Discovery–Versus Hypothesis–Driven Detection of Protein–Protein Interactions and Complexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Targeted and Untargeted Interactome Screens
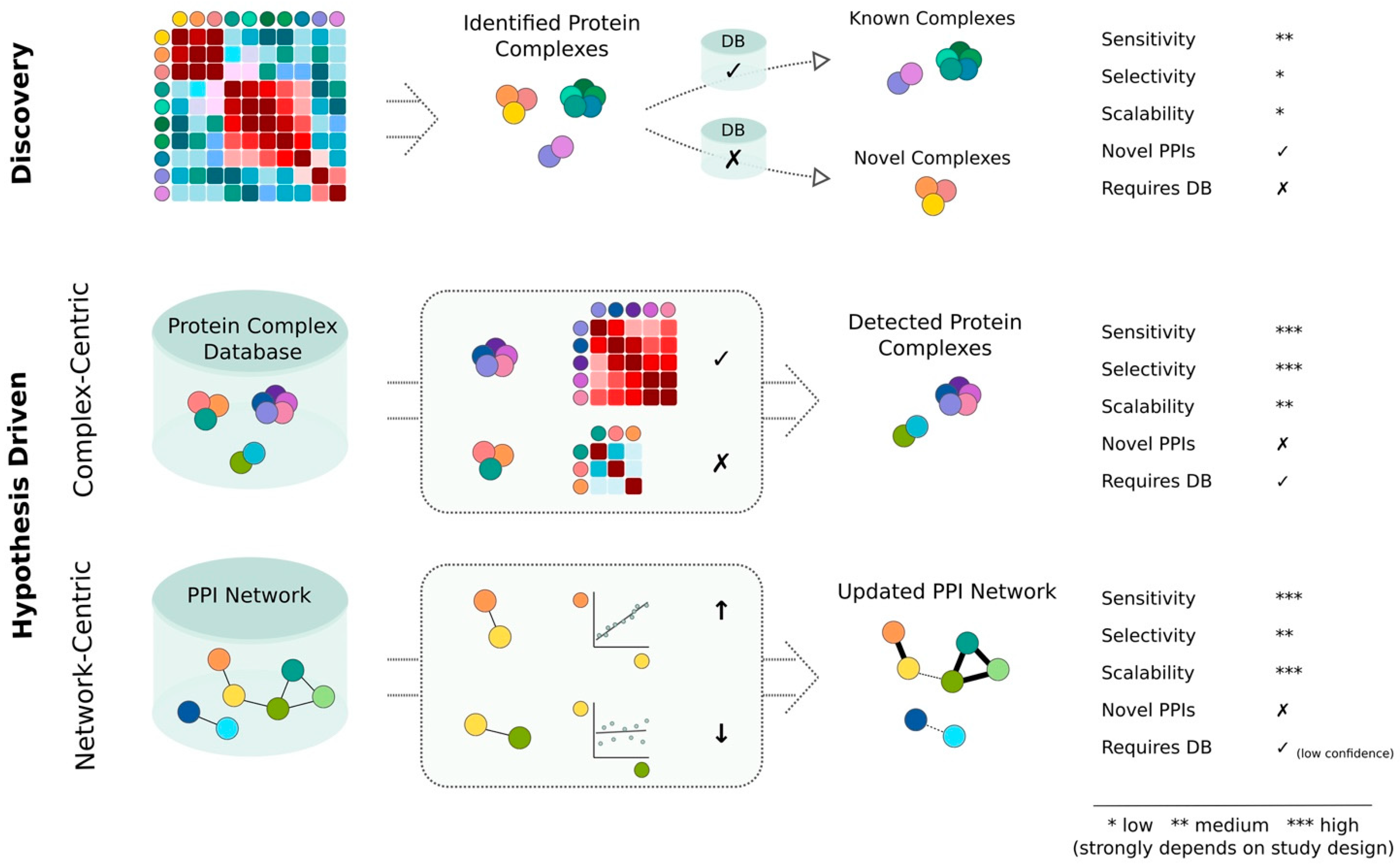
3. Discovery and Hypothesis Driven Data Analysis Strategies
4. Protein Complex and PPI Databases
5. Considerations for the Selection of Interactome Acquisition and Analysis Approaches
6. Summary and Future Perspectives
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, C.; Borgeson, B.; Phanse, S.; Tu, F.; Drew, K.; Clark, G.W.; Xiong, X.; Kagan, O.; Kwan, J.; Berzginov, A.; et al. Panorama of ancient metazoan macromolecular complexes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 525, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergendahl, L.T.; Gerasimavicius, L.; Miles, J.; Macdonald, L.; Wells, J.N.; Welburn, J.P.I.; Marsh, J.A. The role of protein complexes in human genetic disease. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebersold, R.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 422, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebersold, R.; Mann, M. Mass-spectrometric exploration of proteome structure and function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 537, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bludau, I.; Aebersold, R. Proteomic and interactomic insights into the molecular basis of cell functional diversity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttlin, E.L.; Ting, L.; Bruckner, R.J.; Gebreab, F.; Gygi, M.P.; Szpyt, J.; Tam, S.; Zarraga, G.; Colby, G.; Baltier, K.; et al. The BioPlex Network: A Systematic Exploration of the Human Interactome. Cell 2015, 162, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hein, M.Y.; Hubner, N.C.; Poser, I.; Cox, J.; Nagaraj, N.; Toyoda, Y.; Gak, I.A.; Weisswange, I.; Mansfeld, J.; Buchholz, F.; et al. A Human Interactome in Three Quantitative Dimensions Organized by Stoichiometries and Abundances. Cell 2015, 163, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buljan, M.; Ciuffa, R.; van Drogen, A.; Snijder, B.; Aebersold, R.; Gstaiger, M.; Lee, S.; Varjosalo, M.; Pernas, L.E.; Spegg, V.; et al. Kinase Interaction Network Expands Functional and Disease Roles of Human Kinases. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 504–520.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttlin, E.L.; Bruckner, R.J.; Paulo, J.A.; Cannon, J.R.; Ting, L.; Baltier, K.; Colby, G.; Gebreab, F.; Gygi, M.P.; Parzen, H.; et al. Architecture of the human interactome defines protein communities and disease networks. Nature 2017, 545, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttlin, E.L.; Bruckner, R.J.; Navarrete-Perea, J.; Cannon, J.R.; Baltier, K.; Gebreab, F.; Gygi, M.P.; Thornock, A.; Zarraga, G.; Tam, S.; et al. Dual Proteome-scale Networks Reveal Cell-specific Remodeling of the Human Interactome. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roux, K.J.; Kim, D.I.; Raida, M.; Burke, B. A promiscuous biotin ligase fusion protein identifies proximal and interacting proteins in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martell, J.D.; Deerinck, T.J.; Sancak, Y.; Poulos, T.L.; Mootha, V.K.; Sosinsky, G.E.; Ellisman, M.H.; Ting, A.Y. Engineered ascorbate peroxidase as a genetically encoded reporter for electron microscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trinkle-Mulcahy, L. Recent advances in proximity-based labeling methods for interactome mapping [version 1; referees: 2 approved]. F1000Research 2019, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gingras, A.-C.; Abe, K.T.; Raught, B. Getting to know the neighborhood: Using proximity-dependent biotinylation to characterize protein complexes and map organelles. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 48, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, C.D.; Knight, J.D.R.; Rajasekharan, A.; Rathod, B.; Hesketh, G.G.; Abe, K.T.; Youn, J.-Y.; Samavarchi-Tehrani, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.Y.; et al. A proximity biotinylation map of a human cell. BioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holding, A.N. XL-MS: Protein cross-linking coupled with mass spectrometry. Methods 2015, 89, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Lössl, P.; Scheltema, R.; Viner, R.; Heck, A.J.R. Optimized fragmentation schemes and data analysis strategies for proteome-wide cross-link identification. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, M.; Iacobucci, C.; Ihling, C.H.; Sinz, A. A Simple Cross-Linking/Mass Spectrometry Workflow for Studying System-wide Protein Interactions. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10236–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iacobucci, C.; Götze, M.; Sinz, A. Cross-linking/mass spectrometry to get a closer view on protein interaction networks. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 63, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, J.D.; Bruce, J.E. Chemical cross-linking with mass spectrometry: A tool for systems structural biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 48, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, J.S.; Wilkinson, C.J.; Mayor, T.; Mortensen, P.; Nigg, E.A.; Mann, M. Proteomic characterization of the human centrosome by protein correlation profiling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 426, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, M. The Origins of Organellar Mapping by Protein Correlation Profiling. Proteomics 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havugimana, P.C.; Hart, G.T.; Nepusz, T.; Yang, H.; Turinsky, A.L.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.I.; Boutz, D.R.; Fong, V.; Phanse, S.; et al. A Census of Human Soluble Protein Complexes. Cell 2012, 150, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirkwood, K.J.; Ahmad, Y.; Larance, M.; Lamond, A.I. Characterization of Native Protein Complexes and Protein Isoform Variation Using Size-fractionation-based Quantitative Proteomics*. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 3851–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, A.R.; Foster, L.J. Protein Correlation Profiling-SILAC to Study Protein-Protein Interactions; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Bludau, I.; Rosenberger, G.; Hafen, R.; Frank, M.; Banaei-Esfahani, A.; Van Drogen, A.; Collins, B.C.; Gstaiger, M.; Aebersold, R. Complex-centric proteome profiling by SEC SWATH MS. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2019, 15, e8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinnider, M.A.; Scott, N.E.; Prudova, A.; Stoynov, N.; Stacey, R.G.; Gsponer, J.; Foster, L. An Atlas of Protein-Protein Interactions Across Mammalian Tissues. SSRN Electron. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, A.; Li, C.; Uliana, F.; Went, F.; Frommelt, F.; Sykacek, P.; Heusel, M.; Hallal, M.; Bludau, I.; Capraz, T.; et al. PCprophet: A framework for protein complex prediction and differential analysis using proteomic data. Nat. Methods 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitski, M.M.; Reinhard, F.B.M.; Franken, H.; Werner, T.; Savitski, M.F.; Eberhard, D.; Molina, D.M.; Jafari, R.; Dovega, R.B.; Klaeger, S.; et al. Tracking cancer drugs in living cells by thermal profiling of the proteome. Science 2014, 346, 1255784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.S.H.; Go, K.D.; Bisteau, X.; Dai, L.; Yong, C.H.; Prabhu, N.; Ozturk, M.B.; Lim, Y.T.; Sreekumar, L.; Lengqvist, J.; et al. Thermal proximity coaggregation for system-wide profiling of protein complex dynamics in cells. Science 2018, 359, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becher, I.; Andrés-Pons, A.; Romanov, N.; Stein, F.; Schramm, M.; Baudin, F.; Helm, D.; Kurzawa, N.; Mateus, A.; Mackmull, M.-T.; et al. Pervasive Protein Thermal Stability Variation during the Cell Cycle. Cell 2018, 173, 1495–1507.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; Zhao, T.; Bisteau, X.; Sun, W.; Prabhu, N.; Lim, Y.T.; Sobota, R.M.; Kaldis, P.; Nordlund, P. Modulation of Protein-Interaction States through the Cell Cycle. Cell 2018, 173, 1481–1494.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heusel, M.; Frank, M.; Köhler, M.; Amon, S.; Frommelt, F.; Rosenberger, G.; Bludau, I.; Aulakh, S.; Linder, M.I.; Liu, Y.; et al. A Global Screen for Assembly State Changes of the Mitotic Proteome by SEC-SWATH-MS. Cell Syst. 2020, 10, 133–155.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romanov, N.; Kuhn, M.; Aebersold, R.; Ori, A.; Beck, M.; Bork, P. Disentangling Genetic and Environmental Effects on the Proteotypes of Individuals. Cell 2019, 177, 1308–1318.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stalder, L.; Banaei-Esfahani, A.; Ciuffa, R.; Payne, J.L.; Aebersold, R. SWATH-MS Co-Expression Profiles Reveal Paralogue 1 Interference in Protein Complex Evolution 2 3 n.d. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Z.; Goebels, F.; Tan, J.H.; Wolf, E.; Kuzmanov, U.; Wan, C.; Phanse, S.; Xu, C.; Schertzberg, M.; Fraser, A.G.; et al. EPIC: Software toolkit for elution profile-based inference of protein complexes. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, R.G.; Skinnider, M.A.; Scott, N.E.; Foster, L.J. A rapid and accurate approach for prediction of interactomes from co-elution data (PrInCE). BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Yang, W.-C.; Gao, Q.; Regnier, F. Toward chromatographic analysis of interacting protein networks. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1178, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Yang, L.L.; Williams, K.; Fisher, S.J.; Hall, S.C.; Biggin, M.D.; Jin, J.; Witkowska, H.E. A “Tagless” Strategy for Identification of Stable Protein Complexes Genome-wide by Multidimensional Orthogonal Chromatographic Separation and iTRAQ Reagent Tracking. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, A.R.; Gsponer, J.; Foster, L.J. A high-throughput approach for measuring temporal changes in the interactome. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, N.E.; Brown, L.M.; Kristensen, A.R.; Foster, L.J. Development of a computational framework for the analysis of protein correlation profiling and spatial proteomics experiments. J. Proteom. 2015, 118, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bludau, I.; Heusel, M.; Frank, M.; Rosenberger, G.; Hafen, R.; Banaei-Esfahani, A.; Van Drogen, A.; Collins, B.C.; Gstaiger, M.; Aebersold, R. Complex-centric proteome profiling by SEC-SWATH-MS for the parallel detection of hundreds of protein complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2341–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, K.; Lee, C.; Huizar, R.L.; Tu, F.; Borgeson, B.; McWhite, C.D.; Ma, Y.; Wallingford, J.B.; Marcotte, E.M. Integration of over 9000 mass spectrometry experiments builds a global map of human protein complexes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, L.C.; Navarro, P.; Tate, S.; Röst, H.; Selevsek, N.; Reiter, L.; Bonner, R.; Aebersold, R. Targeted Data Extraction of the MS/MS Spectra Generated by Data-independent Acquisition: A New Concept for Consistent and Accurate Proteome Analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ting, Y.S.; Egertson, J.D.; Payne, S.H.; Kim, S.; MacLean, B.; Käll, L.; Aebersold, R.; Smith, R.D.; Noble, W.S.; MacCoss, M.J. Peptide-Centric Proteome Analysis: An Alternative Strategy for the Analysis of Tandem Mass Spectrometry Data. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruepp, A.; Waegele, B.; Lechner, M.; Brauner, B.; Dunger-Kaltenbach, I.; Fobo, G.; Frishman, G.; Montrone, C.; Mewes, H.-W. CORUM: The comprehensive resource of mammalian protein complexes—2009. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 38, D497–D501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ori, A.; Iskar, M.; Buczak, K.; Kastritis, P.; Parca, L.; Andrés-Pons, A.; Singer, S.; Bork, P.; Beck, M. Spatiotemporal variation of mammalian protein complex stoichiometries. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberger, G.; Heusel, M.; Bludau, I.; Collins, B.C.; Martelli, C.; Williams, E.G.; Xue, P.; Liu, Y.; Aebersold, R.; Califano, A. SECAT: Quantifying Protein Complex Dynamics across Cell States by Network-Centric Analysis of SEC-SWATH-MS Profiles. Cell Syst. 2020, 11, 589–607.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, J.I.; Deng, L.; Murray, D.; Shapira, S.; Petrey, N.; Honig, B. A computational interactome and functional annotation for the human proteome. eLife 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepusz, T.; Yu, H.; Paccanaro, A. Detecting overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction networks. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruderer, R.; Bernhardt, O.M.; Gandhi, T.; Miladinović, S.M.; Cheng, L.-Y.; Messner, S.; Ehrenberger, T.; Zanotelli, V.; Butscheid, Y.; Escher, C.; et al. Extending the Limits of Quantitative Proteome Profiling with Data-Independent Acquisition and Application to Acetaminophen-Treated Three-Dimensional Liver Microtissues. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsou, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-F.; Teo, G.C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Nesvizhskii, A.I. Untargeted, spectral library-free analysis of data-independent acquisition proteomics data generated using Orbitrap mass spectrometers. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2257–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Röst, H.L.; Rosenberger, G.; Navarro, P.; Gillet, L.C.J.; Miladinović, S.M.; Schubert, O.T.; Wolski, W.E.; Collins, B.C.; Malmström, J.; Malmström, L.; et al. OpenSWATH enables automated, targeted analysis of data-independent acquisition MS data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.K.; Carlin, D.E.; Yu, M.K.; Zhang, W.; Kreisberg, J.F.; Tamayo, P.; Ideker, T. Systematic Evaluation of Molecular Networks for Discovery of Disease Genes. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 484–495.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giurgiu, M.; Reinhard, J.; Brauner, B.; Dunger-Kaltenbach, I.; Fobo, G.; Frishman, G.; Montrone, C.; Ruepp, A. CORUM: The comprehensive resource of mammalian protein complexes—2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D559–D563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casanova, E.B.; Bye-A-Jee, H.; Perfetto, L.; Lopez, M.R.; del-Toro, N.; Porras, P.; Perfetto, L.; Pokorný, D.; Lopez, M.R.; Türková, A.; et al. Complex Portal 2018: Extended content and enhanced visualization tools for macromolecular complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D550–D558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, K.; Wallingford, J.B.; Marcotte, E.M. hu.MAP 2.0: Integration of over 15,000 proteomic experiments builds a global compendium of human multiprotein assemblies n.d. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, S.; Ammari, M.; Aranda, B.; Breuza, L.; Briganti, L.; Broackes-Carter, F.; Campbell, N.H.; Chavali, G.; Chen, C.; Del-Toro, N.; et al. The MIntAct project—IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D358–D363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oughtred, R.; Rust, J.; Chang, C.; Breitkreutz, B.; Stark, C.; Willems, A.; Boucher, L.; Leung, G.; Kolas, N.; Zhang, F.; et al. TheBioGRIDdatabase: A comprehensive biomedical resource of curated protein, genetic, and chemical interactions. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, D.; Stacey, R.G.; Akinlaja, M.; Foster, L.J. Next-generation Interactomics: Considerations for the Use of Co-elution to Measure Protein Interaction Networks. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larance, M.; Kirkwood, K.J.; Tinti, M.; Murillo, A.B.; Ferguson, M.A.J.; Lamond, A.I. Global Membrane Protein Interactome Analysis using In vivo Crosslinking and Mass Spectrometry-based Protein Correlation Profiling. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 2476–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meier, F.; Brunner, A.-D.; Frank, M.; Ha, A.; Bludau, I.; Voytik, E.; Kaspar-Schoenefeld, S.; Lubeck, M.; Raether, O.; Bache, N.; et al. diaPASEF: Parallel accumulation–serial fragmentation combined with data-independent acquisition. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, A.D.; Thielert, M.; Vasilopoulou, C.; Ammar, C.; Coscia, F.; Mund, A.; Horning, O.B.; Bache, N.; Apalategui, A.; Lubeck, M.; et al. Ultra-high sensitivity mass spectrometry quantifies single-cell proteome changes upon perturbation. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zheng, R.; Bayer, F.P.; Wong, C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Meng, C.; Zolg, D.P.; Reinecke, M.; Zecha, J.; Wiechmann, S.; et al. Robust, reproducible and quantitative analysis of thousands of proteomes by micro-flow LC–MS/MS. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bache, N.; Geyer, P.E.; Bekker-Jensen, D.B.; Hoerning, O.; Falkenby, L.; Treit, P.V.; Doll, S.; Paron, I.; Müller, J.B.; Meier, F.; et al. A Novel LC System Embeds Analytes in Pre-formed Gradients for Rapid, Ultra-robust Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| DB | Information | Interaction type | Organisms | Size | Website | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complexes | CORUM 3.0 | Manually curated from experimental data | Direct (physical) interactions | Human (67%) Mouse (15%) Rat (10%) & other mammals | 4274 complexes based on 4473 genes (including 22% of human protein coding genes) | http://mips.helmholtz-muenchen.de/corum/ (accessed on 9 March 2021) |
| Complex Portal (accessed 9 March 2021) | Manually curated from experimental data | Direct (physical) interactions | 26 organisms across all domains of life |
| http://www.ebi.ac.uk/complexportal (accessed on 9 March 2021) | |
| huMap 2.0 | Integration of over 15,000 mass spectrometry experiments | Direct (physical) interactions (and proximity interactions) | Human | 6969 complexes consisting of 57,178 unique interactions among 9,968 proteins | http://humap2.proteincomplexes.org/ (accessed on 9 March 2021) | |
| PPIs | IntAct (accessed 11 March 2021) | Manually curated from experimental data | Direct (physical) interactions | Human (61%) Yeast (12%) Mouse (8%) & other organisms across all domains of life | 1,130,596 interactions among 119,281 proteins | http://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact (accessed on 9 March 2021) |
| BioGRID 4.3 | Manually curated from experimental data | Direct (physical) interactions and genetic interactions | 70 species |
| https://thebiogrid.org/ (accessed on 9 March 2021) | |
| BioPlex 3.0 | Experimental | Direct (physical) interactions | Human | 118,162 interactions among 14,586 proteins | https://bioplex.hms.harvard.edu/ (accessed on 9 March 2021) | |
| PrePPI | Predicted | Direct (physical) and indirect (functional) interactions | Human | PrePPI contains 1.35 million PPIs for ~85% of the human proteome | http://bhapp.c2b2.columbia.edu/PrePPI (accessed on 9 March 2021) | |
| STRING v11 | Experimental & predicted | Direct (physical) and indirect (functional) interactions | 5090 different organisms | >2000 million unique interactions among 24.6 million proteins | https://string-db.org/ (accessed on 9 March 2021) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bludau, I. Discovery–Versus Hypothesis–Driven Detection of Protein–Protein Interactions and Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094450
Bludau I. Discovery–Versus Hypothesis–Driven Detection of Protein–Protein Interactions and Complexes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094450
Chicago/Turabian StyleBludau, Isabell. 2021. "Discovery–Versus Hypothesis–Driven Detection of Protein–Protein Interactions and Complexes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094450
APA StyleBludau, I. (2021). Discovery–Versus Hypothesis–Driven Detection of Protein–Protein Interactions and Complexes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094450






