Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis of Inflammatory Arthritis
2.1. Traditional Approaches
2.2. Nanoimaging
2.3. Nanodiagnosis
3. Nanomaterials for the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis
3.1. Liposomes
3.2. Polymeric NPs
3.3. Niosomes
3.4. Metal NPs
3.4.1. Silver NPs
3.4.2. Gold NPs
3.4.3. Iron NPs
3.5. Quantum Dots
3.6. Solid Lipid NPs
3.7. Polymeric Micelles
4. Conclusions, Challenges, and Future Opportunities
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenzwajg, M.; Lorenzon, R.; Cacoub, P.; Pham, H.P.; Pitoiset, F.; El Soufi, K.; RIbet, C.; Bernard, C.; Aractingi, S.; Banneville, B. Immunological and clinical effects of low-dose interleukin-2 across 11 autoimmune diseases in a single, open clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molano-González, N.; Rojas, M.; Monsalve, D.M.; Pacheco, Y.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Rodríguez, Y.; Rodríguez-Jimenez, M.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Anaya, J.-M. Cluster analysis of autoimmune rheumatic diseases based on autoantibodies. New insights for polyautoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 98, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, A.; Adawi, M. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and cardiovascular disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, C.; Viniegra, A.; Glogauer, M. Macrophage immunomodulation in chronic osteolytic diseases—The case of periodontitis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, V.E.; Chen, G.; Deutsch, G.H.; Guillerman, R.P.; Birgmeier, J.; Jagadeesh, K.; Canna, S.; Schulert, G.; Deterding, R.; Xu, J. Emergent high fatality lung disease in systemic juvenile arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, L.; Tükel, Ç. Bacterial amyloids: The link between bacterial infections and autoimmunity. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elli, E.M.; Baratè, C.; Mendicino, F.; Palandri, F.; Palumbo, G.A. Mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activity of ruxolitinib. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.M.; Witherden, D.A.; Havran, W.L. γδ T cells in homeostasis and host defence of epithelial barrier tissues. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Pradhan, A.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Solomon, D.H.; Zaharris, E.; Mam, V.; Hasan, A.; Rosenberg, Y.; Iturriaga, E. Low-dose methotrexate for the prevention of atherosclerotic events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracey, E.; Burssens, A.; Cambré, I.; Schett, G.; Lories, R.; McInnes, I.B.; Asahara, H.; Elewaut, D. Tendon and ligament mechanical loading in the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, A.L.; Vukcevic, D.; Leslie, S.; Harris, J.; Lê Cao, K.-A.; Kenna, T.J.; Brown, M.A.; International Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis Consortium. Epistatic interactions between killer immunoglobulin-like receptors and human leukocyte antigen ligands are associated with ankylosing spondylitis. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, X.-Y.; Guo, R.-J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.-D.; Zhang, C.-C.; Jiao, Y.-H.; Ju, Y.-M. Metagenomic profiling of the pro-inflammatory gut microbiota in ankylosing spondylitis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 107, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehlin, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Roddy, E. Global epidemiology of gout: Prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Solecki, M.; Arnaboldi, P.M.; Backenson, P.B.; Benach, J.L.; Cooper, C.L.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Diuk-Wasser, M.; Fikrig, E.; Hovius, J.; Laegreid, W. Protective immunity and new vaccines for Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeley, G.S.; Bakewell, C.; Deodhar, A. The importance of ultrasound in identifying and differentiating patients with early inflammatory arthritis: A narrative review. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, C.; Guimaraes, F.; Yang, Y.; D’Silva, D.; Kratina, T.; Dagley, L.; Hediyeh-Zadeh, S.; Rautela, J.; Masters, S.L.; Davis, M.J. NK cell–derived GM-CSF potentiates inflammatory arthritis and is negatively regulated by CIS. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, H.K.; Kim, H.-A.; Bettner, L.F.; Deane, K.D. Preclinical rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis prevention. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacz, Ł.; Ciosek, Ż.; Gronwald, H.; Skomro, P.; Ardan, R.; Lietz-Kijak, D. Comparative analysis of the influence of selected physical factors on the level of pain in the course of temporomandibular joint disorders. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 1036306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, F.; Zakir, F.; Verma, D.; Aqil, M.; Singh, M.; Jain, P.; Mirza, M.A.; Anwer, M.; Iqbal, Z. Exploration of nanoethosomal transgel of naproxen sodium for the treatment of arthritis. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpouzas, G.A.; Ormseth, S.R.; Hernandez, E.; Budoff, M.J. Impact of cumulative inflammation, cardiac risk factors, and medication exposure on coronary atherosclerosis progression in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, H.; Borisch, C. Analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and antigout medications. In Drugs During Pregnancy and Lactation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 27–58. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, G.S.; Aidar, F.J.; Matos, D.G.; Marçal, A.C.; Santos, J.L.; Souza, R.F.; Carneiro, A.L.; Vasconcelos, A.B.; Silva-Grigoletto, D.; Edir, M. Effects of ibuprofen intake in muscle damage, body temperature and muscle power in paralympic powerlifting athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihalko, W.M.; Haider, H.; Kurtz, S.; Marcolongo, M.; Urish, K. New materials for hip and knee joint replacement: What’s hip and what’s in kneed? J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzichi, L.; Giacomelli, C.; Consensi, A.; Giorgi, V.; Batticciotto, A.; Di Franco, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. One year in review 2020: Fibromyalgia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jeurling, S.; Cappelli, L.C. Treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced inflammatory arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, L.C.; Naidoo, J.; Bingham, C.O., III; Shah, A.A. Inflammatory arthritis due to immune checkpoint inhibitors: Challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Future Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, M.; Caputo, F.; Metcalfe, S.; Tosi, G.; Spring, K.; Åslund, A.K.; Pottier, A.; Schiffelers, R.; Ceccaldi, A.; Schmid, R. Delivering the power of nanomedicine to patients today. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, S.M.; Rabiee, N.; Hajebi, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Fatahi, Y.; Hosseini, M.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Rabiee, M.; Jajarmi, V. Biodegradable nanopolymers in cardiac tissue engineering: From concept towards nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Akhter, H. Surface-engineered cancer nanomedicine: Rational design and recent progress. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, T.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, B. Recent advances of two-dimensional materials in smart drug delivery nano-systems. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufi, G.J.; Iravani, S. Eco-friendly and sustainable synthesis of biocompatible nanomaterials for diagnostic imaging: Current challenges and future perspectives. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2662–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, X.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.-Q. Biodegradable nanoparticles decorated with different carbohydrates for efficient macrophage-targeted gene therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wan, M.; Lyon, C.J.; Hu, T.Y. Nanomedicine therapies modulating macrophage dysfunction: A potential strategy to attenuate cytokine storms in severe infections. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, S.; Ocampo-Pineda, M.; Barakovic, M.; Petit, L.; Descoteaux, M.; Thiran, J.-P.; Daducci, A. A new method for accurate in vivo mapping of human brain connections using microstructural and anatomical information. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Guo, F. Nanoparticle-siRNA: A potential strategy for rheumatoid arthritis therapy? J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liang, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Bottini, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L. Cationic block copolymer nanoparticles with tunable DNA affinity for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aden, K.; Rehman, A.; Waschina, S.; Pan, W.-H.; Walker, A.; Lucio, M.; Nunez, A.M.; Bharti, R.; Zimmerman, J.; Bethge, J. Metabolic functions of gut microbes associate with efficacy of tumor necrosis factor antagonists in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1279–1292.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, F.; Sun, B.; Bellanti, J.A.; Zheng, S.G. Magnetic nanoparticles: A new diagnostic and treatment platform for rheumatoid arthritis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Easha, P.; Tapasvi, G.; Reetika, R. Nanomaterials in biomedical diagnosis. In Nanomaterials in Diagnostic Tools and Devices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 57–83. [Google Scholar]
- Crist, R.M.; Dasa, S.S.K.; Liu, C.H.; Clogston, J.D.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Stern, S.T. Challenges in the development of nanoparticle-based imaging agents: Characterization and biology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 13, e1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lloveras, V.; Pulido, D.; Liko, F.; Pinto, L.F.; Albericio, F.; Royo, M.; Vidal-Gancedo, J. Radical Dendrimers based on biocompatible oligoethylene glycol dendrimers as contrast agents for MRI. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Chi, H.; Liao, E.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Teng, D.; Teng, X. A negative association between urinary iodine concentration and the prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout: A cross-sectional and population-based study in mainland China. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barani, M.; Mirzaei, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Adeli-Sardou, M. Evaluation of carum-loaded niosomes on breast cancer cells: Physicochemical properties, in vitro cytotoxicity, flow cytometric, DNA fragmentation and cell migration assay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barani, M.; Mirzaei, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Lohrasbi-Nejad, A.; Nematollahi, M.H. A new formulation of hydrophobin-coated niosome as a drug carrier to cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barani, M.; Mirzaei, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Nematollahi, M.H. Lawsone-loaded niosome and its antitumor activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line: A nano-herbal treatment for cancer. Daru J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 26, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Nematollahi, M.H.; Zaboli, M.; Mirzaei, M.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Pardakhty, A.; Karam, G.A. In silico and in vitro study of magnetic niosomes for gene delivery: The effect of ergosterol and cholesterol. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Sabir, F.; Rahdar, A.; Arshad, R.; Z Kyzas, G. Nanotreatment and nanodiagnosis of prostate cancer: Recent Updates. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranei, M.; Taheri, R.A.; Tirgar, M.; Saeidi, A.; Oroojalian, F.; Uzun, L.; Asefnejad, A.; Wurm, F.R.; Goodarzi, V. Anticancer effect of green tea extract (GTE)-loaded pH-responsive niosome coated with PEG against different cell lines. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 101751, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikazar, S.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Zoghi, M.; Kyzas, G.Z. Photo-and magnetothermally responsive nanomaterials for therapy, controlled drug delivery and imaging applications. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 12590–12609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazy, E.; Kumar, A.; Barani, M.; Kaur, I.; Rahdar, A.; Behl, T. Scrutinizing the therapeutic and diagnostic potential of nanotechnology in thyroid cancer: Edifying drug targeting by nano-oncotherapeutics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 61, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazy, E.; Rahdar, A.; Barani, M.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials for Parkinson disease: Recent progress. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1231, 129698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Bilal, M.; Sabir, F.; Rahdar, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanotechnology in ovarian cancer: Diagnosis and treatment. Life Sci. 2020, 266, 118914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasankarapillai, V.; Das, S.; Sabir, F.; Sundaramahalingam, M.; Colmenares, J.; Prasannakumar, S.; Rajan, M.; Rahdar, A.; Kyzas, G. Progress in natural polymer engineered biomaterials for transdermal drug delivery systems. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 19, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, M.; Bilal, M.; Rahdar, A.; Barani, M.; Arshad, R.; Behl, T.; Brisc, C.; Banica, F.; Bungau, S. Nanomaterials for diagnosis and treatment of brain cancer: Recent updates. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wei, M.; He, S.; Yuan, W.E. Advances of non-ionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes) and their application in drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Rahdar, A.; Sargazi, G.; Thysiadou, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Progress in the application of nanoparticles and graphene as drug carriers and on the diagnosis of brain infections. Molecules 2021, 26, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, F.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Bilal, M.; Nadeem, M. How to face skin cancer with nanomaterials: A review. Biointerface Rev. Aplied Chem. 2021, 11, 11931–11955. [Google Scholar]
- Reginato, A.M.; Olsen, B.R. The role of structural genes in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritic disorders. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2002, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Macip-Rodriguez, P.; Cabral, A. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis pannus have similar qualitative metabolic characteristics and pro-inflammatory cytokine response. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 554. [Google Scholar]
- Cappelli, L.C.; Gutierrez, A.K.; Baer, A.N.; Albayda, J.; Manno, R.L.; Haque, U.; Lipson, E.J.; Bleich, K.B.; Shah, A.A.; Naidoo, J. Inflammatory arthritis and sicca syndrome induced by nivolumab and ipilimumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Antinuclear antibody testing-misunderstood or misbegotten? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolle, N.A.; Jan, I.; Sibbitt, W.L.; Band, P.A.; Haseler, L.J.; Hayward, W.A.; Muruganandam, M.; Emil, N.S.; Fangtham, M.; Bankhurst, A.D. Extractable synovial fluid in inflammatory and non-inflammatory arthritis of the knee. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, C.; Bell, L.N.; Liang, H.; Haykal, R.; Kaiksow, F.; Mazza, J.J.; Yale, S.H. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein measurements and their relevance in clinical medicine. WMJ 2016, 115, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho Franca, L.F.; da Silva, F.R.P.; di Lenardo, D.; Alves, E.H.P.; Nascimento, H.M.S.; da Silva, I.A.T.; Vasconcelos, A.C.C.G.; Vasconcelos, D.F.P. Comparative analysis of blood parameters of the erythrocyte lineage between patients with chronic periodontitis and healthy patients: Results obtained from a meta-analysis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 97, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugatti, S.; Bogliolo, L.; Vitolo, B.; Manzo, A.; Montecucco, C.; Caporali, R. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and high levels of rheumatoid factor are associated with systemic bone loss in patients with early untreated rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, B.; Baidya, D.; Halder, P.; Mandal, S. Correlation of serum uric acid with disease activity and C-reactive protein in patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Open J. Rheumatol. Autoimmune Dis. 2016, 6, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, M.A.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; van der Laken, C.J. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis; What is the current role of established and new imaging techniques in clinical practice? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 30, 586–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakewell, C.; Aydin, S.Z.; Ranganath, V.K.; Eder, L.; Kaeley, G.S. Imaging techniques: Options for the diagnosis and monitoring of treatment of enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguerol, T.M.; Luna, A.; Cabrera, M.G.; Riofrio, A.D. Clinical applications of advanced magnetic resonance imaging techniques for arthritis evaluation. World J. Orthop. 2017, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, M.; Kay, J.; Ginsberg, L.; de Sa, D.; Simunovic, N.; Samuelsson, K.; Athwal, G.S.; Ayeni, O.R. Arthroscopic management of septic arthritis of the native shoulder: A systematic review. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg 2018, 34, 625–646.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochman, S.; Wieskötter, B.; Langer, M.; Vieth, V.; Raschke, M.; Stehling, C. High-resolution MRI (3T-MRI) in diagnosis of wrist pain: Is diagnostic arthroscopy still necessary? Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, M.; Kashanian, S.; Samavati, S.S.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Jamasb, S.; McInnes, S.J. Nanotechnology application in drug delivery to osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and osteoporosis (OSP). J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 61, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuto, M.A.; Salvioni, L.; Rotem, R.; Colombo, M.; Zanoni, I.; Granucci, F.; Prosperi, D. Are nanotechnological approaches the future of treating inflammatory diseases? Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 2379–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Tian, C.; Xu, G.; Sarazin, J.; Schiopu, E.; Gandikota, G.; Wang, X. Photoacoustic tomography for human musculoskeletal imaging and inflammatory arthritis detection. Photoacoustics 2018, 12, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaudemans, A.W.; Quintero, A.M.; Signore, A. PET/MRI in Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases: Will It Be a Useful Improvement? Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cormode, D.P.; Skajaa, T.; Fayad, Z.A.; Mulder, W.J. Nanotechnology in medical imaging: Probe design and applications. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardzinski, B.J.; Schmithorst, V.J.; Holland, S.K.; Boivin, G.P.; Imagawa, T.; Watanabe, S.; Lewis, J.M.; Hirsch, R. MR imaging of murine arthritis using ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 19, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, A.M.; Seemayer, C.; Corot, C.; Gay, R.E.; Goepfert, K.; Michel, B.A.; Marincek, B.; Gay, S.; Weishaupt, D. Detection of synovial macrophages in an experimental rabbit model of antigen-induced arthritis: Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide–enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2004, 233, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Siow, T.Y.; Chou, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; Wang, S.-J.; Chang, C. Targeted superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of T-cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, A.; Walz, D.; Batista, V.; Mizraji, M.; Roisman, F.; Misher, A. Auranofin. New oral gold compound for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1976, 35, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Tu, G. Bimetallic core-shell nanostars with tunable surface plasmon resonance for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 10885–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wei, Q. Label-free ECL immunosensor for the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis based on asymmetric heterogeneous polyaniline-gold nanomaterial. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournelle, M.; Bost, W.; Tarner, I.H.; Lehmberg, T.; Weiß, E.; Lemor, R.; Dinser, R. Antitumor necrosis factor-α antibody-coupled gold nanorods as nanoprobes for molecular optoacoustic imaging in arthritis. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Levi-Polyachenko, N. Conjugated polymer nano-systems for hyperthermia, imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 163, 40–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Qi, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, T.; Song, L.; Ding, D.; Zhang, P. Tocilizumab-conjugated polymer nanoparticles for NIR-II photoacoustic-imaging-guided therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Quang, H.; Vinding, M.S.; Jakobsen, M.; Song, P.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Nielsen, N.C.; Kjems, J. Imaging rheumatoid arthritis in mice using combined near infrared and 19 F magnetic resonance modalities. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lv, Z.; Chen, L. Tracking osteoarthritis progress through cationic nanoprobe-enhanced photoacoustic imaging of cartilage. Acta Biomater. 2020, 109, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieter, W.J.; Kim, J.S.; Taylor, K.M.; An, H.; Lin, W.; Tarrant, T.; Lin, W. Hybrid silica nanoparticles for multimodal imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3680–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celardo, I.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Traversa, E.; Ghibelli, L. Pharmacological potential of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilă, B.; Ciofu, C.; Stoica, V. Biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis, what is new? J. Med. Life 2016, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Humby, F.C.; Al Balushi, F.; Lliso, G.; Cauli, A.; Pitzalis, C. Can synovial pathobiology integrate with current clinical and imaging prediction models to achieve personalized health care in rheumatoid arthritis? Front. Med. 2017, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veigas, B.; Matias, A.; Calmeiro, T.; Fortunato, E.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V. Antibody modified gold nanoparticles for fast colorimetric screening of rheumatoid arthritis. Analyst 2019, 144, 3613–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, D.W. Compartmentalized bimetal cluster-poly (aniline) hybrid nanostructures for multiplexed detection of autoantibodies in early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.-A.; Chen, W.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hung, Y.-M.; Wei, J.C.-C. Increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis among patients with Mycoplasma pneumonia: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, C.; Rong, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Qie, Z.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Dual dye-loaded Au@ Ag coupled to a lateral flow immunoassay for the accurate and sensitive detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21243–21251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.B.; Fields, J.H.; Clerc, P.G. Rheumatoid arthritis in patients with HIV: Management challenges. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Shukla, S.; Bajpai, V.K.; Han, Y.-K.; Huh, Y.S.; Kumar, A.; Ghosh, A.; Gandhi, S. A smart nanosensor for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus and associated cardiovascular and arthritis diseases using functionalized graphene-based transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, I.M.; Gonçalves, C.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Engineering nanoparticles for targeting rheumatoid arthritis: Past, present, and future trends. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4489–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradkar, M.; Vaghela, S. Thiocolchicoside niosomal gel formulation for the pain management of rheumatoid arthritis through topical drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Lett. 2018, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meka, R.R.; Venkatesha, S.H.; Acharya, B.; Moudgil, K.D. Peptide-targeted liposomal delivery of dexamethasone for arthritis therapy. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabib, L.; Ikawati, Z.; Martien, R.; Ismail, H.; Wahyudi, M.D.P.; Arimurni, D.A.; Muhtadi, W.K.; Hidayat, A. Rheumatoid arthritis and the challenge of using nanoparticles for its treatment. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 154, 4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, L.; Fan, D.; Liang, W.; Fang, J. Improving the anti-inflammatory efficacy of dexamethasone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with polymerized stealth liposomes as a delivery vehicle. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, D.; Noro, J.; Loureiro, A.; Lager, F.; Renault, G.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Increased encapsulation efficiency of methotrexate in liposomes for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; He, Y.; Liang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, C.; Qin, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Role of liposome size, surface charge, and PEGylation on rheumatoid arthritis targeting therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20304–20315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qi, J.; Shu, G.; Du, Y.; Ying, X. Sinomenine hydrochloride loaded thermosensitive liposomes combined with microwave hyperthermia for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 119001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Tuguntaev, R.G.; Mao, C.; Chen, H.; Tao, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Guo, W. Stimuli-responsive polymeric nanomaterials for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 6, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Park, J.-H. Nanomedicine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 18, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Reynaud, F.; Lorscheider, M.; Tsapis, N.; Fattal, E. Nanomedicines for the delivery of glucocorticoids and nucleic acids as potential alternatives in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Cano, E.; Aguilar, M.R.; Portilla, Y.; Barber, D.F.; San Román, J. Anti-inflammatory polymeric nanoparticles based on ketoprofen and dexamethasone. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, D.; O’Dell, K.M.; Bandy, J.L.; Boyce, E.G. Tofacitinib: The first Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2013, 47, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Aamir, M.; Sarfaraz, R.M.; Hussain, Z.; Sarwer, M.U.; Mahmood, A.; Akram, M.R.; Qaisar, M.N. Fabrication, characterization and in vitro release kinetics of tofacitinib-encapsulated polymeric nanoparticles: A promising implication in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 70, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
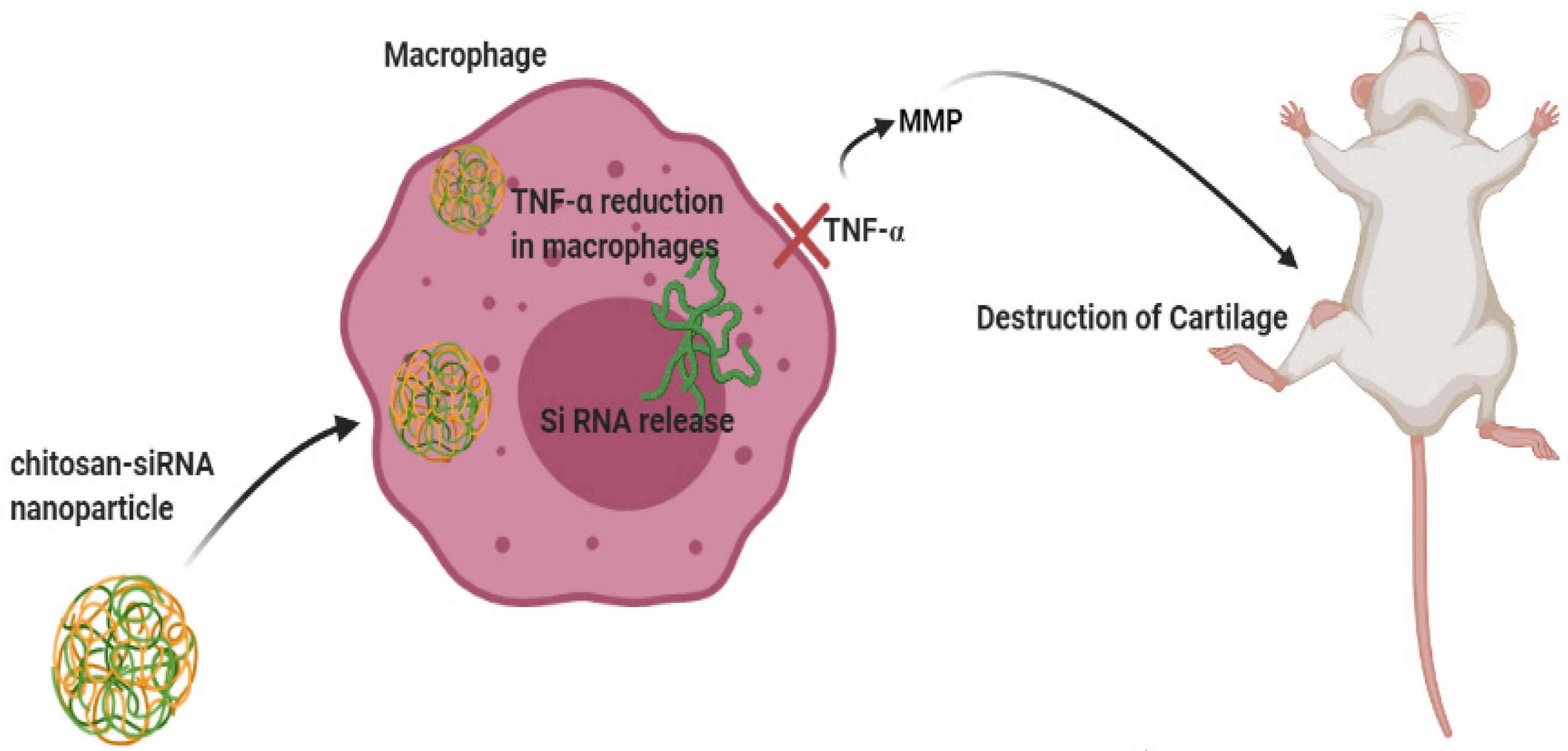
- Howard, K.A.; Paludan, S.R.; Behlke, M.A.; Besenbacher, F.; Deleuran, B.; Kjems, J. Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle–mediated TNF-α knockdown in peritoneal macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment in a murine arthritis model. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Md, S.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Husain, M.; Kotta, S.; Abdullah, S.T.; A Fahmy, U.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Asfour, H.Z. Formulation design, statistical optimization, and in vitro evaluation of a naringenin nanoemulsion to enhance apoptotic activity in a549 lung cancer cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Bhatia, S. Development and characterization of niosomal gel system using Lallementia royaleana Benth. mucilage for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 465–482. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Tripathi, P.; Gupta, R.; Pandey, S. Niosomes: A review on niosomal research in the last decade. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ye, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Long, X. Niosomal nanocarriers for enhanced skin delivery of quercetin with functions of anti-tyrosinase and antioxidant. Molecules 2019, 24, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ag Seleci, D.; Seleci, M.; Walter, J.-G.; Stahl, F.; Scheper, T. Niosomes as nanoparticular drug carriers: Fundamentals and recent applications. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 7372306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashini Rajaram, A.S.; Dharmalingam, S.R.; Chidambaram, K. Fabrication of non-ionic surfactant vesicular gel for effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. JEMDS 2020, 9, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar]
- Mujeeb, S.A.; Sailaja, A.K. Formulation of ibuprofen loaded niosomal gel by different techniques for treating rheumatoid arthritis. J. Bionanosci. 2017, 11, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M. Impact of response surface methodology–optimized synthesis parameters on in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of iron nanoparticles synthesized using Ocimum tenuiflorum Linn. BioNanoScience 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, K.; Krishnaswami, V.; Rajendran, V.; Natesan, S.; Kandasamy, R. Novel nano therapeutic materials for the effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-recent insights. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 17, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Nakara, A.; Shanmugam, V.K. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized using plant extracts: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2561–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W. Targeted silver nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage apoptosis and Re-polarization. Biomaterials 2020, 264, 120390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Song, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, G.; Ma, B.; Wang, X. Development of biofabricated gold nanoparticles for the treatment of alleviated arthritis pain. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Kwon, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Kang, Y.J.; Khang, D. Triamcinolone-gold nanoparticles repolarize synoviocytes and macrophages in an inflamed synovium. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38936–38949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, M.F.H.; Machado, A.R.T.; Antunes, L.M.; Souza, T.E.; Freitas, V.A.; Oliveira, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Pereira, M.C.; Barbosa, F. Gold-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles attenuate collagen-induced arthritis after magnetic targeting. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, J.; Moura, C.C.; Sarmento, B.; Reis, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles: A potential multifunctional approach towards rheumatoid arthritis theranostics. Molecules 2015, 20, 11103–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalangi, S.K.; Swarnakar, N.K.; Sathyavathi, R.; Narayana Rao, D.; Jain, S.; Reddanna, P. Synthesis, characterization, and biodistribution of quantum dot-celecoxib conjugate in mouse paw edema model. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 3090517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Kuhad, A.; Kaur, I.; Chopra, K. Curcumin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles ameliorate adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalekar, M.R.; Madgulkar, A.R.; Desale, P.S.; Marium, G. Formulation of piperine solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarifi, S.; Massadeh, S.; Al-Agamy, M.; Aamery, M.A.; Al Bekairy, A.; Yassin, A.E. Enhancement of ciprofloxacin activity by incorporating it in solid lipid nanoparticles. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kabanov, A.V. Polymeric micelles for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: From nanoformulation to clinical approval. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 80–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, L.; Shang, H.; Gu, H.; Zhang, N. Polymeric micelles for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2019, 36, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Chen, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X. Targeted delivery of low-dose dexamethasone using PCL–PEG micelles for effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Control. Release 2016, 230, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.R.; Firouzian, F.; Haddadi, R.; Nourian, A. Indomethacin loaded dextran stearate polymeric micelles improve adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: Design and in vivo evaluation. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 29, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

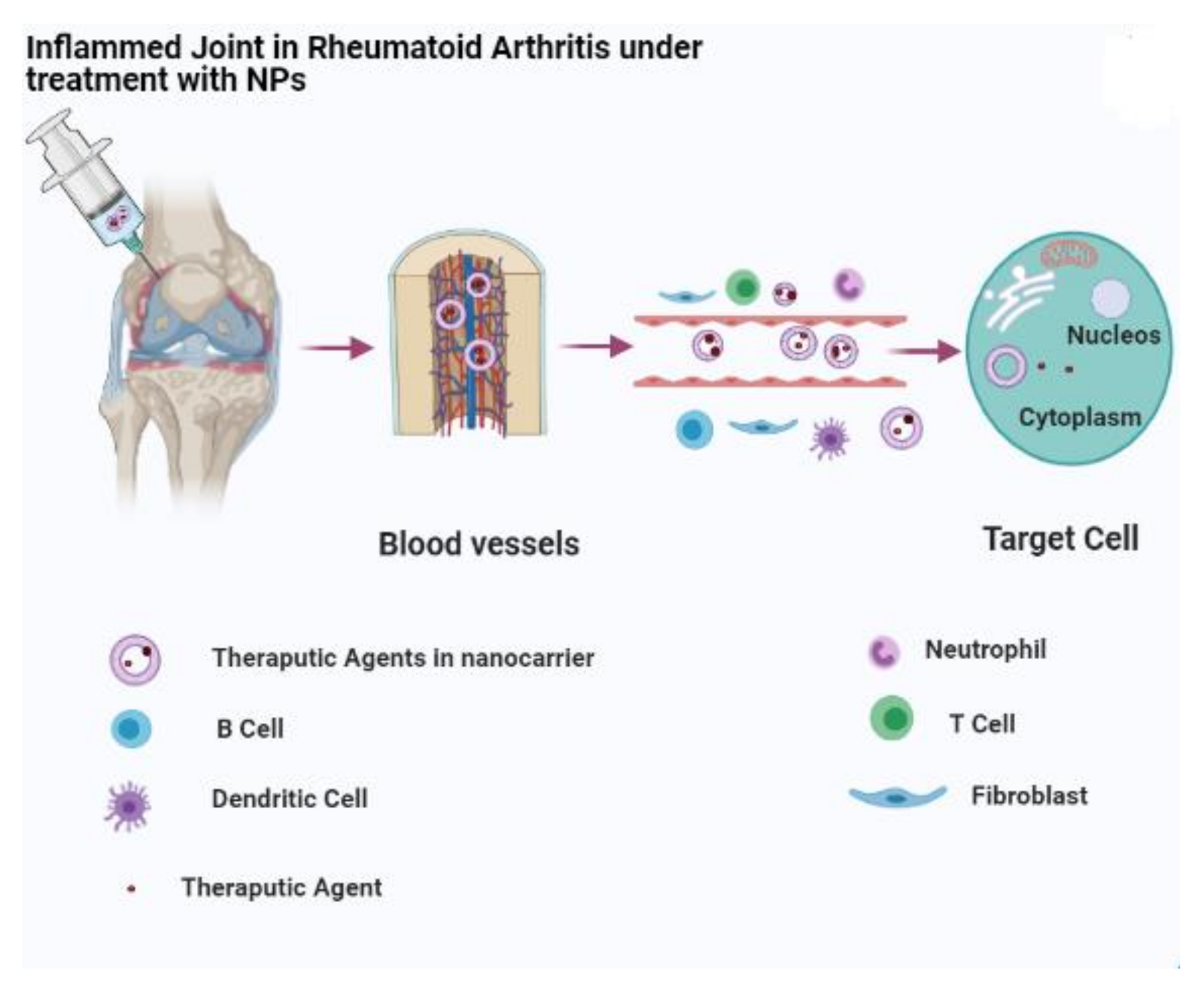

| Nanocarriers | Drugs | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | MTX, Dex, SIN | Improved controlled release, reduced RA signs, decreased side effects | [104] |
| Polymeric NPs | Ket, Dex, TFC, MTX | Decreased inflammation | [110] |
| Niosomes | PC, thiocolchicoside, ibuprofen | Increased drug retention | [119] |
| Silver NPs | FA-AgNPs | Enhanced anti-inflammatory activities | [124] |
| Gold NPs | Triam | Enhanced anti-inflammatory activities | [126] |
| Iron NPs | MTX | Suppression of joint edema and inflammation | [128] |
| Quantum dots | celecoxib | Localized activity in sites of inflammation | [129] |
| Solid lipid NPs | CUR, Pi, CIP | Enhanced anti-inflammatory activities | [130] |
| Polymeric micelles | Dex, indomethacin | Decreased side effects | [135] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosseinikhah, S.M.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Madry, H.; Arshad, R.; Mohammadzadeh, V.; Cucchiarini, M. Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063092
Hosseinikhah SM, Barani M, Rahdar A, Madry H, Arshad R, Mohammadzadeh V, Cucchiarini M. Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):3092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063092
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosseinikhah, Seyedeh Maryam, Mahmood Barani, Abbas Rahdar, Henning Madry, Rabia Arshad, Vahideh Mohammadzadeh, and Magali Cucchiarini. 2021. "Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 3092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063092
APA StyleHosseinikhah, S. M., Barani, M., Rahdar, A., Madry, H., Arshad, R., Mohammadzadeh, V., & Cucchiarini, M. (2021). Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 3092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063092










