Dysregulation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAA) in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2-Possible Clinical Consequences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Angiotensin Metabolism
- angiotensin 2 to angiotensin (1-7) according to the Equation:angiotensin 2 + H2O → angiotensin (1-7) + phenylalanine
- angiotenisin 1 to angiotensin (1-9) according to the Equation:angiotensin 1 + H2O → angiotensin (1-9) + leucine
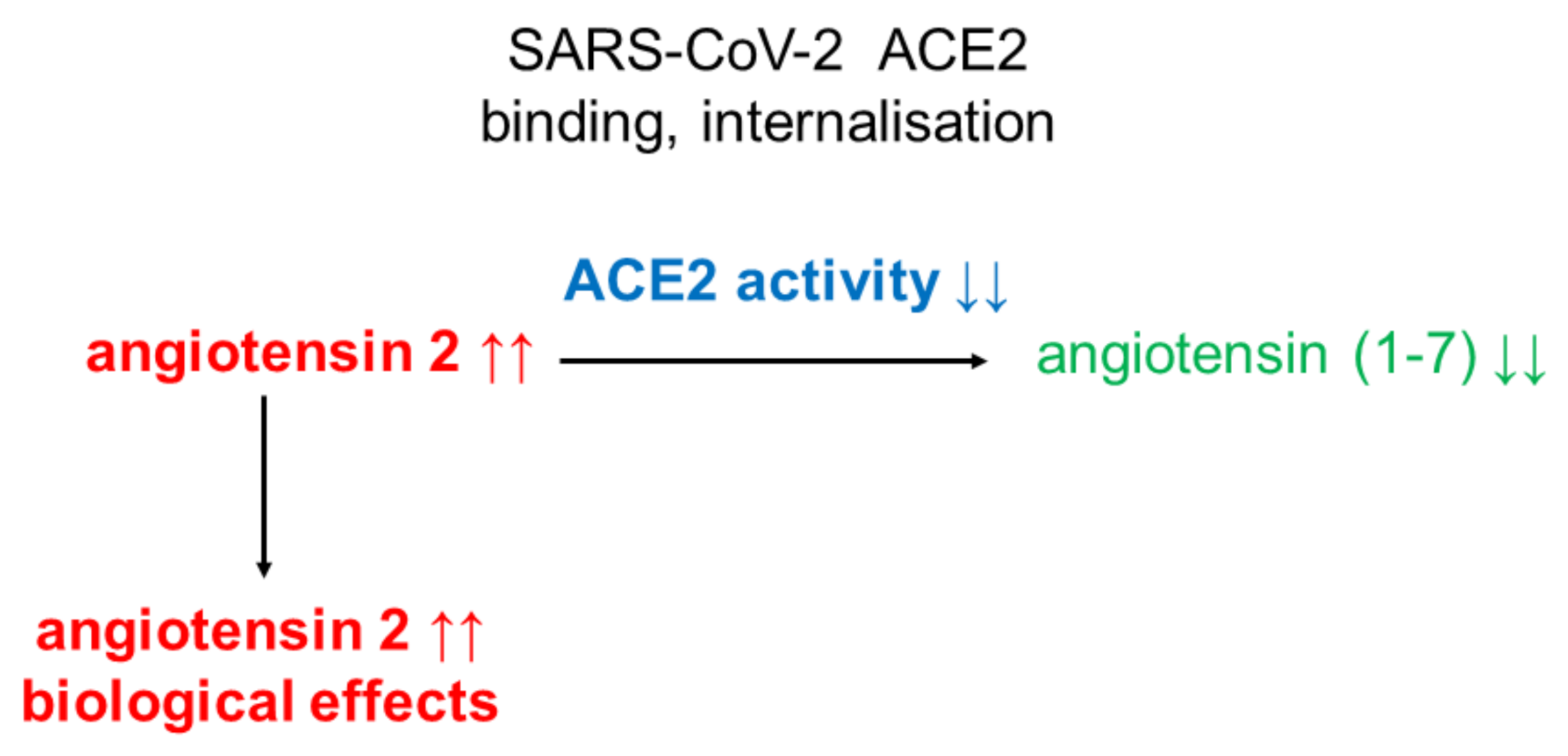
3. SARS-CoV-2
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmerman, B.G. Monoclonal antibodies and nonpeptide antagonists to angiotensin II. Potential implications. Hypertension 1989, 14, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, H.; Bruno, J.G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, T.K. Aptamers in the Therapeutics and Diagnostics Pipelines. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4016–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, A.; Weber, A.; Bayin, M.; Breuers, S.; Fieberg, V.; Famulok, M.; Mayer, G. A SARS-CoV-2 Spike Binding DNA Aptamer that Inhibits Pseudovirus Infection by an RBD-Independent Mechanism. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhinan, A. Applications of Aptasensors in Health Care. Mater. Res. Found. 2019, 47, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Karakiulakis, G.; Roth, M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, A.M.; Tomlinson, L.; Edmonston, D.; Hiremath, S.; Sparks, M.A. Controversies of renin–angiotensin system inhibition during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burrell, L.M.; Risvanis, J.; Kubota, E.; Dean, R.G.; Macdonald, P.S.; Lu, S.; Tikellis, C.; Grant, S.L.; Lew, R.A.; Smith, A.I.; et al. Myocardial infarction increases ACE2 expression in rat and humans. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramchand, J.; Patel, S.K.; Kearney, L.G.; Matalanis, G.; Farouque, O.; Srivastava, P.M.; Burrell, L.M. Plasma ACE2 Activity Predicts Mortality in Aortic Stenosis and Is Associated With Severe Myocardial Fibrosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Rauf, A.; Khan, H.; Abu-Izneid, T. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): The ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M.; Siragy, H.M. Newly recognized components of the renin-angiotensin system: Potential roles in cardiovascular and renal regulation. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atlas, S.A. The Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System: Pathophysiological Role and Pharmacologic Inhibition. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2007, 13, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A Human Homolog of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33238–33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serfozo, P.; Wysocki, J.; Gulua, G.; Schulze, A.; Ye, M.; Liu, P.; Jin, J.; Bader, M.; Myöhänen, T.; García-Horsman, J.A.; et al. Ang II (Angiotensin II) Conversion to Angiotensin-(1-7) in the Circulation Is POP (Prolyloligopeptidase)-Dependent and ACE2 (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2)-Independent. Hypertension 2020, 75, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungnak, W.; Huang, N.; Bécavin, C.; Berg, M.; Queen, R.; Litvinukova, M.; Talavera-López, C.; Maatz, H.; Reichart, D.; Sampaziotis, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamming, V.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.J.; Van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lely, A.T.; Hamming, V.; Van Goor, H.; Navis, G.J. Renal ACE2 expression in human kidney disease. J. Pathol. 2004, 204, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, D.; Wysocki, J.; Soler, M.J.; Ranganath, K. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Enhancing the degradation of angiotensin II as a potential therapy for diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Chappell, M.C.; Tallant, E.A.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Diz, D.I. Counterregulatory Actions of Angiotensin-(1-7). Hypertension 1997, 30, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, C.; Hales, P.; Kaushik, V.; Dick, L.; Gavin, J.; Tang, J.; Godbout, K.; Parsons, T.; Baronas, E.; Hsieh, F.; et al. Hydrolysis of Biological Peptides by Human Angiotensin-converting Enzyme-related Carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14838–14843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme–Related Carboxypeptidase (ACE2) Converts Angiotensin I to Angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M. ACE2: More of Ang-(1–7) or less Ang II? Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2011, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chappell, M.C. Biochemical evaluation of the renin-angiotensin system: The good, bad, and absolute? Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 310, H137–H152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaimes, J.A.; André, N.M.; Chappie, J.S.; Millet, J.K.; Whittaker, G.R. Phylogenetic Analysis and Structural Modeling of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Reveals an Evolutionary Distinct and Proteolytically Sensitive Activation Loop. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 3309–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Pöhlmann, S. A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells. Mol. Cell. 2020, 78, 779–784.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Feng, C.; et al. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.-H.; Deng, W.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Y.-X.; Zhang, L.-F.; Zhu, H.; Gao, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.-L.; Ma, C.-M.; et al. Mice transgenic for human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 provide a model for SARS coronavirus infection. Comp. Med. 2007, 57, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Rao, S.; Huan, Y.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Yang, P.; Sarao, R.; Wada, T.; Leong-Poi, H.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 436, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, T.E.; Kalman, J.M.; Patel, S.K.; Mearns, M.; Velkoska, E.; Burrell, L.M. Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity and human atrial fibrillation: Increased plasma angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity is associated with atrial fibrillation and more advanced left atrial structural remodelling. EP Eur. 2017, 19, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchand, J.; Patel, S.K.; Srivastava, P.M.; Farouque, O.; Burrell, L.M. Elevated plasma angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity is an independent predictor of major adverse cardiac events in patients with obstructive coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelman, S.; Tang, W.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Van Lente, F.; Francis, G.S.; Sen, S. Detection of Soluble Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soro-Paavonen, A.; Gordin, D.; Forsblom, C.; Rosengard-Barlund, M.; Waden, J.; Thorn, L.; Sandholm, N.; Thomas, M.C.; Groop, P.-H. Circulating ACE2 activity is increased in patients with type 1 diabetes and vascular complications. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Jessup, J.; Chappell, M.C.; Averill, D.B.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Tallant, E.A.; Diz, D.I.; Gallagher, P.E. Effect of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on Cardiac Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2. Circulation 2005, 111, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soler, M.J.; Ye, M.; Wysocki, J.; William, J.; Lloveras, J.; Batlle, D. Localization of ACE2 in the renal vasculature: Amplification by angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade using telmisartan. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009, 296, F398–F405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Dong, X.; Cao, Y.Y.; Yuan, Y.D.; Yang, Y.B.; Yan, Y.Q.; Akdis, C.A.; Gao, Y.D. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 2020, 75, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus–induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sriramula, S.; Xia, H.; Moreno-Walton, L.; Culicchia, F.; Domenig, O.; Poglitsch, M.; Lazartigues, E. Clinical Relevance and Role of Neuronal AT1 Receptors in ADAM17-Mediated ACE2 Shedding in Neurogenic Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, J.; Goodling, A.; Burgaya, M.; Whitlock, K.; Ruzinski, J.; Batlle, D.; Afkarian, M. Urine RAS components in mice and people with type 1 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2017, 313, F487–F494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitker, L.; Burrell, L.M. Classic and Nonclassic Renin-Angiotensin Systems in the Critically Ill. Crit. Care Clin. 2019, 35, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendse, L.B.; Danser, A.H.J.; Poglitsch, M.; Touyz, R.M.; Burnett, J.C.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Ehlers, M.R.; Sturrock, E.D. Novel Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System and Associated Peptides in Hypertension and Heart Failure. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 539–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danser, A.J.; Epstein, M.; Batlle, D. Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers and the COVID-19 Pandemic. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Benthin, C.; Zeno, B.; Albertson, T.E.; Boyd, J.; Christie, J.D.; Hall, R.; Poirier, G.; Ronco, J.J.; Tidswell, M.; et al. A pilot clinical trial of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Baker, A. Recombinant human ACE2: Acing out angiotensin II in ARDS therapy. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haschke, M.; Schuster, M.; Poglitsch, M.; Loibner, H.; Salzberg, M.; Bruggisser, M.; Penninger, J.; Krähenbühl, S. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in healthy human subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, K.; Patel, G.; Kumar, S.; Karpe, P.A.; Sanghavi, M.; Malek, V.; Srinivasan, K. Tissue specific up regulation of ACE2 in rabbit model of atherosclerosis by atorvastatin: Role of epigenetic histone modifications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.H.; Min, J.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, G.E.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, J.J.; Ahn, H.J. The effect of fluvastatin on cardiac fibrosis and angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 expression in glucose-controlled diabetic rat hearts. Heart Vessel. 2017, 32, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Aguilar, M.; Ibarra-Lara, L.; Valle-Mondragón, D.; Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Aguilar-Navarro, A.G.; Zamorano-Carrillo, A.; Ramírez-Ortega, M.D.C.; Pastelín-Hernández, G.; Sánchez-Mendoza, A. Rosiglitazone, a Ligand to PPARγ, Improves Blood Pressure and Vascular Function through Renin-Angiotensin System Regulation. PPAR Res. 2019, 2019, 1371758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dettlaff-Pokora, A.; Swierczynski, J. Dysregulation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAA) in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2-Possible Clinical Consequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094503
Dettlaff-Pokora A, Swierczynski J. Dysregulation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAA) in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2-Possible Clinical Consequences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094503
Chicago/Turabian StyleDettlaff-Pokora, Agnieszka, and Julian Swierczynski. 2021. "Dysregulation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAA) in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2-Possible Clinical Consequences" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094503
APA StyleDettlaff-Pokora, A., & Swierczynski, J. (2021). Dysregulation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAA) in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2-Possible Clinical Consequences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094503




