Isolation and Assessment of a Highly-Active Anti-Inflammatory Exopolysaccharide from Mycelial Fermentation of a Medicinal Fungus Cs-HK1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
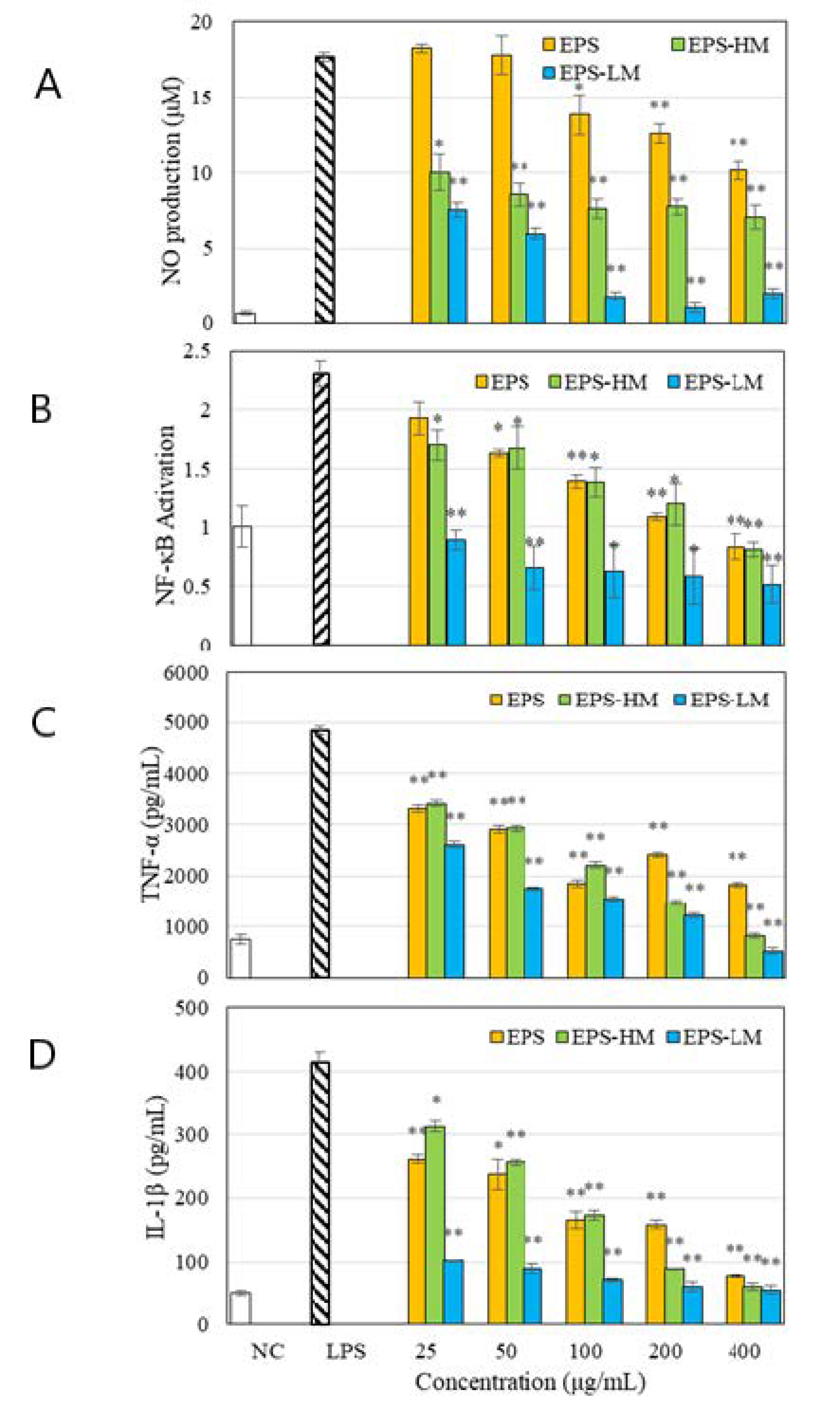
2.1. Compositions and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Different EPS Fractions
2.2. IR Spectral Characteristics of the EPS-LM-1 Structure
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of EPS-LM-1 in THP-1 Cell Culture
2.3.1. Suppression of LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses
2.3.2. Suppression of Inflammatory Protein Expression by EPS-LM-1
2.3.3. Comparison of the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of EPS-LM-1 with Other Polysaccharides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cs-HK1 Mycelial Fermentation and Crude EPS Isolation
3.2. Purification of EPS-LM
3.3. Analysis and Characterization of EPS-LM-1
3.3.1. Analysis of the Molecular Weight
3.3.2. Analysis of the Chemical Composition
3.3.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.4. In Vitro Anti-Inflammation Activity Assay
3.4.1. THP-1 Cell Culture
3.4.2. Analysis of NF-κB Activation and Nitric Oxide Production after LPS and EPS Treatment
3.4.3. Measurement of Cytokines by ELISA
3.4.4. Western Blot Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dumitriu, S. Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility, 2nd ed.; Dekker, M., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Quinn, M.T. Botanical polysaccharides: Macrophage immunomodulation and therapeutic potential. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Yao, J. Astragalus polysaccharide reduces inflammatory response by decreasing permeability of LPS-infected Caco2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, A.R.; Kim, S.J. Fucoidan as bio-functional molecule: Insights into the anti-inflammatory potential and associated molecular mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Perera, C.; Hemar, Y. Antitumor activity of mushroom polysaccharides: A review. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Meran, S.; Nie, S.P.; Midgley, A.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.W.; Xie, M.; Phillips, G.O.; Phillips, A.O. Cordyceps sinensis: Anti-fibrotic and inflammatory effects of a cultured polysaccharide extract. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2018, 14, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszyńska, B.; Grzywacz-Kisielewska, A.; Kała, K.; Gdula-Argasińska, J. Anti-inflammatory properties of edible mushrooms: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.X.; Wang, S.; Nie, S.; Marcone, M.J. Properties of Cordyceps sinensis: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 550–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. An Exopolysaccharide from cultivated Cordyceps sinensis and its effects on cytokine expressions of immunocytes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 163, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.P.; Cui, S.W.; Xie, M.; Phillips, A.O.; Phillips, G.O. Bioactive polysaccharides from Cordyceps sinensis: Isolation, structure features and bioactivities. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2013, 1, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.K.; Wang, W.Q.; Wu, J.Y. Recent advances in Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharides: Mycelial fermentation, isolation, structure, and bioactivities: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, P.H.; Zhao, S.; Ho, K.P.; Wu, J.Y. Chemical properties and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharides from mycelial culture of cordyceps sinensis fungus Cs-HK1. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.L.; Siu, K.C.; Wang, W.Q.; Cheung, Y.C.; Wu, J.Y. Fractionation, characterization and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharides from fermentation broth of a Cordyceps sinensis fungus. Process. Biochem. 2013, 48, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Q.; Song, A.X.; Yin, J.Y.; Siu, K.C.; Wong, W.T.; Wu, J.Y. Anti-inflammation activity of exopolysaccharides produced by a medicinal fungus Cordyceps sinensis Cs-HK1 in cell and animal models. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, A.J.M.C.C. Removeal of protein-Sevag method. Carbohydr. Polym. 1965, 5, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, S.P.; Cui, S.W.; Phillips, A.O.; Xie, M.Y.; Phillips, G.O.; Al-Assaf, S.; Zhang, X.L. Elucidation of the structure of a bioactive hydrophilic polysaccharide from Cordyceps sinensis by methylation analysis and NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nie, S.; Chen, S.; Phillips, A.O.; Phillips, G.O.; Li, Y.; Xie, M.; Cui, S.W. Structural characterization of an α-1, 6-linked galactomannan from natural Cordyceps sinensis. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 78, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zha, X.; Cui, S.; Cao, L.; Luo, J. Immunomodulatory activity on macrophage of a purified polysaccharide extracted from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, P.B.S.; Barros, W.; Santos, G.R.C.; Correia, M.T.S.; Mourão, P.A.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G. Characterization and rheological study of the galactomannan extracted from seeds of Cassia grandis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 104, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Peng, N.; Liang, Y. A novel polysaccharide from mycelia of cultured Phellinus linteus displays antitumor activity through apoptosis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.S.; Bashyam, L.; Manthapuram, N.; Bitla, P.; Kollipara, P.; Tetali, S.D. Ocimum sanctum leaf extracts attenuate human monocytic (THP-1) cell activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.W.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezekowitz, R.A. Molecular characterization of the human macrophage mannose receptor: Demonstration of multiple carbohydrate recognition-like domains and phagocytosis of yeasts in cos-1 cells. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Toyoshima, S.; Osawa, T. Irimura, Dual function of macrophage galactose/n-acetylgalactosamine-specific lectins: Glycoprotein uptake and tumoricidal cellular recognition. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. Gann 2005, 85, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, G.; Brys, L.; Dahal, B.K.; Brandt, J.; Grooten, J.; Brombacher, F.; Vanham, G.; Noël, W.; Bogaert, P.; Boonefaes, T.; et al. Macrophage galactose-type c-type lectins as novel markers for alternatively activated macrophages elicited by parasitic infections and allergic airway inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to nf-kappab: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-κB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of nf-κb in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yoshida, M.; Azuma, T.; Kanazawa, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Mizuno, M. Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of lentinan: Influence on IL-8 and TNFR1 expression in intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auwerx, J. The human leukemia cell line, THP-1: A multifacetted model for the study of monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Experientia 1991, 47, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Fraction | Yield (g/L) | Sugar (wt %) | Protein (wt %) | MW in kDa(GPC Peak Area%) a |
| EPS-HM | 2.27 ± 0.19 | 64.5 ± 5.70 | 9.0 ± 0.39 | 6250 (84.76%) 18.5 (15.24%) |
| EPS-LM | 0.93 ± 0.15 | 25.5 ± 0.60 | 20.1 ± 0.06 | 360 (68.7%) 39.2 (12.3%) 1.61 (19.0%) |
| EPS-LM-1 | 0.074 ± 0.003 | 100 | - | 360 (100%) |
| Monosaccharide composition (molar ratio) | ||||
| Fraction | Mannose | Ribose | Glucose | Galactose |
| EPS-HM | 1.71 | 0.09 | 0.94 | 1 |
| EPS-LM | 7.76 | - | 13.87 | 1 |
| EPS-LM-1 | 3.88 | - | 6.93 | 1 |
| Peak Wavenumber (cm−1) | Functional Groups |
|---|---|
| 3400 | Axial stretch of -OH group |
| 2930 | Weak C-H stretching vibration |
| 1638, 1539 | Asymmetric and symmetric vibration of the ring stretching of the carboxylate group, respectively. |
| 1380 | OH bending vibration |
| 1065 | Pyranoside (e.g., in the glucose residues) |
| Pro-Inflammation Factors | MEC (μg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| EPS | EPS-LM-1 | |
| NF-κB | 67.6 | 4.77 |
| NO | 123.3 | 3.74 |
| IL-1β | 183.6 | 1.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.-Q.; Song, A.-X.; Wong, W.-T.; Wu, J.-Y. Isolation and Assessment of a Highly-Active Anti-Inflammatory Exopolysaccharide from Mycelial Fermentation of a Medicinal Fungus Cs-HK1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052450
Li L-Q, Song A-X, Wong W-T, Wu J-Y. Isolation and Assessment of a Highly-Active Anti-Inflammatory Exopolysaccharide from Mycelial Fermentation of a Medicinal Fungus Cs-HK1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052450
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Long-Qing, Ang-Xin Song, Wing-Tak Wong, and Jian-Yong Wu. 2021. "Isolation and Assessment of a Highly-Active Anti-Inflammatory Exopolysaccharide from Mycelial Fermentation of a Medicinal Fungus Cs-HK1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052450
APA StyleLi, L.-Q., Song, A.-X., Wong, W.-T., & Wu, J.-Y. (2021). Isolation and Assessment of a Highly-Active Anti-Inflammatory Exopolysaccharide from Mycelial Fermentation of a Medicinal Fungus Cs-HK1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052450







