Role of SIRT1 in Isoflurane Conditioning-Induced Neurovascular Protection against Delayed Cerebral Ischemia Secondary to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
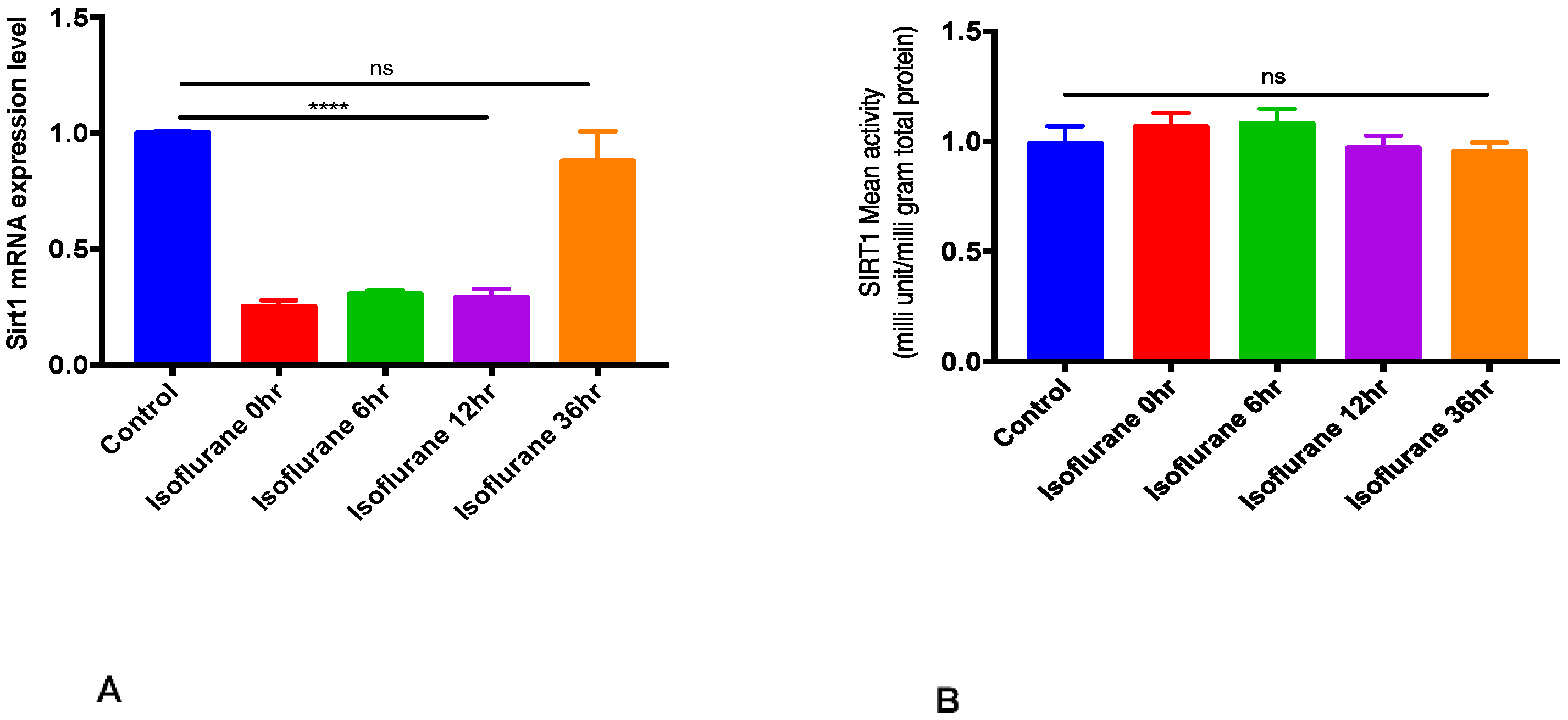
2.1. SIRT1 mRNA Expression and Activity after Isoflurane Conditioning in Naive Animals
2.2. Isoflurane Conditioning with or without EX-527 Administration Attenuated SAH-Induced Large Artery Vasospasm and Improved Neurological Deficits in Wild Type Mice
2.3. Isoflurane Conditioning with or without EX-527 Administration Attenuated SAH-Induced Microvessel Thrombosis in Wild-Type Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Experimental SAH
4.3. Isoflurane Conditioning
4.4. EX-527 (a Selective SIRT1 Inhibitor) Treatment
4.5. Vasospasm Assessment
4.6. Neurobehavioral Assessment
4.7. Microvessel Thrombosis Assessment
4.8. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) for SIRT1 Gene Expression
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for SIRT1 Protein Expression
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAH | Subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| DCI | Delayed Cerebral Ischemia |
| SIRT1 | Silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog |
| NAD | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia inducible factor 1α |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| ECA | External Carotid artery |
| ROX-SE | 5-(and-6)-Carboxy-X-rhodamine, succinimidyl ester |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| TBS-T | Tris-Buffered Saline + Tween |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| Gapdh | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| ActB | Actin Beta |
References
- Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.G.; Duldner, J.E.; Tomsick, T.; Leach, A. Initial and recurrent bleeding are the major causes of death following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 1994, 25, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brathwaite, S.; Macdonald, R.L. Current Management of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia: Update from Results of Recent Clinical Trials. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gijn, J.; Kerr, R.S.; Rinkel, G.J. Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 2007, 369, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernbach, P.D.; Little, J.R.; Jones, S.C.; Ebrahim, Z.Y. Altered Cerebral Autoregulation and CO2 Reactivity after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 1988, 22, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touho, H.; Ueda, H. Disturbance of autoregulation in patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: Mechanism of cortical and motor dysfunction. Surg. Neurol. 1994, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, M.; Ai, J.; Lakovic, K.; D’Abbondanza, J.; Ilodigwe, D.; Macdonald, R. Mechanisms of microthrombi formation after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroscience 2012, 224, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergouwen, M.D.I.; Vermeulen, M.; Coert, B.A.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Roos, Y.B.W.E.M. Microthrombosis after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: An Additional Explanation for Delayed Cerebral Ischemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 28, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidday, J.M. Cerebral preconditioning and ischaemic tolerance. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trendelenburg, G.; Dirnagl, U. Neuroprotective role of astrocytes in cerebral ischemia: Focus on ischemic preconditioning. Glia 2005, 50, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastide, M.; Gelé, P.; Pétrault, O.; Pu, Q.; Caliez, A.; Robin, E.; Deplanque, D.; Duriez, P.; Bordet, R. Delayed Cerebrovascular Protective Effect of Lipopolysaccharide in Parallel to Brain Ischemic Tolerance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 23, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasov, T.D.; Korzhevskii, D.E.; Polyakova, E.A. Ischemic Preconditioning of the Rat Brain as a Method of Endothelial Protection from Ischemic/Repercussion Injury. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2005, 35, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masada, T.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G.; Ennis, S.R.; Keep, R.F. Attenuation of Ischemic Brain EDEMA and Cerebrovascular Injury after Ischemic Preconditioning in the Rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 21, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, A.M.; Altay, T.; Bs, A.B.F.; Gidday, J.M. Repetitive hypoxia extends endogenous neurovascular protection for stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, E.; Johnson, A.W.; Nelson, J.W.; Harries, M.D.; Gidday, J.M.; Han, B.H.; Zipfel, G.J. HIF-1α Mediates Isoflurane-Induced Vascular Protection in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athiraman, U.; Jayaraman, K.; Liu, M.; Giri, T.; Yuan, J.; Zipfel, G.J. Role of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Isoflurane Conditioning-Induced Neurovascular Protection in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadori, G.; Lee, C.E.; Bookout, A.L.; Lee, S.; Williams, K.W.; Anderson, J.; Elmquist, J.K.; Coppari, R. Brain SIRT1: Anatomical Distribution and Regulation by Energy Availability. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9989–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herskovits, A.Z.; Guarente, L. SIRT1 in Neurodevelopment and Brain Senescence. Neuron 2014, 81, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallàs, M.; Pizarro, J.; Gutierrez-Cuesta, J.; Crespo-Biel, N.; Alvira, D.; Tajes, M.; Yeste-Velasco, M.; Folch, J.; Canudas, A.; Sureda, F.; et al. Modulation of SIRT1 expression in different neurodegenerative models and human pathologies. Neuroscience 2008, 154, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.L. Sirt1′s Complex Roles in Neuroprotection. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2009, 29, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Gan, L.; Vosler, P.S.; Gao, Y.; Zigmond, M.J.; Chen, J. Protective effects and mechanisms of sirtuins in the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 95, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellimana, A.K.; Diwan, D.; Clarke, J.; Gidday, J.M.; Zipfel, G.J. SIRT1 Activation: A Potential Strategy for Harnessing Endogenous Protection Against Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2018, 65, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellimana, A.K.; Aum, D.J.; Diwan, D.; Clarke, J.V.; Nelson, J.W.; Lawrence, M.; Han, B.H.; Gidday, J.M.; Zipfel, G.J. SIRT1 mediates hypoxic preconditioning induced attenuation of neurovascular dysfunction following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 334, 113484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattagajasingh, I.; Kim, C.-S.; Naqvi, A.; Yamamori, T.; Hoffman, T.A.; Jung, S.-B.; DeRicco, J.; Kasuno, K.; Irani, K. SIRT1 promotes endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation by activating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14855–14860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, S.; He, M.; Sayed, D.; Vashistha, H.; Malhotra, A.; Sadoshima, J.; Vatner, D.E.; Vatner, S.F.; Abdellatif, M. Downregulation of MiR-199a Derepresses Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α and Sirtuin 1 and Recapitulates Hypoxia Preconditioning in Cardiac Myocytes. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamohan, S.B.; Pillai, V.B.; Gupta, M.; Sundaresan, N.R.; Birukov, K.G.; Samant, S.; Hottiger, M.O.; Gupta, M.P. SIRT1 Promotes Cell Survival under Stress by Deacetylation-Dependent Deactivation of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 4116–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Park, K.Y.; Min, H.G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Kim, W.; Cha, H. Negative regulation of stress-induced matrix metallopro-teinase-9 by Sirt1 in skin tissue. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenstein, A.; Stein, S.; Holy, E.W.; Camici, G.G.; Lohmann, C.; Akhmedov, A.; Spescha, R.; Elliott, P.J.; Westphal, C.H.; Matter, C.M.; et al. Sirt1 inhibition promotes in vivo arterial thrombosis and tissue factor expression in stimulated cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 89, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, G.V.; Alexander, J.S.; Babu, P.P. PARP-1 cleavage fragments: Signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell Commun. Signal. 2010, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellimana, A.K.; Milner, E.; Azad, T.D.; Harries, M.D.; Zhou, M.-L.; Gidday, J.M.; Han, B.H.; Zipfel, G.J. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Mediates Endogenous Protection Against Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Cerebral Vasospasm. Stroke 2011, 42, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillarisetti, S. A Review of Sirt1 and Sirt1 Modulators in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. Recent Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov. 2008, 3, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Stein, L.; Imai, S. The Role of Mammalian Sirtuins in the Regulation of Metabolism, Aging, and Longevity. Organotypic Models Drug Dev. 2011, 206, 125–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, A.P.; Dave, K.R.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Resveratrol Mimics Ischemic Preconditioning in the Brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 26, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pinzon, M.A.; Koronowski, K.B. Sirt1 in cerebral ischemia. Brain Circ. 2015, 1, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-S.; Wu, Q.; Wu, L.-Y.; Ye, Z.-N.; Jiang, T.-W.; Ling-Yun, W.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, M.-L.; Zhang, X.; Hang, C.-H. Sirtuin 1 activation protects against early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Jin, J.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Mo, H.; Chen, G. SIRT1 activation by resveratrol reduces brain edema and neuronal apoptosis in an experimental rat subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 9627–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Han, X. Resveratrol alleviates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage: Possible involvement of the AMPK/SIRT1/autophagy signaling pathway. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athiraman, U.; Aum, D.; Vellimana, A.K.; Osbun, J.W.; Dhar, R.; Tempelhoff, R.; Zipfel, G.J. Evidence for a conditioning effect of inhalational anesthetics on angiographic vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 133, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athiraman, U.; Dhar, R.; Jayaraman, K.; Karanikolas, M.; Helsten, D.; Yuan, J.; Lele, A.V.; Rath, G.P.; Tempelhoff, R.; Roth, S.; et al. Conditioning Effect of Inhalational Anesthetics on Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2020, 88, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athiraman, U.; Liu, M.; Jayaraman, K.; Yuan, J.; Mehla, J.; Zipfel, G.J. Anesthetic and subanesthetic doses of isoflurane conditioning provides strong protection against delayed cerebral ischemia in a mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain Res. 2021, 1750, 147169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athiraman, U.; Zipfel, G.J. Anesthetic Conditioning for Secondary Brain Injury After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2020, 143, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Miguelez, P.; Lima-Cabello, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Almar, M.; Cuevas, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelial nitric oxide synthase induced by eccentric exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alique, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; Bodega, G.; Giannarelli, C.; Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α: The Master Regulator of Endothelial Cell Senescence in Vascular Aging. Cells 2020, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, S.; Papadakis, M.; Chen, R.; Hoyte, L.C.; Brooks, K.J.; Gallichan, D.; Sibson, N.R.; Pugh, C.; Buchan, A.M. Neuroprotection by Dimethyloxalylglycine following Permanent and Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 31, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.-H.; Fang, H.-J.; Zheng, G.-H.; Liang, X.-H.; Ding, Y.-R.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.-P. DPP-4 inhibitors promote proliferation and migration of rat brain microvascular endothelial cells under hypoxic/high-glucose conditions, potentially through the SIRT1/HIF-1/VEGF pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 25, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Qiang, H.; Mang-Qiao, S.; Fen, X.; Shan-Shan, L.; Hui-Juan, C.; Wu-Gang, H.; Wen-Jun, Y.; Zheng-Wu, P. Sirt1 mediates improvement of isoflurane-induced memory impairment following hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning in middle-aged mice. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 195, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Han, Q.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, A. Chikusetsu saponin IVa attenuates isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and cognitive def-icits via SIRT1/ERK1/2 in developmental rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 4288–4299. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Fang, L. AMPK-SIRT1 pathway dysfunction contributes to neuron apoptosis and cognitive impairment induced by sevoflurane. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-Y.; Li, Q.-J.; Zhang, W.-C.; Zheng, S.-Q.; Qu, Z.-J.; Xi, Y.; Wang, G. AMPK-SIRT1-PGC1α Signal Pathway Influences the Cognitive Function of Aged Rats in Sevoflurane-Induced Anesthesia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, B.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ho, K.-K.; Di Fruscia, P.; Myatt, S.S.; Coombes, R.C.; Fuchter, M.J.; Hsiao, C.-D.; Lam, E.W.-F. SIRT Inhibitors Induce Cell Death and p53 Acetylation through Targeting Both SIRT1 and SIRT2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aum, D.J.; Vellimana, A.K.; Singh, I.; Milner, E.; Nelson, J.W.; Han, B.H.; Zipfel, G.J. A novel fluorescent imaging technique for assessment of cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Jayaraman, K.; Giri, T.; Zipfel, G.J.; Athiraman, U. Role of SIRT1 in Isoflurane Conditioning-Induced Neurovascular Protection against Delayed Cerebral Ischemia Secondary to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084291
Liu M, Jayaraman K, Giri T, Zipfel GJ, Athiraman U. Role of SIRT1 in Isoflurane Conditioning-Induced Neurovascular Protection against Delayed Cerebral Ischemia Secondary to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(8):4291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084291
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Meizi, Keshav Jayaraman, Tusar Giri, Gregory J. Zipfel, and Umeshkumar Athiraman. 2021. "Role of SIRT1 in Isoflurane Conditioning-Induced Neurovascular Protection against Delayed Cerebral Ischemia Secondary to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 8: 4291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084291
APA StyleLiu, M., Jayaraman, K., Giri, T., Zipfel, G. J., & Athiraman, U. (2021). Role of SIRT1 in Isoflurane Conditioning-Induced Neurovascular Protection against Delayed Cerebral Ischemia Secondary to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(8), 4291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084291





