis in human adipose tissue: Composition, distribution, and link with lipid metabolism and fat mass loss. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, G.; Silveira, A.L.M.; Martins, L.B.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Clément, K. Deciphering the cellular interplays underlying obesity-induced adipose tissue fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4032–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, P.B.; Charlotte, F.; Liu, Y.; Bedossa, P.; Le Naour, G.; Tordjman, J.; Poitou, C.; Bouillot, J.L.; Genser, L.; Zucker, J.D.; et al. The fat score, a fibrosis score of adipose tissue: Predicting weight-loss outcome after gastric bypass. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessentheiner, A.R.; Ducasa, G.M.; Gordts, P.L.S.M. Proteoglycans in Obesity-Associated Metabolic Dysfunction and Meta-Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proudfoot, A.E.I.; Handel, T.M.; Johnson, Z.; Lau, E.K.; LiWang, P.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Borlat, F.; Wells, T.N.C.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.H. Glycosaminoglycan binding and oligomerization are essential for the in vivo activity of certain chemokines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1885–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwandtner, M.; Piccinini, A.M.; Gerlza, T.; Adage, T.; Kungl, A.J. Interfering with the CCL2-glycosaminoglycan axis as a potential approach to modulate neuroinflammation. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 626, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unamuno, X.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Ramírez, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Silva, C.; Salvador, J.; Frühbeck, G.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces adipose tissue inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumar, A.; Chisanga, D.; Blume, J.; Gloury, R.; Britt, K.; Henstridge, D.C.; Zhan, Y.; Torres, S.V.; Liene, S.; Collins, N.; et al. Sex-specific adipose tissue imprinting of regulatory T cells. Nature 2020, 579, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuziel, G.; Thompson, V.; D’amato, J.V.; Arendt, L.M. Stromal CCL2 signaling promotes mammary tumor fibrosis through recruitment of myeloid-lineage cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.I.; Huh, J.Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Choe, S.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lim, C.Y.; Jo, A.; Park, S.B.; Han, W.; Kim, J.B. Lipid-Overloaded Enlarged Adipocytes Provoke Insulin Resistance Independent of Inflammation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Nakae, J.; Watanabe, N.; Kikuchi, T.; Tateya, S.; Tamori, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Abe, T.; Onodera, M.; Itoh, H. Colonic Pro-inflammatory Macrophages Cause Insulin Resistance in an Intestinal Ccl2/Ccr2-Dependent Manner. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Li, P.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Lu, M.; Kim, J.I.; Ham, M.; Talukdar, S.; Chen, A.; Lu, W.J.; et al. Inflammation is necessary for long-term but not short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, J.-H.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, E.Y. CCR2 knockout ameliorates obesity-induced kidney injury through inhibiting oxidative stress and ER stress. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, S.U.; Cohen, J.L.; Vangala, P.; Tencerova, M.; Nicoloro, S.M.; Yawe, J.C.; Shen, Y.; Czech, M.P.; Aouadi, M. Local proliferation of macrophages contributes to obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobayashi, M.; Albert, V.; Woelnerhanssen, B.; Frei, I.C.; Weissenberger, D.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Clement, N.; Moes, S.; Colombi, M.; Meier, J.A.; et al. Insulin resistance causes inflammation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusi, V.; Ghidoni, A.; Ravera, A.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Calvillo, L. Chemokines and Heart Disease: A Network Connecting Cardiovascular Biology to Immune and Autonomic Nervous Systems. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 5902947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economou, E.; Tousoulis, D.; Katinioti, A.; Stefanadis, C.; Trikas, A.; Pitsavos, C.; Tentolouris, C.; Toutouza, M.G.; Toutouzas, P. Chemokines in patients with ischaemic heart disease and the effect of coronary angioplasty. Int. J. Cardiol. 2001, 80, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lemos, J.A.; Morrow, D.A.; Sabatine, M.S.; Murphy, S.A.; Gibson, C.M.; Antman, E.M.; McCabe, C.H.; Cannon, C.P.; Braunwald, E. Association between plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and long-term clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2003, 107, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Su, D.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Xia, M.; et al. Serum levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among patients with coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucova, M.; Lietava, J.; Penz, P.; Mrazek, F.; Petrkova, J.; Bernadic, M.; Petrek, M. Association of MCP-1 -2518 A/G single nucleotide polymorphism with the serum level of CRP in Slovak patients with ischemic heart disease, angina pectoris, and hypertension. Mediators Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 390951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guzmán-Ornelas, M.-O.; Petri, M.H.; Vázquez-Del Mercado, M.; Chavarría-Ávila, E.; Corona-Meraz, F.-I.; Ruíz-Quezada, S.-L.; Madrigal-Ruíz, P.-M.; Castro-Albarrán, J.; Sandoval-García, F.; Navarro-Hernández, R.-E. CCL2 Serum Levels and Adiposity Are Associated with the Polymorphic Phenotypes -2518A on CCL2 and 64ILE on CCR2 in a Mexican Population with Insulin Resistance. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 5675739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M.; Kamińska, J.; Lisowska, A.; Milewska, A.; Hirnle, T.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. Factors Associated with RANTES Concentration in Cardiovascular Disease Patients. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3026453. [Google Scholar]
- Semple, B.D.; Bye, N.; Rancan, M.; Ziebell, J.M.; Morganti-Kossmann, M.C. Role of CCL2 (MCP-1) in traumatic brain injury (TBI): Evidence from severe TBI patients and CCL2−/− mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabene, P.F.; Bramanti, P.; Constantin, G. The emerging role for chemokines in epilepsy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 224, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Kuang, S.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Guan, M.; Qin, W.; Xu, H.H.K.; Lin, Z. Inhibition of CCL2 by bindarit alleviates diabetes-associated periodontitis by suppressing inflammatory monocyte infiltration and altering macrophage properties. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Johnson, S.; Perwitasari, O.; Mahalingam, S.; Tripp, R.A. Targeting the pro-inflammatory factor CCL2 (MCP-1) with Bindarit for influenza A (H7N9) treatment. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Knight, D.A.; A Snyder, L.; Smyth, M.J.; Stewart, T.J. A role for CCL2 in both tumor progression and immunosurveillance. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e25474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Li, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhang, E.; Huang, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Qu, J.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; et al. CCL2 promotes macrophages-associated chemoresistance via MCPIP1 dual catalytic activities in multiple myeloma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvynet, C.; Baudesson De Chanville, C.; Hermand, P.; Dorgham, K.; Piesse, C.; Pouchy, C.; Carlier, L.; Poupel, L.; Barthélémy, S.; Felouzis, V.; et al. ECL1i, d(LGTFLKC), a novel, small peptide that specifically inhibits CCL2-dependent migration. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2370–2381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monickaraj, F.; Oruganti, S.R.; McGuire, P.; Das, A. A potential novel therapeutic target in diabetic retinopathy: A chemokine receptor (CCR2/CCR5) inhibitor reduces retinal vascular leakage in an animal model. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pienta, K.J.; Machiels, J.P.; Schrijvers, D.; Alekseev, B.; Shkolnik, M.; Crabb, S.J.; Li, S.; Seetharam, S.; Puchalski, T.A.; Takimoto, C.; et al. Phase 2 study of carlumab (CNTO 888), a human monoclonal antibody against CC-chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).