Semi-Lethal Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Rats Lacking the Nme7 Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of an Nme7 Knock-Out Rat Model
2.2. Morphometric Assessment of SDNme7−/− Rats
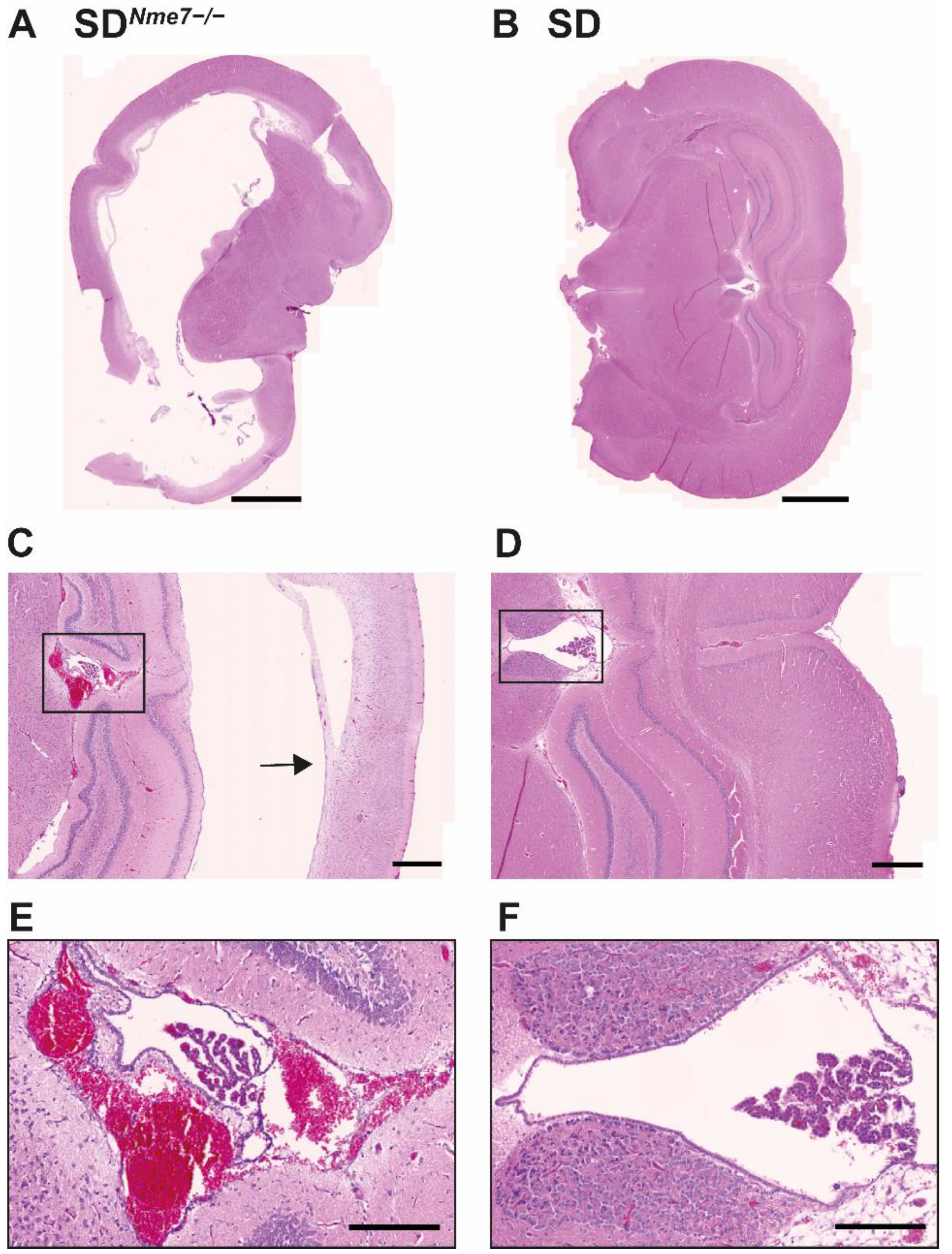
2.3. Histological Assessment of SDNme7−/− Rats
2.4. Nme7 Expression and Transcriptomic Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Genotyping
4.3. Gene Expression
4.4. Transcriptome Profiling
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Necropsy and Histology
4.7. Micro-CT
4.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afzelius, B.A. A human syndrome caused by immotile cilia. Science 1976, 193, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, J.F.; Leroux, M.R. Genes and molecular pathways underpinning ciliopathies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvignes, T.; Pontarotti, P.; Fauvel, C.; Bobe, J. Nme protein family evolutionary history, a vertebrate perspective. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puts, G.S.; Leonard, M.K.; Pamidimukkala, N.V.; Snyder, D.E.; Kaetzel, D.M. Nuclear functions of NME proteins. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Choi, Y.K.; Qi, R.Z. NME7 is a functional component of the gamma-tubulin ring complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.K.; Gupta, N.; Wen, X.; Rangell, L.; Chih, B.; Peterson, A.S.; Bazan, J.F.; Li, L.; Scales, S.J. Functional characterization of putative cilia genes by high-content analysis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1104–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Ma, N.; Lin, Y.T.; Wu, C.C.; Hsiao, M.; Lu, F.L.; Yu, C.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Lu, J. A shRNA functional screen reveals Nme6 and Nme7 are crucial for embryonic stem cell renewal. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2199–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, P.; Ignesti, M.; Gargiulo, G.; Hsu, T.; Cavaliere, V. Extracellular NME proteins: A player or a bystander? Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heit, J.A.; Armasu, S.M.; Asmann, Y.W.; Cunningham, J.M.; Matsumoto, M.E.; Petterson, T.M.; De Andrade, M. A genome-wide association study of venous thromboembolism identifies risk variants in chromosomes 1q24.2 and 9q. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, S.; Wang, L.; Smith, E.N.; Gordon, W.; van Hylckama Vlieg, A.; de Andrade, M.; Brody, J.A.; Pattee, J.W.; Haessler, J.; Brumpton, B.M.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic association studies identify 16 novel susceptibility loci for venous thromboembolism. Blood 2019, 134, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Rivero, M.; Stoll, M.; Hegenbarth, J.C.; Ruhle, F.; Limperger, V.; Junker, R.; Franke, A.; Hoffmann, P.; Shneyder, M.; Stach, M.; et al. Single- and Multimarker Genome-Wide Scans Evidence Novel Genetic Risk Modifiers for Venous Thromboembolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Hellwege, J.N.; Keaton, J.M.; Park, J.; Qiu, C.; Warren, H.R.; Torstenson, E.S.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Sun, Y.V.; Wilson, O.D.; et al. Trans-ethnic association study of blood pressure determinants in over 750,000 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.J.; Ehret, G.B.; Nandakumar, P.; Ranatunga, D.; Schaefer, C.; Kwok, P.Y.; Iribarren, C.; Chakravarti, A.; Risch, N. Genome-wide association analyses using electronic health records identify new loci influencing blood pressure variation. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-Giraldez, R.; Gogarten, S.M.; Below, J.E.; Yao, J.; Seyerle, A.A.; Highland, H.M.; Kooperberg, C.; Soliman, E.Z.; Rotter, J.I.; Kerr, K.F.; et al. GWAS of the electrocardiographic QT interval in Hispanics/Latinos generalizes previously identified loci and identifies population-specific signals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Setten, J.; Verweij, N.; Mbarek, H.; Niemeijer, M.N.; Trompet, S.; Arking, D.E.; Brody, J.A.; Gandin, I.; Grarup, N.; Hall, L.M.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis of 30,000 samples identifies seven novel loci for quantitative ECG traits. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedova, L.; Skolnikova, E.; Hodulova, M.; Vcelak, J.; Seda, O.; Bendlova, B. Expression profiling of Nme7 interactome in experimental models of metabolic syndrome. Physiol. Res. 2018, 67 (Suppl. 3), S543–S550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reish, O.; Aspit, L.; Zouella, A.; Roth, Y.; Polak-Charcon, S.; Baboushkin, T.; Benyamini, L.; Scheetz, T.E.; Mussaffi, H.; Sheffield, V.C.; et al. A Homozygous Nme7 Mutation Is Associated with Situs Inversus Totalis. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, P.; Read, R.; Hansen, G.M.; Freay, L.C.; Zambrowicz, B.P.; Sands, A.T. Situs inversus in Dpcd/Poll-/-, Nme7-/-, and Pkd1l1-/- mice. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, P.; Read, R.W.; Hansen, G.M.; Payne, B.J.; Small, D.; Sands, A.T.; Zambrowicz, B.P. Congenital hydrocephalus in genetically engineered mice. Vet. Pathol. 2012, 49, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fuscoe, J.C.; Zhao, C.; Guo, C.; Jia, M.; Qing, T.; Bannon, D.I.; Lancashire, L.; Bao, W.; Du, T.; et al. A rat RNA-Seq transcriptomic BodyMap across 11 organs and 4 developmental stages. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegstein, A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 32, 149–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Tseng, I.C.; Huang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. SNX27 Deletion Causes Hydrocephalus by Impairing Ependymal Cell Differentiation and Ciliogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 12586–12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtha, L.A.; Yang, Q.; Parsons, M.W.; Levi, C.R.; Beard, D.J.; Spratt, N.J.; McLeod, D.D. Cerebrospinal fluid is drained primarily via the spinal canal and olfactory route in young and aged spontaneously hypertensive rats. Fluids Barriers CNS 2014, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus, D.F.; Orime, K.; Kaminska, D.; Kimura, T.; Basile, G.; Wang, C.H.; Haertle, L.; Riemens, R.; Brown, N.K.; Hu, J.; et al. Parental metabolic syndrome epigenetically reprograms offspring hepatic lipid metabolism in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2391–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzaki, R.; Zhao, S.; Valerius, M.T.; Tsugawa, D.; Oya, Y.; Ray, K.C.; Karp, S.J. SOCS2 Balances Metabolic and Restorative Requirements during Liver Regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti-Rocha, R.; Cramer, A.; Gaio Leite, P.; Antunes, M.M.; Pereira, R.V.S.; Barroso, A.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; David, B.A.; Teixeira, M.M.; Menezes, G.B.; et al. SOCS2 Is Critical for the Balancing of Immune Response and Oxidate Stress Protecting Against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Tanaka, N. PPARs as Metabolic Regulators in the Liver: Lessons from Liver-Specific PPAR-Null Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadjali, F.; Santana-Farre, R.; Vesterlund, M.; Carow, B.; Mirecki-Garrido, M.; Hernandez-Hernandez, I.; Flodstrom-Tullberg, M.; Parini, P.; Rottenberg, M.; Norstedt, G.; et al. SOCS2 deletion protects against hepatic steatosis but worsens insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 3282–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowy-Bieryllo, Z.; Rabiasz, A.; Dabrowski, M.; Pogorzelski, A.; Wojda, A.; Dmenska, H.; Grzela, K.; Sroczynski, J.; Witt, M.; Zietkiewicz, E. Truncating mutations in exons 20 and 21 of OFD1 can cause primary ciliary dyskinesia without associated syndromic symptoms. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 56, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallmeier, J.; Nielsen, K.G.; Kuehni, C.E.; Lucas, J.S.; Leigh, M.W.; Zariwala, M.A.; Omran, H. Motile ciliopathies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Das, P.J.; McQueen, C.M.; Gerber, V.; Swiderski, C.E.; Lavoie, J.P.; Chowdhary, B.P.; Raudsepp, T. Analysis of genomic copy number variation in equine recurrent airway obstruction (heaves). Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejler, G. The emerging role of mast cell proteases in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, I.U.; Choi, N.H.; Lee, K.; Yu, H.Y.; Yun, J.H.; Kong, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, B.J.; et al. Obesity susceptible novel DNA methylation marker on regulatory region of inflammation gene: Results from the Korea Epigenome Study (KES). BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, J.; Roth, M.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Fang, L.; Savic, S.; Tamm, M.; Stolz, D. Adrenomedullin mediates pro-angiogenic and pro-inflammatory cytokines in asthma and COPD. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 56, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.J.; Snyder, E.M.; Richert, M.L.; Wheatley, C.M.; Chase, S.C.; Olson, L.J.; Johnson, B.D. Effect of beta2-adrenergic receptor stimulation on lung fluid in stable heart failure patients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sironen, A.; Shoemark, A.; Patel, M.; Loebinger, M.R.; Mitchison, H.M. Sperm defects in primary ciliary dyskinesia and related causes of male infertility. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2029–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terre, B.; Lewis, M.; Gil-Gomez, G.; Han, Z.; Lu, H.; Aguilera, M.; Prats, N.; Roy, S.; Zhao, H.; Stracker, T.H. Defects in efferent duct multiciliogenesis underlie male infertility in GEMC1-, MCIDAS- or CCNO-deficient mice. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, C.B.; Mays, D.J.; Beeler, J.S.; Rosenbluth, J.M.; Boyd, K.L.; Guasch, G.L.S.; Shaver, T.M.; Tang, L.J.; Liu, Q.; Shyr, Y.; et al. p73 Is Required for Multiciliogenesis and Regulates the Foxj1-Associated Gene Network. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núnez-Ollé, M.; Jung, C.; Terré, B.; Balsiger, N.A.; Plata, C.; Roset, R.; Pardo-Pastor, C.; Garrido, M.; Rojas, S.; Alameda, F.; et al. Constitutive Cyclin O deficiency results in penetrant hydrocephalus, impaired growth and infertility. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99261–99273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terre, B.; Piergiovanni, G.; Segura-Bayona, S.; Gil-Gomez, G.; Youssef, S.A.; Attolini, C.S.; Wilsch-Brauninger, M.; Jung, C.; Rojas, A.M.; Marjanovic, M.; et al. GEMC1 is a critical regulator of multiciliated cell differentiation. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 942–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurkowiak, M.; Zietkiewicz, E.; Witt, M. Recent advances in primary ciliary dyskinesia genetics. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šedová, L.; Buková, I.; Bažantová, P.; Petrezsélyová, S.; Prochazka, J.; Školníková, E.; Zudová, D.; Včelák, J.; Makovický, P.; Bendlová, B.; et al. Semi-Lethal Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Rats Lacking the Nme7 Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083810
Šedová L, Buková I, Bažantová P, Petrezsélyová S, Prochazka J, Školníková E, Zudová D, Včelák J, Makovický P, Bendlová B, et al. Semi-Lethal Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Rats Lacking the Nme7 Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(8):3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083810
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠedová, Lucie, Ivana Buková, Pavla Bažantová, Silvia Petrezsélyová, Jan Prochazka, Elena Školníková, Dagmar Zudová, Josef Včelák, Pavol Makovický, Běla Bendlová, and et al. 2021. "Semi-Lethal Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Rats Lacking the Nme7 Gene" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 8: 3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083810
APA StyleŠedová, L., Buková, I., Bažantová, P., Petrezsélyová, S., Prochazka, J., Školníková, E., Zudová, D., Včelák, J., Makovický, P., Bendlová, B., Šeda, O., & Sedlacek, R. (2021). Semi-Lethal Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Rats Lacking the Nme7 Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(8), 3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083810





