The Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy on Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
2.1. Causes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
2.1.1. Gender
2.1.2. Advanced Age
2.1.3. Obesity and High Body Mass Index
2.1.4. Other Predisposing Factors
3. Hypertension
3.1. How Can Obstructive Sleep Apnea Cause Hypertension?
3.2. The Standard Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension
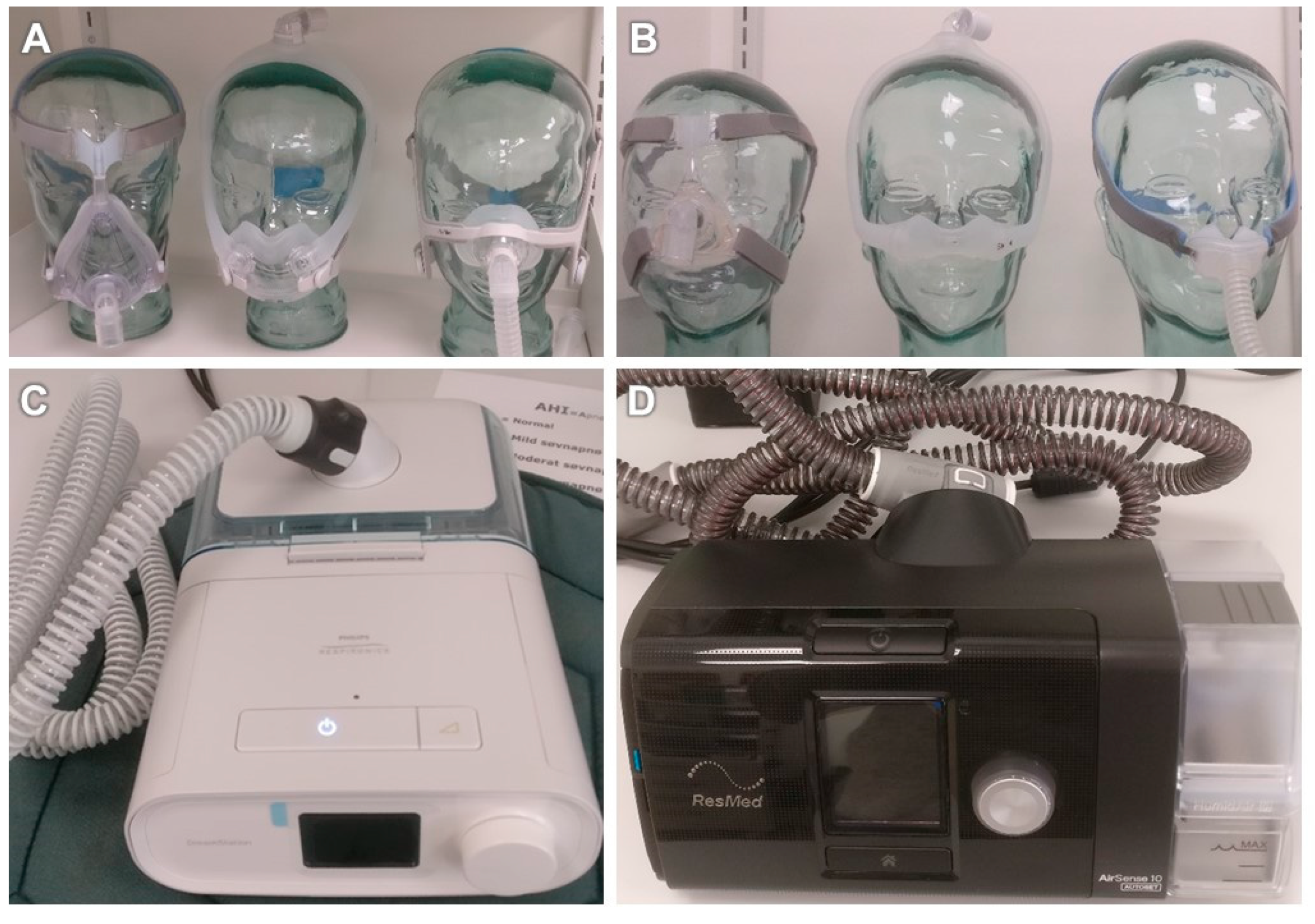
4. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
4.1. The Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Hypertension
4.2. Comparison between the Effects and Side Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure and the Standard Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension
4.3. Clinical Trials Investigating the Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Treatment of Hypertension
5. Discussion
6. Methods
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AASM | American Academy of Sleep Medicine |
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting-enzyme |
| AE | Adverse effect |
| AHI | The Apnea-Hypopnea Index |
| AHM | Antihypertensive medication |
| ARB | Angiotensin II receptor blocker |
| BAA | Beta-adrenoceptor antagonists |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CCB | Calcium channel blocker |
| CPAP | Continuous positive airway pressure |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| ESH | European Society of Hypertension |
| ESS | Epworth Sleepiness Scale |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| HT | Hypertension |
| MBP | Mean blood pressure |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase |
| ODI | Oxygen desaturation index |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| RAAS | Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SDB | Sleep-disordered breathing |
References
- Donovan, L.M.; Kapur, V.K. Prevalence and Characteristics of Central Compared to Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Analyses from the Sleep Heart Health Study Cohort. Sleep 2016, 39, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Bue, A.; Salvaggio, A.; Iacono Isidoro, S.; Romano, S.; Insalaco, G. OSA and CPAP therapy: Effect of gender, somnolence, and treatment adherence on health-related quality of life. Sleep Breath 2020, 24, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveit, R.L.; Lehmann, S.; Bjorvatn, B. Prevalence of several somatic diseases depends on the presence and severity of obstructive sleep apnea. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: A pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19·1 million participants. Lancet 2017, 389, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhawassi, T.M.; Krass, I.; Pont, L.G. Antihypertensive-related adverse drug reactions among older hospitalized adults. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2018, 40, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders—Third Edition (ICSD-3), 3rd ed.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ruehland, W.R.; Rochford, P.D.; O’Donoghue, F.J.; Pierce, R.J.; Singh, P.; Thornton, A.T. The new AASM criteria for scoring hypopneas: Impact on the apnea hypopnea index. Sleep 2009, 32, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.F.; Gillin, J.C.; Littner, M.R.; Shepard, J.W. Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: Recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 1999, 22, 667–689. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, M.W. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: The Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 1991, 14, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pływaczewski, R.; Bednarek, M.; Jonczak, L.; Zieliński, J. Sleep-disordered breathing in a middle-aged and older Polish urban population. J. Sleep Res. 2008, 17, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufik, S.; Santos-Silva, R.; Taddei, J.A.; Bittencourt, L.R. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in the Sao Paulo Epidemiologic Sleep Study. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikermann, M.; Jordan, A.S.; Chamberlin, N.L.; Gautam, S.; Wellman, A.; Lo, Y.L.; White, D.P.; Malhotra, A. The influence of aging on pharyngeal collapsibility during sleep. Chest 2007, 131, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzer, R.; Vat, S.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Marti-Soler, H.; Andries, D.; Tobback, N.; Mooser, V.; Preisig, M.; Malhotra, A.; Waeber, G.; et al. Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in the general population: The HypnoLaus study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Palta, M.; Dempsey, J.; Skatrud, J. Longitudinal study of moderate weight change and sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA 2000, 284, 3015–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1269–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan, S.; Caulfield, M.; Dominiczak, A.F. Genetic and molecular aspects of hypertension. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 937–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Palta, M.; Skatrud, J. Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatureto-Borges, F.; Jenner, R.; Costa-Hong, V.; Lopes, H.F.; Teixeira, S.H.; Marum, E.; Giorgi, D.A.M.; Consolim-Colombo, F.M.; Bortolotto, L.A.; Lorenzi-Filho, G.; et al. Does Obstructive Sleep Apnea Influence Blood Pressure and Arterial Stiffness in Response to Antihypertensive Treatment? Hypertension 2018, 72, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkiewicz, K.; van de Borne, P.J.; Pesek, C.A.; Dyken, M.E.; Montano, N.; Somers, V.K. Selective potentiation of peripheral chemoreflex sensitivity in obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 1999, 99, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, D.S.; Lind, P.; Strunge, B.; Pedersen, E.B. Abnormal vasoactive hormones and 24-h blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Hypertens. 2003, 16, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, M.S.; Lam, B.; Chan, L.Y.; Zheng, L.; Tsang, K.W.; Fung, P.C.; Lam, W.K. Circulating nitric oxide is suppressed in obstructive sleep apnea and is reversed by nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, A.; Barbé, F.; de la Peña, M.; Vila, M.; Pérez, G.; Piérola, J.; Durán, J.; Agustí, A.G. Antioxidant status in patients with sleep apnoea and impact of continuous positive airway pressure treatment. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, A.; Yasuma, F.; Okada, T.; Yokota, M. Influence of movement arousal on circadian rhythm of blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, M.S.; Lam, B.; Ng, M.M.; Lam, W.K.; Tsang, K.W.; Lam, K.S. Obstructive sleep apnea is independently associated with insulin resistance. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhlesi, B.; Hagen, E.W.; Finn, L.A.; Hla, K.M.; Carter, J.R.; Peppard, P.E. Obstructive sleep apnoea during REM sleep and incident non-dipping of nocturnal blood pressure: A longitudinal analysis of the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. Thorax 2015, 70, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loredo, J.S.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Dimsdale, J.E. Sleep quality and blood pressure dipping in obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14 Pt 1, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, G.F.; Reboldi, G.; Fagard, R.H.; Cardoso, C.R.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Verdecchia, P.; Eguchi, K.; Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Polonia, J.; et al. Prognostic Effect of the Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fall in Hypertensive Patients: The Ambulatory Blood Pressure Collaboration in Patients with Hypertension (ABC-H) Meta-Analysis. Hypertension 2016, 67, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryelska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Szemraj, J.; Stawski, R.; Sochal, M.; Białasiewicz, P. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea present with chronic upregulation of serum HIF-1α protein. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabryelska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Panek, M.; Szemraj, J.; Kuna, P.; Białasiewicz, P. Serum hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protein level as a diagnostic marker of obstructive sleep apnea. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Briones, A.M. Reactive oxygen species and vascular biology: Implications in human hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryelska, A.; Sochal, M.; Turkiewicz, S.; Białasiewicz, P. Relationship between HIF-1 and Circadian Clock Proteins in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients-Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryelska, A.; Karuga, F.F.; Szmyd, B.; Białasiewicz, P. HIF-1α as a Mediator of Insulin Resistance, T2DM, and Its Complications: Potential Links with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, L.; Hu, D. Fasting insulin, insulin resistance and risk of hypertension in the general population: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 464, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Teng, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, S.; Feng, J.; Yan, X. CD146-HIF-1α hypoxic reprogramming drives vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabryelska, A.; Łukasik, Z.M.; Makowska, J.S.; Białasiewicz, P. Obstructive Sleep Apnea: From Intermittent Hypoxia to Cardiovascular Complications via Blood Platelets. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapater, A.; Santamaria-Martos, F.; Targa, A.; Pinilla, L.; Sánchez-de-la-Torre, A.; Benítez, I.D.; Martínez-García, M.Á.; Barbé, F.; Sánchez-de-la-Torre, M. Canonical Pathways Associated with Blood Pressure Response to Sleep Apnea Treatment: A Post Hoc Analysis. Respiration 2021, Feb 5, 1–10, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlöf, B.; Lindholm, L.H.; Hansson, L.; Scherstén, B.; Ekbom, T.; Wester, P.O. Morbidity and mortality in the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension (STOP-Hypertension). Lancet 1991, 338, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Teo, K.; Anderson, C.; Pogue, J.; Dyal, L.; Copland, I.; Schumacher, H.; Dagenais, G.; Sleight, P. Effects of the angiotensin-receptor blocker telmisartan on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients intolerant to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, S.; Sleight, P.; Pogue, J.; Bosch, J.; Davies, R.; Dagenais, G. Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchetti, A.; Bond, M.G.; Hennig, M.; Neiss, A.; Mancia, G.; Dal Palù, C.; Hansson, L.; Magnani, B.; Rahn, K.H.; Reid, J.L.; et al. Calcium antagonist lacidipine slows down progression of asymptomatic carotid atherosclerosis: Principal results of the European Lacidipine Study on Atherosclerosis (ELSA), a randomized, double-blind, long-term trial. Circulation 2002, 106, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, N.S.; Peters, R.; Fletcher, A.E.; Staessen, J.A.; Liu, L.; Dumitrascu, D.; Stoyanovsky, V.; Antikainen, R.L.; Nikitin, Y.; Anderson, C.; et al. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parati, G.; Lombardi, C.; Hedner, J.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Grote, L.; Tkacova, R.; Lévy, P.; Riha, R.; Bassetti, C.; Narkiewicz, K.; et al. Recommendations for the management of patients with obstructive sleep apnoea and hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.R.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, T.L.; Lasserson, T.J.; Smith, B.J.; White, J.; Wright, J.; Cates, C.J. Continuous positive airways pressure for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 3, Cd001106. [Google Scholar]
- Ramar, K.; Dort, L.C.; Katz, S.G.; Lettieri, C.J.; Harrod, C.G.; Thomas, S.M.; Chervin, R.D. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring with Oral Appliance Therapy: An Update for 2015. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 773–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurora, R.N.; Casey, K.R.; Kristo, D.; Auerbach, S.; Bista, S.R.; Chowdhuri, S.; Karippot, A.; Lamm, C.; Ramar, K.; Zak, R.; et al. Practice parameters for the surgical modifications of the upper airway for obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Sleep 2010, 33, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthaler, T.I.; Kapen, S.; Lee-Chiong, T.; Alessi, C.; Boehlecke, B.; Brown, T.; Coleman, J.; Friedman, L.; Kapur, V.; Owens, J.; et al. Practice parameters for the medical therapy of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2006, 29, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Kartali, N.; Daskalopoulou, E.; Geleris, P.; Chatzipantazi, S.; Tziomalos, K.; Vlachogiannis, E.; Karagiannis, A. The effect of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on blood pressure and arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 2014, 18, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, C.M.; Yee, B.J.; Wong, K.K.; Grunstein, R.R.; Phillips, C.L. Treatment of Sleep Apnea with CPAP Lowers Central and Peripheral Blood Pressure Independent of the Time-of-Day: A Randomized Controlled Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Xi, Q.; Yang, D. Predictors of Blood Pressure Fall with Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment in Hypertension with Coronary Artery Disease and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015, 31, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Lan, C.C.; Wu, Y.K.; Huang, K.F. Beneficial Effects of Long-Term CPAP Treatment on Sleep Quality and Blood Pressure in Adherent Subjects with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.; Mahmoudi, S.; Hattar, K.; Sibelius, U.; Olschewski, H.; Mayer, K.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F. Enhanced release of superoxide from polymorphonuclear neutrophils in obstructive sleep apnea. Impact of continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162 Pt 1, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Grote, L.; Eder, D.N.; Radlinski, J.; Hedner, J. A double-blind, crossover study of Doxazosin and Enalapril on peripheral vascular tone and nocturnal blood pressure in sleep apnea patients. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pépin, J.L.; Tamisier, R.; Barone-Rochette, G.; Launois, S.H.; Lévy, P.; Baguet, J.P. Comparison of continuous positive airway pressure and valsartan in hypertensive patients with sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, T.; Gandhi, T.K.; Fiskio, J.M.; Seger, A.C.; So, J.W.; Cook, E.F.; Fukui, T.; Bates, D.W. An evaluation of risk factors for adverse drug events associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2004, 10, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cove-Smith, J.R.; Kirk, C.A. CNS-related side-effects with metoprolol and atenolol. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1985, 28 (Suppl. 1), 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nifedipine-Atenolol Study Review Committee. Nifedipine and atenolol singly and combined for treatment of essential hypertension: Comparative multicentre study in general practice in the United Kingdom. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1988, 296, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lacourcière, Y.; Asmar, R. A comparison of the efficacy and duration of action of candesartan cilexetil and losartan as assessed by clinic and ambulatory blood pressure after a missed dose, in truly hypertensive patients: A placebo-controlled, forced titration study. Candesartan/Losartan study investigators. Am. J. Hypertens. 1999, 12 Pt 1–2, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Engbaek, M.; Hjerrild, M.; Hallas, J.; Jacobsen, I.A. The effect of low-dose spironolactone on resistant hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2010, 4, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparil, S.; Williams, D.; Chrysant, S.G.; Marbury, T.C.; Neutel, J. Comparative efficacy of olmesartan, losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan in the control of essential hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 2001, 3, 283–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunström, E.; Manhem, K.; Rosengren, A.; Peker, Y. Blood Pressure Response to Losartan and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Hypertension and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, F.; Muxfeldt, E.S.; Margallo, V.; Cortez, A.F.; Cavalcanti, A.H.; Salles, G.F. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on aldosterone excretion in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea and resistant hypertension: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muxfeldt, E.S.; Margallo, V.; Costa, L.M.; Guimarães, G.; Cavalcante, A.H.; Azevedo, J.C.; de Souza, F.; Cardoso, C.R.; Salles, G.F. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on clinic and ambulatory blood pressures in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and resistant hypertension: A randomized controlled trial. Hypertension 2015, 65, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotenberg, B.W.; Murariu, D.; Pang, K.P. Trends in CPAP adherence over twenty years of data collection: A flattened curve. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) Severity | AHI Per Hour of Sleep |
|---|---|
| None/Normal | <5 |
| Mild | 5–15 |
| Moderate | >15–30 |
| Severe | >30 |
| Category | Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) (mmHg) | Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) (mmHg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal blood pressure (BP) | 120–129 | and/or | 80–84 |
| High normal BP | 130–139 | and/or | 85–89 |
| Grade 1 hypertension | 140–159 | and/or | 90–99 |
| Grade 2 hypertension | 160–179 | and/or | 100–109 |
| Grade 3 hypertension | ≥180 | and/or | ≥110 |
| Isolated systolic hypertension | ≥140 | and | <90 |
| CPAP without Humidification | CPAP with Humidification |
|---|---|
| Bleeding nose | Water condensation in the CPAP system |
| Dry nose | Water condensation on the face |
| Nasal congestion and discharge | Water condensation in the nose |
| Headaches | Water condensation in the mouth |
| Dry mouth | |
| Dry and sore throat | |
| Pain in sinuses | |
| Reduced smell | |
| Changed voice |
| ACE Inhibitors | Lipophilic Beta-Adrenoreceptor Antagonists (BAAs) | Hydrophilic BAA | Calcium Channel Blockers (CCBs) | Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) | Diuretics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coughing [56] | Difficulties staying asleep [57] | Dyspepsia [58] | Flushing [58] | No significant differences to placebo [59] | Dizziness [60] |
| Dizziness [56] | Restless nights [57] | Diarrhea [58] | Edema [58] | Headache [61] | Male gynecomastia [60] |
| Angioedema [56] | Sexual intercourse problems [57] | Fatigue [58] | Fatigue [58] | Fatigue [61] | Male impotence [60] |
| Renal dysfunction [56] | Dyspnea [58] | Dyspnea [58] | Dizziness [61] | Hyperkalemia [60] | |
| Dizziness [58] | Dizziness [58] | Back pain [61] | Orthostatic hypotension [60] | ||
| Headaches [58] | Headaches [58] | Dyspepsia [60] |
| Title and Identification Number | Participants | Design | Objective | Status/Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnea Is Associated With Myocardial Injury Independent of Blood Pressure Control in Hypertension (NCT00843583) | 98 | Observational Case-Only Cross-sectional Study | Find the prevalence of OSA between resistant hypertension patients. The aim is also to assess the relation be-tween the severity of OSA and BP control. | Completed. In patients with difficult-to-control HT, it was common to find unrecognized severe OSA, and the severity of OSA was associated with myocardial injury. |
| Effects of OSA Treatment on BP in Patients With Resistant Hyper-tension: A Randomized Trial (NCT00812695) | 40 | Interventional Randomized Parallel assignment No masking Study Phase III | Investigate CPAP therapy effect on BP control in patients with OSA and refractory hypertension. The aim is also to study how CPAP therapy affects arterial stiffness and cardiac remodeling. | Completed. CPAP therapy on patients with resistant HT significantly reduces the daytime BP. |
| Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment on Aldosterone Excretion in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnoea and Resistant Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial (NCT01508754) | 125 | Interventional Randomized-Parallel Assignment Single Masked Study Phase IV | Investigate CPAP therapy effect on BP (both ambulatory and clinical) on patients with OSA and resistant hypertension. | Completed. Significantly reduced aldosterone excretion in patients with uncontrolled resistant HT only under optimal CPAP (per protocol group). The effect was borderline significant in the intention-to-treat group [63,64]. |
| Effects of CPAP on “Vascular” Risk Factors in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Arterial Hypertension (NCT00801671) | 44 | Interventional Randomized Crossover Assignment Double-blind Study Phase III | Investigate CPAP therapy effectiveness in treating systemic hypertension. | Completed. In a group of OSA patients with HT, three weeks of effective CPAP therapy gave a significant decrease in office BP, central BP and augmentation index, and there was an improvement of arterial stiffness parameters. |
| Long-term Effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Blood Pressure and Prognosis in Hypertensive Patients With Coronary Heart Disease and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Randomized Controlled Trial (NCT02059993) | 83 | Interventional Randomized Parallel Assignment Single Masked Study | Evaluate the effect of CPAP therapy on BP, cerebrovascular events, metabolic disorder and cardiovascular events in patients who were suffering from OSA and coronary heart disease who used conventional treatment. | Completed. In patients with uncontrolled HT, coronary heart disease and OSA, long-term CPAP therapy reduces daytime SBP. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baran, R.; Grimm, D.; Infanger, M.; Wehland, M. The Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy on Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052300
Baran R, Grimm D, Infanger M, Wehland M. The Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy on Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052300
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaran, Ronni, Daniela Grimm, Manfred Infanger, and Markus Wehland. 2021. "The Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy on Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Hypertension" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052300
APA StyleBaran, R., Grimm, D., Infanger, M., & Wehland, M. (2021). The Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy on Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052300







