Real-Time Monitoring the Effect of Cytopathic Hypoxia on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Barrier Functionality Using Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance Sensing (ECIS) Biosensor Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Cytopathic Hypoxia on ARPE-19 Barrier Function Using Real-Time Bioimpedance Analysis
2.2. Real-Time Spreading of ARPE-19 Cells over the Electrode under Cytopathic Hypoxia
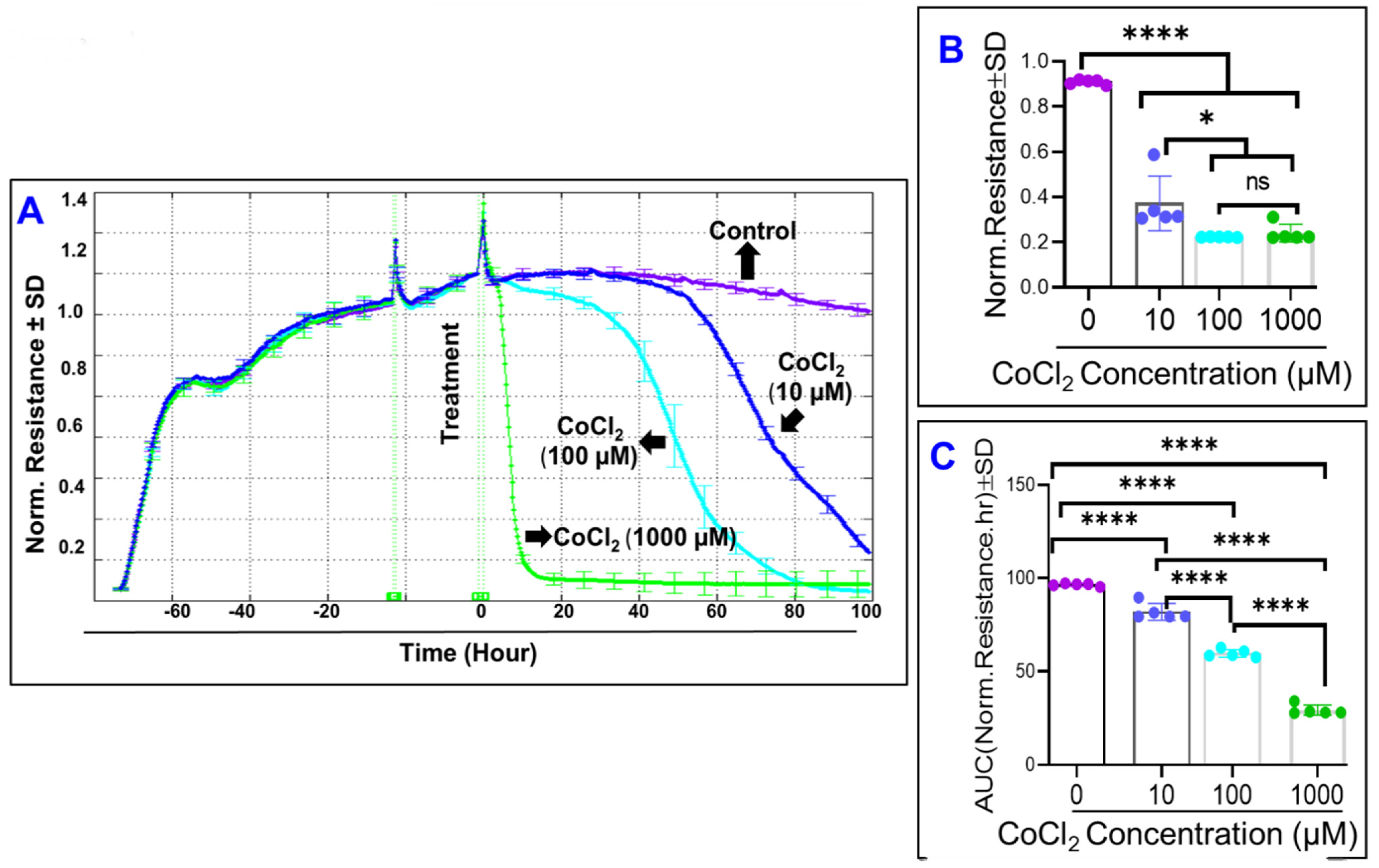
2.3. Real-Time Monitoring of ARPE-19 Total Resistance under Cytopathic Hypoxia
2.4. Effects of Cytopathic Hypoxia on ARPE-19 Cell Viability
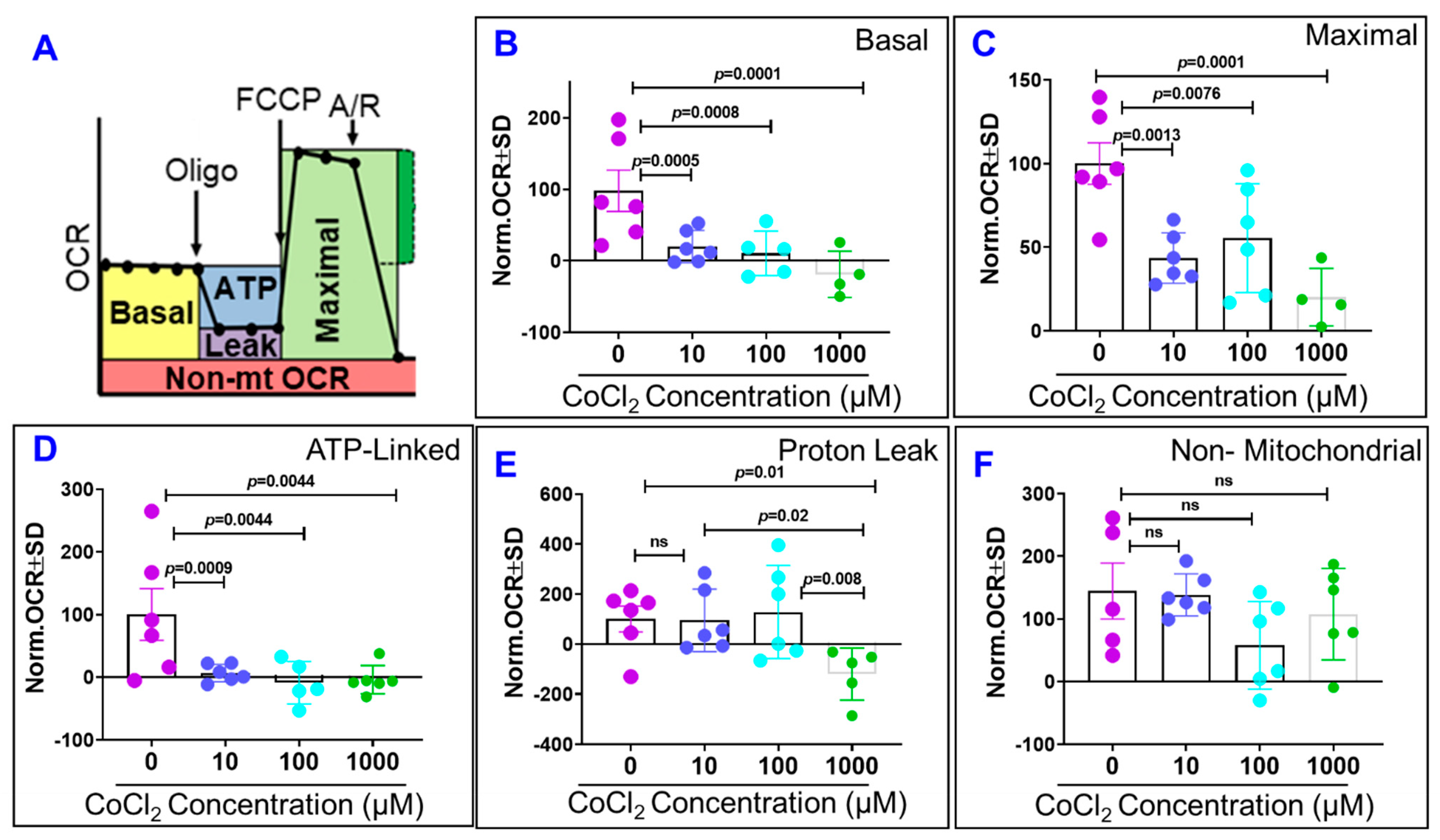
2.5. Effects of Cytopathic Hypoxia on ARPE-19 Cell Mitochondrial Bioenergetics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cell Line (ARPE-19)
3.2. Conducting ECIS Experiment and Modelling
3.3. Immunofluorescence of Zonula Occludens (ZO)-1
3.4. Assessment of Cytopathic Hypoxia Toxicity with MTT
3.5. Western Blot Analysis
3.6. Measurement of Mitochondrial Bioenergetics
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brody, B.L.; Gamst, A.C.; Williams, R.A.; Smith, A.R.; Lau, P.W.; Dolnak, D.; Rapaport, M.H.; Kaplan, R.M.; Brown, S.I. Depression, visual acuity, comorbidity, and disability associated with age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2001, 108, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.W.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, W.R.; Enger, C. Age-related macular degeneration histopathologic studies. The 1992 Lorenz E. Zimmerman Lecture. Ophthalmology 1993, 100, 1519–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlingemann, R.O. Role of growth factors and the wound healing response in age-related macular degeneration. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2004, 242, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossniklaus, H.E.; Ling, J.X.; Wallace, T.M.; Dithmar, S.; Lawson, D.H.; Cohen, C.; Elner, V.M.; Elner, S.G.; Sternberg, P., Jr. Macrophage and retinal pigment epithelium expression of angiogenic cytokines in choroidal neovascularization. Mol. Vis. 2002, 8, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gehrs, K.M.; Anderson, D.H.; Johnson, L.V.; Hageman, G.S. Age-related macular degeneration—Emerging pathogenetic and therapeutic concepts. Ann. Med. 2006, 38, 450–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufai, S.R.; Almuhtaseb, H.; Paul, R.M.; Stuart, B.L.; Kendrick, T.; Lee, H.; Lotery, A.J. A systematic review to assess the ‘treat-and-extend’ dosing regimen for neovascular age-related macular degeneration using ranibizumab. Eye 2017, 31, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gemenetzi, M.; Patel, P.J. A Systematic Review of the Treat and Extend Treatment Regimen with Anti-VEGF Agents for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2017, 6, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacconi, R.; Corbelli, E.; Querques, L.; Bandello, F.; Querques, G. A Review of Current and Future Management of Geographic Atrophy. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2017, 6, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yonekawa, Y.; Miller, J.W.; Kim, I.K. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Advances in Management and Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.W. Age-related macular degeneration revisited—Piecing the puzzle: The LXIX Edward Jackson memorial lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 155, 1–35 e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayreh, S.S. Role of retinal hypoxia in diabetic macular edema: A new concept. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Shah, S.M.; Van Anden, E.; Sung, J.U.; Vitale, S.; Campochiaro, P.A. Supplemental oxygen improves diabetic macular edema: A pilot study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, T.; Westenskow, P.D.; Gantner, M.L.; Usui, Y.; Schultz, A.; Bravo, S.; Aguilar, E.; Wittgrove, C.; Friedlander, M.; Paris, L.P.; et al. Hypoxia-induced metabolic stress in retinal pigment epithelial cells is sufficient to induce photoreceptor degeneration. Elife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, I.R.; Nair, K.S. Mitochondrial function as a determinant of life span. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2010, 459, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, A.P.; Price, N.L.; Ling, A.J.; Moslehi, J.J.; Montgomery, M.K.; Rajman, L.; White, J.P.; Teodoro, J.S.; Wrann, C.D.; Hubbard, B.P.; et al. Declining NAD(+) induces a pseudohypoxic state disrupting nuclear-mitochondrial communication during aging. Cell 2013, 155, 1624–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowluru, R.A. Mitochondrial Stability in Diabetic Retinopathy: Lessons Learned From Epigenetics. Diabetes 2019, 68, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munoz-Sanchez, J.; Chanez-Cardenas, M.E. The use of cobalt chloride as a chemical hypoxia model. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robilliard, L.D.; Kho, D.T.; Johnson, R.H.; Anchan, A.; O’Carroll, S.J.; Graham, E.S. The Importance of Multifrequency Impedance Sensing of Endothelial Barrier Formation Using ECIS Technology for the Generation of a Strong and Durable Paracellular Barrier. Biosensors 2018, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giaever, I.; Keese, C.R. A morphological biosensor for mammalian cells. Nature 1993, 366, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Hussein, K.; Wang, F.; Wan, M.; Saad, N.; Essa, M.; Kim, I.; Shakoor, A.; Owen, L.A.; DeAngelis, M.M.; et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)4 But Not BMP2 Disrupts the Barrier Integrity of Retinal Pigment Epithelia and Induces Their Migration: A Potential Role in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Tawfik, A.M.; Hussein, K.A.; Elshafey, S.; Markand, S.; Rizk, N.; Duh, E.J.; Smith, S.B.; Al-Shabrawey, M. Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits retinal microvascular dysfunction induced by 12/15-lipoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dranka, B.P.; Benavides, G.A.; Diers, A.R.; Giordano, S.; Zelickson, B.R.; Reily, C.; Zou, L.; Chatham, J.C.; Hill, B.G.; Zhang, J.; et al. Assessing bioenergetic function in response to oxidative stress by metabolic profiling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1621–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahuja, M.; Ammal Kaidery, N.; Yang, L.; Calingasan, N.; Smirnova, N.; Gaisin, A.; Gaisina, I.N.; Gazaryan, I.; Hushpulian, D.M.; Kaddour-Djebbar, I.; et al. Distinct Nrf2 Signaling Mechanisms of Fumaric Acid Esters and Their Role in Neuroprotection against 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Induced Experimental Parkinson’s-Like Disease. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6332–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, H.; Anderson, J.M.; Farquhar, M.G. Increased Tyr phosphorylation of ZO-1 during modification of tight junctions between glomerular foot processes. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, F514–F524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Wobben, M.; Marti, H.H.; Renz, D.; Schaper, W. Hypoxia-induced hyperpermeability in brain microvessel endothelial cells involves VEGF-mediated changes in the expression of zonula occludens-1. Microvasc. Res. 2002, 63, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mousa, S.A.; Lorelli, W.; Campochiaro, P.A. Role of hypoxia and extracellular matrix-integrin binding in the modulation of angiogenic growth factors secretion by retinal pigmented epithelial cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 74, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullapalli, V.K.; Sugino, I.K.; Zarbin, M.A. Culture-induced increase in alpha integrin subunit expression in retinal pigment epithelium is important for improved resurfacing of aged human Bruch’s membrane. Exp. Eye Res. 2008, 86, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, F.T.; Kwok, J.C.; Andrews, M.R.; Blits, B.; Martin, K.R.; Faissner, A.; Ffrench-Constant, C.; Fawcett, J.W. Integrin activation or alpha 9 expression allows retinal pigmented epithelial cell adhesion on Bruch’s membrane in wet age-related macular degeneration. Brain 2010, 133, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eamegdool, S.S.; Sitiwin, E.I.; Cioanca, A.V.; Madigan, M.C. Extracellular matrix and oxidative stress regulate human retinal pigment epithelium growth. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 146, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Tan, W.; Li, T.; Yan, Q.; Zhu, H.; Sun, X. Human retinal pigment epithelial cells are protected against hypoxia by BNIP3. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hauck, C.R.; Sieg, D.J. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1999, 71, 435–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marmorstein, A.D. The polarity of the retinal pigment epithelium. Traffic 2001, 2, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarniranta, K.; Tokarz, P.; Koskela, A.; Paterno, J.; Blasiak, J. Autophagy regulates death of retinal pigment epithelium cells in age-related macular degeneration. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2017, 33, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Negi, A.; Marmor, M.F. Quantitative estimation of metabolic transport of subretinal fluid. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1986, 27, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Xu, Y.P.; Liu, G.P.; Ye, X.H. Involvement of acid-sensing ion channel 1a in functions of cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2013, 33, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlapatla, R.K.; Vadlapudi, A.D.; Ponnaluri, V.K.; Pal, D.; Mukherji, M.; Mitra, A.K. Molecular expression and functional activity of efflux and influx transporters in hypoxia induced retinal pigment epithelial cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajala, R.V.S. Aerobic Glycolysis in the Retina: Functional Roles of Pyruvate Kinase Isoforms. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollborn, M.; Ulbricht, E.; Reichenbach, A.; Wiedemann, P.; Bringmann, A.; Kohen, L. Transcriptional regulation of aquaporin-3 in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 7949–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, D.; Motani, H.; Hayakawa, M.; Sato, Y.; Sato, K.; Iwase, H. The relationship between cell membrane damage and lipid peroxidation under the condition of hypoxia-reoxygenation: Analysis of the mechanism using antioxidants and electron transport inhibitors. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2009, 27, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utepbergenov, D.I.; Mertsch, K.; Sporbert, A.; Tenz, K.; Paul, M.; Haseloff, R.F.; Blasig, I.E. Nitric oxide protects blood-brain barrier in vitro from hypoxia/reoxygenation-mediated injury. FEBS Lett. 1998, 424, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guerra, M.H.; Yumnamcha, T.; Ebrahim, A.-S.; Berger, E.A.; Singh, L.P.; Ibrahim, A.S. Real-Time Monitoring the Effect of Cytopathic Hypoxia on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Barrier Functionality Using Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance Sensing (ECIS) Biosensor Technology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094568
Guerra MH, Yumnamcha T, Ebrahim A-S, Berger EA, Singh LP, Ibrahim AS. Real-Time Monitoring the Effect of Cytopathic Hypoxia on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Barrier Functionality Using Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance Sensing (ECIS) Biosensor Technology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094568
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuerra, Michael H., Thangal Yumnamcha, Abdul-Shukkur Ebrahim, Elizabeth A. Berger, Lalit Pukhrambam Singh, and Ahmed S. Ibrahim. 2021. "Real-Time Monitoring the Effect of Cytopathic Hypoxia on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Barrier Functionality Using Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance Sensing (ECIS) Biosensor Technology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094568
APA StyleGuerra, M. H., Yumnamcha, T., Ebrahim, A.-S., Berger, E. A., Singh, L. P., & Ibrahim, A. S. (2021). Real-Time Monitoring the Effect of Cytopathic Hypoxia on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Barrier Functionality Using Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance Sensing (ECIS) Biosensor Technology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094568





