Transient Vasodilation in Mouse 4T1 Tumors after Intragastric and Intravenous Administration of Gold Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
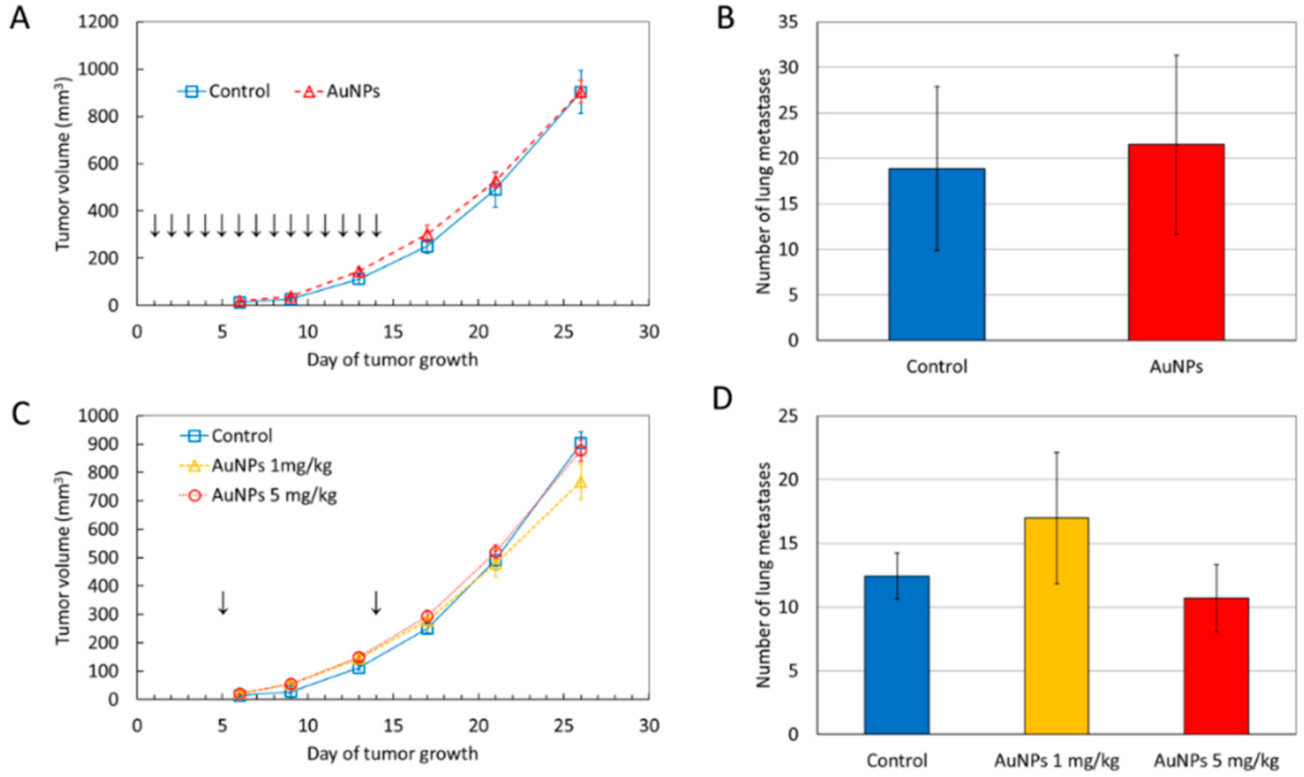
2.1. AuNPs Have No Significant Effect on Tumor Growth and Metastatic Potential
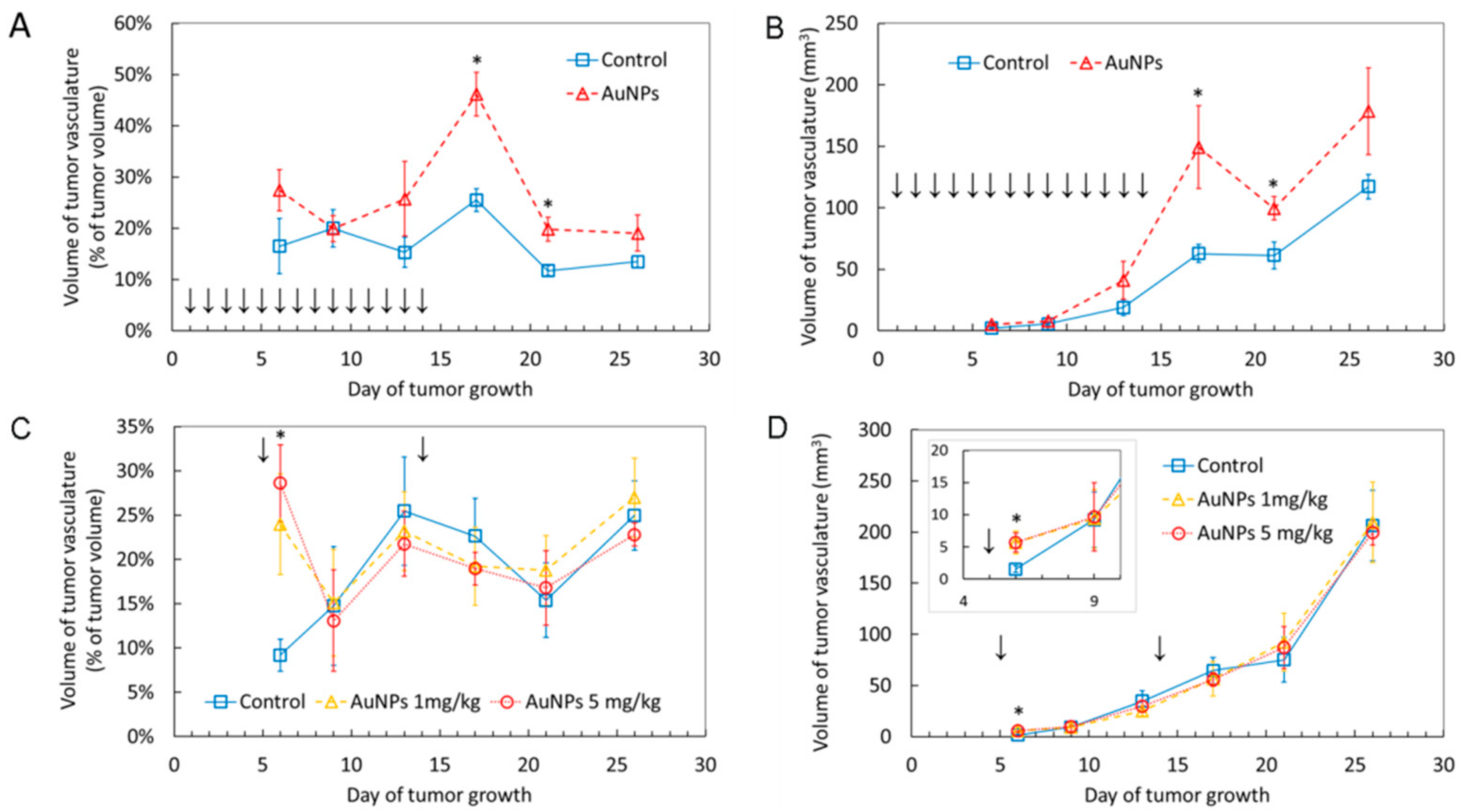
2.2. AuNPs Transiently Increase Volume of Blood Vessels in the Tumor
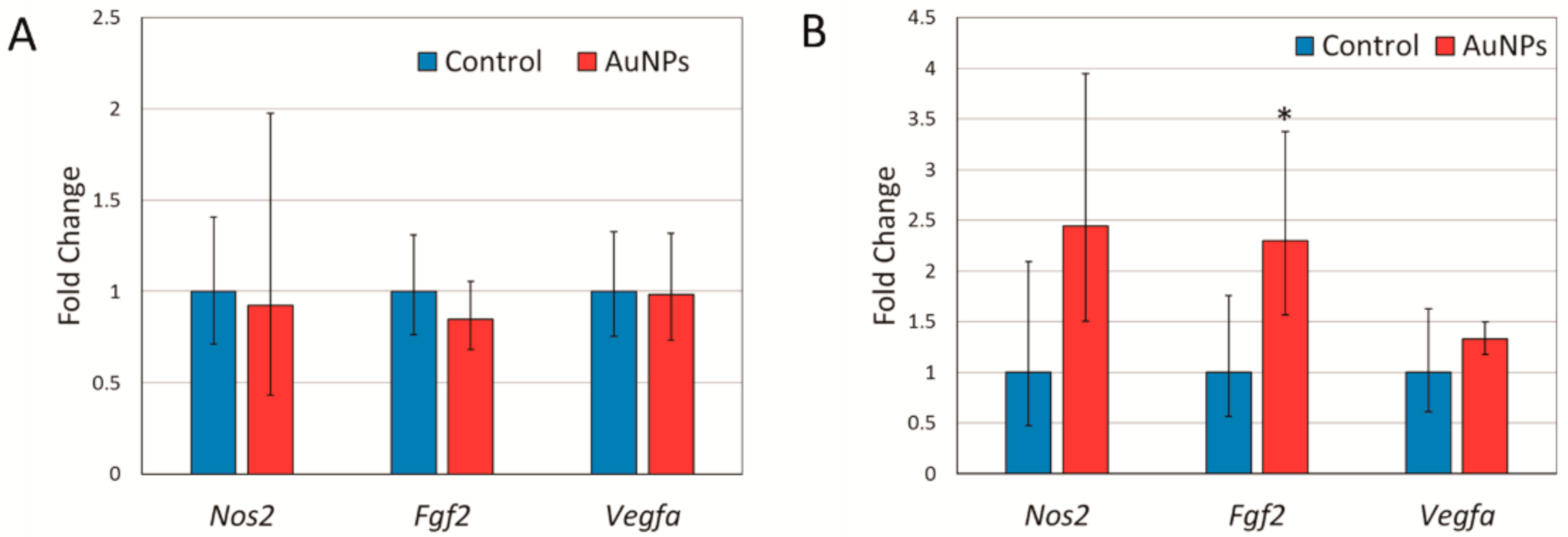
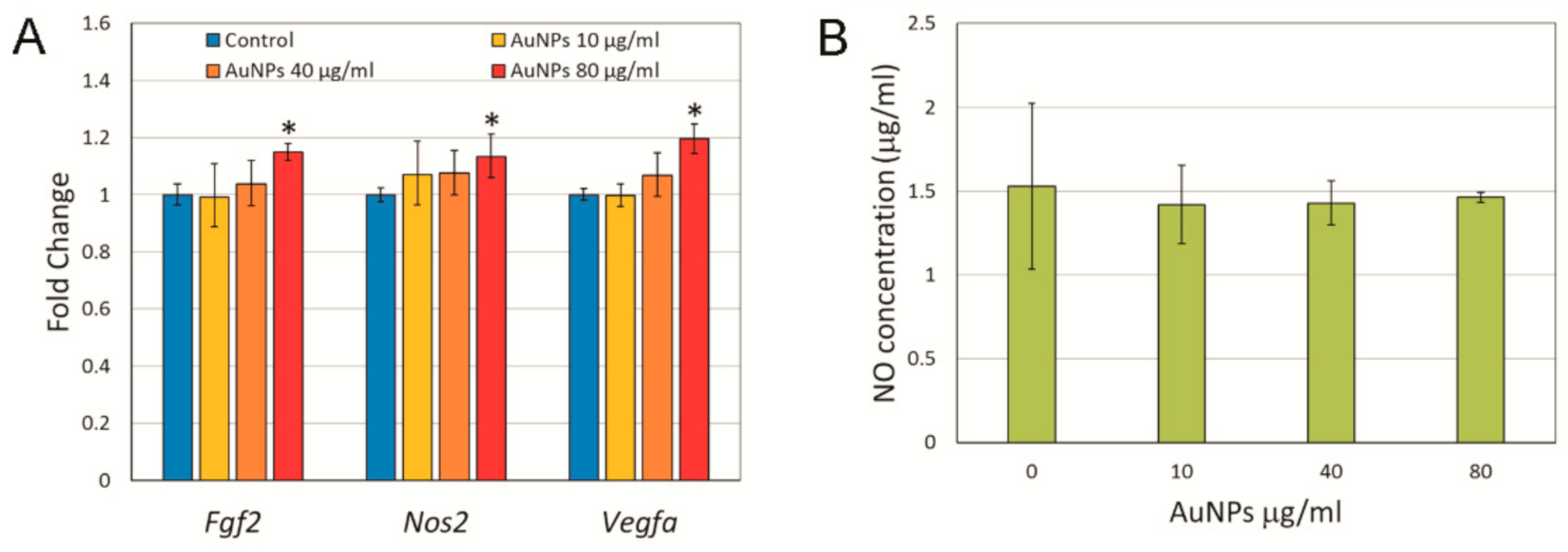
2.3. Expression of Angiogenesis Related Genes and Nitric Oxide Synthase in Response to AuNP Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Nanoparticles
4.2. Animals
4.3. 4T1 Breast Tumor Cells Implantation
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Nitrite Determination
4.6. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription and Real-Time PCR
4.7. Statistical Evaluation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Yan, L. Application of Au, SiO2@Au, and Au@SiO2 nanoparticles in PTB7:PC71BM polymer solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 13698–13704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.D.; Park, Y.M.; Chun, H.J.; Yoon, H.C. A low-cost optical transducer utilizing common electronics components for the gold nanoparticle-based immunosensing application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nita, R.; Trammell, S.A.; Ellis, G.A.; Moore, M.H.; Soto, C.M.; Leary, D.H.; Fontana, J.; Talebzadeh, S.F.; Knight, D.A. Kinetic analysis of the hydrolysis of methyl parathion using citrate-stabilized 10 nm gold nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1916–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Her, S.; Jaffray, D.A.; Allen, C. Gold nanoparticles for applications in cancer radiotherapy: Mechanisms and recent advancements. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 109, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarasan, S.; Focsan, M.; Potara, M.; Soritau, O.; Florea, A.; Maniu, D.; Astilean, S. Doxorubicin-Incorporated nanotherapeutic delivery system based on gelatin-coated gold nanoparticles: Formulation, drug release, and multimodal imaging of cellular internalization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22900–22913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhou, J.; Duan, H. Self-Assembled plasmonic vesicles of SERS-encoded amphiphilic gold nanoparticles for cancer cell targeting and traceable intracellular drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13458–13469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornos Carneiro, M.F.; Barbosa, F.J. Gold nanoparticles: A critical review of therapeutic applications and toxicological aspects. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2016, 19, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewale, O.B.; Davids, H.; Cairncross, L.; Roux, S. Toxicological behavior of gold nanoparticles on various models: Influence of physicochemical properties and other factors. Int. J. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Bartneck, M.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 509, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratoddi, I.; Venditti, I.; Cametti, C.; Russo, M.V. How toxic are gold nanoparticles? The state-of-the-art. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1771–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, A.; Bundschuh, M.; Klingelhofer, D.; Groneberg, D.A. Gold nanoparticles: Recent aspects for human toxicology. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2013, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falagan-Lotsch, P.; Grzincic, E.M.; Murphy, C.J. One low-dose exposure of gold nanoparticles induces long-term changes in human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13318–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramalingam, V.; Revathidevi, S.; Shanmuganayagam, T.; Muthulakshmi, L.; Rajaram, R. Biogenic gold nanoparticles induce cell cycle arrest through oxidative stress and sensitize mitochondrial membranes in A549 lung cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 20598–20608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ding, H.; Qin, L.; Zhao, X.; Cai, J.; Du, B. Gold nanoparticles induce nanostructural reorganization of VEGFR2 to repress angiogenesis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1746–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Li, W.; Yang, W.; Yang, X.Y.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Ding, H.; Qin, L.; Pan, Y. Anterior gradient 2 as a supervisory marker for tumor vessel normalization induced by anti-angiogenic treatment. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, P.; Bhattacharya, R.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Basu, S.; Nagy, J.A.; Atala, A.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Soker, S. Antiangiogenic properties of gold nanoparticles. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3530–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Pan, F.; Yang, X.Y.; Du, B.; Qin, L.; Pan, Y. Gold nanoparticles attenuate metastasis by tumor vasculature normalization and epithelial-mesenchymal transition inhibition. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3509–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brzoska, K.; Gradzka, I.; Kruszewski, M. Impact of silver, gold, and iron oxide nanoparticles on cellular response to tumor necrosis factor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 356, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzoska, K.; Gradzka, I.; Kruszewski, M. Silver, gold, and iron oxide nanoparticles alter miRNA expression but do not affect DNA methylation in HepG2 cells. Materials 2019, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tozman, E.C.; Gottlieb, N.L. Adverse reactions with oral and parenteral gold preparations. Med. Toxicol. 1987, 2, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felson, D.T.; Anderson, J.J.; Meenan, R.F. The comparative efficacy and toxicity of second-line drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Results of two metaanalyses. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darweesh, R.S.; Ayoub, N.M.; Nazzal, S. Gold nanoparticles and angiogenesis: Molecular mechanisms and biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7643–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Pittman, R.N.; Popel, A.S. Nitric oxide in the vasculature: Where does it come from and where does it go? A quantitative perspective. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vannini, F.; Kashfi, K.; Nath, N. The dual role of iNOS in cancer. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Pastoriza-Santos, V.; Perez-Juste, J.; Herves, P. Controllable nitric oxide release in the presence of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8061–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Han, L.; Du, L.B.; Tian, Q.; Xu, J.C. Potential oxidative stress of gold nanoparticles by induced-NO releasing in serum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, Q.; Miao, X.; Du, L.; Liu, Y. Gold nanoparticles-based catalysis for detection of S-Nitrosothiols in blood serum. Talanta 2011, 85, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamler, J.S.; Jaraki, O.; Osborne, J.; Simon, D.I.; Keaney, J.; Vita, J.; Singel, D.; Valeri, C.R.; Loscalzo, J. Nitric oxide circulates in mammalian plasma primarily as an S-Nitroso adduct of serum albumin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7674–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiesa, J.J.; Baidanoff, F.M.; Golombek, D.A. Don’t just say no: Differential pathways and pharmacological responses to diverse nitric oxide donors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyurin, V.A.; Liu, S.X.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Sussman, N.B.; Hubel, C.A.; Roberts, J.M.; Taylor, R.N.; Kagan, V.E. Elevated levels of S-Nitrosoalbumin in preeclampsia plasma. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aranda, E.; Lopez-Pedrera, C.; De La Haba-Rodriguez, J.R.; Rodriguez-Ariza, A. Nitric oxide and cancer: The emerging role of S-Nitrosylation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. Protein S-Nitrosylation and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012, 320, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.; Connolly, C.; Schettino, G.; Butterworth, K.T.; Prise, K.M. Biological mechanisms of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Kataoka, K. Chemo-Physical strategies to advance the in vivo functionality of targeted nanomedicine: The next generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 538–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, V.; Sechi, M. Therapeutic potential of targeted nanoparticles and perspective on nanotherapies. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, H. Vascular permeability in cancer and infection as related to macromolecular drug delivery, with emphasis on the EPR effect for tumor-selective drug targeting. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2012, 88, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomayko, M.M.; Reynolds, C.P. Determination of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 24, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisham, M.B.; Johnson, G.G.; Lancaster, J.R., Jr. Quantitation of nitrate and nitrite in extracellular fluids. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 268, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brzoska, K.; Szczygiel, M.; Drzał, A.; Sniegocka, M.; Michalczyk-Wetula, D.; Biela, E.; Elas, M.; Kapka-Skrzypczak, L.; Lewandowska-Siwkiewicz, H.; Urbańska, K.; et al. Transient Vasodilation in Mouse 4T1 Tumors after Intragastric and Intravenous Administration of Gold Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052361
Brzoska K, Szczygiel M, Drzał A, Sniegocka M, Michalczyk-Wetula D, Biela E, Elas M, Kapka-Skrzypczak L, Lewandowska-Siwkiewicz H, Urbańska K, et al. Transient Vasodilation in Mouse 4T1 Tumors after Intragastric and Intravenous Administration of Gold Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052361
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrzoska, Kamil, Małgorzata Szczygiel, Agnieszka Drzał, Martyna Sniegocka, Dominika Michalczyk-Wetula, Eva Biela, Martyna Elas, Lucyna Kapka-Skrzypczak, Hanna Lewandowska-Siwkiewicz, Krystyna Urbańska, and et al. 2021. "Transient Vasodilation in Mouse 4T1 Tumors after Intragastric and Intravenous Administration of Gold Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052361
APA StyleBrzoska, K., Szczygiel, M., Drzał, A., Sniegocka, M., Michalczyk-Wetula, D., Biela, E., Elas, M., Kapka-Skrzypczak, L., Lewandowska-Siwkiewicz, H., Urbańska, K., & Kruszewski, M. (2021). Transient Vasodilation in Mouse 4T1 Tumors after Intragastric and Intravenous Administration of Gold Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052361








