Tezepelumab: A Potential New Biological Therapy for Severe Refractory Asthma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
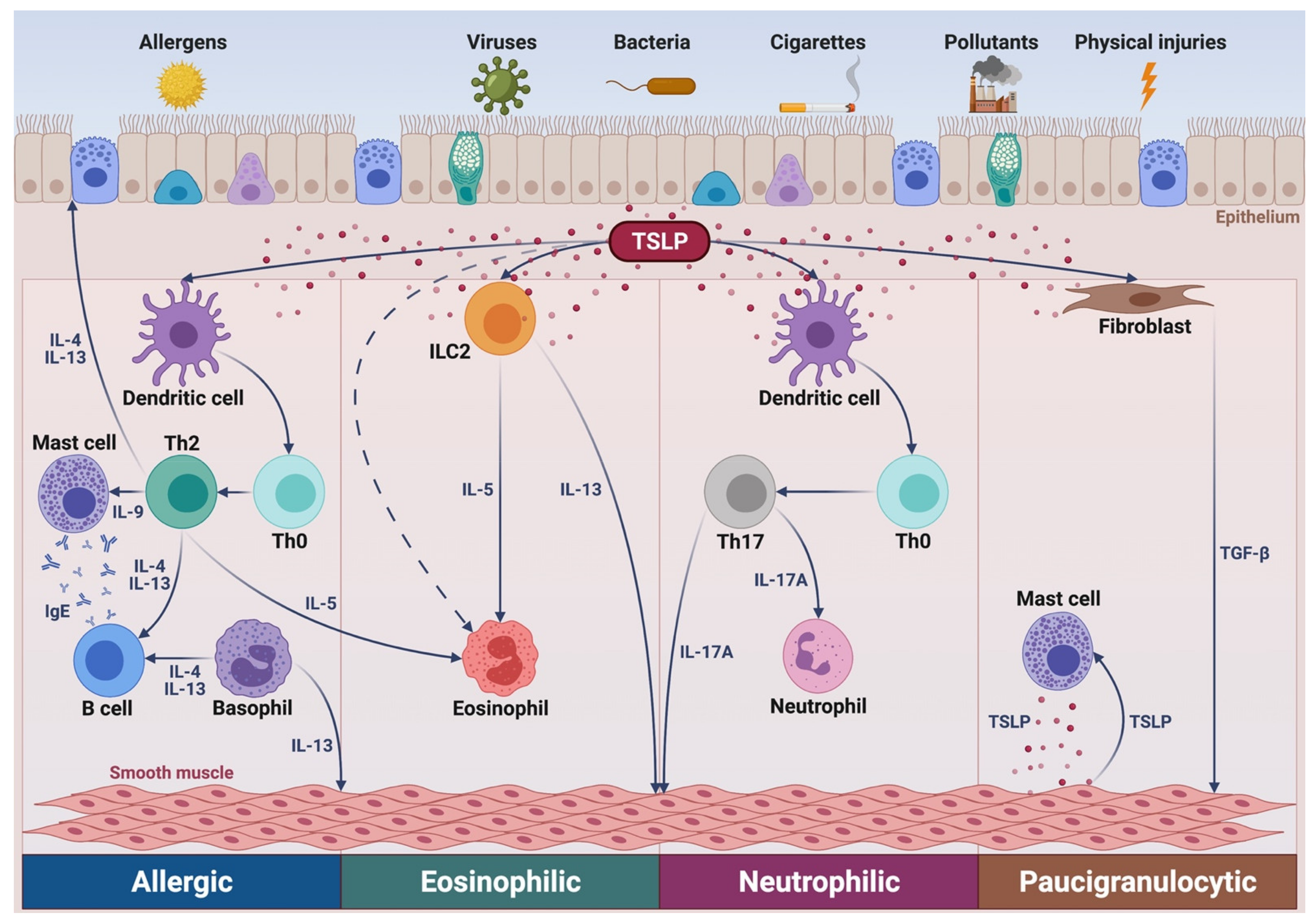
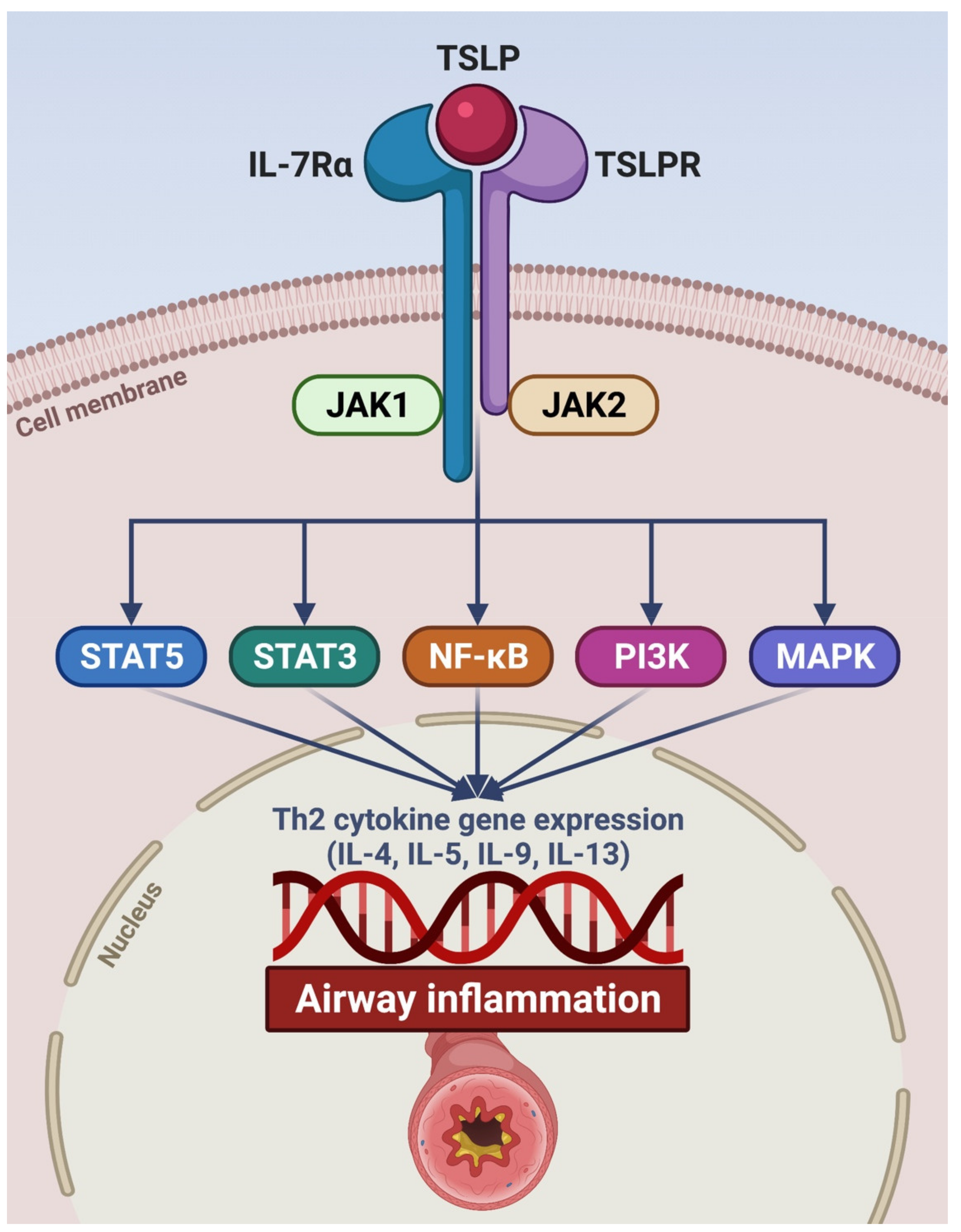
2. Pathogenic Role of TSLP in Asthma
3. Tezepelumab: An Emerging Biologic Therapy for Treatment of Severe Asthma
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, K.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; De Luca, F.; Giorgis, V.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Asthma from immune pathogenesis to precision medicine. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 46, 101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, P.J.; Heaney, L.G. Different endotypes and phenotypes drive the heterogeneity in severe asthma. Allergy 2020, 75, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suraya, R.; Nagano, T.; Katsurada, M.; Sekiya, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Molecular mechanism of asthma and its novel molecular target therapeutic agent. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Vatrella, A.; Tinello, C.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Molecular Targets for Biological Therapies of Severe Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 603312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Zeiger, R.S.; Peters, S.P.; Colice, G.; Newbold, P.; Goldman, M.; Chipps, B.E. Overlap of atopic, eosinophilic, and TH2-high asthma phenotypes in a general population with current asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 116, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.K.; Bush, A.; Stokes, J.; Nair, P.; Akuthota, P. Eosinophilic Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 8, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, T.F.; Zeki, A.A.; Kraft, M. Eosinophilic and Noneosinophilic Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, M.E.; Lee, F.E.-H.; Lee, G.B. Understanding Asthma Phenotypes, Endotypes, and Mechanisms of Disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 56, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tliba, O.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr. Paucigranulocytic asthma: Uncoupling of airway obstruction from inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Philp, A.M.; Corte, T.; Travis, M.A.; Schilter, H.; Hansbro, N.G.; Burns, C.J.; Eapen, M.S.; Sohal, S.S.; Burgess, J.K.; et al. Therapeutic targets in lung tissue remodelling and fibrosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 225, 107839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoettler, N.; Strek, M.E. Recent advances in severe asthma: From phenotypes to personalized medicine. Chest 2020, 157, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The Cytokines of Asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauvreau, G.M.; Sehmi, R.; Ambrose, C.S.; Griffiths, J.M. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: Its role and potential as a therapeutic target in asthma. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Kabata, H.; Kabashima, K.; Asano, K. Anti-TSLP antibodies: Targeting a master regulator of type 2 immune responses. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, P.P.; Tan, Z.; Page, B.D.; Hedtrich, S. TSLP as druggable target—A silver-lining for atopic diseases? Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 217, 107648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, M.M.; Dixon, A.E.; Krishnan, J.A.; Lemanske, R.F.; Pace, W.; Schatz, M. Managing asthma in adolescents and adults: 2020 asthma guideline update from the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. JAMA 2020, 324, 2301–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2020. Available online: www.ginasthma.org (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wangberg, H.; Woessner, K. Choice of biologics in asthma endotypes. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 21, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Calabrese, C.; Terracciano, R.; De Blasio, F.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G. Omalizumab, the first available antibody for biological treatment of severe asthma: More than a decade of real-life effectiveness. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelaia, C.; Vatrella, A.; Busceti, M.T.; Gallelli, L.; Terracciano, R.; Savino, R.; Pelaia, G. Severe eosinophilic asthma: From the pathogenic role of interleukin-5 to the therapeutic action of mepolizumab. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelaia, G.; Vatrella, A.; Busceti, M.T.; Gallelli, L.; Preianò, M.; Lombardo, N.; Terracciano, R.; Maselli, R. Role of biologics in severe eosinophilic asthma—focus on reslizumab. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelaia, C.; Vatrella, A.; Bruni, A.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Benralizumab in the treatment of severe asthma: Design, development and potential place in therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelaia, C.; Vatrella, A.; Gallelli, L.; Terracciano, R.; Navalesi, P.; Maselli, R.; Pelaia, G. Dupilumab for the treatment of asthma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Pelaia, G.; Crimi, C.; Longhini, F.; Lombardo, N.; Savino, R.; Sciacqua, A.; Vatrella, A. Biologics in severe asthma. Minerva Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Spadaro, G.; Braile, M.; Poto, R.; Criscuolo, G.; Pahima, H.; Loffredo, S.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Varricchi, G. Tezepelumab: A novel biological therapy for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP: From allergy to cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilingiri, K.; Fornasa, G.; Rescigno, M. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin: To Cut a Long Story Short. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matera, M.G.; Rogliani, P.; Calzetta, L.; Cazzola, M. TSLP Inhibitors for Asthma: Current Status and Future Prospects. Drugs 2020, 80, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Pecoraro, A.; Marone, G.; Criscuolo, G.; Spadaro, G.; Genovese, A.; Marone, G. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Isoforms, Inflammatory Disorders, and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marković, I.; Savvides, S.N. Modulation of Signaling Mediated by TSLP and IL-7 in Inflammation, Autoimmune Diseases, and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.D.; O’Byrne, P.M. Epithelial-Derived Cytokines in Asthma. Chest 2017, 151, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, D.G.; Ampleford, E.J.; Chiu, G.Y.; Gauderman, W.J.; Gignoux, C.R.; Graves, P.E.; Himes, B.E.; Levin, A.M.; Mathias, R.A.; Hancock, D.B.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of asthma in ethnically diverse North American populations. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 887–892. [Google Scholar]
- Berraïes, A.; Hamdi, B.; Ammar, J.; Hamzaoui, K.; Hamzaoui, A. Increased expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in induced sputum from asthmatic children. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 178, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glück, J.; Rymarczyk, B.; Kasprzak, M.; Rogala, B. Increased Levels of Interleukin-33 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Exhaled Breath Condensate in Chronic Bronchial Asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 169, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Lv, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Corrigan, C.J.; Ying, S. Elevated Expression of IL-33 and TSLP in the Airways of Human Asthmatics In Vivo: A Potential Biomarker of Severe Refractory Disease. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchheit, K.M.; Cahill, K.N.; Katz, H.R.; Murphy, K.C.; Feng, C.; Lee-Sarwar, K.; Lai, J.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Israel, E.; Boyce, J.A.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin controls prostaglandin D 2 generation in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1566–1576.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klose, C.S.N.; Artis, D. Innate lymphoid cells as regulators of immunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camelo, A.; Rosignoli, G.; Ohne, Y.; Stewart, R.A.; Overed-Sayer, C.; Sleeman, M.A.; May, R.D. IL-33, IL-25, and TSLP induce a distinct phenotypic and activation profile in human type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.G.; Chen, R.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Huang, C.; Oliveria, J.-P.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Boulet, L.-P.; Lemiere, C.; Martin, J.; et al. Increased numbers of activated group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of patients with severe asthma and persistent airway eosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 75–86.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Verma, M.; Michalec, L.; Liu, W.; Sripada, A.; Rollins, D.; Good, J.; Ito, Y.; Chu, H.; Gorska, M.M.; et al. Steroid resistance of airway type 2 innate lymphoid cells from patients with severe asthma: The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 257–268.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shikotra, A.; Choy, D.F.; Ohri, C.M.; Doran, E.; Butler, C.; Hargadon, B.; Shelley, M.; Abbas, A.R.; Austin, C.D.; Jackman, J.; et al. Increased expression of immunoreactive thymic stromal lymphopoietin in patients with severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 104–111.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-J.; Fu, C.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, P.-H.; Chen, Y.-W.; Wu, C.-C.; Wu, C.-L.; Kuo, H.-P. Impact of chronic rhinosinusitis on severe asthma patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Hu, S.; Cheung, P.F.; Lam, C.W.K. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces chemotactic and prosurvival effects in eosinophils: Implications in allergic inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, E.B.; Stahl, J.L.; Schwantes, E.A.; Fox, K.E.; Mathur, S.K. IL-3 and TNF-α increase thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor (TSLPR) expression on eosinophils and enhance TSLP-stimulated degranulation. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2012, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Sajee, D.; Sehmi, R.; Hawke, T.J.; El-Gammal, A.; Howie, K.J.; Watson, R.M.; Londei, M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’Byrne, P.M. Expression of IL-33 and TSLP and Their Receptors in Asthmatic Airways after Inhaled Allergen Challenge. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.; Yousefi, S.; Stöckle, C.; Simon, H.-U.; Simon, D. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin stimulates the formation of eosinophil extracellular traps. Allergy 2012, 67, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, B.M.A.; Smith, S.G.; Mukherjee, M.; Plante, S.; Krisna, S.; Nusca, G.; Oliveria, J.P.; Irshad, A.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Chakir, J.; et al. Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell–derived Factors from Severe Asthmatic Subjects Stimulate Eosinophil Differentiation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.G.; Gugilla, A.; Mukherjee, M.; Merim, K.; Irshad, A.; Tang, W.; Kinoshita, T.; Watson, B.; Oliveria, J.-P.; Comeau, M.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and IL-33 modulate migration of hematopoietic progenitor cells in patients with allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, B.M.; Oliveria, J.P.; Nusca, G.; Smith, S.G.; Watson, R.M.; Comeau, M.; Sehmi, R.; Gauvreau, G.M. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin activation of basophils in patients with allergic asthma is IL-3 dependent. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, B.M.; Oliveria, J.P.; Nusca, G.; Smith, S.G.; Tworek, D.; Mitchell, P.D.; Watson, R.M.; Sehmi, R.; Gauvreau, G.M. IL-25 and IL-33 induce Type 2 inflammation in basophils from subjects with allergic asthma. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagarkar, D.R.; Poposki, J.A.; Comeau, M.R.; Biyasheva, A.; Avila, P.C.; Schleimer, R.P.; Kato, A. Airway epithelial cells activate TH2 cytokine production in mast cells through IL-1 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 225–232.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Vatrella, A.; Busceti, M.T.; Gaudio, A.; Garofalo, E.; Bruni, A.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. New treatments for asthma: From the pathogenic role of prostaglandin D2 to the therapeutic effects of fevipiprant. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, P.-D.; Kim, H.-M. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is expressed and produced by caspase-1/NF-κB pathway in mast cells. Cytokine 2011, 54, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allakhverdi, Z.; Comeau, M.R.; Jessup, H.K.; Delespesse, G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a mediator of crosstalk between bronchial smooth muscles and mast cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumelis, V.; Reche, P.A.; Kanzler, H.; Yuan, W.; Edward, G.; Homey, B.; Gilliet, M.; Ho, S.; Antonenko, S.; Lauerma, A.; et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell–mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. The cytokine network in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elder, M.J.; Webster, S.J.; Williams, D.L.; Gaston, J.S.H.; Goodall, J.C. TSLP production by dendritic cells is modulated by IL-1β and components of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 46, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, N.; Hanabuchi, S.; Soumelis, V.; Yuan, W.; Ho, S.; Malefyt, R.D.W.; Liu, Y.-J. Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin promotes dendritic cell–mediated CD4+ T cell homeostatic expansion. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Wang, Y.-H.; Duramad, O.; Hori, T.; Delespesse, G.J.; Watanabe, N.; Qin, F.X.-F.; Yao, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.-J. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Angkasekwinai, P.; Lu, N.; Voo, K.S.; Arima, K.; Hanabuchi, S.; Hippe, A.; Corrigan, C.J.; Dong, C.; Homey, B.; et al. IL-25 augments type 2 immune responses by enhancing the expansion and functions of TSLP-DC–activated Th2 memory cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froidure, A.; Shen, C.; Gras, D.; Van Snick, J.; Chanez, P.; Pilette, C. Myeloid dendritic cells are primed in allergic asthma for thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated induction of Th2 and Th9 responses. Allergy 2014, 69, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Gu, W.; Tan, J.; Jiang, W.; Ji, W. Exosomes from Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin-Activated Dendritic Cells Promote Th2 Differentiation through the OX40 Ligand. Pathobiol. 2019, 86, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattarini, L.; Trichot, C.; Bogiatzi, S.; Grandclaudon, M.; Meller, S.; Keuylian, Z.; Durand, M.; Volpe, E.; Madonna, S.; Cavani, A.; et al. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce human T follicular helper cell differentiation through OX40-ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1529–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, J.-F.; Thompson, L.J.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP drives acute TH2-cell differentiation in lungs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1406–1418.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, Y.; Dienger-Stambaugh, K.; Richgels, P.K.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Kartashov, A.V.; Barski, A.; Hershey, G.K.K.; Leonard, W.J.; Singh, H. TSLP signaling in CD4+T cells programs a pathogenic T helper 2 cell state. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaam8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akamatsu, T.; Watanabe, N.; Kido, M.; Saga, K.; Tanaka, J.; Kuzushima, K.; Nishio, A.; Chiba, T. Human TSLP directly enhances expansion of CD8+ T cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.D.; Vanichsarn, C.; Nadeau, K.C. TSLP directly impairs pulmonary Treg function: Association with aberrant tolerogenic immunity in asthmatic airway. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ray, A.; Kolls, J.K. Neutrophilic Inflammation in Asthma and Association with Disease Severity. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, J.; Watanabe, N.; Kido, M.; Saga, K.; Akamatsu, T.; Nishio, A.; Chiba, T. Human TSLP and TLR3 ligands promote differentiation of Th17 cells with a central memory phenotype under Th2-polarizing conditions. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Bihui, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Yang, B.; Lu, Q. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin epigenetically upregulates Fc receptor γ subunit-related receptors on antigen-presenting cells and induces TH2/TH17 polarization through dectin-2. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1025–1035.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhu, N.S.; Gounni, A.S. Function and mechanisms of TSLP/TSLPR complex in asthma and COPD. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 42, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Redhu, N.S.; Saleh, A.; Halayko, A.J.; Chakir, J.; Gounni, N.S. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor-mediated IL-6 and CC/CXC chemokines expression in human airway smoot muscle: Role of MAPKs (ERK1/2, p38, and JNK) and STAT3 pathways. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 7134–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Dong, L. TSLP promotes asthmatic airway remodeling via p38-STAT3 signaling pathway in human lung fibroblast. Exp. Lung Res. 2018, 44, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczfinska, J.; Pawliczak, R. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and apocynin alter the expression of airway remodeling factors in human rhinovirus-infected cells. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, K.; Peelman, F.; Braun, H.; Lopez, J.; Van Rompaey, D.; Dansercoer, A.; Vandenberghe, I.; Pauwels, K.; Tavernier, J.; Lambrecht, B.N.; et al. Structure and antagonism of the receptor complex mediated by human TSLP in allergy and asthma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauvreau, G.M.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Boulet, L.-P.; Wang, Y.; Cockcroft, D.; Bigler, J.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; Boedigheimer, M.; Davis, B.E.; Dias, C.; et al. Effects of an Anti-TSLP Antibody on Allergen-Induced Asthmatic Responses. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Parnes, J.R.; Wang, L.; Mo, M.; Roseti, S.L.; Griffiths, J.M.; van der Merwe, R. Tezepelumab in adults with uncontrolled asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emson, C.; Corren, J.; Sałapa, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Parnes, J.R.; Colice, G. Efficacy of Tezepelumab in Patients with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma with and without Nasal Polyposis: A Post Hoc Analysis of the Phase 2b PATHWAY Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Karpefors, M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Parnes, J.R.; Colice, G. Tezepelumab Reduces Exacerbations Across All Seasons in Patients with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma: A Post Hoc Analysis of the PATHWAY Phase 2b Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorey-Sten, Z.L.; Shenoy, K.V. Tezepelumab as an emerging therapeutic option for the treatment of severe asthma: Evidence to date. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Colice, G.; Griffiths, J.M.; Almqvist, G.; Ponnarambil, S.; Kaur, P.; Ruberto, G.; Bowen, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Mo, M.; et al. NAVIGATOR: A phase 3 multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tezepelumab in adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Colice, G.; Griffiths, J.M.; Almqvist, G.; Skärby, T.; Piechowiak, T.; Kaur, P.; Bowen, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Mo, M.; et al. SOURCE: A phase 3, multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tezepelumab in reducing oral corticosteroid use in adults with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canonica, G.W.; Colombo, G.L.; Bruno, G.M.; Di Matteo, S.; Martinotti, C.; Blasi, F.; Bucca, C.; Crimi, N.; Paggiaro, P.; Pelaia, G.; et al. Shadow cost of oral corticosteroids-related adverse events: A pharmacoeconomic evaluation applied to real-life data from the Severe Asthma Network in Italy (SANI) registry. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Ponnarambil, S.; Downie, J.; Bowen, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Colice, G. DESTINATION: A phase 3, multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate the long-term safety and tolerability of tezepelumab in adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emson, C.; Diver, S.; Chachi, L.; Megally, A.; Small, C.; Downie, J.; Parnes, J.R.; Bowen, K.; Colice, G.; Brightling, C.E. CASCADE: A phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate the effect of tezepelumab on airway inflammation in patients with uncontrolled asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E. Unmet need in severe, uncontrolled asthma: Can anti-TSLP therapy with tezepelumab provide a valuable new treatment option? Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsbjerg, C.M.; Sverrild, A.; Lloyd, C.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Bel, E.H. Anti-alarmins in asthma: Targeting the airway epithelium with next-generation biologics. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.C.; Wenzel, S.E. Intersection of biology and therapeutics: Type 2 targeted therapeutics for adult asthma. Lancet 2020, 395, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, A.; De Feyter, S.; Maes, T.; Joos, G.; LaHousse, L. Monoclonal antibodies in type 2 asthma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelaia, C.; Pelaia, G.; Crimi, C.; Maglio, A.; Gallelli, L.; Terracciano, R.; Vatrella, A. Tezepelumab: A Potential New Biological Therapy for Severe Refractory Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094369
Pelaia C, Pelaia G, Crimi C, Maglio A, Gallelli L, Terracciano R, Vatrella A. Tezepelumab: A Potential New Biological Therapy for Severe Refractory Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094369
Chicago/Turabian StylePelaia, Corrado, Giulia Pelaia, Claudia Crimi, Angelantonio Maglio, Luca Gallelli, Rosa Terracciano, and Alessandro Vatrella. 2021. "Tezepelumab: A Potential New Biological Therapy for Severe Refractory Asthma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094369
APA StylePelaia, C., Pelaia, G., Crimi, C., Maglio, A., Gallelli, L., Terracciano, R., & Vatrella, A. (2021). Tezepelumab: A Potential New Biological Therapy for Severe Refractory Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094369










