Systematic Assessment of Chemokine Signaling at Chemokine Receptors CCR4, CCR7 and CCR10
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cognate Chemokines Stimulate β-Arrestin Recruitment at CCR4, CCR7 and CCR10
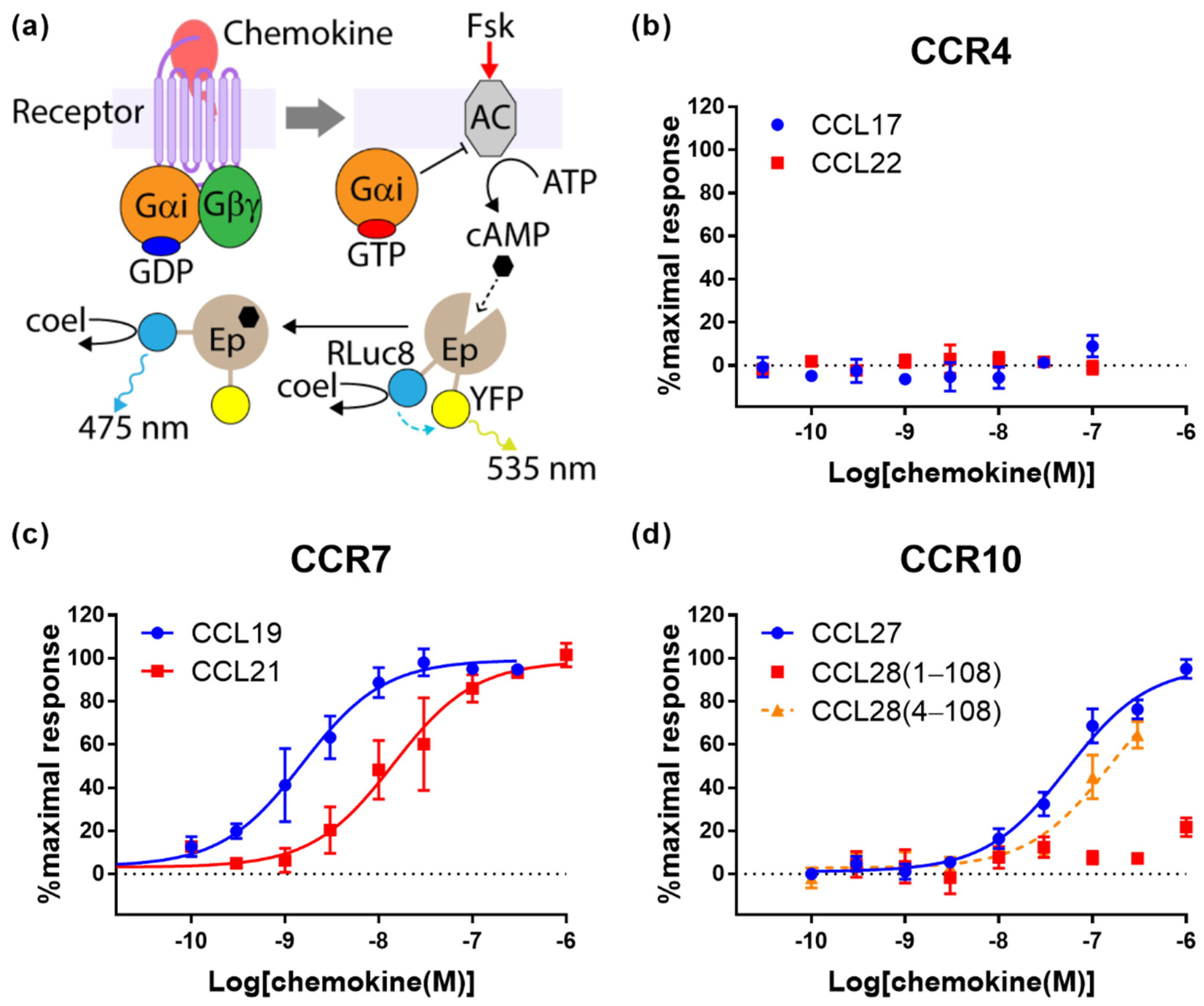
2.2. Cognate Chemokines Stimulate G Protein-Mediated Signaling at CCR7 and CCR10 But Not at CCR4
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Lines Stably Expressing Human CCR4, CCR7, and CCR10
4.3. β-Arrestin Recruitment Assay
4.4. G Protein Activation Assay
4.5. cAMP Inhibition Assay
4.6. NFAT Activation Assay
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Data Analysis and Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| BRET | bioluminescence resonance energy transfer |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| cAMP | 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CCL | C-C motif chemokine ligand |
| CCR | C-C motif chemokine receptor |
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary |
| CXCR | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor |
| DC | dendritic cell |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| Emax | maximal response |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| pEC50 | log10(EC50) where EC50 is the concentration (in molar) required for 50% activation |
| NFAT | nuclear factor of activated T cells |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PEI | polyethyleneimine |
| PLC | phospholipase C |
| RLuc8 | Renilla luciferase 8 |
| Th2 | T helper type 2 |
| YFP | yellow fluorescent protein |
References
- Murphy, P.M. Chemokines and chemokine receptors. In Clinical Immunology E-Book: Principles and Practice, 5th ed.; Rich, R.R.E.A., Ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M.J.; Hayward, J.A.; Huang, C.; e Huma, Z.; Sanchez, J. Mechanisms of Regulation of the Chemokine-Receptor Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bachelerie, F.; Graham, G.J.; Locati, M.; Mantovani, A.; Murphy, P.M.; Nibbs, R.; Rot, A.; Sozzani, S.; Thelen, M. New nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, S.; Bassoni, D.L.; Campbell, J.J.; Gerard, N.P.; Gerard, C.; Wehrman, T.S. Biased agonism as a mechanism for differential signaling by chemokine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35039–35048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, J.; Lane, J.R.; Canals, M.; Stone, M.J. Influence of Chemokine N-Terminal Modification on Biased Agonism at the Chemokine Receptor CCR1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ajram, L.; Begg, M.; Slack, R.; Cryan, J.; Hall, D.; Hodgson, S.; Ford, A.; Barnes, A.; Swieboda, D.; Mousnier, A.; et al. Internalization of the chemokine receptor CCR4 can be evoked by orthosteric and allosteric receptor antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 729, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zidar, D.A.; Violin, J.D.; Whalen, E.J.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Selective engagement of G protein coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) encodes distinct functions of biased ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9649–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, A.S.; Larsen, O.; Uetz-von Allmen, E.; Luckmann, M.; Legler, D.F.; Frimurer, T.M.; Veldkamp, C.T.; Hjorto, G.M.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Biased Signaling of CCL21 and CCL19 Does Not Rely on N-Terminal Differences, but Markedly on the Chemokine Core Domains and Extracellular Loop 2 of CCR7. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbisier, J.; Gales, C.; Huszagh, A.; Parmentier, M.; Springael, J.Y. Biased signaling at chemokine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 9542–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huma, Z.E.; Sanchez, J.; Lim, H.D.; Bridgford, J.L.; Huang, C.; Parker, B.J.; Pazhamalil, J.G.; Porebski, B.T.; Pfleger, K.D.G.; Lane, J.R.; et al. Key determinants of selective binding and activation by the monocyte chemoattractant proteins at the chemokine receptor CCR2. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshie, O.; Matsushima, K. CCR4 and its ligands: From bench to bedside. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pease, J.E.; Horuk, R. Recent progress in the development of antagonists to the chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR4. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comerford, I.; Harata-Lee, Y.; Bunting, M.D.; Gregor, C.; Kara, E.E.; McColl, S.R. A myriad of functions and complex regulation of the CCR7/CCL19/CCL21 chemokine axis in the adaptive immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, N.; Fu, Y.; Hu, S.; Xia, M.; Yang, J. CCR10 and its ligands in regulation of epithelial immunity and diseases. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, T.; Chantry, D.; Raport, C.J.; Wood, C.L.; Nishimura, M.; Godiska, R.; Yoshie, O.; Gray, P.W. Macrophage-derived chemokine is a functional ligand for the CC chemokine receptor 4. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariani, M.; Lang, R.; Binda, E.; Panina-Bordignon, P.; D’Ambrosio, D. Dominance of CCL22 over CCL17 in induction of chemokine receptor CCR4 desensitization and internalization on human Th2 cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viney, J.M.; Andrew, D.P.; Phillips, R.M.; Meiser, A.; Patel, P.; Lennartz-Walker, M.; Cousins, D.J.; Barton, N.P.; Hall, D.A.; Pease, J.E. Distinct conformations of the chemokine receptor CCR4 with implications for its targeting in allergy. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, M.A.; Legler, D.F. Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otero, C.; Groettrup, M.; Legler, D.F. Opposite fate of endocytosed CCR7 and its ligands: Recycling versus degradation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bardi, G.; Lipp, M.; Baggiolini, M.; Loetscher, P. The T cell chemokine receptor CCR7 is internalized on stimulation with ELC, but not with SLC. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorto, G.M.; Larsen, O.; Steen, A.; Daugvilaite, V.; Berg, C.; Fares, S.; Hansen, M.; Ali, S.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Differential CCR7 Targeting in Dendritic Cells by Three Naturally Occurring CC-Chemokines. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. GPCR Signaling Regulation: The Role of GRKs and Arrestins. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, M.; Schmitz, R.; Xiao, W.; Goldman, C.K.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Waldmann, T.A.; Staudt, L.M. Gain-of-function CCR4 mutations in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hieshima, K.; Imai, T.; Baba, M.; Shoudai, K.; Ishizuka, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Tsuruta, J.; Takeya, M.; Sakaki, Y.; Takatsuki, K.; et al. A novel human CC chemokine PARC that is most homologous to macrophage-inflammatory protein-1 alpha/LD78 alpha and chemotactic for T lymphocytes, but not for monocytes. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.A.; Patel, P.; Viney, J.M.; Phillips, R.M.; Solari, R.; Pease, J.E. A degradatory fate for CCR4 suggests a primary role in Th2 inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Fang, L.Y.; Xie, X. Development of a universal high-throughput calcium assay for G-protein- coupled receptors with promiscuous G-protein Galpha15/16. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Black, J.W.; Leff, P.; Shankley, N.P.; Wood, J. An operational model of pharmacological agonism: The effect of E/[A] curve shape on agonist dissociation constant estimation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 84, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kenakin, T.; Watson, C.; Muniz-Medina, V.; Christopoulos, A.; Novick, S. A simple method for quantifying functional selectivity and agonist bias. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Kunkel, E.J.; Gosslar, U.; Lazarus, N.; Langdon, P.; Broadwell, K.; Vierra, M.A.; Genovese, M.C.; Butcher, E.C.; Soler, D. A novel chemokine ligand for CCR10 and CCR3 expressed by epithelial cells in mucosal tissues. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.; Choi, Y.H.; Zidar, D.A.; Walker, J.K.L. beta-Arrestin-2-Dependent Signaling Promotes CCR4-mediated Chemotaxis of Murine T-Helper Type 2 Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, R.J.; Hall, D.A. Development of operational models of receptor activation including constitutive receptor activity and their use to determine the efficacy of the chemokine CCL17 at the CC chemokine receptor CCR4. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 1774–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonecchi, R.; Graham, G.J. Atypical Chemokine Receptors and Their Roles in the Resolution of the Inflammatory Response. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volpe, S.; Cameroni, E.; Moepps, B.; Thelen, S.; Apuzzo, T.; Thelen, M. CCR2 acts as scavenger for CCL2 during monocyte chemotaxis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliland, C.T.; Salanga, C.L.; Kawamura, T.; Trejo, J.; Handel, T.M. The chemokine receptor CCR1 is constitutively active, which leads to G protein-independent, beta-arrestin-mediated internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 32194–32210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.N.; Campbell, J.J.; Salanga, C.L.; Ertl, L.S.; Wang, Y.; Yau, S.; Dang, T.; Zeng, Y.; McMahon, J.P.; Krasinski, A.; et al. CCR2-Mediated Uptake of Constitutively Produced CCL2: A Mechanism for Regulating Chemokine Levels in the Blood. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Kelly, R.S.; See, H.B.; Johnstone, E.K.; McCall, E.A.; Williams, J.H.; Kelly, D.J.; Pfleger, K.D. Functional interaction between angiotensin II receptor type 1 and chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 with implications for chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollins, B.; Kuravi, S.; Digby, G.J.; Lambert, N.A. The c-terminus of GRK3 indicates rapid dissociation of G protein heterotrimers. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.I.; Collins, J.; Davis, R.; Lin, K.M.; DeCamp, D.; Roach, T.; Hsueh, R.; Rebres, R.A.; Ross, E.M.; Taussig, R.; et al. Use of a cAMP BRET sensor to characterize a novel regulation of cAMP by the sphingosine 1-phosphate/G13 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10576–10584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Receptor | Assay | Ligand | Potency pEC50 ± SE 1 (EC50 in nM) | Maximal Effect (%) Emax ± SE 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCR4 | β-arrestin recruitment | CCL17 | 7.31 ± 0.32 (48) | 28 ± 6 ** |
| CCL22 | 8.11 ± 0.10 (8) | 100 | ||
| G protein activation | CCL17 | ND | ND | |
| CCL22 | ND | ND | ||
| cAMP inhibition | CCL17 | ND | ND | |
| CCL22 | ND | ND | ||
| CCR7 | β-arrestin recruitment | CCL19 | 7.93 ± 0.06 (12) | 100 |
| CCL21 | 6.45 ± 0.03 (352) *** | 100 (2) | ||
| G protein activation | CCL19 | 8.71 ± 0.09 (2) | 100 | |
| CCL21 | 7.54 ± 0.05 (29) *** | 103 ± 3 | ||
| cAMP inhibition | CCL19 | 8.81 ± 0.12 (2) | 100 | |
| CCL21 | 7.84± 0.16 (14) * | 99 ± 6 | ||
| CCR10 | β-arrestin recruitment | CCL27 | 7.01 ± 0.06 (97) | 100 |
| CCL28(1-108) | ND | ND | ||
| CCL28(4-108) | ND | 82 (3) | ||
| G protein activation | CCL27 | 7.66 ± 0.05 (22) | 100 | |
| CCL28(1-108) | ND | ND | ||
| CCL28(4-108) | 6.92 ± 0.14 (121) | 80 (3) | ||
| cAMP inhibition | CCL27 | 7.27 ± 0.10 (54) | 100 | |
| CCL28(1-108) | ND | ND | ||
| CCL28(4-108) | 6.82 ± 0.23 (152) | 64 (3) | ||
| NFAT Ca2+ reporter | CCL27 | 8.24 ± 0.12 (6) | 100 | |
| CCL28(1-108) | ND | ND | ||
| CCL28(4-108) | 7.18 ± 0.10 (65) ** | 106 ± 8 |
| Receptor | Normalized Expression Level |
|---|---|
| CCR4ΔC29 CCR4 | 100 4.2 ± 1.2 |
| CCR7 | 7.9 ± 2.0 |
| CCR10 | 120 ± 24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, H.D.; Lane, J.R.; Canals, M.; Stone, M.J. Systematic Assessment of Chemokine Signaling at Chemokine Receptors CCR4, CCR7 and CCR10. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084232
Lim HD, Lane JR, Canals M, Stone MJ. Systematic Assessment of Chemokine Signaling at Chemokine Receptors CCR4, CCR7 and CCR10. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(8):4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084232
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Herman D., J. Robert Lane, Meritxell Canals, and Martin J. Stone. 2021. "Systematic Assessment of Chemokine Signaling at Chemokine Receptors CCR4, CCR7 and CCR10" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 8: 4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084232
APA StyleLim, H. D., Lane, J. R., Canals, M., & Stone, M. J. (2021). Systematic Assessment of Chemokine Signaling at Chemokine Receptors CCR4, CCR7 and CCR10. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(8), 4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084232







