The Interaction of Human and Epstein–Barr Virus miRNAs with Multiple Sclerosis Risk Loci
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MS Risk miRNAs Are Differentially Expressed between LCLs and B Cells
2.2. Which MS Risk Genes Are Targeted by MS Risk miRNAs?
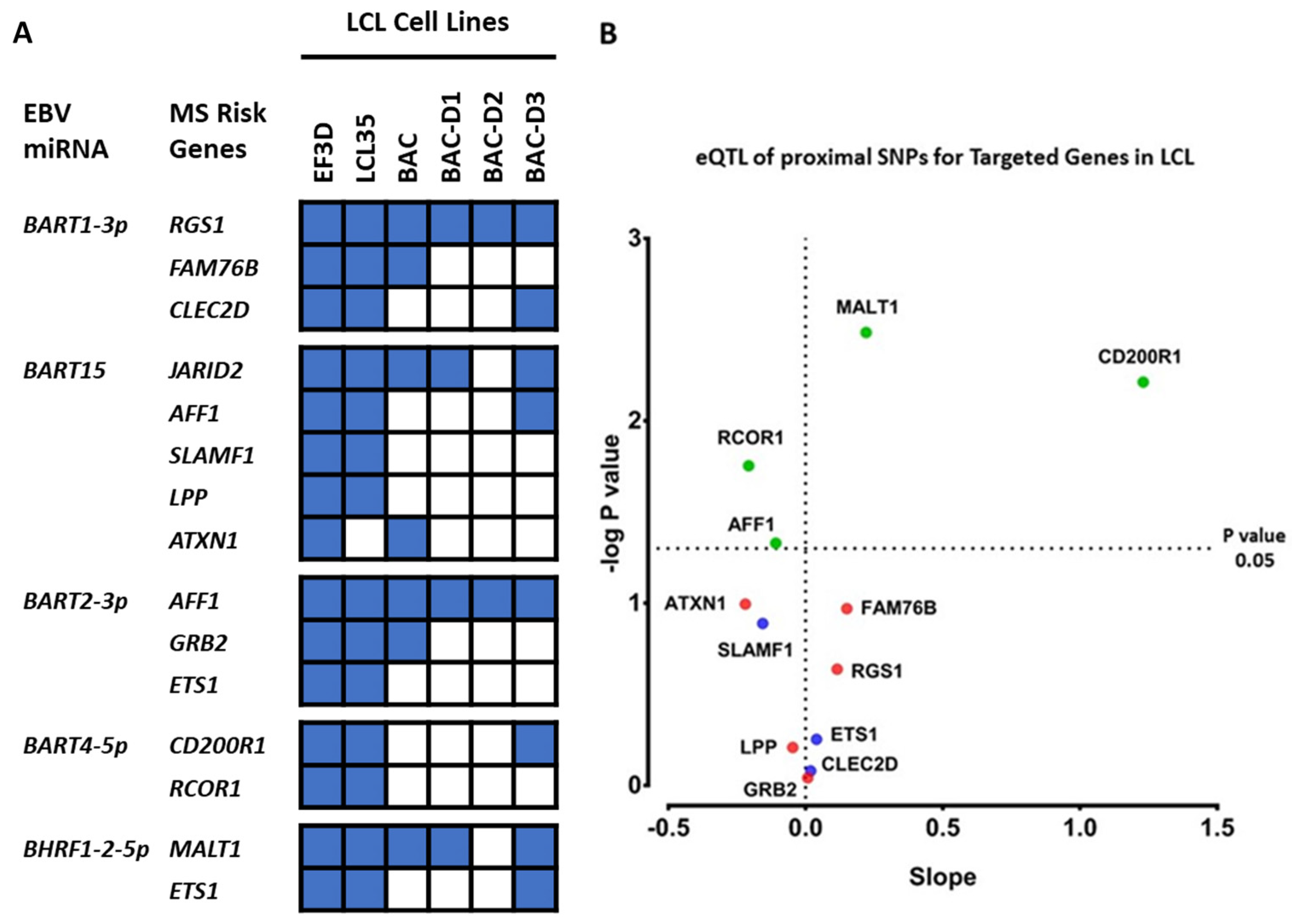
2.3. Which EBV miRNAs Target the Host MS Risk Genes?
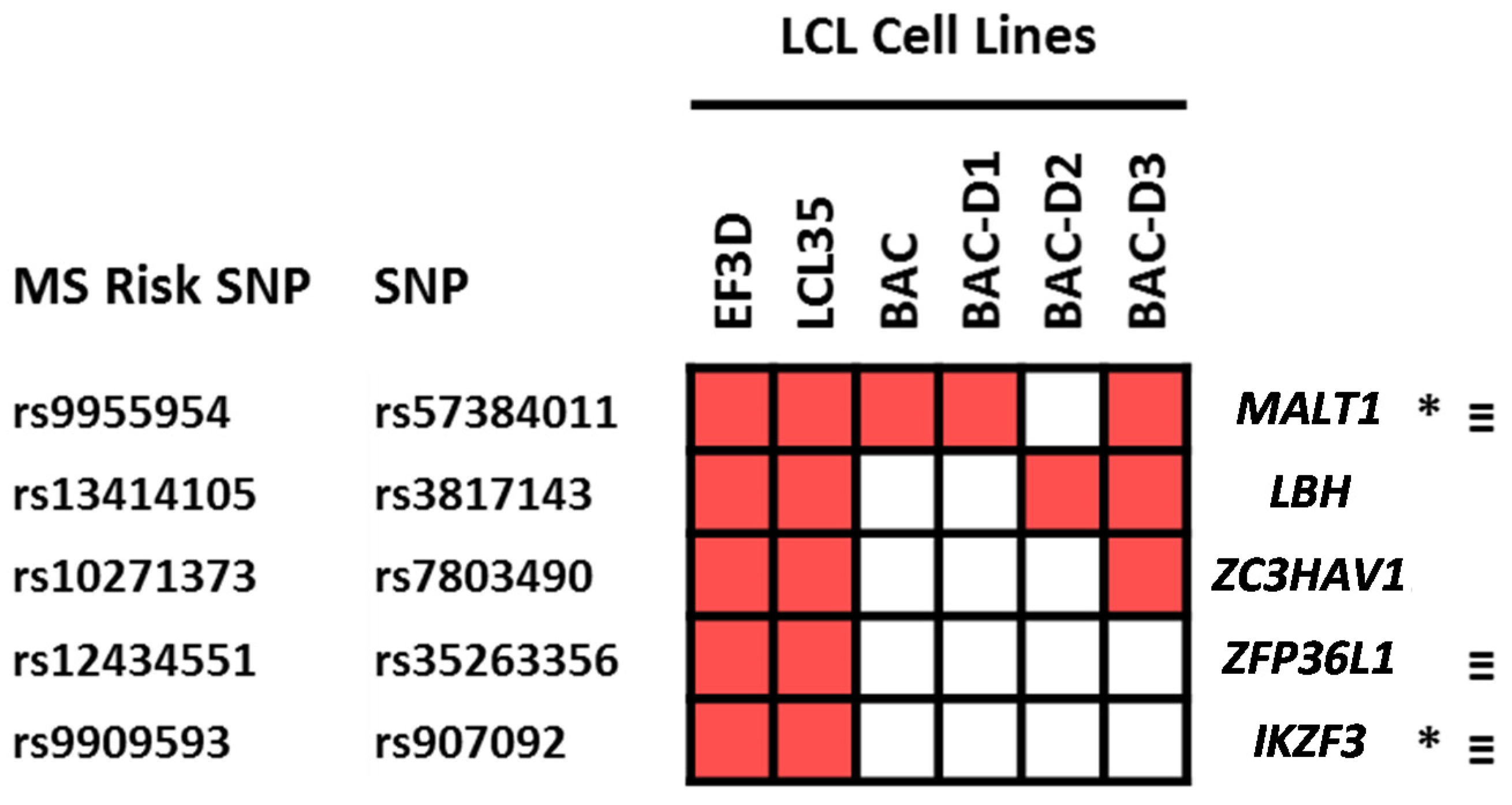
2.4. Which Host and EBV miRNA Binding Sites among Host MS Risk Genes Are Affected by MS Risk SNP Genotype?
2.5. Which Host and EBV miRNA Binding Sites among Host MS Risk Genes Are Affected by MS Risk SNP Genotype?
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Dataset Preparation
4.2. miRNA Target Site Prediction
4.3. EBV and MS Risk miRNA Target Identification (Pipeline A)
4.4. MS Risk SNP Interaction with EBV and Host miRNA Analysis (Pipeline B)
4.5. Genotyping and Gene Expression
4.6. Small RNA-Seq
4.7. Statistics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rolak, L.A. Multiple sclerosis: It’s not the disease you thought it was. Clin. Med. Res. 2003, 1, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium. Multiple sclerosis genomic map implicates peripheral immune cells and microglia in susceptibility. Science 2019, 365, eaav7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakalacheva, K.; Munz, C.; Lunemann, J.D. Viral triggers of multiple sclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, K.; Klein, G.; Henle, W.; Henle, G. The establishment of lymphoblastoid lines from adult and fetal human lymphoid tissue and its dependence on EBV. Int. J. Cancer 1971, 8, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, P.F.; Bloomer, L.C.; Salmon, V.C.; Bagley, M.H.; Larsen, P.D. Epstein-Barr virus infection and antibody synthesis in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 1983, 40, 406–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andinger, K.; Jabs, W.; Siekhaus, A.; Bubel, S.; Trillenberg, P.; Wagner, H.; Wessel, K.; Kirchner, H.; Hennig, H. Association between clinical disease activity and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in MS. Neurology 2000, 55, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Munger, K.L. Environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Part I: The role of infection. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, M.P. The essential role of Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Neuroscientist 2011, 17, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pender, M.P. CD8+ T-Cell Deficiency, Epstein-Barr Virus Infection, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Steps to Autoimmunity: A Unifying Hypothesis. Autoimmune Dis. 2012, 2012, 189096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albanese, M.; Tagawa, T.; Bouvet, M.; Maliqi, L.; Lutter, D.; Hoser, J.; Hastreiter, M.; Hayes, M.; Sugden, B.; Martin, L.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs reduce immune surveillance by virus-specific CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6467–E6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassani, A.; Khan, G. Epstein-Barr Virus and miRNAs: Partners in Crime in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis? Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Bartel, D.P. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010, 466, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afrasiabi, A.; Parnell, G.P.; Fewings, N.; Schibeci, S.D.; Basuki, M.A.; Chandramohan, R.; Zhou, Y.; Taylor, B.; Brown, D.A.; Swaminathan, S.; et al. Evidence from genome wide association studies implicates reduced control of Epstein-Barr virus infection in multiple sclerosis susceptibility. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Fachko, D.; Ivanov, N.S.; Skinner, C.M.; Skalsky, R.L. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs regulate B cell receptor signal transduction and lytic reactivation. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejnar, C.E.; Zdobnov, E.M. MiRmap: Comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11673–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elefant, N.; Berger, A.; Shein, H.; Hofree, M.; Margalit, H.; Altuvia, Y. RepTar: A database of predicted cellular targets of host and viral miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D188–D194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Corcoran, D.L.; Gottwein, E.; Frank, C.L.; Kang, D.; Hafner, M.; Nusbaum, J.D.; Feederle, R.; Delecluse, H.J.; Luftig, M.A.; et al. The viral and cellular microRNA targetome in lymphoblastoid cell lines. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Luo, R.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Fu, Z.; Fu, Q.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Liang, Z.; et al. miR-3188 regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation and chemosensitivity through a FOXO1-modulated positive feedback loop with mTOR-p-PI3K/AKT-c-JUN. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.F.; He, D.D.; Liang, H.W.; Yang, D.; Yue, H.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, R.; Li, B.; Yang, H.X.; Liu, Y.; et al. The identification of up-regulated ebv-miR-BHRF1-2-5p targeting MALT1 and ebv-miR-BHRF1-3 in the circulation of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 189, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.; Pan, Q.; Blencowe, B.J.; Claycomb, J.M.; Frappier, L. Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 protein regulates viral latency through effects on let-7 microRNA and dicer. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11166–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Goraya, M.U.; Chen, N.; Xu, L.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, M.; Chen, J.L. Zinc Finger CCCH-Type Antiviral Protein 1 Restricts the Viral Replication by Positively Regulating Type I Interferon Response. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrasiabi, A.; Parnell, G.P.; Swaminathan, S.; Stewart, G.J.; Booth, D.R. The interaction of Multiple Sclerosis risk loci with Epstein-Barr virus phenotypes implicates the virus in pathogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: MicroRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiela, M.J.; Chanock, S.J. LDlink: A web-based application for exploring population-specific haplotype structure and linking correlated alleles of possible functional variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3555–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lappalainen, T.; Sammeth, M.; Friedlander, M.R.; t Hoen, P.A.; Monlong, J.; Rivas, M.A.; Gonzalez-Porta, M.; Kurbatova, N.; Griebel, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; et al. Transcriptome and genome sequencing uncovers functional variation in humans. Nature 2013, 501, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.G. GTEx Analysis V7 (dbGaP Accession phs000424.v7.p2). GTEx Portal. Available online: https://gtexportal.org/home/datasets (accessed on 12 February 2018).
- Harley, J.B.; Chen, X.; Pujato, M.; Miller, D.; Maddox, A.; Forney, C.; Magnusen, A.F.; Lynch, A.; Chetal, K.; Yukawa, M.; et al. Transcription factors operate across disease loci, with EBNA2 implicated in autoimmunity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, A.S.; Karolchik, D.; Baertsch, R.; Barber, G.P.; Bejerano, G.; Clawson, H.; Diekhans, M.; Furey, T.S.; Harte, R.A.; Hsu, F.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser Database: Update 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D590–D598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kertesz, M.; Iovino, N.; Unnerstall, U.; Gaul, U.; Segal, E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Samal, E.; Srivastava, D. Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature 2005, 436, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ransom, J.F.; Li, A.; Vedantham, V.; von Drehle, M.; Muth, A.N.; Tsuchihashi, T.; McManus, M.T.; Schwartz, R.J.; Srivastava, D. Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell 2007, 129, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Deng, N.; Zhao, Z.; Judeh, T.; Flemington, E.; Zhu, D. SAMMate: A GUI tool for processing short read alignments in SAM/BAM format. Source Code Biol. Med. 2011, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leong, H.S.; Kipling, D. Text-based over-representation analysis of microarray gene lists with annotation bias. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| MS Risk SNP | miRNA Gene Name | Status | Mature miRNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs6589939 | MIR100HG | Proximal | hsa-miR-125b-5p |
| hsa-miR-125b-1-3p | |||
| hsa-let-7a-5p | |||
| hsa-let-7a-2-3p | |||
| hsa-miR-100-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-100-3p | |||
| rs13385171 | MIR4778 | Proximal | hsa-miR-4778-5p |
| hsa-miR-4778-3p | |||
| rs12971909 | MIR4746 | Proximal | hsa-miR-4746-5p |
| hsa-miR-4746-3p | |||
| rs34026809 | MIR6716 | Proximal | hsa-miR-6716-5p |
| hsa-miR-6716-3p | |||
| rs2150879 | MIR21 | Proximal | hsa-miR-21-5p |
| hsa-miR-21-3p | |||
| rs71252597 | MIR4435-1HG | Proximal | hsa-miR-4435 |
| rs6990534 | MIR1204 | Proximal | hsa-miR-1204 |
| rs7819665 | MIR1208 | Proximal | hsa-miR-1208 |
| rs77654077 | MIR623 | Proximal | hsa-miR-623 |
| rs149114341 | MIR4492 | Proximal | hsa-miR-4492 |
| rs4808760 | MIR3188 | eQTL | hsa-miR-3188 |
| MS risk miRNA | Expression Status |
|---|---|
| hsa-miR-100-5p | Expressed in LCLs and B cells |
| hsa-miR-3188 | |
| hsa-miR-21-3p | Upregulated in LCLs compared to B cells |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | |
| hsa-miR-4746-5p | |
| hsa-let-7b-5p | Downregulated in LCLs compared to B cells |
| hsa-let-7e-5p | |
| hsa-miR-4435 | Only expressed in B cells |
| hsa-miR-4492 | Only expressed in LCLs |
| hsa-miR-125b-1-3p | Not expressed in LCLs or B cells |
| hsa-let-7a-2-3p | |
| hsa-miR-100-3p | |
| hsa-miR-4778-5p | |
| hsa-miR-4778-3p | |
| hsa-miR-4746-3p | |
| hsa-miR-6716-5p | |
| hsa-miR-6716-3p | |
| hsa-miR-1204 | |
| hsa-miR-1208 | |
| hsa-miR-623 |
| MS Risk miRNAs | Number of Targeted Genes | Number of Targeted MS Risk Genes |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-mir-3188-3p | 35 | None |
| hsa-miR-21-3p | 67 | None |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 11 | 5 |
| hsa-miR-125b-5p | 18 | 4 |
| hsa-let-7a-5p | 73 | 1 |
| MS Risk SNP | miRNA | Targeted Gene | Genotype Condition | Correlation Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs6589939 | hsa-let-7a-5p | MAVS | Whole population | Rho = −0.16, p value 0.0005, FDR 0.02 |
| END4 | Protective | Rho = −0.18, p value 0.03, FDR 0.37 | ||
| ARID3A | Protective | Rho = −0.18, p value 0.02, FDR 0.37 | ||
| USP38 | Protective | Rho = −0.21, p value 0.01, FDR 0.27 | ||
| rs6589939 | hsa-miR-125b-1-5p | CD74 | Whole population | Rho = −0.09, p value 0.04, FDR 0.32 |
| MAP3K10 | Protective | Rho = −0.17, p value 0.04, FDR 0.38 | ||
| rs2150879 | hsa-miR-21-5p | MKNK2 | Risk | Rho = −0.27, p value 0.02, FDR 0.63 |
| TBL1XR1 | Risk | Rho = −0.28, p value 0.02, FDR 0.63 | ||
| ALDH9A1 | Risk | Rho = −0.24, p value 0.04, FDR 0.77 | ||
| CPEB3 | Risk | Rho = −0.29, p value 0.01. FDR 0.63 | ||
| KLHL15 | Risk | Rho = −0.33, p value 0.006, FDR 0.63 | ||
| ZFP36L1 | Whole population | Rho = −0.13, p value 0.003, FDR 0.06 | ||
| rs4808760 | hsa-miR-3188-3p | PPP2R4 | Risk | Rho = −0.18, p value 0.01, FDR 0.63 |
| MCL1 | Protective | Rho = −0.49, p value 0.01, FDR 0.27 | ||
| TSPYL4 | Protective | Rho = −0.42, p value 0.03, FDR 0.37 | ||
| DNAH10OS | Protective | Rho = −0.4, p value 0.04, FDR 0.38 | ||
| rs2150879 | hsa-miR-21-3p | CNIH | Whole population | Rho = −0.11, p value 0.01, FDR 0.11 |
| UPF1 | Protective | Rho = −0.21, p value 0.02, FDR 0.37 | ||
| DDAH1 | Risk | Rho = −0.26, p value 0.02, FDR 0.63 | ||
| ZC3H12C | Whole population | Rho = −0.1, p value 0.02, FDR 0.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afrasiabi, A.; Fewings, N.L.; Schibeci, S.D.; Keane, J.T.; Booth, D.R.; Parnell, G.P.; Swaminathan, S. The Interaction of Human and Epstein–Barr Virus miRNAs with Multiple Sclerosis Risk Loci. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062927
Afrasiabi A, Fewings NL, Schibeci SD, Keane JT, Booth DR, Parnell GP, Swaminathan S. The Interaction of Human and Epstein–Barr Virus miRNAs with Multiple Sclerosis Risk Loci. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062927
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfrasiabi, Ali, Nicole L. Fewings, Stephen D. Schibeci, Jeremy T. Keane, David R. Booth, Grant P. Parnell, and Sanjay Swaminathan. 2021. "The Interaction of Human and Epstein–Barr Virus miRNAs with Multiple Sclerosis Risk Loci" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062927
APA StyleAfrasiabi, A., Fewings, N. L., Schibeci, S. D., Keane, J. T., Booth, D. R., Parnell, G. P., & Swaminathan, S. (2021). The Interaction of Human and Epstein–Barr Virus miRNAs with Multiple Sclerosis Risk Loci. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062927






