The Unique Phenotype of Lipid-Laden Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Lysosome
Regulation of Lysosome Biogenesis
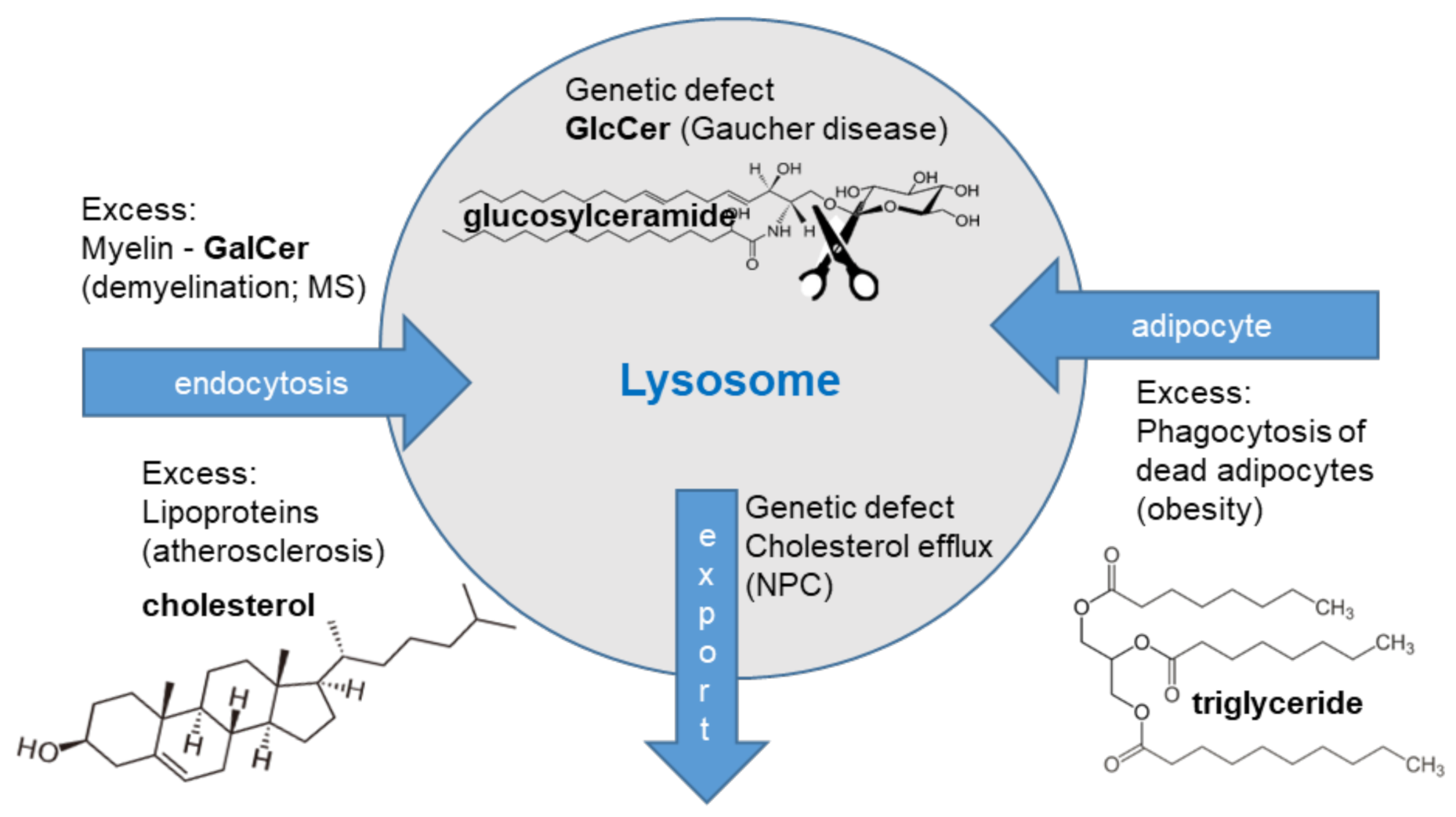
3. The Catabolic Defective Storage Macrophages
3.1. Glycosphingolipid Metabolism
3.2. The Gaucher Cell
3.3. The Niemann-Pick Type C Macrophage
4. The Acquired Storage Macrophages
4.1. Multiple Sclerosis
4.2. Obesity
4.3. Cardiovascular Disease
5. In Vitro Models
6. Summary and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissmann, F.; Manz, M.G.; Jung, S.; Sieweke, M.H.; Merad, M.; Ley, K. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science 2010, 327, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginhoux, F.; Jung, S. Monocytes and macrophages: Developmental pathways and tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Natoli, G. Molecular control of activation and priming in macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saftig, P.; Klumperman, J. Lysosome biogenesis and lysosomal membrane proteins: Trafficking meets function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.E.; Zoncu, R. The lysosome as a cellular centre for signalling, metabolism and quality control. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Duve, C.; Pressman, B.C.; Gianetto, R.; Wattiaux, R.; Appelmans, F. Tissue fractionation studies. Biochem. J. 1955, 60, 604–617. [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff, A.B.; Beaufay, H.; De Duve, C. Electron microscopy of lysosomerich fractions from rat liver. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1956, 2, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio, A.; Bonifacino, J.S. Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardiello, M.; Palmieri, M.; di Ronza, A.; Medina, D.L.; Valenza, M.; Gennarino, V.A.; Di Malta, C.; Donaudy, F.; Embrione, V.; Polishchuk, R.S.; et al. A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function. Science 2009, 325, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settembre, C.; Di Malta, C.; Polito, V.A.; Arencibia, M.G.; Vetrini, F.; Erdin, S.; Erdin, S.U.; Huynh, T.; Medina, D.; Colella, P.; et al. TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis. Science 2011, 332, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, Y.; Bar-Peled, L.; Zoncu, R.; Markhard, A.L.; Nada, S.; Sabatini, D.M. Ragulator-rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids. Cell 2010, 141, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settembre, C.; Zoncu, R.; Medina, D.L.; Vetrini, F.; Erdin, S.; Erdin, S.; Huynh, T.; Ferron, M.; Karsenty, G.; Vellard, M.C.; et al. A lysosome-to-nucleus signalling mechanism senses and regulates the lysosome via mTOR and TFEB. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, J.A.; Diab, H.I.; Lishu, L.; Jeong-A, L.; Patange, S.; Raben, N.; Puertollano, R. The nutrient-responsive transcription factor TFE3 promotes autophagy, lysosomal biogenesis, and clearance of cellular debris. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, N.; Brady, O.A.; Diab, H.I.; Martina, J.A.; Sun, L.; Huynh, T.; Lim, J.A.; Zare, H.; Raben, N.; Ballabio, A.; et al. TFEB and TFE3 cooperate in the regulation of the innate immune response in activated macrophages. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1240–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tol, M.J.; van der Lienden, M.J.C.; Gabriel, T.L.; Hagen, J.J.; Scheij, S.; Veenendaal, T.; Klumperman, J.; Donker-Koopman, W.E.; Verhoeven, A.J.; Overkleeft, H.; et al. HEPES activates a MiT/TFE-dependent lysosomal-autophagic gene network in cultured cells: A call for caution. Autophagy 2018, 14, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eijk, M.; Ferra, M.J.; Boot, R.G.; Aerts, J.M.F.G. Lyso-glycosphingolipids: Presence and consequences. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.M.F.G.; Kuo, C.L.; Lelieveld, L.T.; Boer, D.E.C.; van der Lienden, M.J.C.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Artola, M. Glycosphingolipids and lysosomal storage disorders as illustrated by gaucher disease. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 53, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitelon, Y.; Kopec, A.M.; Belin, S. Myelin Fat Facts: An Overview of Lipids and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Cells 2020, 9, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, F.M.; d’Azzo, A.; Davidson, B.L.; Neufeld, E.F.; Tifft, C.J. Lysosomal storage diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollak, C.E.M.; Van Weely, S.; Van Oers, M.H.J.; Aerts, J.M.F.G. Marked elevation of plasma chitotriosidase activity. A novel hallmark of Gaucher disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boven, L.A.; Van Meurs, M.; Boot, R.G.; Mehta, A.; Boon, L.; Aerts, J.M.; Laman, J.D. Gaucher cells demonstrate a distinct macrophage phenotype and resemble alternatively activated macrophages. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 122, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.T.; Schofield, J.P.; Hayman, A.R.; Shi, G.P.; Young, E.; Cox, T.M. Pathologic gene expression in Gaucher disease: Up-regulation of cysteine proteinases including osteoclastic cathepsin K. Blood 2000, 96, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.; Wegdam, W.; Donker-Koopman, W.; Ottenhoff, R.; Gaspar, P.; Verhoek, M.; Nelson, J.; Gabriel, T.; Kallemeijn, W.; Boot, R.G.; et al. Elevation of glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma protein B in type 1 Gaucher disease patients and mouse models. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, R.G.; Verhoek, M.; de Fost, M.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Maas, M.; Bleijlevens, B.; van Breemen, M.J.; van Meurs, M.; Boven, L.A.; Laman, J.D.; et al. Marked elevation of the chemokine CCL18/PARC in Gaucher disease: A novel surrogate marker for assessing therapeutic intervention. Blood 2004, 103, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, V.; Liu, J.; Yang, R.; Lin, H.; Lischuk, A.; Pastores, G.; Zhang, X.; Chuang, W.L.; Mistry, P.K. Validating glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B (gpNMB, osteoactivin), a new biomarker of Gaucher disease. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2018, 68, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigdon, H.; Savidor, A.; Levin, Y.; Meshcheriakova, A.; Schiffmann, R.; Futerman, A.H. Identification of a biomarker in cerebrospinal fluid for neuronopathic forms of Gaucher disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.K.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Nottoli, T.; McGrath, J.; Jain, D.; Zhang, K.; Keutzer, J.; Chuang, W.L.; Mehal, W.Z.; et al. Erratum: Glucocerebrosidase gene-deficient mouse recapitulates Gaucher disease displaying cellular and molecular dysregulation beyond the macrophage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Jia, L.; Quinn, B.; Zamzow, M.; Stringer, K.; Aronow, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Grabowski, G.A. Global gene expression profile progression in Gaucher disease mouse models. BMC Genom. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskes, E.C.B.; Sjouke, B.; Vaz, F.M.; Goorden, S.M.I.; van Kuilenburg, A.B.P.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; Hollak, C.E.M. Biochemical and imaging parameters in acid sphingomyelinase deficiency: Potential utility as biomarkers. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 130, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, M.T. Biochemical studies in niemann-pick disease I. Major sphingolipids of liver and spleen. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipids Lipid Metab. 1983, 750, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Getz, M.; Safeukui, I.; Yi, S.; Tamez, P.; Shin, J.; Velázquez, P.; Haldar, K. Genomic Expression Analyses Reveal Lysosomal, Innate Immunity Proteins, as Disease Correlates in Murine Models of a Lysosomal Storage Disorder. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluzeau, C.V.M.; Watkins-Chow, D.E.; Fu, R.; Borate, B.; Yanjanin, N.; Dail, M.K.; Davidson, C.D.; Walkley, S.U.; Ory, D.S.; Wassif, C.A.; et al. Microarray expression analysis and identification of serum biomarkers for niemann-pick disease, type c1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3632–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Getz, M.; Yi, S.; Kurkewich, J.; Safeukui, I.; Haldar, K. Plasma signature of neurological disease in the monogenetic disorder Niemann-Pick type C. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 8051–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.R.A.; Gabriel, T.L.; Aten, J.; Van Roomen, C.P.A.A.; Ottenhoff, R.; Claessen, N.; Alfonso, P.; Irún, P.; Giraldo, P.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; et al. Gpnmb is a potential marker for the visceral pathology in Niemann-Pick type C disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendrou, C.A.; Fugger, L.; Friese, M.A. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadelmann, C.; Timmler, S.; Barrantes-Freer, A.; Simons, M. Myelin in the central nervous system: Structure, function, and pathology. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1381–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cuzner, M.L.; Newcombe, J. Microglia-derived macrophages in early multiple sclerosis plaques. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1996, 22, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Valk, P.; de Groot, C.J.A. Staging of multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions: Pathology of the time frame of MS. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2000, 26, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, T.; Ludwin, S.; Prat, A.; Antel, J.; Brück, W.; Lassmann, H. An updated histological classification system for multiple sclerosis lesions. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boven, L.A.; van Meurs, M.; van Zwam, M.; Wierenga-Wolf, A.; Hintzen, R.Q.; Boot, R.G.; Aerts, J.M.; Amor, S.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E.; Laman, J.D. Myelin-laden macrophages are anti-inflammatory, consistent with foam cells in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2006, 129, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, D.A.E.; Koning, N.; Schuurman, K.G.; van Strien, M.E.; van Eden, C.G.; Hamann, J.; Huitinga, I. Selective upregulation of scavenger receptors in and around demyelinating areas in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, D.A.E.; van Scheppingen, J.; van der Poel, M.; Bossers, K.; Schuurman, K.G.; van Eden, C.G.; Hol, E.M.; Hamann, J.; Huitinga, I. Gene expression profiling of multiple sclerosis pathology identifies early patterns of demyelination surrounding chronic active lesions. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Poel, M.; Ulas, T.; Mizee, M.R.; Hsiao, C.C.; Miedema, S.S.M.; Adelia; Schuurman, K.G.; Helder, B.; Tas, S.W.; Schultze, J.L.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of human microglia reveals grey–white matter heterogeneity and multiple sclerosis-associated changes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren-Shaul, H.; Spinrad, A.; Weiner, A.; Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Ulland, T.K.; David, E.; Baruch, K.; Lara-Astaiso, D.; Toth, B.; et al. A Unique Microglia Type Associated with Restricting Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 1276–1290.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, A.A.; Lin, K.; van Lengerich, B.; Lianoglou, S.; Przybyla, L.; Davis, S.S.; Llapashtica, C.; Wang, J.; Kim, D.J.; Xia, D.; et al. TREM2 Regulates Microglial Cholesterol Metabolism upon Chronic Phagocytic Challenge. Neuron 2020, 105, 837–854.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvera, S. Cellular Heterogeneity in Adipose Tissues. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNelis, J.C.; Olefsky, J.M. Macrophages, Immunity, and Metabolic Disease. Immunity 2014, 41, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.M.; Saltiel, A.R. Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Mitchell, G.; Barbatelli, G.; Murano, I.; Ceresi, E.; Faloia, E.; Wang, S.; Fortier, M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieur, X.; Mok, C.Y.L.; Velagapudi, V.R.; Núñez, V.; Fuentes, L.; Montaner, D.; Ishikawa, K.; Camacho, A.; Barbarroja, N.; O’Rahilly, S.; et al. Differential lipid partitioning between adipocytes and tissue macrophages modulates macrophage lipotoxicity and M2/M1 polarization in obese mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eijk, M.; Aten, J.; Bijl, N.; Ottenhoff, R.; van Roomen, C.P.; Dubbelhuis, P.F.; Seeman, I.; Ghauharali-van der Vlugt, K.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Arbeeny, C.; et al. Reducing glycosphingolipid content in adipose tissue of obese mice restores insulin sensitivity, adipogenesis and reduces inflammation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Grijalva, A.; Skowronski, A.; van Eijk, M.; Serlie, M.J.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity activates a program of lysosomal-dependent lipid metabolism in adipose tissue macrophages independently of classic activation. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, T.L.; Tol, M.J.; Ottenhof, R.; van Roomen, C.; Aten, J.; Claessen, N.; Hooibrink, B.; de Weijer, B.; Serbe, M.J.; Argmann, C.; et al. Lysosomal stress in obese adipose tissue macrophages contributes to MITF-dependent Gpnmb induction. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3310–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, M.; Coats, B.R.; Hisert, K.B.; Hagman, D.; Mutskov, V.; Peris, E.; Schoenfelt, K.Q.; Kuzma, J.N.; Larson, I.; Billing, P.S.; et al. Metabolic dysfunction drives a mechanistically distinct proinflammatory phenotype in adipose tissue macrophages. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, B.R.; Schoenfelt, K.Q.; Barbosa-Lorenzi, V.C.; Peris, E.; Cui, C.; Hoffman, A.; Zhou, G.; Fernandez, S.; Zhai, L.; Hall, B.A.; et al. Metabolically Activated Adipose Tissue Macrophages Perform Detrimental and Beneficial Functions during Diet-Induced Obesity. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 3149–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.A.; Lim, H.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Ho, W.Y.; Foong, Y.H.; Nelson, V.L.; Nguyen, H.C.B.; Chegireddy, K.; Kim, J.; Habertheuer, A.; et al. Distinct macrophage populations direct inflammatory versus physiological changes in adipose tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5096–E5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaitin, D.A.; Adlung, L.; Thaiss, C.A.; Weiner, A.; Li, B.; Descamps, H.; Lundgren, P.; Bleriot, C.; Liu, Z.; Deczkowska, A.; et al. Lipid-Associated Macrophages Control Metabolic Homeostasis in a Trem2-Dependent Manner. Cell 2019, 178, 686–698.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Park, S.-Y.; Cho, Y.; Lim, Y.; Ahn, J.W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Chung, S.; et al. TFEB–GDF15 axis protects against obesity and insulin resistance as a lysosomal stress response. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Noels, H. Atherosclerosis: Current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.K.; Hermansson, A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, D.R.; Gordon, S. Recent insights into the biology of macrophage scavenger receptors. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yuan, X.M.; Olsson, A.G.; Brunk, U.T. Uptake of oxidized LDL by macrophages results in partial lysosomal enzyme inactivation and relocation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Duve, C. The participation of lysosomes in the transformation of smooth muscle cells to foamy cells in the aorta of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Acta Cardiol. 1974, 20, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Boot, R.G.; Van Achterberg, T.A.E.; van Aken, B.E.; Renkema, G.H.; Jacobs, M.J.H.M.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; De Vries, C.J.M. Strong induction of members of the chitinase family of proteins in atherosclerosis: Chitotriosidase and human cartilage gp-39 expressed in lesion macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, W.G. Advanced atherosclerotic foam cell formation has features of an acquired lysosomal storage disorder. Rejuvenation Res. 2006, 9, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikx, T.; Walenbergh, S.M.A.; Hofker, M.H.; Shiri-Sverdlov, R. Lysosomal cholesterol accumulation: Driver on the road to inflammation during atherosclerosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, R.; Sergin, I.; Bhattacharya, S.; Turner, J.N.; Epelman, S.; Settembre, C.; Diwan, A.; Ballabio, A.; Razani, B. Induction of lysosomal biogenesis in atherosclerotic macrophages can rescue lipid-induced lysosomal dysfunction and downstream sequelae. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergin, I.; Evans, T.D.; Zhang, X.; Bhattacharya, S.; Stokes, C.J.; Song, E.; Ali, S.; Dehestani, B.; Holloway, K.B.; Micevych, P.S.; et al. Exploiting macrophage autophagy-lysosomal biogenesis as a therapy for atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochain, C.; Vafadarnejad, E.; Arampatzi, P.; Pelisek, J.; Winkels, H.; Ley, K.; Wolf, D.; Saliba, A.E.; Zernecke, A. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the transcriptional landscape and heterogeneity of aortic macrophages in murine atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1661–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shim, D.; Lee, J.S.; Zaitsev, K.; Williams, J.W.; Kim, K.W.; Jang, M.Y.; Jang, H.S.; Yun, T.J.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals nonfoamy rather than foamy plaque macrophages are proinflammatory in atherosclerotic murine models. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkels, H.; Ehinger, E.; Vassallo, M.; Buscher, K.; Dinh, H.Q.; Kobiyama, K.; Hamers, A.A.J.; Cochain, C.; Vafadarnejad, E.; Saliba, A.E.; et al. Atlas of the immune cell repertoire in mouse atherosclerosis defined by single-cell RNA-sequencing and mass cytometry. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.M.; Rahman, A.H.; Fernandez, N.F.; Chudnovskiy, A.; Amir, E.D.; Amadori, L.; Khan, N.S.; Wong, C.K.; Shamailova, R.; Hill, C.A.; et al. Single-cell immune landscape of human atherosclerotic plaques. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, L.; de Winther, M.P.J. Macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis as defined by single-cell technologies. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, M.A.C.; Prange, K.H.M.; Slenders, L.; Örd, T.; Elbersen, D.; Boltjes, A.; De Jager, S.C.A.; Asselbergs, F.W.; De Borst, G.J.; Aavik, E.; et al. Microanatomy of the Human Atherosclerotic Plaque by Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Circ. Res. 2020, 1437–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aflaki, E.; Stubblefield, B.K.; Maniwang, E.; Lopez, G.; Moaven, N.; Goldin, E.; Marugan, J.; Patnaik, S.; Dutra, A.; Southall, N.; et al. Macrophage Models of Gaucher Disease for Evaluating Disease Pathogenesis and Candidate Drugs. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 240ra73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.K.; Burrow, T.A.; Rani, R.; Martin, L.J.; Witte, D.; Setchell, K.D.; McKay, M.A.; Magnusen, A.F.; Zhang, W.; Liou, B.; et al. Complement drives glucosylceramide accumulation and tissue inflammation in Gaucher disease. Nature 2017, 543, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Lienden, M.J.C.; Gaspar, P.; Boot, R.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; van Eijk, M. Glycoprotein non-metastatic protein B: An emerging biomarker for lysosomal dysfunction in macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; O’Neill, L.A.; Menon, D. Macrophage Immunometabolism: Where Are We (Going)? Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutens, L.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Dhingra, S.; Cramer, R.A.; Netea, M.G.; Stienstra, R. Unique metabolic activation of adipose tissue macrophages in obesity promotes inflammatory responses. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T.; Prange, K.H.M.; Glass, C.K.; de Winther, M.P.J. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of macrophages in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigamonti, E.; Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G.; Staels, B. Regulation of macrophage functions by PPAR- α, PPAR- γ, and LXRs in mice and men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.A.; Summers, S.A. A ceramide-centric view of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, O.; Brunner, J.S.; Korosec, A.; Martins, R.; Jais, A.; Snijder, B.; Vogel, A.; Caldera, M.; Hladik, A.; Lakovits, K.; et al. Beneficial Metabolic Effects of TREM2 in Obesity are Uncoupled from its Expression on Macrophages. Diabetes 2021, db200572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliani, P.L.; Wang, Y.; Fontana, E.; Robinette, M.L.; Yamanishi, Y.; Gilfillan, S.; Colonna, M. TREM2 sustains microglial expansion during aging and response to demyelination. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignarella, F.; Filipello, F.; Bollman, B.; Cantoni, C.; Locca, A.; Mikesell, R.; Manis, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Deng, L.; Benitez, B.A.; et al. TREM2 activation on microglia promotes myelin debris clearance and remyelination in a model of multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 513–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deczkowska, A.; Weiner, A.; Amit, I. The Physiology, Pathology, and Potential Therapeutic Applications of the TREM2 Signaling Pathway. Cell 2020, 181, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-S.; Dougherty, I.; Cruz, P.D.; Ariizumi, K. Syndecan-4 mediates the coinhibitory function of DC-HIL on T cell activation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5778–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Castano, A.P.; Hudson, T.E.; Nowlin, B.T.; Lin, S.-L.; Bonventre, J.V.; Swanson, K.D.; Duffield, J.S. The melanoma-associated transmembrane glycoprotein Gpnmb controls trafficking of cellular debris for degradation and is essential for tissue repair. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4767–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhuo, H.; Ouyang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Sun, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, H. Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein b (Gpnmb) is highly expressed in macrophages of acute injured kidney and promotes M2 macrophages polarization. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 316, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Riopel, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Dong, Y.; Birmingham, A.; Seo, J.B.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Wollam, J.; Hernandez-Carretero, A.; Fu, W.; et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Can Modulate in Vivo and in Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell 2017, 171, 372–384.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Eijk, M.; Aerts, J.M.F.G. The Unique Phenotype of Lipid-Laden Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084039
van Eijk M, Aerts JMFG. The Unique Phenotype of Lipid-Laden Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(8):4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084039
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Eijk, Marco, and Johannes M. F. G. Aerts. 2021. "The Unique Phenotype of Lipid-Laden Macrophages" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 8: 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084039
APA Stylevan Eijk, M., & Aerts, J. M. F. G. (2021). The Unique Phenotype of Lipid-Laden Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(8), 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084039





