UV-Irradiation- and Inflammation-Induced Skin Barrier Dysfunction Is Associated with the Expression of Olfactory Receptor Genes in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Skin Barrier Genes Are Downregulated in UVB-Irradiated HaCaT Cells
2.2. Skin Barrier Genes Are Downregulated in Inflamed HaCaT Cells
2.3. Presence of Olfactory Signaling Pathway Components in HaCaT Cells
2.4. OR Profile in HaCaT Cells
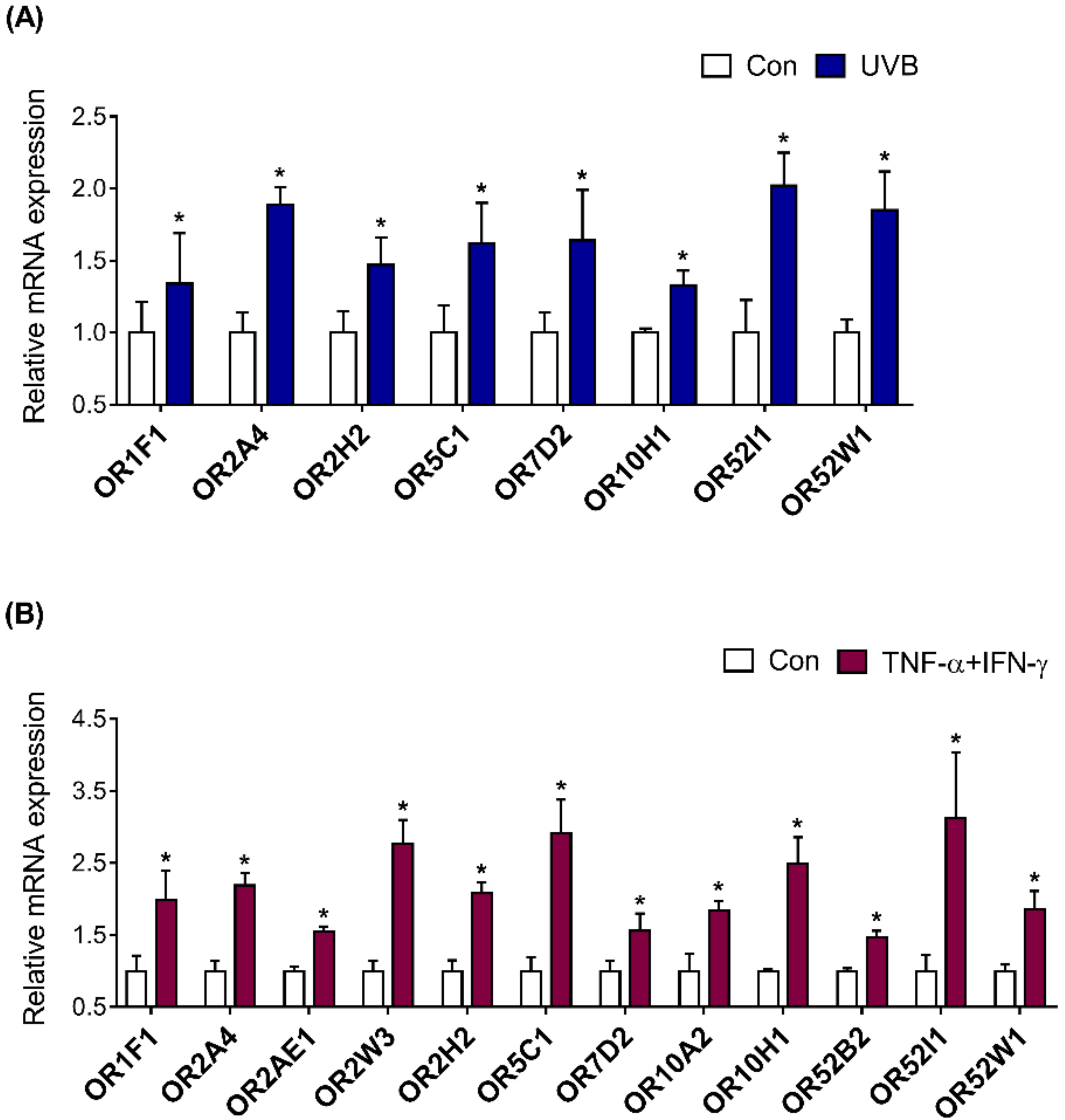
2.5. Investigation of OR Expression in UVB-Irradiated and Inflamed HaCaT Cells
2.6. OR Involvement in the Skin Barrier Disruption Pathway in HaCaT Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. WST-1 Assay
4.3. RNA Extraction and PCR
4.4. RNA-Sequencing
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawlings, A.; Davies, A.; Carlomusto, M.; Pillai, S.; Zhang, K.; Kosturko, R.; Verdejo, P.; Feinberg, C.; Nguyen, L.; Chandar, P. Effect of lactic acid isomers on keratinocyte ceramide synthesis, stratum corneum lipid levels and stratum corneum barrier function. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1996, 288, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Green, H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell 1980, 19, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E.; Brandner, J.M.; Jensen, J.M. The skin: An indispensable barrier. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.; Proksch, E. The skin’s barrier. G. Ital. Di Dermatol. E Venereol. Organo Uff. Soc. Ital. Di Dermatol. E Sifilogr. 2009, 144, 689–700. [Google Scholar]
- Van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Gooris, G.; Bouwstra, J. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2014, 1841, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniek, K.; Levi, K.; Dauskardt, R.H. Solar UV radiation reduces the barrier function of human skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17111–17116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meguro, S.; Aral, Y.; Masukawa, K.; Uie, K.; Tokimitsu, I. Stratum Corneum Lipid Abnormalities in UVB-lrradiated Skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 69, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Skin barrier abnormalities and immune dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hänel, K.H.; Cornelissen, C.; Lüscher, B.; Baron, J.M. Cytokines and the skin barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6720–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maßberg, D.; Hatt, H. Human olfactory receptors: Novel cellular functions outside of the nose. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1739–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Fu, N.; Chen, L. The diversified function and potential therapy of ectopic olfactory receptors in non-olfactory tissues. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitinger, S.; Hatt, H. Ectopic expression of mammalian olfactory receptors. In Springer Handbook of Odor; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kalbe, B.; Knobloch, J.; Schulz, V.M.; Wecker, C.; Schlimm, M.; Scholz, P.; Jansen, F.; Stoelben, E.; Philippou, S.; Hecker, E. Olfactory receptors modulate physiological processes in human airway smooth muscle cells. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manteniotis, S.; Wójcik, S.; Göthert, J.R.; Dürig, J.; Dührsen, U.; Gisselmann, G.; Hatt, H. Deorphanization and characterization of the ectopically expressed olfactory receptor OR51B5 in myelogenous leukemia cells. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, T.; Kim, M.; Park, T. α-Cedrene, a Newly Identified Ligand of MOR23, Increases Skeletal Muscle Mass and Strength. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovancevic, N.; Khalfaoui, S.; Weinrich, M.; Weidinger, D.; Simon, A.; Kalbe, B.; Kernt, M.; Kampik, A.; Gisselmann, G.; Gelis, L. Odorant receptor 51E2 agonist β-ionone regulates RPE cell migration and proliferation. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gelis, L.; Jovancevic, N.; Bechara, F.G.; Neuhaus, E.M.; Hatt, H. Functional expression of olfactory receptors in human primary melanoma and melanoma metastasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, R.-R.; Shi, D.-B.; Wang, Y.-W.; Li, X.-M.; He, J.-Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, P. The olfactory receptor family 2, subfamily T, member 6 (OR2T6) is involved in breast cancer progression via initiating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and MAPK/ERK pathway. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, B.D.; Koepsell, H.; Pluznick, J.L. Renal olfactory receptor 1393 contributes to the progression of type 2 diabetes in a diet-induced obesity model. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F372–F381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Thach, T.T.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-J. Olfactory receptor 43 reduces hepatic lipid accumulation and adiposity in mice. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Dakle, P.; Sinha, A.; Vishweswaraiah, S.; Nagori, A.; Salimath, S.; Prakash, Y.; Lodha, R.; Kabra, S.; Ghosh, B. Genetic variations in olfactory receptor gene OR2AG2 in a large multigenerational family with asthma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, L.; Schulz, W.A.; Philippou, S.; Eckardt, J.; Ubrig, B.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Tannapfel, A.; Kalbe, B.; Gisselmann, G.; Hatt, H. Characterization of the olfactory receptor OR10H1 in human urinary bladder cancer. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, E.H.; Dyjack, N.; Kim, B.E.; Rios, C.; Seibold, M.A.; Leung, D.Y.; Goleva, E. Expression and function of the ectopic olfactory receptor OR10G7 in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, D.; Kudella, P.; Grüning, N.-M.; Gisselmann, G.; Ständer, S.; Luger, T.; Jacobsen, F.; Steinsträßer, L.; Paus, R.; Gkogkolou, P. A synthetic sandalwood odorant induces wound-healing processes in human keratinocytes via the olfactory receptor OR2AT4. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y. Significance of skin barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmuth, M.; Blunder, S.; Dubrac, S.; Gruber, R.; Moosbrugger-Martinz, V. Epidermal barrier in hereditary ichthyoses, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis. JDDG J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.; Kang, W.; Park, T. Anti-Allergic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Undecane on Mast Cells and Keratinocytes. Molecules 2020, 25, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, W.; Han, E.J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Fernando, I.S.; Ahn, G.; Kim, K.-N. Eckol from Ecklonia cava ameliorates TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammatory responses via regulating MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathway in HaCaT cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.S.; Jin, S.E.; Kim, O.S.; Shin, H.K.; Jeong, S.J. Alantolactone from Saussurea lappa Exerts Antiinflammatory Effects by Inhibiting Chemokine Production and STAT1 Phosphorylation in TNF-α and IFN-γ-induced in HaCaT cells. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lim, J.-Y.; Jo, E.H.; Noh, H.M.; Park, S.; Park, M.C.; Kim, D.-K. Chijabyukpi-Tang Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines via the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Stimulated HaCaT Cells and Ameliorates 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-H.; Yoo, J.-M.; Lee, E.; Lee, B.; Cho, W.-K.; Park, K.-I.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of Perillae Herba ethanolic extract against TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 211, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.; Veitinger, S.; Peek, I.; Busse, D.; Eckardt, J.; Vladimirova, D.; Jovancevic, N.; Wojcik, S.; Gisselmann, G.; Altmüller, J. Two olfactory receptors—OR 2A4/7 and OR 51B5—differentially affect epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbe, B.; Osterloh, M.; Schulz, V.M.; Altmüller, J.; Becker, C.; Osterloh, S.; Hatt, H. OR2H2 regulates the differentiation of human myoblast cells by its ligand aldehyde 13-13. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 645, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, C.; Vogel, F.; Hofreuter, A.; Schreiner, B.S.; Osthold, S.; Veitinger, S.; Becker, C.; Brockmeyer, N.H.; Muschol, M.; Wennemuth, G. Characterization of the olfactory receptors expressed in human spermatozoa. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 2, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flegel, C.; Manteniotis, S.; Osthold, S.; Hatt, H.; Gisselmann, G. Expression profile of ectopic olfactory receptors determined by deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, I.; Sangiovanni, E.; Maggio, R.; Mattozzi, C.; Zava, S.; Corbett, Y.; Fumagalli, M.; Carlino, C.; Corsetto, P.A.; Scaccabarozzi, D. HaCaT cells as a reliable in vitro differentiation model to dissect the inflammatory/repair response of human keratinocytes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 7435621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyrieux, A.F.; Wilson, V.G. In vitro culture conditions to study keratinocyte differentiation using the HaCaT cell line. Cytotechnology 2007, 54, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, T.; Wilson, S.R.; Choi, Y.G.; Risso, D.; Dudoit, S.; Speed, T.P.; Ngai, J. Silencing of odorant receptor genes by G protein βγ signaling ensures the expression of one odorant receptor per olfactory sensory neuron. Neuron 2014, 81, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verbeurgt, C.; Wilkin, F.; Tarabichi, M.; Gregoire, F.; Dumont, J.E.; Chatelain, P. Profiling of olfactory receptor gene expression in whole human olfactory mucosa. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96333. [Google Scholar]
- Skalhegg, B.; Tasken, K. Specificity in the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. Differential expression, regulation, and subcellular localization of subunits of PKA. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, D678–D693. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, T.; Ryu, S.E.; Min, Y.; Claire, A.; Bushdid, C.; Golebiowski, J.; Moon, C.; Park, T. Olfactory receptor 10J5 responding to α-cedrene regulates hepatic steatosis via the cAMP–PKA pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Jia, Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, D.; Pathiraja, D.; Choi, I.-G.; Koo, S.-H.; Lee, S.-J. Olfactory receptor 544 reduces adiposity by steering fuel preference toward fats. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 4118–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatelain, P.; Veithen, A.; Wilkin, F.; Philippeau, M. Deorphanization and characterization of human olfactory receptors in heterologous cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 1764–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.-M.; Ma, M.; Li, H.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Y.-T.; Yan, Y.-X.; Shen, Y.-F.; Yang, X.-Q.; Zhu, F.-H.; He, S.-J. Topical administration of reversible SAHH inhibitor ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice via suppression of TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammatory response in keratinocytes and T cell-derived IL-17. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedoszytko, B.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M.; Ruckemann-Dziurdzińska, K.; Roszkiewicz, J.; Nowicki, R.J. Chemokines and cytokines network in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory skin diseases: Atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and skin mastocytosis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol./Postȩpy Dermatol. I Alergol. 2014, 31, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, S.-R.; Caruntu, C.; Sarbu, M.-I.; Mitran, C.-I.; Mitran, M.-I.; Matei, C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Advances in understanding the immunological pathways in psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kligman, L.H.; Akin, F.J.; Kligman, A.M. The contributions of UVA and UVB to connective tissue damage in hairless mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1985, 84, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfau, R.; HOOD, A.F.; Morison, W. Photoageing: The role of UVB, solar-simulated UVB, visible and psoralen UVA radiation. Br. J. Dermatol. 1986, 114, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Hölzle, E.; Melnik, B.; Plewig, G. Effects of ultraviolet A and B on the skin barrier: A functional, electron microscopic and lipid biochemical study. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1991, 8, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Choi, D.; Park, T. Dietary suberic acid protects against UVB-induced skin photoaging in hairless mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.-S.; Ahn, Y.; Bae, I.-H.; Min, D.; Park, N.H.; Jung, W.; Kim, S.-H.; Hong, Y.D.; Park, W.S.; Lee, C.S. Synthetic retinoid seletinoid G improves skin barrier function through wound healing and collagen realignment in human skin equivalents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.-Y.; Lyu, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-J.; Chien, T.-Y.; Hsu, H.-C.; Wen, K.-C.; Chiang, H.-M. Fisetin regulates Nrf2 expression and the inflammation-related signaling pathway to prevent UVB-induced skin damage in hairless mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Woo, Y.-K.; Cho, H.-J. Regulation of Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Activity of Advanced Cooling Composition (ACC) in UVB-Irradiated Human HaCaT Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Bioinformatics, Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, W.; Son, B.; Park, S.; Choi, D.; Park, T. UV-Irradiation- and Inflammation-Induced Skin Barrier Dysfunction Is Associated with the Expression of Olfactory Receptor Genes in Human Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062799
Kang W, Son B, Park S, Choi D, Park T. UV-Irradiation- and Inflammation-Induced Skin Barrier Dysfunction Is Associated with the Expression of Olfactory Receptor Genes in Human Keratinocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062799
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Wesuk, Bomin Son, Soyoon Park, Dabin Choi, and Taesun Park. 2021. "UV-Irradiation- and Inflammation-Induced Skin Barrier Dysfunction Is Associated with the Expression of Olfactory Receptor Genes in Human Keratinocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062799
APA StyleKang, W., Son, B., Park, S., Choi, D., & Park, T. (2021). UV-Irradiation- and Inflammation-Induced Skin Barrier Dysfunction Is Associated with the Expression of Olfactory Receptor Genes in Human Keratinocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062799





