An Overview of Next-Generation Androgen Receptor-Targeted Therapeutics in Development for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
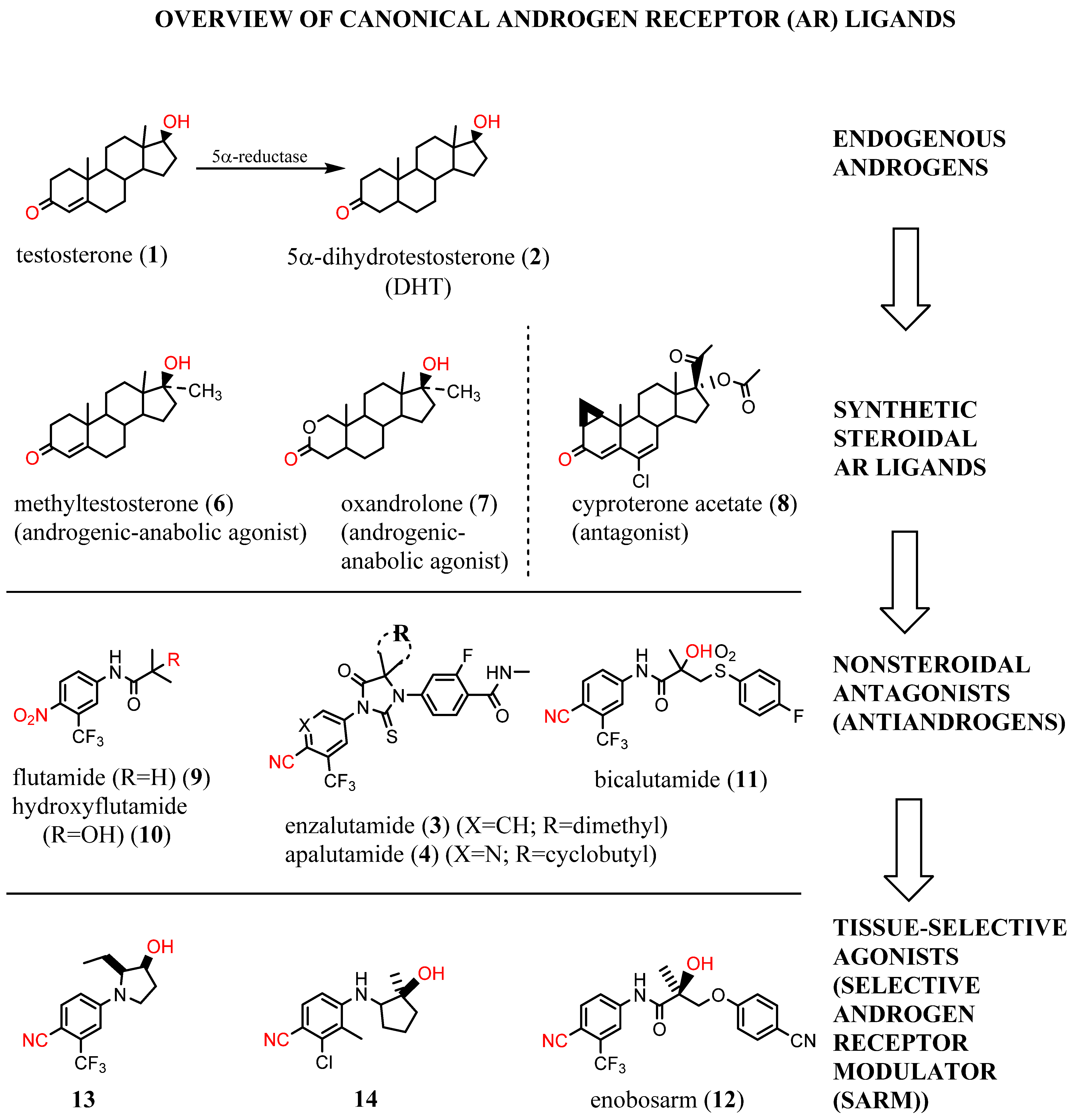
1. Background

2. Structural Basis for Antagonist Development
3. Need for AR-Directed Therapy Beyond Canonical Antiandrogens
3.1. LBD-Targeted SARDs
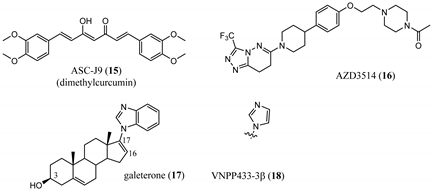
3.2. Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs) as Nonsteroidal AR Degraders
3.3. Summary of Hormone Binding Pocket (HPB)-Targeted Antiandrogens
4. Noncompetitive Antiandrogens
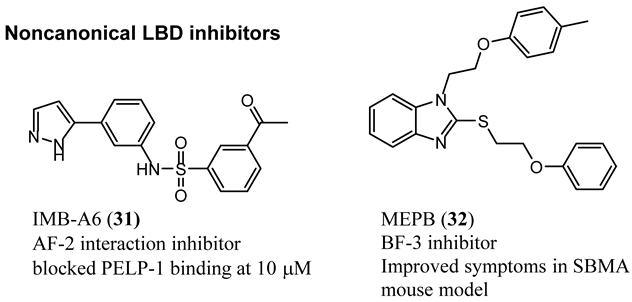
4.1. Noncanonical (Noncompetitive) LBD Ligands
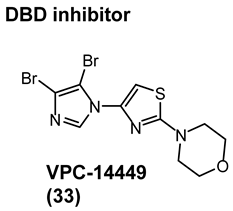
4.2. Noncanonical DBD Antiandrogens
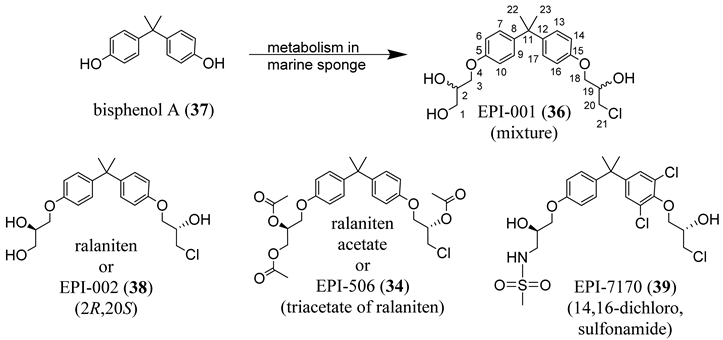
4.3. Noncanonical NTD Antiandrogens
4.4. AF-1 Inhibitors Derived from Natural Products
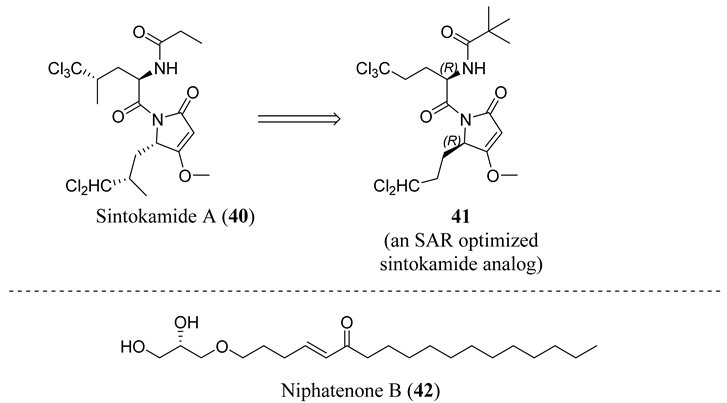
4.5. Propanamide AF-1 Inhibitors
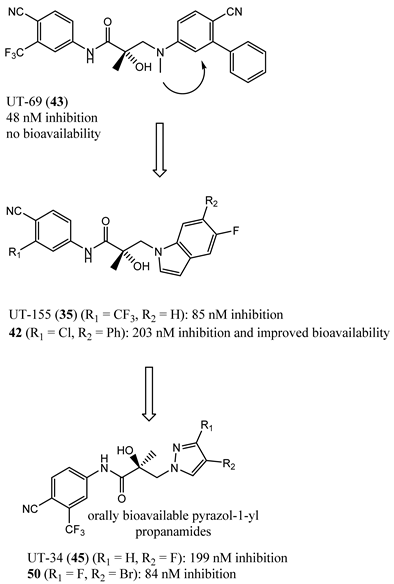
5. Future Antiandrogen Design and Screening Paradigms
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.B.; Mehra, R.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Shen, R.; Ghosh, D.; Zhou, M.; Macvicar, G.R.; Varambally, S.; Harwood, J.; Bismar, T.A.; et al. Androgen-independent prostate cancer is a heterogeneous group of diseases: Lessons from a rapid autopsy program. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 9209–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, A.O.; Faber, P.W.; van Rooij, H.C.; Kuiper, G.G.; Ris, C.; Klaassen, P.; van der Korput, J.A.; Voorhorst, M.M.; van Laar, J.H.; Mulder, E.; et al. The human androgen receptor: Domain structure, genomic organization and regulation of expression. J. Steroid Biochem. 1989, 34, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus, H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, C. Effect of Orchiectomy and Irradiation on Cancer of the Prostate. Ann. Surg. 1942, 115, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluemn, E.G.; Coleman, I.M.; Lucas, J.M.; Coleman, R.T.; Hernandez-Lopez, S.; Tharakan, R.; Bianchi-Frias, D.; Dumpit, R.F.; Kaipainen, A.; Corella, A.N.; et al. Androgen Receptor Pathway-Independent Prostate Cancer Is Sustained through FGF Signaling. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 474–489.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Amin, M.B.; Beltran, H.; Lotan, T.L.; Mosquera, J.M.; Reuter, V.E.; Robinson, B.D.; Troncoso, P.; Rubin, M.A. Proposed morphologic classification of prostate cancer with neuroendocrine differentiation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadosky, K.M.; Koochekpour, S. Androgen receptor splice variants and prostate cancer: From bench to bedside. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18550–18576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, L.J.; Dehm, S.M. Androgen receptor gene rearrangements: New perspectives on prostate cancer progression. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qiu, Y. Role of androgen receptor splice variants in prostate cancer metastasis. Asian J. Urol. 2016, 3, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, J.E.; Steri, V.; Nguyen, H.G.; Hann, B.; Feng, F.Y.; Shokat, K.M. The splicing modulator sulfonamide indisulam reduces AR-V7 in prostate cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Luo, J.; Nanus, D.M.; Giannakakou, P.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Danila, D.C.; Healy, P.; Anand, M.; Berry, W.R.; Zhang, T.; et al. Prospective Multicenter Study of Circulating Tumor Cell AR-V7 and Taxane Versus Hormonal Treatment Outcomes in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Jco. Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Armstrong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lou, W.; Gao, A.C. Niclosamide enhances abiraterone treatment via inhibition of androgen receptor variants in castration resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32210–32220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Nadiminty, N.; Schwartz, C.T.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Niclosamide inhibits androgen receptor variants expression and overcomes enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3198–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainwaring, W.I. The separation of androgen receptor and 5 alpha-reductase activities in subcellular fractions of rat prostate. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1970, 40, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, J.S.; Kish, K.F.; Wang, C.; Attar, R.M.; Kiefer, S.E.; An, Y.; Wu, G.Y.; Scheffler, J.E.; Salvati, M.E.; Krystek, S.R., Jr.; et al. Crystallographic structures of the ligand-binding domains of the androgen receptor and its T877A mutant complexed with the natural agonist dihydrotestosterone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4904–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobo, E.; Schmidt, J.D.; Weinstein, S.H.; Flocks, R.H. Comparison of flutamide (SCH-13521) and diethylstilbestrol in untreated advanced prostatic cancer. Urology 1976, 8, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furr, B.J.; Valcaccia, B.; Curry, B.; Woodburn, J.R.; Chesterson, G.; Tucker, H. ICI 176,334: A novel non-steroidal, peripherally selective antiandrogen. J. Endocrinol. 1987, 113, R7–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, J.T.; Mukherjee, A.; Zhu, Z.; Kirkovsky, L.; Miller, D.D. Discovery of nonsteroidal androgens. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 244, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Gao, W.; Kearbey, J.D.; Xu, H.; Chung, K.; He, Y.; Marhefka, C.A.; Veverka, K.A.; Miller, D.D.; Dalton, J.T. Pharmacodynamics of selective androgen receptor modulators. J. Pharm. Exp. 2003, 304, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhefka, C.A.; Gao, W.; Chung, K.; Kim, J.; He, Y.; Yin, D.; Bohl, C.; Dalton, J.T.; Miller, D.D. Design, synthesis, and biological characterization of metabolically stable selective androgen receptor modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, Z.J.; Mirabal, J.R.; Mazur, D.J.; Kohn, T.P.; Lipshultz, L.I.; Pastuszak, A.W. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators: Current Knowledge and Clinical Applications. Sex. Med. Rev. 2019, 7, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Liu, J.S.; Wu, P.L.; Guan, H.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, A.C.; Ting, H.J.; Pang, S.T.; Yeh, S.D.; Ma, W.L.; et al. Identification of a new androgen receptor (AR) co-regulator BUD31 and related peptides to suppress wild-type and mutated AR-mediated prostate cancer growth via peptide screening and X-ray structure analysis. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikawa, K.; Asano, M.; Ono, K.; Habuka, N.; Yano, J.; Wilson, K.; Fujita, H.; Kandori, H.; Hara, T.; Morimoto, M.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) Part III: Discovery of 4-(5-oxopyrrolidine-1-yl) benzonitrile derivative 2f as a clinical candidate. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3330–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohl, C.E.; Miller, D.D.; Chen, J.; Bell, C.E.; Dalton, J.T. Structural basis for accommodation of nonsteroidal ligands in the androgen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37747–37754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Vaught, G.M.; Gavardinas, K.; Matthews, D.; Green, J.E.; Losada, P.G.; Bullock, H.A.; Calvert, N.A.; Patel, N.J.; Sweetana, S.A.; et al. 2-Chloro-4-[[(1R,2R)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-cyclopentyl]amino]-3-methyl-benzonitrile: A Transdermal Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) for Muscle Atrophy. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Connolly, P.J.; Lim, H.K.; Pande, V.; Meerpoel, L.; Teleha, C.; Branch, J.R.; Ondrus, J.; Hickson, I.; Bush, T.; et al. Discovery of JNJ-63576253: A Clinical Stage Androgen Receptor Antagonist for F877L Mutant and Wild-Type Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC). J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, R.; Xu, X.; Xu, P.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Bian, J. Degradation of Androgen Receptor through Small Molecules for Prostate Cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, W.; Lin, C.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Chang, C. ASC-J9((R)) suppresses castration resistant prostate cancer progression via degrading the enzalutamide-induced androgen receptor mutant AR-F876L. Cancer Lett. 2016, 379, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omlin, A.; Jones, R.J.; van der Noll, R.; Satoh, T.; Niwakawa, M.; Smith, S.A.; Graham, J.; Ong, M.; Finkelman, R.D.; Schellens, J.H.; et al. AZD3514, an oral selective androgen receptor down-regulator in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer—Results of two parallel first-in-human phase I studies. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latysheva, A.S.; Zolottsev, V.A.; Veselovsky, A.V.; Scherbakov, K.A.; Morozevich, G.E.; Pokrovsky, V.S.; Novikov, R.A.; Timofeev, V.P.; Tkachev, Y.V.; Misharin, A.Y. New steroidal oxazolines, benzoxazoles and benzimidazoles related to abiraterone and galeterone. Steroids 2020, 153, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njar, V.C.; Brodie, A.M. Discovery and development of Galeterone (TOK-001 or VN/124–1) for the treatment of all stages of prostate cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyamani, M.; Li, Z.; Berk, M.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Upadhyay, S.; Auchus, R.J.; Sharifi, N. Steroidogenic Metabolism of Galeterone Reveals a Diversity of Biochemical Activities. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 825–832.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Cai, C.; Gao, S.; Simon, N.I.; Shen, H.C.; Balk, S.P. Galeterone prevents androgen receptor binding to chromatin and enhances degradation of mutant androgen receptor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4075–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwegyir-Afful, A.K.; Ramalingam, S.; Purushottamachar, P.; Ramamurthy, V.P.; Njar, V.C. Galeterone and VNPT55 induce proteasomal degradation of AR/AR-V7, induce significant apoptosis via cytochrome c release and suppress growth of castration resistant prostate cancer xenografts in vivo. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27440–27460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwegyir-Afful, A.K.; Ramalingam, S.; Ramamurthy, V.P.; Purushottamachar, P.; Murigi, F.N.; Vasaitis, T.S.; Huang, W.; Kane, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Ambulos, N.; et al. Galeterone and The Next Generation Galeterone Analogs, VNPP414 and VNPP433–3beta Exert Potent Therapeutic Effects in Castration-/Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Preclinical Models In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers (Basel.) 2019, 11, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Protacs: Chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8554–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneekloth, A.R.; Pucheault, M.; Tae, H.S.; Crews, C.M. Targeted intracellular protein degradation induced by a small molecule: En route to chemical proteomics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5904–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohbeck, J.; Miller, A.K. Practical synthesis of a phthalimide-based Cereblon ligand to enable PROTAC development. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5260–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, C.; Qin, C.; Xiang, W.; Fernandez-Salas, E.; Yang, C.Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Xu, T.; Chinnaswamy, K.; et al. Discovery of ARD-69 as a Highly Potent Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Degrader of Androgen Receptor (AR) for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 941–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Linton, A.; Kephart, S.; Ornelas, M.; Pairish, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Greasley, S.; Nagata, A.; Burke, B.J.; Edwards, M.; et al. Discovery of aryloxy tetramethylcyclobutanes as novel androgen receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7693–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Han, X.; Lu, J.; McEachern, D.; Wang, S. A highly potent PROTAC androgen receptor (AR) degrader ARD-61 effectively inhibits AR-positive breast cancer cell growth in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Nagai, K.; Morita, Y.; Ujikawa, O.; Ohoka, N.; Hattori, T.; Koyama, R.; Sano, O.; Imaeda, Y.; Nara, H.; et al. Development of Protein Degradation Inducers of Androgen Receptor by Conjugation of Androgen Receptor Ligands and Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 543–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.E.; Rooney, T.P.C.; Bayle, E.D.; Mirza, T.; Willems, H.M.G.; Clarke, J.H.; Andrews, S.P.; Skidmore, J. Systematic Investigation of the Permeability of Androgen Receptor PROTACs. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, J.J.; Neklesa, T.K. Targeting Nuclear Receptors with PROTAC degraders. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 493, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, G.L.; Zaffaroni, N. Androgen Receptor-Directed Molecular Conjugates for Targeting Prostate Cancer. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbas, M.D.; Evans, M.J.; Hosfield, D.J.; Wongvipat, J.; Arora, V.K.; Watson, P.A.; Chen, Y.; Greene, G.L.; Shen, Y.; Sawyers, C.L. Overcoming mutation-based resistance to antiandrogens with rational drug design. Elife 2013, 2, e00499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Miyazaki, J.; Araki, H.; Yamaoka, M.; Kanzaki, N.; Kusaka, M.; Miyamoto, M. Novel mutations of androgen receptor: A possible mechanism of bicalutamide withdrawal syndrome. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; An, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Interaction mechanism exploration of R-bicalutamide/S-1 with WT/W741L AR using molecular dynamics simulations. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, M.A.; Shuster, T.D.; Fertig, A.M.; Taplin, M.E.; Kolvenbag, G.; Bubley, G.J.; Balk, S.P. Functional characterization of mutant androgen receptors from androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Hamil, Y.S.K.G.; Gregory, C.W.; Zang, D.Y.; Sar, M.; Gumerlock, P.H.; White, R.W.D.; Pretlow, T.G.; Harris, S.E.; Wilson, E.M.; et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone activates mutant androgen receptors expressed in the androgen-dependent human prostate cancer xenograft CWR22 and LNCaP cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glucocorticoids can promote androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells through a mutated androgen receptor. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 703–706. [CrossRef]
- Korpal, M.; Korn, J.M.; Gao, X.; Rakiec, D.P.; Ruddy, D.A.; Doshi, S.; Yuan, J.; Kovats, S.G.; Kim, S.; Cooke, V.G.; et al. An F876L mutation in androgen receptor confers genetic and phenotypic resistance to MDV3100 (enzalutamide). Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Kagechika, H. Androgen receptor modulators: A review of recent patents and reports (2012–2018). Expert Opin. Pat. 2019, 29, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ban, F.; Dalal, K.; Leblanc, E.; Frewin, K.; Ma, D.; Adomat, H.; Rennie, P.S.; Cherkasov, A. Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors selectively targeting the DNA-binding domain of the human androgen receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6458–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, M.; Prekovic, S.; Gallastegui, N.; Helsen, C.; Abella, M.; Zielinska, K.; Gay, M.; Vilaseca, M.; Taules, M.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; et al. Structure of the homodimeric androgen receptor ligand-binding domain. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, K.; Ban, F.; Li, H.; Morin, H.; Roshan-Moniri, M.; Tam, K.J.; Shepherd, A.; Sharma, A.; Peacock, J.; Carlson, M.L.; et al. Selectively targeting the dimerization interface of human androgen receptor with small-molecules to treat castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 437, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munuganti, R.S.; Leblanc, E.; Axerio-Cilies, P.; Labriere, C.; Frewin, K.; Singh, K.; Hassona, M.D.; Lack, N.A.; Li, H.; Ban, F.; et al. Targeting the binding function 3 (BF3) site of the androgen receptor through virtual screening. 2. development of 2-((2-phenoxyethyl) thio)-1H-benzimidazole derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, T.; Xie, Y.; Cui, X.; He, L.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Hu, L.; et al. Structural Based Screening of Antiandrogen Targeting Activation Function-2 Binding Site. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lack, N.A.; Axerio-Cilies, P.; Tavassoli, P.; Han, F.Q.; Chan, K.H.; Feau, C.; LeBlanc, E.; Guns, E.T.; Guy, R.K.; Rennie, P.S.; et al. Targeting the binding function 3 (BF3) site of the human androgen receptor through virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8563–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badders, N.M.; Korff, A.; Miranda, H.C.; Vuppala, P.K.; Smith, R.B.; Winborn, B.J.; Quemin, E.R.; Sopher, B.L.; Dearman, J.; Messing, J.; et al. Selective modulation of the androgen receptor AF2 domain rescues degeneration in spinal bulbar muscular atrophy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, K.; Roshan-Moniri, M.; Sharma, A.; Li, H.; Ban, F.; Hassona, M.D.; Hsing, M.; Singh, K.; LeBlanc, E.; Dehm, S.; et al. Selectively targeting the DNA-binding domain of the androgen receptor as a prospective therapy for prostate cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26417–26429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, K.; Che, M.; Que, N.S.; Sharma, A.; Yang, R.; Lallous, N.; Borgmann, H.; Ozistanbullu, D.; Tse, R.; Ban, F.; et al. Bypassing Drug Resistance Mechanisms of Prostate Cancer with Small Molecules that Target Androgen Receptor-Chromatin Interactions. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, E.A.; Steele, T.M.; Tsamouri, M.M.; Hejazi, N.; Gao, A.C.; Mudryj, M.; Ghosh, P.M. The Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: Effect of Structure, Ligands and Spliced Variants on Therapy. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenster, G.; van der Korput, H.A.; Trapman, J.; Brinkmann, A.O. Identification of two transcription activation units in the N-terminal domain of the human androgen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7341–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mol, E.; Fenwick, R.B.; Phang, C.T.; Buzon, V.; Szulc, E.; de la Fuente, A.; Escobedo, A.; Garcia, J.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Estebanez-Perpina, E.; et al. EPI-001, A Compound Active against Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer, Targets Transactivation Unit 5 of the Androgen Receptor. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, S.; Coss, C.C.; Thiyagarajan, T.; Watts, K.; Hwang, D.J.; He, Y.; Selth, L.A.; McEwan, I.J.; Duke, C.B.; Pagadala, J.; et al. Novel Selective Agents for the Degradation of Androgen Receptor Variants to Treat Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6282–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenster, G.; van der Korput, H.A.; van Vroonhoven, C.; van der Kwast, T.H.; Trapman, J.; Brinkmann, A.O. Domains of the human androgen receptor involved in steroid binding, transcriptional activation, and subcellular localization. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, I.J. Intrinsic disorder in the androgen receptor: Identification, characterisation and drugability. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.J.; Mawji, N.R.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Haile, S.; Myung, J.K.; Watt, K.; Tam, T.; Yang, Y.C.; Banuelos, C.A.; et al. Regression of castrate-recurrent prostate cancer by a small-molecule inhibitor of the amino-terminus domain of the androgen receptor. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, J.K.; Banuelos, C.A.; Fernandez, J.G.; Mawji, N.R.; Wang, J.; Tien, A.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Tavakoli, I.; Haile, S.; Watt, K.; et al. An androgen receptor N-terminal domain antagonist for treating prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2948–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Lu, C.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Gurel, M.; Tannahill, C.; Edwards, J.; Isaacs, W.B.; Nelson, P.S.; Bluemn, E.; et al. Distinct transcriptional programs mediated by the ligand-dependent full-length androgen receptor and its splice variants in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Tam, T.; Jian, K.; Andersen, R.J.; Sadar, M.D. Combination therapy with androgen receptor N-terminal domain antagonist EPI-7170 and enzalutamide yields synergistic activity in AR-V7-positive prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2455–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banuelos, C.A.; Tavakoli, I.; Tien, A.H.; Caley, D.P.; Mawji, N.R.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Imamura, Y.; Yan, L.; et al. Sintokamide A Is a Novel Antagonist of Androgen Receptor That Uniquely Binds Activation Function-1 in Its Amino-terminal Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22231–22243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Banuelos, C.A.; Mawji, N.R.; Patrick, B.O.; Sadar, M.D.; Andersen, R.J. Structure-Activity Relationships for the Marine Natural Product Sintokamides: Androgen Receptor N-Terminus Antagonists of Interest for Treatment of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Nat. Prod. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banuelos, C.A.; Lal, A.; Tien, A.H.; Shah, N.; Yang, Y.C.; Mawji, N.R.; Meimetis, L.G.; Park, J.; Kunzhong, J.; Andersen, R.J.; et al. Characterization of niphatenones that inhibit androgen receptor N-terminal domain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, S.; He, Y.; Hwang, D.J.; Thiyagarajan, T.; Houtman, R.; Bocharova, V.; Sumpter, B.G.; Fernandez, E.; Johnson, D.L.; Du, Z.; et al. Orally-Bioavailable Androgen Receptor Degrader, A Potential Next-Generation Therapeutic for Enzalutamide-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6764–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.J.; He, Y.; Ponnusamy, S.; Mohler, M.L.; Thiyagarajan, T.; McEwan, I.J.; Narayanan, R.; Miller, D.D. New Generation of Selective Androgen Receptor Degraders: Our Initial Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of New Compounds with Enzalutamide-Resistant Prostate Cancer Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Hwang, D.J.; Ponnusamy, S.; Thiyagarajan, T.; Mohler, M.L.; Narayanan, R.; Miller, D.D. Pyrazol-1-yl-propanamides as SARD and Pan-Antagonists for the Treatment of Enzalutamide-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12642–12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haendler, B.; Cleve, A. Recent developments in antiandrogens and selective androgen receptor modulators. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 352, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
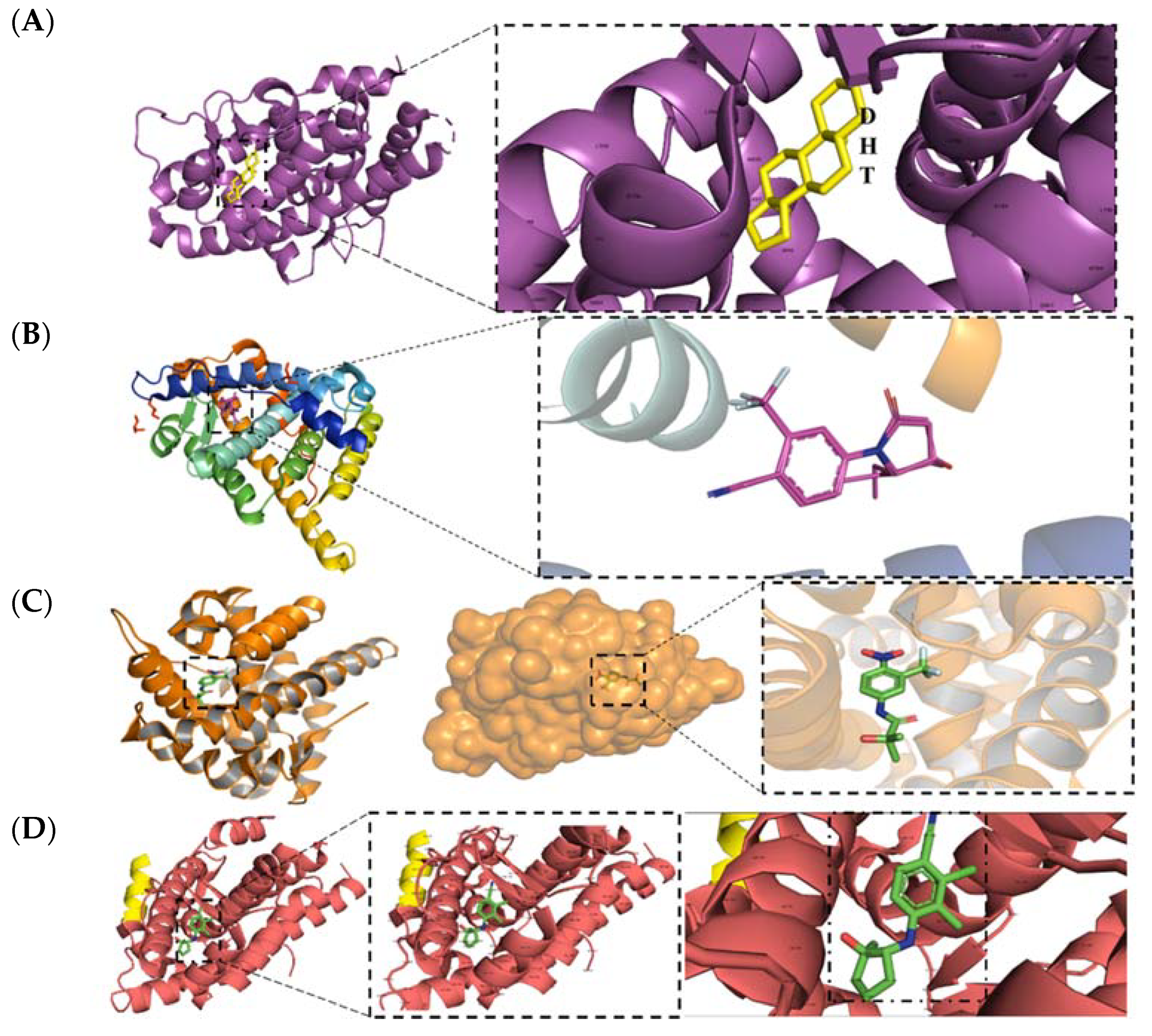

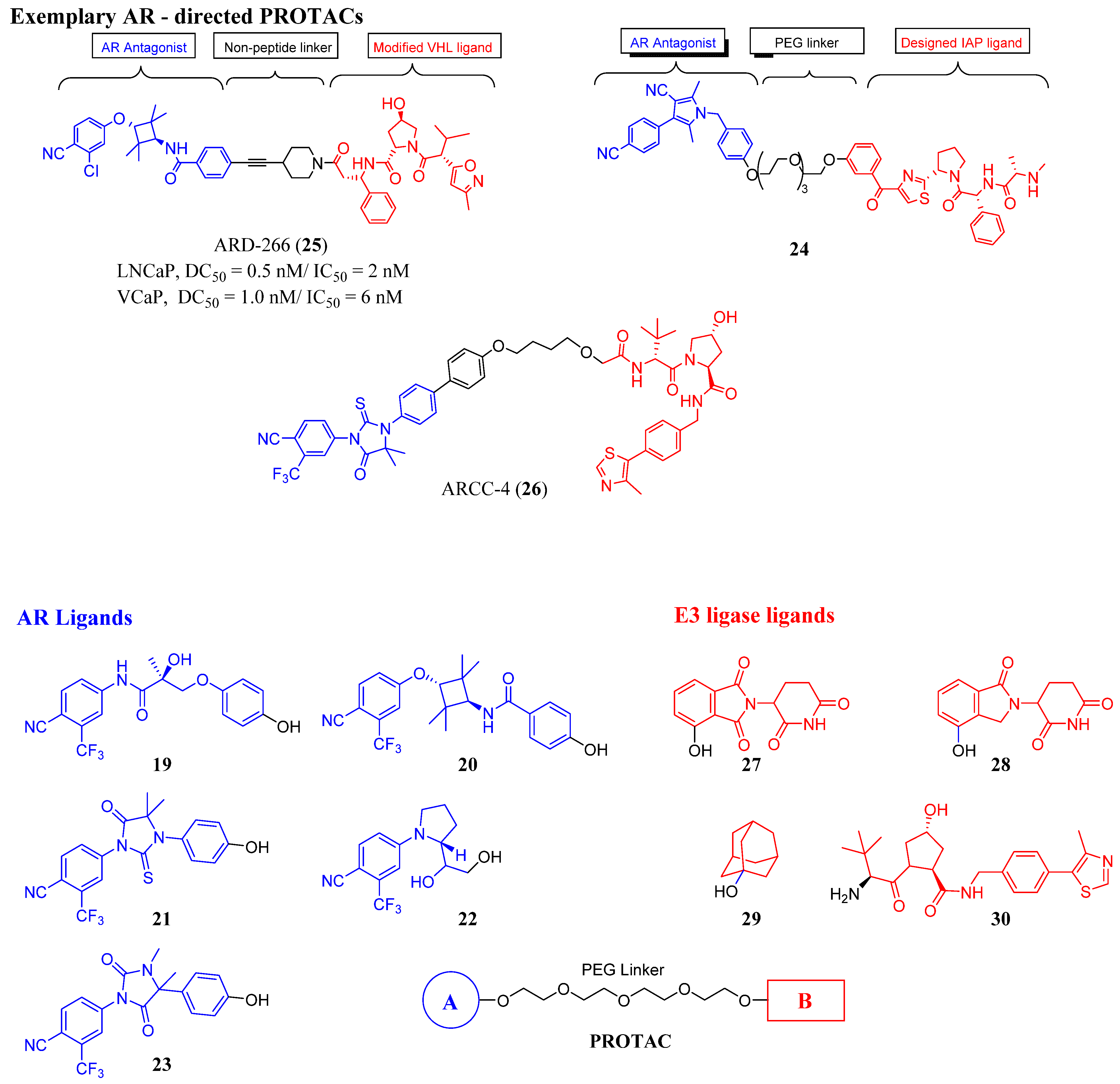
| Structure/Cmpd ID (Target Activity) | In Vitro Data | In Vivo or Clinical Data |
|---|---|---|
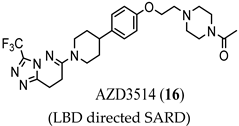 (LBD directed SARD) |
|
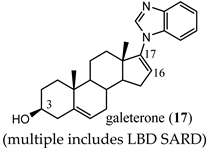
|
 (multiple includes LBD SARD) |
|
|
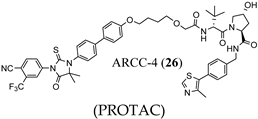 (PROTAC) |
|
|
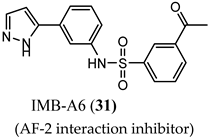 (AF-2 interaction inhibitor) |
| N.R. |
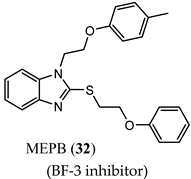 (BF-3 inhibitor) |
|
|
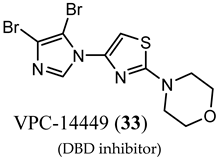 (DBD inhibitor) |
| No clinical data. |
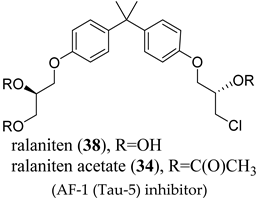 (AF-1 (Tau-5) inhibitor) |
|
|
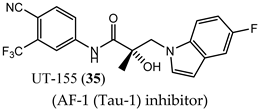 (AF-1 (Tau-1) inhibitor) |
|
|
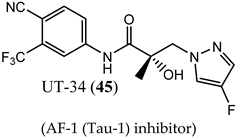 (AF-1 (Tau-1) inhibitor) |
|
|
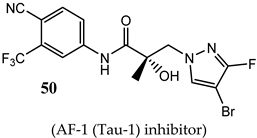 (AF-1 (Tau-1) inhibitor) |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohler, M.L.; Sikdar, A.; Ponnusamy, S.; Hwang, D.-J.; He, Y.; Miller, D.D.; Narayanan, R. An Overview of Next-Generation Androgen Receptor-Targeted Therapeutics in Development for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22042124
Mohler ML, Sikdar A, Ponnusamy S, Hwang D-J, He Y, Miller DD, Narayanan R. An Overview of Next-Generation Androgen Receptor-Targeted Therapeutics in Development for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22042124
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohler, Michael L., Arunima Sikdar, Suriyan Ponnusamy, Dong-Jin Hwang, Yali He, Duane D. Miller, and Ramesh Narayanan. 2021. "An Overview of Next-Generation Androgen Receptor-Targeted Therapeutics in Development for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22042124
APA StyleMohler, M. L., Sikdar, A., Ponnusamy, S., Hwang, D.-J., He, Y., Miller, D. D., & Narayanan, R. (2021). An Overview of Next-Generation Androgen Receptor-Targeted Therapeutics in Development for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22042124







