Recapitulating Actin Module Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Reveals New Roles for Bristle-Actin-Modulating Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Combination of Jv, Fascin, and Forked Generate Unique Actin Bundles in the Drosophila Oocyte
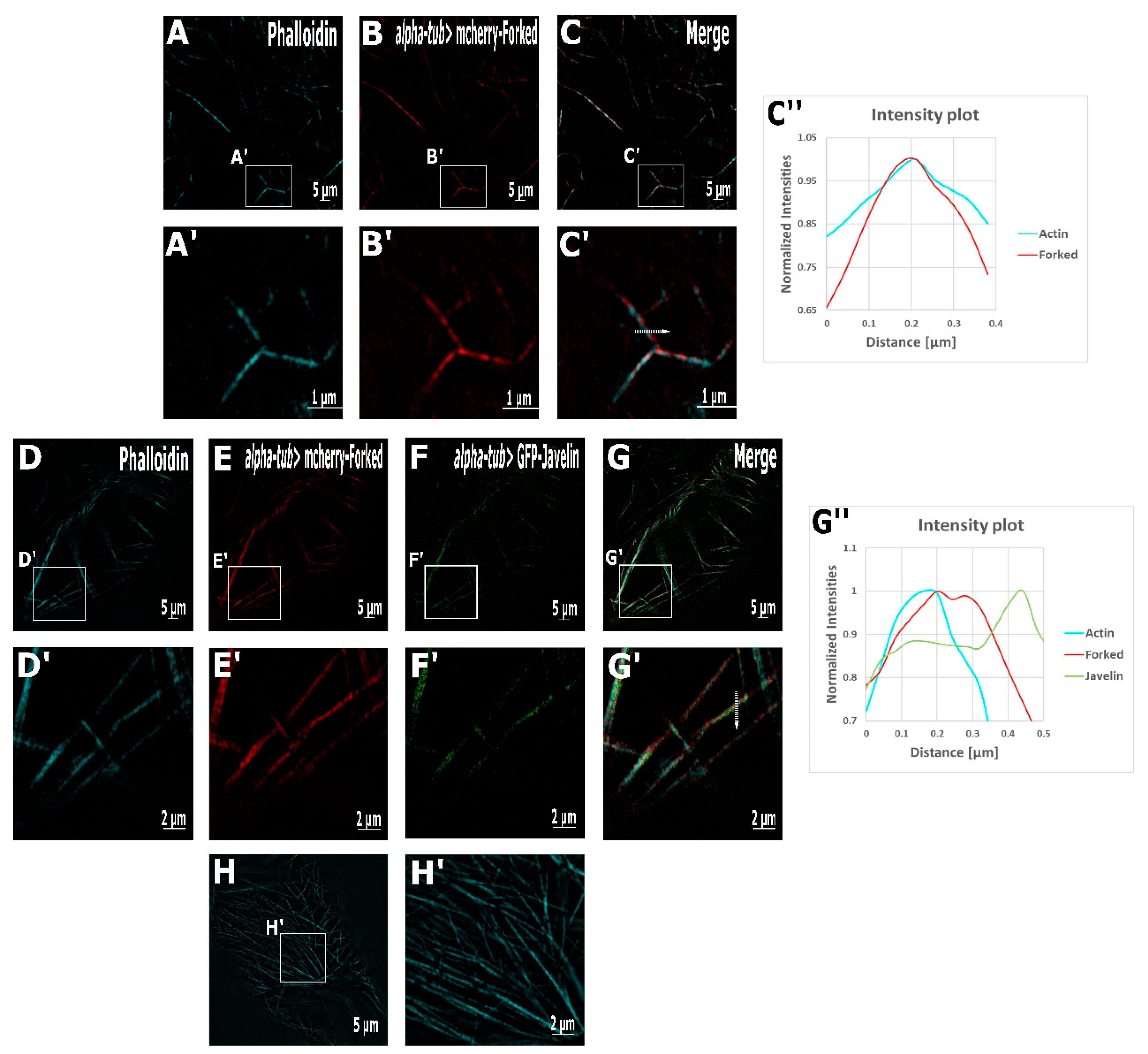
2.2. Super-Resolution Microscopy Revealed the Co-Localization of the Actin-Bundling Proteins
2.3. Analysis of the Internal Organization of the Ectopic Oocyte Actin Bundles Generated by Forked, Javelin, and Fascin by CLEM
2.4. Structure–Function Analysis of Javelin Protein
3. Discussion
3.1. The Drosophila Ovary as a Model Tissue to Study Bristle Actin Bundle Formation
3.2. Fascin Acts Not Only in Hexagonal Packing of Actin Bundles, But Also Enhances Forked Actin Crosslinking Activity
3.3. Jv May Have a Role in Actin Bundle Compactization and Elongation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drosophila Stocks
4.2. Fertility Assay
4.3. Confocal Microscopy
4.4. SR-SIM Imaging
4.5. On-Section CLEM
4.5.1. Sample Preparation
4.5.2. Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging
4.5.3. Electron Tomography
4.5.4. Correlation and Segmentation
4.6. Constructs and Transgenic Flies
4.7. Data Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furukawa, R.; Fechheimer, M. The Structure, Function, and Assembly of Actin Filament Bundles. Adv. Clin. Chem. 1997, 175, 29–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bartles, J.R. Parallel actin bundles and their multiple actin-bundling proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CRevenu, C.; Athman, R.; Robine, S.; Louvard, D. The co-workers of actin filaments: From cell structures to signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokawa, N.; Tilney, L.G.; Fujiwara, K.; Heuser, J.E. Organization of actin, myosin, and intermediate filaments in the brush border of intestinal epithelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 94, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drenckhahn, D.; Dermietzel, R. Organization of the actin filament cytoskeleton in the intestinal brush border: A quantitative and qualitative immunoelectron microscope study. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurana, S.; George, S.P. The role of actin bundling proteins in the assembly of filopodia in epithelial cells. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGrath, J.; Roy, P.; Perrin, B.J. Stereocilia morphogenesis and maintenance through regulation of actin stability. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 65, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacentine, I.; Chatterjee, P.; Barr-Gillespie, P.G. Stereocilia Rootlets: Actin-Based Structures That Are Essential for Structural Stability of the Hair Bundle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, S.; Thumkeo, D.; Ohta, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, S.; Kanchanawong, P.; Fuu, T.; Watanabe, S.; Shimada, K.; Fujihara, Y.; et al. mDia1/3 generate cortical F-actin meshwork in Sertoli cells that is continuous with contractile F-actin bundles and indispensable for spermatogenesis and male fertility. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2004874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogl, A.W. Arrangement and possible function of actin filament bundles in ectoplasmic specializations of ground squirrel Sertoli cells. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guild, G.M.; Connelly, P.S.; Shaw, M.K.; Tilney, L.G.; Tang, S.; Shen, Y.J.; DeBellard, M.E.; Mukhopadhyay, G.; Salzer, J.L.; Crocker, P.R.; et al. Actin Filament Cables in Drosophila Nurse Cells Are Composed of Modules That Slide Passively Past One Another during Dumping. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 138, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan-Miklos, S.; Cooley, L. The villin-like protein encoded by the Drosophila quail gene is required for actin bundle assembly during oogenesis. Cell 1994, 78, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, U. Cytoskeletal elements in insect sensilla. Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1997, 26, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokic, S.; Bakhrat, A.; Tsurim, I.; Urakova, N.; Rasgon, J.L.; Abdu, U. Actin bundles play a different role in shaping scales compared to bristles in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinwiddie, A.; Null, R.; Pizzano, M.; Chuong, L.; Krup, A.L.; Tan, H.E.; Patel, N.H. Dynamics of F-actin prefigure the structure of butterfly wing scales. Dev. Biol. 2014, 392, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, G.M. Structure and organization of actin filaments. In The Cell a Molecular Approach, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tilney, L.G.; Connelly, P.S.; Vranich, K.A.; Shaw, M.K.; Guild, G.M. Actin filaments and microtubules play different roles during bristle elongation in Drosophila. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tilney, L.G.; Connelly, P.S.; Vranich, K.A.; Shaw, M.K.; Guild, G.M. Regulation of Actin Filament Cross-linking and Bundle Shape in Drosophila Bristles. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fei, X. The growth of Drosophila bristles and laterals is not restricted to the tip or base. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3797–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopmann, R.; Miller, K.G. A Balance of Capping Protein and Profilin Functions Is Required to Regulate Actin Polymerization in Drosophila Bristle. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilney, L.G.; Tilney, M.S.; Guild, G.M. F actin bundles in Drosophila bristles. I. Two filament cross-links are involved in bundling. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Claessens, M.M.A.E.; Semmrich, C.; Ramos, L.; Bausch, A.R. Helical twist controls the thickness of F-actin bundles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8819–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilney, L.G.; DeRosier, D.J. How to make a curved Drosophila bristle using straight actin bundles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18785–18792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shapira, S.; Bakhrat, A.; Bitan, A.; Abdu, U. The Drosophila javelin Gene Encodes a Novel Actin-Associated Protein Required for Actin Assembly in the Bristle. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 4582–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baskar, R.; Bakrhat, A.; Abdu, U. GFP-Forked, a genetic reporter for studying Drosophila oocyte polarity. Biol. Open 2018, 8, bio039552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullins, R.D.; Hansen, S.D. In vitro studies of actin filament and network dynamics. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cant, K.; Knowles, B.A.; Mooseker, M.S.; Cooley, L. Drosophila singed, a fascin homolog, is required for actin bundle formation during oogenesis and bristle extension. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, P.O.; Llimargas, M. Fascin, may the Forked be with you. Fly 2014, 8, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overton, J. The fine structure of developing bristles in wild type and mutantDrosophila melanogaster. J. Morphol. 1967, 122, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilney, L.G.; Connelly, P.S.; Vranich, K.A.; Shaw, M.K.; Guild, G.M. Why Are Two Different Cross-linkers Necessary for Actin Bundle Formation In Vivo and What Does Each Cross-link Contribute? J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, N.S.; Lankenau, D.H.; Mitchell, H.K.; Young, P.; Corces, V.G. Forked proteins are components of fiber bundles present in developing bristles of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1994, 136, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guild, G.M.; Connelly, P.S.; Ruggiero, L.; Vranich, K.A.; Tilney, L.G. Actin Filament Bundles in Drosophila Wing Hairs: Hairs and Bristles Use Different Strategies for Assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 3620–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilney, L.G.; Connelly, P.; Smith, S.; Guild, G.M. F-actin bundles in Drosophila bristles are assembled from modules composed of short filaments. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1291–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkelman, J.D.; Bilancia, C.G.; Peifer, M.; Kovar, D.R. Ena/VASP Enabled is a highly processive actin polymerase tailored to self-assemble parallel-bundled F-actin networks with Fascin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4121–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanet, J.; Jayo, A.; Plaza, S.; Millard, T.; Parsons, M.; Stramer, B. Fascin promotes filopodia formation independent of its role in actin bundling. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spracklen, A.J.; Fagan, T.N.; Lovander, K.E.; Tootle, T.L. The pros and cons of common actin labeling tools for visualizing actin dynamics during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2014, 393, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heintzmann, R.; Cremer, C.G. Laterally modulated excitation microscopy: Improvement of resolution by using a diffraction grating. Opt. Biopsies Microsc. Tech. III 1999, 3568, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulski, W.; Schorb, M.; Welsch, S.; Picco, A.; Kaksonen, M.; Briggs, J.A. Correlated fluorescence and 3D electron microscopy with high sensitivity and spatial precision. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, J.R.; Mastronarde, D.N.; Mc Intosh, J.R. Computer Visualization of Three-Dimensional Image Data Using IMOD. J. Struct. Biol. 1996, 116, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul-Gilloteaux, P.; Heiligenstein, X.; Belle, M.; Domart, M.-C.; Larijani, B.; Collinson, L.; Raposo, G.; Salamero, J. eC-CLEM: Flexible multidimensional registration software for correlative microscopies. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chaumont, F.; Dallongeville, S.; Chenouard, N.; Hervé, N.; Pop, S.; Provoost, T.; Meas-Yedid, V.; Pankajakshan, P.; LeComte, T.; Le Montagner, Y.; et al. Icy: An open bioimage informatics platform for extended reproducible research. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalling, D.; Westerhoff, M.; Hege, H.-C. Amira: A Highly Interactive System for Visual Data Analysis. In Visualization Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 749–767. [Google Scholar]




| S. No. | Genotype | Average No. of Progeny from 24 h Egg Collection | % Relative Fertility |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kr/CyO; alpha-tub | 87 ± 6.1 | 100 a |
| 2 | mCherry-Forked/CyO; alpha-tub | 77 ± 1.7 | 88.5 a |
| 3 | GFP-Fascin/CyO; alpha-tub | 74.6 ± 7.6 | 85.8 a |
| 4 | GFP-Javelin/CyO; alpha-tub | 76 ± 5.1 | 87.3 a |
| 5 | GFP-Fascin/GFP-Javelin; alpha-tub | 73.3 ± 9.3 | 84.2 a |
| 6 | GFP-Fascin/CyO; mCherry-Forked/alpha-tub | 74 ± 4.7 | 85.1 a |
| 7 | GFP-Javelin/CyO; mCherry-Forked/alpha-tub | 72.3 ± 9.2 | 83.1 a |
| 8 | GFP-Fascin/GFP-Javelin; mCherry-Forked/alpha-tub | 70.6 ± 8.1 | 81.2 a |
| Confocal Projections | SR-SIM Projections | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. | Genotype | Length (µm) | Interbundle Distance (µm) | Width (µm) |
| 1 | mCherry Forked | 6.17 ± 1.2 a | 2.18 ± 0.15 a | 0.25 ± 0.006 a |
| 2 | mCherry Forked_GFP Javelin | 16.17 ± 3.4 b | 0.73 ± 0.06 b | 0.47 ± 0.017 b |
| 3 | mCherry Forked_GFP Fascin_ GFP Javelin | 23.96 ± 1.11 c | 0.34 ± 0.15 c | 0.67 ± 0.023 c |
| S. No. | Genotype | Interfilament Distance (nm) | Total Width (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | mChFk | 11.7 ± 0.5 a | 47.8 ± 2.6 |
| 2 | mChFk_GFPJv | 10.3 ± 0.6 b | 52.6 ± 2.3 |
| 3 | mChFk_GFPFascin | 10.4 ± 0.3 b | 81.1± 4.2 |
| 4 | mChFk_GFPJv_GFPFascin | 10.9 ± 0.3 b | 75.1 ± 3.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnan, R.K.; Baskar, R.; Anna, B.; Elia, N.; Boermel, M.; Bausch, A.R.; Abdu, U. Recapitulating Actin Module Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Reveals New Roles for Bristle-Actin-Modulating Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084006
Krishnan RK, Baskar R, Anna B, Elia N, Boermel M, Bausch AR, Abdu U. Recapitulating Actin Module Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Reveals New Roles for Bristle-Actin-Modulating Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(8):4006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084006
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnan, Ramesh Kumar, Raju Baskar, Bakhrat Anna, Natalie Elia, Mandy Boermel, Andreas R. Bausch, and Uri Abdu. 2021. "Recapitulating Actin Module Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Reveals New Roles for Bristle-Actin-Modulating Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 8: 4006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084006
APA StyleKrishnan, R. K., Baskar, R., Anna, B., Elia, N., Boermel, M., Bausch, A. R., & Abdu, U. (2021). Recapitulating Actin Module Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Reveals New Roles for Bristle-Actin-Modulating Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(8), 4006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084006








