Therapeutic Evaluation of Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin 9 in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Production and Characterization of IL9 Based Immunocytokines
2.2. Experimental Design of IL9 Treatment on MCT-Induced PH in Mice
2.3. Effect of IL9 on Haemodynamic Parameter of MCT-Induced PH
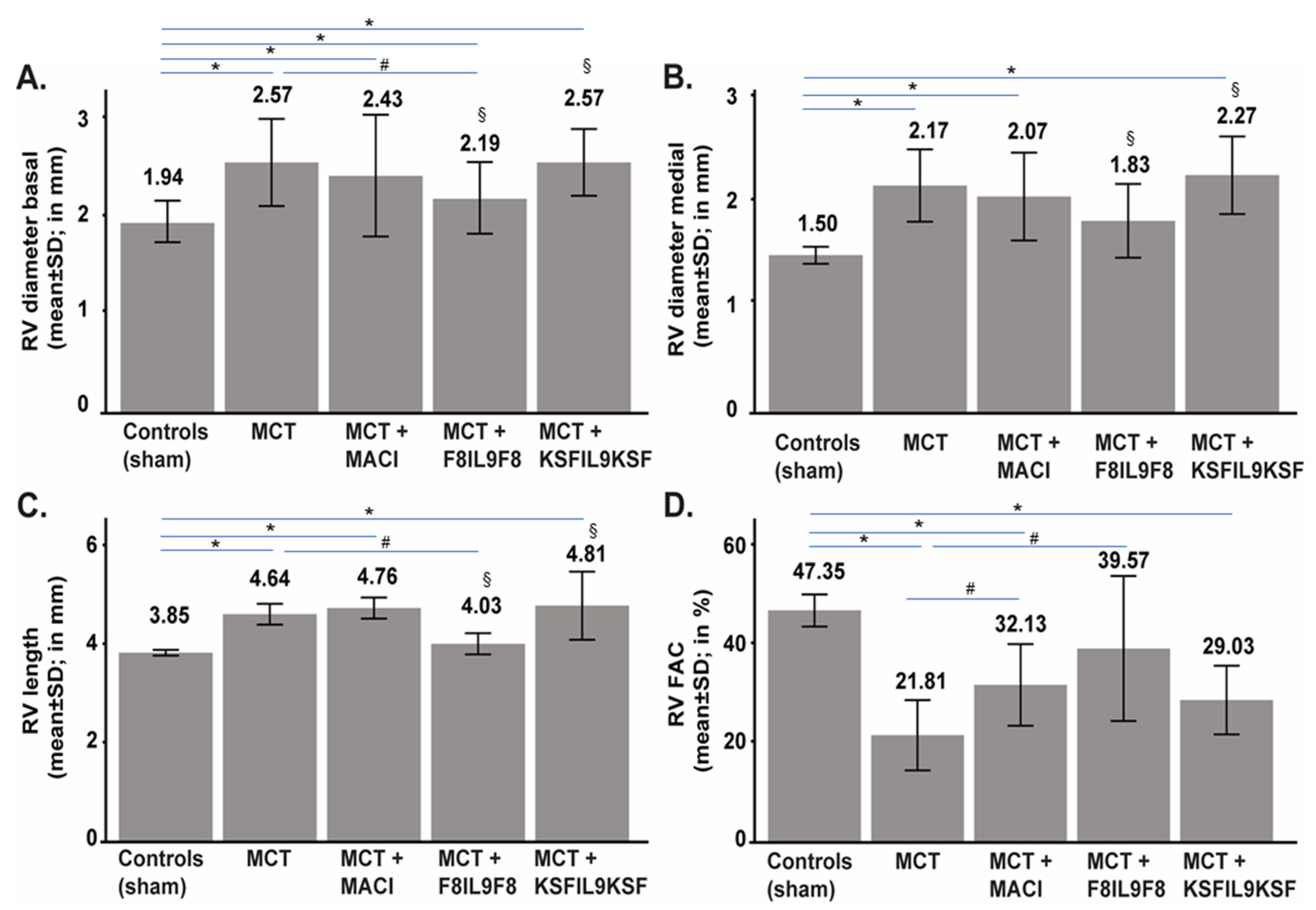
2.4. Effect of IL9 on Echocardiographic Parameters of MCT-Induced PH
2.5. Effect of IL9 on Lung and Right Ventricular Cardiac Tissue Damage in MCT-Induced PH
2.5.1. Lung Tissue Damage
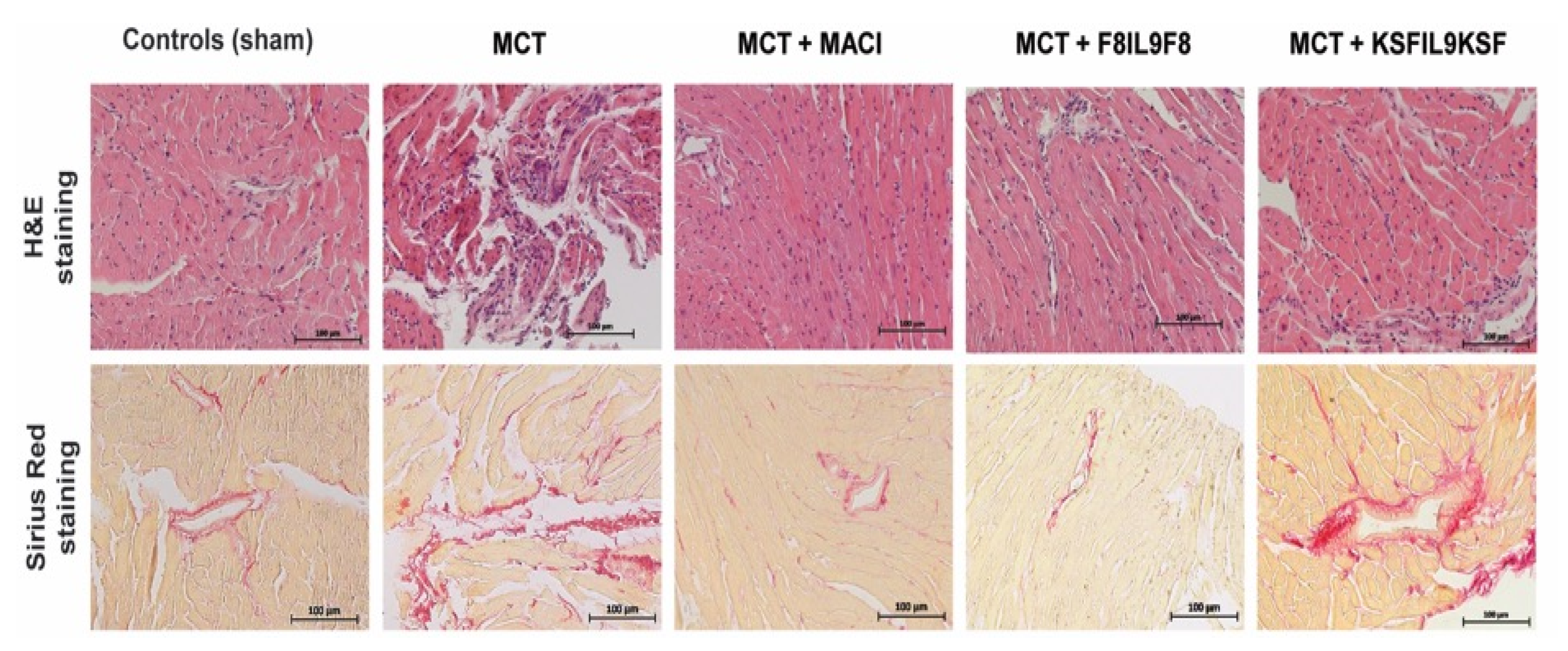
2.5.2. Right Ventricular Cardiac Tissue Damage
2.6. Effect of IL9 on the Accumulation of Leukocytes and Macrophages in Lung and Right Ventricular Cardiac Tissue in MCT-Induced PH
2.7. EDA(+)-Fibronectin Expression in Lung and Right Ventricular Cardiac Tissue in MCT-Induced PH Compared to Sham-Treated Controls in the Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Expression Plasmids
4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
4.3. Protein Analysis
4.4. Mouse Model of MCT-Induced PH and Treatment Schedule
4.5. Echocardiographic Assessment
4.6. Right Heart Catheterization
4.7. Histological Assessment of Lung and Right Ventricular Cardiac Tissue Damage
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining of CD45 (Pan-Leukocyte Antigen) and CD68
(Macrophage Marker) in Lung and Right Ventricular Cardiac Tissue
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining of EDA(+) Fibronectin in Lung and Right Ventricular
Cardiac Tissue
4.10. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoeper, M.M.; Bogaard, H.J.; Condliffe, R.; Frantz, R.; Khanna, D.; Kurzyna, M.; Langleben, D.; Manes, A.; Satoh, T.; Torres, F.; et al. Definitions and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, D42–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, L.C.; Bye, H.; Brock, M. Swiss Society of Pulmonary Hypertension. The pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension—An update. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2015, 145, w14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galie, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Noordegraaf, A.V.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perros, F.; Humbert, M. Physiopathology of pulmonary arterial hypertension—Cellular and molecular aspects. Presse Méd. 2005, 34, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Grün, K.; Betge, S.; Rohm, I.; Ndongson-Dongmo, B.; Bauer, R.; Schulze, P.C.; Lichtenauer, M.; Petersen, I.; Neri, D.; et al. Lung tissue remodelling in MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension: A proposal for a novel scoring system and changes in extracellular matrix and fibrosis associated gene expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81241–81254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bootz, F.; Schmid, A.S.; Neri, D. Alternatively Spliced EDA Domain of Fibronectin Is a Target for Pharmacodelivery Applications in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bootz, F.; Ziffels, B.; Neri, D. Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin-22 Promotes Rapid Clinical Recovery in Mice With DSS-Induced Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doll, F.; Schwager, K.; Hemmerle, T.; Neri, D. Murine analogues of etanercept and of F8-IL10 inhibit the progression of collagen-induced arthritis in the mouse. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemmerle, T.; Doll, F.; Neri, D. Antibody-based delivery of IL4 to the neovasculature cures mice with arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12008–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemmerle, T.; Zgraggen, S.; Matasci, M.; Halin, C.; Detmar, M.; Neri, D. Antibody-mediated delivery of interleukin 4 to the neo-vasculature reduces chronic skin inflammation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 76, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, M.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Fibronectin as target for tumor therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.-N.; Roesli, C.; Kaspar, M.; Villa, A.; Neri, D. The extra-domain A of fibronectin is a vascular marker of solid tumors and metastases. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10948–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwager, K.; Bootz, F.; Imesch, P.; Kaspar, M.; Trachsel, E.; Neri, D. The antibody-mediated targeted delivery of interleukin-10 inhibits endometriosis in a syngeneic mouse model. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwager, K.; Kaspar, M.; Bootz, F.; Marcolongo, R.; Paresce, E.; Neri, D.; Trachsel, E. Preclinical characterization of DEKAVIL (F8-IL10), a novel clinical-stage immunocytokine which inhibits the progression of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiozawa, K.; Hino, K.; Shiozawa, S. Alternatively spliced EDA-containing fibronectin in synovial fluid as a predictor of rheumatoid joint destruction. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruijnen, S.T.G.; Chandrupatla, D.M.S.H.; Giovanonni, L.; Neri, D.; Vugts, D.J.; Huisman, M.C.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Musters, R.J.P.; Lammertsma, A.A.; van Dongen, G.A.M.S.; et al. F8-IL10: A New Potential Antirheumatic Drug Evaluated by a PET-Guided Translational Approach. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, A.; Trachsel, E.; Kaspar, M.; Schliemann, C.; Sommavilla, R.; Rybak, J.-N.; Rösli, C.; Borsi, L.; Neri, D. A high-affinity human monoclonal antibody specific to the alternatively spliced EDA domain of fibronectin efficiently targets tumor neo-vasculature in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, E.; Germann, T.; Goedert, S.; Hoehn, P.; Huels, C.; Koelsch, S.; Kühn, R.; Müller, W.; Palm, N.; Rüde, E. IL-9 production of naive CD4+ T cells depends on IL-2, is synergistically enhanced by a combination of TGF-beta and IL-4, and is inhibited by IFN-gamma. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 3989–3996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kubatzky, K.F.; Mitra, D.K. An Update on Interleukin-9: From Its Cellular Source and Signal Transduction to Its Role in Immunopathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, B.L.; Azzawi, M.; Jacobson, M.; Assoufi, B.; Collins, J.V.; Irani, A.M.; Schwartz, L.B.; Durham, S.R.; Jeffery, P.K.; Kay, A.B. Eosinophils, T-lymphocytes, mast cells, neutrophils, and macrophages in bronchial biopsy specimens from atopic subjects with asthma: Comparison with biopsy specimens from atopic subjects without asthma and normal control subjects and relationship to bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 88, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.B. Asthma and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 87, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.-F.; Lind, E.F.; Gondek, D.C.; Bennett, K.A.; Gleeson, M.W.; Pino-Lagos, K.; Scott, Z.A.; Coyle, A.J.; Reed, J.L.; Van Snick, J.; et al. Mast cells are essential intermediaries in regulatory T-cell tolerance. Nature 2006, 442, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arras, M.; Huaux, F.; Vink, A.; Delos, M.; Coutelier, J.P.; Many, M.C.; Barbarin, V.; Renauld, J.C.; Lison, D. Interleukin-9 reduces lung fibrosis and type 2 immune polarization induced by silica particles in a murine model. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 24, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, N.; Suzukawa, M.; Nagase, H.; Koizumi, Y.; Ro, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshihara, H.; Kojima, Y.; Kamiyama-Hara, A.; Hebisawa, A.; et al. IL-9 Blockade Suppresses Silica-induced Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, R.; Schlapbach, C.; Xiao, S.; Kang, H.S.; Elyaman, W.; Jiang, X.; Jetten, A.M.; Khoury, S.J.; Fuhlbrigge, R.C.; Kuchroo, V.K.; et al. Robust tumor immunity to melanoma mediated by interleukin-9-producing T cells. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gouyou, B.; Ongaro, T.; Cazzamalli, S.; Luca, R.D.; Kerschenmeyer, A.; Valet, P.; Villa, A.; Neri, D.; Matasci, M. Antibody-based delivery of Interleukin-9 to neovascular structures: Therapeutic evaluation in cancer and arthritis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenmark, K.R.; Meyrick, B.; Galie, N.; Mooi, W.J.; McMurtry, I.F. Animal models of pulmonary arterial hypertension: The hope for etiological discovery and pharmacological cure. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L1013–L1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarman, G.; Lecour, S.; Butrous, G.; Thienemann, F.; Sliwa, K. A comprehensive review: The evolution of animal models in pulmonary hypertension research; are we there yet? Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogueira-Ferreira, R.; Vitorino, R.; Ferreira, R.; Henriques-Coelho, T. Exploring the monocrotaline animal model for the study of pulmonary arterial hypertension: A network approach. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 35, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, P.M.; Mouthon, L.; Barberà, J.A.; Eddahibi, S.; Flores, S.C.; Grimminger, F.; Jones, P.L.; Maitland, M.L.; Michelakis, E.D.; Morrell, N.W.; et al. Inflammation, growth factors, and pulmonary vascular remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, S10–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasche, N.; Wulhfard, S.; Pretto, F.; Carugati, E.; Neri, D. The antibody-based delivery of interleukin-12 to the tumor neovasculature eradicates murine models of cancer in combination with paclitaxel. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4092–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutmacher, C.; Núñez, N.G.; Liuzzi, A.R.; Becher, B.; Neri, D. Targeted Delivery of IL2 to the Tumor Stroma Potentiates the Action of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors by Preferential Activation of NK and CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Neri, D. The antibody-mediated targeted delivery of interleukin-13 to syngeneic murine tumors mediates a potent anticancer activity. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2015, 64, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Neri, D. Tumor-targeting properties of novel immunocytokines based on murine IL1β and IL6. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. PEDS 2014, 27, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemmerle, T.; Probst, P.; Giovannoni, L.; Green, A.J.; Meyer, T.; Neri, D. The antibody-based targeted delivery of TNF in combination with doxorubicin eradicates sarcomas in mice and confers protective immunity. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerle, T.; Neri, D. The dose-dependent tumor targeting of antibody-IFNγ fusion proteins reveals an unexpected receptor-trapping mechanism in vivo. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pullamsetti, S.S.; Savai, R.; Janssen, W.; Dahal, B.K.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Weissmann, N.; Schermuly, R.T. Inflammation, immunological reaction and role of infection in pulmonary hypertension. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorfmüller, P.; Perros, F.; Balabanian, K.; Humbert, M. Inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimbara, A.; Christodoulopoulos, P.; Soussi-Gounni, A.; Olivenstein, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Levitt, R.C.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Holroyd, K.J.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Lafitte, J.J.; et al. IL-9 and its receptor in allergic and nonallergic lung disease: Increased expression in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, E.C.; Weaver, C.T.; Turner, H.; Begum-Haque, S.; Becher, B.; Schreiner, B.; Coyle, A.J.; Kasper, L.H.; Noelle, R.J. IL-9 as a mediator of Th17-driven inflammatory disease. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, S.; Sopel, N.; Finotto, S. Th9 and other IL-9-producing cells in allergic asthma. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.-C.; Pang, L.-L.; Mao, Q.-S.; Wu, S.-Y.; Xiao, Q.-F. IL-9 exacerbates the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through oxidative stress. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergadi, E.; Chang, M.S.; Lee, C.; Liang, O.D.; Liu, X.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S. Early macrophage recruitment and alternative activation are critical for the later development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2011, 123, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuder, R.M.; Groves, B.; Badesch, D.B.; Voelkel, N.F. Exuberant endothelial cell growth and elements of inflammation are present in plexiform lesions of pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 144, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thenappan, T.; Goel, A.; Marsboom, G.; Fang, Y.-H.; Toth, P.T.; Zhang, H.J.; Kajimoto, H.; Hong, Z.; Paul, J.; Wietholt, C.; et al. A central role for CD68(+) macrophages in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Reversal by macrophage depletion. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabinovitch, M.; Guignabert, C.; Humbert, M.; Nicolls, M.R. Inflammation and immunity in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttica, M.J.; Langenickel, T.; Noguchi, A.; Machado, R.F.; Gladwin, M.T.; Boehm, M. Perivascular T-cell infiltration leads to sustained pulmonary artery remodeling after endothelial cell damage. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Austin, E.D.; Rock, M.T.; Mosse, C.A.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Yoder, S.M.; Robbins, I.M.; Loyd, J.E.; Meyrick, B.O. T lymphocyte subset abnormalities in the blood and lung in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolls, M.R.; Mizuno, S.; Taraseviciene-Stewart, L.; Farkas, L.; Drake, J.I.; Al Husseini, A.; Gomez-Arroyo, J.G.; Voelkel, N.F.; Bogaard, H.J. New models of pulmonary hypertension based on VEGF receptor blockade-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. Pulm. Circ. 2012, 2, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamosiuniene, R.; Tian, W.; Dhillon, G.; Wang, L.; Sung, Y.K.; Gera, L.; Patterson, A.J.; Agrawal, R.; Rabinovitch, M.; Ambler, K.; et al. Regulatory T cells limit vascular endothelial injury and prevent pulmonary hypertension. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamosiuniene, R.; Manouvakhova, O.; Mesange, P.; Saito, T.; Qian, J.; Sanyal, M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Nguyen, L.P.; Luria, A.; Tu, A.B.; et al. Dominant Role for Regulatory T Cells in Protecting Females Against Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sada, Y.; Dohi, Y.; Uga, S.; Higashi, A.; Kinoshita, H.; Kihara, Y. Non-suppressive regulatory T cell subset expansion in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart Vessel. 2016, 31, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilette, C.; Ouadrhiri, Y.; Van Snick, J.; Renauld, J.C.; Staquet, P.; Vaerman, J.P.; Sibille, Y. Oxidative burst in lipopolysaccharide-activated human alveolar macrophages is inhibited by interleukin-9. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donninelli, G.; Saraf-Sinik, I.; Mazziotti, V.; Capone, A.; Grasso, M.G.; Battistini, L.; Reynolds, R.; Magliozzi, R.; Volpe, E. Interleukin-9 regulates macrophage activation in the progressive multiple sclerosis brain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauber, S.; Luber, M.; Weber, S.; Maul, L.; Soare, A.; Wohlfahrt, T.; Lin, N.-Y.; Dietel, K.; Bozec, A.; Herrmann, M.; et al. Resolution of inflammation by interleukin-9-producing type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mindt, B.C.; Fritz, J.H.; Duerr, C.U. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Pulmonary Immunity and Tissue Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frey, K.; Zivanovic, A.; Schwager, K.; Neri, D. Antibody-based targeting of interferon-alpha to the tumor neovasculature: A critical evaluation. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, D.L.; Kiseljak, D.; Rajendra, Y.; Thurnheer, S.; Baldi, L.; Wurm, F.M. Polyethyleneimine-based transient gene expression processes for suspension-adapted HEK-293E and CHO-DG44 cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 92, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, I.; Grün, K.; Müller, L.M.; Bäz, L.; Förster, M.; Schrepper, A.; Kretzschmar, D.; Pistulli, R.; Yilmaz, A.; Bauer, R.; et al. Cellular inflammation in pulmonary hypertension: Detailed analysis of lung and right ventricular tissue, circulating immune cells and effects of a dual endothelin receptor antagonist. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2019, 73, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gouyou, B.; Grün, K.; Kerschenmeyer, A.; Villa, A.; Matasci, M.; Schrepper, A.; Pfeil, A.; Bäz, L.; Jung, C.; Schulze, P.C.; et al. Therapeutic Evaluation of Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin 9 in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073460
Gouyou B, Grün K, Kerschenmeyer A, Villa A, Matasci M, Schrepper A, Pfeil A, Bäz L, Jung C, Schulze PC, et al. Therapeutic Evaluation of Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin 9 in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073460
Chicago/Turabian StyleGouyou, Baptiste, Katja Grün, Anne Kerschenmeyer, Alessandra Villa, Mattia Matasci, Andrea Schrepper, Alexander Pfeil, Laura Bäz, Christian Jung, P. Christian Schulze, and et al. 2021. "Therapeutic Evaluation of Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin 9 in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073460
APA StyleGouyou, B., Grün, K., Kerschenmeyer, A., Villa, A., Matasci, M., Schrepper, A., Pfeil, A., Bäz, L., Jung, C., Schulze, P. C., Neri, D., & Franz, M. (2021). Therapeutic Evaluation of Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin 9 in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073460






