Distinct Pharmacological Properties of Gaseous CO and CO-Releasing Molecule in Human Platelets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
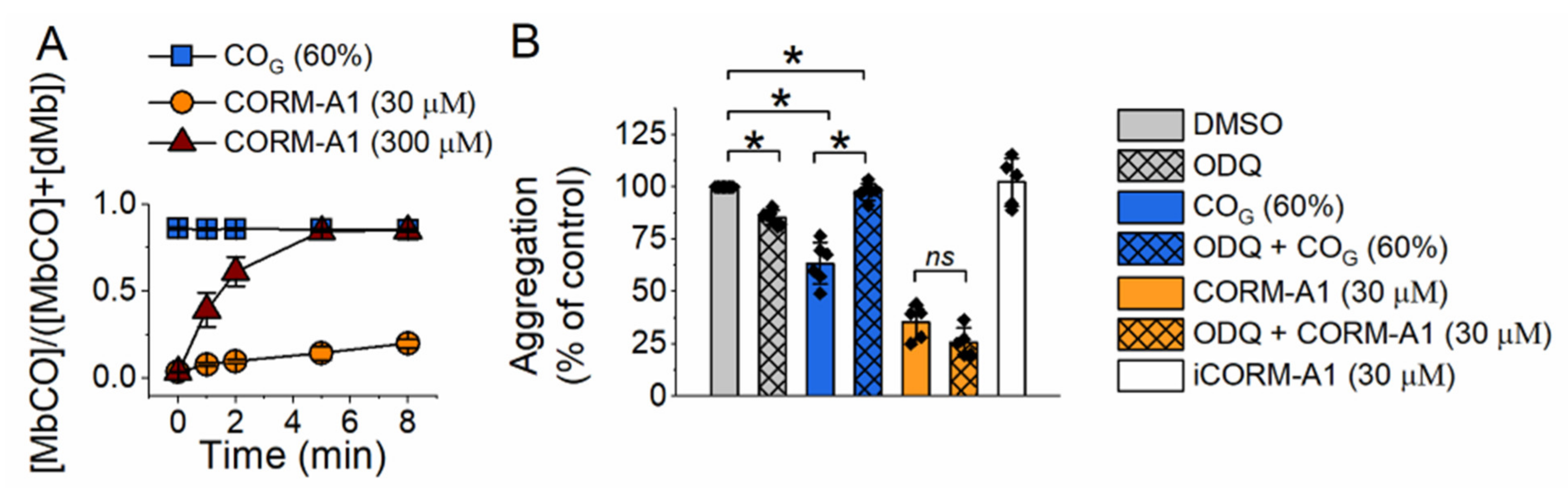
2.1. Effect of Carbon Monoxide on Platelet Aggregation—Involvement of sGC
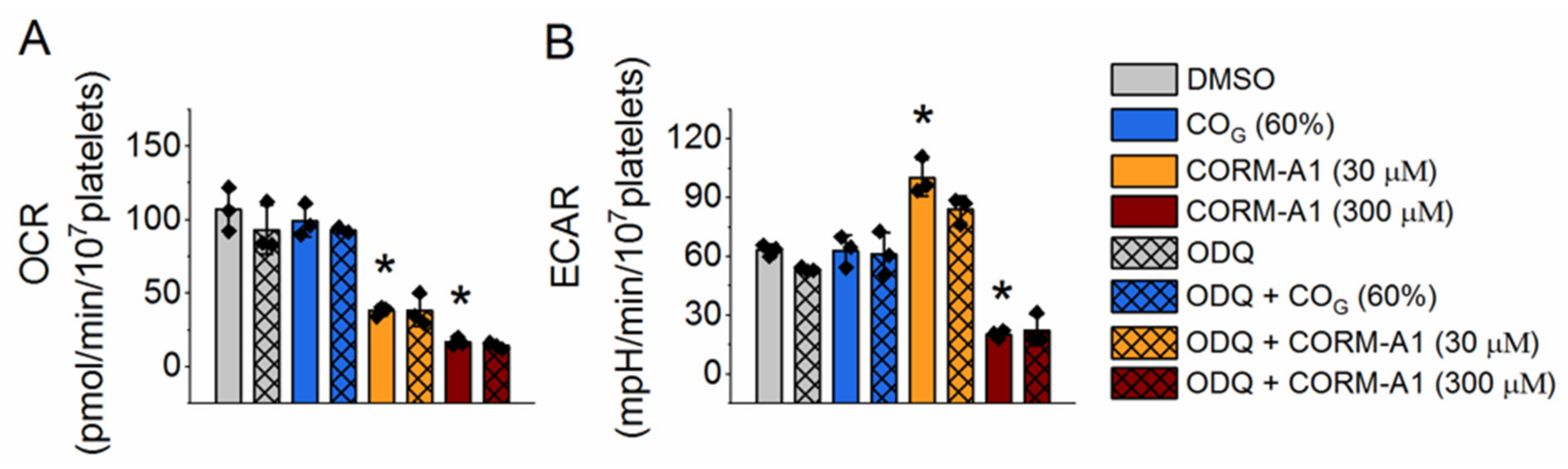
2.2. Effect of Carbon Monoxide on Platelet Energy Metabolism
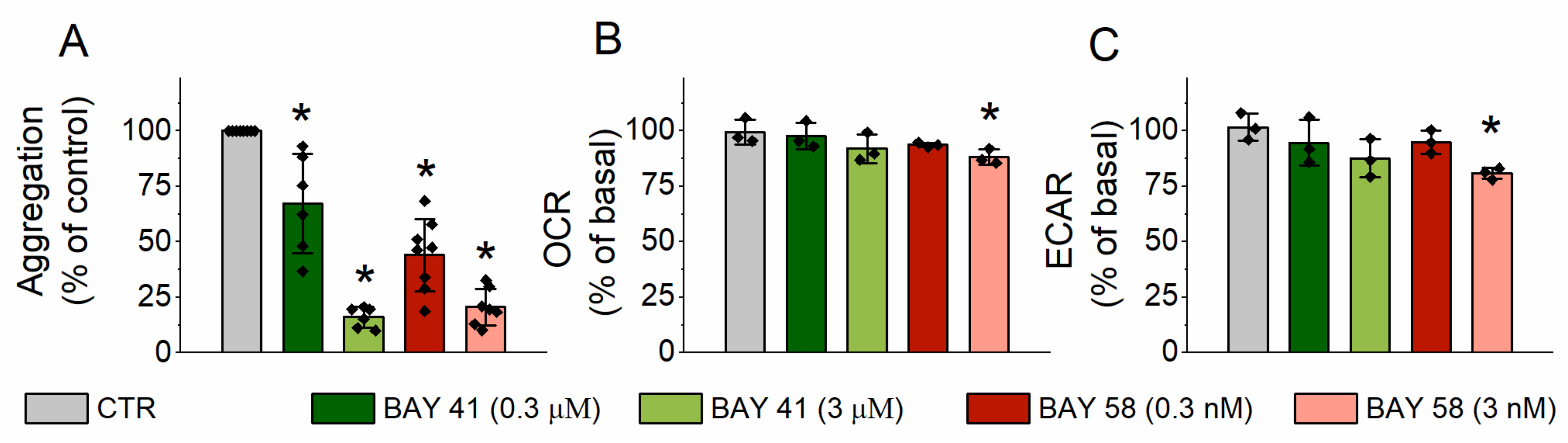
2.3. Effect of sGC Activation on Platelet Aggrgation and Energy Metabolism
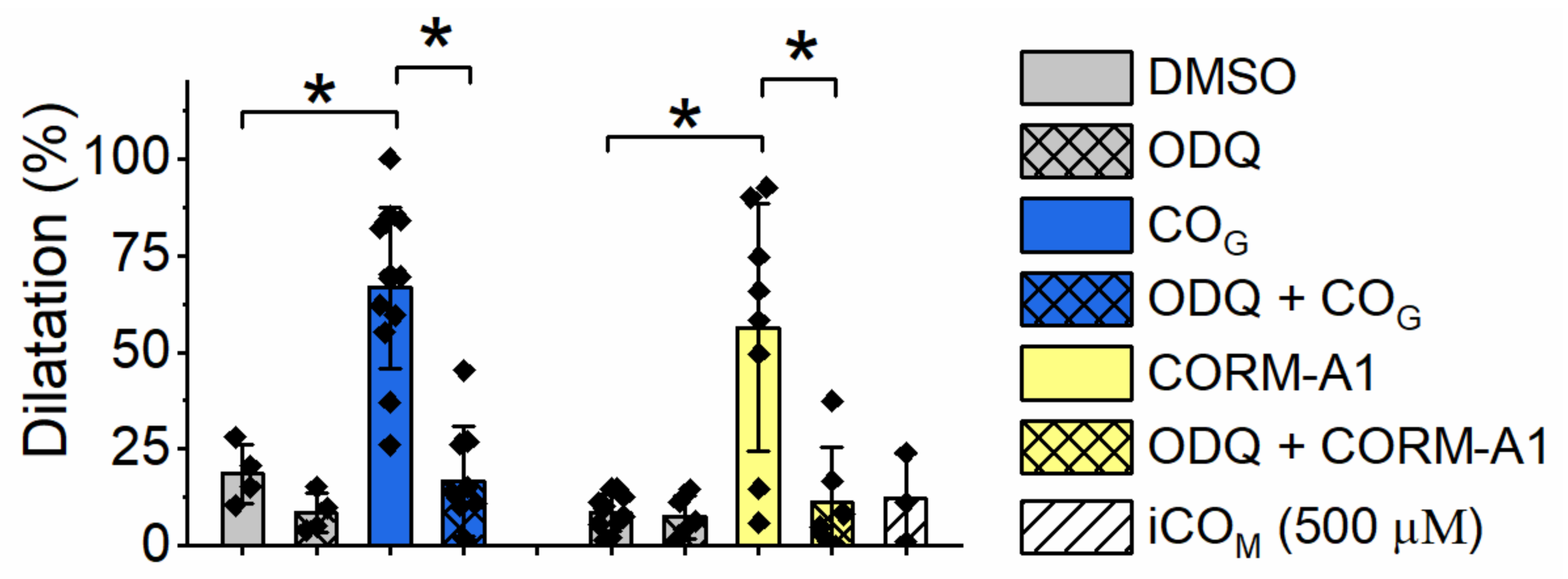
2.4. Effect of Carbon Monoxide on Aortic Rings Vasodilatation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Isolation of Human Platelets
4.4. Platelet Aggregation Assay
4.5. Analysis of Cellular Bioenergetics Using Seahorse Extracellular Flux Technology
4.6. Myoglobin Assay for Quantification of CO
4.7. Assessment of Endothelial Function in Isolated Mouse Aortic Rings
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- True, A.L.; Olive, M.; Boehm, M.; San, H.; Westrick, R.J.; Raghavachari, N.; Xu, X.; Lynn, E.G.; Sack, M.N.; Munson, P.J.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 deficiency accelerates formation of arterial thrombosis through oxidative damage to the endothelium, which is rescued by inhaled carbon monoxide. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tracz, M.J.; Juncos, J.P.; Grande, J.P.; Croatt, A.J.; Ackerman, A.W.; Katusic, Z.S.; Nath, K.A. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 is a beneficial response in a murine model of venous thrombosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Guo, L.; Fan, C.; Bolisetty, S.; Joseph, R.; Wright, M.M.; Agarwal, A.; George, J.F. Carbon monoxide rescues heme oxygenase-1-deficient mice from arterial thrombosis in allogeneic aortic transplantation. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, T.; Kondo, T.; Ogawa, K.; Fukunaga, K.; Ohkohchi, N. Protective effect of heme oxygenase-1 on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of platelet adhesion to the sinusoids. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Balla, J.; Otterbein, L.; Smith, R.N.; Brouard, S.; Lin, Y.; Csizmadia, E.; Sevigny, J.; Robson, S.C.; Vercellotti, G.; et al. Carbon Monoxide Generated by Heme Oxygenase-1 Suppresses the Rejection of Mouse-to-Rat Cardiac Transplants. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramkowski, K.; Leszczynska, A.; Mogielnicki, A.; Chlopicki, S.; Grochal, E.; Mann, B.; Brzoska, T.; Urano, T.; Motterlini, R.; Buczko, W. Antithrombotic properties of water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecules. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soni, H.; Jain, M.; Mehta, A.A. Investigation into the mechanism(s) of antithrombotic effects of carbon monoxide releasing molecule-3 (CORM-3). Thromb. Res. 2011, 127, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüne, B.; Ullrich, V. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by carbon monoxide is mediated by activation of guanylate cyclase. Mol. Pharmacol. 1987, 32, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Chlopicki, S.; Olszanecki, R.; Marcinkiewicz, E.; Lomnicka, M.; Motterlini, R. Carbon monoxide released by CORM-3 inhibits human platelets by a mechanism independent of soluble guanylate cyclase. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 71, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlopicki, S.; Łomnicka, M.; Fedorowicz, A.; Grochal, E.; Kramkowski, K.; Mogielnicki, A.; Buczko, W.; Motterlini, R. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CO-RMs): Comparison with NO donors. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaczara, P.; Sitek, B.; Przyborowski, K.; Kurpinska, A.; Kus, K.; Stojak, M.; Chlopicki, S. Antiplatelet effect of carbon monoxide is mediated by NAD+and ATP depletion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2376–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Sawle, P.; Hammad, J.; Bains, S.; Alberto, R.; Foresti, R.; Green, C.J. CORM-A1: A new pharmacologically active carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foresti, R.; Braud, L.; Motterlini, R. Chapter 7: Signaling by CO: Molecular and Cellular Functions. In RSC Metallobiology; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 161–191. [Google Scholar]
- Brüne, B.; Schmidt, K.U.; Ullrich, V. Activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by carbon monoxide and inhibition by superoxide anion. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 192, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hsu, A.; Moore, P.K. Actions and interactions of nitric oxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulphide in the cardiovascular system and in inflammation—a tale of three gases! Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.R.; Marletta, M.A. Soluble Guanylate Cyclase from Bovine Lung: Activation with Nitric Oxide and Carbon Monoxide and Spectral Characterization of the Ferrous and Ferric States. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5636–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sayed, N.; Beuve, A.; Van Den Akker, F. NO and CO differentially activate soluble guanylyl cyclase via a heme pivot-bend mechanism. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrova, O. Regulation, Activation, and Deactivation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase and NO-Sensors. Doctoral Dissertation, Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, Universite Paris Saclay (COmUE), Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pyriochou, A.; Papapetropoulos, A. Soluble guanylyl cyclase: More secrets revealed. Cell. Signal. 2005, 17, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebe, A.; Müllershausen, F.; Smolenski, A.; Walter, U.; Schultz, G.; Koesling, D. YC-1 potentiates nitric oxide- and carbon monoxide-induced cyclic GMP effects in human platelets. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, C.E.; Brown, G.C. The inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase by the gasescarbon monoxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen cyanide and hydrogensulfide: Chemical mechanism and physiological significance. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2008, 40, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, I.; Zatsepin, N.A.; Hikita, M.; Conrad, C.E.; Nelson, G.; Coe, J.D.; Basu, S.; Grant, T.D.; Seaberg, M.H.; Sierra, R.G.; et al. Crystal structure of CO-bound cytochrome c oxidase determined by serial femtosecond X-ray crystallography at room temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8011–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Amico, G.; Lam, F.; Hagen, T.; Moncada, S. Inhibition of cellular respiration by endogenously produced carbon monoxide. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stojak, M.; Kaczara, P.; Motterlini, R.; Chlopicki, S. Modulation of cellular bioenergetics by CO-releasing molecules and NO-donors inhibits the interaction of cancer cells with human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, L.; Rossier, J.; Derszniak, K.; Dybas, J.; Oetterli, R.M.; Kottelat, E.; Chlopicki, S.; Zelder, F.; Zobi, F. Modified biovectors for the tuneable activation of anti-platelet carbon monoxide release. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6840–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, L.; Mundada, L.; Stomel, J.M.; Liu, J.J.; Sun, J.; Yet, S.F.; Fay, W.P. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 expression inhibits platelet-dependent thrombosis. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2004, 6, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, A.; Bourguignon, M.-P.; Clavreul, N.; Badier-Commander, C.; Gosgnach, W.; Simonet, S.; Vayssettes-Courchay, C.; Cordi, A.; Fabiani, J.-N.; Verbeuren, T.J.; et al. Mechanisms of the vasorelaxing effects of CORM-3, a water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule: Interactions with eNOS. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch Pharmacol. 2013, 386, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. Carbon monoxide-induced vasorelaxation and the underlying mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggar, J.H.; Leffler, C.W.; Cheranov, S.Y.; Tcheranova, D.E.S.; Cheng, X. Carbon monoxide dilates cerebral arterioles by enhancing the coupling of Ca2+ sparks to Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Failli, P.; Vannacci, A.; Mannelli, L.D.C.; Motterlini, R.; Masini, E. Relaxant effect of a water soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM-3) on spontaneously hypertensive rat aortas. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2012, 26, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naik, J.S.; Walker, B.R. Homogeneous segmental profile of carbon monoxide-mediated pulmonary vasodilation in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 281, L1436–L1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, L.; Deitch, E.A.; Szabó, C. Hydrogen sulfide decreases adenosine triphosphate levels in aortic rings and leads to vasorelaxation via metabolic inhibition. Life Sci. 2008, 83, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffith, T.M.; Edwards, D.H.; Newby, A.C.; Lewis, M.J.; Henderson, A.H. Production of endothelium derived relaxant factor is dependent on oxidative phosphorylation and extracellular calcium. Cardiovasc. Res. 1986, 20, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, C.J.; Gibson, I.F.; Martin, W. Effects of metabolic inhibitors on endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent vasodilatation of rat and rabbit aorta. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 102, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodman, D.M.; Mallet, J.; McMurtry, I.F. Difference in effect of inhibitors of energy metabolism on endothelium-dependent relaxation of rat pulmonary artery and aorta. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1991, 4, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotko, D.; Bednarczyk, P.; Koprowski, P.; Kunz, W.S.; Szewczyk, A.; Kulawiak, B. Heme is required for carbon monoxide activation of mitochondrial BKCa channel. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 881, 173191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Burg, R. Carbon monoxide. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1999, 19, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad-Kobeissi, S.; Ratovonantenaina, J.; Dabiré, H.; Wilson, J.L.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Berdeaux, A.; Dubois-Randé, J.L.; Mann, B.E.; Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R. Vascular and angiogenic activities of CORM-401, an oxidant-sensitive CO-releasing molecule. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 102, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, U.; Van Der Vlies, A.J.; Simeoni, E.; Wandrey, C.; Hubbell, J.A. Carbon monoxide-releasing micelles for immunotherapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18273–18280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, T.; Buczek, E.; Majzner, K.; Kolodziejczyk, A.; Miszczyk, J.; Kaczara, P.; Kwiatek, W.; Baranska, M.; Szymonski, M.; Chlopicki, S. Comparative endothelial profiling of doxorubicin and daunorubicin in cultured endothelial cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorowicz, A.; Buczek, E.; Mateuszuk, L.; Czarnowska, E.; Sitek, B.; Jasztal, A.; Chmura-Skirlińska, A.; Dib, M.; Steven, S.; Daiber, A.; et al. Comparison of pulmonary and systemic NO- And PGI2-dependent endothelial function in diabetic mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczara, P.; Przyborowski, K.; Mohaissen, T.; Chlopicki, S. Distinct Pharmacological Properties of Gaseous CO and CO-Releasing Molecule in Human Platelets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073584
Kaczara P, Przyborowski K, Mohaissen T, Chlopicki S. Distinct Pharmacological Properties of Gaseous CO and CO-Releasing Molecule in Human Platelets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073584
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczara, Patrycja, Kamil Przyborowski, Tasnim Mohaissen, and Stefan Chlopicki. 2021. "Distinct Pharmacological Properties of Gaseous CO and CO-Releasing Molecule in Human Platelets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073584
APA StyleKaczara, P., Przyborowski, K., Mohaissen, T., & Chlopicki, S. (2021). Distinct Pharmacological Properties of Gaseous CO and CO-Releasing Molecule in Human Platelets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073584





